Water Turbidity Retrieval Based on UAV Hyperspectral Remote Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data Acquisition
2.1. Manual Control Experiment
2.1.1. Solution Concentration Configuration
2.1.2. Water Reflection Spectrum Acquisition
2.2. UAV Field Data Acquisition
2.2.1. Image Acquisition and Sampling
2.2.2. Image Preprocessing and Water Extraction
3. Methods
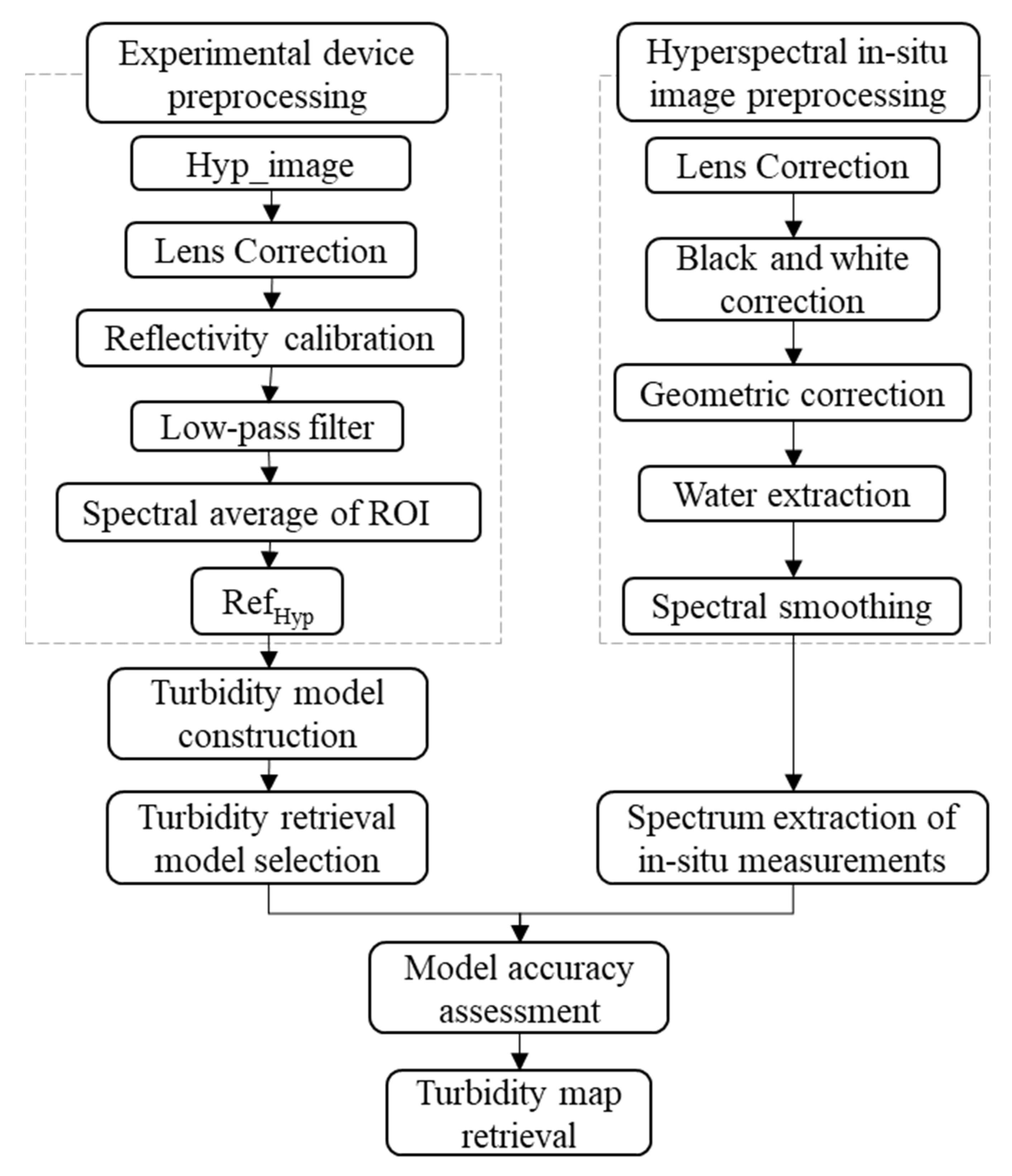
3.1. Experimental Process
3.2. Model Construction
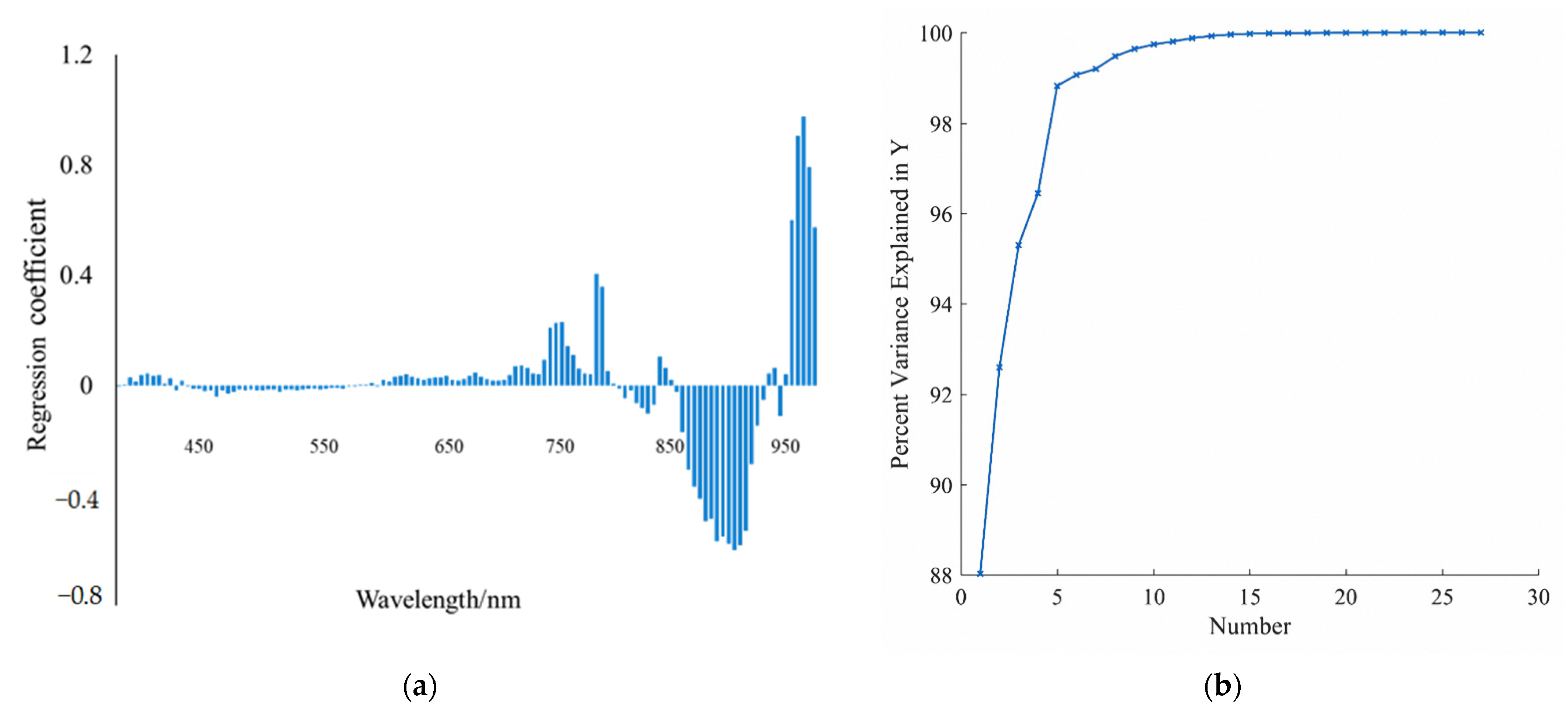
3.2.1. Model Selection
3.2.2. Modeling through Artificial Control Experiment
3.3. Accuracy Assessment
4. Results and Discussion
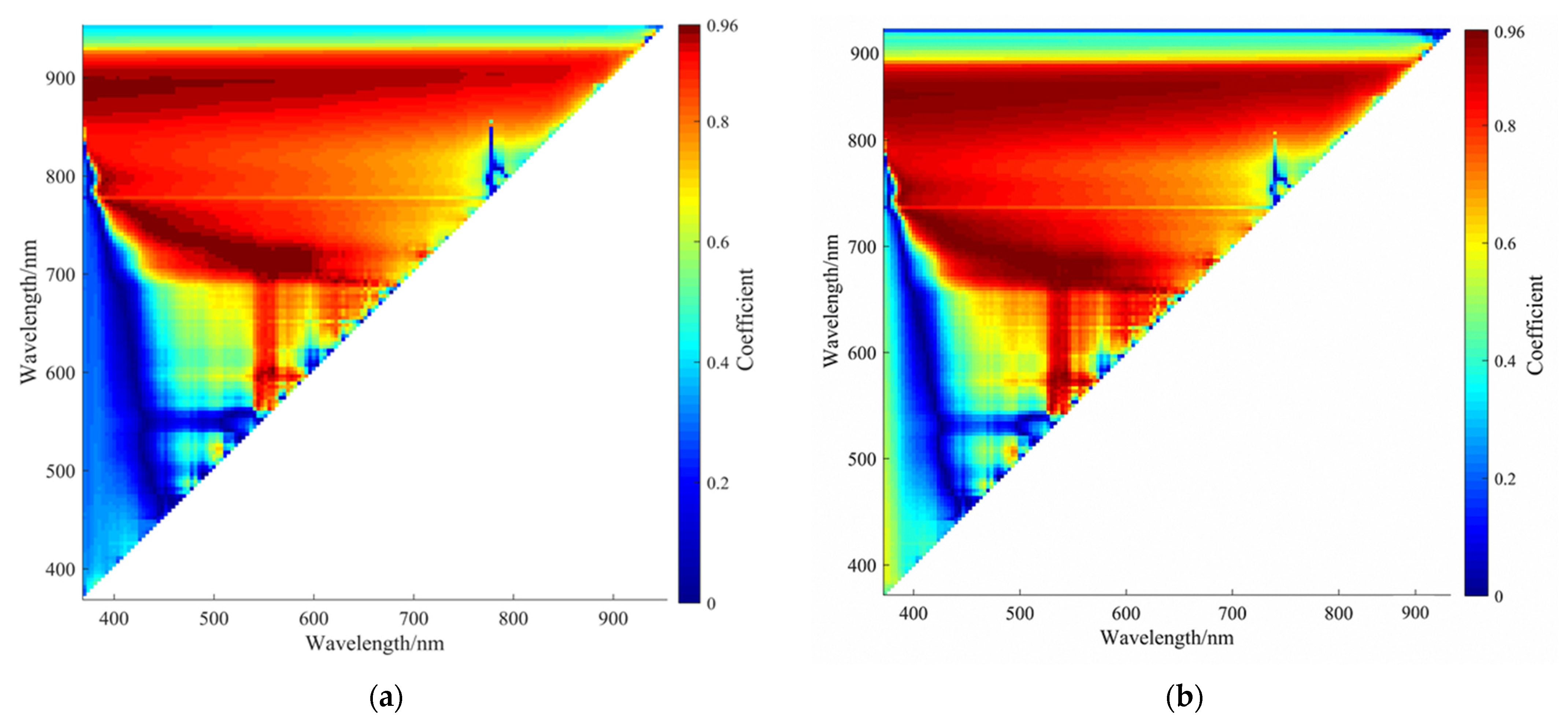
4.1. Spectral Characteristic Analysis
4.2. Model Retrieval of Turbidity Standard Solution
4.2.1. Manual Control Experimental Models for Hyperspectral Image
4.2.2. Verification of Model Accuracy
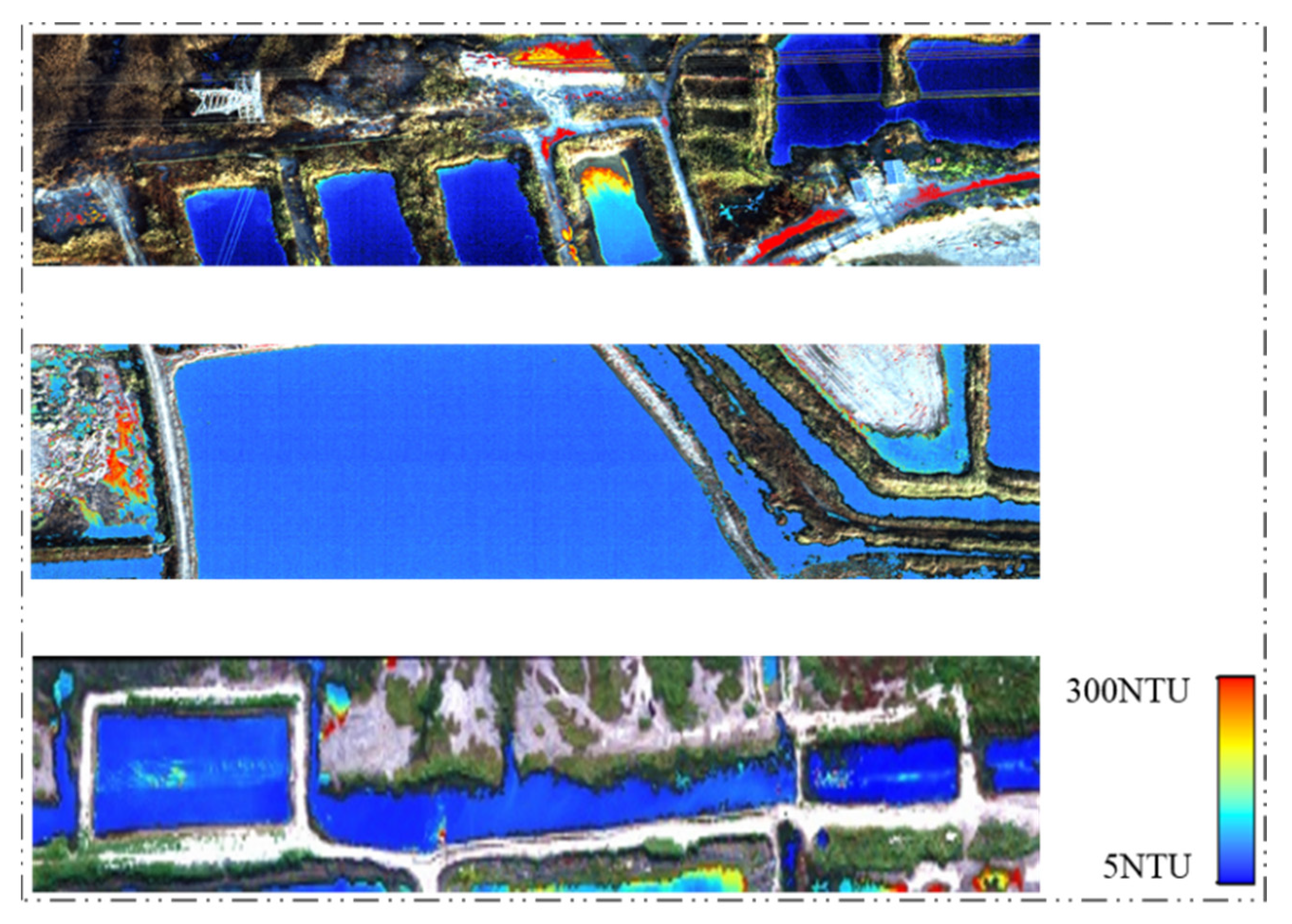
4.3. UAV Image Turbidity Retrieval Using the Optimal Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allam, M.; Khan, M.Y.A.; Meng, Q. Retrieval of Turbidity on a Spatio-Temporal Scale Using Landsat 8 SR: A Case Study of the Ramganga River in the Ganges Basin, India. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Xu, J.; Zhao, D.Z.; Zhao, B.C.; Xu, J.; Cheng, X.J.; Li, G.Z. Research on Combined Remote Sensing Retrieval of Turbidity for River Based on Domestic Satellite data. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2021, 38, 128. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Q.; Gong, C.L.; Kuang, D.B.; Zhou, N.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, F.L.; Xu, W.D.; Ma, Y.Q. Method of Satellite Remote Sensing of Lake Water Quality and Its Applications. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2005, 24, 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Güttler, F.N.; Niculescu, S.; Gohin, F. Turbidity Retrieval and Monitoring of Danube Delta Waters Using Multi-Sensor Optical Remote Sensing Data: An Integrated View from the Delta Plain Lakes to the Western-Northwestern Black Sea Coastal Zone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.J.; Wang, X.J. The Spectral Features Analysis and Quantitative Remote Sensing Advances of Inland Water Quality Parameters. Geogr. Territ. Res. 2002, 18, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, Y.S.; Shen, Y.L. Measurement Uncertainty-Aware Quantitative Remote Sensing Inversion to Retrieve Suspended Matter Concentration in Inland Water. Acta Opt. Sin. 2016, 36, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.P.; Zhang, F.; Abduwasit, G.Y.; Yu, H.; Ren, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. The Relationship Between the Surface Water Quality Indices and Hydrology of Ebinur Lake Watershed. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2017, 37, 900–909. [Google Scholar]
- Sibanda, M.; Mutanga, O.; Chimonyo, V.G.P.; Clulow, A.D.; Shoko, C.; Mazvimavi, D.; Dube, T.; Mabhaudhi, T. Application of Drone Technologies in Surface Water Resources Monitoring and Assessment: A Systematic Review of Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities in the Global South. Drones 2021, 5, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Du, P.; Shen, Q.; Xu, Z.B. Research on Remote Sensing Inversion Mode of Suspended Matter Density and Turbidity based on GF-1 WFV Image Data in Hunhe River. J. Shenyang Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2017, 35, 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Goodin, D.G.; Harrington, J.A.; Nellis, M.D.; Rundquist, D. Mapping Reservoir Turbidity Patterns Using SPOT-HRV Data. Geocarto Int. 1996, 11, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornelia, A.W.; Robert, J.B.; Maria, O.; Marek, F. Investigation of Sediment-Rich Glacial Meltwater Plumes Using a High-Resolution Multispectral Sensor Mounted on an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Water 2019, 11, 2405. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, H.L.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Mao, W.S.; Zhu, Y.R. Modeling of Turbidity Retrieval of Hulunnaoer Lake Based on Airborne Hyperspectral Imagery. South-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 111, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Song, T.; Shi, J.Z.; Liu, Z.J.; Xu, W.Y.; Yan, F.; Xu, C.; Zhu, B.C. Research on Remote Sensing Quantitative Inversion Models of Blue-Green Algae Density and Turbidity Based on Landsat-8 OLI Image Data in Lake Taihu. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2015, 22, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Cheng, X.J.; Shen, X.; Xiao, X.; Wang, L.H.; Zhang, W. Inland Riverine Turbidity Estimation for Hanjiang River with Landsat 8 OLI Image. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2017, 42, 643–647. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Luo, X.W.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Zang, Y.; Hu, L. Key Technology for Remote Sensing Information Acquisition based on Micro UAV. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Wu, Y.D. Research and Application of UAS Borne Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. Inf. 2010, 2, 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Ren, G.B. Study on Monitoring Alien Invasive Species Spartina Alterniflora using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Hyperspectral Remote Sensing-a Case Study of the Yellow River Delta. Mar. Sci. 2017, 41, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Li, X.W.; Niu, Z.C.; Li, W.Z.; Wang, T.T.; Zhang, Y. Preliminary Study on Remote Sensing Information Extraction of Urban Water Environment based on Micro UAV Images. Environ. Monit. China 2018, 34, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Lu, X.P.; Wu, Y.B.; Miao, P.J.; Zhou, J.L. Retrieval and Model Construction of Water Quality Parameters for UAV Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2020, 267, 64–68, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Yan, L.; Gou, Z.Y.; Zhao, H.Y.; Liu, D.P.; Duan, Y.N. In-Flight Absolute Radiometric Calibration of UAV Multispectral Sensor. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2012, 32, 3169–3174. [Google Scholar]
- Mark, P.; Dmitry, B.; Kevin, G.; Felipe, G. UAVs, Hyperspectral Remote Sensing, and Machine Learning Revolutionizing Reef Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 2026. [Google Scholar]
- McFeeters, S.K. The Use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the Delineation of Open Water Features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiden, U.; Segl, K.; Roessner, S.; Kaufmann, H. Determination of Robust Spectral Features for Identification of Urban Surface Materials in Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.M.; Wei, Y.C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, X.P.; Zhou, Y. A First Derivative Estimation Model of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Turbidity Water Based on Spectral Smoothing. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2013, 29, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava, D.S.; Mariam, D.W. Light Penetration Depth, Turbidity and Reflectance Related Relationship and Models. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1991, 46, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.T.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, B.; Song, K.S.; Wang, Z.M. Application Hyperspectral Data in Remote Sensing Inverse of Water Quality Variables in Lake Chagan. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2006, 20, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, I.D.; D’Sa, E.J.; Osburn, C.L.; Bianchi, T.S. Turbidity in Apalachicola Bay, Florida from Landsat 5 TM and Field Data: Seasonal Patterns and Response to Extreme Events. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, G.; Potes, M.; Costa, M.J.; Novais, M.H.; Morais, M.M. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Secchi Depth and Diffuse Attenuation Coefficient from Sentinel-2 MSI over a Large Reservoir. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.J.; Piao, X.Y.; Dai, Y.N. Correlations Between Reflectance Spectra and Contents of Chlorophyll-a in Chaohu Lake. J. Lake Sci. 2002, 14, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, X.Z.; Yin, Q.; Kuang, D.B. Relationship between Algal Chlorophyll Concentration and Spectral Reflectance of Inland Water. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 4, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhou, B.; Xu, H.W.; Shen, Z.Q. Preliminary Study on Hyperspectral Remote Sensing of Qiandao Lake Chlorophyll-a Concentration. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Agric. Life Sci.) 2003, 29, 621–626. [Google Scholar]
- Pulliainen, J.; Kallio, K.; Eloheimo, K.; Koponen, S.; Hallikainen, M. A Semi-Operative Approach to Lake Water Quality Retrieval from Remote Sensing Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 268, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koponen, S.; Pulliainen, J.; Kallio, K.; Hallikainen, M. Lake Water Quality Classification with Airborne Hyperspectral Spectrometer and Simulated MERIS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ye, Y.T.; Zhao, H.L.; Shi, Y.B.; Jiang, Y.Z. Remote-Sensing Retrieval Method of Suspended Solid Concentration and Turbidity in Lakes and Reservoirs based on Discrete Particle Swarm and Partial Least Squares. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2015, 34, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, S.; Li, Y.M.; Lv, H.; Zhu, L.; Mu, M.; Lei, S.H.; Xu, J.; Wen, S.; Ding, X.L. Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Lake Erhai based on OLCI Data. J. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.J. Comparison of Lake Turbidity Inversion Based on GF-1 and Landsat-8 Satellite Images. Geomat. Spat. Inf. Technol. 2017, 40, 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, C.; Tao, Y.Y.; Juan, X.Z.; Bo, Y.S.; Zhong, Y.J.; Li, H.Z. Quantitative Inversion Model of Hyperspectral for Turbidity in the Nansi Lake. South-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 13, 883–887. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, H.; Xiao, S.; Nie, P.; Tao, D.; Qu, F.; Lei, L. Research on the Optimum Water Content of Detecting Soil Nitrogen using Near Infrared Sensor. Sensors 2017, 17, 2045. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Z.; Shi, T.Z.; Yu, D.L.; Teng, D.X.; Ge, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.P.; Yang, X.D.; Wang, H.X.; Wu, G.F. Ensemble Machine-Learning-Based Framework for Estimating Total Nitrogen Concentration in Water Using Drone-Borne Hyperspectral Imagery of Emergent Plants: A Case Study in an Arid Oasis, NW China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Gao, L.R.; Chen, D.M. An Improved Noise Evaluation Algorithm of Hyperspectral Image Based on MNF. Sci. China Press 2009, 39, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, M.K.; Porwal, A.; Rasmussen, T.M. Noise Reduction and Destriping Using Local Spatial Statistics and Quadratic Regression from Hyperion Images. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.H.; Li, Y.M.; Lv, H.; Xu, Y.F.; Xu, X.; Huang, J.Z.; Tan, J.; Guo, Y.L. Inversion of Suspended Matter Concentration in Lake Chaohu based on Partial Least-Squares Regression. J. Lake Sci. 2011, 23, 357–365. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.W.; Wang, B.; Ji, T.; Xu, J.; Ju, F.; Wang, C.L. Simulation Estimation of BOD Content in Water Based on Hyperspectra. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2021, 41, 978–983. [Google Scholar]





| Sampling Time | Location | Numbers | Max/NTU | Min/NTU | Average/NTU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019.09 | 121°59′44″–121°59′51″ E, 40°48′38″–40°48′51″ N | 10 | 40.47 | 3.26 | 18.32 |
| 2020.10 | 121°57′8″–121°57′15″ E, 40°47′14″–40°47′20″ N | 8 | 56.37 | 3.2 | 25.42 |
| Name | Formula |
|---|---|
| Determination coefficient (R2) | |
| Root mean square error (RMSE) | |
| Mean bias error (MBE) | |
| Mean absolute percent error (MAPE) |
| Model Type | Equation Form | R2 | RMSE/NTU | MBE | MAPE/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single band | T = 17.9 × e19.5 × Rrs (809) | 0.86 | 4 | 5.66 | 28.54 |
| Band ratio | )+876.2 | 0.92 | 3.67 | 5.23 | 12.93 |
| Normalized ratio | +936.7 | 0.87 | 8.82 | 3.61 | 20.26 |
| PLS | 0.98 | 6.09 | 3.81 | 15.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, M.; Sun, Y.; Huang, C.; Li, M. Water Turbidity Retrieval Based on UAV Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Water 2022, 14, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010128
Cui M, Sun Y, Huang C, Li M. Water Turbidity Retrieval Based on UAV Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Water. 2022; 14(1):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010128
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Mengying, Yonghua Sun, Chen Huang, and Mengjun Li. 2022. "Water Turbidity Retrieval Based on UAV Hyperspectral Remote Sensing" Water 14, no. 1: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010128
APA StyleCui, M., Sun, Y., Huang, C., & Li, M. (2022). Water Turbidity Retrieval Based on UAV Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Water, 14(1), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010128






