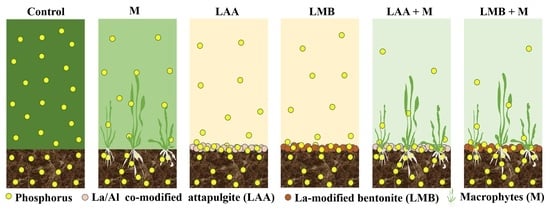
Synergistic Effects and Ecological Responses of Combined In Situ Passivation and Macrophytes toward the Water Quality of a Macrophytes-Dominated Eutrophic Lake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mesocosm Establishment
2.2. DGT Deployments and Analysis
2.3. Sediments Characteristics
2.4. Macrophytes Traits
3. Results
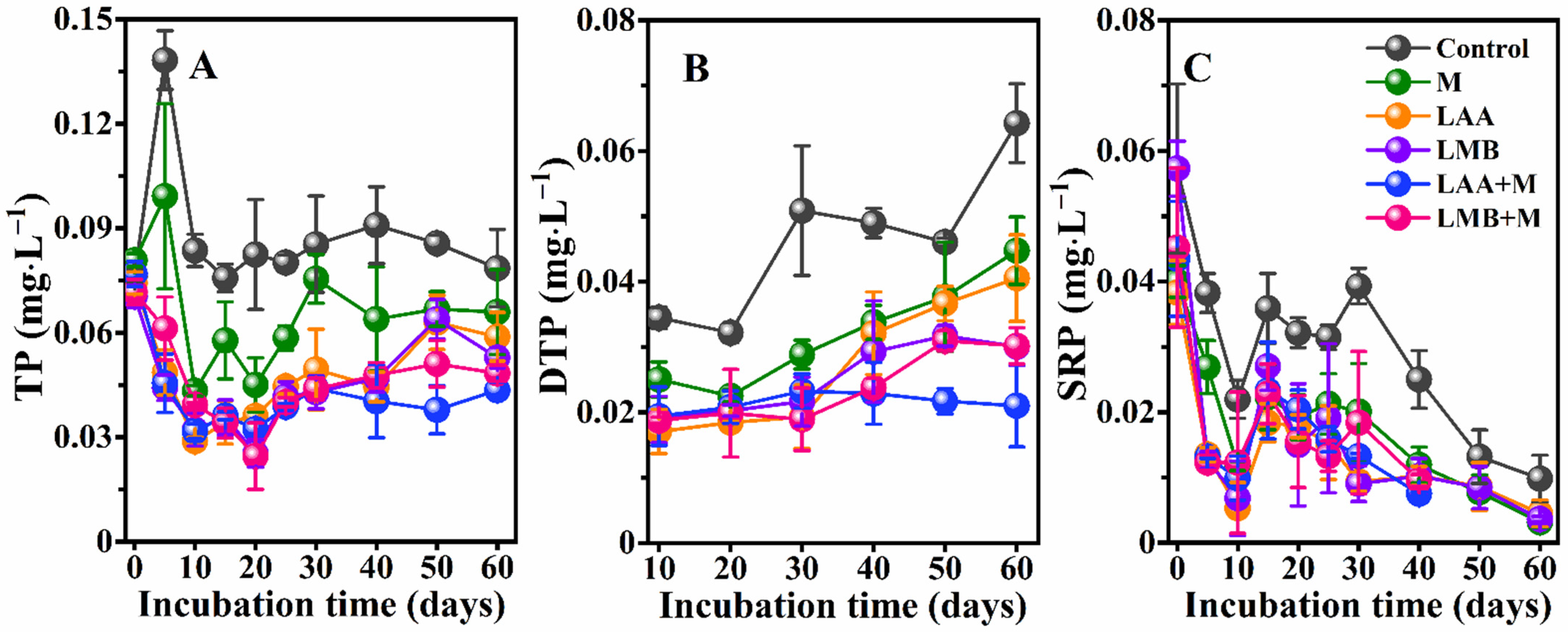
3.1. Water Quality
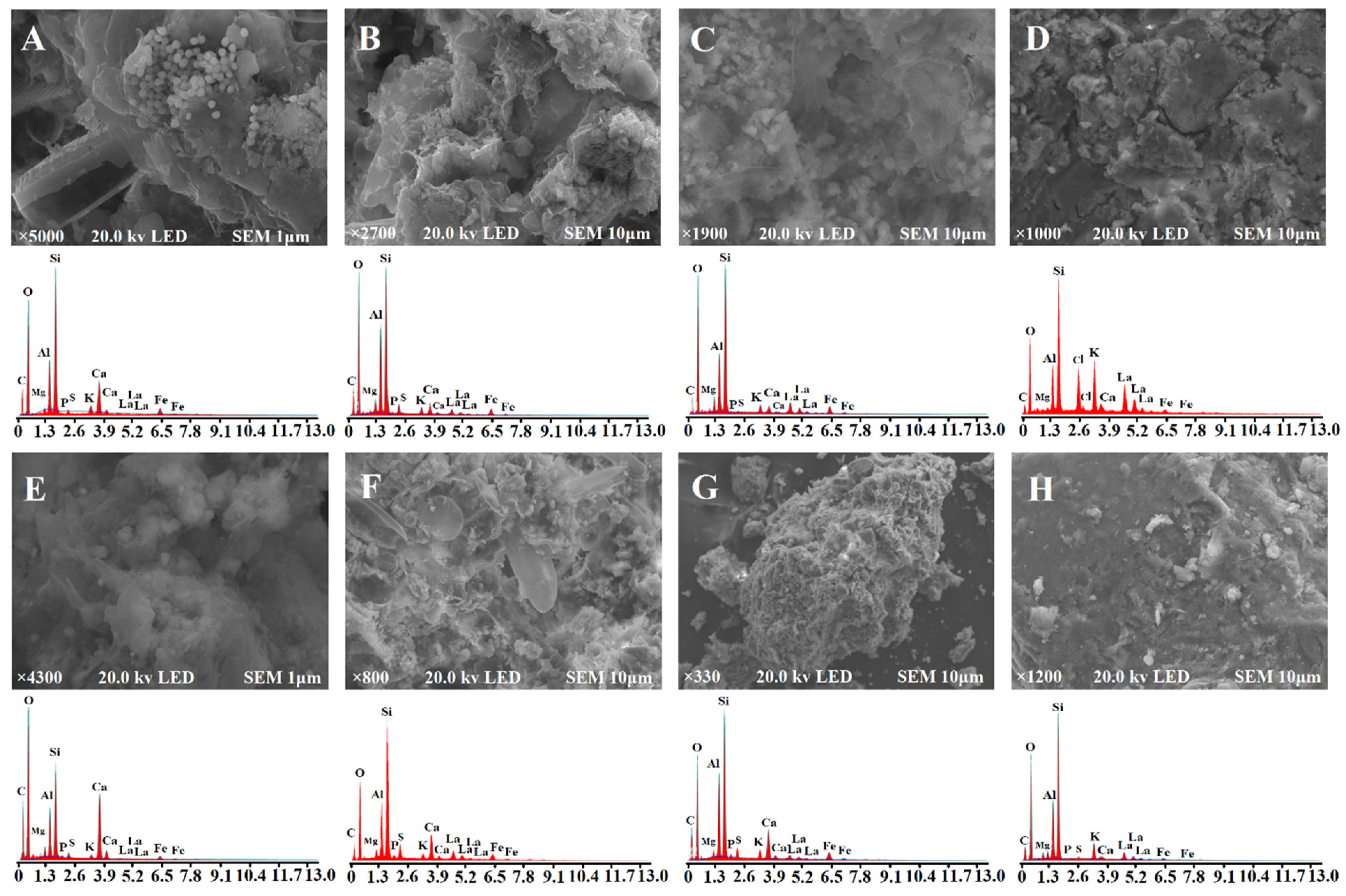
3.2. Physicochemical Characterization of Sediments
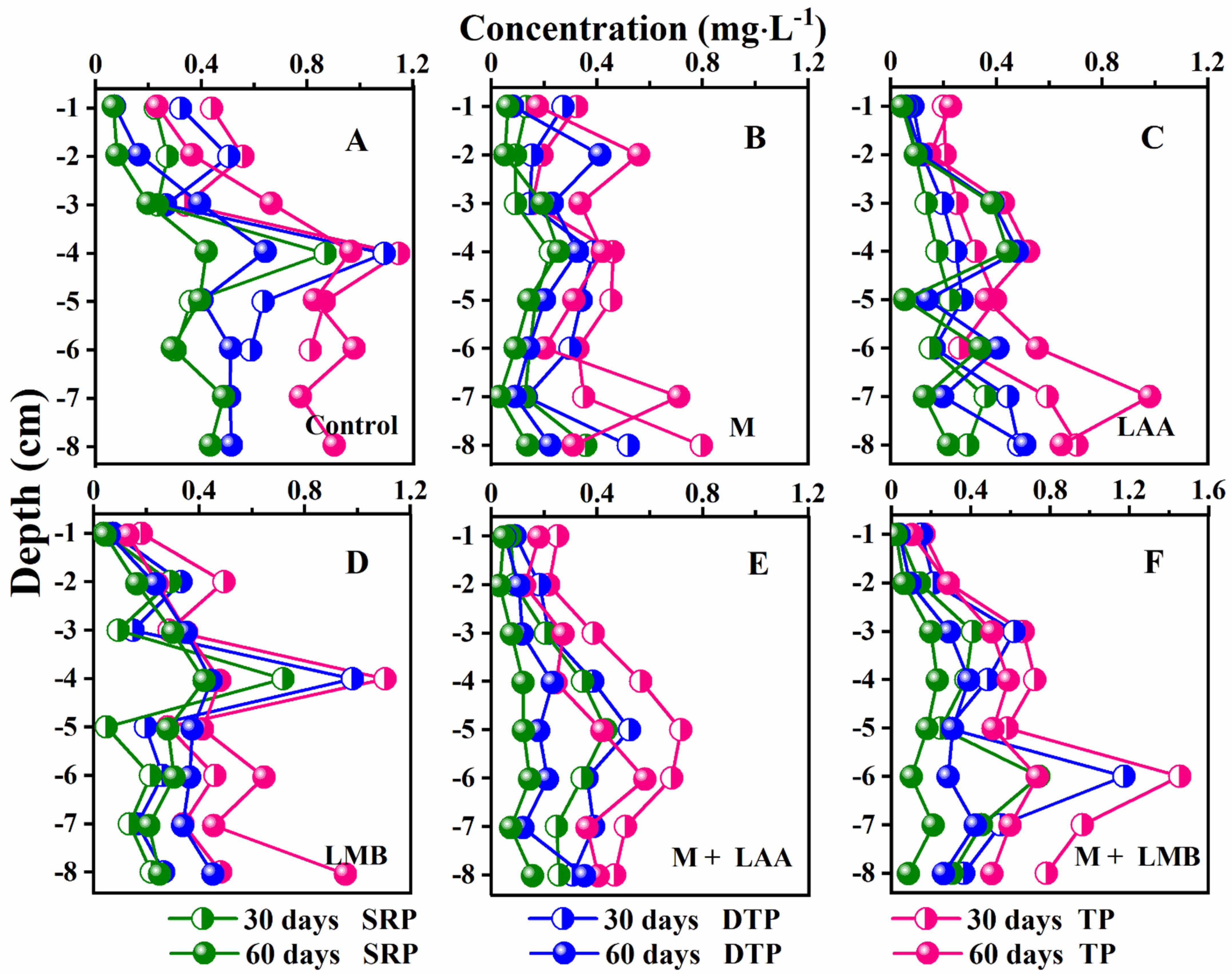
3.3. Sediments P
3.4. DGT-Labile P, Fe, and S Variation
3.5. Macrophytes
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of LMM and Macrophytes on P Concentrations
4.2. Effects of LMM on Macrophytes Physiological Indices
4.3. Effects of LMM on Surface Sediments Microenvironment
4.4. P Biogeochemical Behaviour
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, V.H.; Schindler, D.W. Eutrophication science: Where do we go from here? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oosterhout, F.V.; Waajen, G.; Yasseri, S.; Manzi Marinho, M.; Pessoa Noyma, N.; Mucci, M.; Douglas, G.; Lürling, M. Lanthanum in Water, Sediment, Macrophytes and chironomid larvae following application of Lanthanum modified bentonite to lake Rauwbraken (The Netherlands). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.M.; Zhen, W.; Jensen, H.S.; Reitzel, K.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, Z.W. The combined effects of macrophytes (Vallisneria denseserrulata) and a lanthanum-modified bentonite on water quality of shallow eutrophic lakes: A mesocosm study. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tammeorg, O.; Nürnberg, G.; Horppila, J.; Haldna, M.; Niemistö, J. Redox-related release of phosphorus from sediments in large and shallow Lake Peipsi: Evidence from sediment studies and long-term monitoring data. J. Great Lakes Res. 2020, 46, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recknagel, F.; Hosomi, M.; Fukushima, T.; Kong, D.S. Short- and long-term control of external and internal phosphorus loads in lakes—A scenario analysis. Water Res. 1995, 29, 1767–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, T.Q.; Zhao, Y.C.; Ciborowski, J.J.H.; Zhao, Y.M.; O’Halloran, I.P.; Qi, Z.M.; Tan, C.S. Characterization of sedimentary phosphorus in Lake Erie and on-site quantification of internal phosphorus loading. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Wu, F.C.; Song, B.A. Phosphorus speciation in the sediment profile of Lake Erhai, southwestern China: Fractionation and 31P NMR. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waajen, G.; Pauwels, M.; Lürling, M. Effects of combined flocculant–Lanthanum modified bentonite treatment on aquatic macroinvertebrate fauna. Water Res. 2017, 122, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilt, S.; Gross, E.M. Can allelopathically active submerged macrophytes stabilise clear-water states in shallow lakes? Basic Appl. Ecol. 2008, 9, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Hosper, S.H.; Meijer, M.L.; Moss, B.; Jeppesen, E. Alternative Equilibria in Shallow Lakes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1993, 8, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahzadeh, H.; Kaczala, F.; Bhatnagar, A.; Hogland, W. Significance of environmental dredging on metal mobility from contaminated sediments in the Oskarshamn Harbor, Sweden. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Yang, C.; Yang, P.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Douglas, G.B. Contrasting effects and mode of dredging and in situ adsorbent amendment for the control of sediment internal phosphorus loading in eutrophic lakes. Water Res. 2020, 189, 116644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.W.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Zhan, Y.H.; Wang, Y. Control of internal phosphorus release from sediments using magnetic lanthanum/iron-modified bentonite as active capping material. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.B.; Yang, P.; Kong, M.; Li, W. Use of lanthanum/aluminum co-modified granulated attapulgite clay as a novel phosphorus (P) sorbent to immobilize P and stabilize surface sediment in shallow eutrophic lakes. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goscianska, J.; Ptaszkowska-Koniarz, M.; Frankowski, M.; Franus, M.; Panek, R.; Franus, W. Removal of phosphate from water by lanthanum-modified zeolites obtained from fly ash. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 513, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.L.; Zhou, W.B. Phosphorus forms and distribution in the sediments of Poyang Lake, China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2011, 26, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Yang, H.Q.; Chen, J.A.; Liao, P.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.Q.; Liu, Y. Organic Phosphorus Mineralization Dominates the Release of Internal Phosphorus in a Macrophyte-Dominated Eutrophication Lake. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 9, 812834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barik, S.K.; Bramha, S.; Bastia, T.K.; Behera, D.; Kumar, M.; Mohanty, P.K.; Rath, P. Characteristics of geochemical fractions of phosphorus and its bioavailability in sediments of a largest brackish water lake, South Asia. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2019, 19, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.R.; Kukkadapu, R.K.; Burdige, D.J.; Bowden, M.E.; Sparks, D.L.; Jaisi, D.P. Organic matter remineralization predominates phosphorus cycling in the mid-Bay sediments in the Chesapeake Bay. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5887–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.R.; Feng, W.Y.; Liu, S.S.; He, Z.Q.; Zhao, X.L.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J.Y.; Giesy, J.P.; Wu, F.C. Bioavailability and preservation of organic phosphorus in lake sediments: Insights from enzymatic hydrolysis and 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.W.; He, J.; Zuo, L.; Vogt, R.D.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, B.; Mohr, C.W.; Guan, R.; Wang, W.Y.; Yan, D.H. Processes and their explanatory factors governing distribution of organic phosphorous pools in lake sediments. Chemosphere 2016, 145, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, J.A.; Wang, J.F.; Guo, J.Y.; Jin, Z.F.; Yu, P.; Ma, Z. In situ, high-resolution evidence of phosphorus release from sediments controlled by the reductive dissolution of iron-bound phosphorus in a deep reservoir, southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.M.; Han, C.; Wang, Y.P.; Yao, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Sun, Q.; Williams, P.N.; Zhang, C.S. In situ, high-resolution imaging of labile phosphorus in sediments of a large eutrophic lake. Water Res. 2015, 74, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crusius, J.; Anderson, R.F. Core Compression and Surficial Sediment Loss of Lake Sediments of High Porosity Caused by Gravity Coring. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupfer, M.; Gfichter, R.; Giovanoli, R. Transformation of phosphorus species in settling seston and during early sediment diagenesis. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 57, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rita, J.C.D.O.; Gama-Rodrigues, A.C.; Gama-Rodrigues, E.F.; Zaia, F.C.; Nunes, D.A.D. Mineralization of organic phosphorus in soil size fractions under different vegetation covers in the north of Rio de Janeiro. Content Uploaded Emanuela Gama-Rodrigues 2013, 37, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hupfer, M.; Lewandowski, J. Retention and early diagenetic transformation of phosphorus in Lake Arendsee (Germany)-consequences for management strategies. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2005, 164, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Han, F.E.; Li, D.P.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Y. Transformation of internal sedimentary phosphorus fractions by point injection of CaO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 343, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, D.; Moss, B.; Phillips, G. Do rooted macrophytes increase sediment phosphorus release? Hydrobiologia 1997, 342, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E. Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506–509, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, S.M.; Wang, D.; Sun, Q.; Lin, J.; Shi, L.; Chen, M.S.; Zhang, C.S. Static layer: A key to immobilization of phosphorus in sediments amended with lanthanum modified bentonite (Phoslock®). Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 325, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, N.H.; Andersen, F.Ø.; Jensen, H.S. Phosphate uptake kinetics for four species of submerged freshwater macrophytes measured by a 33P phosphate radioisotope technique. Aquat. Bot. 2016, 128, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.S.; Fu, Y.Y.; Min, H.L.; Cai, S.J.; Sha, S.; Cheng, G.Y. Laboratory assessment of uptake and toxicity of lanthanum (La) in the leaves of Hydrocharis dubia (Bl.) Backer. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 3950–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shi, G.X.; Xu, Q.S.; Xu, B.J.; Zhao, J. Lanthanum- and cerium-induced oxidative stress in submerged Hydrilla verticillata plants. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2007, 54, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, H.; Nolde, J.; Berger, S.; Heise, S. Aquatic ecotoxicity of lanthanum-A review and an attempt to derive water and sediment quality criteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 124, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slomp, C.P.; Mort, H.P.; Jilbert, T.; Reed, D.C.; Gustafsson, B.G.; Wolthers, M. Coupled dynamics of iron and phosphorus in sediments of an oligotrophic coastal basin and the impact of anaerobic oxidation of methane. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Z.; Wang, Y.C.; Wu, J.K.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, C.C.; Zhao, F.X.; Li, Y.; Hu, M.M.; Bao, Y.F. The influence of cascade reservoir construction on sediment biogenic substance cycle in Lancang River from the perspective of phosphorus fractions. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 158, 106051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, D.H.; Jeon, Y.T.; Duck, H.Y. Phosphorus fractionation and release characteristics of sediment in the Saemangeum Reservoir for seasonal change. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2018, 33, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, M.; Chesnyuk, A.; Gudimov, A.; McCulloch, J.; Quazi, S.; Young, J.; Winter, J.; Stainsby, E.; Arhonditsis, G. Phosphorus retention in a mesotrophic lake under transient loading conditions: Insights from a sediment phosphorus binding form study. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1433–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, D.; Kleeberg, A.; Hupfer, M. Sulphate-mediated phosphorus mobilization in riverine sediments at increasing sulphate concentration, River Spree, NE Germany. Biogeochemistry 2006, 80, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Xiao, R.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, M.X. Phosphorus fraction and phosphate sorption-release characteristics of the wetland sediments in the Yellow River Delta. Phys. Chem. Earth 2018, 103, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.X.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Ye, Z.H. Root porosity, radial oxygen loss and iron plaque on roots of wetland plants in relation to zinc tolerance and accumulation. Plant. Soil 2013, 374, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, D.E.; Thamdrup, B.; Hansen, J.W. The anaerobic degradation of organic matter in Danish coastal sediments: Iron reduction, manganese reduction, and sulfate reduction. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 3867–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiessen, H.; Stewart, J.W.B.; Cole, C.V. Pathways of Phosphorus Transformations in Soils of Differing Pedogenesis. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1984, 48, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydin, E. Potentially mobile phosphorus in Lake Erken sediment. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2037–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, J.Y.; Chang, N.; Wan, L.H.; Chen, J.H. Phosphate adsorption on lanthanum hydroxide-doped activated carbon fiber. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 185–186, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, Y.L.; Li, X.H.; Wang, Y.Y. Investigation of phosphate removal mechanisms by a lanthanum hydroxide adsorbent using p-XRD, FTIR and XPS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 557, 149838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennafirme, S.; Pereira, D.C.; Pedrosa, L.G.M.; Machado, A.S.; Silva, G.O.A.; Keim, C.N.; Lima, I.; Lopes, R.T.; Paixão, I.C.N.P.; Crapez, M.A.C. Characterization of microbial mats and halophilic virus-like particles in a eutrophic hypersaline lagoon (Vermelha Lagoon, RJ, Brazil). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 31, 100769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasuk, M.C.; Fernandez, A.B.; Kurth, D.; Contreras, M.; Novoa, F.; Poire, D.; Farias, M.E. Bacterial Diversity in Microbial Mats and Sediments from the Atacama Desert. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 71, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
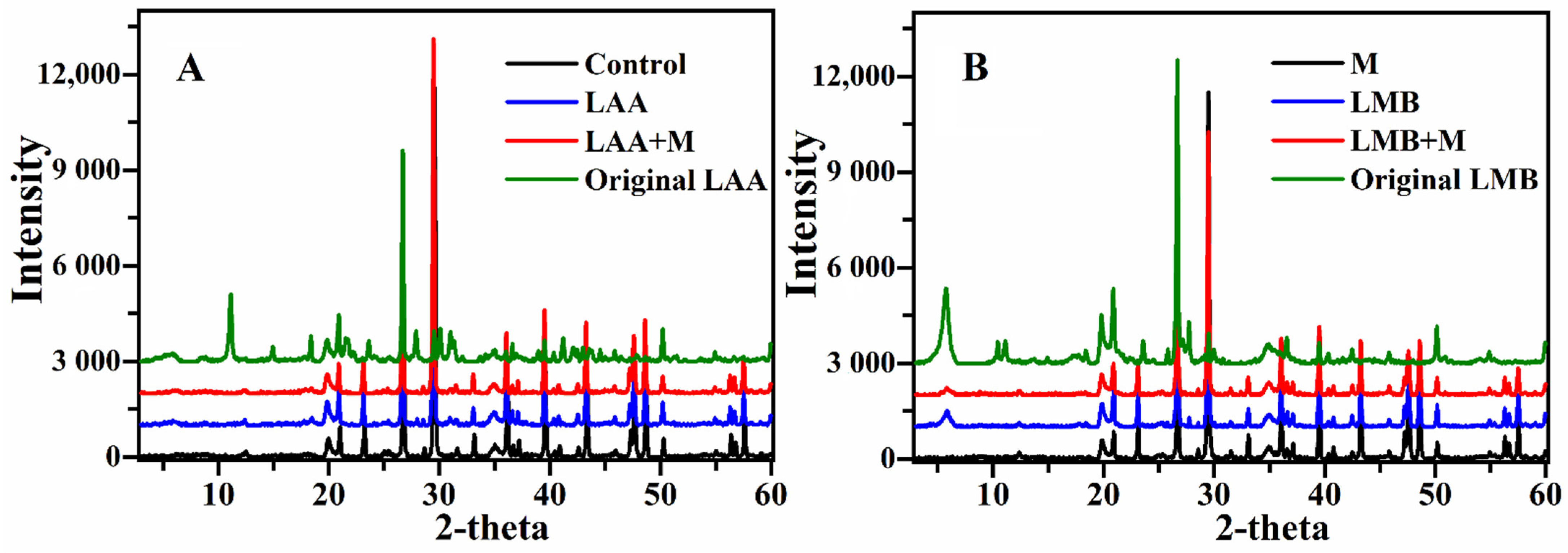
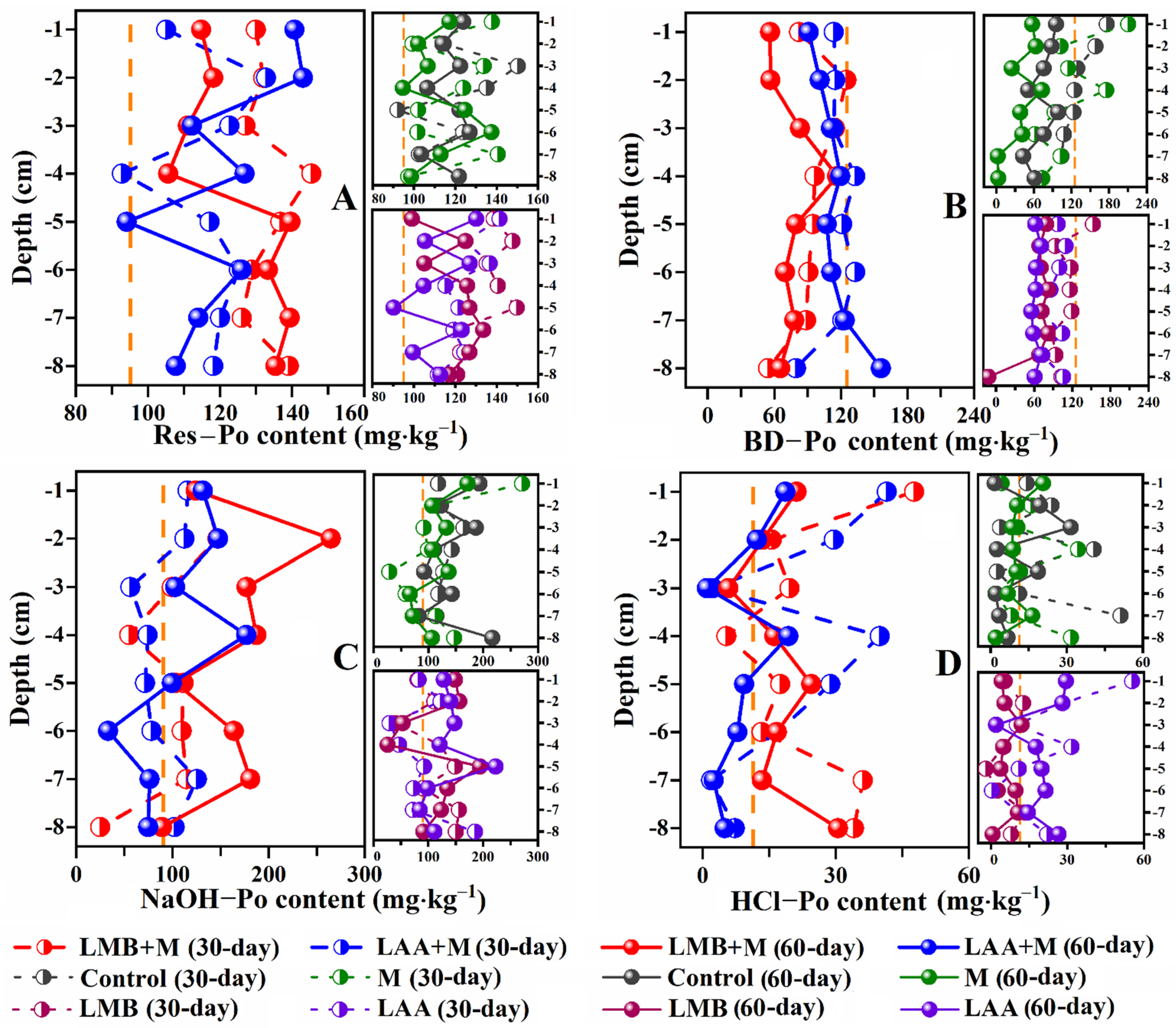
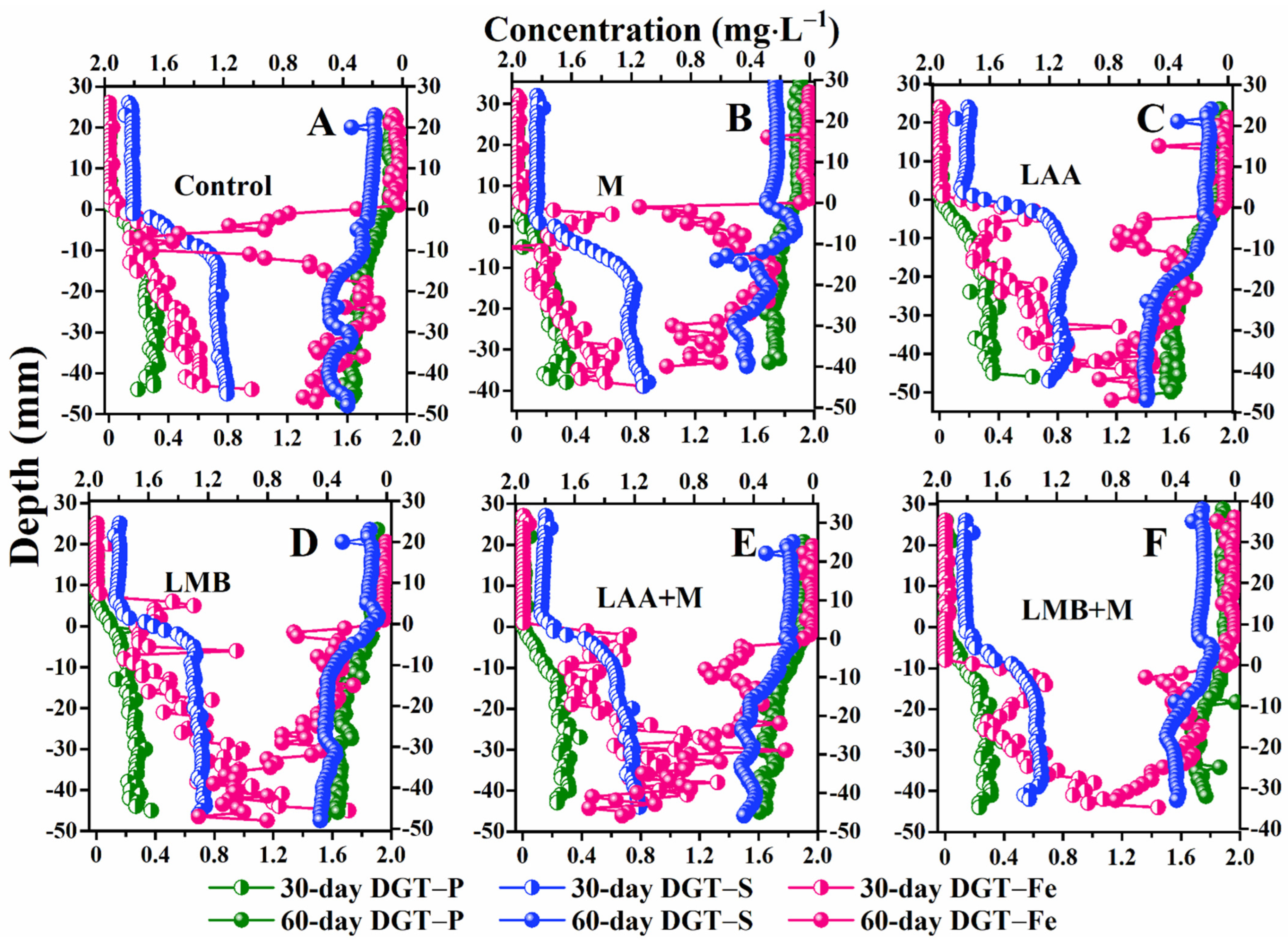
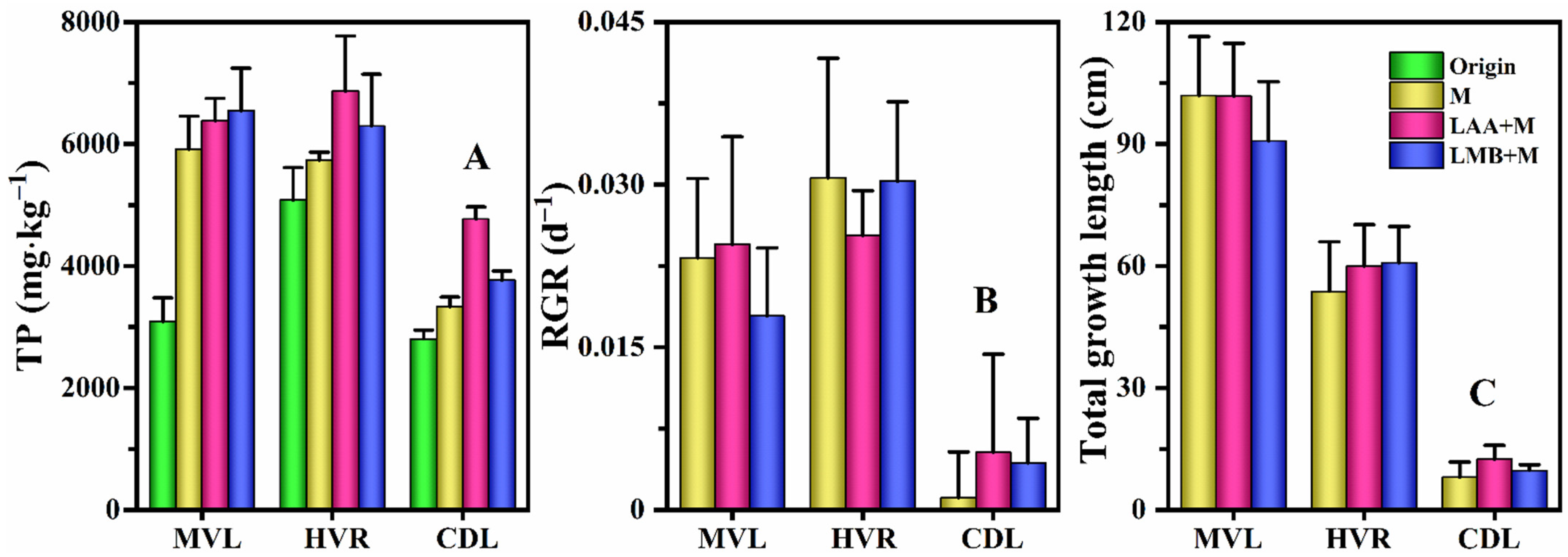
| Material | Control | M | LAA | LMB | LAA+M | LMB+M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaCO3 | 55.6% | 57.8% | 45.5% | 46.1% | 58.6% | 46.3% |
| SiO2 | 18.1% | 18.0% | 22.0% | 25.6% | 19.2% | 24.0% |
| K0.77Al1.93(Al0.5Si3.5)O10(OH)2 | 15.7% | 14.1% | 19.5% | 19.4% | 13.9% | 16.7% |
| Al2(Si2O5)(OH)4 | 6.0% | 4.7% | 7.8% | 4.9% | 3.6% | 3.4% |
| FeS2 | 3.1% | 3.3% | 2.4% | 2.6% | 2.9% | 2.7% |
| Ca(PO3)2 | 1.4% | 2.2% | 1.0% | 1.6% | 0.5% | 0.9% |
| Sample | 30-Day | 60-Day | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P/Fe | P/S | Fe/S | P/Fe | P/S | Fe/S | |
| Control | 0.76 | 0.95 | 0.78 | 0.08 | 0.79 | 0.01 |
| M | 0.55 | 0.91 | 0.43 | 0.48 | 0.41 | 0.13 |
| LAA | 0.66 | 0.77 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.83 | 0.42 |
| LMB | 0.67 | 0.91 | 0.57 | 0.70 | 0.86 | 0.60 |
| LAA+M | 0.73 | 0.91 | 0.77 | 0.64 | 0.86 | 0.54 |
| LMB+M | 0.66 | 0.93 | 0.75 | 0.38 | 0.77 | 0.43 |
| Time | Control | M | LAA | LMB | LAA+M | LMB+M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30-day | 0.95 | 0.68 | 0.77 | 0.86 | 0.50 | 0.40 |
| 60-day | 0.70 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.41 | 0.28 | 0.34 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, W.; Yang, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Liao, P.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; He, Y.; Xu, D. Synergistic Effects and Ecological Responses of Combined In Situ Passivation and Macrophytes toward the Water Quality of a Macrophytes-Dominated Eutrophic Lake. Water 2022, 14, 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121847
Yu W, Yang H, Yang Y, Chen J, Liao P, Wang J, Wu J, He Y, Xu D. Synergistic Effects and Ecological Responses of Combined In Situ Passivation and Macrophytes toward the Water Quality of a Macrophytes-Dominated Eutrophic Lake. Water. 2022; 14(12):1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121847
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Wei, Haiquan Yang, Yongqiong Yang, Jingan Chen, Peng Liao, Jingfu Wang, Jiaxi Wu, Yun He, and Dan Xu. 2022. "Synergistic Effects and Ecological Responses of Combined In Situ Passivation and Macrophytes toward the Water Quality of a Macrophytes-Dominated Eutrophic Lake" Water 14, no. 12: 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121847
APA StyleYu, W., Yang, H., Yang, Y., Chen, J., Liao, P., Wang, J., Wu, J., He, Y., & Xu, D. (2022). Synergistic Effects and Ecological Responses of Combined In Situ Passivation and Macrophytes toward the Water Quality of a Macrophytes-Dominated Eutrophic Lake. Water, 14(12), 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121847