Nanobubble Technology Enhanced Ozonation Process for Ammonia Removal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
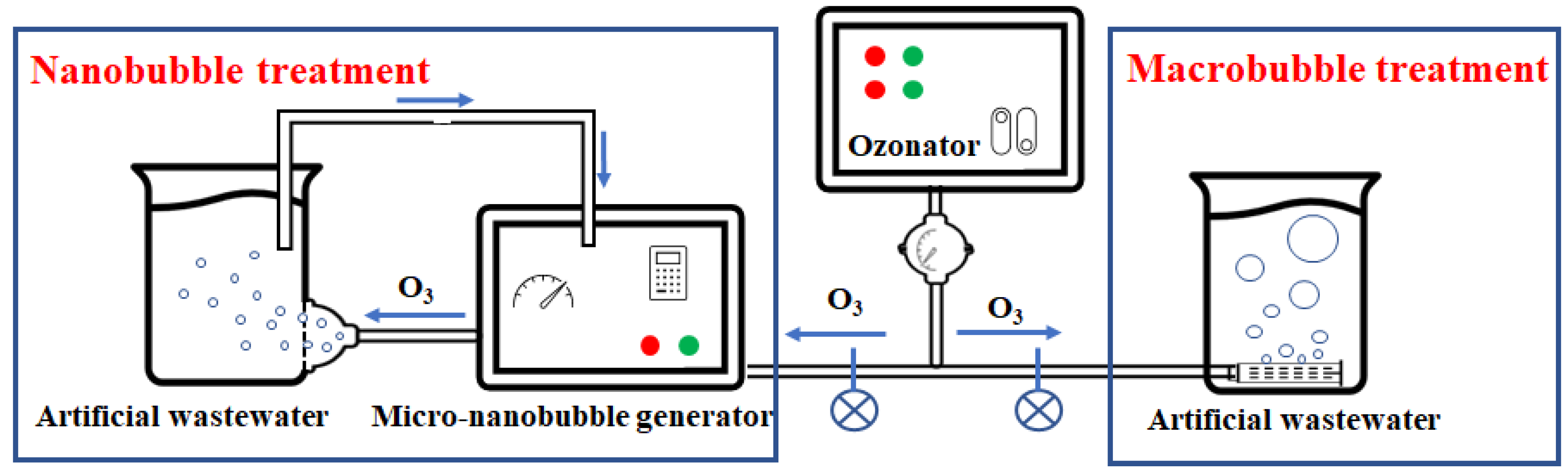
2.1. Ozone-Nanobubble Solution Preparation
2.2. Experimental Prozcedure
2.3. Analytical Parameters Determination
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
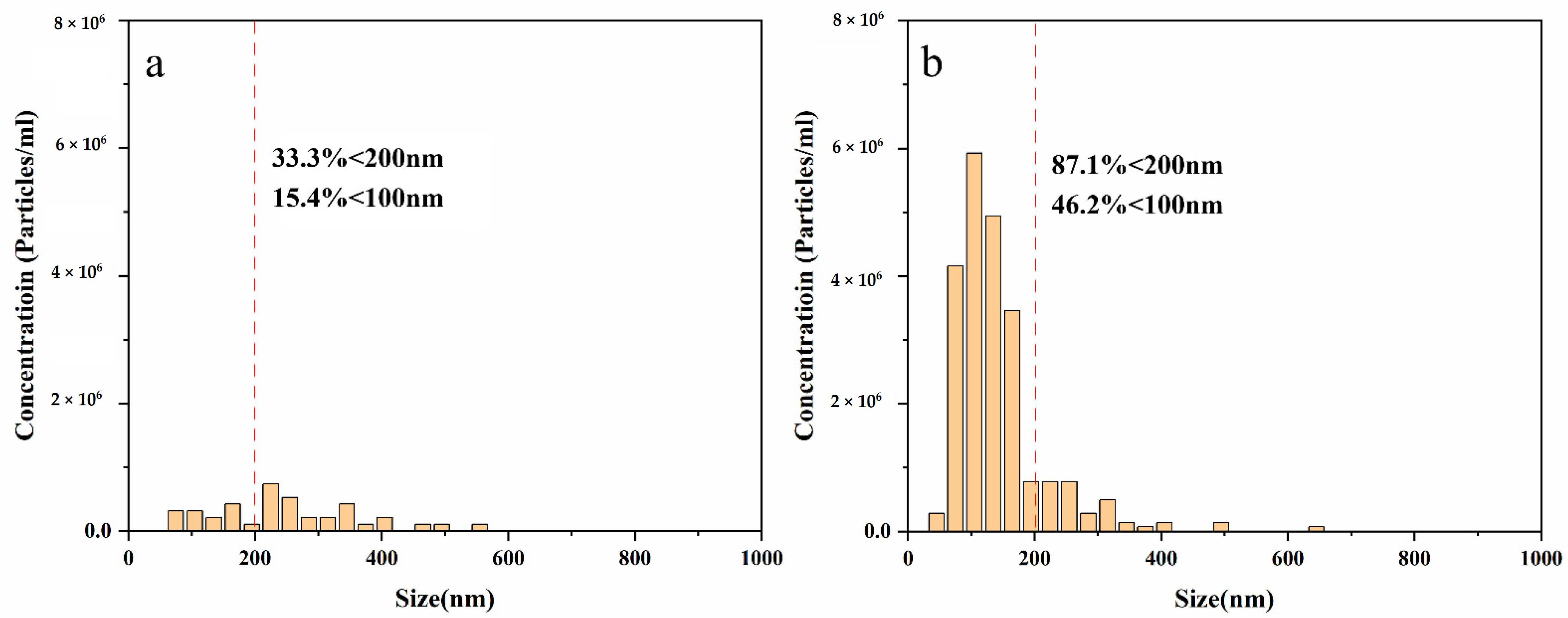
3.1. Characterisation of the Bubble Size and Distribution
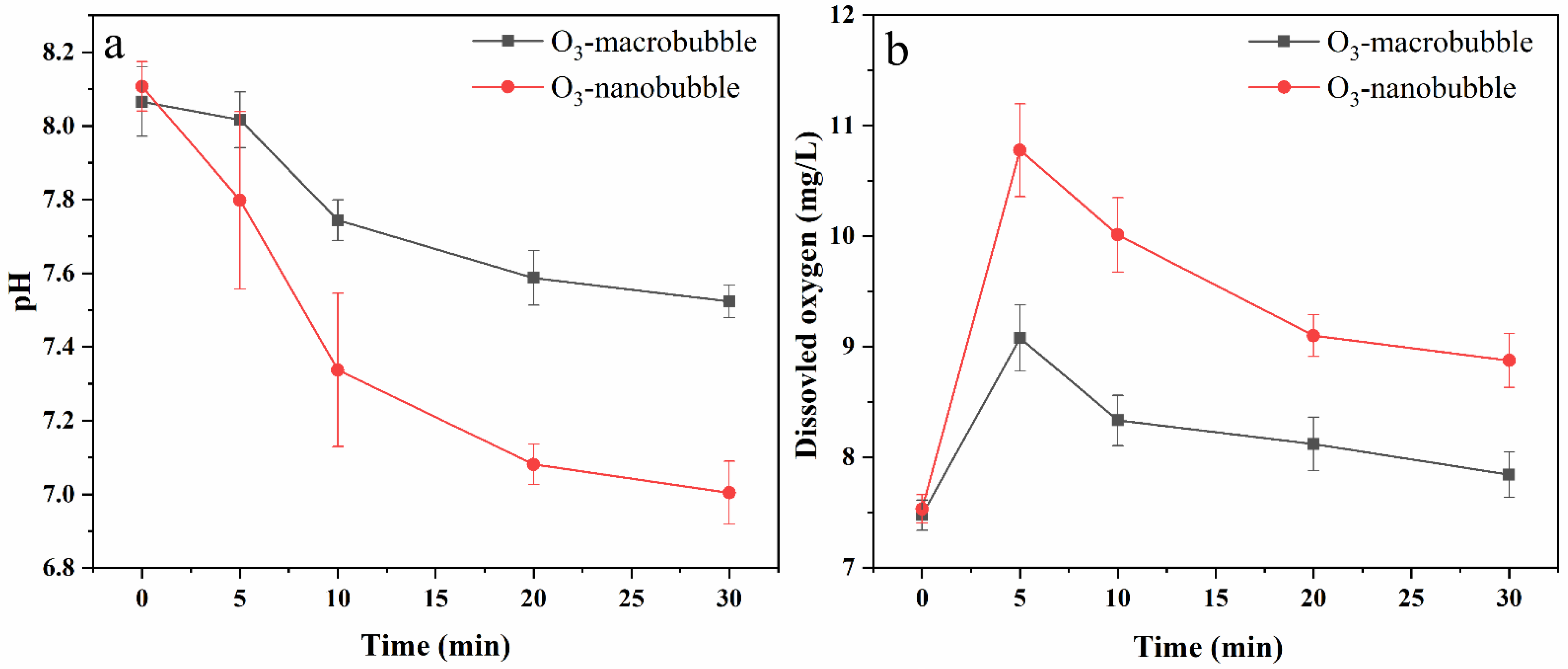
3.2. The Changes in pH and Dissolved Oxygen (DO) during the Treatment
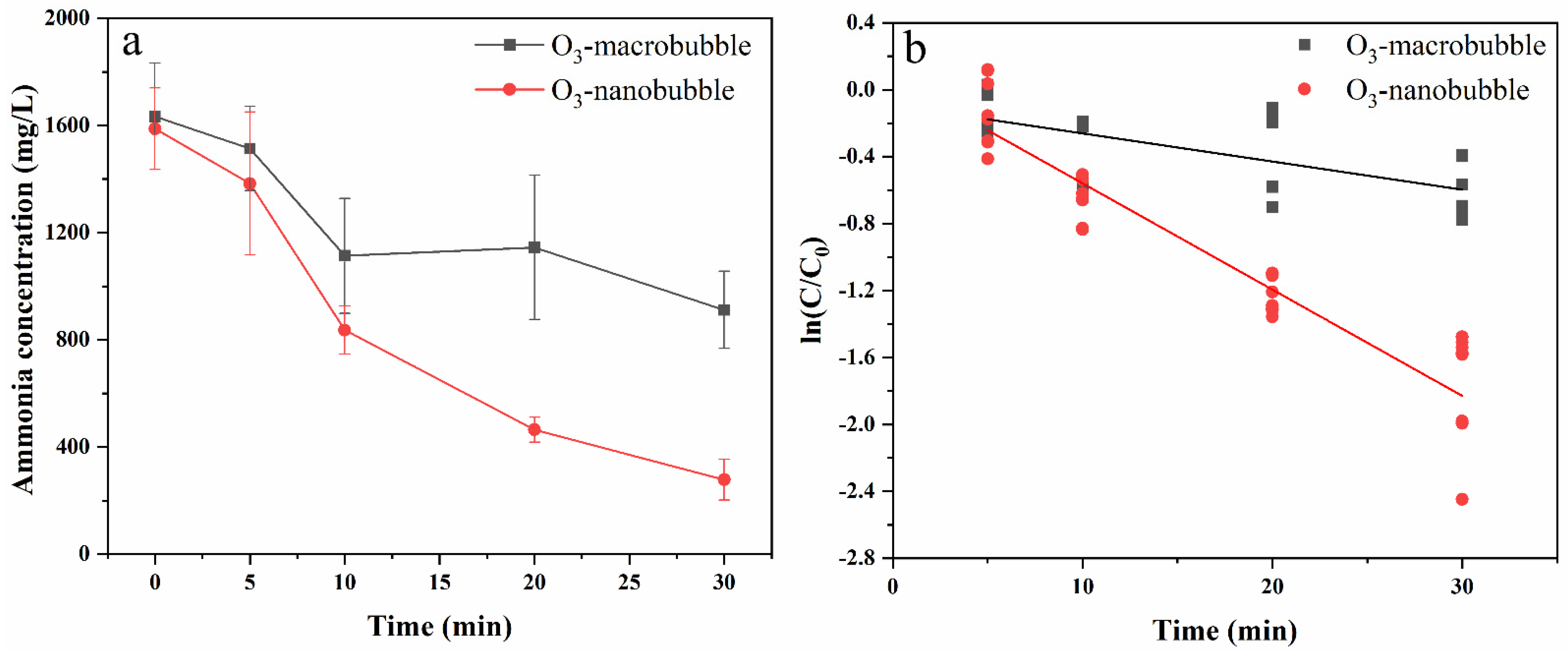
3.3. Ammonia Nitrogen Removal Performance and Kinetics
3.4. Implementation Potential
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ikeura, H.; Kobayashi, F.; Tamaki, M. Removal of residual pesticides in vegetables using ozone microbubbles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 956–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lyu, T.; Song, L.; Chen, Q.; Pan, G. Lake and River Restoration: Method, Evaluation and Management. Water 2020, 12, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bejan, D.; Graham, T.; Bunce, N.J. Chemical methods for the remediation of ammonia in poultry rearing facilities: A review. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 115, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, T.; He, K.; Dong, R.; Wu, S. The intensified constructed wetlands are promising for treatment of ammonia stripped effluent: Nitrogen transformations and removal pathways. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khuntia, S.; Majumder, S.K.; Ghosh, P. Removal of ammonia from water by ozone microbubbles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, N.B.; Krishna, B.K.C.; Sathasivan, A. Effectiveness of Breakpoint Chlorination and Rechlorination on Nitrified Chloraminated Water. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Environment, Resources and Energy Engineering (EREE), Bangkok, Thailand, 9–11 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Tao, C. Electrokinetic remediation with solar powered for electrolytic manganese residue and researching on migration of ammonia nitrogen and manganese. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.R.; Othman, M.H.D.; Abu Samah, R.; Puteh, M.H.; Ismail, A.F.; Mustafa, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Jaafar, J. Current trends and future prospects of ammonia removal in wastewater: A comprehensive review on adsorptive membrane development. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 213, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.W.; Mavinic, D.S.; Oldham, W.K.; Koch, F.A. Controlling factors for simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in a two-stage intermittent aeration process treating domestic sewage. Water Res. 1999, 33, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Tsai, J.Y.; Chang, C.Y. Ammonia removal from ammonia-rich wastewater by air stripping using a rotating packed bed. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 102, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafvert, C.T.; Valentine, R.L. Reaction scheme for the chlorination of ammoniacal water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.X.; Giannis, A.; Zhang, J.F.; Chang, V.W.C.; Wang, J.Y. Air stripping process for ammonia recovery from source-separated urine: Modeling and optimization. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 2208–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; An, W.; Huo, M.; Xiao, D.; Lyu, T.; Cui, J. An integrated approach using ozone nanobubble and cyclodextrin inclusion complexation to enhance the removal of micropollutants. Water Res. 2021, 196, 117039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.G.; Lyu, T.; Bi, L.; Tempero, G.; Hamilton, D.P.; Pan, G. Combating hypoxia/anoxia at sediment-water interfaces: A preliminary study of oxygen nanobubble modified clay materials. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Ai, H.; Fu, M.-L.; Hu, Y.-B.; Liu, J.; Ji, Y.; Vasanthakumar, V.; Yuan, B. A new insight into catalytic ozonation of ammonia by MgO/Co3O4 composite: The effects, reaction kinetics and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettmer, A.; Ball, R.; Boving, T.B.; Khan, N.A.; Schaub, T.; Sudasinghe, N.; Fernandez, C.A.; Carroll, K.C. Stabilization and prolonged reactivity of aqueous-phase ozone with cyclodextrin. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2016, 196, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Choi, H. Modeling in situ ozonation for the remediation of nonvolatile PAH-contaminated unsaturated soils. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2002, 55, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Carroll, K.C. Natural attenuation method for contaminant remediation reagent delivery assessment for in situ chemical oxidation using aqueous ozone. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakness, K.L. Ozone in Drinking Water Treatment: Process Design, Operation, and Optimization; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, G.; He, G.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Q.; Tyliszczak, T.; Tai, R.; Guo, J.; Bi, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H. Nanobubbles at Hydrophilic Particle-Water Interfaces. Langmuir 2016, 32, 11133–11137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyu, T.; Wu, S.; Mortimer, R.; Pan, G. Nanobubble Technology in Environmental Engineering: Revolutionization Potential and Challenges. Environ. Ence Technol. 2019, 53, 7175–7176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Miao, X.J.; Ali, J.; Lyu, T.; Pan, G. Quantification of Oxygen Nanobubbles in Particulate Matters and Potential Applications in Remediation of Anaerobic Environment. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 10624–10630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.H.; An, H.; Ohl, C.D. Stability of surface and bulk nanobubbles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 53, 101428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, A.; Etchepare, R.; Calgaroto, S.; Rubio, J. Aqueous dispersions of nanobubbles: Generation, properties and features. Miner. Eng. 2016, 94, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favvas, E.P.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Efthimiadou, E.K.; Mitropoulos, A.C. Bulk nanobubbles, generation methods and potential applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 54, 101455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Chiba, K.; Li, P. Formation of Hydroxyl Radicals by Collapsing Ozone Microbubbles under Strongly Acidic Conditions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 11443–11446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Cui, J.; Li, Q.; Huo, Y.; Xiao, D.; Yang, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, C.; Jarvis, P.; Lyu, T.; et al. Bactericidal efficiency and photochemical mechanisms of micro/nano bubble-enhanced visible light photocatalytic water disinfection. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lyu, T.; Liu, L.; Hu, Z.; Chen, J.; Su, B.; Yu, J.; Pan, G. Exploring a multifunctional geoengineering material for eutrophication remediation: Simultaneously control internal nutrient load and tackle hypoxia. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 127206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Tao, L.; Yue, B.; Tonoli, E.; Pan, G. Enhancement of tomato plant growth and productivity in organic farming by agri-nanotechnology using nanobubble oxygation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10823–11083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, L.B.; Xing, X.H.; Yu, A.; Zhou, Y.N.; Sun, X.L.; Jurcik, B. Enhanced ozonation of simulated dyestuff wastewater by microbubbles. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 1854–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, M.; Teng, C.H.; Yang, T.H. Dissolution enhancement and mathematical modeling of removal of residual trichloroethene in sands by ozonation during flushing with micro-nano-bubble solution. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2017, 202, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluthgun Hewage, S.; Batagoda, J.H.; Meegoda, J.N. In situ remediation of sediments contaminated with organic pollutants using ultrasound and ozone nanobubbles. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2020, 37, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.; Carra, I.; Jefferson, B.; Jodkowska, M.; Brookes, A.; Jarvis, P. Are microbubbles magic or just small? a direct comparison of hydroxyl radical generation between microbubble and conventional bubble ozonation under typical operational conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, M.T.; Reisinger, A.J. Effects of ciprofloxacin on metabolic activity and algal biomass of urban stream biofilms. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 706, 135728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, C.-R.; Wang, J.; Fang, Z.; Zhou, L.-M.; Zhang, L.-J.; Hu, J. Formation and stability of ultrasonic generated bulk nanobubbles. Chin. Phys. B 2018, 27, 118104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.M.; Xia, Z.R. Application of ozone micro-nano-bubbles to groundwater remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.H.; Yen, Y.L. Ammonia and nitrite removal from sea water by ozonation. Environ. Technol. 1997, 18, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavasso, I.; Montanaro, D.; Di Palma, L.; Petrucci, E. Electrochemically assisted decomposition of ozone for degradation and mineralization of Diuron. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 331, 135423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Shi, Z.; Tian, Y.; Shi, S.; Smale, N.; Wang, J. Microbubble enhanced ozonation process for advanced treatment of wastewater produced in acrylic fiber manufacturing industry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 287, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Tao, L.; Cooper, M.; Pan, G. Reducing arsenic toxicity using the interfacial oxygen nanobubble technology for sediment remediation. Water Res. 2021, 205, 117657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Maeda, N.; Craig, V.S.J. Physical properties of nanobubbles on hydrophobic surfaces in water and aqueous solutions. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5025–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, T.; Pan, G.; Li, P. Aquatic Macrophytes in Morphological and Physiological Responses to the Nanobubble Technology Application for Water Restoration. ACS EST Water 2021, 1, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; An, W.G.; Huo, M.X.; Yang, W.; Zhu, S.Y.; Lin, S.S. Solubilization and stabilization for prolonged reactivity of ozone using micro-nano bubbles and ozone-saturated solvent: A promising enhancement for ozonation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 238, 116484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffino, B.; Zanetti, M. Orthophosphate vs. bicarbonate used as a buffering substance for optimizing the bromide-enhanced ozonation process for ammonia nitrogen removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almaguer, M.A.; Cruz, Y.R.; da Fonseca, F.V. Combination of Advanced Oxidation Processes and Microalgae Aiming at Recalcitrant Wastewater Treatment and Algal Biomass Production: A Review. Environ. Processes 2021, 8, 483–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Ji, L. Ozonation of ammonia at low temperature in the absence and presence of MgO. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 376, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryskie, S.; Gonzalez-Merchan, C.; Neculita, C.M.; Genty, T. Efficiency of ozone microbubbles for ammonia removal from mine effluents. Miner. Eng. 2020, 145, 106071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoigné, J.; Bader, H. Ozonation of Water: Role of Hydroxyl Radicals as Oxidizing Intermediates. Science 1975, 190, 782–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Yen, Y.L. Ozonation kinetics of ammonia and nitrite removal from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Sci. Health 1996, 31, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Shi, J.L.; von Gunten, U.; McCurry, D.L. Ozonation of Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater: A Critical Review. Water Res. 2022, 213, 118053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.; Ohde, D.; Matthes, S.; Engelmann, C.; Bubenheim, P.; Terasaka, K.; Schluter, M.; Liese, A. Comparative investigation of fine bubble and macrobubble aeration on gas utility and biotransformation productivity. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2021, 118, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Tian, W.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, W.; Liu, F.; Zhao, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, T. Nanobubble Technology Enhanced Ozonation Process for Ammonia Removal. Water 2022, 14, 1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121865
Wu Y, Tian W, Zhang Y, Fan W, Liu F, Zhao J, Wang M, Liu Y, Lyu T. Nanobubble Technology Enhanced Ozonation Process for Ammonia Removal. Water. 2022; 14(12):1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121865
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yuncheng, Wei Tian, Yang Zhang, Wei Fan, Fang Liu, Jiayin Zhao, Mengmeng Wang, Yu Liu, and Tao Lyu. 2022. "Nanobubble Technology Enhanced Ozonation Process for Ammonia Removal" Water 14, no. 12: 1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121865
APA StyleWu, Y., Tian, W., Zhang, Y., Fan, W., Liu, F., Zhao, J., Wang, M., Liu, Y., & Lyu, T. (2022). Nanobubble Technology Enhanced Ozonation Process for Ammonia Removal. Water, 14(12), 1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121865







