Impacts of Climate Change and Non-Point-Source Pollution on Water Quality and Algal Blooms in the Shoalhaven River Estuary, NSW, Australia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
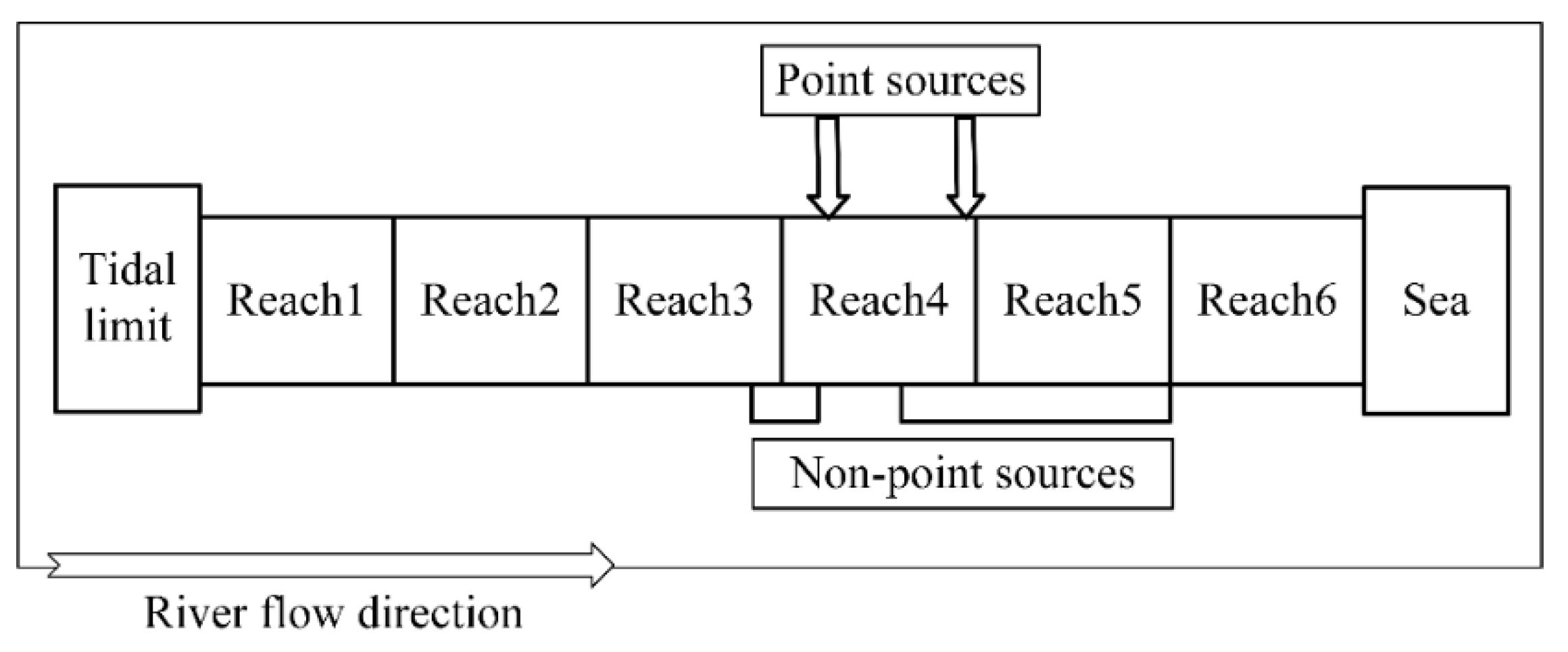
2.1. Geography
2.2. QUAL2K Model Setting
2.3. Data Collection
2.3.1. Climate
2.3.2. Inflows
2.3.3. Point Sources: Bomaderry Creek and Broughton Creek
2.3.4. Water Quality Measurements
2.3.5. Non-Point Source Inputs
2.3.6. Phytoplankton
2.4. QUAL2K Initial Conditions Setting
3. Results and Discussion
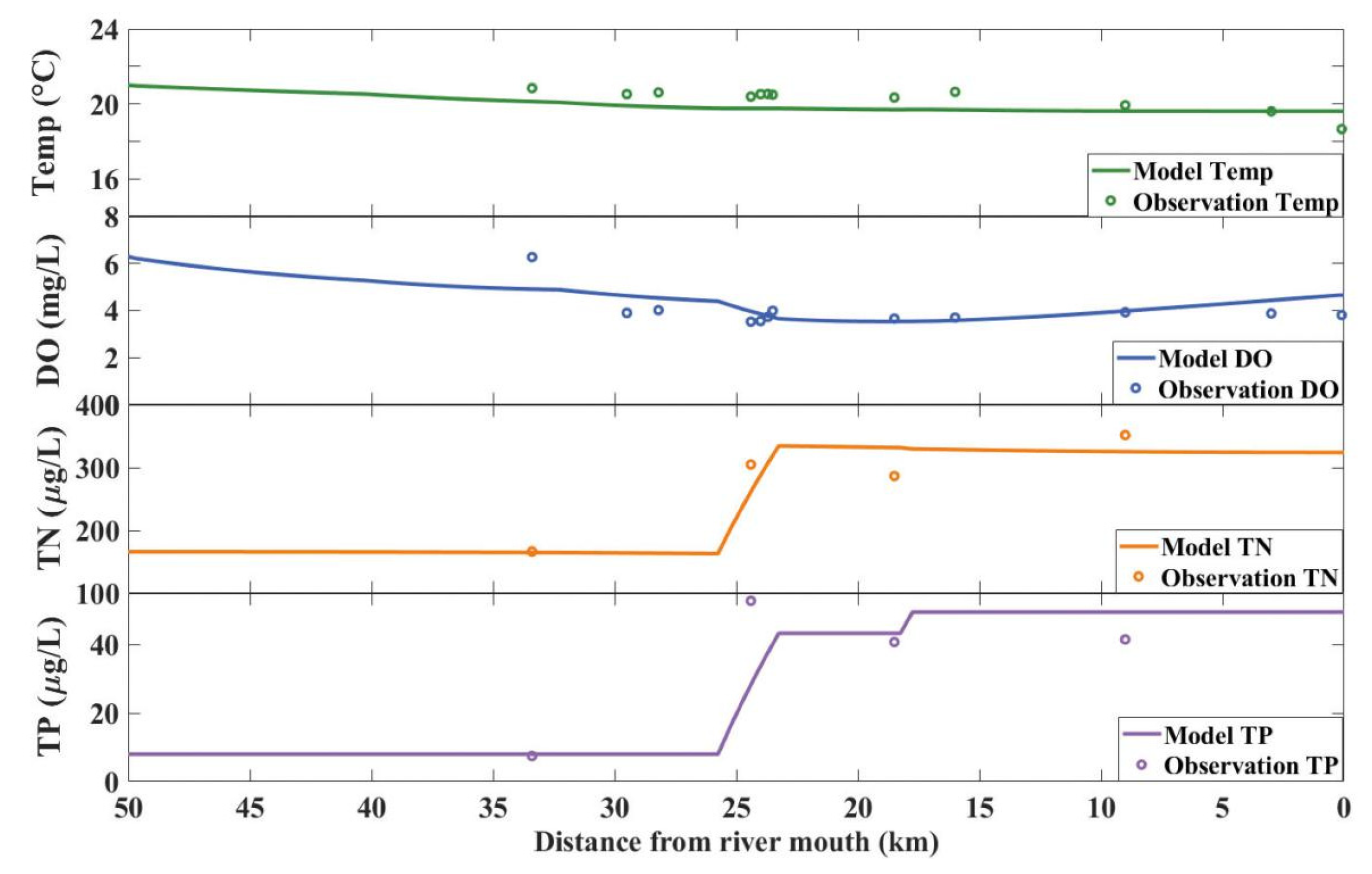
3.1. Calibration and Validation
3.2. Future Scenarios Setting
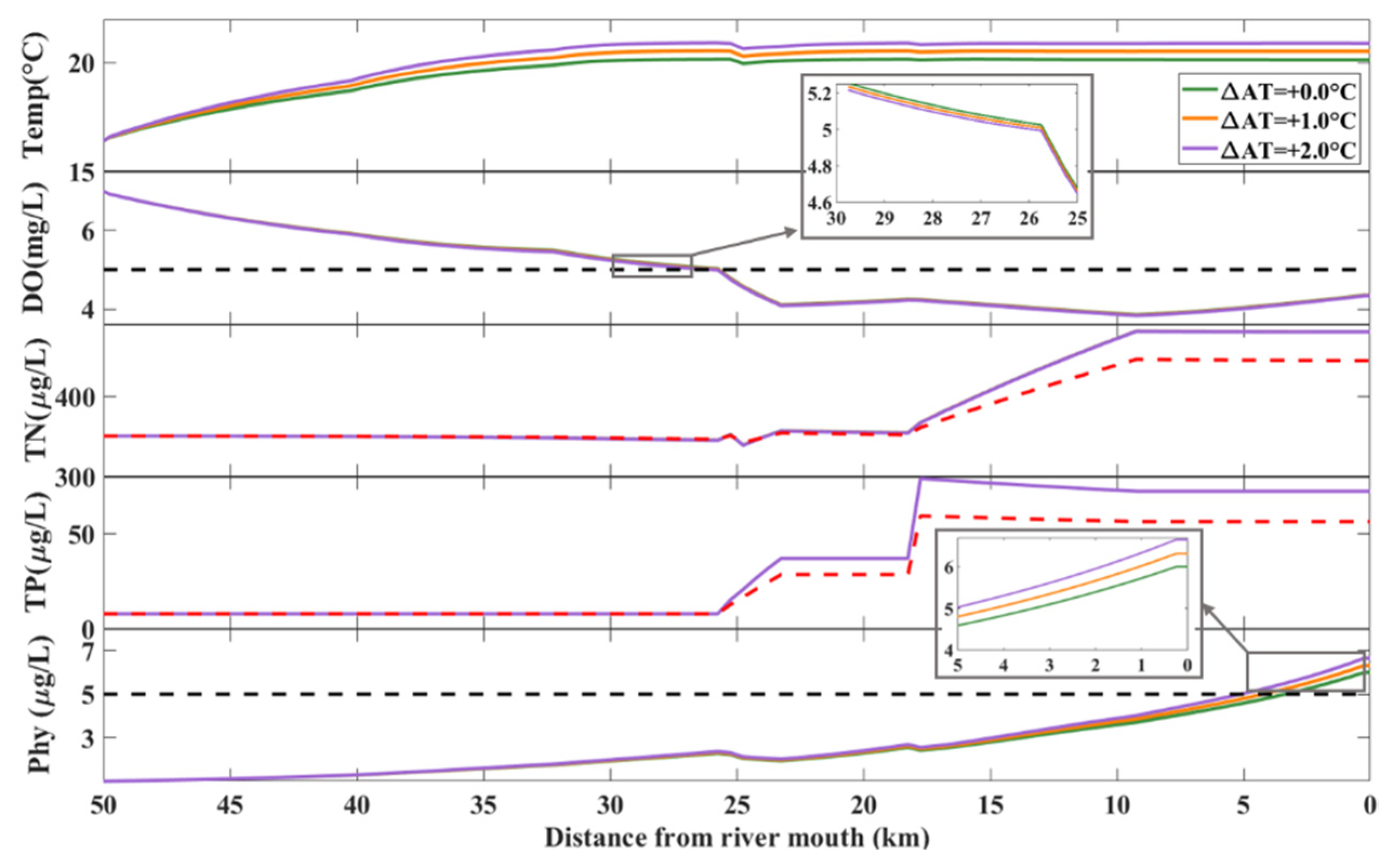
3.3. Assessment of the Effects of Air-Temperature Increase Only
3.4. Assessment of the Effects of Air-Temperature Increase with Reduced Streamflow
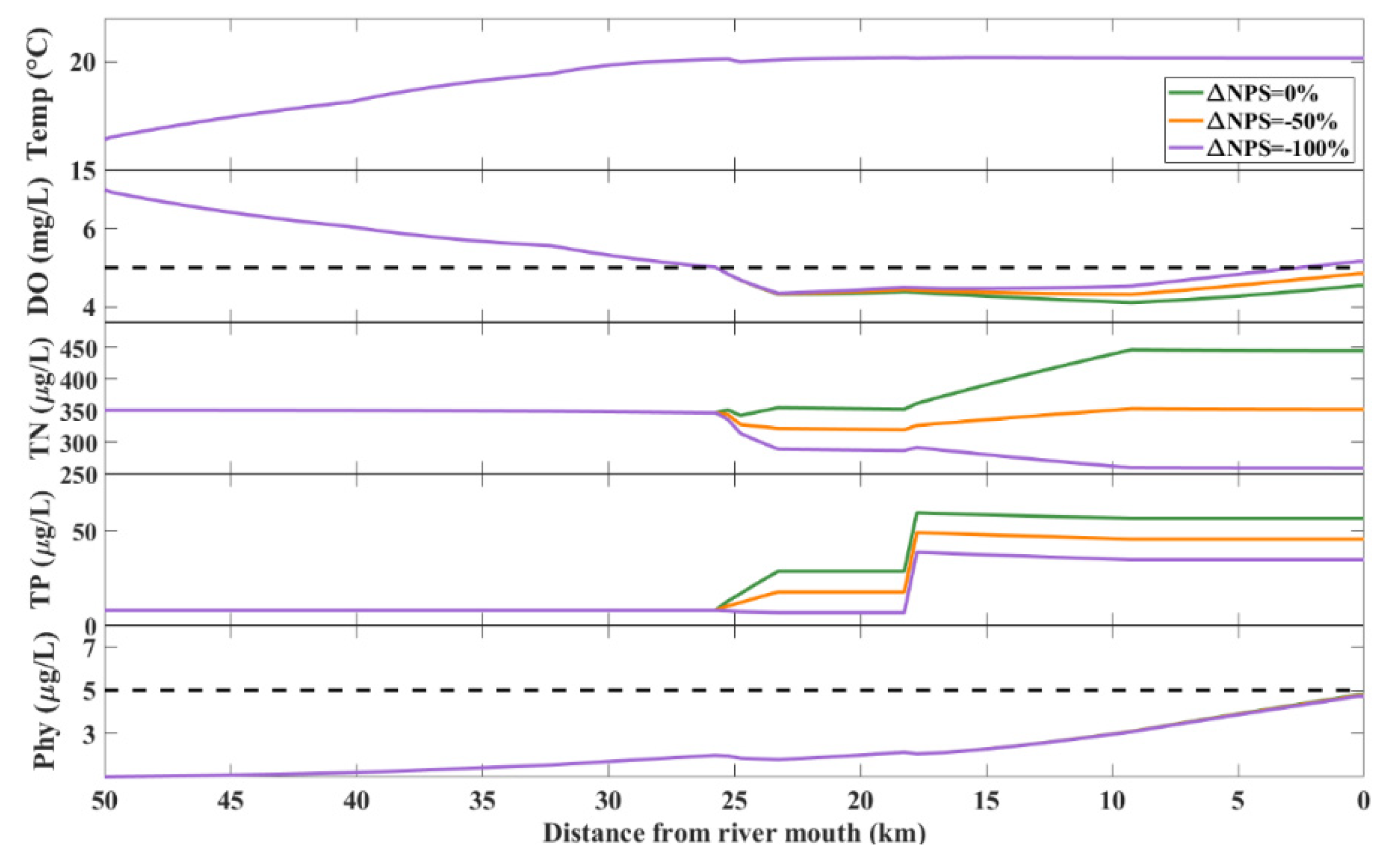
3.5. Assessment of the Effects of Changes in NPS Pollution Input
4. Mitigation Option for Water Quality Improvement under Climate Change
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Water Temperature T [°C]
Appendix A.1.1. Air-Water Heat Flux: Solar Radiation
Appendix A.1.2. Air-Water Heat Flux: Atmospheric Long-Wave Radiation
Appendix A.2. DO Concentration per Day [mg/L/day]
Appendix A.3. Total Nitrogen (TN) Concentration [μg/L]
Appendix A.4. Total Phosphorus (TP) Concentration [μg/L]
Appendix A.5. Phytoplankton (Sap) Concentration per Day [μg/L/day]
Appendix A.6. Residence Time [Day]
References
- Lu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Lu, X.; Su, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Cao, X.; Li, Q.; Su, J.; Ittekkot, V.; et al. Major Threats of Pollution and Climate Change to Global Coastal Ecosystems and Enhanced Management for Sustainability. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darby, S.E.; Hackney, C.R.; Leyland, J.; Kummu, M.; Lauri, H.; Parsons, D.R.; Best, J.L.; Nicholas, A.P.; Aalto, R. Fluvial Sediment Supply to a Mega-Delta Reduced by Shifting Tropical-Cyclone Activity. Nature 2016, 539, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scavia, D.; Field, J.C.; Boesch, D.F.; Buddemeier, R.W.; Burkett, V.; Cayan, D.R.; Fogarty, M.; Harwell, M.A.; Howarth, R.W.; Mason, C.; et al. Climate Change Impacts on U.S. Coastal and Marine Ecosystems. Estuaries 2002, 25, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, K.; Fitzharris, B.; Bates, B.C.; Harvey, N.; Howden, S.M.; Hughes, L.; Salinger, J.; Warrick, R. Australia and New Zealand. In Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Parry, M.L., Canziani, O.F., Palutikof, J.P., van der Linden, P.J., Hanson, C.E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 507–540. [Google Scholar]
- Scanes, E.; Scanes, P.R.; Ross, P.M. Climate Change Rapidly Warms and Acidifies Australian Estuaries. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillanders, B.M.; Elsdon, T.S.; Halliday, I.A.; Jenkins, G.P.; Robins, J.B.; Valesini, F.J. Potential Effects of Climate Change on Australian Estuaries and Fish Utilising Estuaries: A Review. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1115–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Littleboy, M.; Young, J.; Rahman, J. Climate Change Impacts on Surface Runoff and Recharge to Groundwater; NSW Office of Environment and Heritage: Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alamdari, N.; Sample, D.J.; Ross, A.C.; Easton, Z.M. Evaluating the Impact of Climate Change on Water Quality and Quantity in an Urban Watershed Using an Ensemble Approach. Estuaries Coasts 2020, 43, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Aramaki, T.; Hanaki, K.; Matsuo, T.; Wilby, R. Lake Stratification and Temperature Profiles Simulated Using Downscaled GCM Output. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 38, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, D.; Pryce, A.R. Using Science to Create a Better Place: Climate Change Impacts and Water Temperature; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead, P.G.; Wilby, R.L.; Battarbee, R.W.; Kernan, M.; Wade, A.J. A Review of the Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Surface Water Quality. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Wong, P.P.; Burkett, V.R.; Codignotto, J.O.; Hay, J.E.; Mclean, R.; Ragoonaden, S.; Woodroffe, C. Coastal Systems and Low-Lying Areas. In Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Parry, M.L., Canziani, O.F., Palutikof, J.P., van der Linden, P.J., Hanson, C.E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 315–356. [Google Scholar]
- Vaze, J.; Teng, J.; Post, D.; Chiew, F.; Perraud, J.-M.; Kirono, D. Future Climate and Runoff Projections (~2030) for New South Wales and Australian Capital Territory; NSW Department of Water and Energy: Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, G.L.; Milligan, D.B. Some Geomorphological Observations in the Kara Sea. Deep Res. Oceanogr. Abstr. 1967, 14, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, A.; Ksiaszek, L.; Vericat, D.; Batalla, R.J. Assessing the Geomorphic Effects of a Flushing Flow in a Large Regulated River. River Res. Appl. 2013, 29, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimikou, M.A.; Baltas, E.; Varanou, E.; Pantazis, K. Regional Impacts of Climate Change on Water Resources Quantity and Quality Indicators. J. Hydrol. 2000, 234, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, M.D.; Peirson, W.L.; Peters, G.M.; Cox, R.J. Managing Adaptation of Urban Water Systems in a Changing Climate. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 1953–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turral, H.; Burke, J.; Faures, J.M.; Faures, J.M. Climate Change, Water and Food Security. In FAO Water Reports; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2011; Volume 148, p. 204. [Google Scholar]
- Peirson, W.; Davey, E.; Jones, A.; Hadwen, W.; Bishop, K.; Beger, M.; Capon, S.; Fairweather, P.; Creese, B.; Smith, T.F.; et al. Opportunistic Management of Estuaries under Climate Change: A New Adaptive Decision-Making Framework and Its Practical Application. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 163, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lotze, H.K.; Lenihan, H.S.; Bourque, B.J.; Bradbury, R.H.; Cooke, R.G.; Kay, M.C.; Kidwell, S.M.; Kirby, M.X.; Peterson, C.H.; Jackson, J.B.C. Depletion Degradation, and Recovery Potential of Estuaries and Coastal Seas. Science 2006, 312, 1806–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, N.E.; Meybeck, M. Water Quality Degradation Effects on Freshwater Availability: Impacts of Human Activities. Water Int. 2000, 25, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaouzas, I.; Smeti, E.; Vourka, A.; Vardakas, L.; Mentzafou, A.; Tornés, E.; Sabater, S.; Muñoz, I.; Skoulikidis, N.T.; Kalogianni, E. Assessing the Ecological Effects of Water Stress and Pollution in a Temporary River-Implications for Water Management. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1591–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkholder, J.A.; Libra, B.; Weyer, P.; Heathcote, S.; Kolpin, D.; Thorne, P.S.; Wichman, M. Impacts of Waste from Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations on Water Quality. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.D.; Wu, W.L.; Zhang, J. Regional Differentiation of Non-Point Source Pollution of Agriculture-Derived Nitrate Nitrogen in Groundwater in Northern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 107, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongley, E.D.; Xiaolan, Z.; Tao, Y. Current Status of Agricultural and Rural Non-Point Source Pollution Assessment in China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coad, P.; Cathers, B.; Ball, J.E.; Kadluczka, R. Proactive Management of Estuarine Algal Blooms Using an Automated Monitoring Buoy Coupled with an Artificial Neural Network. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 61, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Gazi, N.H. Random Excitations in Modelling of Algal Blooms in Estuarine Systems. Ecol. Model 2011, 222, 2495–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, A.M.; Winberg, P.C.; Kirkendale, L.A. Oyster Information Portal—A User-Group Focused ‘Coastal Google’ for the Future. In Proceedings of the 21st NSW Coastal Conference Australia, Kiama, NSW, Australia, 6–9 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ajani, P.; Hallegraeff, G.; Pritchard, T. Historic Overview of Algal Blooms in Marine and Estuarine Waters of New South Wales, Australia. Proc. Linn. Soc. N. S. W. 2001, 123, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Dove, M.C.; Sammut, J. Acid Sulfate Soil Induced Acidification of Estuarine Areas Used for the Production of Sydney Rock Oysters, Saccostrea glomerata. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2013, 5, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hallegraeff, G.M. Ocean Climate Change, Phytoplankton Community Responses, and Harmful Algal Blooms: A Formidable Predictive Challenge. J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X. QUAL2K Model Used in the Water Quality Assessment of Qiantang River, China. Water Environ. Res. 2008, 80, 2125–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Qian, X.; Li, H.; Yuan, X.; Ye, R. Selection of Optimal River Water Quality Improvement Programs Using QUAL2K: A Case Study of Taihu Lake Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 431, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Qian, X.; Yuan, X.; Ye, R.; Xia, B.; Wang, Y. Simulation of Water Environmental Capacity and Pollution Load Reduction Using QUAL2K for Water Environmental Management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 4504–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, H.; Guo, S.; Li, F.; Li, G. Water Quality Evaluation in Tidal River Reaches of Liaohe River Estuary, China Using a Revised QUAL2K Model. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Growns, I.; Reinfelds, I.; Williams, S.; Coade, G. Longitudinal Effects of a Water Supply Reservoir (Tallowa Dam) on Downstream Water Quality, Substrate and Riffle Macroinvertebrate Assemblages in the Shoalhaven River, Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2009, 60, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyes, B. Determining and Managing Environmental Flows for the Shoalhaven River; Shoalhaven Environmental Flows Knowledge Review; NSW Department of Natural Resources: Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2006. Available online: https://catalogue.nla.gov.au/Record/3820242 (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Bureau of Meteorology Nowra RAN Air Station AWS. Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Australia Bureau of Statistics Nowra-Bomaderry Population. Available online: www.abs.gov.au/AUSSTATS/abs@.nsf/Previousproducts/11507Population/People12004-2008?opendocument&tabname=Summary&prodno=11507&issue=2004-2008 (accessed on 16 December 2019).
- Walling, B.; Chaudhary, S.; Dhanya, C.T.; Kumar, A. Estimation of Environmental Flow Incorporating Water Quality and Hypothetical Climate Change Scenarios. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, N.; Muhammad, N.S.; Abdullah, J. Scenario-Based Pollution Discharge Simulations and Mapping Using Integrated QUAL2K-GIS. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, B.; Dhanya, C.T.; Kumar, A. Impact of Climate Change on River Water Quality: A Case Study on the Yamuna River. In Environmental Sustainability: Concepts, Principles, Evidences and Innovations; Excellent Publishing House: Tamilnadu, India, 2014; Volume 57, pp. 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Rehana, S.; Mujumdar, P.P. River Water Quality Response to Climate Change. In Proceedings of the 34th IAHR Congress 2011—Balance and Uncertainty: Water in a Changing World, Incorporating the 33rd Hydrology and Water Resources Symposium and the 10th Conference on Hydraulics in Water Engineering, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 26 June–1 July 2011; Engineers Australia: Barton, ACT, Australia; Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2011; pp. 2153–2160. Available online: http://qatest.informit.com.au/browsePublication;isbn=9780858258686;res=IELENG;subject=Engineering (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Chapra, S.C.; Pelletier, G.J.; Tao, H. QUAL2K: A Modeling Framework for Simulating River and Stream Water Quality, Version 2.12; Civil and Environmental Engineering Dept., Tufts University: Medford, MA, USA, 2012.
- Water NSW Water NSW Realtime Data. Available online: https://realtimedata.waternsw.com.au/ (accessed on 6 November 2019).
- Willy Weather Nowra RAN Air Station. Available online: https://www.willyweather.com.au/climate/weather-stations/nsw/illawarra/nowra-ran-air-station.html?superGraph=plots:temperature,grain:daily,startDate:2019-07-25,endDate:2019-08-23&climateRecords=period:all-time&longTermGraph=plots:temperature,period:all-time,month:all&windRose=period:1-year,month:all-months (accessed on 6 November 2019).
- SCC Shoalhaven City Council Environmental Water. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20160204011916/https://shoalhaven.nsw.gov.au/soe/region/Indicator results 09/Environmentalflows 09.htm (accessed on 6 November 2019).
- SCC Shoalhaven City Council, Aqua Data. Available online: https://www.shoalhaven.nsw.gov.au/For-Residents/Our-Environment/Coast-Waterways/Shoalhaven-Water-Quality (accessed on 6 November 2019).
- Water NSW. Annual Water Quality Monitoring Report 2019–20; WaterNSW: Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson, P.R.; Pavia, H.; Toth, G. Formation of Harmful Algal Blooms Cannot Be Explained by Allelopathic Interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11177–11182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowie, G.L.; Mills, W.B.; Porcella, D.B.; Campbell, C.L.; Pagenkopf, J.R.; Rupp, G.L.; Johnson, K.M.; Chan, P.W.H.; Gherini, S.A. Rates, Constants, and Kinetics Formulations in Surface Water Quality Modeling, 2nd ed.; EPA/600/3-85/040, United States Environmental Protection Agency, Environmental Research Laboratory: Athens, GA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Baca, R.G.; Arnett, R.C. A Limnological Model for Eutrophic Lakes and Impoundments; Battelle, Inc. Pacific Northwest Laboratories: Richland, WA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Nakicenovic, N.; Alcamo, J.; Davis, G.; de Vries, B.; Fenhann, J.; Gaffin, S.; Gregory, K.; Grubler, A.; Jung, T.Y.; Kram, T.; et al. Special Report on Emissions Scenarios: A Special Report of Working Group III of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Suppiah, R.; Hennessy, K.J.; Whetton, P.H.; McInnes, K.; Macadam, I.; Bathols, J.; Ricketts, J.; Page, C.M. Australian Climate Change Projections Derived from Simulations Performed for the IPCC 4th Assessment Report. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 2007, 56, 131–152. [Google Scholar]
- Chiew, F.; Harrold, T.; Siriwardena, L.; Jones, R.; Srikanthan, R. Simulation of Climate Change Impact on Runoff Using Rainfall Scenarios That Consider Daily Patterns of Change from GCMs. In MODSIM 2003, Proceedings of the International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Townsville, QLD, Australia, 14–17 July 2003; Post, D.A., Ed.; Modelling and Simulation Society of Australia and New Zealand: Canberra, ACT, Australia, 2003; pp. 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Beare, S.; Heaney, A. Climate Change and Water Resources in the Murray Darling Basin, Australia. In Proceedings of the 2002 World Congress of Environmental and Resource Economists, Monterey, CA, USA, 24–27 June 2002; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.N.; Page, C.M. Assessing the Risk of Climate Change on the Water Resources of the Macquarie River Catchment: Integrating Models for Natural Resources Management across Disciplines. Int. Congr. Model. Simul. 2001, 2, 673–678. [Google Scholar]
- Caraco, N.F.; Cole, J.J. Contrasting Impacts of a Native and Alien Macrophyte on Dissolved Oxygen in a Large River. Ecol. Appl. 2002, 12, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.V.; Pace, M.L.; Mather, J.R.; Murdoch, P.S.; Howarth, R.W.; Folt, C.L.; Chen, C.Y.; Hemond, H.F.; Flebbe, P.A.; Driscoll, C.T. Potential Effects of Climate Change on Freshwater Ecosystems of the New England/Mid-Atlantic Region. Hydrol. Process. 1997, 11, 925–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commoner, B.; Corr, M.; Stamler, P.J. The Causes of Pollution. Environment 1971, 13, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, D.J. A Review of Intensified Land Use Effects on the Ecosystems of Botany Bay and Its Rivers, Georges River and Cooks River, in Southern Sydney, Australia. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 39, 101396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P.J.; Stolzenbach, K.D. Engineering Aspects of Heat Disposal from Power Generation; Harleman, D.R.F., Ed.; MIT: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Brutsaert, W. Evaporation into the Atmosphere: Theory, History, and Applications; D. Reidel Publishing Co.: Hingham, MA, USA, 1982; 299p. [Google Scholar]



| Variables | Shoalhaven River | Bomaderry Creek | Broughton Creek |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | |||
| Inflow (m3/s) | 6.51 | 0.27 | 0.41 |
| Temperature (°C) | 16.4 | 19.5 | 19.6 |
| DO conc. (mg/L) | 7.00 | 6.88 | 4.48 |
| TN conc. (μg/L) | 350 | 400 | 425 |
| TP conc. (μg/L) | 8.00 | 66.7 | 650 |
| 2018 | |||
| Inflow (m3/s) | 6.51 | 0.02 | 0.19 |
| Temperature (°C) | 21.0 | 20.6 | 20.3 |
| DO conc. (mg/L) | 6.30 | 7.33 | 3.44 |
| TN conc. (μg/L) | 165 | 358 | 260 |
| TP conc. (μg/L) | 8.00 | 34.5 | 295 |
| Reach | Site Number | Temperature (°C) | DO Conc. (mg/L) | TN Conc. (μg/L) | TP Conc. (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | E-3 | 19.5/20.8 | 5.77/6.27 | 350/166 | 7.50/7.50 |
| R3 | E-414 | 19.7/20.5 | 5.28/3.90 | ||
| E-342 | 19.7/20.6 | 5.33/4.02 | |||
| R4 | E-148 | 19.6/20.5 | 4.83/3.56 | 350/305 | 22.5/52.8 |
| E-149 | 20.7/20.4 | 4.86/3.53 | |||
| E-346 | 19.9/20.5 | 4.50/3.73 | |||
| E-7 | 19.9/20.5 | 3.44/3.99 | |||
| E-294 | 19.9/20.3 | 4.57/3.66 | 350/287 | 32.5/40.8 | |
| R5 | E-295 | 20.4/20.6 | 4.26/3.7 | ||
| E-548 | 14.5/19.9 | 5.00/3.93 | 450/352 | 56.3/41.5 | |
| R6 | E-777 | 20.1/19.6 | 4.95/3.88 | ||
| E-776 | 20.0/18.7 | 5.13/3.81 |
| Model Performance Measurement Tools | Calibration (2017) | Validation (2018) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | DO | TN | TP | Temperature | DO | TN | TP | |
| Correlation coefficient (R) | 0.69 | 0.68 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.66 | 0.83 | 0.90 | 0.75 |
| Root mean square error (RMSE) | 0.25 | 0.49 | 3.91 | 2.71 | 0.69 | 0.76 | 31.17 | 11.96 |
| Hypothetical Scenarios | Results in Percentage Changes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario | ΔAT (°C) | ΔSF (%) | ΔNPS (%) | Range | ΔT | ΔDO | ΔTN | ΔTP | ΔPhy |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | TE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| LE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 2 | +1.0 | 0 | 0 | TE | 1.5 | −0.24 | −0.03 | 0 | 2.34 |
| LE | 1.8 | −0.34 | −0.05 | 0 | 3.12 | ||||
| 3 | +2.0 | 0 | 0 | TE | 3.0 | −0.48 | −0.07 | 0 | 4.79 |
| LE | 3.7 | −0.67 | −0.10 | 0 | 6.40 | ||||
| 4 | 0 | −35 | 0 | TE | 0.87 | −2.8 | 2.9 | 25.5 | 15.90 |
| LE | −0.12 | −6.7 | 5.0 | 27.6 | 19 | ||||
| 5 | +1.0 | −35 | 0 | TE | 2.5 | −3.1 | 2.8 | 25.5 | 19.41 |
| LE | 1.7 | −7.0 | 4.9 | 27.6 | 23.64 | ||||
| 6 | +2.0 | −35 | 0 | TE | 4.1 | −3.4 | 2.8 | 25.5 | 23.11 |
| LE | 3.5 | −7.4 | 4.9 | 27.6 | 28.55 | ||||
| 7 | 0 | 0 | −50 | TE | 0 | 1.5 | −8.9 | −18.7 | −0.23 |
| LE | 0 | 3.6 | −16 | −21.6 | 0.34 | ||||
| 8 | 0 | 0 | −100 | TE | 0 | 3.1 | −18 | −37.4 | −0.45 |
| LE | 0 | 7.2 | −33 | −43.2 | 0.65 | ||||
| Scenario | ΔAT (°C) | ΔSF (%) | ΔNPS (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | −35 | 0 | −30 | −50 | −70 | +30 | +50 | +70 |
| 2 | +1.0 | −35 | 0 | −30 | −50 | −70 | +30 | +50 | +70 |
| 3 | +2.0 | −35 | 0 | −30 | −50 | −70 | +30 | +50 | +70 |
| Scenario 1 | Scenario 2 | Scenario 3 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔNPS | ΔT | ΔDO | ΔTN | ΔTP | ΔPhy | ΔT | ΔDO | ΔTN | ΔTP | ΔPhy | ΔT | ΔDO | ΔTN | ΔTP | ΔPhy |
| 0 | 0.8 | −2.7 | 2.7 | 25.5 | 2.3 | 2.5 | −3 | 2.8 | 25.5 | 3.3 | 4.1 | −3.2 | 2.8 | 25.5 | 4.3 |
| −30 | 0.8 | −1.4 | −4.4 | 10.2 | 2.1 | 2.5 | −1.6 | −4.4 | 10.2 | 3.1 | 4.1 | −1.8 | −4.4 | 10.2 | 4.1 |
| −50 | 0.8 | −0.5 | −9.2 | 0 | 2.0 | 2.5 | −0.7 | −9.2 | 0 | 3.0 | 4.1 | −0.9 | −9.2 | 0 | 4.0 |
| −70 | 0.8 | 0.4 | −14 | −10.2 | 1.9 | 2.5 | 0.2 | −14 | −10.2 | 2.9 | 4.1 | 0 | −14 | −10.2 | 3.9 |
| +30 | 0.8 | −4.0 | 10.1 | 40.8 | 2.5 | 2.5 | −4.2 | 10.1 | 40.8 | 3.5 | 4.1 | −4.5 | 10.0 | 40.8 | 4.6 |
| +50 | 0.8 | −4.8 | 14.9 | 51 | 2.7 | 2.5 | −5.1 | 14.9 | 51 | 3.7 | 4.1 | −5.3 | 14.8 | 51.0 | 4.7 |
| +70 | 0.8 | −5.7 | 19.7 | 61.2 | 2.8 | 2.5 | −6.0 | 19.7 | 61.2 | 3.9 | 4.1 | −6.2 | 19.6 | 61.2 | 4.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, L.; Wang, X.H.; Peirson, W. Impacts of Climate Change and Non-Point-Source Pollution on Water Quality and Algal Blooms in the Shoalhaven River Estuary, NSW, Australia. Water 2022, 14, 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121914
Wan L, Wang XH, Peirson W. Impacts of Climate Change and Non-Point-Source Pollution on Water Quality and Algal Blooms in the Shoalhaven River Estuary, NSW, Australia. Water. 2022; 14(12):1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121914
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Liu, Xiao Hua Wang, and William Peirson. 2022. "Impacts of Climate Change and Non-Point-Source Pollution on Water Quality and Algal Blooms in the Shoalhaven River Estuary, NSW, Australia" Water 14, no. 12: 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121914
APA StyleWan, L., Wang, X. H., & Peirson, W. (2022). Impacts of Climate Change and Non-Point-Source Pollution on Water Quality and Algal Blooms in the Shoalhaven River Estuary, NSW, Australia. Water, 14(12), 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121914






