A Comparison Study of the Nutrient Fluxes in a Newly Impounded Riverine Lake (Longjing Lake): Model Calculation and Sediment Incubation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
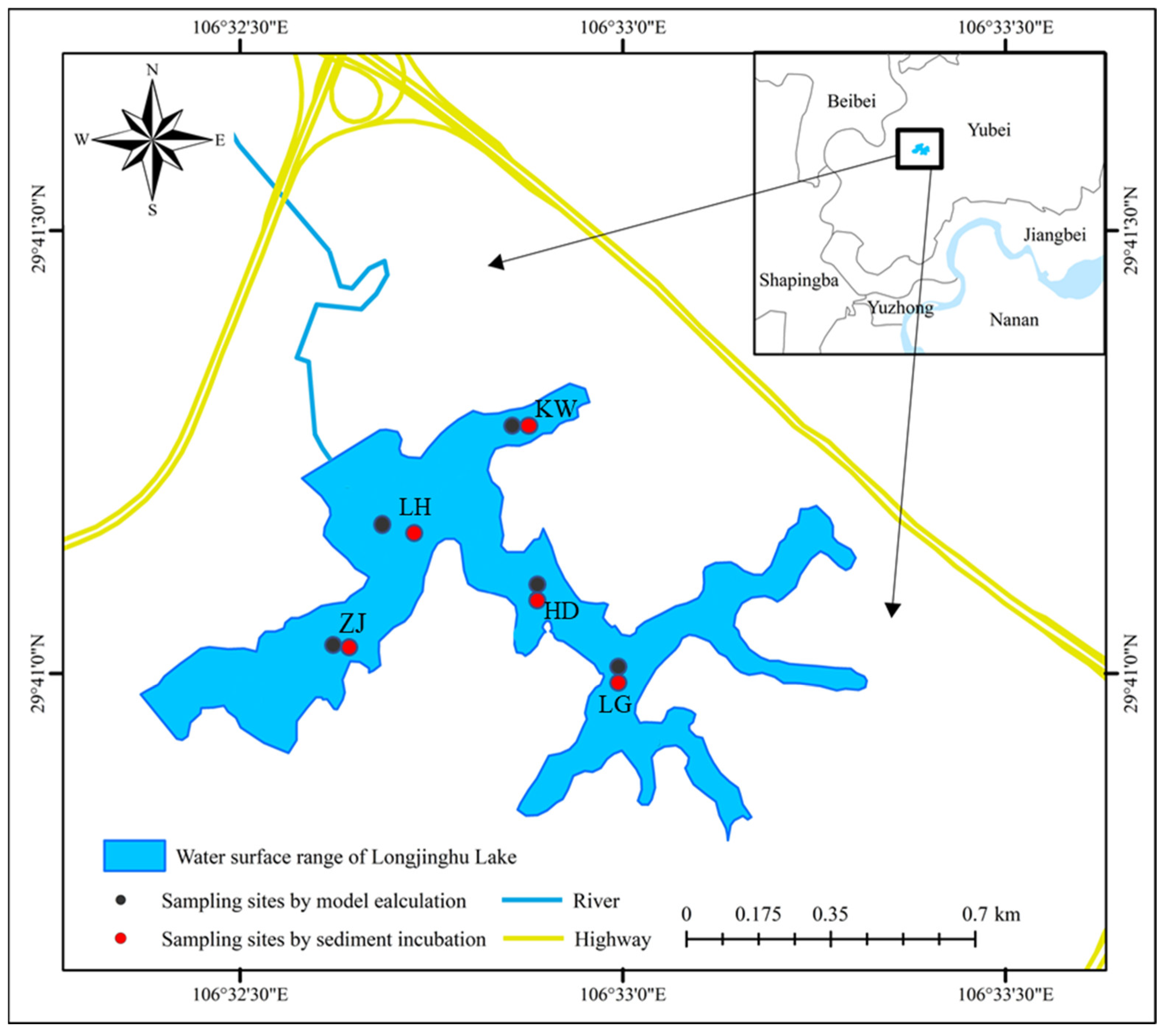
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sediment Sampling
2.3. Incubation and Analyses
2.4. Methodology of Flux Estimation for N and P
- (1)
- Flux of N and P during incubations
- (2)
- One-dimensional transport-reaction model for porewater fluxes of N and P
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Flux of DTP and SRP in Incubation
3.2. Flux of DTN, NO3−-N, and NH4+-N in Incubation
3.3. The Comparison of Diffusion Flux between Sediment Incubation and Model Calculation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grall, J.; Chauvaud, L. Marine eutrophication and benthos: The need for new and concepts. Glob. Change Biol. 2010, 8, 813–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.Z.; Pei, Y.S.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shu, L.M.; Zhang, H. Twenty years of China’s water pollution control: Experiences and challenges. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.W.; Gao, G. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Ecology controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, P.; Li, D.; Zhu, X. Eutrophication in the newly built Laohutan Reservoir during the initial impoundment period: The role of nutrient loading. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 4803–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H. Eutrophication of freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems a global problem. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2003, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.N.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, H.Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Bian, S.J.; Liang, X.M.; Martin, S.; Erik, J. Effects of nitrate on phosphorus release from lake sediments. Water Res. 2021, 194, 116894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.K.; Zeng, X.L.; Xu, D.Y.; Gao, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Gao, B. Chemical fractions, diffusion flux and risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in sediments of Baiyangdian Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cui, L.; Pan, X.; Lei, Y. Winter decomposition of emergent macrophytes affects water quality under ice in a temperate shallow Lake. Water 2020, 12, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Bao, X.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Li, Q.M.; Gu, S. Evaluation of the potential release risk of internal N and P from sediments—A preliminary study in two freshwater reservoirs in South China. Water 2022, 14, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.Y.; Zhu, G.W.; Zhao, L.L.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Gao, G.; Qin, B.Q. Influence of algal bloom degradation on nutrient release at the sediment-water interface in Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 20, 1803–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.H.; Zhong, J.C.; Chen, Q.W.; Huang, W.; Hu, L.M.; Zhang, Y.L.; Fan, C.X. An investigation of the effects of capping on internal phosphorus release from sediments under rooted macrophytes (Phragmites australis) revegetation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 24682–24694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarado, J.N.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, C.G.; Park, S.J. Comparison of capping and mixing of calcined dolomite and zeolite for interrupting the release of nutrients from contaminated lake sediment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 15045–15056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydin, E. Potentially mobile phosphorus in Lake Erken sediment. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2037–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, K.M.; Vavrus, C.E.; Lofton, M.E.; Mcclure, R.P.; Schreiber, M.E. Iron and manganese fluxes across the sediment-water interface in a drinking water reservoir. Water Res. 2020, 182, 116003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berelson, W.M.; Heggie, D.; Longmore, A.; Kilgore, T.; Nicholson, G.; Skyring, G. Benthic nutrient recycling in Port Phillip Bay, Australia. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1998, 46, 917–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.W.; Qin, B.Q.; Zhang, L.; Luo, L.C.; Sun, X.J.; Hong, D.L.; Gao, Y.J.; Xie, R. Water effects on nutrient release of sediments from Lake Taihu by flume experiment. J. Lake Sci. 2005, 17, 61–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Yang, Y.T.; Jing, X.Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Chen, J.; Rensing, C.; Luan, T.G.; Zhou, S.G. Enhanced aging of polystyrene microplastics in sediments under alternating anoxic-oxic conditions. Water Res. 2021, 207, 117782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadi, T.; Rinke, K.; Friese, K. Trajectories of sediment-water interactions in reservoirs as a result of temperature and oxygen conditions. Water 2020, 12, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.A.; Lei, P.; Zhang, H.; Shan, B.Q.; Li, J. Distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus in the sediments and estimation of the nutrient fluxes in Longjinghu Lake, Chongqing City, during the initial impoundment period. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 1727–1734. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg, A.E.; Trussell, R.R.; Clesceri, L.S.; American Water Works Association. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater: Supplement to the sixteenth edition. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 2005, 56, 387. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, B.; Wang, Y.; Dittrich, M.; Wehrli, B. Influence of organic carbon decomposition on calcite dissolution in surficial sediments of a freshwater lake. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4524–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szal, D.; Gruca-Rokosz, R. Anaerobic oxidation of methane in freshwater sediments of Rzeszów Reservoir. Water 2020, 12, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Z.B.; Yang, L.; Song, N.; Wang, C.H.; Jiang, H.L. Effect of organic matter derived from algae and macrophyte on anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to ferric iron reduction in the sediment of a shallow freshwater lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 25899–25907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, B.J. Control of nitrogen export from watersheds by headwater streams. Science 2001, 292, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.H.; Alexander, V. Dissolved nitrogen uptake by a cyanobacterial bloom (Anabaena flos-aquae) in a Subarctic Lake. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francis, C.A.; Beman, J.M.; Kuypers, M. New processes and players in the nitrogen cycle: The microbial ecology of anaerobic and archaeal ammonia oxidation. ISME J. 2007, 1, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, P.; Lavik, G.; Jensen, M.M.; van de Vossenberg, J.; Schmid, M.; Woebken, D.; Dimitri, G.; Amann, R.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Kuypers, M.M.M. Revising the nitrogen cycle in the Peruvian oxygen minimum zone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4752–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.P.; Zeng, F.T.; Huang, H.M.; Xiong, L.; Yu, Q.; Wang, Z.Y. Advances in research of migration and transformation of nitrogen in environmental media. Water Resour. Prot. 2014, 30, 1–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qian, C.P.; Chen, A.L.; Hu, L.Z.; Deng, H.G. Effects of sediment resuspension on nitrogen and phosphate exchange at the sediment-water interface in East Chongming Tidal Flat. Environ. Sci. 2003, 24, 114–119. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nika, N.; Zilius, M.; Ruginis, T.; Giordani, G.; Bartoli, M. Benthic metabolism in fluvial sediments with larvae of Lampetra sp. Water 2021, 13, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eek, E.; Cornelissen, G.; Breedveld, G.D. Field measurement of diffusional mass transfer of HOCs at the sediment-water interface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6752–6759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Sites | Flux of NH4+-N (mg/d·m2) | Flux of DTN (mg/d·m2) | Flux of SRP (mg/d·m2) | Flux of DTP (mg/d·m2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model Calculation a | Incubation b/c | Model Calculation a | Incubation b/c | Model Calculation a | Incubation b/c | Model Calculation a | Incubation b/c | |
| LH | 28.3 | 8.46/25.0 | - | 14.8/44.6 | 3.94 ** | 19.4 **/8.59 | - | 18.4/8.20 |
| KW | 2.03 | −12.0/−6.86 | - | 12.4/33.1 | −1.93 ** | 9.59/12.5 ** | - | 2.34/12.5 |
| LG | 47.2 * | 13.9/69.0 * | - | 39.1/98.0 | 6.13 * | 12.2 */4.67 | - | 11.0/6.71 |
| ZJ | 30.1 * | 46.1/1.14 * | - | 45.4/27.4 | −2.50 ** | 9.41/8.06 ** | - | 5.96/6.31 |
| HD | 14.6 | −17.2 */−7.10 * | - | 16.3/18.7 | 0.839 * | 8.59/8.52 * | - | 4.75/6.41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, C.; Pan, Y.; Tang, W.; Yue, Q.; Zhang, H. A Comparison Study of the Nutrient Fluxes in a Newly Impounded Riverine Lake (Longjing Lake): Model Calculation and Sediment Incubation. Water 2022, 14, 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132015
Du C, Pan Y, Tang W, Yue Q, Zhang H. A Comparison Study of the Nutrient Fluxes in a Newly Impounded Riverine Lake (Longjing Lake): Model Calculation and Sediment Incubation. Water. 2022; 14(13):2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132015
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Cheng, Yan’an Pan, Wenzhong Tang, Qiansheng Yue, and Hong Zhang. 2022. "A Comparison Study of the Nutrient Fluxes in a Newly Impounded Riverine Lake (Longjing Lake): Model Calculation and Sediment Incubation" Water 14, no. 13: 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132015
APA StyleDu, C., Pan, Y., Tang, W., Yue, Q., & Zhang, H. (2022). A Comparison Study of the Nutrient Fluxes in a Newly Impounded Riverine Lake (Longjing Lake): Model Calculation and Sediment Incubation. Water, 14(13), 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132015






