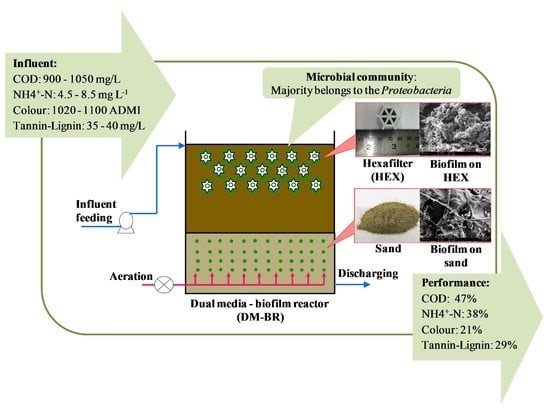
Potential of Using Dual-Media Biofilm Reactors as a Real Coffee Industrial Effluent Pre-Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling of Coffee Industry Effluent
2.2. Bacterial Inoculation and Acclimatisation
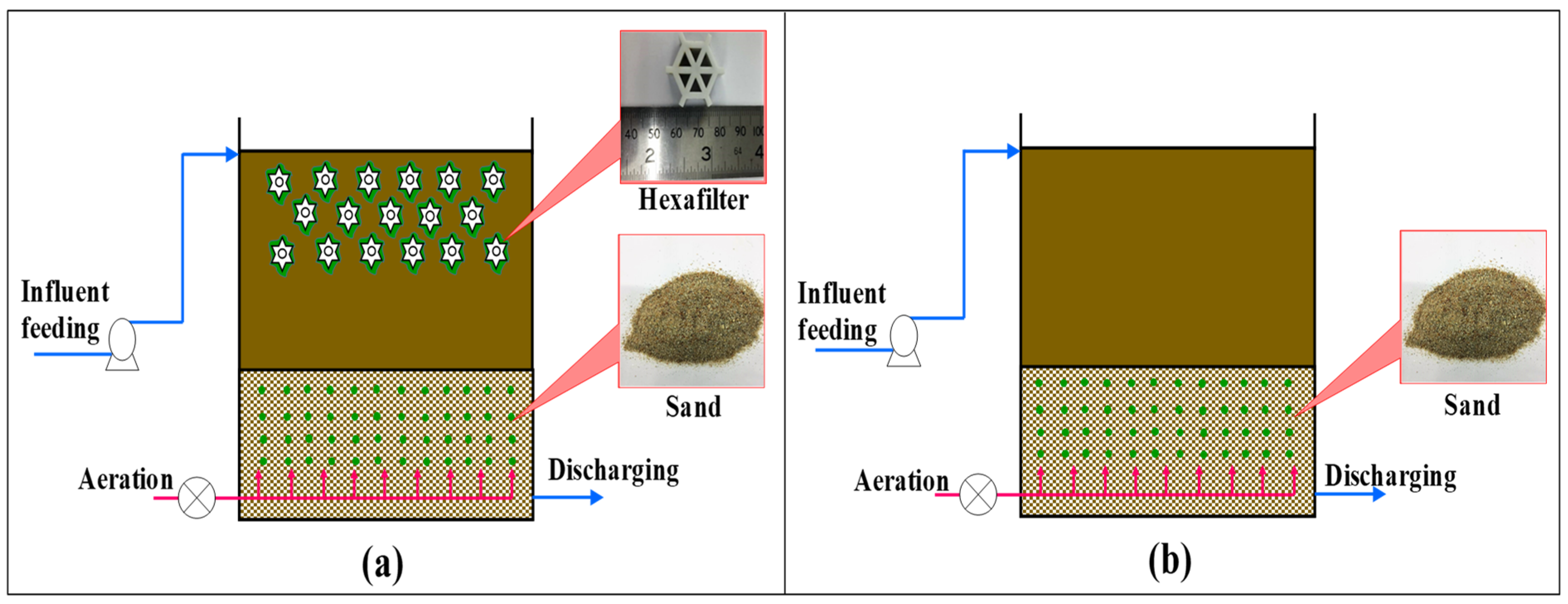
2.3. Configuration of the Dual-Media Biofilm Reactor
2.3.1. Biofilm Carriers
2.3.2. Setup and Operation of the Biofilm Reactors
2.4. Wastewater Quality Parameter Analysis
2.5. Bacterial Analysis
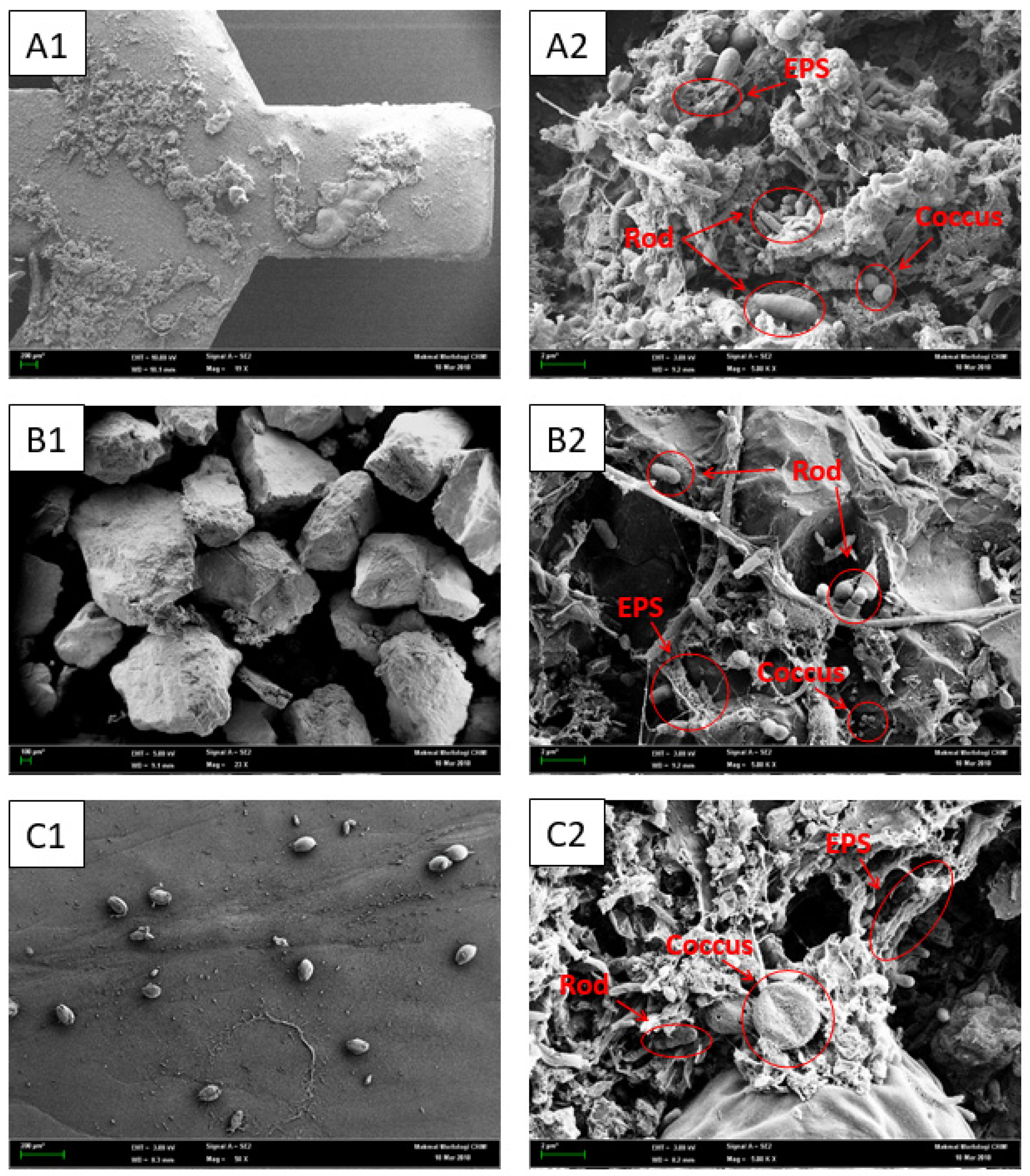
2.5.1. Biofilm Observation under Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.5.2. Microbial Cell Number
2.5.3. Microbial Community Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Bacterial Enhancement and Acclimatisation
3.2. Performance of the Biofilm Reactors
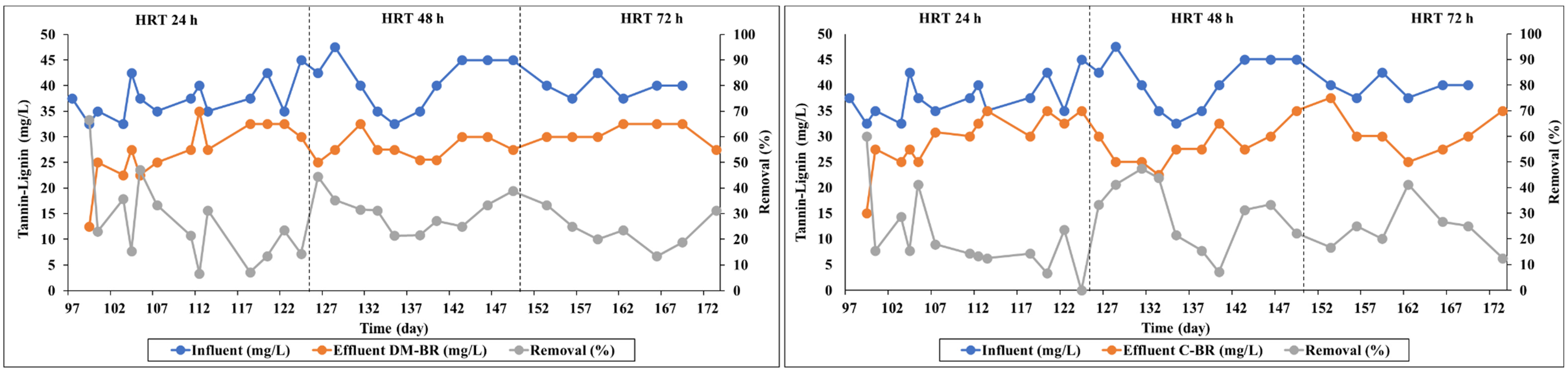
3.2.1. Removal of Tannin–Lignin
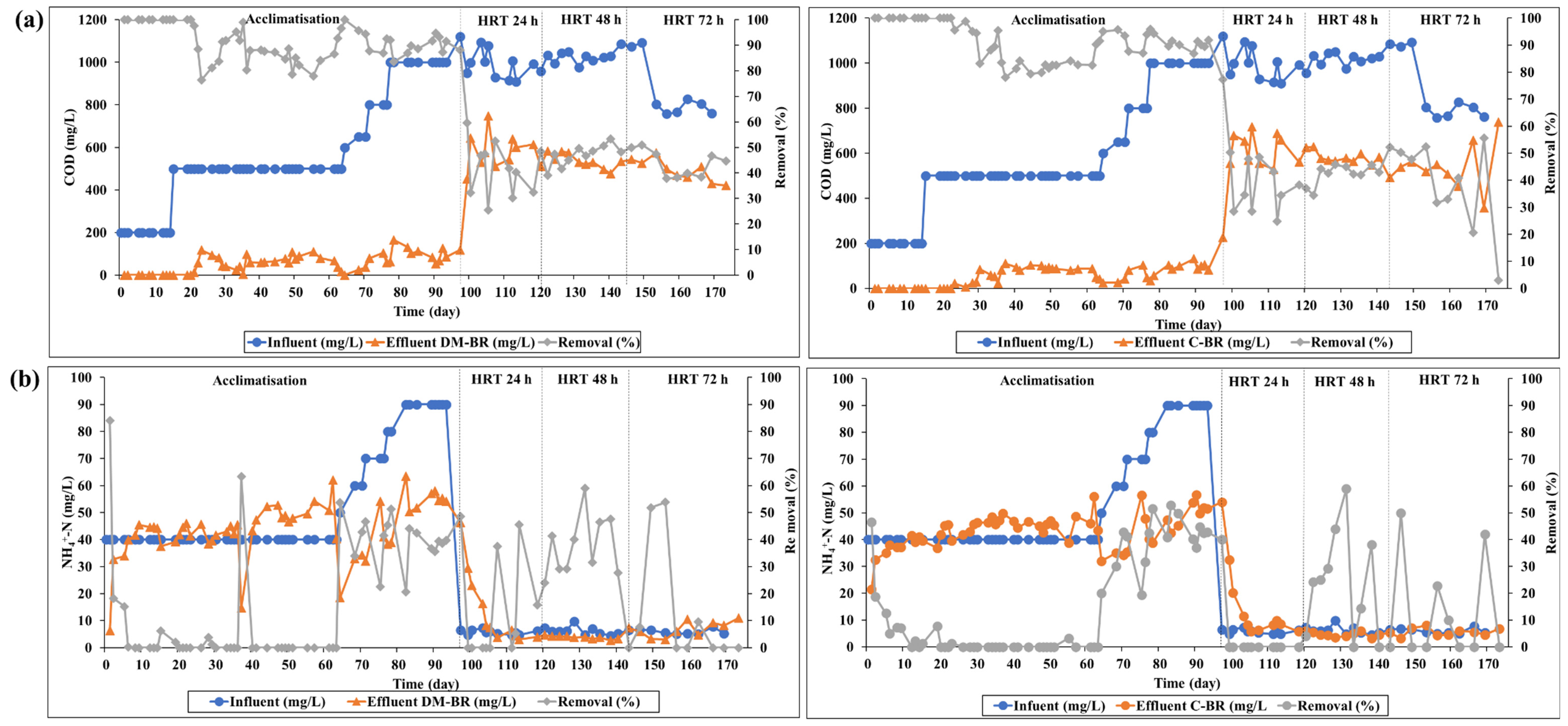
3.2.2. Removal of COD and NH4+-N
3.2.3. Removal of Colour and Turbidity
3.3. Monitoring of Operational Parameters
3.4. Microbial Community Structure and Analysis
3.4.1. Microbial Observation via SEM
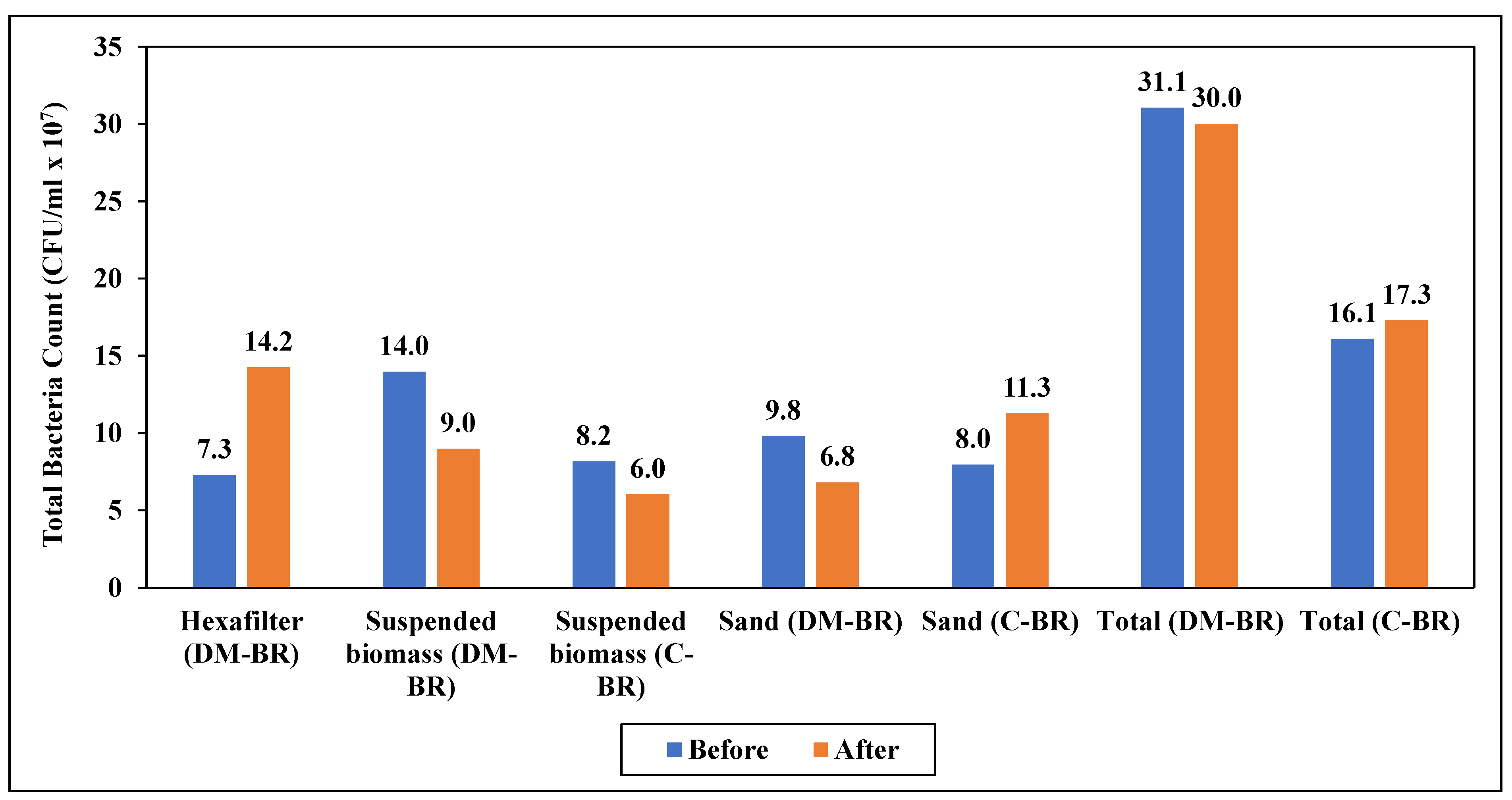
3.4.2. Microbial Cell Number
3.4.3. Microbial Community Diversity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murthy, P.S.; Naidu, M.M. Sustainable management of coffee industry by-products and value addition—A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 66, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, N.S.M.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Ismail, N.; Abu Hasan, H.; Othman, A.R. Phytoremediation of real coffee industry effluent through a continuous two-stage constructed wetland system. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 100502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros, V.G.; Rodrigues, C.S.D.; Suarez, W.A.B.; Duda, R.M.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Da Silva, E.S.; Faria, J.L.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Madeira, L.M. Treatment of biodigested coffee processing wastewater using Fenton’s oxidation and coagula-tion/flocculation. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Salomón, A.; Valdovinos, E.R.; Albores, F.P.; Rivera, S.L.; Gordillo, R.M.; Valdiviezo, V.M.R. Evaluation of hydraulic retention time on treatment of coffee processing wastewater (CPWW) in EGSB bioreactor. Sustainability 2018, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ijanu, E.M.; Kamaruddin, M.A.; Norashiddin, F.A. Coffee processing wastewater treatment: A critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tokumura, M.; Ohta, A.; Znad, H.; Kawase, Y. UV light assisted decolorization of dark brown colored coffee effluent by photo-Fenton reaction. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3775–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumura, M.; Znad, H.; Kawase, Y. Decolorization of dark brown colored coffee effluent by solar photo-Fenton reaction: Effect of solar light dose on decolorization kinetics. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4665–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddis, A.; Devi, R. Effect of effluent generated from coffee processing plant on the water bodies and human health in its vicinity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fia, F.R.; Matos, A.T.; Borges, A.C.; Fia, R.; Cecon, P.R. Treatment of wastewater from coffee bean processing in anaerobic fixed bed reactors with different support materials: Performance and kinetic modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 108, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, M.; Kurosu, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Kawase, Y. Zero-valent iron treatment of dark brown colored coffee effluent: Contributions of a core-shell structure to pollutant removals. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 183, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, M.M.; Leite, K.U.C.G.; Silva, M.R.; Reis, A.D.P. Fenton and Photo-Fenton Processes Coupled to UASB to Treat Coffee Pulping Wastewater. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 1506–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashina, T.A.; Leifeld, V.; Zelinski, D.W.; Mafra, M.; Igarashi-Mafra, L. Application of Response Surface Methodology for Coffee Effluent Treatment by Ozone and Combined Ozone/UV. Ozone: Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Taquez, H.N.; Gil Pavas, E.; Blatchley, E.R.; Gómez-García, M.Á.; Dobrosz-Gómez, I. Integrated electro-coagulation–electrooxidation process for the treatment of soluble coffee effluent: Optimization of COD degradation and oper-ation time analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 200, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacias-Pascacio, V.G.; Cruz-Salomón, A.; Castañón-González, J.H.; Torrestiana-Sanchez, B. Wastewater Treatment of Wet Coffee Processing in an Anaerobic Baffled Bioreactor Coupled to Microfiltration System. Curr. Environ. Eng. 2019, 6, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, W.L.; Balakrishnan, T.; Veeraiya, T.; Elham, M.H.M.; Faidzal, M.S. Performance evaluation of tubular ceramic membrane for palm oil mill effluent treatment. J. Kej. 2020, 32, 157–165. [Google Scholar]
- Sahana, M.; Srikantha, H.; Mahesh, S.; Swamy, M.M. Coffee processing industrial wastewater treatment using batch electrochemical coagulation with SS and Fe electrodes and its combinations, recovery and reuse of sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Vaishnavi, D.; Sahu, N.; Sridhar, S. Design of an integrated membrane bioreactor process for effective and environmentally safe treatment of highly complex coffee industrial effluent. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.; Ghaly, A. Maximizing sustainability of the Costa Rican coffee industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 15, 1716–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Subsidiary Legislation Malaysia. Environmental Quality (Industrial Effluent) Regulations. Environ. Qual. Act 1974. 2009. Available online: https://www.doe.gov.my/portalv1/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/Environmental_Quality_Industrial_Effluent_Regulations_2009_-_P.U.A_434-2009.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Al-Amshawee, S.; Yunus, M.Y.B.M.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Tran, N.H. Biocarriers for biofilm immobilization in wastewater treatments: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1925–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Díaz, J.C.; Martín-Pascual, J.; Poyatos, J.M. Moving bed biofilm reactor to treat wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 881–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Bakar, S.N.H.; Abu Hasan, H.; Mohammad, A.W.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Haan, T.Y.; Ngteni, R.; Yusof, K.M.M. A review of moving-bed biofilm reactor technology for palm oil mill effluent treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 1532–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hasan, H.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Kofli, N.T.; Anuar, N. Kinetic evaluation of simultaneous COD, ammonia and manganese removal from drinking water using a biological aerated filter system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 130, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Bakar, S.N.H.; Abu Hasan, H.; Mohammad, A.W.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Haan, T.Y.; Ngteni, R.; Yusof, K.M.M. Performance of a laboratory-scale moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) and its microbial diversity in palm oil mill effluent (POME) treatment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 142, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhamad, M.H.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Abu Hasan, H.; Abu Bakar, S.N.H. Multimedia-sequencing batch biofilm reactor in treating recycled paper mill effluent containing high level of pentachlorophenol: Long-term performance, mechanism and kinetic studies. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, C.P.L., Jr.; Daigger, G.T.; Love, N.G.; Filipe, C. Biological Wastewater Treatment, 3rd ed.; CRC Press, Francis and Taylor Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, H.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Kofli, N.T.; Kamaruddin, S. Biosorption of Manganese in Drinking Water by Isolated Bacteria. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 2653–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imron, M.F.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Soegianto, A. Characterization of mercury-reducing potential bacteria isolated from Keputih non-active sanitary landfill leachate, Surabaya, Indonesia under different saline conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 241, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; He, P.; Guo, X.-L.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.-J. Fifteen-year no tillage of a Mollisol with residue retention indirectly affects topsoil bacterial community by altering soil properties. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 205, 104804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, J.A.; Sundarapandian, S. Patterns of plant diversity in seven temperate forest types of Western Himalaya, India. J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2016, 9, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berndt, L.; Vargas, J. Sulfur, organic matter and the black layer. Golf. Course Manag. 1989, 57, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Bajpai, P.; Bajpai, P.K. Biological colour removal of pulp and paper mill wastewaters. J. Biotechnol. 1994, 33, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashi, H.; Iorhemen, O.; Tay, J. Degradation of industrial tannin and lignin from pulp mill effluent by aerobic granular sludge technology. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 26, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, M.C.; Castillo, G.; Aguilar, L.; Vidal, G.; Mora, M.L. Operational factors and nutrient effects on activated sludge treatment of Pinus radiata kraft mill wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinsdale, R.M.; Hawkes, F.R.; Hawkes, D.L. The mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestion of coffee waste containing coffee grounds. Water Res. 1996, 30, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzola-Rojas, M.D.P.; da Fonseca, S.G.; da Silva, C.C.; de Oliveira, V.M.; Zaiat, M. The use of the carbon/nitrogen ratio and specific organic loading rate as tools for improving biohydrogen production in fixed-bed reactors. Biotechnol. Rep. 2014, 5, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imron, M.F.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Ismail, N.I.; Abdullah, S.R.S. Future challenges in diesel biodegradation by bacteria isolates: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péerez, T.Z.; Geissler, G.; Hernandez, F. Chemical oxygen demand reduction in coffee wastewater through chemical flocculation and advanced oxidation processes. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolella, C.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Heijnen, J.J. Wastewater Treatment with Particulate Biofilm Reactors. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 80, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-F.; Santhanam, N.; Badri, D.V.; Hunter, W.J.; Manter, D.K.; Decker, S.R.; Vivanco, J.M.; Reardon, K.F. Isolation and characterization of lignin-degrading bacteria from rainforest soils. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2013, 110, 1616–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.-H.; Pourcher, A.-M.; Bouchez, T.; Gelhaye, E.; Peu, P. Occurrence of lignin degradation genotypes and phenotypes among prokaryotes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9527–9544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, D.P.; Ravi, K.; Lidén, G.; Gorwa-Grauslund, M.F. Mapping the diversity of microbial lignin catabolism: Experiences from the eLignin database. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3979–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Shen, M.; Li, J.; Huang, S.; Li, Z.; Yan, Z.; Peng, Y. Cooperation between partial-nitrification, complete ammonia oxidation (comammox), and anaerobic ammonia oxidation (anammox) in sludge digestion liquid for nitrogen re-moval. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrani, M.-J.; Sobotka, D.; Kowal, P.; Ciesielski, S.; Makinia, J. The occurrence and role of Nitrospira in nitrogen removal systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 303, 122936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameter | Coffee Effluent Mean Values | Standard B (Federal Subsidiary Legislation Malaysia 2009) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | 10% Coffee + 90% Water | ||
| COD (mg/L) | 15,700 | 900–1050 | 200 |
| NH4+-N (mg/L) | 93 | 4.5–8.5 | 20 |
| pH | 4.6 | 4.5 | 5.5–9.0 |
| MLSS (mg/L) | 123 | <10 | 100 |
| MLVSS (mg/L) | 111 | - | - |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 74.7 | 15–20 | - |
| Colour (ADMI) | 1867 | 1020–1100 | 200 |
| Tanin–Lignin (mg/L) | 510 | 35–40 | - |
| Day | Influent (mg/L) | Average Removal (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-BR | DM-BR | |||||
| COD | NH4+-N | COD | NH4+-N | COD | NH4+-N | |
| 0–15 | 200 | 40 | 100 | 12.4 | 100 | 10 |
| 16–64 | 500 | 40 | 88.8 | 4.4 | 88.6 | 1.2 |
| 65–77 | 600–800 | 50–70 | 91.6 | 38.8 | 92.3 | 34.6 |
| 78–97 | 1000 | 80–90 | 89.6 | 39.7 | 89.3 | 44.2 |
| Reactor | Day | HRT (h) | Average Removal (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tannin–Lignin a | COD a | NH4+-N a | Colour a | Turbidity a | |||
| DM-BR | 97–118 | 24 | 28.8 ± 18.5 | 40.9 ± 10.9 | 10.4 ± 1.2 | 21.1 ± 19.2 | 21.2 ± 23.1 |
| 119–140 | 48 | 26.4 ± 9.6 | 47.0 ± 4.2 | 37.6 ± 0.6 | 6.7 ± 2.1 | 32.7 ± 12.3 | |
| 141–173 | 72 | 26.3 ± 7.9 | 44.2 ± 5.2 | 12.3 ± 2.9 | 5.4 ± 4.9 | 23.8 ± 18.7 | |
| C-BR | 97–118 | 24 | 23.3 ± 15.7 | 37.9 ± 9.2 | 0 | 10.0 ± 1.6 | 14.0 ± 18.9 |
| 119–140 | 48 | 24.0 ± 16.9 | 42.2 ± 3.7 | 23.4 ± 19.7 | 4.7 ± 3.6 | 46.0 ± 21.4 | |
| 141–173 | 72 | 25.4 ± 8.4 | 38.7 ± 16.9 | 12.5 ± 19.2 | 4.6 ± 4.3 | 32.8 ± 25.2 | |
| Diversity Parameters | DM-BR | C-BR |
|---|---|---|
| OTU | 3641 | 3359 |
| Chao1 | 3051 | 2941 |
| ACE | 24 | 21 |
| Shannon | 24.1 | 22.8 |
| Simpson | 6.01 | 5.9 |
| Fisher | 801 | 99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu Hasan, H.; Sai Annanda Shanmugam, D.; Sheikh Abdullah, S.R.; Muhamad, M.H.; Budi Kurniawan, S. Potential of Using Dual-Media Biofilm Reactors as a Real Coffee Industrial Effluent Pre-Treatment. Water 2022, 14, 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132025
Abu Hasan H, Sai Annanda Shanmugam D, Sheikh Abdullah SR, Muhamad MH, Budi Kurniawan S. Potential of Using Dual-Media Biofilm Reactors as a Real Coffee Industrial Effluent Pre-Treatment. Water. 2022; 14(13):2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132025
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu Hasan, Hassimi, Dheenesh Sai Annanda Shanmugam, Siti Rozaimah Sheikh Abdullah, Mohd Hafizuddin Muhamad, and Setyo Budi Kurniawan. 2022. "Potential of Using Dual-Media Biofilm Reactors as a Real Coffee Industrial Effluent Pre-Treatment" Water 14, no. 13: 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132025
APA StyleAbu Hasan, H., Sai Annanda Shanmugam, D., Sheikh Abdullah, S. R., Muhamad, M. H., & Budi Kurniawan, S. (2022). Potential of Using Dual-Media Biofilm Reactors as a Real Coffee Industrial Effluent Pre-Treatment. Water, 14(13), 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132025