Multi-Isotope Characterization of Water in the Water Supply System of the City of Ljubljana, Slovenia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
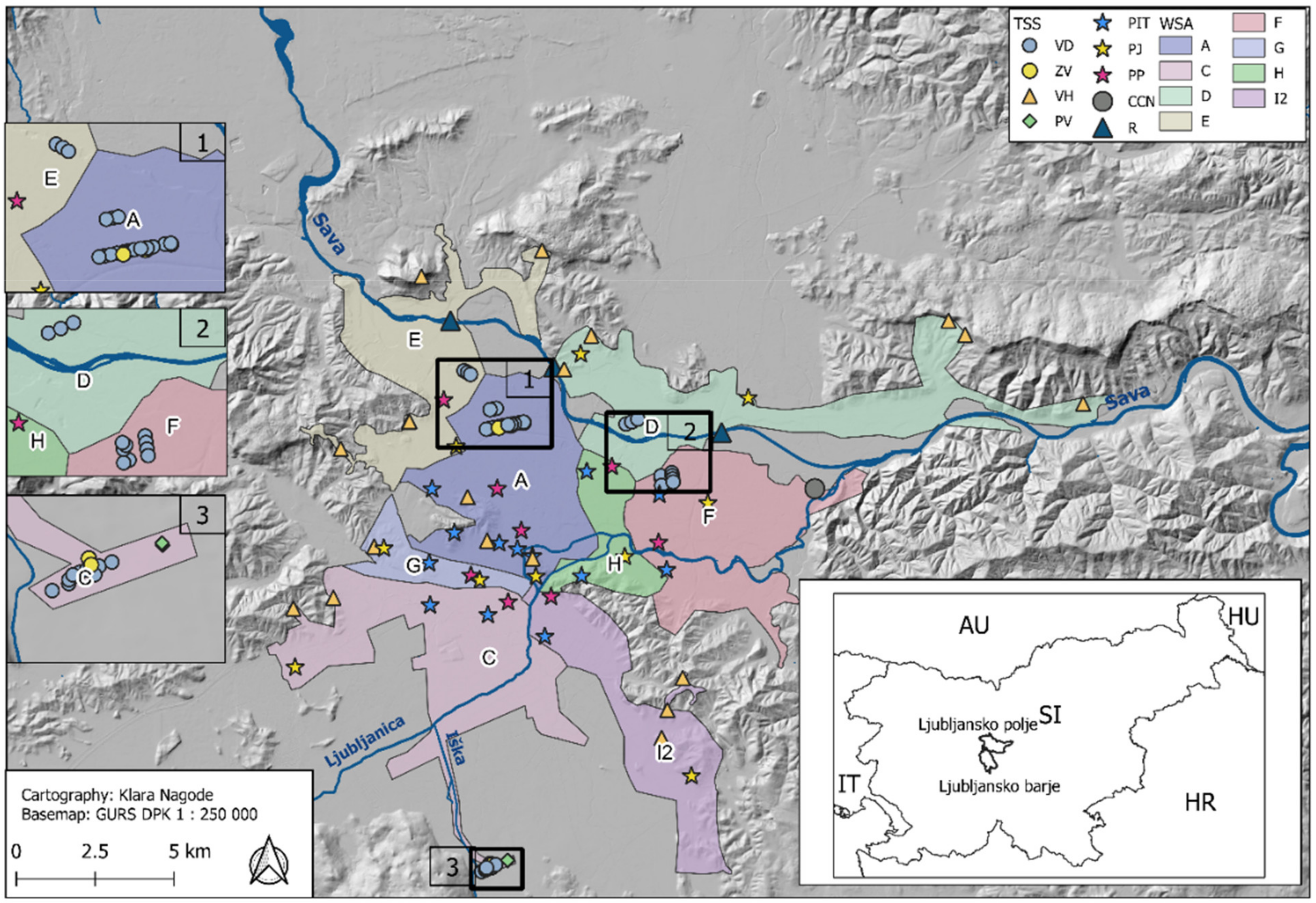
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Selection of Sampling Sites and Sampling
2.3. In-Situ Measurements
2.4. Analytical Procedures
2.4.1. Determination of Total Alkalinity (TA)
2.4.2. Determination of δ2H, δ18O and d-Excess
2.4.3. Determination of δ13CDIC
2.5. Data Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Meteorology and Hydrology
3.2. Isotope Composition of Precipitation
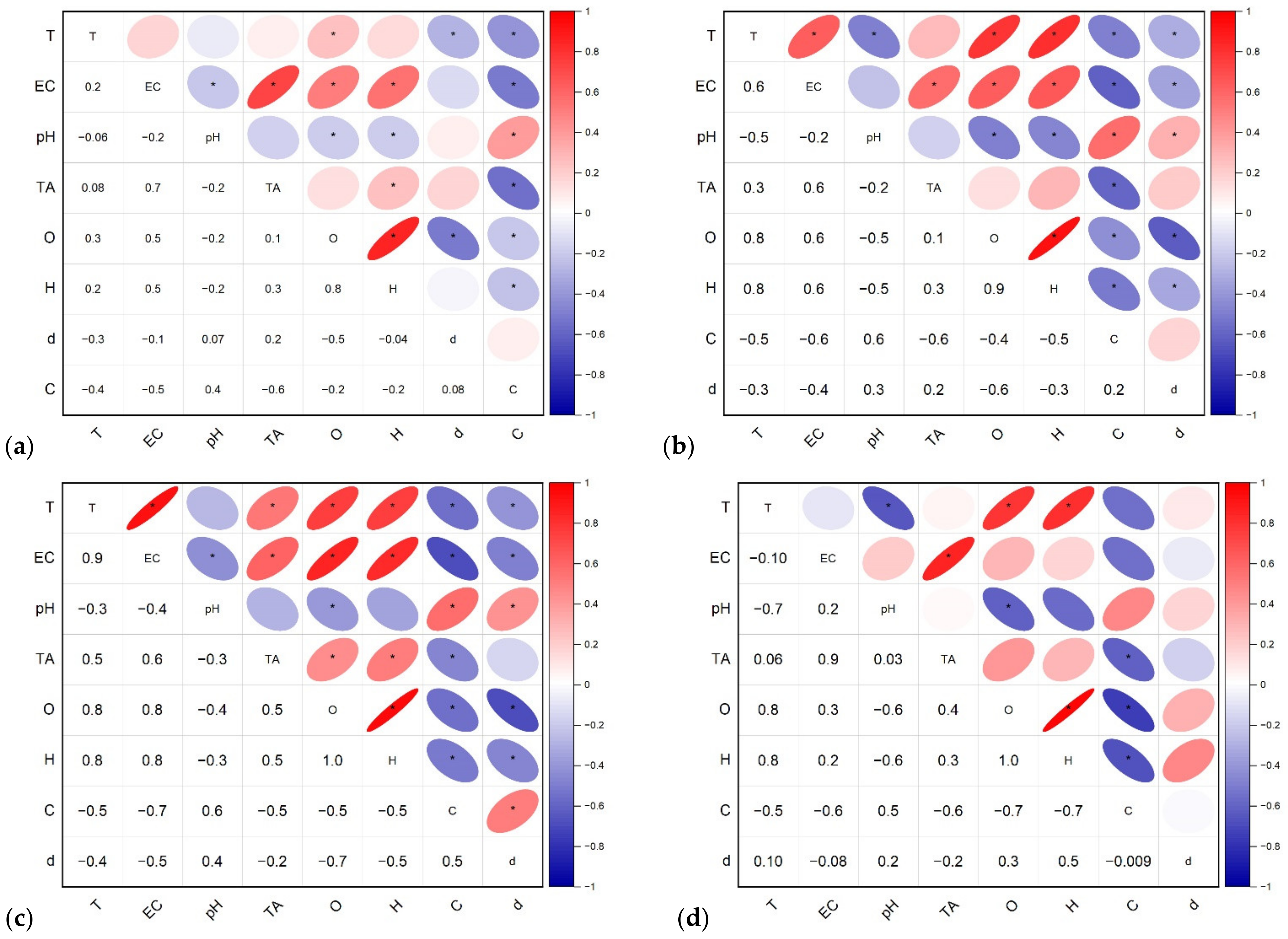
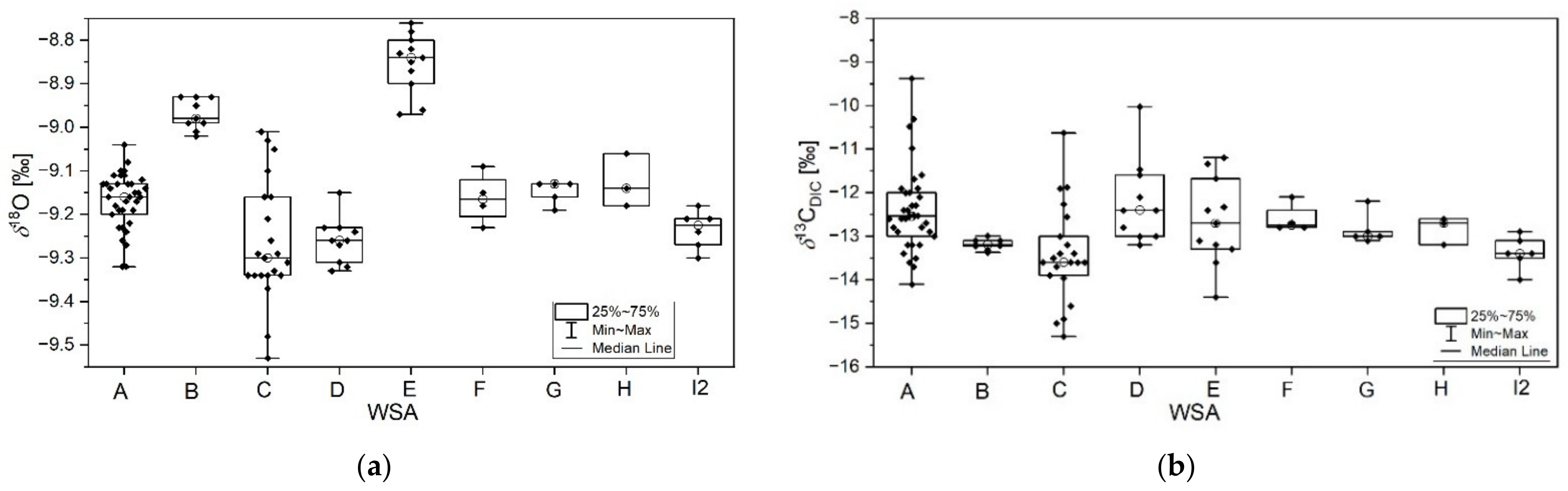
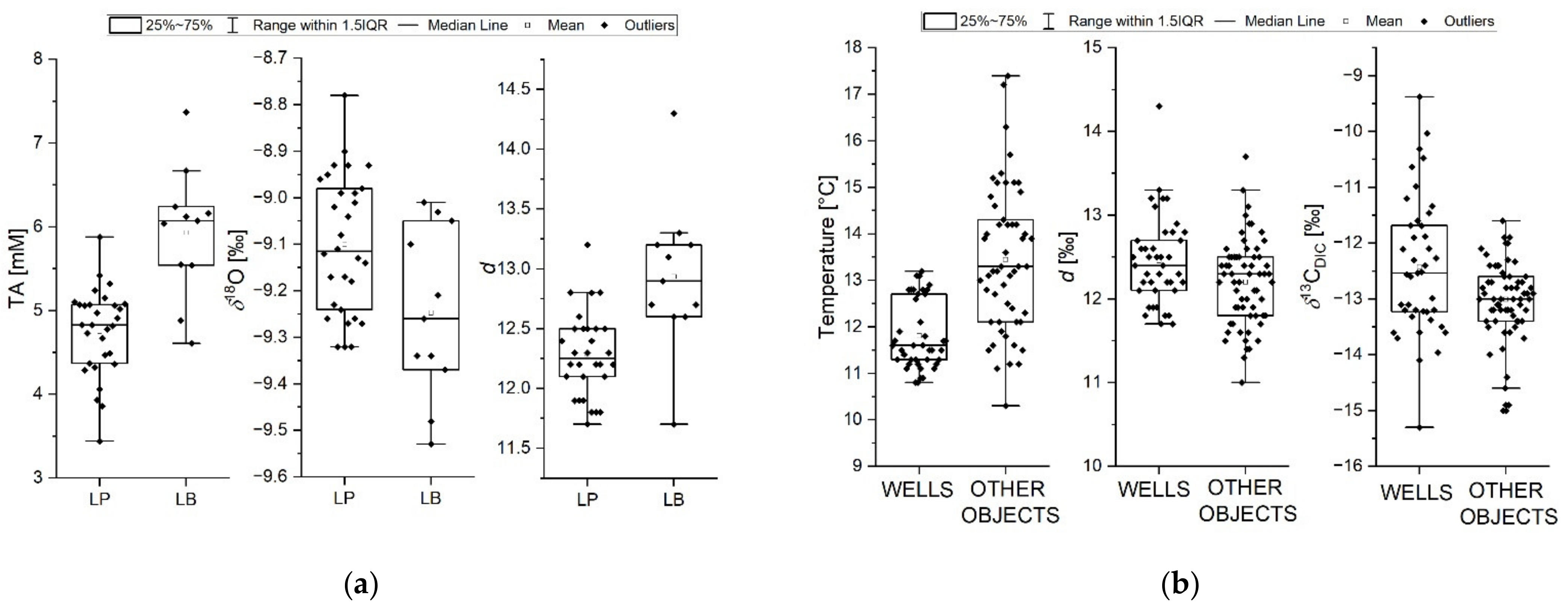
3.3. The Whole Urban Water Supply System
3.3.1. Characteristics of the Groundwater from Wells
3.3.2. Characteristics of Other Components in the Water Supply System
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larsen, T.A.; Hoffmann, S.; Lüthi, C.; Truffer, B.; Maurer, M. Emerging Solutions to the Water Challenges of an Urbanizing World. Science 2016, 352, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrane, S.J. Impacts of Urbanisation on Hydrological and Water Quality Dynamics, and Urban Water Management: A Review. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 2295–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipple, B.; Jameel, Y.; Chau, T.; Mancuso, C.; Bowen, G.; Dufour, A.; Chesson, L.; Ehleringer, J. Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes of Tap Water Reveal Structure of the San Francisco Bay Area’s Water System and Adjustments during a Major Drought. Water Res. 2017, 119, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameel, Y.; Brewer, S.; Fiorella, R.P.; Tipple, B.J.; Terry, S.; Bowen, G.J. Isotopic Reconnaissance of Urban Water Supply System Dynamics. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6109–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuhlemann, L.; Tetzlaff, D.; Soulsby, C. Urban Water Systems under Climate Stress: An Isotopic Perspective from Berlin, Germany. Hydrol. Processes 2020, 34, 3758–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, C.; Doctor, D.H. Stable Isotope Applications in Hydrologic Studies. Treatise Geochem. 2003, 5, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997; Volume 1997, ISBN 978-0-429-06957-4. [Google Scholar]
- Du, M.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Meng, H.; Che, C.; Guo, R. Stable Isotope Reveals Tap Water Source under Different Water Supply Modes in the Eastern Margin of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Water 2019, 11, 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atekwana, E.A.; Krishnamurthy, R.V. Seasonal Variations of Dissolved Inorganic Carbon and δ13C of Surface Waters: Application of a Modified Gas Evolution Technique. J. Hydrol. 1998, 205, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wet, R.F.; West, A.G.; Harris, C. Seasonal Variation in Tap Water δ2H and δ18O Isotopes Reveals Two Tap Water Worlds. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Murillo, R.; Esquivel-Hernández, G.; Birkel, C.; Ortega, L.; Sánchez-Guerrero, M.; Rojas-Jiménez, L.D.; Vargas-Víquez, J.; Castro-Chacón, L. From Mountains to Cities: A Novel Isotope Hydrological Assessment of a Tropical Water Distribution System. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2020, 56, 606–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, D.; Welch, K.; Lyons, W.B. Domestic Water Supply Dynamics Using Stable Isotopes δ18O, δD, and d-Excess. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2014, 6, 1517–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bračič Železnik, B.; Jamnik, B. Javna oskrba s pitno vodo. In Podtalnica Ljubljanskega Polja; Rejec Brancelj, I., Smrekar, A., Kladnik, D., Eds.; Založba ZRC: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2005; pp. 101–120. (In Slovene) [Google Scholar]
- Vrzel, J.; Solomon, D.K.; Blažeka, Ž.; Ogrinc, N. The Study of the Interactions between Groundwater and Sava River Water in the Ljubljansko Polje Aquifer System (Slovenia). J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizintin, G.; Souvent, P.; Veselič, M.; Cencur Curk, B. Determination of Urban Groundwater Pollution in Alluvial Aquifer Using Linked Process Models Considering Urban Water Cycle. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerar, S.; Urbanc, J. Carbonate Chemistry and Isotope Characteristics of Groundwater of Ljubljansko Polje and Ljubljansko Barje Aquifers in Slovenia. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, e948394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanc, J.; Jamnik, B. Isotopic investigations of the Ljubljansko barje water resources. Geologija 2002, 45, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrinc, N.; Tamše, S.; Zavadlav, S.; Vrzel, J.; Jin, L. Evaluation of Geochemical Processes and Nitrate Pollution Sources at the Ljubljansko Polje Aquifer (Slovenia): A Stable Isotope Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 1588–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagode, K.; Kanduč, T.; Lojen, S.; Bračič Železnik, B.; Jamnik, B.; Vreča, P. Synthesis of Past Isotope Hydrology Investigations in the Area of Ljubljana, Slovenia. Geologija 2020, 63, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagode, K.; Kanduč, T.; Zuliani, T.; Bračič Železnik, B.; Jamnik, B.; Vreča, P. Daily Fluctuations in the Isotope and Elemental Composition of Tap Water in Ljubljana, Slovenia. Water 2021, 13, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejec Brancelj, I.; Smrekar, A.; Kladnik, D. Podtalnica Ljubljanskega Polja; ZRC SAZU, Založba ZRC: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2004; Volume 10, ISBN 978-961-254-508-6. (In Slovene) [Google Scholar]
- Mencej, Z. The Gravel Fill beneath the Lacustrine Sediments of the Ljubljansko Barje. Geologija 1988, 31, 517–553. [Google Scholar]
- Jamnik, B.; Žitnik, M. Letno Poročilo o Skladnosti Pitne Vode na Oskrbovalnih Območjih v Upravljanju Javnega Podjetja Vodovod Kanalizacija Snaga d. o. o. v Letu 2019; Javno Podjetje Vodovod-Kanalizacija d.o.o.: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2020; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Vreča, P.; Nagode, K.; Kanduč, T.; Lojen, S.; Šlejkovec, Z.; Žigon, S.; Močnik, N.; Bračič Železnik, B.; Jamnik, B.; Žitnik, M. Multi-Isotope Characterization of Water Resources for Domestic Supply in Ljubljana, Slovenia. Pangaea 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meteo.Si—Uradna Vremenska Napoved Za Slovenijo—Državna Meteorološka Služba RS—Vreme Podrobneje. Available online: https://meteo.arso.gov.si/met/sl/app/webmet/#webmet=vUHcs9WYkN3LtVGdl92LhBHcvcXZi1WZ09Cc1p2cvAncvd2LyVWYs12L3VWY0hWZy9SaulGdugXbsx3cs9mdl5WahxHf (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Jožef Stefan Institute SLONIP: Slovenian Network of Isotopes in Precipitation. Available online: https://slonip.ijs.si (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Kern, Z.; Hatvani, I.G.; Czuppon, G.; Fórizs, I.; Erdélyi, D.; Kanduč, T.; Palcsu, L.; Vreča, P. Isotopic ‘Altitude’ and ‘Continental’ Effects in Modern Precipitation across the Adriatic–Pannonian Region. Water 2020, 12, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreča, P.; Malenšek, N. Slovenian Network of Isotopes in Precipitation (SLONIP)—A Review of Activities in the Period 1981–2015. Geologija 2016, 59, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieskes, J.M. The Alkalinity-Total Carbon Dioxide System in Seawater. Mar. Chem. 1974, 5, 123–151. [Google Scholar]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable Isotopes in Precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spötl, C. A Robust and Fast Method of Sampling and Analysis of δ13C of Dissolved Inorganic Carbon in Ground Waters. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2005, 41, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanduč, T.; Mori, N.; Kocman, D.; Stibilj, V.; Grassa, F. Hydrogeochemistry of Alpine Springs from North Slovenia: Insights from Stable Isotopes. Chem. Geol. 2012, 300–301, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.; Hughes, C.E.; Lykoudis, S. Alternative Least Squares Methods for Determining the Meteoric Water Line, Demonstrated Using GNIP Data. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2331–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavšek, A.; Vreča, P. Isotopes in Precipitation—Statistics. Available online: https://github.com/nyuhanc/Isotopes-in-precipitation-statistics (accessed on 7 May 2022).
- Kozjek, K.; Dolinar, M.; Skok, G. Objective Climate Classification of Slovenia. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meteo.Si—Uradna Vremenska Napoved Za Slovenijo—Državna Meteorološka Služba RS—Ljubljana. Available online: http://www.meteo.si/met/sl/climate/diagrams/ljubljana/ (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Cegnar, T. Podnebne razmere v Sloveniji leta 2018. Ujma 2019, 33, 24–39. (In Slovene) [Google Scholar]
- Agencija Republike Slovenije za Okolje. Naše Okolje, Mesečni Bilten Agencije RS za Okolje—September 2018; ARSO: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2018; p. 102. (In Slovene)
- Agencija Republike Slovenije za Okolje. Naše Okolje, Mesečni Bilten Agencije RS za Okolje—Oktober 2018; ARSO: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2018; p. 90. (In Slovene)
- Agencija Republike Slovenije za Okolje. Naše Okolje, Mesečni Bilten Agencije RS za Okolje—November 2018; ARSO: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2018; p. 102. (In Slovene)
- Arhivski Podatki. Available online: http://vode.arso.gov.si/hidarhiv/pov_arhiv_tab.php (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Vreča, P.; Kanduč, T.; Šlejkovec, Z.; Žigon, S.; Nagode, K.; Močnik, N.; Bračič-Železnik, B.; Jamnik, B.; Žitnik, M. Karakterizacija vodnih virov za javno oskrbo s pitno vodo v Ljubljani s pomočjo različnih geokemičnih analiz. Raziskave S Področja Geod. Geofiz. 2018, 2019, 111–119. (In Slovene) [Google Scholar]
- Ogrinc, N.; Kanduč, T.; Stichler, W.; Vreča, P. Spatial and Seasonal Variations in δ18O and δD Values in the River Sava in Slovenia. J. Hydrol. 2008, 359, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanduč, T.; Szramek, K.; Ogrinc, N.; Walter, L.M. Origin and Cycling of Riverine Inorganic Carbon in the Sava River Watershed (Slovenia) Inferred from Major Solutes and Stable Carbon Isotopes. Biogeochemistry 2007, 86, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamnik, B.; Žitnik, M. Poročilo o Ugotovitvah Nadzora Podzemne in Pitne Vode v Vodarni Kleče v Obdobju 2011–2020; JP VOKA SNAGA: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2021. (In Slovene) [Google Scholar]
- Jamnik, B.; Žitnik, M.; Auersperger, P.; Bračič Železnik, B.; Nataša, Č.; Kalšek, I.; Kozjek, M.; Lah, K.; Vrbec, A.; Prestor, J. Poročilo o Ugotovitvah Nadzora Podzemne in Pitne Vode v Vodarni Brest v Obdobju 2011–2019; JP VOKA SNAGA: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2020; p. 39. (In Slovene) [Google Scholar]
- Jamnik, B.; Auersperger, P. Interne Priloge k Letnemu Poročilu o Skladnosti Pitne Vode na Oskrbovalnih Območjih v Upravljanju Javnega Podjetja Vodovod Kanalizacija Snaga v Letu 2020; JP VOKA SNAGA: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2021; p. 48. (In Slovene) [Google Scholar]
- Barth, J.A.C.; Cronin, A.A.; Dunlop, J.; Kalin, R.M. Influence of Carbonates on the Riverine Carbon Cycle in an Anthropogenically Dominated Catchment Basin: Evidence from Major Elements and Stable Carbon Isotopes in the Lagan River (N. Ireland). Chem. Geol. 2003, 200, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucour, A.-M.; Sheppard, S.M.F.; Guyomar, O.; Wattelet, J. Use of 13C to Trace Origin and Cycling of Inorganic Carbon in the Rhône River System. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Year | Parameters | December–February | March–May | June–August | September–November |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016–2018 | P [mm] | 98.2 | 104.8 | 119.8 | 146.7 |
| T [°C] | 1.8 | 12.5 | 22.0 | 11.9 | |
| δ18O [‰] | −10.91 | −7.93 | −5.60 | −8.27 | |
| δ2H [‰] | −76.5 | −53.8 | −35.6 | −53.0 | |
| 2018 | P [mm] | 72.5 | 118.6 | 148.0 | 119.8 |
| T [°C] | 2.3 | 12.6 | 22.0 | 13.0 | |
| δ18O [‰] | −10.88 | −7.18 | −5.95 | −7.20 | |
| δ2H [‰] | −76.2 | −47.8 | −38.7 | −44.3 |
| T (°C) | EC (µS/cm) | pH | TA (mM) | δ2H (‰) | δ18O (‰) | d (‰) | δ13CDIC (‰) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 12.7 | 508.55 | 7.7 | 4.9 | −61.2 | −9.16 | 12.3 | −12.9 |
| Standard deviation | 1.5 | 58.1 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.15 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| Minimum | 10.3 | 365.2 | 7.2 | 3.4 | −63.6 | −9.53 | 11.0 | −15.3 |
| Maximum | 17.4 | 660 | 8.4 | 7.4 | −57.8 | −8.76 | 14.3 | −9.4 |
| Range | 7.1 | 294.8 | 1.2 | 4.0 | 5.8 | 0.77 | 3.3 | 5.9 |
| Sava 1–Šentjakob | 15.0 | 345 | 8.17 | 3.3 | −63.0 | −9.40 | 12.2 | −8.0 |
| Sava 2–Črnuče | 15.1 | 345 | 8.23 | 3.4 | −62.4 | −9.39 | 12.7 | −9.2 |
| Sava 3–Brod | 15.1 | 343 | 8.24 | 3.3 | −63.3 | −9.45 | 12.3 | −7.7 |
| CČN | 21.7 | 1086 | 9.9 | 5.9 | −58.2 | −8.68 | 11.2 | −11.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagode, K.; Kanduč, T.; Bračič Železnik, B.; Jamnik, B.; Vreča, P. Multi-Isotope Characterization of Water in the Water Supply System of the City of Ljubljana, Slovenia. Water 2022, 14, 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132064
Nagode K, Kanduč T, Bračič Železnik B, Jamnik B, Vreča P. Multi-Isotope Characterization of Water in the Water Supply System of the City of Ljubljana, Slovenia. Water. 2022; 14(13):2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132064
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagode, Klara, Tjaša Kanduč, Branka Bračič Železnik, Brigita Jamnik, and Polona Vreča. 2022. "Multi-Isotope Characterization of Water in the Water Supply System of the City of Ljubljana, Slovenia" Water 14, no. 13: 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132064
APA StyleNagode, K., Kanduč, T., Bračič Železnik, B., Jamnik, B., & Vreča, P. (2022). Multi-Isotope Characterization of Water in the Water Supply System of the City of Ljubljana, Slovenia. Water, 14(13), 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132064







