Abstract
The present study focuses on the adsorption of Pb(II) by the H-form of titanosilicates (ETS-4, GTS-1) and clinoptilolite. The H-forms were prepared by first exchanging the extra-framework cations—Na+, K+, Ca2+, etc.—with NH4+, and by subsequent thermal treatment for obtaining H-forms. The purity and thermal behaviour of the initial, NH4+, and H-forms of ETS-4, GTS-1, and clinoptilolite were analysed by powder XRD, while the morphology and size of the particles were determined by SEM. The chemical composition of the solids and the solutions was obtained by WDXRF and ICP-OES, respectively. The kinetics research of the Pb(II) adsorption processes was based on WDXRF and ICP-OES. The H-forms of the materials displayed favourable properties for the adsorption of Pb(II). The best behaviour in this respect was demonstrated by GTS-1 when compared to ETS-4 and clinoptilolite.
1. Introduction
Heavy metals are amongst the most dangerous pollutants in the environment, even when they are present at low concentrations. Open-pit mining and flotation processing of mineral resources for obtaining precious metals are common causes of severe water pollution. Industrial wastewaters released after the processing of mineral resources often contain high levels of heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, mercury, etc.; therefore, appropriate treatment of the wastewaters is crucial to prevent negative impacts on the environment. To the best of our knowledge, one of the most suitable techniques for the extraction of heavy metals from solutions is based on sorption/exchange processes with the use of porous materials such as natural and synthetic zeolites [1], mesoporous silica [2,3], clays [4,5,6,7,8], carbon nanotubes [9,10,11], activated carbon [12,13], biomass adsorbents [12,13,14,15], polymers [16], etc. The adsorption, separation, and ion-exchange properties of zeolites stem from their distinctive three-dimensional porous framework structure [17]. Natural zeolites such as clinoptilolite (CPT) [18,19] and chabazite (CHZ) [20] are extensively studied because of their natural abundance and low cost of procurement, making them economically suitable for large-scale application in agriculture [21,22,23], construction [24,25], as molecular sieves [26], and in the field of environmental preservation [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35]. The vast majority of the studies on natural zeolites are concentrated on their application as adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment, for the removal of heavy metals and organic pollutants (e.g., dyes, ammonia, aniline, etc.) [1]. An important criterion characterising the effectiveness of any porous material as a heavy metal adsorbent is the cation-exchange capacity (CEC). The CEC of zeolite materials is mostly related to two major factors: the type and concentration of the cations present in the zeolite channels, and the charge (Si/Al ratio) of the zeolite framework. For example, the increase in the Si/Al ratio in the natural zeolites enhances their thermal stability, acid strength, and hydrophobicity, whereas the ion-exchange capacity decreases, and vice versa [27].
In order to further enhance the metal extraction capability of the porous materials (e.g., to increase their CEC), natural zeolites were subjected to modifications, and many zeolite-like compounds were synthetically made [36]. The most common modifications of natural zeolites aiming to improve their adsorption characteristics are the acid–base treatment and surfactant impregnation by ion exchange. The acid washing of natural zeolites usually targets the removal of the impurities that block the pores and removes the extra-framework cations, creating the proton-exchanged form (H-form) of the zeolite. The main problem with the acid wash is the dealumination process that destroys the crystal structure. An alternative procedure to achieve the H-form is ammonium exchange followed by calcination for removal of NH4+. While the ammonium exchange process does not produce “dealumination”, the calcination requires elevated temperatures, which may have a negative effect on the zeolite framework structure. The production of synthetic zeolites that are acid-resistant or can withstand the temperature treatment for ammonia removal and generating the H-form also presents an opportunity. Amongst the acid-resistant synthetic analogues of zeolites are the titanium silicates. Firstly the Engelhard Titanium Silicate-4, and 10 (ETS-4 and ETS-10) were synthesised [29] and lately the ETS-14 [37] and Grace titanium silicate-1 (GTS-1) [38,39] were also reported. The titanium silicates are characterised by a porous crystal framework with uniform pore size—in the case of ETS-4 about 3.7 Å, for ETS-10 about 10 Å, and for ETS-14 about 14 Å. Unlike natural zeolites, the titanium silicate analogues are more acid-resistant but thermally more unstable. This can be linked to framework differences, as natural zeolites’ structure is composed of silicon [SiO4]4− and aluminium [AlO4]5− coordinated polyhedra, while in the titanosilicates aluminium is replaced by titanium [TiO6]2− octahedra [27,28].
Compared to GTS-1, the Engelhard titanium silicates-4 has been extensively investigated for the adsorption of Hg2+, Cd2+, Co2+, Sr2+ [40,41,42,43,44], and radioactive metals such as 241Am3+ and 236,239,240Pu3+ [45,46], as well as for the separation, adsorption, and diffusion of gases [47,48,49], etc. It has been reported that the replacement of monovalent K/Na+ cations with divalent cations (M2+) such as Sr2+ and Ba2+ alters the adsorptive properties as well as the stability of ETS-4 adsorbents [50]. The dehydration of M2+-ETS-4 occurs at higher temperatures and causes a relocation of the M2+ cations in the structure [51] that is accompanied by pore contraction (a contracted titanosilicate is manufactured [52]) and, thus, reduction in adsorptive properties. This is probably why most of the reported H-ETS-4 preparation involves treatment of the Na-K-ETS-4 with hydrochloric acid [53]. Unfortunately, the structure of ETS-4 allows the substitution of halogen anions instead of terminal hydroxyl groups in O7 sites bonded to TiO5 units [54]. The effect of this substitution also results in pore size reduction. The control of the pore size in reduced-pore zorite (RPZ), which is an analogue of ETS-4, is achieved by controlling the levels of structural chloride ions [53,55].
There are very few studies on GTS-1 uptake properties. Based on the literature data, the CEC and selectivity of GTS-1 decreases in the order Cs+ > K+ > Na+ > Li+ [39,56,57,58]. Data are also available for the removal of Hg from natural waters by GTS-1, and of 137Cs2+ and 89Sr2+ by different cationic forms of synthetic pharmacosiderite [59]. To the best of our knowledge, no data are available in the literature for the preparation and adsorption properties of the proton-exchanged form of GTS-1 (H-GTS-1). Based on the aforementioned, it is clear that titanosilicates are effective adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. However, the industrial implementation requires adjustment of the activation technique to obtain materials with enhanced properties, e.g., increase the uptake of harmful components. The goal of this work is to expand the data on the sorption/exchange properties of the titanosilicate GTS-1 towards Pb(II) cations, as information on the Pb(II)-exchange properties of GTS-1 is very scarce in the scientific literature [38]. The study is focused on obtaining detailed uptake equilibrium and kinetic data for Pb(II) exchange on the synthesised GTS-1 and its produced H-form. It is well known that both clinoptilolite and ETS-4 possess good adsorption properties towards Pb(II); therefore, clinoptilolite and ETS-4 were chosen as reference materials [27,28,60,61,62,63,64,65].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The studied materials the titanosilicates Na-K-ETS-4 and Na-K-GTS-1 were synthesised by our team. And clinoptilolite (CPT) was from the Beli Plast deposit, Bulgaria. The analytical-grade starting reagents used in the synthesis of Na-K-ETS-4 and Na-K-GTS-1, and for the ion exchange, were as follows: titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4, 99.6%), sodium hydroxide (NaOH, 97%), potassium hydroxide (KOH, >85%), silicon dioxide (SiO2, 99.5%), ammonium chloride (NH4Cl, 98+%), lead nitrate (Pb(NO3)2, 99%), and ultrapure distilled water (electrical conductivity of 0.055 µS/cm). All starting reagents were purchased from Alfa Aesar, and were used without further purification.
2.1.1. Synthesis of Na-K-ETS-4
The synthesis of Na-K-ETS-4 (molar composition: 9.25Na2O:1.11K2O:3.49TiO2:10SiO2:675H2O) was carried out based on a known procedure reported by Kytin et al. [66]. The synthesis was conducted at autogenous pressure, at 200 °C and a crystallisation time of 24 h.
Solution 1: 8.235 g of NaOH, 1.135 g of KOH, and 6.660 g of SiO2 were added to 90 mL of distilled water, and the mixture was homogenised for 120 min with stirring.
Solution 2: 2.740 mL of TiCl4 was added to 45 mL of distilled water, and the mixture was homogenised mechanically for 10 min.
After that, solution 2 was added to solution 1 under constant stirring; the resulting white gel mass was re-homogenised with stirring for 40–45 min and then transferred into the Teflon chamber of a stainless steel autoclave. The autoclave was then placed in a furnace, preheated to 200 °C, and was kept at that temperature for 24 h. The hot autoclave was cooled down to room temperature under running water (cooling time is a function of the autoclave volume, e.g., ~3 h of cooling for a 1 L autoclave). The obtained insoluble product was vacuum-filtered and washed several times with distilled water until the pH reached ~7–8. After that, the product was dried at 100 °C.
2.1.2. Synthesis of Na-K-GTS-1
The synthesis of Na-K-GTS-1 (molar composition: 3Na2O:3K2O:0.6TiO2:10SiO2:675H2O) was carried out based on a known procedure reported by Ferdov et al. [67], with slight adjustments to the time and temperature of crystallisation. The synthesis was conducted at autogenous pressure with a temperature of 200 °C and for a crystallisation time of 19 h.
Solution 3: 16.425 g of NaOH, 10.350 g of KOH, and 5.40 g of SiO2 were added to 112.5 mL of distilled water, and the mixture was homogenised with stirring for 120 min.
Solution 4: 9.00 mL of TiCl4 was added to 27 mL of distilled water, and the solution was homogenised mechanically for 10 min.
After that, solution 3 was added to solution 4 with constant stirring; the resulting white gel mass was re-homogenised with a magnetic stirrer for about 40–45 min and transferred into a stainless steel autoclave with a Teflon chamber. The autoclave was placed in a furnace preheated to 200 °C for 19 h, and the resulting insoluble nano-sized product was centrifuged (6000 rpm) several times by adding fresh distilled water until the pH dropped to ~7–8. The product was then dried at 100 °C.
2.1.3. Preparation of Modified Ammonium (NH4+) Forms
All studied samples were modified to ammonium forms by ion exchange with 0.2 M NH4Cl solution (NH4Cl:material—100:1 weight ratio). Ultrapure (0.055 µS/cm) H2O was used for the NH4+ exchange. The aqueous mixture of NH4Cl and Na-K-ETS-4/Na-K-GTS-1/CPT was stirred for 120 min, after which the solvent was decanted and fresh 0.2 M NH4Cl solution was added. The mixture was then stirred for another 120 min. Due to the different thermal stability of the studied materials, the NH4+-ion exchange was conducted at different temperatures—for CPT, the mixture was heated to 70–80 °C, for Na-K-ETS-4 to about 60–70 °C, and for Na-K-GTS-1 to about 80 °C—using a water bath. The samples were then dried and heated at different temperatures to release the ammonium and to obtain the respective activated “H”-forms. It was found that the optimal (i.e., the lowest) temperature for obtaining the “H”-form of CPT was 520 °C for 120 min, for H-ETS-4 it was 140 °C for 60 min, and for H-GTS-1 it was 100 °C for 60 min.
2.1.4. Equilibrium Uptake and Kinetic Studies
The equilibrium uptake studies were conducted at room temperature as follows: 1.00 g of the corresponding H-CPT, H-ETS-4, and H-GTS-1 forms was added to a vessel containing 100 mL of Pb(NO3)2 aqueous solution (pH 5.4) as a Pb2+ source. At least five different Pb2+ concentrations varying from 5 to 400 mg/L (for H-CPT) and from 10 to 4400 mg/L (for H-ETS-4 and H-GTS-1) were used to deduce the saturation concentration of Pb2+. After 2 h of stirring at 250 rpm, the solid adsorbent was separated by filtration (blue filter grade < 2 µm, for Pb-CPT and Pb-ETS-4) or centrifugation (at 6000 rpm for Pb-GTS-1). The solid and solution were both analysed for Pb(II) content.
The adsorption kinetics studies were conducted using the Pb2+ saturation concentrations determined from the equilibrium uptake isotherms. The time intervals were 4, 8, 12, 15, 30, 60, 120, and 180 min, keeping all other conditions unchanged (i.e., amounts of sorbent, volume of the solution, pH, temperature, and stirring).
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD) Analysis
PXRD was used for monitoring the synthesis and for phase identification. The PXRD patterns of the samples were collected at room temperature on an Empyrean, Malvern Panalytical diffractometer. Data collection was performed using Cu radiation (λ = 1.5406 Å) at 40 kV and 30 mA, along with a PIXcel3D detector in the range 2–50° 2θ and with a step size of 0.013° 80 s.
In addition, in situ PXRD studies were performed with stepwise heating from 50 to 450 °C (50 °C per step) and from 450 to 50 °C in an ambient atmosphere using an Anton Parr TTK600 chamber (the start and end temperatures were 35 °C). This analysis was used to determine the thermal stability of the tested samples for subsequent exchange of NH4Cl, and then for producing the activated H-forms.
2.2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
The SEM analysis was performed on a Philips 515 microscope operating at 20 keV in secondary electron mode. The samples were mounted on a specimen holder with a conductive carbon coating. The results were used to characterise the size and morphology of the particles and crystallites.
2.2.3. Wavelength Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy (WDXRF)
WDXRF was used to determine the chemical composition of the solids (Table 1). The chemical elemental composition was determined on a Supermini200 spectrometer (Rigaku, Japan). Data collection was performed by wavelength-dispersive X-ray fluorescence at 50 kV and 4.00 mA. The sample was crushed and then pressed to obtain a tablet. The sample/tablet was placed in a holder with an irradiated area of 30 mm in diameter. The weight ratio of the amount of sample to the amount of glue (Acrawax C powder) was 5:1. A semi-quantitative method (SQX) was used to determine the elemental composition, without the need for reference materials.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of the initial samples, H-forms and Pb-forms obtained after 120 min of exchange at saturation concentrations.
2.2.4. Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES)
ICP-OES was used to determine the concentration of the remaining Pb(II) ions in the aqueous solution after treatment with the H-ETS-4, H-GTS-1, or H-CPT (sorbents). The ICP data provided the equilibrium concentration, and were used in the kinetic studies. The Pb2+ concentration was obtained as the average of three studies. The equipment used was a Prodigy High-Dispersion spectrometer (Teledyne Leeman Labs, Hudson, NH, USA). The spectrometer was equipped with a dual-view torch, cyclonic spray chamber, and concentric nebuliser. The measurements were performed with the following settings: power 1.2 kW; coolant flow 18 LPM; auxiliary flow 0.1 LPM; nebuliser pressure 34 LPM; pump tubing 1.2 mL/min; axial view 30.0 s. The results, including standard deviations, are provided in Table S1.
2.2.5. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was used to determine the degree of exchange of NH4+ forms. The samples were examined using a Bruker Tensor 37 spectrometer using KBr pellets. For each sample, 128 scans were collected at a resolution of 2 cm−1 over the wavenumber region 4000–400 cm−1.
2.2.6. Specific Surface Area Analysis
The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area, pore volume, and pore size properties of the CPT, Na-K-ETS-4, Na-K-GTS-1, H-CPT, H-ETS-4, H-GTS-1, Pb-CPT, Pb-ETS-4, and Pb-GTS-1 samples were assessed by N2 adsorption/desorption at −196 °C using a Quantachrome Autosorb-iQ-AG instrument. The results are presented in Figures S1–S3 and Table S2.
3. Results and Discussion
The initial idea was to employ Na-K-ETS-4 and Na-K-GTS-1 directly for the removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions. However, the results of the performed pre-experiments for Pb2+ ion exchange using the Na-K-forms revealed that Pb2+ cannot displace the Na+ or K+ extra-framework cations. This result necessitated obtaining the “extra framework cation free” H-forms of the studied compounds. The H-form may be obtained either by acid attack of the Na-K-forms, or through ammonium exchange. The acid attack is suitable for titanosilicates, which are acid-“resistant”, but are not applicable for Si/Al zeolites such as CPT. However, even titanosilicates show significant structural damage after multiple cycles of acid treatment and, thus, their reusability is limited. Considering the advantages and disadvantages of acid treatment, we chose to obtain the H-forms via ammonium exchange.
3.1. Characterisation of the Initial Materials
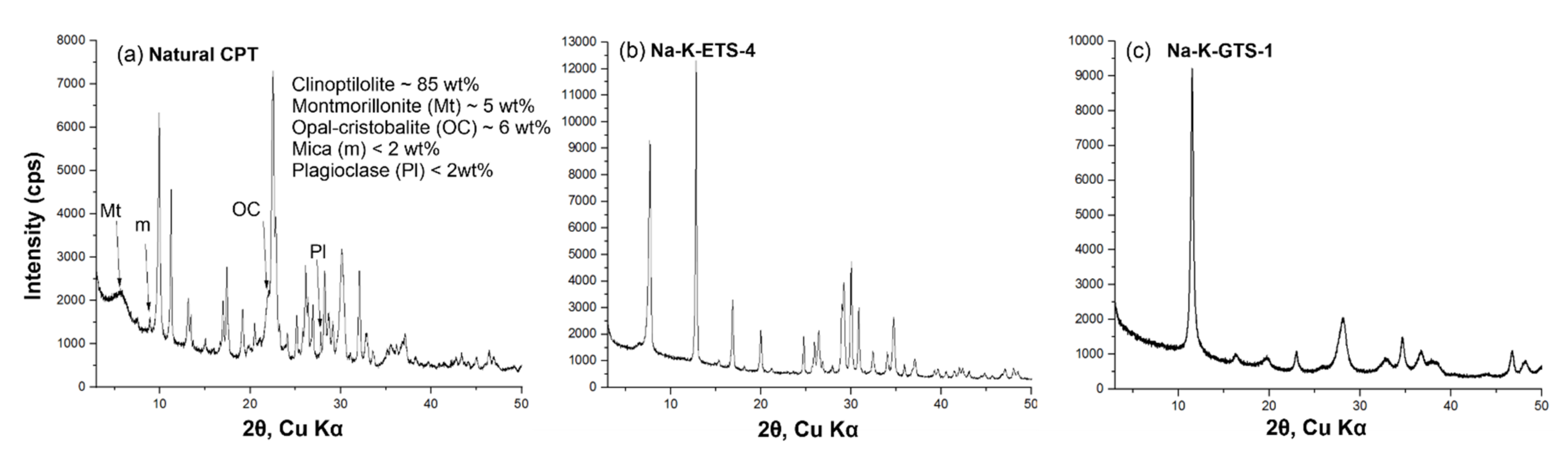
The initial assessment of the purity of the synthesised Na-K-ETS-4 and Na-K-GTS-1, as well as of the natural CPT, was made on the basis of PXRD analysis (Figure 1). The semi-quantitative phase analysis of the natural CPT (Figure 1a) performed using the DDM Semi-QPA method [68], incorporated in the HighScore software [69], revealed clinoptilolite content of 85% and some impurities such as opal cristobalite ~6 wt%, montmorillonite ~5 wt%, mica < 2 wt%, and plagioclase < 2 wt%. The diffractograms of Na-K-ETS-4 (Figure 1b) and Na-K-GTS-1 (Figure 1c) clearly show only the presence of pure phases of the desired products.
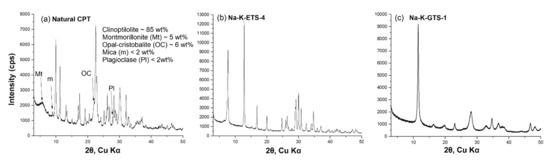
Figure 1.
Powder XRD patterns of (a) natural CPT from the Beli Plast deposit, Bulgaria, (b) Na-K-ETS-4, and (c) Na-K-GTS-1. The diffraction peaks corresponding to the impurities in the clinoptilolite—e.g., montmorillonite (Mt), opal cristobalite (OC), mica (m), and plagioclase (Pl)—are marked with arrows.
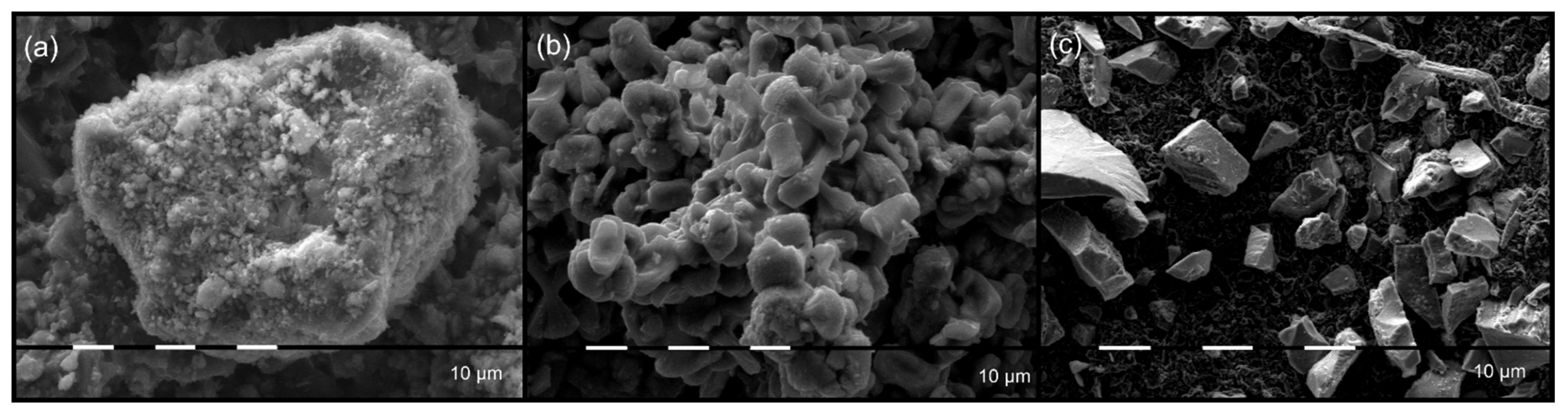
The SEM images of CPT, Na-K-ETS-4, and Na-K-GTS-1 are shown in Figure 2. Based on SEM observation, all samples appeared to be finely crystalline, and were similar in size (particle size of 10–15 µm). However, the SEM images do not correlate with the observed broadening of the XRD peaks (Figure 1c), suggesting nanosized Na-K-GTS-1.
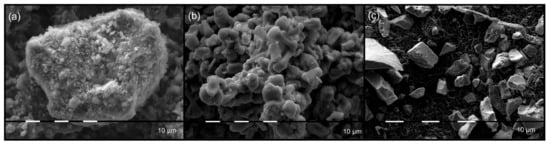
Figure 2.
SEM images of (a) CPT, (b) Na-K-ETS-4, and (c) Na-K-GTS-1; magnification is ×1100.
3.2. Ion Exchange (IE), Theoretical Exchange Capacity (TEC), and Cation-Exchange Capacity (CEC)
3.2.1. NH4+-Exchanged and H-Forms
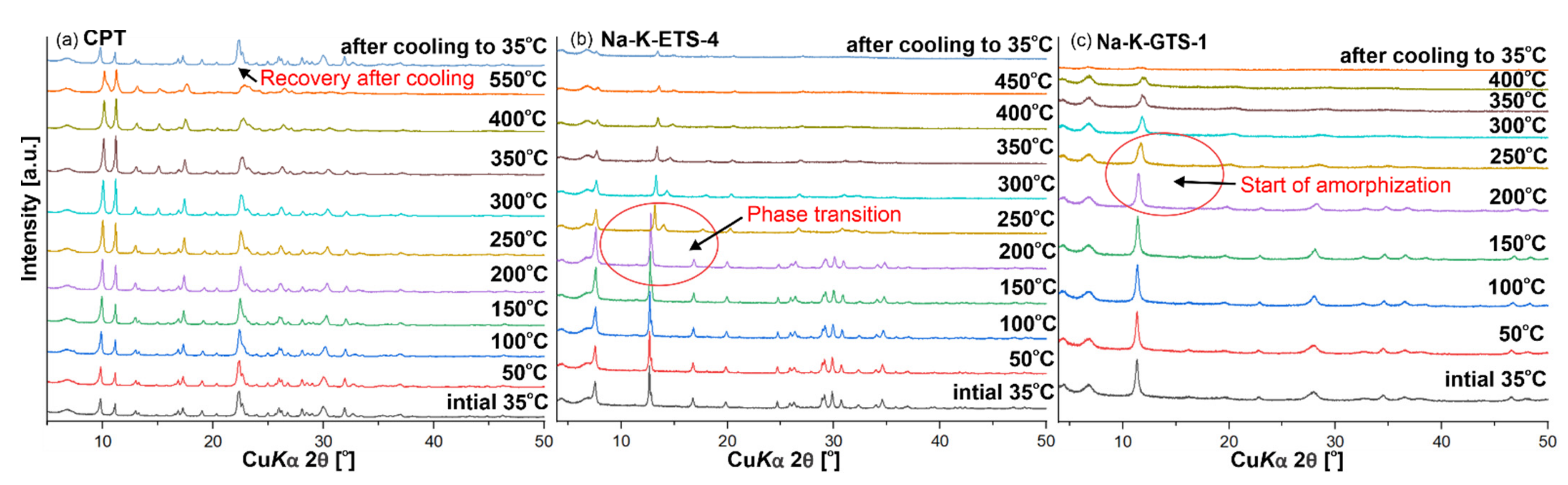
The in situ PXRD showed that CPT is thermally stable at least up to 550 °C. After cooling to room temperature, a recovery of the CPT crystal structure (Figure 3a) was observed (based on intensities). This was probably due to rehydration processes. In the case of Na-K-ETS-4, a phase transition was observed between 200 and 250 °C (Figure 3b), while for Na-K-GTS-1 an amorphisation process began after 200 °C. Thus, the removal of NH4+ by heating is limited to 200 °C for NH4-ETS-4 and NH4-GTS, while for NH4-CPT the used temperature may be higher e.g., 550 °C. Due to the limitations of our XRF equipment for the detection of nitrogen, the presence/absence of NH4+ in the studied samples was detected with FTIR, based on the N-H bending vibration observed around ~1440 cm−1.
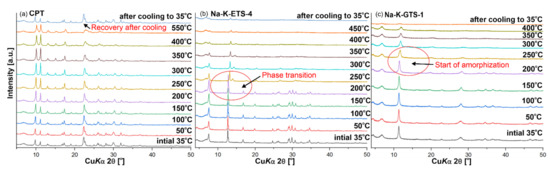
Figure 3.
In situ temperature PXRD analysis of (a) CPT, (b) Na-K-ETS-4, and (c) Na-K-GTS-1. The topmost diffractograms at 35 °C were measured after cooling down in order to see whether the material would return to its initial crystalline form.
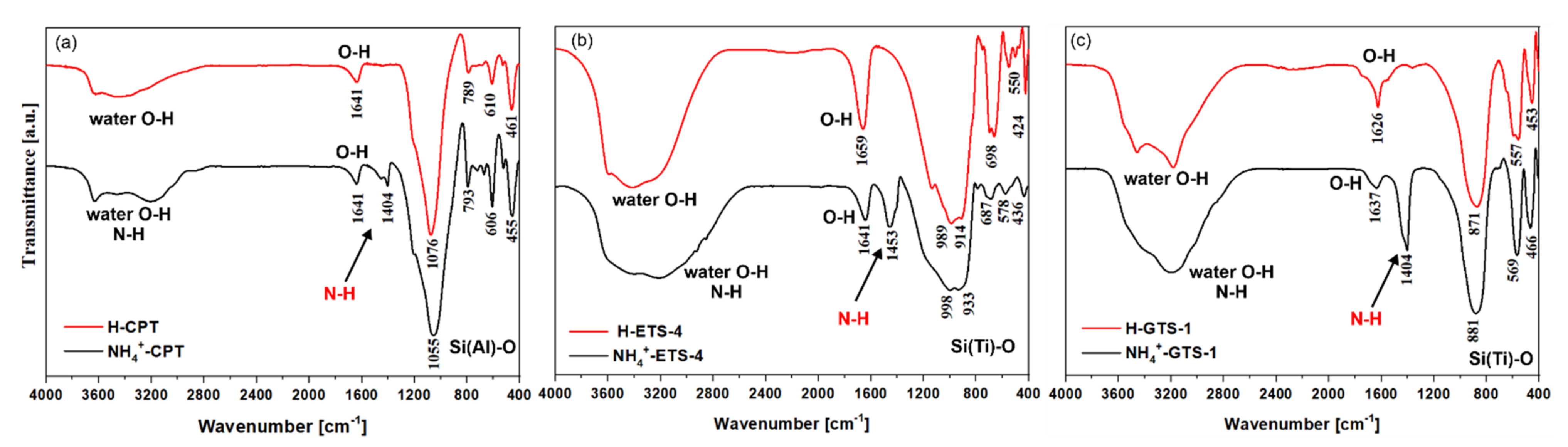
The FTIR spectra of the H- and NH4-forms of CPT, ETS-4, and GTS-1 are shown in Figure 4. The most intensive bands observed in the 1100–430 cm−1 region of the FTIR spectra correspond to the framework vibrations. For NH4-CPT and H-CPT the Si (Al)-O stretching/bending vibrations were observed at 1076–450 cm−1 [70], while for NH4-ETS-4, H-ETS-4, NH4-GTS-1, and H-GTS-1 the framework vibrations were slightly shifted towards lower values, and could be found between 990–430 cm−1 [71,72]. The broad intensive bands observed in all spectra in the 3500–3200 cm−1 region were associated with the asymmetric stretching vibrations of O-H (water) and/or N-H groups. The band at 1660–1620 cm−1 was the result of deformation vibrations of molecularly bound water in the structure. What is interesting in our case is the N-H band around 1440 cm−1 in the FTIR spectra of the NH4+-forms and its absence in the H-forms (the framework of the materials remains unchanged). In fact, the removal of ammonium from NH4-ETS-4 and NH4-GTS-1 occurred at 140 and 100 °C, before the allowed maximal temperature of 200 °C (for at least 60 min of heating). For NH4-CPT, the required temperature for ammonium removal was 520 °C, again for at least 120 min of heating.
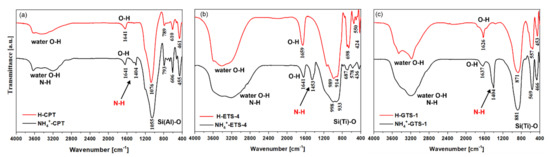
Figure 4.
Comparative FTIR spectra of the H- and NH4+-forms of (a) CPT, (b) ETS-4, and (c) GTS-1. One can note the additional N-H band at ~1440 cm−1 due to the presence of NH4+.
The BET surface areas and pore volume of the samples are given in Figures S1–S3 and Table S1. The BET surface areas of the H-forms are distinctively larger than those of the Na-K- and Pb-forms, while no tendency can be drawn from the pore dimeter data (except that the materials remain mesoporous).
3.2.2. Theoretical Ion-Exchange Capacity
The theoretical ion-exchange capacity (TEC) value for CPT is related to the exchangeable cations Mg2+, Ca2+, K+, and Na+ situated in the pores/channels. According to the general empirical formula of CPT—(Na,Mg,K,Ca)3–6(Si30Al6)O72·20H2O)—the TEC is between 2.4 and 2.64 meq/g [29,30], and the typical values for the Si/Al ratio are between 4 and 5.3 [61,73]. The typical TEC values for Na-K-ETS-4—(NaK)9Ti5Si12O38OH·12H2O—varies between 5.54 and 6.39 meq/g [19,23], and those for GTS-1—(Na)3Ti4O4(SiO4)3·4H2O—are around 6.65 meq/g [74]. The Si/Ti ratios in Na-ETS-4 and GTS-1 are 2.4 [75] and 0.75 [39,76], respectively.
3.2.3. Cation-Exchange Capacity
The cation-exchange capacity (CEC) of the studied samples was calculated on the basis of their empirical formulae, derived from the WDXRF analysis (Table 1) using the following equation:
where EECin—exchangeable equivalents of cations (derived from the chemical formula) of the initial samples divided by their charge; EECrem—exchangeable equivalents of cations of the NH4+-modified samples divided by their charge.
The resulting CEC values for CPT (2.17 meq/g), ETS-4 (3.85 meq/g), and GTS-1 (5.96 meq/g) were within the range of the theoretical values, as well as the Si/Al ratio for CPT (6.20) and the Si/Ti ratios for ETS-4 and GTS-1 of 2.13 and 0.72, respectively. The obtained CEC shows that, experimentally, 82% exchange was achieved for ETS-4, while more than 90% was observed for CPT and GTS-1.
3.3. Equilibrium Uptake Isotherms
Sorption is usually described in terms of equilibrium isotherms. The uptake depends on initial concentration of the solution in contact with the exchanger, the temperature, and the characteristics of the ion-exchange system, such as solution composition, pH, and substance type.
When the equilibrium is unfavourable, the plot of solid concentration vs. solution concentration of the cation is concave-upward. This type of curve implies that equilibrium prevents the ion exchanger from taking as many cations as its capacity would allow. In this case, the equilibrium is the process-controlling factor in the ion exchange. In contrast, when the cations are strongly preferred by the ion exchanger, equilibrium is favourable, and the ion-exchange process is controlled by both equilibrium and kinetic factors.
The analyses terminate with a final Pb2+ concentration (e.g., 4400 mg/L) when no further uptake from the adsorbents is observed or a plateau is reached. In the present work, the amount of Pb(II) in the solids and the solutions was tested with WDXRF and ICP-OES, respectively.
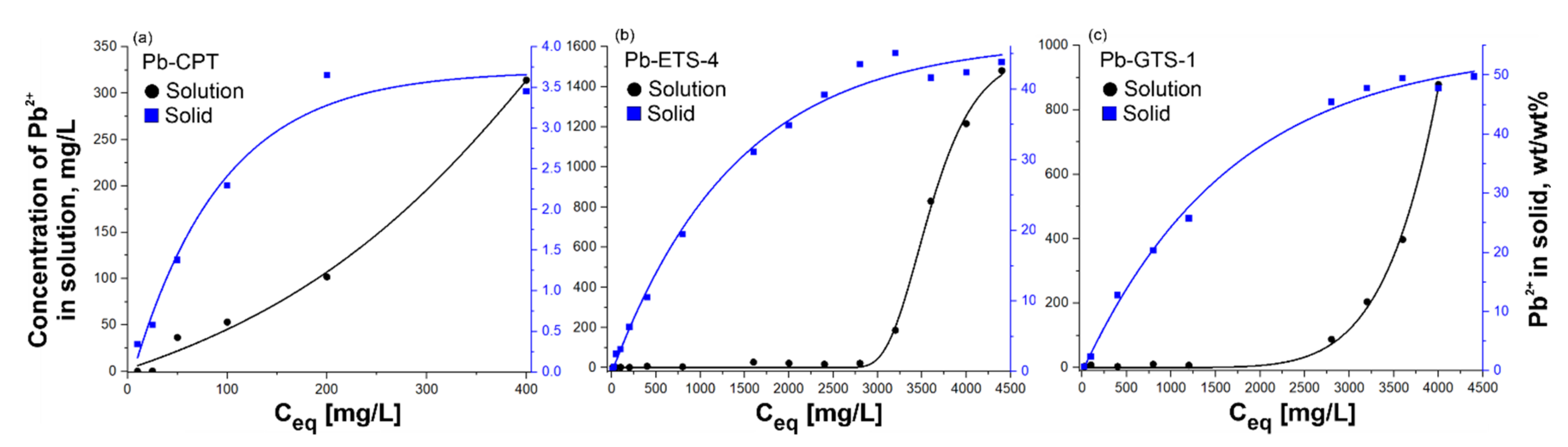
H-ETS-4 and H-GTS-1 showed similar trends, with almost complete Pb2+ removal from aqueous solutions up to around 2700 and 2000 mg/L, respectively (Figure 5b,c). On the other hand, complete removal of Pb2+ by clinoptilolite was observed for concentrations up to around 25 mg/L, and afterwards the increase was proportional to the volume-to-mass ratio. The amount of Pb2+ taken up by H-ETS-4 and H-GTS-1 corresponds well to the solution data, even if the saturation plateau is reached at higher concentrations. The H-CPT profile of the Pb2+ uptake is also in accordance with the data for the solution (Figure 5a). For H-CPT, the saturation concentration (plateau) was observed after ~180 mg/L initial concentration. The maximum adsorption capacity for clinoptilolite was calculated to be about 99% of 25 mg/L, for H-ETS-4 it was 98–99% of 2800 mg/L, and for H-GTS-1 it was 99% of 2000 mg/L. The chosen concentrations of lead at equilibrium were 400 mg/L for CPT, and 3600 mg/L for both H-ETS-4 and H-GTS-1.
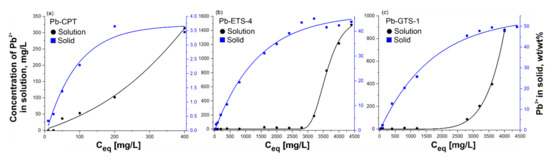
Figure 5.
Representation of the adsorption isotherms for Pb(II) ion removal of (a) Pb-CPT, (b) Pb-ETS-4, and (c) Pb-GTS-1; experimental conditions: 1 g of adsorbent, initial pH 5.4, Pb(II) concentration 5–4500 mg/L, and adsorption period 2 h.
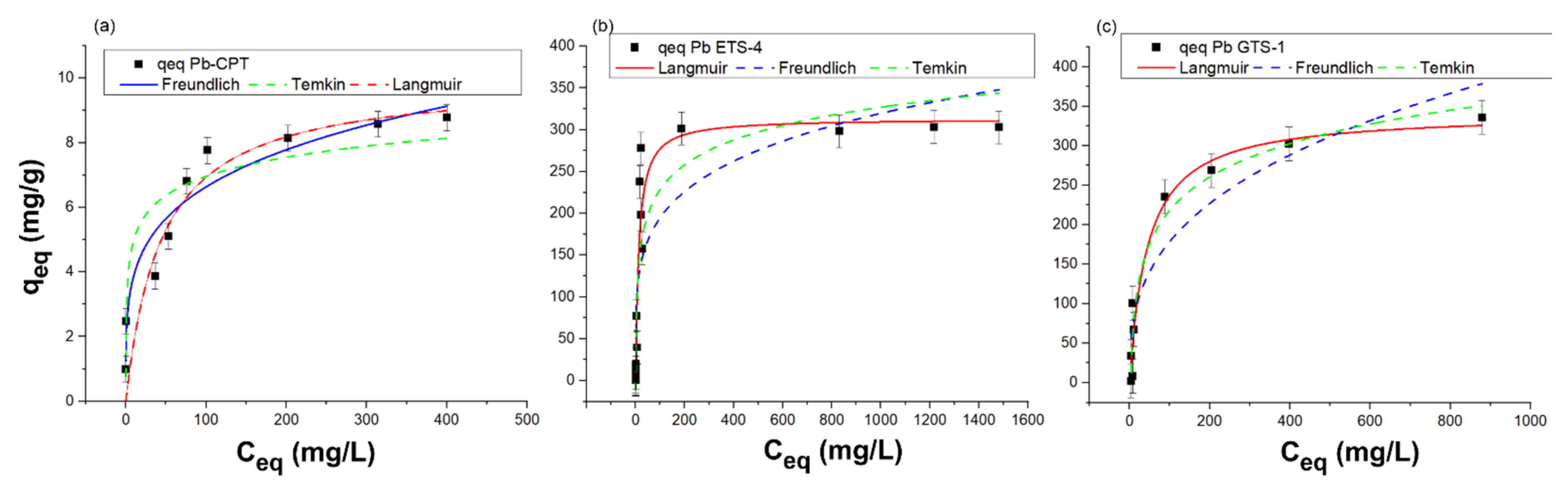
The equilibrium isotherms of lead adsorption by H-ETS-4, H-GTS-1, and H-CPT with respect to the concentration of species in the solid phase as a function of its value in the solution are presented in Figure 6.
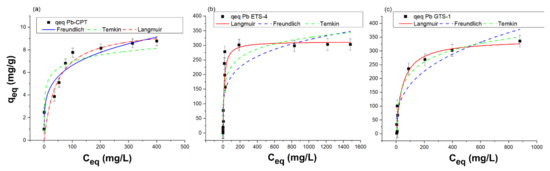
Figure 6.
Equilibrium uptake isotherms of Pb(II) with (a) H-CPT, (b) H-ETS-4, and (c) H-GTS-1 in the liquid phase. The best fit of the experimental data (qeq) for H-CPT, H-ETS-4, and H-GTS-1 is given with solid line.
The experimental amount of Pb2+ adsorption was calculated according to Equation (2):
where m (g)—the mass of adsorbent; V (L)—the volume of the adsorbate solution; C0 (mg/L)—the initial concentrations of Pb2+ in the liquid phase; Ce (mg/L)—the equilibrium concentrations of Pb2+ in the liquid phase.
The Langmuir isotherm considers adsorption as a chemical phenomenon, assuming that all of the available active adsorption sites are similar, the adsorbed species does not interact, and only a monolayer is formed. Freundlich, on the other hand, assumes a heterogeneous surface and an exponential distribution of active sites and their energies. According to the Temkin model, it is assumed that the adsorption heat of all molecules in the layer decreases linearly with the coverage area due to the adsorbent–adsorbate interactions, and the adsorption is characterised by a homogeneous distribution of binding energies up to a maximum binding energy. The nonlinear forms of these models (Equations (3)–(5)) were applied for the calculation of the corresponding parameters, given in Table 2.

Table 2.
Freundlich, Temkin, and Langmuir adsorption isotherm parameters.
The equilibrium solute concentration in the adsorbent phase “qeq” is determined through the following Langmuir nonlinear regression isotherm:
where Ceq—the equilibrium concentration of remaining Pb2+ ions (mg/L); qeq—the amount of adsorbed Pb2+ (mg/g); Qmax—the monolayer capacity (mg/g), i.e., the maximum adsorption capacity of the solid phase; KL—the mass transfer coefficient (L/mg).
The nature of the adsorption can also be estimated by the dimensionless Langmuir separation factor RL:
where KL is the mass transfer coefficient (L/mg) and C0 is the initial adsorbate concentration (mg/L). The RL values can be classified as unfavourable (RL > 1), linear (RL = 1), favourable (0 < RL < 1), or irreversible (RL = 0).
Freundlich nonlinear model:
where KF is the Freundlich partition coefficient, and n is a constant indicative of the intensity of the adsorption.
Temkin nonlinear model:
where B is a constant related to the heat of adsorption, and B = RT/b, where b is the Temkin constant (J/mol), T is the absolute temperature (K), R is the gas constant (8.14 J/mol K), and KT is the Temkin isotherm constant (L/g).
The results indicate that the adsorption of lead on H-ETS-4 and H-GTS-1 follows the Langmuir model (Figure 6b,c) while for H-CPT the Freundlich model fits the experimental data better (Figure 6a). The adsorption capacity corresponding to the monolayer adsorption (Qmax) is 313.42 and 342.20 mg/g for Pb-ETS-4 and Pb-GTS-1, respectively, while KL (the Langmuir constant related to the free energy of adsorption) is 0.07663 and 0.0226 (L/mg) for Pb-ETS-4 and Pb-GTS-1, respectively. The RL values are 0.04 and 0.012, indicating that the adsorption of Pb2+ is a favourable process. The higher R2 recorded for the Freundlich equation indicates that this isotherm is the best-suited model to describe the Pb2+ adsorption on H-CPT. The better fit obtained with the Freundlich model suggests the heterogeneous nature of the H-CPT, and multilayer adsorption of Pb2+ onto the adsorbent. The heterogeneous character of the H-CPT surface is also confirmed by the n parameter from the Freundlich equation. The 1/n describes the intensity of the adsorption or surface heterogeneity—for favourable adsorption, 0 < 1/n < 1; if 1/n > 1, unfavourable adsorption; and the process is irreversible when 1/n = 1. The 1/n value of 0.23 indicates that the adsorption could be considered as favourable and the adsorbent surface as heterogeneous, which is also known from the PXRD data.
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
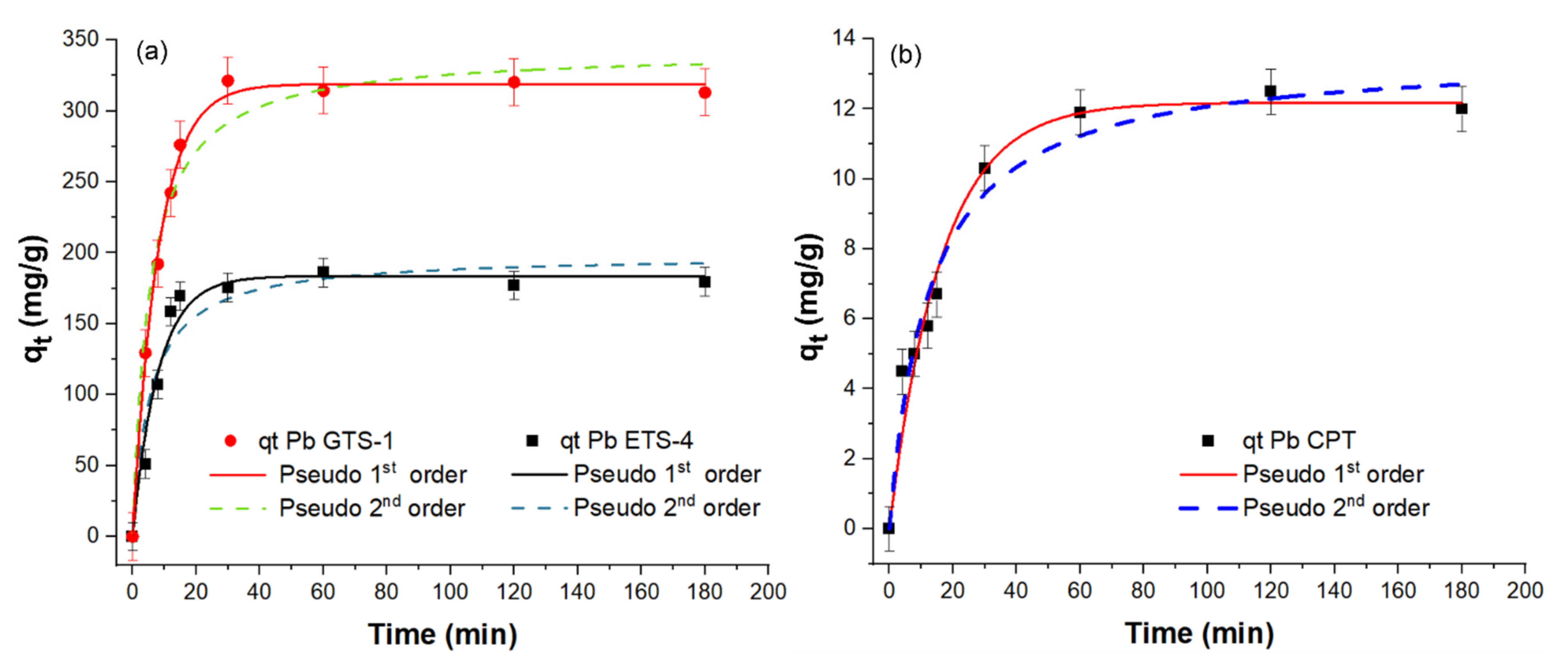
The saturation concentrations were used for performing the kinetics studies of Pb2+ sorption for different sorption intervals (t) of 4, 8, 12, 15, 30, 60, 120, and 180 min. Adsorption kinetics data for Pb2+ uptake by H-CPT, H-ETS-4, and H-GTS-1 are presented in Figure 7.
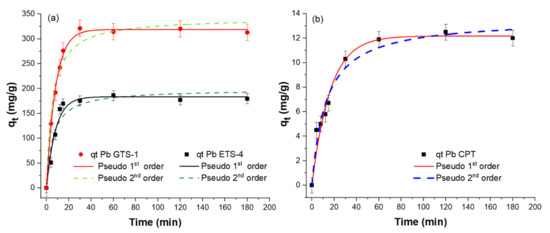
Figure 7.
Pb2+ adsorption kinetics of (a) H-ETS-4 and H-GTS-1, and (b) H-CPT. The kinetics were followed for 4, 8, 12, 15, 30, 60, 120, and 180 min using Pb2+ aqueous solutions with concentrations of 400 mg/L for CPT and 3600 mg/L for ETS-4 and GTS-1. The best fit of the experimental data (qt) for H-CPT, H-ETS-4, and H-GTS-1 is given with solid lines.
Pseudo-first-order kinetic model:
Pseudo-second-order kinetic model:
To investigate the mechanism controlling the adsorption processes, the kinetic data collected in this study were fitted to the pseudo-first-order (PFO) and pseudo-second-order (PSO) models. The pseudo-first-order model assumes that the adsorption rate is based on the adsorption capacity. The pseudo-second-order model is based on the assumption that the adsorption is controlled by the chemisorption mechanism, involving valence forces through electron sharing or transfer between the adsorbent and adsorbate. The calculated kinetic parameters are given in Table 3. Herein, the two models showed a good fit with the experimental data. However, comparing the R2 values of the PFO and PSO fit, one can notice that the Pb2+ adsorption by H-ETS-4 and H-GTS-1 is better described by the PFO kinetic model (R2H-ETS-4 = 0.96632 and R2H-GTS-1 = 0.99623), while for CPT distinguishing the better fit is not possible (R2 PFO ~ R2 PSO). Additionally, the sorption of Pb(II) is the fastest for GTS-1—89% (for 20 min of uptake)—followed by ETS-4—77% (after 25 min of uptake)—and CPT—75% (after 60 min of uptake).

Table 3.
PFO and PSO parameters.
The adsorption capacities of other adsorbents of Pb2+, taken from the literature, are provided in Table 4 for comparison. The values of the maximum adsorption capacity, qm, (mg/g) reported in this work for H-ETS-4 and H-GTS-1 are significantly higher than that of H-CPT, and compete with the most promising candidates.

Table 4.
Comparative adsorption capacities (qm) for Pb2+ uptake of various adsorbents.
4. Conclusions
The results of this study present insights into the adsorption of Pb2+ on the synthetic ETS-4 and GTS-1 and natural CPT. Na-K-ETS-4 and Na-K-GTS-1 were successfully synthesised and along with clinoptilolite modified to H-ETS-4, H-GTS-1, and H-CPT by ammonium ion exchange, followed by calcination. The obtained materials were characterised by SEM, FTIR, surface area analyses/BET, WDXRF, and XRD. The adsorption studies demonstrated that H-ETS-4 and H-GTS-1 are promising adsorbents for the removal of lead ions from their aqueous solutions. Adsorption equilibrium was attained within 1 h. The adsorption kinetics obeyed the pseudo-first-order model, suggesting that the rate-limiting step is probably diffusion. The adsorption equilibrium of Pb2+ was satisfactorily described by the Langmuir equation for Pb-ETS-4 and Pb-GTS-1, and by the Freundlich equation for the Pb-CPT isotherm. The maximum adsorption (qm) calculated from the Langmuir equation was 313 and 342 mg/g for Pb-ETS-4 and Pb-GTS-1, respectively.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w14142152/s1, Figure S1. Low-temperature nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms (at 77 K, squares adsorption and circles desorption of (a) CPT, (b) H-CPT, and (c) Pb-CPT); Figure S2. Low-temperature nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms (at 77 K, squares adsorption and circles desorption of (a) Na-K-ETS-4, (b) H-ETS-4, and (c) Pb-ETS-4); Figure S3. Low-temperature nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms (at 77 K, squares adsorption and circles desorption of (a) Na-K-GTS-1, (b) H-GTS-1, and (c) Pb-GTS-1); Table S1. Lead concentrations in solutions and their standard deviation (SD) determined by ICP-OES after treatment with (a) H-CPT, (b) H-GTS-1, and (c) H-ETS-4; Table S2. The BET surface area and porosity analysis of CPT, H-CPT, Pb-CPT, Na-K-ETS-4, H-ETS-4, Pb-ETS-4, Na-K-GTS-1, H-GTS-1, and Pb-GTS-1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, L.T. and B.S.; methodology, L.T. and B.S.; investigation, L.T., R.R., Z.D. and B.B.; writing—original draft preparation, L.T., R.R. and B.S.; writing—review and editing, B.B. and Z.D.; visualisation, L.T. and R.R.; supervision B.S.; project administration, L.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors are grateful for the financial support of the Bulgarian National Science Fund (project contract KП-06-M34/1).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the technical support of project PERIMED BG05M2OP001-1.002-0005/29.03.2018 (2018–2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yuna, Z. Review of the natural, modified, and synthetic zeolites for heavy metals removal from wastewater. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2016, 33, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashin, V.B.; Eldridge, D.S.; Yu, A.; Zhao, D. Surface functionalization and manipulation of mesoporous silica adsorbents for improved removal of pollutants: A review. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prelot, B.; Einhorn, V.; Marchandeau, F.; Douillard, J.-M.; Zajac, J. Bulk hydrolysis and solid–liquid sorption of heavy metals in multi-component aqueous suspensions containing porous inorganic solids: Are these mechanisms competitive or cooperative? J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 386, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Chen, Y.; Khan, M.A.; Xu, H.; Wang, F.; Xia, M. In-depth study of heavy metal removal by an etidronic acid-functionalized layered double hydroxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 7450–7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Khan, M.A.; Kameda, T.; Xu, H.; Wang, F.; Xia, M.; Yoshioka, T. New insights into the capture performance and mechanism of hazardous metals Cr3+ and Cd2+ onto an effective layered double hydroxide based material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Gupta, S.S. Adsorption of a few heavy metals on natural and modified kaolinite and montmorillonite: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 140, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, R.; Tahir, S. Removal of Pb (II) from aqueous/acidic solutions by using bentonite as an adsorbent. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3982–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpomie, G.; Ogbu, I.; Osunkunle, A.; Abuh, M.; Abonyi, M. Equilibrium isotherm studies on the sorption of Pb (II) from solution by Ehandiagu clay. J. Emerg. Trends Eng. Appl. Sci. 2012, 3, 354–358. [Google Scholar]
- Egbosiuba, T.C.; Egwunyenga, M.C.; Tijani, J.O.; Mustapha, S.; Abdulkareem, A.S.; Kovo, A.S.; Krikstolaityte, V.; Veksha, A.; Wagner, M.; Lisak, G. Activated multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated with zero valent nickel nanoparticles for arsenic, cadmium and lead adsorption from wastewater in a batch and continuous flow modes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ding, X.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, X.-F.; Maganti, S.; Jiang, Q.; Huang, M.; Guo, Z.; Cao, D. Heavy Metal Removal from Wastewater by a Polypyrrole-derived N-doped Carbon Nanotube Decorated with Fish Scale-like Molybdenum Disulfide Nanosheets. Eng. Sci. 2022, 18, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesali-Naseh, M.; Naseh, M.R.V.; Ameri, P. Adsorption of Pb (II) ions from aqueous solutions using carbon nanotubes: A systematic review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.-C.; Zhang, H.-R.; Li, J.-B.; Ding, W.-Y. Biomass based activated carbon obtained from sludge and sugarcane bagasse for removing lead ion from wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherugar, P.; Padaki, M.; Naik, N.S.; George, S.D.; Murthy, D.H. Biomass-derived versatile activated carbon removes both heavy metals and dye molecules from wastewater with near-unity efficiency: Mechanism and kinetics. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, S.; Ali, F.A.A.; Haider, A.; Al-Masry, W.A.; Al-Zeghayer, Y. Novel route for amine grafting to chitosan electrospun nanofibers membrane for the removal of copper and lead ions from aqueous medium. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 199, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Ma, Q.; Lin, Q.; Chang, J.; Ma, H. A novel approach to extract SiO2 from fly ash and its considerable adsorption properties. Mater. Des. 2017, 116, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, Z.; Sun, G. Highly efficient removal of trace metal ions by using poly (acrylic acid) hydrogel adsorbent. Mater. Des. 2019, 181, 107934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCusker, L.B.; Baerlocher, C. Zeolite Structures. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 13–37. [Google Scholar]
- Haemmerle, M.M.; Fendrych, J.; Matiasek, E.; Tschegg, C. Adsorption and Release Characteristics of Purified and Non-Purified Clinoptilolite Tuffs towards Health-Relevant Heavy Metals. Crystals 2021, 11, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajitno, M.Y.; Taufiqurrakhman, M.; Harbottle, D.; Hunter, T.N. Kinetic Studies of Cs+ and Sr2+ Ion Exchange Using Clinoptilolite in Static Columns and an Agitated Tubular Reactor (ATR). ChemEngineering 2021, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warchoł, J.K.; Sobolewska, P.; Tylus, W.; Petrus, R. Fixed-Bed Modification of Zeolitic Tuffs and Their Application for Cr(VI) Removal. Materials 2021, 14, 7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviello, M.; Gattullo, C.E.; Faccia, M.; Paradiso, V.M.; Gambacorta, G. Application of natural and synthetic zeolites in the oenological field. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzia, C.; Zorpas, A.A. Zeolites in Food Processing Industries. In Handbook of Natural Zeolites; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2012; pp. 601–651. [Google Scholar]
- Nakhli, S.A.A.; Delkash, M.; Bakhshayesh, B.E.; Kazemian, H. Application of zeolites for sustainable agriculture: A review on water and nutrient retention. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milović, T.; Šupić, S.; Malešev, M.; Radonjanin, V. The Effects of Natural Zeolite as Fly Ash Alternative on Frost Resistance and Shrinkage of Blended Cement Mortars. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, N.-Q.; Peng, G.-F. Applications of natural zeolite to construction and building materials in China. Constr. Build. Mater. 2005, 19, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Yu, J. Applications of zeolites in sustainable chemistry. Chem 2017, 3, 928–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y. Characteristics and Mechanisms of Heavy Metal and MTBE Adsorption on Zeolites and Applications in Permeable Reactive Barriers. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- De Raffele, G.; Aloise, A.; De Luca, P.; Vuono, D.; Tagarelli, A.; Nagy, J. Kinetic and thermodynamic effects during the adsorption of heavy metals on ETS-4 and ETS-10 microporous materials. J. Porous Mater. 2016, 23, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznicki, S. Preparation of Small-Pored Crystalline Titanium Molecular Sieve Zeolites. U.S. Patent No. 4,938,939, 3 July 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Guan, J.-J.; Chen, W.; Ke, Q.-F.; Zhang, C.-Q.; Guo, Y.-P. Fabrication of hydroxyapatite/chitosan porous materials for Pb (II) removal from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 25462–25470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Shao, C.-T.; Chen, W.; Lei, Y.; Ke, Q.-F.; Guo, Y.-P. Mesoporous carbonated hydroxyapatite/chitosan porous materials for removal of Pb (ii) ions under flow conditions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 113940–113950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Shamim, S.; Jana, A.K.; Basu, J.K. Insights into the competitive adsorption of pollutants on a mesoporous alumina–silica nano-sorbent synthesized from coal fly ash and a waste aluminium foil. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 15514–15522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizidou, M.; Haralambous, K.; Loukatos, A.; Dimitrakopoulou, D. Natural zeolites and their ion exchange behavior towards chromium. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 1992, 27, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senila, M.; Cadar, O.; Senila, L.; Angyus, B.S. Simulated Bioavailability of Heavy Metals (Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn) in Contaminated Soil Amended with Natural Zeolite Using Diffusive Gradients in Thin-Films (DGT) Technique. Agriculture 2022, 12, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inchaurrondo, N.S.; Font, J. Clay, Zeolite and Oxide Minerals: Natural Catalytic Materials for the Ozonation of Organic Pollutants. Molecules 2022, 27, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, H. Verified Synthesis of Zeolitic Materials; Gulf Professional Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznicki, S.M.; Curran, J.S.; Yang, X. ETS-14 Crystalline Titanium Silicate Molecular Sieves, Manufacture and Use Thereof. U.S. Patent No. 5,882,624, 16 March 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Samburov, G.O.; Kalashnikova, G.O.; Panikorovskii, T.L.; Bocharov, V.N.; Kasikov, A.; Selivanova, E.; Bazai, A.V.; Bernadskaya, D.; Yakovenchuk, V.N.; Krivovichev, S.V. A Synthetic Analog of the Mineral Ivanyukite: Sorption Behavior to Lead Cations. Crystals 2022, 12, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D.M.; Roe, A.L. Synthesis, characterization and crystal chemistry of microporous titanium-silicate materials. Zeolites 1990, 10, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.R.; Lopes, C.B.; Lito, P.F.; Otero, M.; Lin, Z.; Rocha, J.; Pereira, E.; Silva, C.M.; Duarte, A. Cadmium(II) removal from aqueous solution using microporous titanosilicate ETS-4. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 147, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C.B.; Otero, M.; Lin, Z.; Silva, C.M.; Pereira, E.; Rocha, J.; Duarte, A.C. Effect of pH and temperature on Hg2+ water decontamination using ETS-4 titanosilicate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C.B.; Pereira, E.; Lin, Z.; Pato, P.; Otero, M.; Silva, C.M.; Rocha, J.; Duarte, A.C. Fixed-bed removal of Hg2+ from contaminated water by microporous titanosilicate ETS-4: Experimental and theoretical breakthrough curves. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 145, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.D.; Komarneni, S. Selective Cobalt (II) Exchange Properties of Na-2-Mica and Na-ETS-4. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2012, 30, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, S.; Bai, P.; Hu, H.; Jin, L. Adsorption separation performance of H2/CH4 on ETS-4 by concentration pulse chromatography. J. Energy Chem. 2014, 23, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Attar, L.; Dyer, A. Sorption of uranium onto titanosilicate materials. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2001, 247, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Attar, L.; Dyer, A.; Harjula, R. Uptake of radionuclides on microporous and layered ion exchange materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 2963–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maple, M.J.; Williams, C.D. Separating nitrogen/methane on zeolite-like molecular sieves. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 111, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosoughi, M.; Maghsoudi, H. Characterization of size-selective kinetic-based Ba-ETS-4 titanosilicate for nitrogen/methane separation: Chlorine-enhanced steric effects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 284, 120243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, P.; Li, L.; Tang, X.; Shang, H.; Li, J.; Chen, B. K-Chabazite Zeolite Nanocrystal Aggregates for Highly Efficient Methane Separation. Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202116850. [Google Scholar]
- Bhadra, S.; Farooq, S. Separation of methane–nitrogen mixture by pressure swing adsorption for natural gas upgrading. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 14030–14045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, R.; Farooq, S.; Srinivasan, M. Effects of site occupancy, cation relocation, and pore geometry on adsorption kinetics in ETS-4. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 3257–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznicki, S.M.; Bell, V.A.; Nair, S.; Hillhouse, H.W.; Jacubinas, R.M.; Braunbarth, C.M.; Toby, B.H.; Tsapatsis, M. A titanosilicate molecular sieve with adjustable pores for size-selective adsorption of molecules. Nature 2001, 412, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anson, A.; Lin, C.; Kuznicki, T.; Kuznicki, S. Separation of ethylene/ethane mixtures by adsorption on small-pored titanosilicate molecular sieves. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Sawada, J.A.; Wu, L.; Haastrup, T.; Kuznicki, S.M. Anion-controlled pore size of titanium silicate molecular sieves. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, J.A.; Rode, E.J.; Kuznicki, S.M.; Lin, C.C.I. Silicate Materials, Method for Their Manufacture, and Method for Using Such Silicate Materials for Adsorptive Fluid Separations. U.S. Patent No. 8,545,608, 1 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Clearfield, A. Structure and ion exchange properties of tunnel type titanium silicates. Solid State Sci. 2001, 3, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, E.A.; Sylvester, P.; Graziano, G.; Clearfield, A. Evaluation of a Sodium Nonatitanate, Sodium Titanosilicate, and Pharmacosiderite-Type Ion Exchangers for Strontium Removal from DOE Waste and Hanford N-Springs Groundwater Simulants. In Science and Technology for Disposal of Radioactive Tank Wastes; Schulz, W.W., Lombardo, N.J., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lihareva, N.; Kostov-Kytin, V. Sorption of Cs+ by nano-sized microporous titanium silicates with pharmacosiderite structure. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2014, 46, 569–575. [Google Scholar]
- Dyer, A.; Pillinger, M.; Amin, S. Ion exchange of caesium and strontium on a titanosilicate analogue of the mineral pharmacosiderite. J. Mater. Chem. 1999, 9, 2481–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langella, A.; Pansini, M.; Cappelletti, P.; De Gennaro, B.; De’Gennaro, M.; Colella, C. NH+4, Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ exchange for Na+ in a sedimentary clinoptilolite, North Sardinia, Italy. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2000, 37, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.; Loizidou, M.; Grigoropoulou, H. Equilibrium and kinetic ion exchange studies of Pb2+, Cr3+, Fe3+ and Cu2+ on natural clinoptilolite. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2784–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oter, O.; Akcay, H. Use of natural clinoptilolite to improve water quality: Sorption and selectivity studies of lead (II), copper (II), zinc (II), and nickel (II). Water Environ. Res. 2007, 79, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, Y.; Kocaoba, S. Adsorption of toxic metals by natural and modified clinoptilolite. Ann. Chim. J. Anal. Environ. Cult. Herit. Chem. 2007, 97, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bai, P.; Yan, Y.; Yan, W.; Shi, W.; Xu, R. Removal of Zn2+, Pb2+, Cd2+, and Cu2+ from aqueous solution by synthetic clinoptilolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 273, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tian, R.; Ding, W.; He, Y.; Li, H. Adsorption selectivity of heavy metals by Na-clinoptilolite in aqueous solutions. Adsorption 2019, 25, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostov-Kytin, V.; Ferdov, S.; Kalvachev, Y.; Mihailova, B.; Petrov, O. Hydrothermal synthesis of microporous titanosilicates. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 105, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdov, S.; Lengauer, C.; Petrov, O.; Kostov-Kytin, V. A rapid method for low-temperature synthesis of the Na analogue of the microporous titanosilicate GTS-1. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 4343–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toraya, H. A new method for quantitative phase analysis using X-ray powder diffraction: Direct derivation of weight fractions from observed integrated intensities and chemical compositions of individual phases. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2016, 49, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, T.; Sadki, M.; Bron, E.; König, U.; Nénert, G. The highscore suite. Powder Diffr. 2014, 29, S13–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hieu, D.T.; Kosslick, H.; Riaz, M.; Schulz, A.; Springer, A.; Frank, M.; Jaeger, C.; Thu, N.T.M.; Son, L.T. Acidity and Stability of Brønsted Acid Sites in Green Clinoptilolite Catalysts and Catalytic Performance in the Etherification of Glycerol. Catalysts 2022, 12, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeeli, N.; Faghihian, H. Synthesis and characterization of magnetized ETS-4 modified with lanthanum and iron for fluoride adsorption. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2020, 39, e13420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.; Jeong, H.-K.; Chandrasekaran, A.; Braunbarth, C.M.; Tsapatsis, M.; Kuznicki, S.M. Synthesis and structure determination of ETS-4 single crystals. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 4247–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, P.; Sprynskyy, M.; Terzyk, A.P.; Lebedynets, M.; Namieśnik, J.; Buszewski, B. Porous structure of natural and modified clinoptilolites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 297, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, E.A.; Clearfield, A. Titanium silicates, M3HTi4O4(SiO4)3·4H2O (M = Na+, K+),with three-dimensional tunnel structures for the selective removal of strontium and cesium from wastewater solutions. Microporous Mater. 1997, 11, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warzywoda, J.; Yilmaz, B.; Miraglia, P.Q.; Sacco, A., Jr. Characterization of titanosilicate ETS-4 crystals grown from synthesis mixtures of different alkalinity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 71, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, E.A.; Poojary, D.M.; Clearfield, A. Syntheses, Crystal Structures, and Ion-Exchange Properties of Porous Titanosilicates, HM3Ti4O4(SiO4)3·4H2O (M = H+, K+, Cs+), Structural Analogues of the Mineral Pharmacosiderite. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pan, Z.; Wang, Y. Enhanced adsorption of cationic Pb (II) and anionic Cr (VI) ions in aqueous solution by amino-modified nano-sized illite-smectite clay. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 11126–11139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouki, S.K.; Kavannagh, M. Performance of natural zeolites for the treatment of mixed metal-contaminated effluents. Waste Manag. Res. 1997, 15, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.A.; Al-Odayni, A.-B.; Saeed, W.S.; Al-Kahtani, A.; Alharthi, F.A.; Aouak, T. Efficient adsorption of lead (II) from aqueous phase solutions using polypyrrole-based activated carbon. Materials 2019, 12, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, R.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, C. Adsorption of Pb (II) on activated carbon prepared from Polygonum orientale Linn.: Kinetics, isotherms, pH, and ionic strength studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5808–5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y. Adsorption of Pb (II) and Cr (VI) from Aqueous Solution by Synthetic Allophane Suspension: Isotherm, Kinetics, and Mechanisms. Toxics 2022, 10, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiew, C.S.C.; Yeoh, H.K.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Krishnaiah, K.; Poh, P.E.; Tey, B.T.; Chan, E.S. Halloysite/alginate nanocomposite beads: Kinetics, equilibrium and mechanism for lead adsorption. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Singh, A.; Sharma, A. Studies on the uptake of lead and zinc by lignin obtained from black liquor–a paper industry waste material. Environ. Technol. 1994, 15, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, K.; Haider, S.; Oh, T.-J.; Park, S.-Y. Preparation of amidoxime-modified polyacrylonitrile (PAN-oxime) nanofibers and their applications to metal ions adsorption. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 322, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, L.; Zhou, L.; Chen, P. Magnetic thiolated/quaternized-chitosan composites design and application for various heavy metal ions removal, including cation and anion. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 136, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyairo, W.N.; Eker, Y.R.; Kowenje, C.; Akin, I.; Bingol, H.; Tor, A.; Ongeri, D.M. Efficient adsorption of lead (II) and copper (II) from aqueous phase using oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes/polypyrrole composite. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1498–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, M.S.; Azar, P.A.; Namin, P.E.; Dehaghi, S.M. Removal of lead ions from wastewater using functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes with tris (2-aminoethyl) amine. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 4, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamshidian, M.; Sadeghalvad, B.; Ghasemi, I.; Ebrahimi, H.; Rezaeian, I. Fabrication of polyethersulfone/functionalized MWCNTs nanocomposite and investigation its efficiency as an adsorbent of Pb (II) ions. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 6259–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, S.; Kouvelos, E.; Katsaros, F. Calcium alginate beads from Laminaria digitata for the removal of Cu+2 and Cd+2 from dilute aqueous metal solutions. Desalination 2008, 224, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdes, D.; Duran, C.; Senturk, H.B. Adsorptive removal of Cd (II) and Pb (II) ions from aqueous solutions by using Turkish illitic clay. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 3082–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, V.K.; Matsuda, M.; Miyake, M. Sorption properties of the activated carbon-zeolite composite prepared from coal fly ash for Ni2+, Cu2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bektaş, N.; Kara, S. Removal of lead from aqueous solutions by natural clinoptilolite: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 39, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćurković, L.; Cerjan-Stefanović, Š.; Filipan, T. Metal ion exchange by natural and modified zeolites. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).