Microbial Networks Reveal the Structure of Water Microbial Communities in Kalamaili Mountain Ungulate Nature Reserve
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Management
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.2.1. Sampling
2.2.2. 16S rDNA Sequencing and Water Microbiota Analysis
2.2.3. Construction and Visualization of Co-Occurrence Ecology Networks
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Microbial Diversity
3.2. Differential Analysis
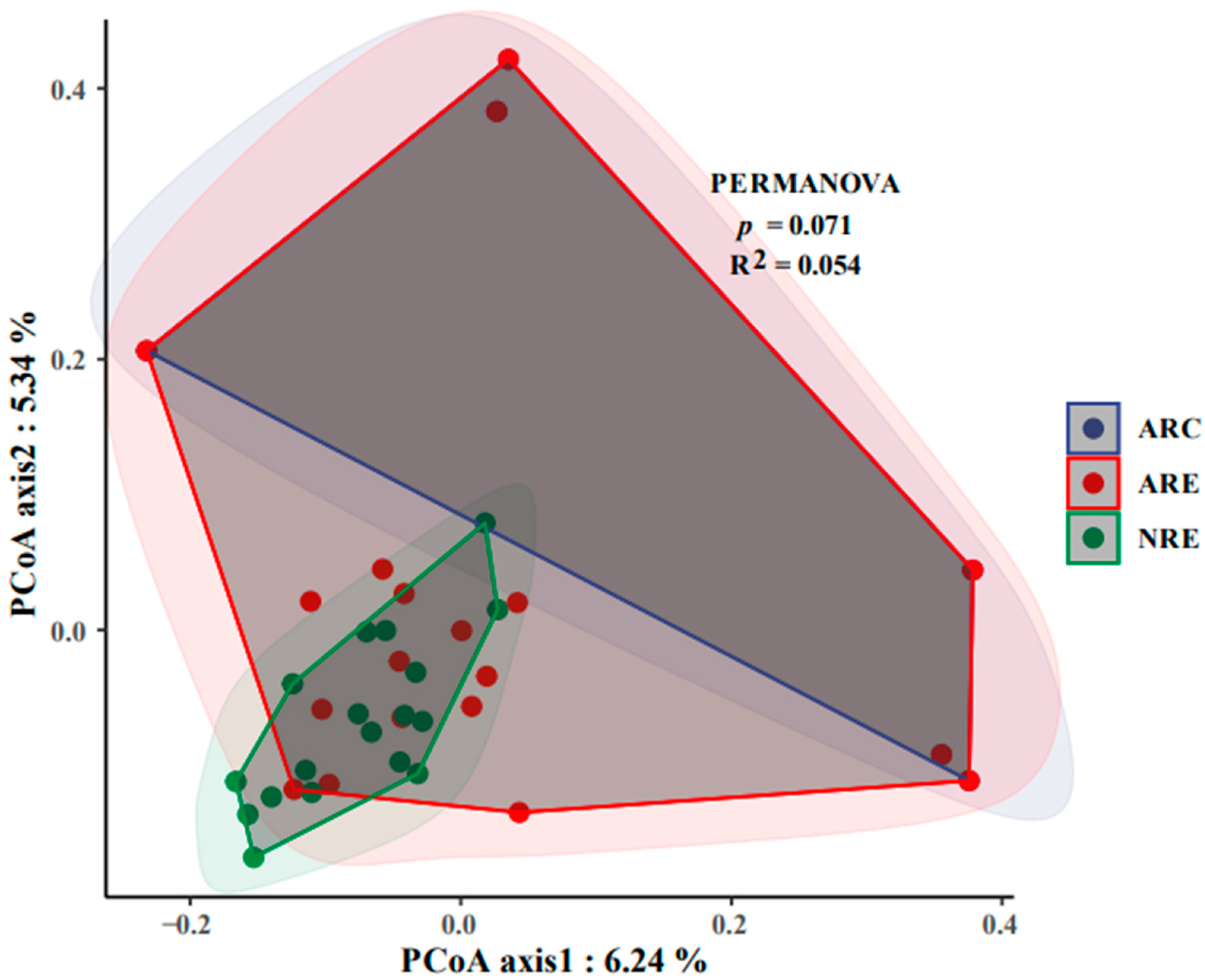
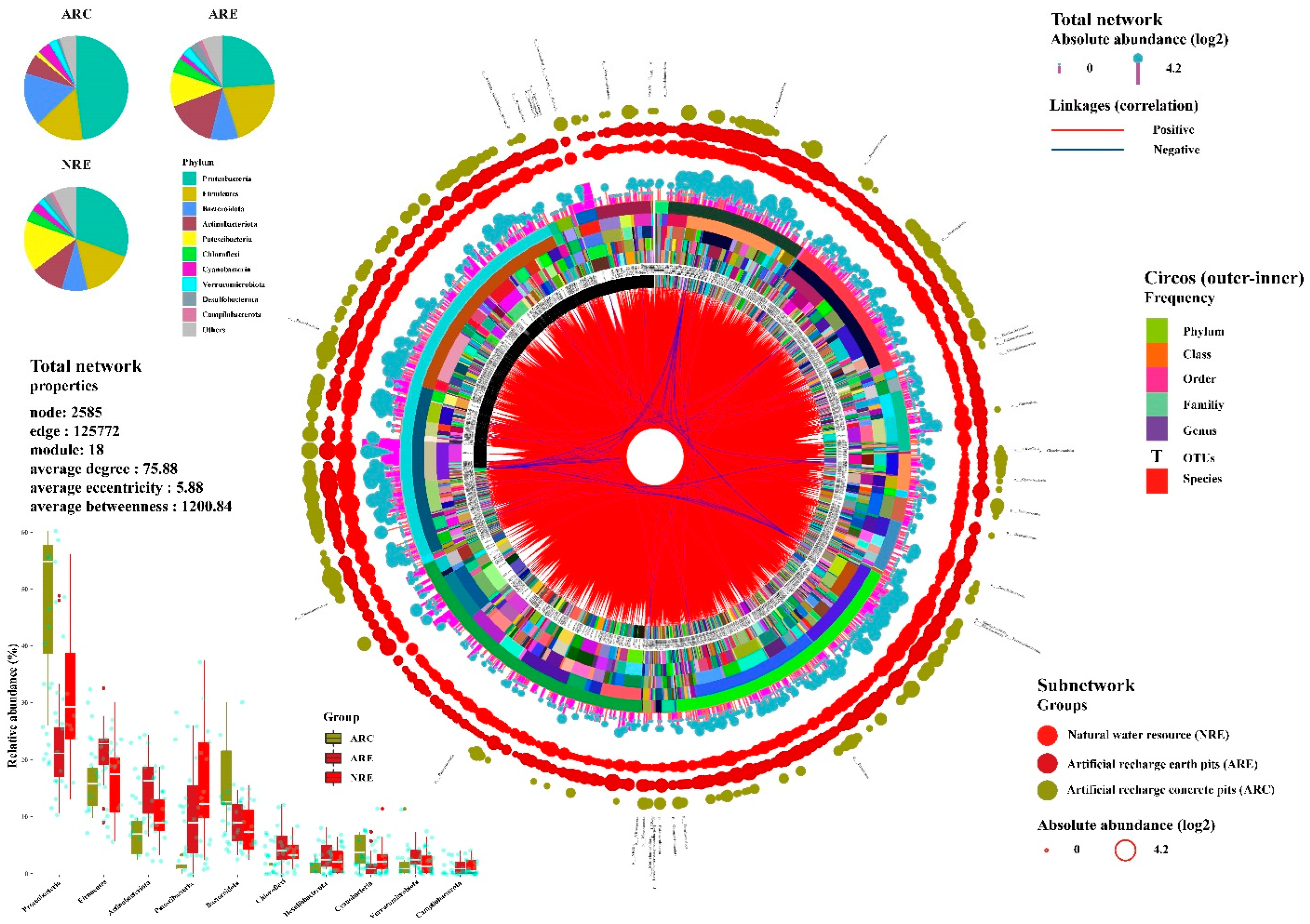
3.3. Water Microbial Co-Occurrence Network
3.4. Topological Roles
4. Discussion
4.1. Microbial Community Structure Characteristics of Water
4.2. Microbial Co-Occurrence Network Composition of Water
4.3. Microbial Co-Occurrence Network Topological Roles of Water
4.4. Microbial Co-Occurrence Network Modular Structures of Water
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramakrishna, B.S. Role of the gut microbiota in human nutrition and metabolism. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, J.M.; Pimm, S.L.; Solé, R.V. Ecological networks and their fragility. Nature 2006, 442, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junier, P.; Molina, V.; Dorador, C.; Hadas, O.; Kim, O.-S.; Junier, T.; Witzel, J.-P.; Imhoff, J.F. Phylogenetic and functional marker genes to study ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms (AOM) in the environment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, D.H.P.; Kumar, A.; Cao, B. Microorganisms meet solid minerals: Interactions and biotechnological applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6935–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Han, C. Interaction between intestinal microorganisms and carbohydrates of mammals and its influence. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 3959–3968. [Google Scholar]
- Isobe, K.; Koba, K.; Otsuka, S.; Senoo, K. Nitrification and nitrifying microbial communities in forest soils. J. For. Res. 2011, 16, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppert, B.; Martynov, A.G.; Elpidina, E.N. Bacillus thuringiensis Cry3Aa protoxin intoxication of Tenebrio molitor induces widespread changes in the expression of serine peptidase transcripts. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2012, 7, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, R.G.D.; Shen, M.A. Influence of probiotics on the growth and digestive enzyme activity of white Pacific shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). J. Ocean. Univ. Chin. 2008, 7, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Guo, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, H.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y. Advances in interaction between medicinal plants and rhizosphere microorganisms. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2020, 45, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar]
- Tremaroli, V.; Bäckhed, F. Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 2012, 489, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Hui, W.; Deng, X.; Wang, A.; Hu, Y.; Liu, B.; Chen, K.; Liu, F.; Tian, H.; Gu, X.; et al. Dietary Haematococcus pluvialis promotes growth of red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) via positive regulation of the gut microbial co-occurrence network. Aquaculture 2022, 551, 737900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Luo, F.; Zhou, J. Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinf. 2012, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Lange, J.; Marinos, G.; Bathia, J.; Harris, D.; Soluch, R.; Vaibhvi, V.; Deines, P.; Hassani, M.A.; Wagner, K.-S.; et al. Advancing our functional understanding of host-microbiota interactions: A need for new types of studies. Bioessays 2020, 42, e1900211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coyte, K.Z.; Schluter, J.; Foster, K.R. The ecology of the microbiome: Networks, competition, and stability. Science 2015, 350, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Watanabe, K.; Kimura, I. Gut microbiota dysbiosis drives and implies novel therapeutic strategies for diabetes mellitus and related metabolic diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, W.T.; Pape, T.; Pei, W.Y.; Zhang, D. Flesh flies (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) of Kalamaili Mountain Ungulate Nature Reserve (China: Xinjiang): Checklist and description of four new species. Zootaxa 2021, 5063, 1–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeely, J.A. Today’s protected areas: Supporting a more sustainable future for humanity. Integr. Zool. 2020, 15, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, S.J.; Bergman, J.N.; Nyboer, E.A.; Reid, A.J.; Gallagher, A.J.; Hammerschlag, N.; Van de Riet, K.; Vermaire, J.C. Overcoming the concrete conquest of aquatic ecosystems. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 247, 108589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; Cong, W.; Jiang, Z.; Liang, Z. Comparative Analysis of the Ecological Succession of Microbial Communities on Two Artificial Reef Materials. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Bing, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, K.; Pan, X.; Yan, X.; Li, B.; Xie, S.; Guo, Q. Influence of plantation on microbial community in porous concrete treating polluted surface water. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 117, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysschaert, B.; Favere, J.; Vermijs, L.; Baetens, V.; Naka, A.; Boon, N.; Gusseme, B.D. Flow cytometric fingerprinting to assess the microbial community response to changing water quality and additives. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, E.M.; Davis, J.; Duncan, R.P. Identifying error and accurately interpreting environmental DNA metabarcoding results: A case study to detect vertebrates at arid zone waterholes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 1259–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, M.; Li, H.; Gu, X.; Tian, H.; Liu, F.; Yang, W.; Ren, S.; Chu, W.; Hu, Y.; Wang, A.; et al. Re-aliment regains feed deprivation-induced microflora dysbiosis and immune stress in the gut of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Aquacult. Rep. 2022, 22, 100992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Chen, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xie, S. Phylogenetic diversity of microbial communities in real drinking water distribution systems. Biotechnol. Bioprocess. Eng. 2013, 1, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Chakhtoura, J.; Saikaly, P.E.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Impact of distribution and network flushing on the drinking water microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glasl, B.; Smith, C.E.; Bourne, D.G.; Webster, N.S. Exploring the diversity-stability paradigm using sponge microbial communities. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Luqueño, F.; Valenzuela-Encinas, C.; Marsch, R.; Martínez-Suárez, C.; Vázquez-Núñez, E.; Dendooven, L. Microbial communities to mitigate contamination of PAHs in soil—Possibilities and challenges: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 12–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Wang, Y.; Ye, S.; Liu, S.; Stirling, E.; Gilbert, J.A.; Faust, K.; Knight, R.; Jansson, J.K.; Cardona, C.; et al. Earth microbial co-occurrence network reveals interconnection pattern across microbiomes. Microbiome 2020, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Mudassir, S.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Chang, Y.; Che, Q.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, G.; Li, D. Secondary metabolites from deep-sea derived microorganisms. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 6244–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.L.; Heaver, S.L.; Walters, W.A.; Ley, R.E. Microbiome and metabolic disease: Revisiting the bacterial phylum bacteroidetes. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Luo, F.; He, Z.; Yang, Y. Phylogenetic molecular ecological network of soil microbial communities in response to elevated CO2. mBio 2011, 2, e00122-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, C.; Zhang, H. Mutualism between antagonists: Its ecological and evolutionary implications. Integr. Zool. 2021, 16, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Tang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, W.; Wang, B.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, X.; Hu, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, D. Metagenomics reveals contrasting energy utilization efficiencies of captive and wild camels (Camelus ferus). Integr. Zool. 2022, 17, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tourinho, L.; Vale, M.M. Choosing among correlative, mechanistic, and hybrid models of species’ niche and distribution. Integr. Zool. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mee, M.T.; Collins, J.J.; Church, G.M.; Wang, H.H. Syntrophic exchange in synthetic microbial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E2149–E2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pande, S.; Kaftan, F.; Lang, S.; Svatoš, A.; Germerodt, S.; Kost, C. Privatization of cooperative benefits stabilizes mutualistic cross-feeding interactions in spatially structured environments. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.M.; Bascompte, J.; Dupont, Y.L.; Jordano, P. The modularity of pollination networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19891–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramos-Jiliberto, R.; Valdovinos, F.S.; Moisset de Espanés, P.; Flores, J.D. Topological plasticity increases robustness of mutualistic networks. J. Anim. Ecol. 2012, 81, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McWilliams, C.; Lurgi, M.; Montoya, J.M.; Sauve, A.; Montoya, D. The stability of multitrophic communities under habitat loss. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, K.K.; Wang, D.; Rozowsky, J.; Zheng, H.; Cheng, C.; Gerstein, M. OrthoClust: An orthology-based network framework for clustering data across multiple species. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



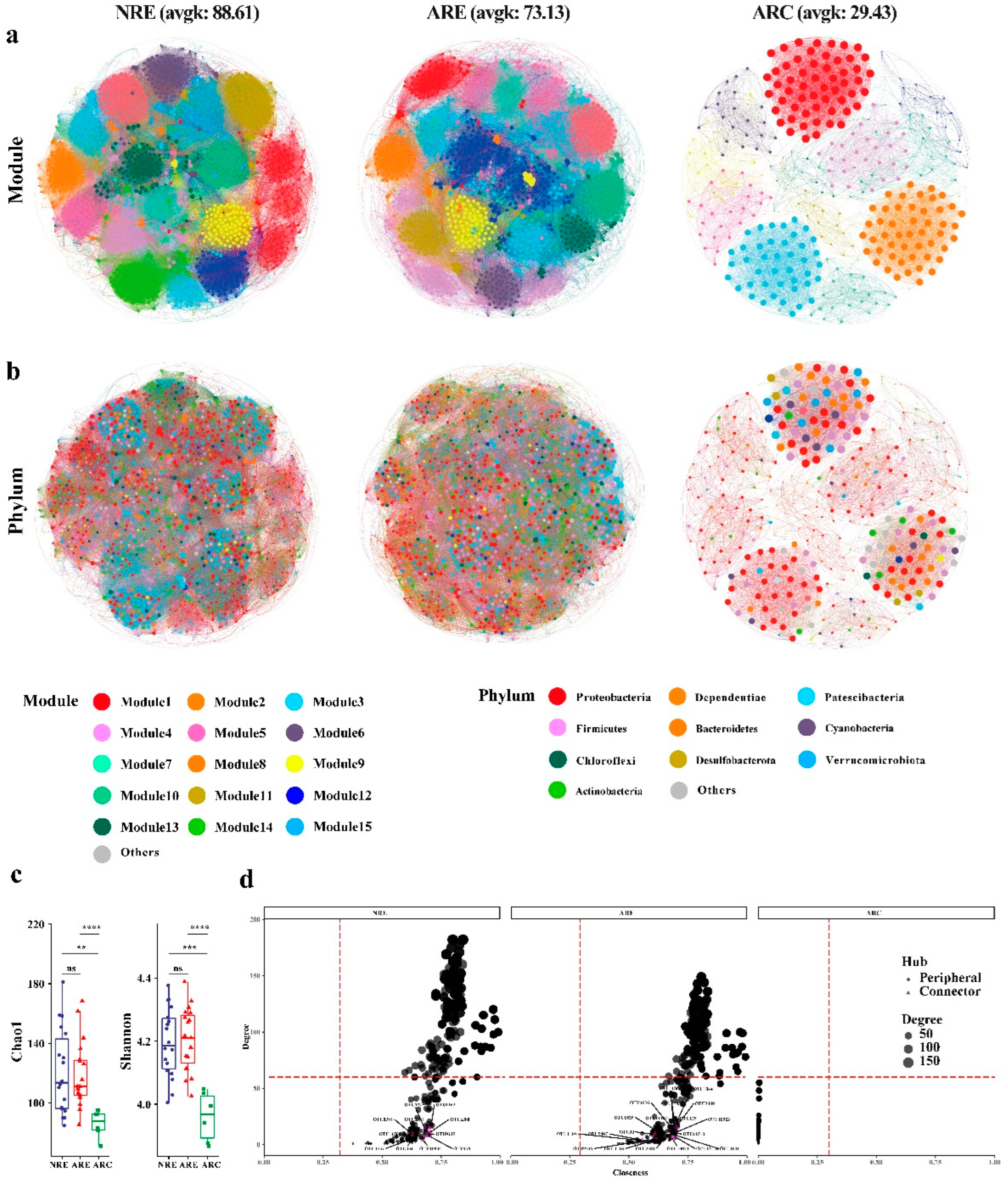
| Item | Empirical Network | Random Network | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network Size (Node) | Network Size (Edge) | Average Degree (avgK) | Average Clustering Coefficient (avgCC) | Average Path Distance (GD) | Modularity (No. of Modules) | Average Clustering Coefficient (avgCC) | Average Path Distance (GD) | Modularity | |
| NRE | 1532 | 67874 | 88.61 | 0.798 | 3.033 | 0.751 (15) | 0.0579 ± 0.0002 | 1.9477 ± 0.0001 | 0.0489 ± 0.0013 |
| ARE | 1453 | 53127 | 73.13 | 0.734 | 3.144 | 0.720 (13) | 0.0504 ± 0.0002 | 1.9735 ± 0.0002 | 0.0574 ± 0.0014 |
| ARC | 353 | 5195 | 29.43 | 0.969 | 1.024 | 0.720 (18) | 0.0837 ± 0.0012 | 1.9943 ± 0.0014 | 0.1233 ± 0.0047 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, Y.; Tang, L.; Jia, H.; Shao, C.; Tang, J.; Xu, Y.; Yan, L.; Zhang, D. Microbial Networks Reveal the Structure of Water Microbial Communities in Kalamaili Mountain Ungulate Nature Reserve. Water 2022, 14, 2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142188
Xiong Y, Tang L, Jia H, Shao C, Tang J, Xu Y, Yan L, Zhang D. Microbial Networks Reveal the Structure of Water Microbial Communities in Kalamaili Mountain Ungulate Nature Reserve. Water. 2022; 14(14):2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142188
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Yu, Liping Tang, Huiping Jia, Changliang Shao, Junyu Tang, Yanping Xu, Liping Yan, and Dong Zhang. 2022. "Microbial Networks Reveal the Structure of Water Microbial Communities in Kalamaili Mountain Ungulate Nature Reserve" Water 14, no. 14: 2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142188
APA StyleXiong, Y., Tang, L., Jia, H., Shao, C., Tang, J., Xu, Y., Yan, L., & Zhang, D. (2022). Microbial Networks Reveal the Structure of Water Microbial Communities in Kalamaili Mountain Ungulate Nature Reserve. Water, 14(14), 2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142188





