Treatment of Wastewater Effluent with Heavy Metal Pollution Using a Nano Ecological Recycled Concrete
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Procedure of Producing the Nano Ecological Recycled Concrete
2.2. Characterization of the Nano Powder and the Recycled Concrete Aggregates
2.3. Procedure of Wastewater Effluent Treatment by the Nano-ERC
2.4. Relative Weighted Average Removal Percentage of Heavy Metals
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
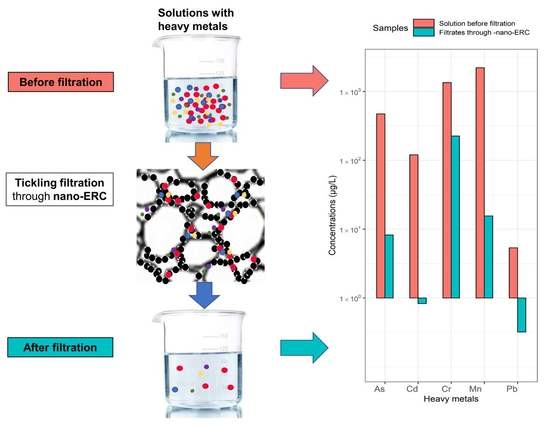
3.1. Heavy Metal Concentrations before and after Filtration by ERCs
3.2. Mechanisms of Heavy Metal Removal by Nano-ERC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Solecki, W.; Friedman, E. At the water’s edge: Coastal settlement, transformative adaptation, and well-being in an era of dynamic climate risk. Ann. Rev. Publ. Health 2021, 42, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Ren, B.; Luo, J.; Yuan, J.; Ding, X.; Bian, H.; Yao, X. Trends and health risks of dissolved heavy metal pollution in global river and lake water from 1970 to 2017. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Drinking Water. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/drinking-water (accessed on 21 March 2022).
- Zhang, J.; Guan, K.; Peng, B.; Pan, M.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, C.; Kimm, H.; Franz, T.E.; Grant, R.F.; Yang, Y.; et al. Sustainable irrigation based on co-regulation of soil water supply and atmospheric evaporative demand. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Kaur, P.; Sy, N.D.; Gan, J. Contaminants of emerging concerns in recycled water: Fate and risks in agroecosystems. Sci Total Environ 2022, 814, 152527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huhmann, L.B.; Harvey, C.F.; Gross, J.; Uddin, A.; Choudhury, I.; Ahmed, K.M.; Duxbury, J.M.; Bostick, B.; van Geen, A. Evaluation of a field kit for testing arsenic in paddy soil contaminated by irrigation water. Geoderma 2021, 382, 114755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Yang, Y.; Xia, J. Hydrological cycle and water resources in a changing world: A review. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, J.; Zheng, X. Wastewater: China’s next water source. Science 2021, 374, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burakov, A.E.; Galunin, E.V.; Burakova, I.V.; Kucherova, A.E.; Agarwal, S.; Tkachev, A.G.; Gupta, V.K. Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Guest, J.S.; Peters, C.A.; Zhu, X.; Rau, G.H.; Ren, Z.J. Wastewater treatment for carbon capture and utilization. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Valero, L.; Moral-Parajes, E.; Román-Sánchez, I.M. Wastewater treatment costs: A research overview through bibliometric analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.L.; Valenzuela-Heredia, D.; Pedrouso, A.; del Rio, A.V.; Belmonte, M.; Mosquera-Corral, A. Greenhouse gases emissions from wastewater treatment plants: Minimization, treatment, and prevention. J. Chem. 2016, 2016, 3796352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, R.; Ban, S.; Devkota, S.; Sharma, S.; Joshi, R.; Tiwari, A.P.; Kim, H.Y.; Joshi, M.K. Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S. A review on sources, identification and treatment strategies for the removal of toxic Arsenic from water system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Ding, J.; Han, X.; Deng, Y.; Lv, X.; Xie, Y.; Chen, B.; Hu, W.; et al. Battery Technologies for Grid-Level Large-Scale Electrical Energy Storage. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 2020, 26, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerur, S.; Bandekar, S.; Hanagadakar, M.S.; Nandi, S.S.; Ratnamala, G.; Hegde, P.G. Removal of hexavalent Chromium-Industry treated water and Wastewater: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yan, L.; Fu, Q.; Kasal, B. A Comprehensive Review on Recycled Aggregate and Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 171, 105565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yuan, H. Investigation of construction waste recycling decisions by considering consumers’ quality perceptions. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijeyawardana, P.; Nanayakkara, N.; Gunasekara, C.; Karunarathna, A.; Law, D.; Pramanik, B.K. Improvement of heavy metal removal from urban runoff using modified pervious concrete. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Jin, Y.; Gong, Y.; Li, A.; Li, J.; Li, F. Recycled aggregates from construction and demolition waste as wetland substrates for pollutant removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Cui, L.; An, Y.; Chen, B.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, R.; Cui, S.; Wang, S.; Kou, Y. Investigating the pollutant-removal performance and DOM characteristics of rainfall surface runoff during different ecological concrete revetments treatment. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.; Shi, Y. Effect of ecological concrete applied to water pollution control of urban river. Desalination Water Treat 2018, 121, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ji, J.; Guo, Y.; Chen, J. Use of ecological concrete for nutrient removal in coastal sediment and its effects on sediment microbial communities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 162, 111911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erfan, A.M.; Hassan, H.E.; Hatab, K.M.; El-Sayed, T.A. The flexural behavior of nano concrete and high strength concrete using GFRP. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 247, 118664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.K.; Hou, W.M.; Hwang, C.L. A study on the microstructure of the nano concrete cornposite materials. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Mechanical Properties of Nanostructured Materials and Nanocomposites, Boston, MA, USA, 1–5 December 2003; pp. 231–247. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, S.; Yu, X.; Han, B.; Ou, J. Reactive powder concrete reinforced with nano SiO2-coated TiO2. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 148, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, M.A.; Cheah, C.B.; Ramli, M.; Ahmed, N.M.; Al-Shwaiter, A. Effect of nano zinc oxide and silica on mechanical, fluid transport and radiation attenuation properties of steel furnace slag heavyweight concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 274, 121785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Yang, W.; Ge, Y.; Du, Y.; Liu, P. Effects of nano-SiO2 and nano-Al2O3 on mechanical and durability properties of cement-based materials: A comparative study. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 34, 101936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, C.; Chen, Y. The effect of nano-SiO2 on concrete properties: A review. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2019, 8, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhilash, P.P.; Nayak, D.K.; Sangoju, B.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, V. Effect of nano-silica in concrete; A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 278, 122347. [Google Scholar]
- Murad, Y. Compressive strength prediction for concrete modified with nanomaterials. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Bai, E.L.; Xu, J.Y.; Du, Y.H.; Zhu, J.S. Effect of nano-SiO2 and nano-CaCO3 on the static and dynamic properties of concrete. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.A.; Yeshwanth, M.; Kumar, B.K.; Panwar, J.; Gupta, S. Functionalized Cu-based metal oxide nanoparticles with enhanced Cd+2 adsorption capacity and their ecotoxicity assessment by molecular docking. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 307, 114523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.E.; Al-Qahtani, K.M.; Alflaij, S.O.; Al-Qahtani, S.F.; Alsamhan, F.A. Green copper oxide nanoparticles for lead, nickel, and cadmium removal from contaminated water. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wolfe, K.; Potter, P.M.; Cobb, G.P. Distribution and speciation of copper and arsenic in rice plants (Oryza sativa japonica ‘Koshihikari’) treated with copper oxide nanoparticles and arsenic during a life cycle. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4988–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Tang, W.; Peijnenburg, W.J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, M.; Xiao, H.; He, Y.; Luo, L.; Yang, G.; et al. Aggregation, solubility and cadmium-adsorption capacity of CuO nanoparticles in aquatic environments: Effects of pH, natural organic matter and component addition sequence. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 310, 114770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Yan, P.; Zhao, X. A Novel Mix Design Method for Mixed Recycled Coarse Aggregate Concrete. J. Mater. Civil. Eng. 2022, 34, 04022071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alighardashi, A.; Mehrani, M.J.; Ramezanianpour, A.M. Pervious concrete reactive barrier containing nano-silica for nitrate removal from contaminated water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 29481–29492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuaklong, P.; Sata, V.; Wongsa, A.; Srinavin, K.; Chindaprasirt, P. Recycled aggregate high calcium fly ash geopolymer concrete with inclusion of OPC and nano-SiO2. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 174, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ukhurebor, K.E.; Aigbe, U.O.; Onyancha, R.B.; Nwankwo, W.; Osibote, O.A.; Paumo, H.K.; Ama, O.M.; Adetunji, C.O.; Siloko, I.U. Effect of hexavalent chromium on the environment and removal techniques: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GracePavithra, K.; Jaikumar, V.; Kumar, P.S.; SundarRajan, P. A review on cleaner strategies for chromium industrial wastewater: Present research and future perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Guo, J. Removal of chromium from wastewater by membrane filtration, chemical precipitation, ion exchange, adsorption electrocoagulation, electrochemical reduction, electrodialysis, electrodeionization, photocatalysis and nanotechnology: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 2055–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasaki, S.A.; Bingxue, Z.; Guarecuco, R.; Thomas, T.; Minghui, Y. Geopolymer for use in heavy metals adsorption, and advanced oxidative processes: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, T.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, T.; Chen, W. Facet-Dependent Adsorption and fractionation of natural organic matter on crystalline metal oxide nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8622–8631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Mass of water (kg) | 146.2 |
| 2% liquid water reducer (kg) | 16.0 |
| Mass of cement (kg) | 314.2 |
| Mass of fly ash (kg) | 104.8 |
| Mass of recycled aggregates (kg) | 785.1 |
| Mass of natural aggregates (kg) | 785.1 |
| Scale of aggregate scale (mm) | 5–20 |
| Concrete Blocks | Weights (kg) | Porosity |
|---|---|---|
| Control ERC | 2.77 | 27% |
| Nano-ERC 1 | 1.98 | 26% |
| Nano-ERC 2 | 2.52 | 26% |
| Solution Samples | As (μg/L) | Cd (μg/L) | Cr (μg/L) | Mn (μg/L) | Pb (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solution before filtration | 472.31 ± 25.30 | 120.31 ± 1.44 | 1347.63 ± 49.32 | 2209.76 ± 106.25 | 5.34 ± 2.09 |
| Filtrates through control-ERC | 12.15 ± 1.58 * | 0.65 ± 0.01 * | 492.53 ± 23.66 * | 8.05 ± 0.12 * | 0.56 ± 0.02 * |
| Filtrates through nano-ERC1 | 16.01 ± 0.02 * | 1.53 ± 0.04 * | 365.07 ± 2.64 * | 29.19 ± 1.40 * | 0.36 ± 0.18 * |
| Filtrates through nano-ERC2 | 0.44 ± 0.01 ** | 0.13 ± 0.00 ** | 85.35 ± 2.86 ** | 1.93 ± 0.33 ** | 0.28 ± 0.14 ** |
| GB 5084-2021 | 50-100 a | 10 | 100 | none | 200 |
| GB 388-2002 (V class) | 100 | 10 | 100 | none | 100 |
| Sample | As | Cd | Cr | Mn | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control-ERC | 60.29 | 61.55 | 39.27 | 61.66 | 55.42 |
| Nano-ERC1 | 70.28 | 71.83 | 53.05 | 71.79 | 67.85 |
| Nano-ERC2 | 65.30 | 65.29 | 61.22 | 65.31 | 61.94 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Su, J.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, W.; Song, S. Treatment of Wastewater Effluent with Heavy Metal Pollution Using a Nano Ecological Recycled Concrete. Water 2022, 14, 2334. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152334
Liu J, Su J, Zhao Z, Feng W, Song S. Treatment of Wastewater Effluent with Heavy Metal Pollution Using a Nano Ecological Recycled Concrete. Water. 2022; 14(15):2334. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152334
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jing, Jiayi Su, Zhenyu Zhao, Weiying Feng, and Shuai Song. 2022. "Treatment of Wastewater Effluent with Heavy Metal Pollution Using a Nano Ecological Recycled Concrete" Water 14, no. 15: 2334. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152334
APA StyleLiu, J., Su, J., Zhao, Z., Feng, W., & Song, S. (2022). Treatment of Wastewater Effluent with Heavy Metal Pollution Using a Nano Ecological Recycled Concrete. Water, 14(15), 2334. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152334