Icings of the Kunlun Mountains on the Northern Margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Western China: Origins, Hydrology and Distribution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
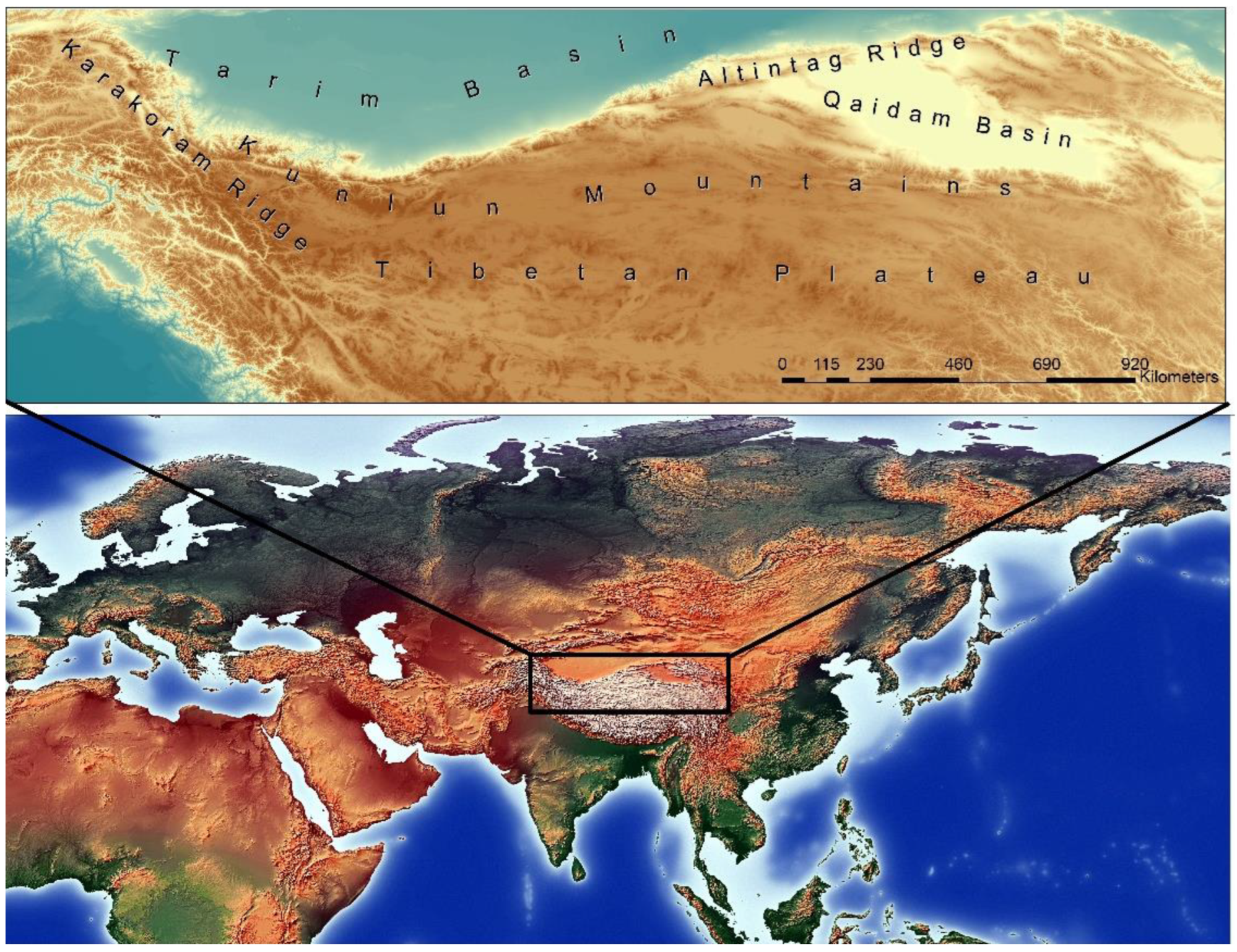
2. Study Area
2.1. Geology of the Kunlun Mountains
2.2. Climate of the Kunlun Mountains
2.3. Hydrogeology of the Kunlun Mountains
2.4. Geocryology of the Kunlun Mountains
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Regional Aufeis Analysis
3.2. Applied Classification for Icing Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Aufeis Spreadings and Geometry
4.2. Icing Relation to Permafrost and Hydrology
5. Discussion
5.1. Tectonic and Topography Factors of Aufeis Distribution
5.2. Source of Aufeis Recharging
5.3. Icing Process Response to Climate Change
5.4. River Valley Evolution under Icing Process
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Kane, D.L. Physical Mechanics of Aufeis Growth. J. Civ. Eng. 1981, 8, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.D.; Lauriol, B. Aufeis of the Firth River Basin, Northern Yukon, Canada: Insights into Permafrost Hydrogeology and Karst. Source Arct. Alp. Res. 1997, 29, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.K.; Kane, D.L.; Carey, S.K.; Yang, D. Progress in Permafrost Hydrology in the New Millennium. Permafr. Periglac. Processes 2008, 19, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensom, T.; Makarieva, O.; Morse, P.; Kane, D.; Alekseev, V.; Marsh, P. The Distribution and Dynamics of Aufeis in Permafrost Regions. Permafr. Periglac. Processes 2020, 31, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khmiznikov, P.K. Hydrology of the Yana River Basin; Publ. of Academy of Science USSR and Hydrographic Department of GUSMP under Sovnarkom of USSR: Leningrad, Russia, 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Kalabin, A. Perennial Permafrost and Hydrogeology of the North-East of USSR; Publ. of the All-Union Research Institute of Gold and Rare Metals: Magadan, Russia, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Shvetsov, P.F. Cryogenic Geochemical Fields at Perennial Cryolitozone. Lett. Acad. Sci. USSR. Geol. 1961, 1, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Tolstikhin, O.N. Icings and Ground Waters of North-East of USSR; Science: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Romanovskii, N.N. Groundwater of Cryolitozone; MSU: Moscow, Russia, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Alekseev, V.R. Icings; Science: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Kane, D.L.; Slaughter, C.W. Seasonal Regime and Hydrological Significance of Stream Icings in Central Alaska. In The Role of Snow and Ice in Hydrology, Proc. of Banff Symposia; IAHS Publ.: Gentbrugge, Belgium, 1972; Volume 2, pp. 528–540. [Google Scholar]
- Reedyk, S.; Woo, M.-K.; Prowse, T.D. Contribution of Icing Ablation to Streamflow in a Discontinuous Permafrost Area. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1995, 32, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, B.L. Icings and River Runoff; Hydrology and Meteorology Publishing: Leningrad, Russia, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, I.D.; Lauriol, B.; Harwood, L.; Marschner, M. Groundwater Contributions to Discharge in a Permafrost Setting, Big Fish River, NWT, Canada. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2001, 33, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilnikovskaya, Z.G. Cadastre to the Map of the Naleds of the North-East of the USSR; Central complex thematic expedition of the North-Eastern Geological Survey: Magadan, Russia, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Alekseev, V.R. Landscape Indication of Icing Processes; Science: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Makarieva, O.; Shikhov, A.; Nesterova, N.; Ostashov, A. Historical and Recent Aufeis in the Indigirka River Basin (Russia). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morse, P.D.; Wolfe, S.A. Long-Term River Icing Dynamics in Discontinuous Permafrost, Subarctic Canadian Shield. Permafr. Periglac. Processes 2017, 28, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, P.D.; Wolfe, S.A. Geological and Meteorological Controls on Icing (Aufeis) Dynamics (1985 to 2014) in Subarctic Canada. J. Geophys. Res. F Earth Surf. 2015, 120, 1670–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kane, D.L.; Yoshikawa, K.; McNamara, J.P. Regional Groundwater Flow in an Area Mapped as Continuous Permafrost, NE Alaska (USA). Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yu, W.; Yi, X.; Han, F.; Chen, L. Designing and Numerical Simulations of Aufeis Mitigation Structure on Cut-Slope Roadway. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2017, 141, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brombierstäudl, D.; Schmidt, S.; Nüsser, M. Distribution and Relevance of Aufeis (Icing) in the Upper Indus Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serquet, G.; Marty, C.; Dulex, J.P.; Rebetez, M. Seasonal Trends and Temperature Dependence of the Snowfall/Precipitation-Day Ratio in Switzerland. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, N.; Bradley, R.S.; Diaz, H.F.; Baraer, M.; Caceres, E.B.; Forsythe, N.; Fowler, H.; Greenwood, G.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Liu, X.D.; et al. Elevation-Dependent Warming in Mountain Regions of the World. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 424–430. [Google Scholar]
- Hatchett, B.J.; Rhoades, A.M.; Mcevoy, D.J. Monitoring the Daily Evolution and Extent of Snow Drought. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 869–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Siebert, S.; Huning, L.S.; AghaKouchak, A.; Mankin, J.S.; Hong, C.; Tong, D.; Davis, S.J.; Mueller, N.D. Agricultural Risks from Changing Snowmelt. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, S. Mountain Geoecology and Sustainable Development of the Tibetan Plateau; Zheng, D., Zhang, Q., Wu, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; ISBN 978-94-010-3800-3. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Niu, Y.; Nowell, G.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhu, D.C.; Mo, X.; Ding, S. Geochemical Constraints on the Petrogenesis of Granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northern Tibetan Plateau: Implications for Continental Crust Growth through Syn-Collisional Felsic Magmatism. Chem. Geol. 2014, 370, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, B. A Preliminary Study of the Uplift and Environment Evolution of the Karakorum and West Kunlun Mountains Area since Late Cenozoic Era. J. Nat. Resour. 1989, 4, 234–240. [Google Scholar]
- Database, S. 90m D.D.E. SRTM 90m DEM Digital Elevation Database. Available online: https://srtm.csi.cgiar.org/srtmdata (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Yang, J.S.; Robinson, P.T.; Jiang, C.F.; Xu, Z.Q. Ophiolites of the Kunlun Mountains, China and Their Tectonic Implications. Tectonophysics 1996, 258, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Awata, Y. Displacement and Timing of Left-Lateral Faulting in the Kunlun Fault Zone, Northern Tibet, Inferred from Geologic and Geomorphic Features. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2007, 29, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Proterozoic to Triassic Aulacogens and Rift-Geosynclines in China. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Deep Internal Processes and Continental Rifting, Chengdu, China, 9–13 September 1985; Acad. Publishers: Beijing, China, 1985; pp. 174–175. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Nelson, F.E.; Shiklomanov, N.I.; Guo, D.; Wan, G. Permafrost Degradation and Its Environmental Effects on the Tibetan Plateau: A Review of Recent Research. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010, 103, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Kunlun Mountains Region. In Mountain Geoecology and Sustainable Development of the Tibetan Plateau; Springer Science and Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 349–372. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, S.; Huai, B.; An, W.; Pang, H.; Liu, Y. Glacier Anomaly over the Western Kunlun Mountains, Northwestern Tibetan Plateau, since the 1970s. J. Glaciol. 2018, 64, 624–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiao, K. Modern Glaciers on the South Slope of West Kunlun Mountains (In Aksayqin Lake and Guozha Co Lake Drainage Areas). Bull. Glacier Resour. 1987, 5, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; An, R.; Yang, H.; Jiao, K. Conditions of Glacier Development and Some Glacial Features in the West Kunlun Mountains. Bull. Glacier Resour. 1989, 7, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Jin, H. Groundwater in the Permafrost Regions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and It Changes. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2013, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.L.; Bian, C.Y.; Wang, J. Features of Hydrogeology in Permafrost Regions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Qinghai Geol. 1994, 1, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.; Sun, Z.; Hu, Y.; Chang, Q.; Wang, S.; Xing, W.; Ge, M. Hydrological Connectivity from Glaciers to Rivers in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Roles of Suprapermafrost and Subpermafrost Groundwater. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 4803–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Z. Thermal Springs and Geothermal Energy in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and the Surroundings; Springer: Singapore, 2018; ISBN 9789811034848. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.M.; Wu, Q.B.; Tian, M.Z. Impacts of the Lowering Groundwater Table in the Source Areas of the Yellow River on Ecological Environments. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2003, 25, 667–670. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, F.; Li, A.; Luo, J.; Lin, Z.; Yin, G.; Liu, M.; Zheng, H.; Liu, H. Soil Moisture, Ground Temperatures, and Deformation of a High-Speed Railway Embankment in Northeast China. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2017, 133, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Jin, H.; He, R.; Lü, L.; Harris, S. Evolution and Changes of Permafrost on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during the Late Quaternary. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2017, 9, 0001–0019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Luo, D.; Wang, S.; Lü, L.; Wu, J. Spatiotemporal Variability of Permafrost Degradation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2011, 3, 281–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Luo, H.; Chen, L.; Yu, Z.; Jin, H.; Chen, X.; Wan, C.; Aldahan, A.; Zheng, M.; Hu, Q. Evaluation of Groundwater Discharge into Surface Water by Using Radon-222 in the Source Area of the Yellow River, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Environ. Radioact. 2018, 192, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, J.; Zhang, J.; Polyakov, I.; Gerdes, R.; Inoue, J.; Wu, P. Enhanced Poleward Moisture Transport and Amplified Northern High-Latitude Wetting Trend. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhao, L.; Li, R.; Wang, Q.; Xie, C.; Pang, Q. Recent Ground Surface Warming and Its Effects on Permafrost on the Central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Nan, Z.; Che, J.; Sheng, Y.; Wu, Q.; Jin, H.; Luo, D.; Tang, Z.; et al. Mapping the Permafrost Stability on the Tibetan Plateau for 2005–2015. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 62–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y. Permafrost Temperatures and Thickness on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2010, 72, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.W.; Qiu, G.Q.; Guo, D.X.; Li, S.D. Frozen Ground in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, T. Recent Permafrost Warming on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copland, L.; Sylvestre, T.; Bishop, M.; Shroder, J.; Seong, Y.; Owen, L.; Bush, A.; Kamp, U. Expanded and Recently Increased Glacier Surging in the Karakoram. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2011, 43, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muhammad, S.; Tian, L. Mass Balance and a Glacier Surge of Guliya Ice Cap in the Western Kunlun Shan between 2005 and 2015. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 244, 111832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veillette, J.J.; Thomas, R.D. Icings and Seepage in Frozen Glaciofluvial Deposits, District of Keewatin, NWT. Can. Geotech. J. 1979, 16, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkins, R.; Tranter, M.; Dowdeswell, J.A. The Characteristics and Formation of a High-Arctic Proglacial Icing. Geogr. Ann. Ser. A Phys. Geogr. 2004, 86, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallinson, L.; Swift, D.A.; Sole, A. Proglacial Icings as Indicators of Glacier Thermal Regime: Ice Thickness Changes and Icing Occurrence in Svalbard. Geogr. Ann. Ser. A Phys. Geogr. 2019, 101, 334–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesnokova, A.; Baraër, M.; Bouchard, É. Proglacial Icings as Records of Winter Hydrological Processes. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 4145–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Salomonson, V.V. Development of Methods for Mapping Global Snow Cover Using Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 54, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmanov, D.M.; Kozhurin, A.I.; Trifonov, V.G. The Active Faults of Eurasia Database. Geodyn. Tectonophys. 2017, 8, 711–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Hinzman, L.D.; Kane, D.L. Spring and Aufeis (Icing) Hydrology in Brooks Range, Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2007, 112, G4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tolstikhin, N.I. Ground Waters of Frozen Zone of Lithosphere; Gosgeolizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Markov, M.L. Role of Cryogenic Barrage in River Runoff Formation of Perennial Permafrost Region. Meteorol. Hydrol. 1994, 2, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Kravchenko, V.V. Water Exchange in Small Riversheds with Severe Climatic Conditions during a Cold Perioad of a Year. Geogr. Nat. Resour. 2020, 41, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanovskiy, N.N. On Geological Action of Aufeis. Permafr. Study 1973, XIII, 66–89. [Google Scholar]
- Fotiev, S.M. Ground Waters and Permafrost of the South Yakutian Coal Basin; Science: Moscow, Russia, 1965. [Google Scholar]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gagarin, L.; Wu, Q.; Cao, W.; Jiang, G. Icings of the Kunlun Mountains on the Northern Margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Western China: Origins, Hydrology and Distribution. Water 2022, 14, 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152396
Gagarin L, Wu Q, Cao W, Jiang G. Icings of the Kunlun Mountains on the Northern Margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Western China: Origins, Hydrology and Distribution. Water. 2022; 14(15):2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152396
Chicago/Turabian StyleGagarin, Leonid, Qingbai Wu, Wei Cao, and Guanli Jiang. 2022. "Icings of the Kunlun Mountains on the Northern Margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Western China: Origins, Hydrology and Distribution" Water 14, no. 15: 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152396
APA StyleGagarin, L., Wu, Q., Cao, W., & Jiang, G. (2022). Icings of the Kunlun Mountains on the Northern Margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Western China: Origins, Hydrology and Distribution. Water, 14(15), 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152396






