Seasonal Variations in Water Quality and Algal Blooming in Hypereutrophic Lake Qilu of Southwestern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sampling and Methods
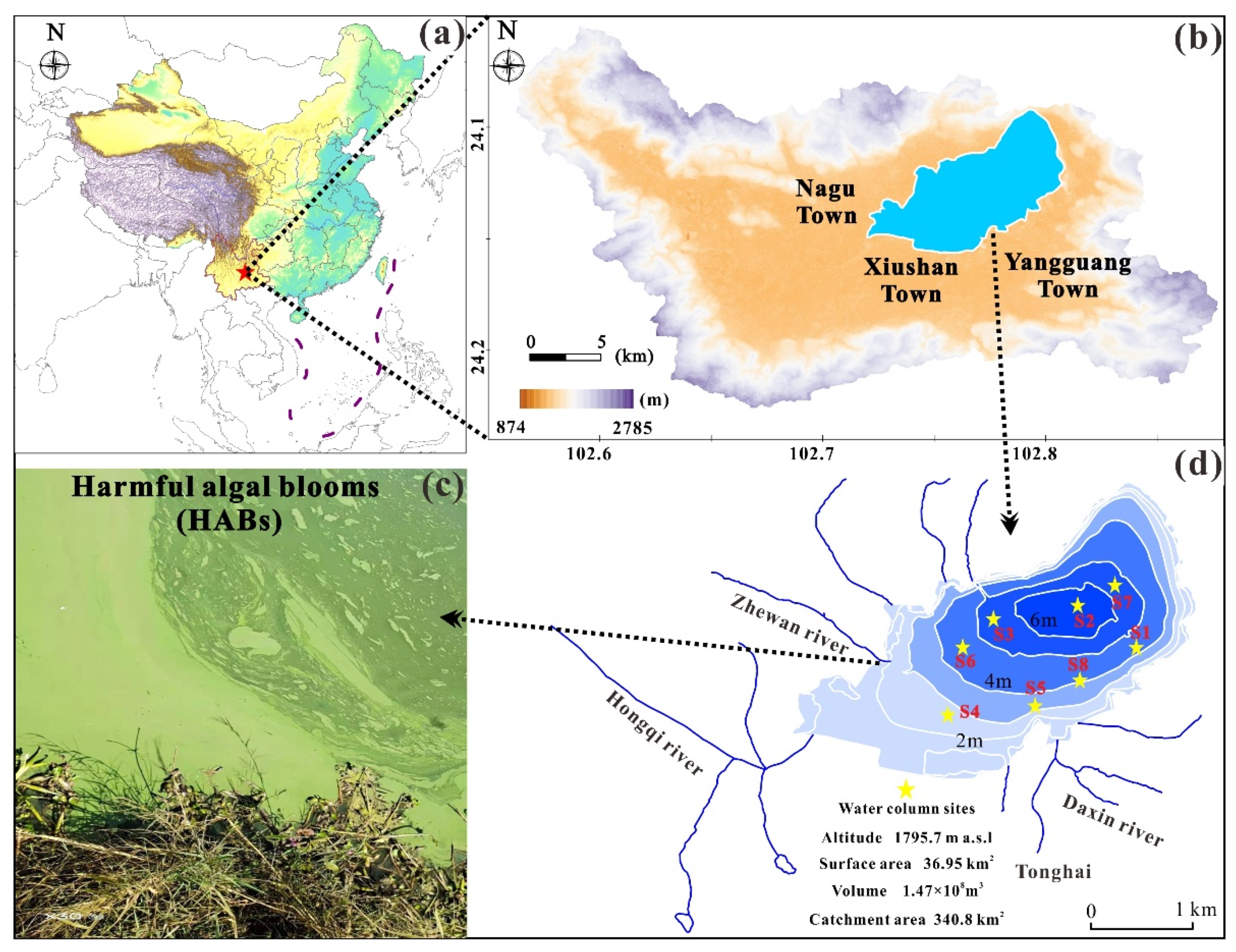
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Measurements and Sampling
2.3. Water Quality and Trophic State Assessment
2.4. Statistical Procedures
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Water Temperature Changes
3.2. Dissolved Oxygen (DO) Characteristics and Variability
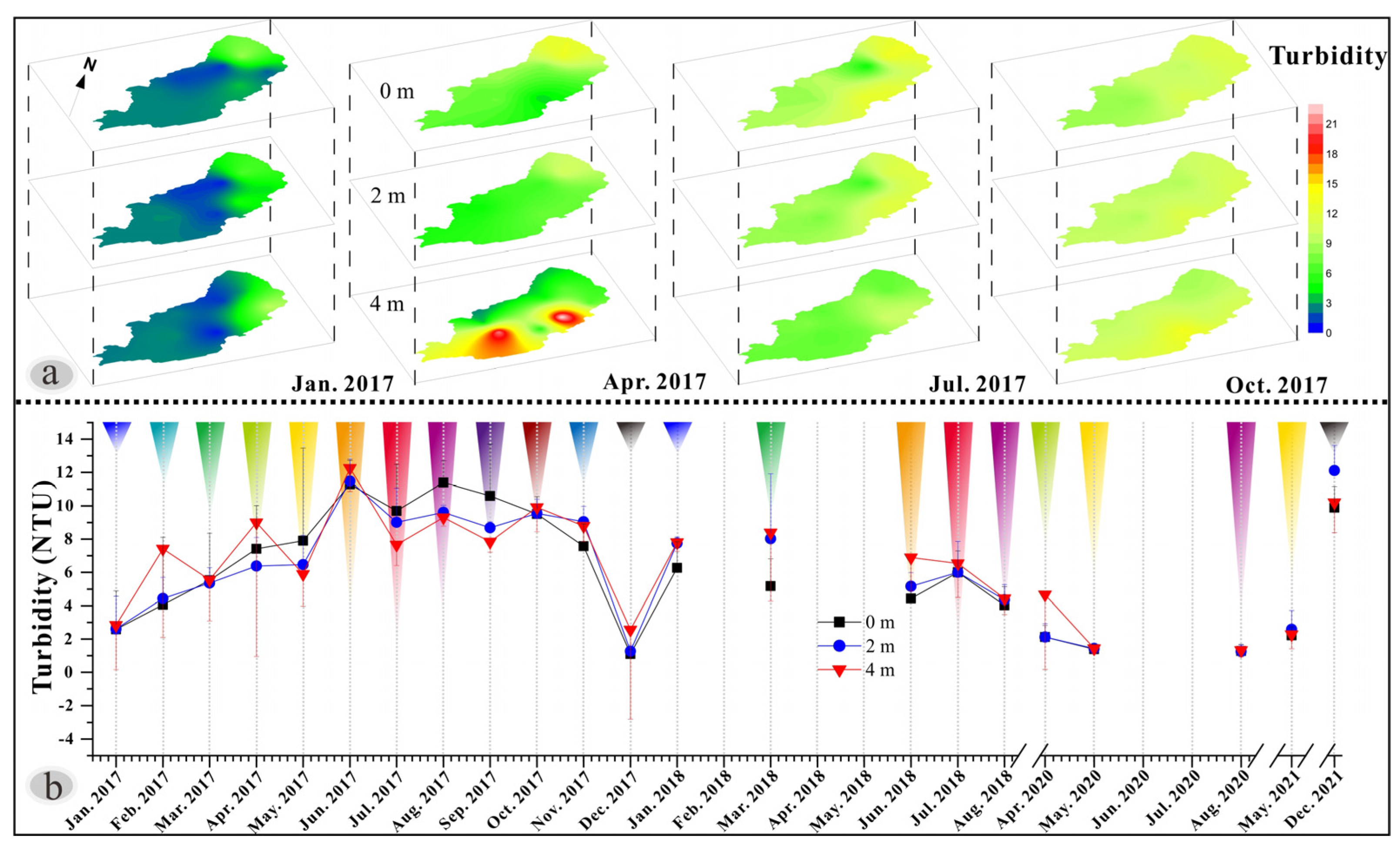
3.3. Variations in Water Turbidity
3.4. pH Characteristics and Variability
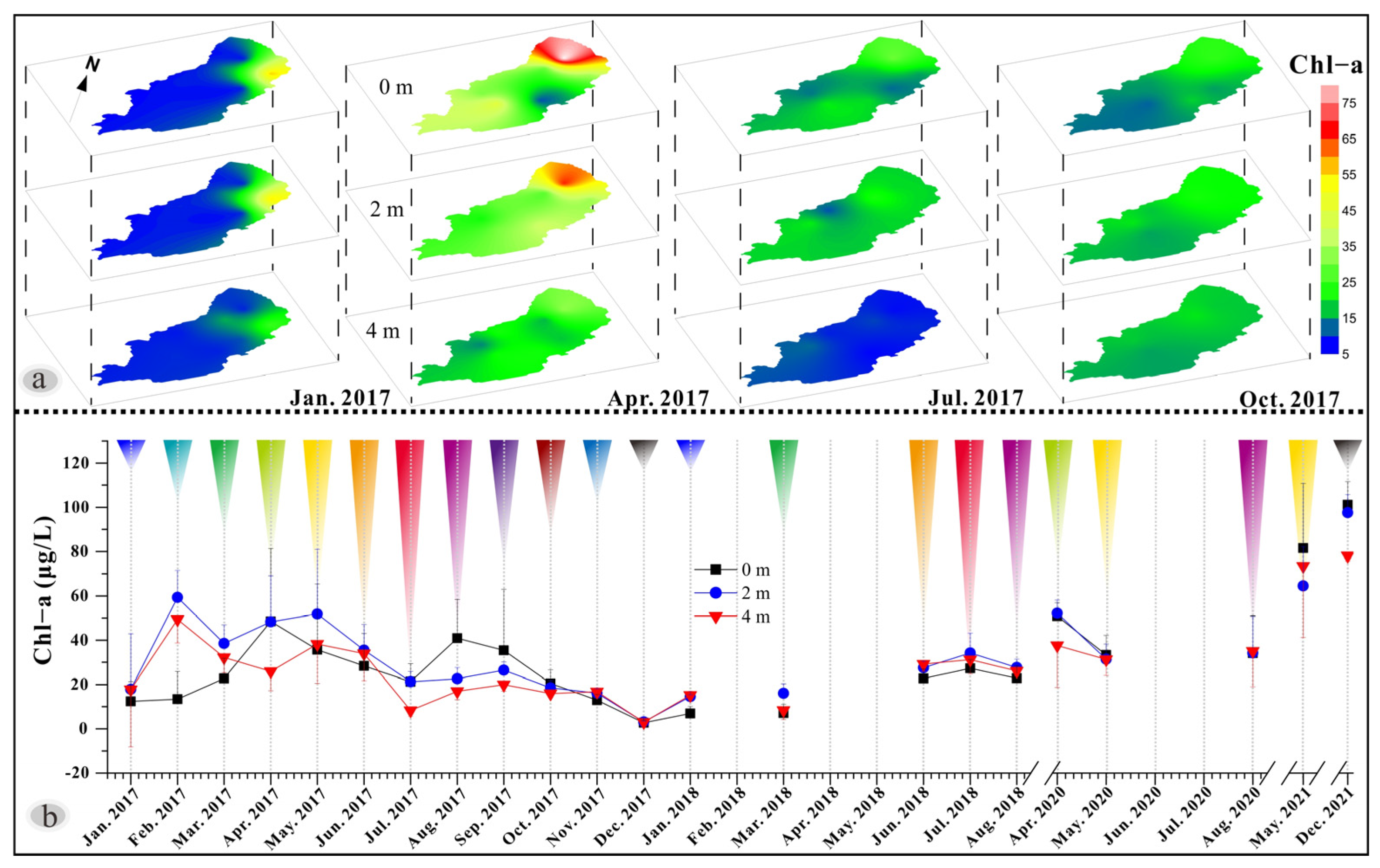
3.5. Chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) Characteristics and Variability
3.6. Assessment of Trophic State and Water Quality
3.7. Control Factors of Harmful Algal Blooms
3.8. Environmental Implication
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CA | Correlation analysis |
| Chl-a | Chlorophyll-a |
| DO | Dissolved oxygen |
| HABs | Harmful algal blooms |
| NSFWQI | National Sanitation Foundation Water Quality Index |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| QL | Qilu |
| RFM | Random Forest Model |
| SD | Secchi disk depth |
| SEPAC | State Environmental Protection Administration of China |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| TN/TP | Total nitrogen/total phosphorus |
| TP | Total phosphorus |
| TSI | Trophic State Index |
| WT | Water temperature |
References
- Paerl, H.W.; Paul, V.J. Climate change: Links to global expansion of harmful cyanobacteria. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przytulska, A.; Bartosiewicz, M.; Vincent, W.F. Increased risk of cyanobacterial blooms in northern high-latitude lakes through climate warming and phosphorus enrichment. Freshw. Biol. 2017, 62, 1986–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, M.H.; Hamilton, D.P.; Etemad-Shahidi, A.; Helfer, F. Impacts of atmospheric stilling and climate warming on cyanobacterial blooms: An individual-based modelling approach. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinçon-Leite, B.; Casenave, C. Modelling eutrophication in lake ecosystems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2985–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, J.; Zeng, G.; Tang, W.; Lu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Xing, W.; Tang, N.; Ye, S.; Li, X.; et al. How climate change and eutrophication interact with microplastic pollution and sediment resuspension in shallow lakes: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chang, F.; Duan, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, H.; Wen, X.; Wu, H.; Lu, Z.; Rongxin, B.; et al. Water Quality Characteristics and Variations of Lake Dian. Adv. Earth Sci. 2017, 32, 651–659, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yu, Z.Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, X.L.; Shang, C.X. Spatial-Temporal Variation of Lake Surface Water Temperature and Its Driving Factors in Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 4688–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, W.M.; Curless, S.E.; Hood, J.M. River phosphorus cycling during high flow may constrain Lake Erie cyanobacteria blooms. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading Dead Zones and Consequences for Marine Ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Li, M.; Zhao, C.; Yang, K.; Li, K.; Peng, M.; Yang, Z.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Bai, R.; et al. Concentrations of toxic metals and ecological risk assessment for sediments of major freshwater lakes in China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 157, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Yan, C.; Guo, J.; Zhen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D. Influence of algal blooms decay on arsenic dynamics at the sediment-water interface of a shallow lake. Chemosphere 2018, 219, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, W.K.; Smith, V.H.; Lohman, K. Nitrogen and phosphorus relationships to benthic algal biomass in temperate streams. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 59, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Duan, L.; Zhou, Q. Total nitrogen and community turnover determine phosphorus use efficiency of phytoplankton along nutrient gradients in plateau lakes. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 124, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J. Biogeochemical nutrient cycles and nutrient management strategies. Hydrobiologia 1999, 410, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Soranno, P.A.; Wagner, T. The role of phosphorus and nitrogen on chlorophyll a: Evidence from hundreds of lakes. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhou, J.; Elser, J.J.; Gardner, W.S.; Deng, J.; Brookes, J.D. Water Depth Underpins the Relative Roles and Fates of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3191–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W.; Hecky, R.E. Eutrophication: More Nitrogen Data Needed. Science 2009, 324, 721–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Climate change: A catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2009, 1, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, J.T.; Wyatt, K.H.; Doll, J.C.; Rubenstein, E.M.; Rober, A.R. Hot and toxic: Temperature regulates microcystin release from cyanobacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-K.; Lee, H.-J.; Heo, J.; Yun, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, H.-M.; Hong, D.-G.; Lee, I.-J. Deciphering the key factors determining spatio-temporal heterogeneity of cyanobacterial bloom dynamics in the Nakdong River with consecutive large weirs. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 143079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-J.; Nam, G.-S.; Jang, J.-S.; Won, C.-H.; Kim, H.-W. Cold Plasma Treatment for Efficient Control over Algal Bloom Products in Surface Water. Water 2019, 11, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Sondergaard, M.; Meerhoff, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Jensen, J.P. Shallow lake restoration by nutrient loading reduction—Some recent findings and challenges ahead. Hydrobiologia 2007, 584, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlson, B.; Andersen, P.; Arneborg, L.; Cembella, A.; Eikrem, W.; John, U.; West, J.J.; Klemm, K.; Kobos, J.; Lehtinen, S.; et al. Harmful algal blooms and their effects in coastal seas of Northern Europe. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, R.; Yang, G. Succession of Nine Plateau Lakes and Regulation of Ecological Safety in Yunnan Province. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 31, 185–191, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Y.; Yang, K.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Y.L. Secchi depth inversion and its temporal and spatial variation analysis-A case study of nine plateau lakes in Yunnan Province of China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 100, 102344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, A.L.; O’Quinn, R.F.; Abbott, M.B.; Bain, D.J. A Holocene history of the Indian monsoon from Qilu Lake, southwestern China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 227, 106051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.Y.; Oh, H.M.; Park, Y.S. Evaluation of Environmental Factors on Cyanobacterial Bloom in Eutrophic Reservoir Using Artificial Neural Networks. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Steinman, A.D.; Oudsema, M.; Hassett, M.; Xie, L. The influence of nutrients limitation on phytoplankton growth and microcystins production in Spring Lake, USA. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.M.; Li, L.L.; Hussain, S.; Lee, J.L.; Mumtaz, F.; Elbeltagi, A.; Waqas, M.S.; Dilawar, A. Analysis of Seasonal Variations in Surface Water Quality over Wet and Dry Regions. Water 2022, 14, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R. Analysis on Factors of Ecological Vulnerability of Qilu Lake in Yunnan Province. Environ. Sci. Surv. 2011, 30, 24–29, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Yan, Z.; Chao, C.; Yu, H.; Yu, D.; Liu, C. Effectiveness of dredging on internal phosphorus loading in a typical aquacultural lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.S.; Huang, Y.Y.; Hu, J.; Li, P.P.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Xu, P.; Zhang, J.Y.; Chen, X.C. The nitrogen reduction in eutrophic water column driven by Microcystis blooms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.M.; Shoaib, M.; Farid, H.U.; Lee, J.L. Assessment of Water Quality Profile Using Numerical Modeling Approach in Major Climate Classes of Asia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acuña-Alonso, C.; Álvarez, X.; Lorenzo, O.; Cancela, Á.; Valero, E.; Sánchez, Á. Assessment of water quality in eutrophized water bodies through the application of indexes and toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valera, C.A.; Pissarra, T.C.T.; Martins, M.V.; do Valle, R.F.; Oliveira, C.F.; Moura, J.P.; Fernandes, L.F.S.; Pacheco, F.A.L. The Buffer Capacity of Riparian Vegetation to Control Water Quality in Anthropogenic Catchments from a Legally Protected Area: A Critical View over the Brazilian New Forest Code. Water 2019, 11, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E.; Simpson, J. A Coordinator’s Guide to Volunteer Lake Monitoring Methods. N. Am. Lake Manag. Soc. 1996, 99, 96. [Google Scholar]
- Tanvir, R.U.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J. Cyanobacterial community succession and associated cyanotoxin production in hypereutrophic and eutrophic freshwaters. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lyu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z. Using the multidimensional synthesis methods with non-parameter test, multiple time scales analysis to assess water quality trend and its characteristics over the past 25 years in the Fuxian Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Chang, F.; Duan, L.; Zhang, X.; Peng, W.; Liu, Q.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y. Plateau lake ecological response to environmental change during the last 60 years: A case study from freshwater Lake Yangzong, SW China. J. Soils Sed. 2021, 21, 1550–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, X. Aquatic flora and assemblge characteristic of submerged macrophytics in five lakes of the Yunnan province. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin. 2010, 19, 9, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, C.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, J.; Jiang, F.; et al. Arsenic pollution and its treatment in Yangzonghai lake in China: In situ remediation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Ding, S.; Sun, Q.; Gao, S.; Fu, Z.; Gong, M.; Lin, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y. High resolution spatiotemporal sampling as a tool for comprehensive assessment of zinc mobility and pollution in sediments of a eutrophic lake. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, F.; Guo, Z.; Cai, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Fu, Y.; Wang, B.; Gao, A. Kinetic Exchange of Remobilized Phosphorus Related to Phosphorus-Iron-Sulfur Biogeochemical Coupling in Coastal Sediment. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 10494–10517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Yang, Y.; Li, F.; Ge, F.; Kuang, Y. Importance of controlling pH-depended dissolved inorganic carbon to prevent algal bloom outbreaks. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Yang, P. Exploring the influence of lake water chemistry on chlorophyll a: A multivariate statistical model analysis. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, G.; Han, R. High-resolution distribution of internal phosphorus release by the influence of harmful algal blooms (HABs) in Lake Taihu. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Janssen, A.B.G.; de Klein, J.J.M.; Kroeze, C.; Strokal, M.; Ma, L.; Zheng, Y. Modeling nutrients in Lake Dianchi (China) and its watershed. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Sharma, B.; Singh, P. Water Quality Assessment in Terms of Water Quality Index. Am. J. Water Resour. 2013, 1, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Wu, X.; Gao, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, Q.; Luo, W. Study on Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Chl-a and Water Quality Factors in Qilu Lake and Their Correlations. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2012, 40, 345–348, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Han, X.; Brookes, J.D.; Qin, B. High probability of nitrogen and phosphorus co-limitation occurring in eutrophic lakes. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, K.M.; Vavrus, C.E.; Lofton, M.E.; McClure, R.P.; Gantzer, P.; Carey, C.C.; Schreiber, M.E. Iron and manganese fluxes across the sediment-water interface in a drinking water reservoir. Water Res. 2020, 182, 116003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, N.M.; Patoine, A.; Haig, H.A.; Simpson, G.L.; Swarbrick, V.J.; Wiik, E.; Leavitt, P.R. Spatial and temporal variation in nitrogen fixation and its importance to phytoplankton in phosphorus-rich lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2019, 64, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Water Quality | Excellent | Good | Medium | Bad | Very bad |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSFWQI 1 | 91–100 | 71–90 | 51–70 | 26–50 | 0–25 |
| Trophic status | Classification | Oligotrophic | Mesotrophic | Eutrophic | Hypereutrophic |
| Chl-a 2 | <0.95 | 0.95–7.3 | 7.3–56 | >56 | |
| SD 2 | >8 | 8–2 | 2–0.5 | <0.5 | |
| TP 2 | <6 | 6–24 | 24–96 | >96 | |
| TSI 2 | <30 | 30–50 | 30–70 | >70 | |
| Mean. TP 3 | <10 | 10 | 30–100 | >100 | |
| Max.Chl-a 3 | <8 | 30 | 25–75 | >75 |
| TSI | TP (μg/L) | TN (mg/L) | Chl-a (μg/L) | SD (meter) | TP (μg/L) | TSI | WQI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oligotrophic | 0–50 | 0–1.4 | <0.95 | >8 | <6 | <30 | 0–25 |
| 1.40% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 100.00% | |
| Mesotrophic | 50–100 | 1.4–2 | 0.95–7.3 | 2-8 | 6–24 | 30–50 | 26–50 |
| 31.20% | 31.90% | 13.19% | 0.00% | 0.35% | 0.00% | 0.00% | |
| Eutrophic | >100 | >2 | 7.3–56 | 0.5-2 | 24–96 | 50–70 | 50–75 |
| 68.40% | 68.10% | 80.21% | 34.72% | 30.21% | 70.14% | 0.00% | |
| Hypereutrophic | >56 | <0.5 | >96 | >70 | 75–100 | ||
| 6.60% | 65.28% | 69.44% | 29.86% | 0.00% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Chang, F.; Wen, X.; Duan, L.; Zhang, H. Seasonal Variations in Water Quality and Algal Blooming in Hypereutrophic Lake Qilu of Southwestern China. Water 2022, 14, 2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172611
Li D, Chang F, Wen X, Duan L, Zhang H. Seasonal Variations in Water Quality and Algal Blooming in Hypereutrophic Lake Qilu of Southwestern China. Water. 2022; 14(17):2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172611
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Donglin, Fengqin Chang, Xinyu Wen, Lizeng Duan, and Hucai Zhang. 2022. "Seasonal Variations in Water Quality and Algal Blooming in Hypereutrophic Lake Qilu of Southwestern China" Water 14, no. 17: 2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172611
APA StyleLi, D., Chang, F., Wen, X., Duan, L., & Zhang, H. (2022). Seasonal Variations in Water Quality and Algal Blooming in Hypereutrophic Lake Qilu of Southwestern China. Water, 14(17), 2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172611







