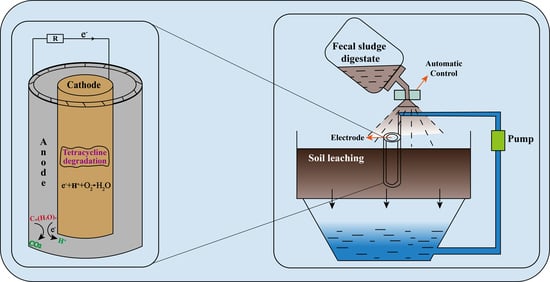
Digestate of Fecal Sludge Enhances the Tetracycline Removal in Soil Microbial Fuel Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. FS Pretreatment and AD
2.2. The Addition of FS Digestate on Simulated TC-Contaminated Soil
2.3. Soil Microbial Fuel Cell Construction
2.4. MFC Performance Characterizations
2.5. Microbiome Analysis Based on 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.6. Statistics Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of FS Digestate Addition on TC and Organics Leaching
3.2. Effect of FS Digestate Addition on TC Removal in SMFC
3.3. Electricity Generation by SMFC
3.4. Anodic Biofilm Microbiome
3.5. Cathodic Biofilm Microbiome
3.6. Economic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, F.-Z.; He, L.-Y.; He, L.-X.; Zou, H.-Y.; Zhang, M.; Wu, D.-L.; Liu, Y.-S.; Shi, Y.-J.; Bai, H.; Ying, G.-G. Untreated swine wastes changed antibiotic resistance and microbial community in the soils and impacted abundances of antibiotic resistance genes in the vegetables. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.; Chu, L.M. Adsorption and degradation of five selected antibiotics in agricultural soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545–546, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Zhen, Z.; Luo, S.; Ren, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y.-Q.; Song, Z.; Li, Y. Effects of two ecological earthworm species on tetracycline degradation performance, pathway and bacterial community structure in laterite soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santás-Miguel, V.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Díaz-Raviña, M.; Fernández-Sanjurjo, M.J.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, E.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Fernández-Calviño, D. Interactions between soil properties and tetracycline toxicity affecting to bacterial community growth in agricultural soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 147, 103437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijbers, P.M.; Blaak, H.; de Jong, M.C.; Graat, E.A.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.; Husman, A.M.d. Role of the environment in the transmission of antimicrobial resistance to humans: A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11993–12004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y. Cathodic microbial community adaptation to the removal of chlorinated herbicide in soil microbial fuel cells. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 16900–16912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Weng, L.; Ren, T.; Li, Y. Bioelectrochemical removal of tetracycline from four typical soils in China: A performance assessment. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 129, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathuriya, A.S.; Jadhav, D.A.; Ghangrekar, M.M. Architectural adaptations of microbial fuel cells. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 9419–9432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Cizmas, L.; Wang, Z.; Sharma, V.K. Synergistic effect of aqueous removal of fluoroquinolones by a combined use of peroxymonosulfate and ferrate (VI). Chemosphere 2017, 177, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Weng, L.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Y. Microbial fuel cells for organic-contaminated soil remedial applications: A review. Energy Technol. 2017, 5, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Xiao, Y.; Yan, W.; Ding, R.; Wang, S.; Zhao, F. The effect of bioelectrochemical systems on antibiotics removal and antibiotic resistance genes: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1421–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Li, J.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fang, Y.; Xin, F.; Dong, W.; Wei, P.; Ma, J.; Jiang, M. Progress and prospects of bioelectrochemical systems: Electron transfer and its applications in the microbial metabolism. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semiyaga, S.; Okure, M.A.; Niwagaba, C.B.; Katukiza, A.Y.; Kansiime, F. Decentralized options for faecal sludge management in urban slum areas of Sub-Saharan Africa: A review of technologies, practices and end-uses. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 104, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, J.; Cai, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, B.; Xing, D. Accelerating nutrient release and pathogen inactivation from human waste by different pretreatment methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harder, R.; Wielemaker, R.; Molander, S.; Öberg, G. Reframing human excreta management as part of food and farming systems. Water Res. 2020, 175, 115601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, X.; Zhu, C.; Luo, L.; Chen, Z.; Jin, S.; Geng, B. Influences of human waste–based ectopic fermentation bed fillers on the soil properties and growth of Chinese pakchoi. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Zhu, H.; Xu, Y.; Yan, B.; Shutes, B.; Bañuelos, G.; Wang, X. Removal of sulfamethoxazole and tetracycline in constructed wetlands integrated with microbial fuel cells influenced by influent and operational conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 115988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ren, L.; Pu, Y.; Logan, B.E. Electricity generation from fermented primary sludge using single-chamber air-cathode microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fang, A.; Liu, B.; Xie, G.; Lou, Y.; Xing, D. Effect of different co-treatments of waste activated sludge on biogas production and shaping microbial community in subsequent anaerobic digestion. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, C.; Deng, D.; Li, Y.; Luo, L. Factors affecting sorption behaviors of tetracycline to soils: Importance of soil organic carbon, pH and Cd contamination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ying, H.; Yin, Y.; Zheng, H.; Cui, Z. Estimating soil nitrate leaching of nitrogen fertilizer from global meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkharabsheh, H.M.; Seleiman, M.F.; Battaglia, M.L.; Shami, A.; Jalal, R.S.; Alhammad, B.A.; Almutairi, K.F.; Al-Saif, A.M. Biochar and its broad impacts in soil quality and fertility, nutrient leaching and crop productivity: A review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Huggins, T.; Jin, S.; Zuo, Y.; Ren, Z.J. Microbial metabolism and community structure in response to bioelectrochemically enhanced remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4021–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Ren, N.; Xing, D. Magnetic cathode stimulates extracellular electron transfer in bioelectrochemical systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 15012–15018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahampath Arachchige Don, C.D.; Babel, S. Circulation of anodic effluent to the cathode chamber for subsequent treatment of wastewater in photosynthetic microbial fuel cell with generation of bioelectricity and algal biomass. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Mei, X.; Liu, B.; Xie, G.; Xing, D. Magnet anode enhances extracellular electron transfer and enrichment of exoelectrogenic bacteria in bioelectrochemical systems. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clesceri, L.S.; American Public Health Association. Standard Method for Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2017; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; You, S.; Liu, B.; Ren, N.; Xing, D. Oxygen reduction reaction activity and the microbial community in response to magnetite coordinating nitrogen-doped carbon catalysts in bioelectrochemical systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 122, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhuang, H.; Cui, H.; Liu, B.; Xie, G.; Xing, D. Effect of waterproof breathable membrane based cathodes on performance and biofilm microbiomes in bioelectrochemical systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 142281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, K.; Lou, Y.; Lu, B.; Liu, B.; Xie, G.; Ren, N.; Xing, D. The synergistic effect of potassium ferrate and peroxymonosulfate application on biogas production and shaping microbial community during anaerobic co-digestion of a cow manure-cotton straw mixture. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 333, 125166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Liguoro, M.; Cibin, V.; Capolongo, F.; Halling-Sørensen, B.; Montesissa, C. Use of oxytetracycline and tylosin in intensive calf farming: Evaluation of transfer to manure and soil. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamscher, G.; Pawelzick, H.T.; Hoper, H.; Nau, H. Different behavior of tetracyclines and sulfonamides in sandy soils after repeated fertilization with liquid manure. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, K.; Gao, B.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y. Adsorption of tetracycline on soil and sediment: Effects of pH and the presence of Cu (II). J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Quan, X.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Y. Application of slow-release carbon sources embedded in polymer for stable and extended power generation in microbial fuel cells. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbella, C.; Puigagut, J. Improving domestic wastewater treatment efficiency with constructed wetland microbial fuel cells: Influence of anode material and external resistance. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.-L.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.-L.; Zhang, L.-M.; Xu, H.; Yang, X.-L. Fate of sulfadiazine and its corresponding resistance genes in up-flow microbial fuel cell coupled constructed wetlands: Effects of circuit operation mode and hydraulic retention time. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Qu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Feng, Y.; Guo, C.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Peijnenburg, W.J.; Zhang, Y. Continuous flow electrosorption-microbial fuel cell system for efficient removal of oxytetracycline without external electrical supply. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 290, 121751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardenhorst, S.K.; Vital, M.; Karch, A.; Rubsamen, N. Richness estimation in microbiome data obtained from denoising pipelines. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfennig, N.; Biebl, H. Desulfuromonas acetoxidans gen. nov. and sp. nov., a new anaerobic, sulfur-reducing, acetate-oxidizing bacterium. Arch. Microbiol. 1976, 110, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rago, L.; Cristiani, P.; Villa, F.; Zecchin, S.; Colombo, A.; Cavalca, L.; Schievano, A. Influences of dissolved oxygen concentration on biocathodic microbial communities in microbial fuel cells. Bioelectrochemistry 2017, 116, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, B.E.; Rossi, R.; Ragab, A.a.; Saikaly, P.E. Electroactive microorganisms in bioelectrochemical systems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ji, B.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Gu, J.; Liu, Y. Defensive responses of microalgal-bacterial granules to tetracycline in municipal wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 312, 123605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhang, L. Enhanced electricity generation for biocathode microbial fuel cell by in situ microbial-induced reduction of graphene oxide and polarity reversion. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 12574–12582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, Z.; Tang, H.; Wang, C.; Ye, Z. Response of immobilized denitrifying bacterial consortium to tetracycline exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, M.; Aulenta, F.; Villano, M.; Angenent, L.T. Cathodes as electron donors for microbial metabolism: Which extracellular electron transfer mechanisms are involved? Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-Z.; Livermore, D.M.; Nikaido, H. Role of efflux pump (s) in intrinsic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Resistance to tetracycline, chloramphenicol, and norfloxacin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 1732–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, H.; Wang, J.; Feng, K.; Xing, D. Digestate of Fecal Sludge Enhances the Tetracycline Removal in Soil Microbial Fuel Cells. Water 2022, 14, 2752. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172752
Cui H, Wang J, Feng K, Xing D. Digestate of Fecal Sludge Enhances the Tetracycline Removal in Soil Microbial Fuel Cells. Water. 2022; 14(17):2752. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172752
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Han, Jing Wang, Kun Feng, and Defeng Xing. 2022. "Digestate of Fecal Sludge Enhances the Tetracycline Removal in Soil Microbial Fuel Cells" Water 14, no. 17: 2752. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172752
APA StyleCui, H., Wang, J., Feng, K., & Xing, D. (2022). Digestate of Fecal Sludge Enhances the Tetracycline Removal in Soil Microbial Fuel Cells. Water, 14(17), 2752. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172752