Long-Term Assessment of a Water Safety Plan (WSP) in Salta, Argentina
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Review of the WSP
2.2. Assessment of the WSP
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Review of the WSP
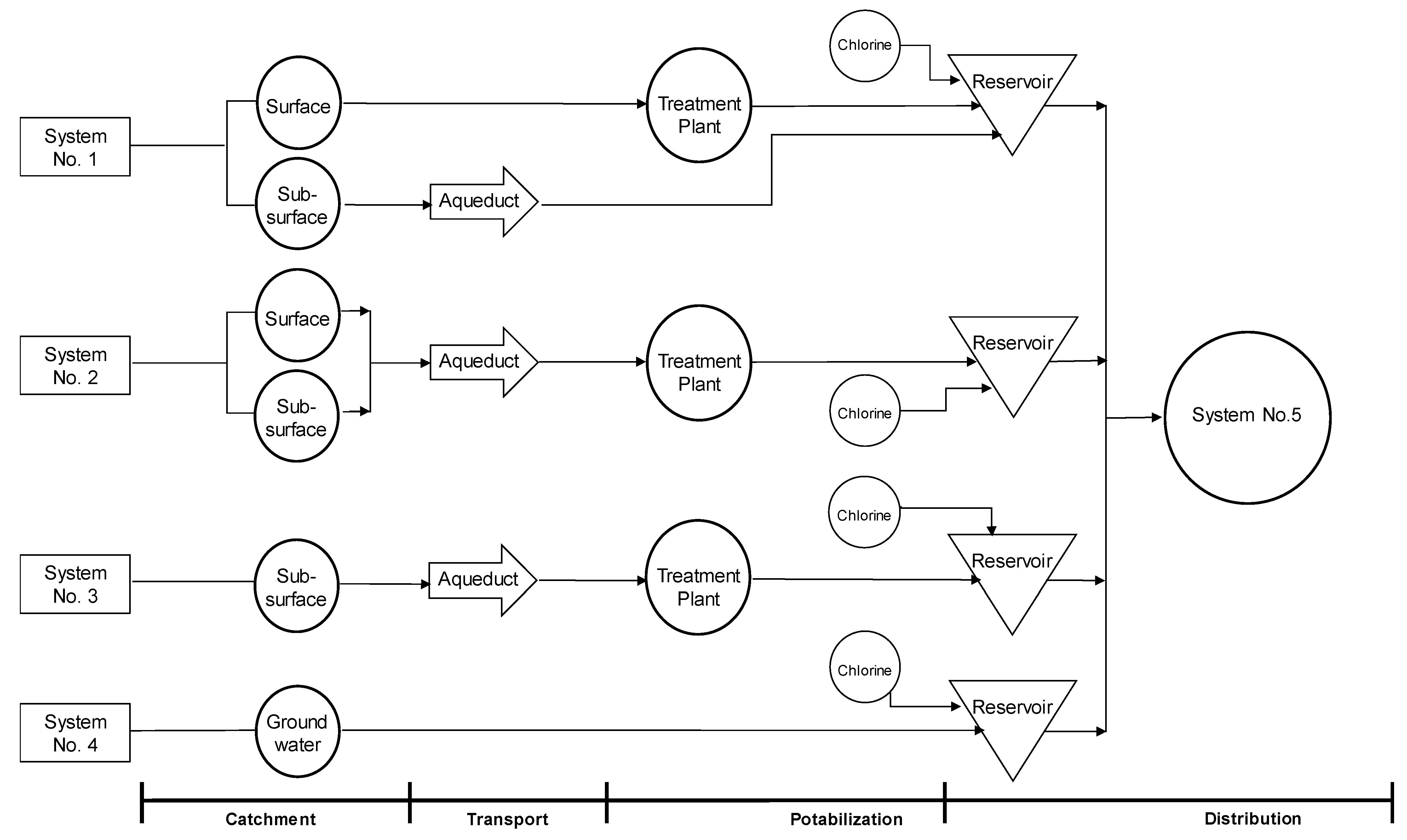
3.1.1. Review of Control Measures
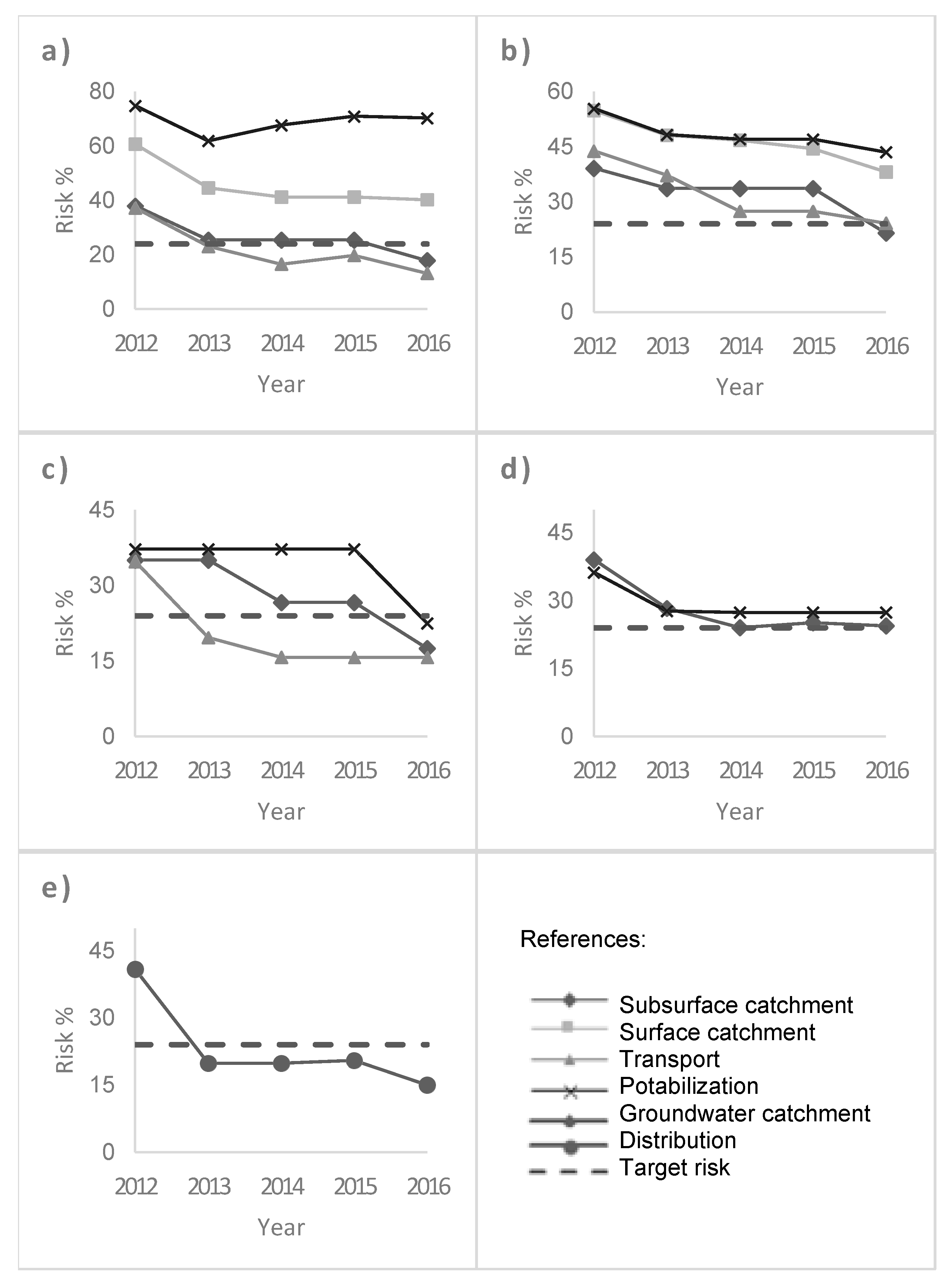
3.1.2. Analysis of Compliance with Control Measures and Annual Risk Calculation
3.2. Assessment of the WSP
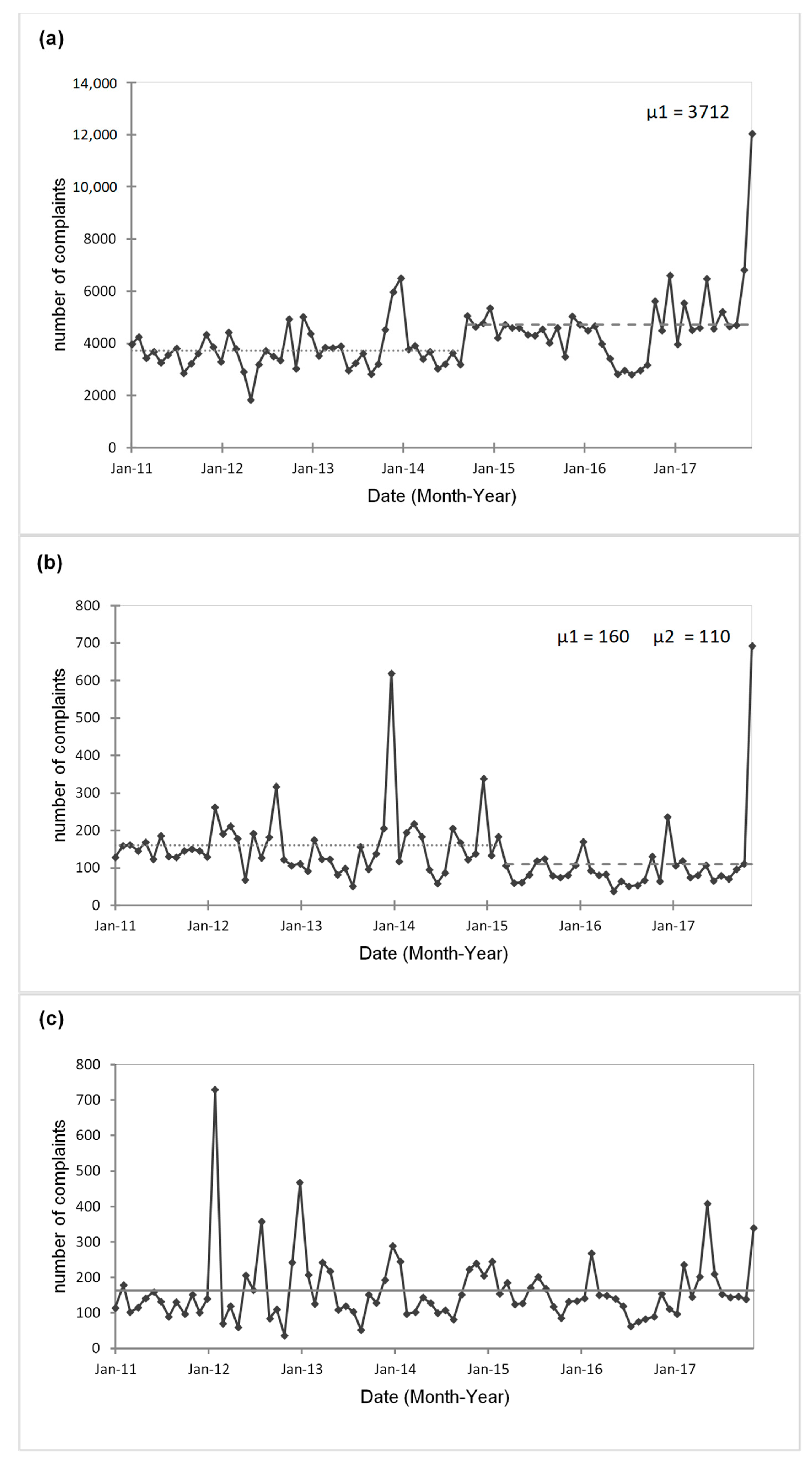
3.2.1. Analysis of Complaints
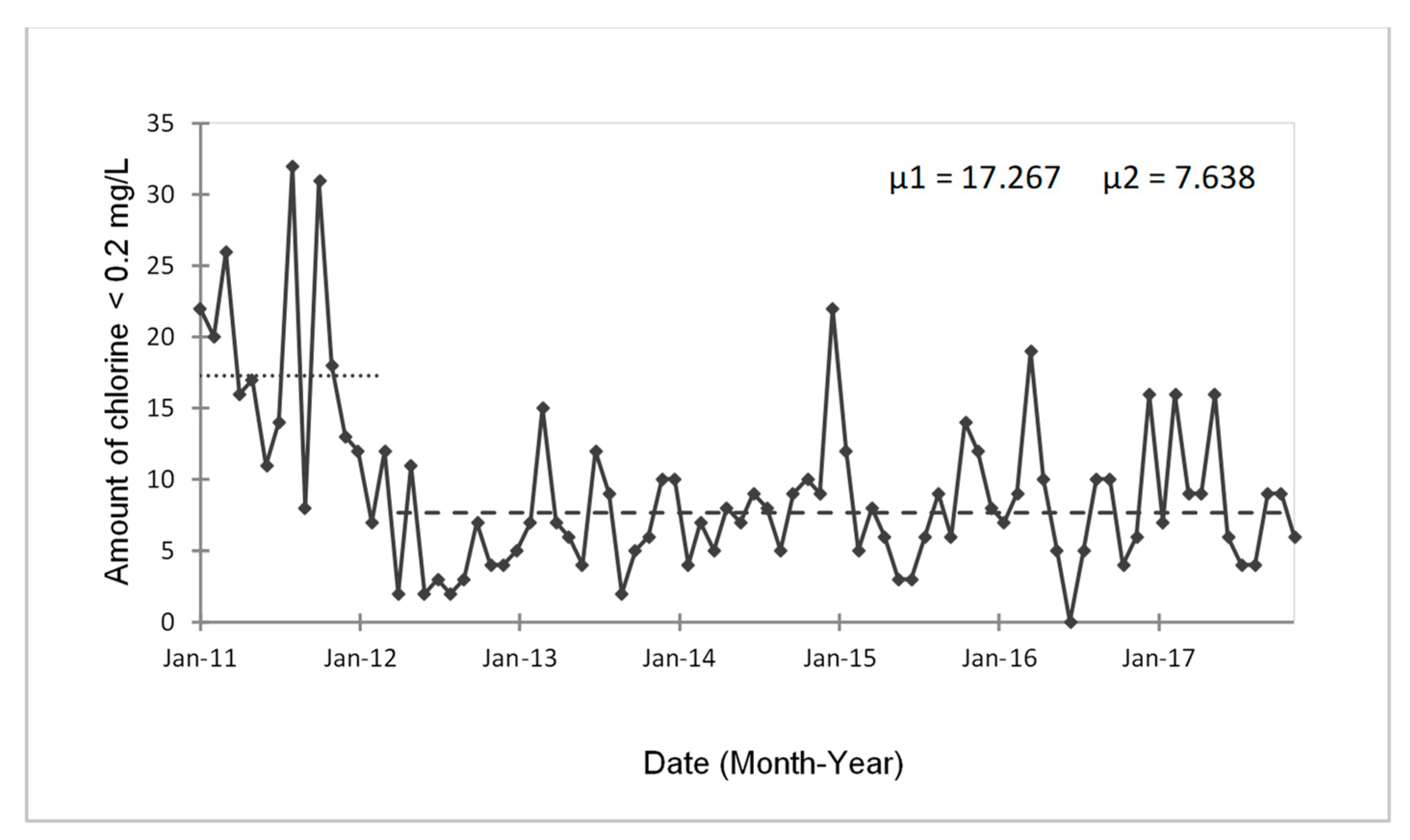
3.2.2. Time-Series Analysis of Water Quality Parameters
3.2.3. Limitations and Challenges
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gatto D’Andrea, M.L. Aplicación y Adaptación de una Metodología Estandarizada de Gestión de Riesgos en los Sistemas de Abastecimiento de Agua Potable de la Ciudad de Salta (Application and Adaptation of a Standardized Risk Management Methodology in the Drinking Water Supply Systems of the City of Salta). Ph.D. Thesis, Facultad de Ciencias Naturales, Universidad Nacional de Salta, Salta, Argentina, 2012; p. 100. (In Spanish). [Google Scholar]
- Seghezzo, L.; Gatto D’Andrea, M.L.; Iribarnegaray, M.A.; Liberal, V.I.; Fleitas, A.; Bonifacio, J.L. Improved risk assessment and risk reduction strategies in the Water Safety Plan (WSP) of Salta, Argentina. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2013, 13, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 3rd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- IWA. Bonn Charter for Safe Drinking Water; International Water Association: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th Edition, Incorporating the 1st Addendum. 2017. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/254637/9789241549950-eng.pdf;jsessionid=129B614988B395796D1B6A99AA126B0C?sequence=1 (accessed on 13 October 2020).
- Bartram, J.; Corrales, L.; Davison, A.; Deere, D.; Drury, D.; Gordon, B.; Howard, G.; Rinehold, A.; Stevens, M. Manual para el Desarrollo de planes de Seguridad del Agua: Metodología Pormenorizada de Gestión de Riesgos para Proveedores de Agua de Consumo (Water Safety Plan Manual: Step-by-step Risk Management for Drinking-water Suppliers). 2009. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/75142 (accessed on 13 September 2022). (In Spanish).
- WHO. Water Safety Planning for Small Community Water Supplies: Step-by-step Risk Management Guidance for Drinking-Water Supplies in Small Communities; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rickert, B.; Schmoll, O.; Rinehold, A.; Barrenberg, E. Water Safety Plan: A Field Guide to Improving Drinking-water Safety in Small Communities. World Health Organization, 2014. Regional Office for Europe. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/329537 (accessed on 29 January 2022).
- WHO. Global Status Report on Water Safety Plans: A Review of Proactive Risk Assessment and Risk Management Practices to Ensure the Safety of Drinking-Water; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, D. Observations and lessons learnt from more than a decade of water safety planning in South-East Asia. WHO South-East Asia J. Public Health 2017, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoukalas, D.S.; Tsitsifli, S. A critical evaluation of Water Safety Plans (WSPs) and HACCP implementation in water utilities. In Multidiscip. Digit. Publ. Inst. Proc. 2018, 2, 600. [Google Scholar]
- Kanyesigye, C.; Marks, S.J.; Nakanjako, J.; Kansiime, F.; Ferrero, G. Status of water safety plan development and implementation in Uganda. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayser, G.; Loret, J.F.; Setty, K.; Blaudin De Thé, C.; Martin, J.; Puigdomenech, C.; Bartram, J. Water safety plans for water supply utilities in China, Cuba, France, Morocco and Spain: Costs, benefits, and enabling environment elements. Urban Water J. 2019, 16, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsdottir, M.J.; Gardarsson, S.M.; Figueras, M.J.; Puigdomènech, C.; Juárez, R.; Saucedo, G.; Arnedo, M.J.; Santos, R.; Monteiro, S.; Avery, L.; et al. Water safety plan enhancements with improved drinking water quality detection techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Smith, C.D.; Cohen, A.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R. Implementation of water safety plans in China: 2004–2018. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 223, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- String, G.M.; Singleton, R.I.; Mirindi, P.N.; Lantagne, D.S. Operational research on rural, community-managed Water Safety Plans: Case study results from implementations in India, DRC, Fiji, and Vanuatu. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudaliar, M.M. Success or failure: Demonstrating the effectiveness of a Water Safety Plan. Water Supply 2012, 12, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, G.; Setty, K.; Rickert, B.; George, S.; Rinehold, A.; DeFrance, J.; Bartram, J. Capacity building and training approaches for water safety plans: A comprehensive literature review. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishipour, A.; Mostafaloo, R.; Mehdipour Rabori, M.; Ghordouei-Milan, E.; Hosseini, F.; Aali, R. Experience of implementing Water Safety Plan in Iran: A systematic review. J. Environ. Health Sustain. Dev. 2021, 6, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, G.; Bichai, F.; Rusca, M. Experiential learning through role-playing: Enhancing stakeholder collaboration in Water Safety Plans. Water 2018, 10, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, E.; Lukas, A.; Aichlseder, W.; Perfler, R. Experiences and lessons learned from practical implementation of a software-supported water safety plan (WSP) approach. Water Sci Technol Water Supply. 2012, 12, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpel, E.; Delaire, C.; Peletz, R.; Kisiangani, J.; Rinehold, A.; De France, J.; Khush, R. Measuring the impacts of water safety plans in the Asia-Pacific region. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, R.; Bartram, J. A systematic literature review of the enabling environment elements to improve implementation of water safety plans in high-income countries. J. Water Health 2018, 16, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, H.; Parker, A.; Pollard, S.J.T. Whither regulation, risk and water safety plans? Case studies from Malaysia and from England and Wales. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeger, A.; Tavares, A.F. Do governance arrangements affect the voluntary adoption of water safety plans? An empirical study of water utilities in Portugal. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 1757–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setty, K.E.; Enault, J.; Loret, J.F.; Serra, C.P.; Martin-Alonso, J.; Bartram, J. Time series study of weather, water quality, and acute gastroenteritis at Water Safety Plan implementation sites in France and Spain. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muoio, R.; Caretti, C.; Rossi, L.; Santianni, D.; Lubello, C. Water safety plans and risk assessment: A novel procedure applied to treated water turbidity and gastrointestinal diseases. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 223, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setty, K.; O’Flaherty, G.; Enault, J.; Lapouge, S.; Loret, J.; Bartram, J. Assessing operational performance benefits of a Water Safety Plan implemented in Southwestern France. Perspect. Public Health 2018, 138, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ente Regulador de Servicios Sanitarios. Provincia de Santa Fe. Resolución No. 1008 (Sanitary Services Regulatory Entity. Province of Santa Fe. Resolution No. 1008). 2016. Available online: http://www.enress.gov.ar/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/1008_GuiaPracticaPlandeAguaSegura-1.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2010). (In Spanish)
- Agua y Saneamientos Argentinos. Reporte de Sustentabilidad (Argentine Water and Sanitation. Sustainability Report). 2011. Available online: https://www.aysa.com.ar/media-library/rse/RSE_2011.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2020). (In Spanish).
- Arias, M.; Bianchi, A.R. Estadísticas Climatológicas de la Provincia de Salta. Dirección de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales de la Provincia de Salta. Estación Experimental Agropecuaria Salta, INTA (Climate statistics of the province of Salta. Department of Environment and Natural Resources of the Province of Salta. Salta Agricultural Experimental Station, INTA); INTA: Salta, Argentina, 1996; p. 189. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Bossel, H. Indicators for Sustainable Development: Theory, Method, Applications. A report to the Balaton Group; International Institute for Sustainable Development (IISD): Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Código Alimentario Argentino. Capítulo XII, Bebidas Hídricas, Agua y Agua Gasificada (Argentine Food Code. Chapter XII, Hydrous Drinks, Water and Carbonated Water). 2019. Available online: http://www.anmat.gov.ar/alimentos/normativas_alimentos_caa.asp (accessed on 10 June 2019). (In Spanish)
- Chang, H. Spatial analysis of water quality trends in the Han River basin, South Korea. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3285–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisi, O.; Ay, M. Comparison of Mann–Kendall and innovative trend method for water quality parameters of the Kizilirmak River, Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Barraud, S.; Castebrunet, H.; Aubin, J.B.; Marmonier, P. Long-term stormwater quantity and quality analysis using continuous measurements in a French urban catchment. Water Res. 2015, 85, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Alvarez, M.S.; Weir, M.H.; Pope, J.M.; Seghezzo, L.; Rajal, V.B.; Salusso, M.M.; Moraña, L.B. Development of a relative risk model for drinking water regulation and design recommendations for a peri urban region of Argentina. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2015, 218, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarnegaray, M.A.; D’Andrea ML, G.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, M.S.; Hernández, M.E.; Brannstrom, C.; Seghezzo, L. From indicators to policies: Open sustainability assessment in the water and sanitation sector. Sustainability 2015, 7, 14537–14557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mraz, A.L.; Tumwebaze, I.K.; McLoughlin, S.R.; McCarthy, M.E.; Verbyla, M.E.; Hofstra, N.; Rose, J.B.; Murphy, H.M. Why pathogens matter for meeting the united nations’ sustainable development goal on safely managed water and sanitation. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsdottir, M.J.; Gardarsson, S.M.; Elliott, M.; Sigmundsdottir, G.; Bartram, J. Benefits of water safety plans: Microbiology, compliance, and public health. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7782–7789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setty, K.E.; Kayser, G.L.; Bowling, M.; Enault, J.; Loret, J.F.; Serra, C.P.; Alonso, J.M.; Mateu, A.P.; Bartram, J. Water quality, compliance, and health outcomes among utilities implementing Water Safety Plans in France and Spain. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 513–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setty, K.E.; Bartram, J.; De Roos Anneclaire, J.; Beaudeau, P. Letter to the Editor: Water safety plans and risk assessment: A novel procedure applied to treated water turbidity and gastrointestinal diseases. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 229, 113435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muoio, R.; Caretti, C.; Rossi, L.; Santianni, D.; Lubello, C. Letter to the Editor: Water safety plans and risk assessment: A novel procedure applied to treated water turbidity and gastrointestinal diseases. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 229, 113455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannetti, B.F.; Sevegnani, F.; García, R.R.M.; Agostinho, F.; Almeida, C.M.V.B.; Coscieme, L.; Liu, G.; Lombardi, G.V. Enhancing the assessment of cleaner production practices for sustainable development: The five-sector sustainability model applied to water and wastewater treatment companies. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarnegaray, M.A.; Seghezzo, L. Governance, sustainability and decision making in water and sanitation management systems. Sustainability 2012, 4, 2922–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavijo, A.; Iribarnegaray, M.A.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, M.S.; Seghezzo, L. Closing the cycle? Potential and limitations of Water and Sanitation Safety Plans (WSSPs) for Latin American metropolitan areas. J. Water Sanitation Hyg. Dev. 2020, 10, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Data Used | Period | Systems | Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complaints | Number of complaints | 2011–2017 | Salta city/System No. 1/System No. 2 | MKT-PT |
| Turbidity | All available data | 2011–2017 | Salta city/System No. 1/System No. 2 | MKT-PT |
| Turbidity | Number of deviations (turbidities greater than 3 NTU) per month per year | 2011–2017 | Salta city/System No. 1/System No. 2 | MKT-PT |
| Chlorine | Amount of deviations (chlorine values less than 0.2 mg/L) per month per year | 2011–2017 | Salta city | MKT-PT |
| E. coli | All available data | 2011–2017 | Salta city | MKT-PT |
| Systems | Sub-Processes | Number of Hazardous Events in Each Sub-Process | Number of Control Measures in Each System |
|---|---|---|---|
| System No. 1 | Sub-surface catchment Surface catchment Transport Potabilization | 5 11 4 8 | 26 |
| System No. 2 | Sub-surface catchment Surface catchment Transport Potabilization | 9 7 8 7 | 25 |
| System No. 3 | Sub-surface catchment Transport Potabilization | 7 6 2 | 11 |
| System No. 4 | Groundwater catchment Potabilization | 9 5 | 18 |
| System No. 5 | Distribution | 10 | 20 |
| TOTAL | 14 sub-processes | 98 hazardous events | 100 control measures |
| Hazards (i) | Control Measures (j) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Recreational misuse | 1. Fence in the catchment area. | 50% | 100% | 47% | 7% |
| 2. Work in cooperation with the competent entity to establish access restrictions in the catchment areas. | 50% | 70% | |||
| 2. Domestic and livestock animals | 1. Agreeing on the regulation of livestock with the manager of the protected area. | 5% | 50% | 100% | 92% |
| 2. Housing of livestock in suitable areas. | 20% | 0% | |||
| 3. Fencing in of the catchment area. | 5% | 100% | |||
| 4. Construction of a new water-treatment plant. | 70% | 0% |
| System | Turbidity Data | Residual Chlorine Data | E. coli Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Available | >3 UNT | Available | <0.2 mg/L | Available | Presence of E. coli | |
| Salta city | 35,341 | 2247 | 35,577 | 786 | 34,831 | 145 |
| System No.1 | 1297 | 432 | 1320 | 40 | 1268 | 11 |
| System No.2 | 1085 | 203 | 1129 | 4 | 1060 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodriguez-Alvarez, M.S.; Gutiérrez-López, A.; Iribarnegaray, M.A.; Weir, M.H.; Seghezzo, L. Long-Term Assessment of a Water Safety Plan (WSP) in Salta, Argentina. Water 2022, 14, 2948. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14192948
Rodriguez-Alvarez MS, Gutiérrez-López A, Iribarnegaray MA, Weir MH, Seghezzo L. Long-Term Assessment of a Water Safety Plan (WSP) in Salta, Argentina. Water. 2022; 14(19):2948. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14192948
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodriguez-Alvarez, María Soledad, Aimé Gutiérrez-López, Martín Alejandro Iribarnegaray, Mark Howard Weir, and Lucas Seghezzo. 2022. "Long-Term Assessment of a Water Safety Plan (WSP) in Salta, Argentina" Water 14, no. 19: 2948. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14192948
APA StyleRodriguez-Alvarez, M. S., Gutiérrez-López, A., Iribarnegaray, M. A., Weir, M. H., & Seghezzo, L. (2022). Long-Term Assessment of a Water Safety Plan (WSP) in Salta, Argentina. Water, 14(19), 2948. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14192948





