Response of the Headcut Erosion Process to Flow Energy Variation in the Loess Gully Region of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
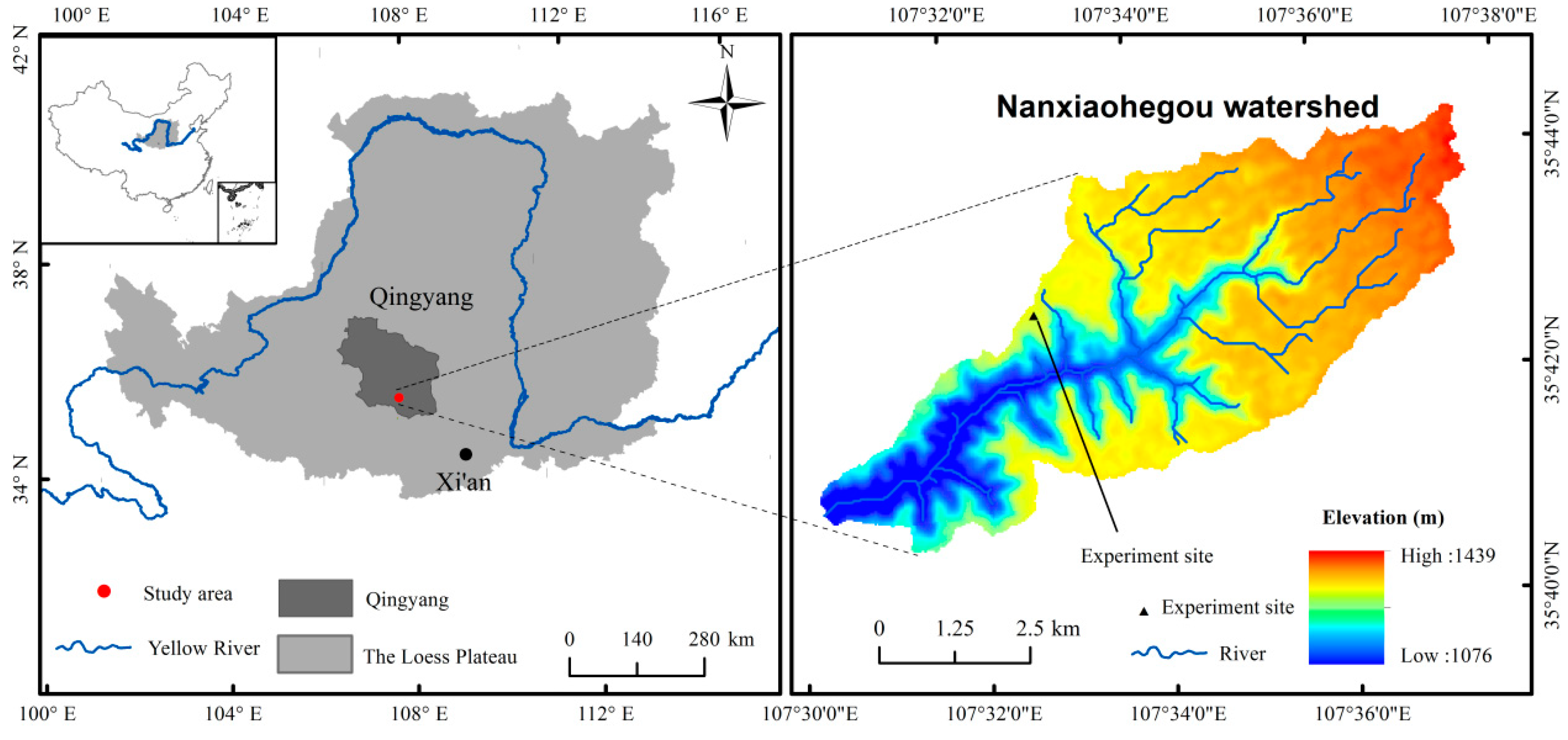
2.1. Study Area
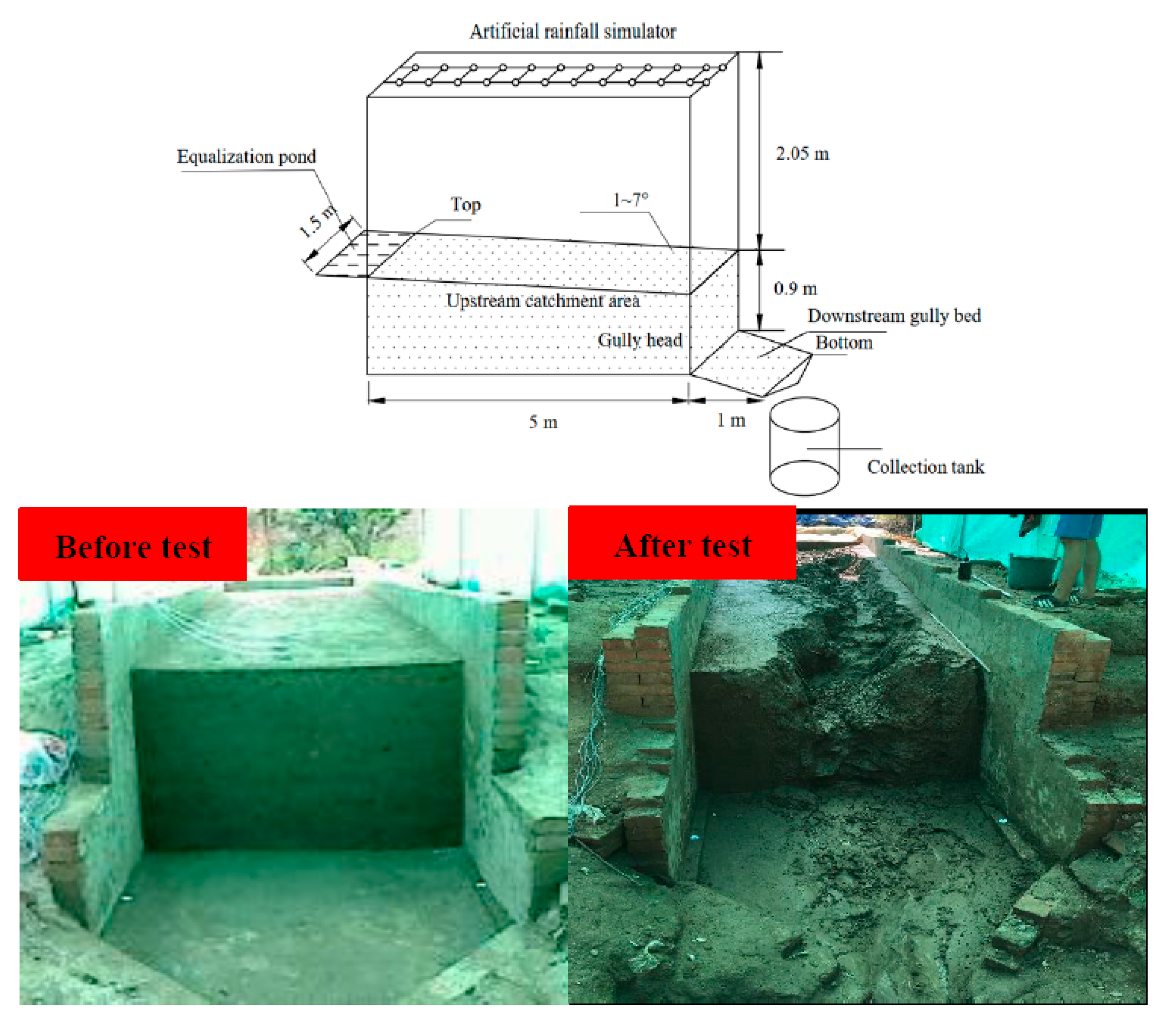
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.4. Parameter Calculation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Flow Energy Variation
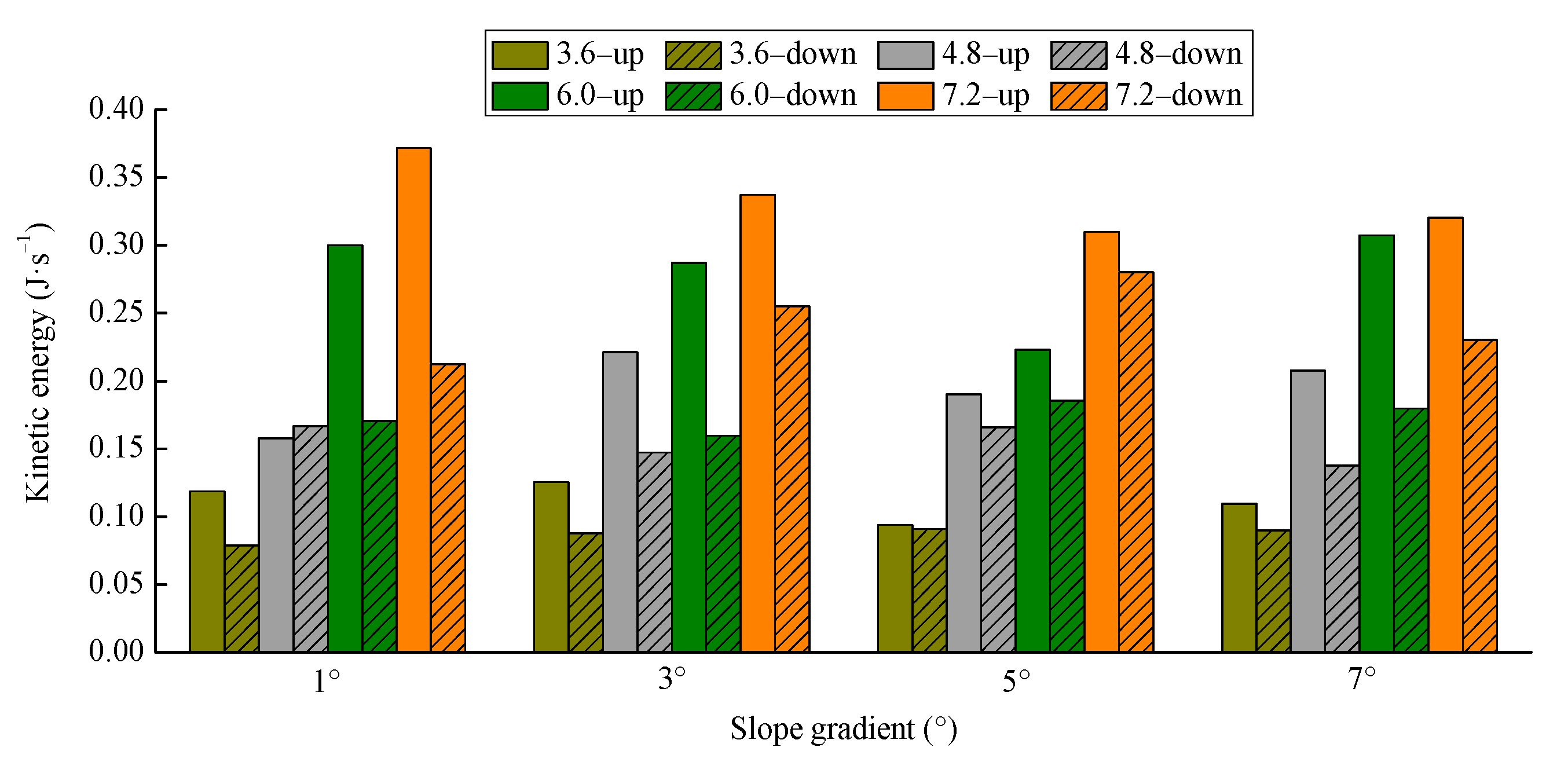
3.1.1. Changes in Kinetic Energy
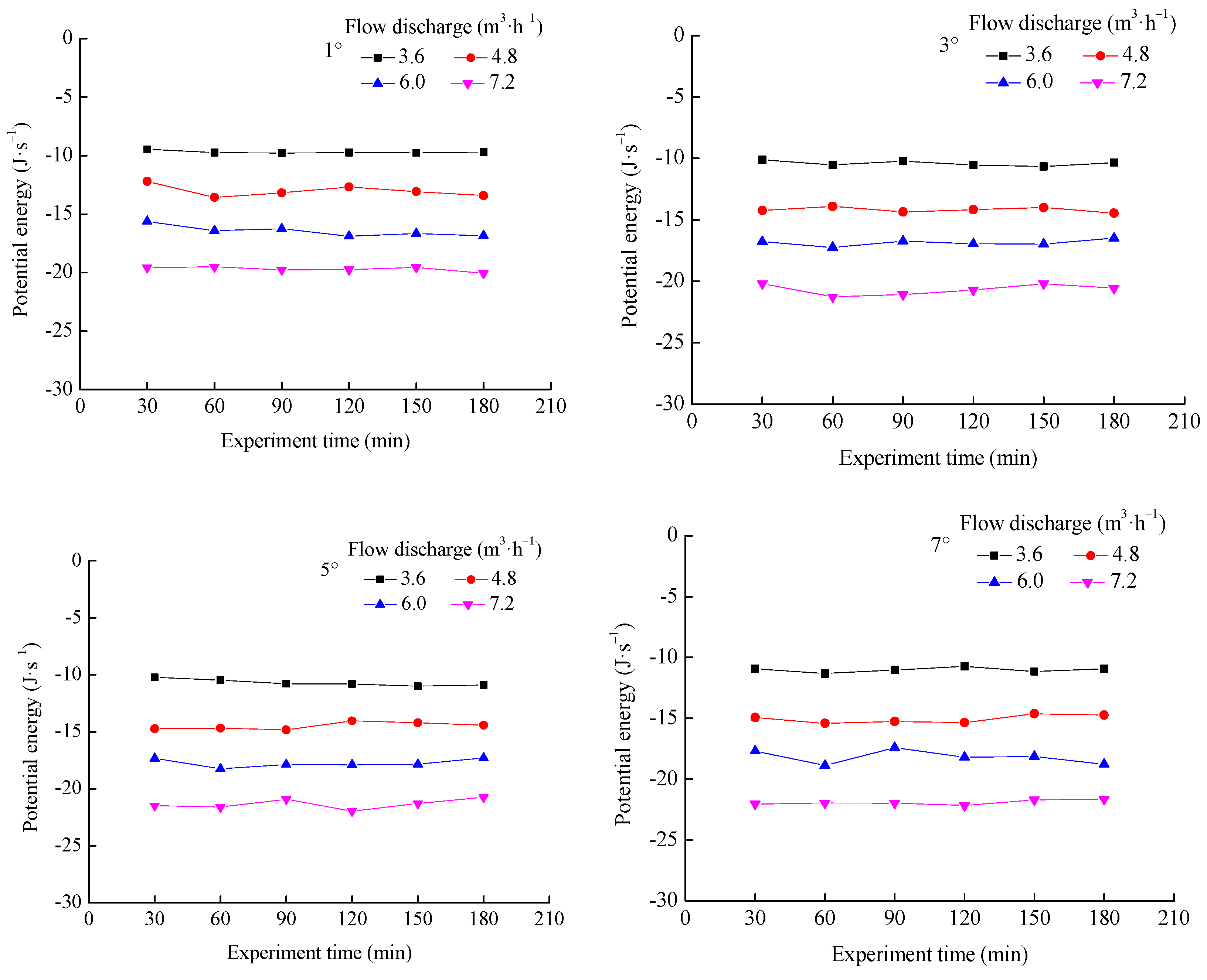
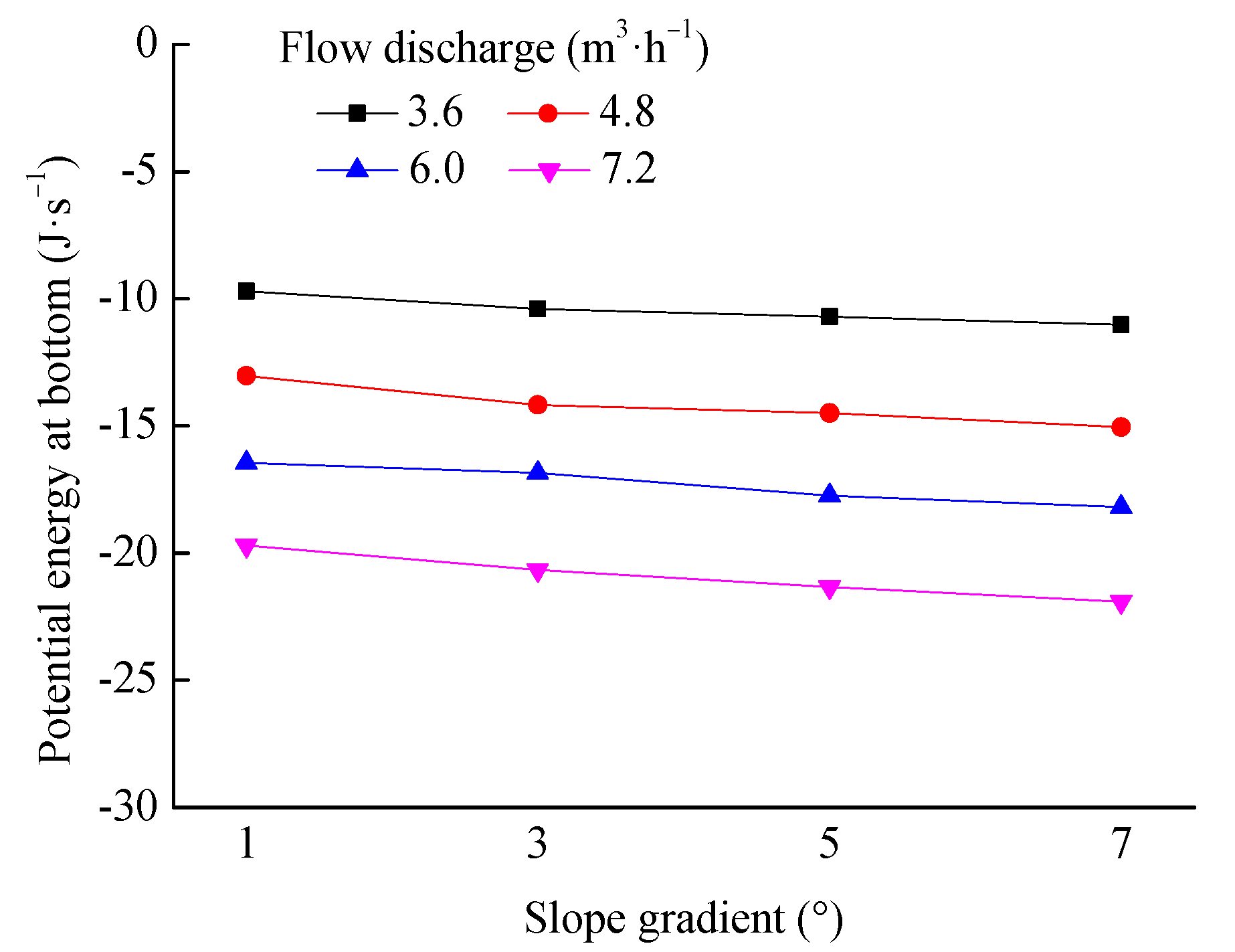
3.1.2. Changes in Potential Energy
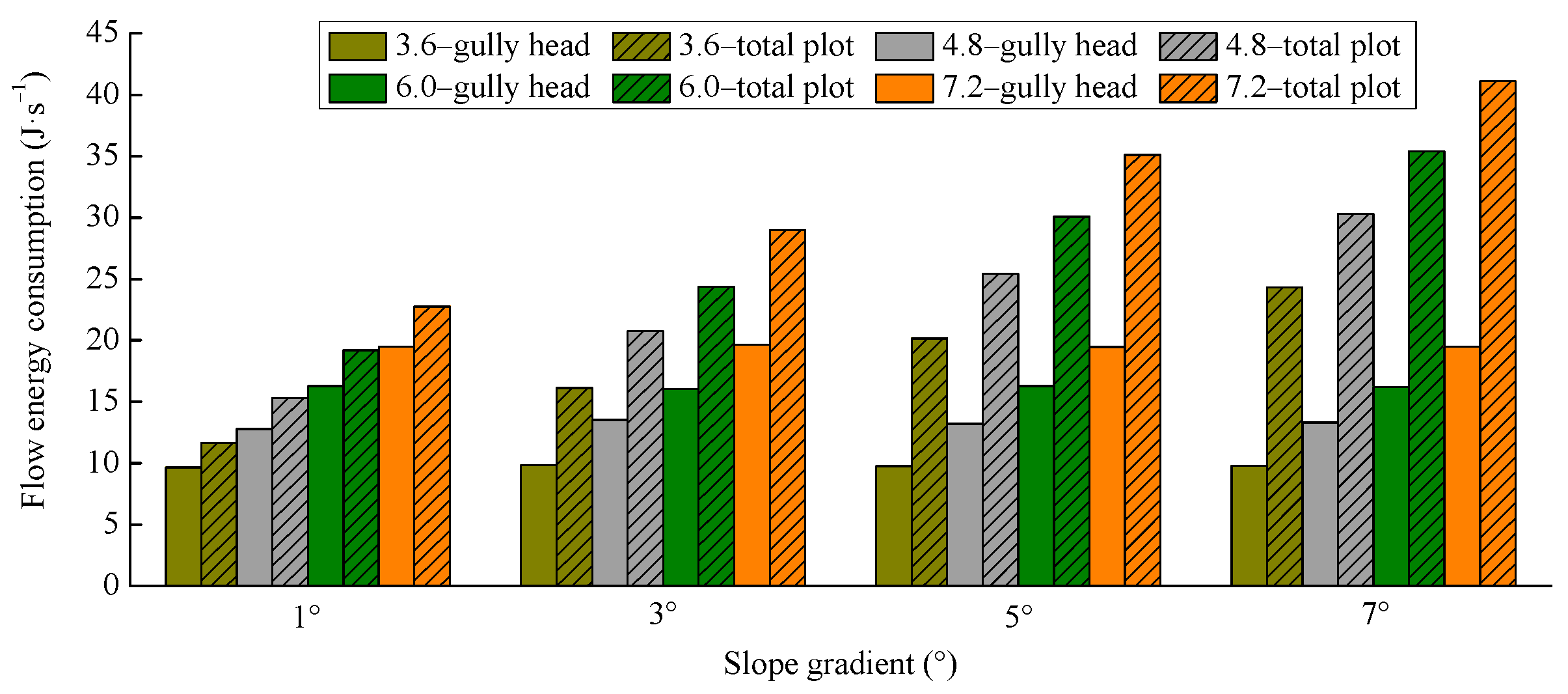
3.1.3. Changes in Flow Energy Consumption
3.2. Soil Loss Variation
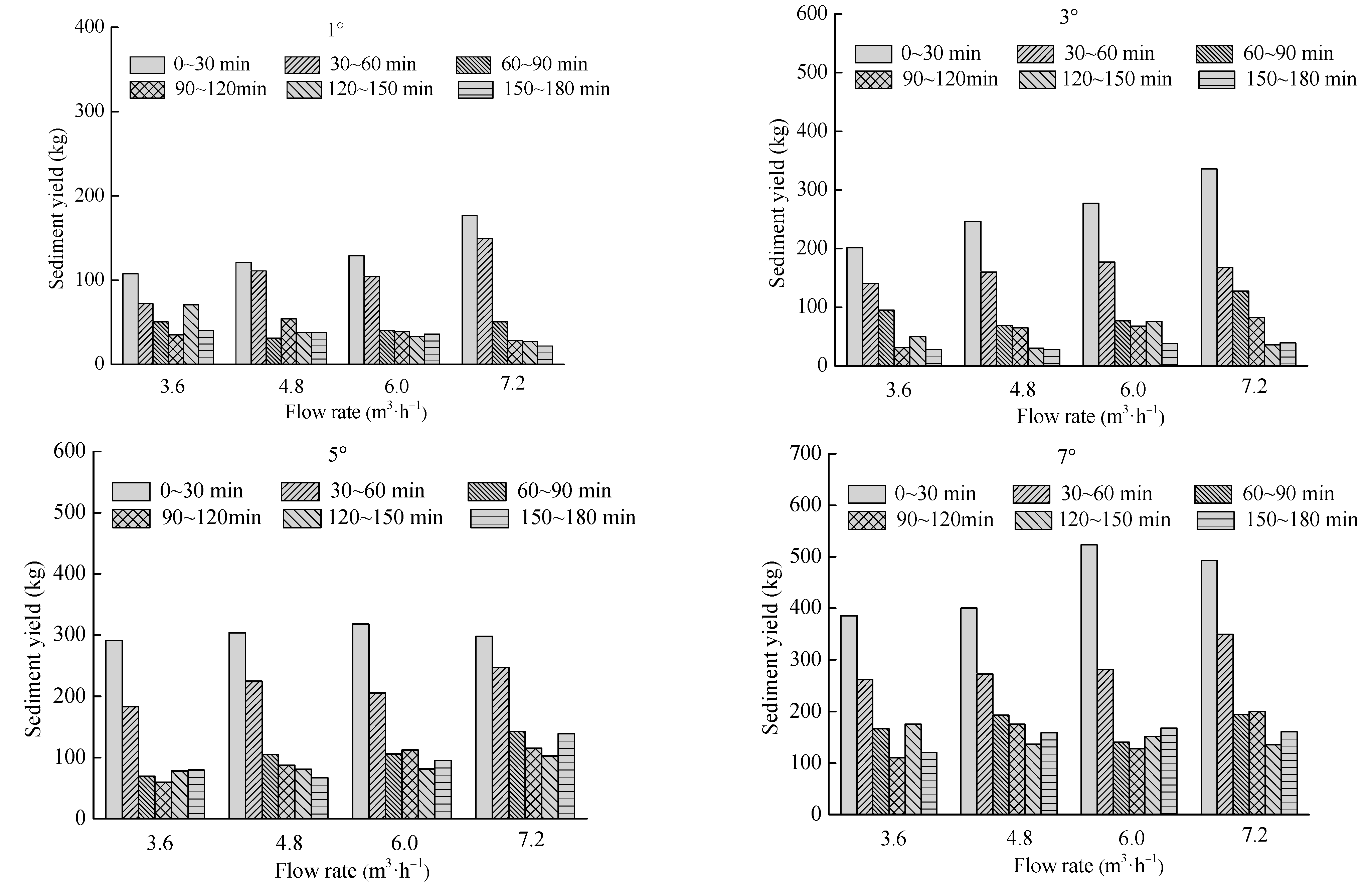
3.2.1. Temporal Variation in Sediment Yield
3.2.2. Impact of Slope Gradient and Inflow Discharge on Sediment Yield
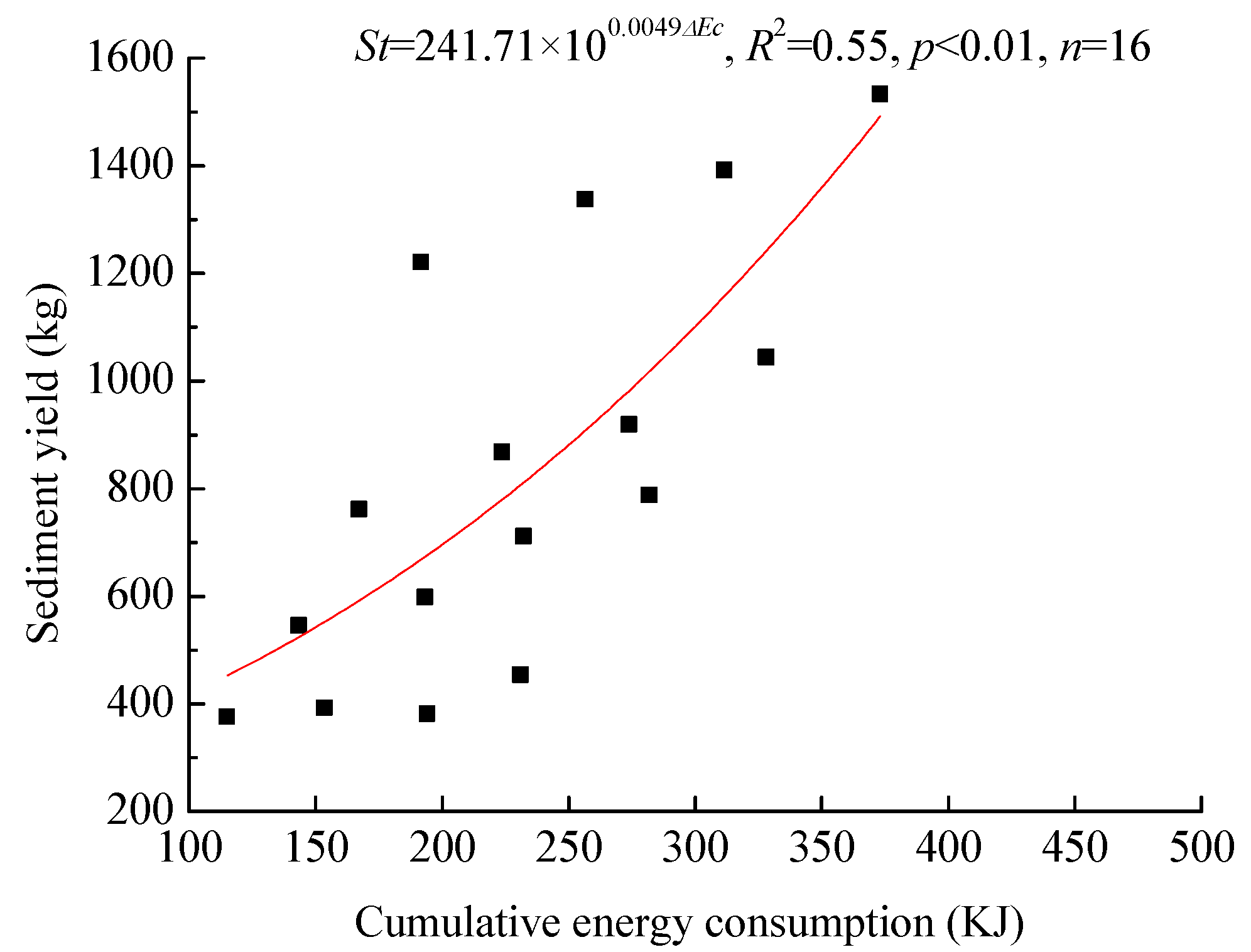
3.3. Response of Flow Energy Consumption to Sediment Yield
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Slope Gradient and Inflow Discharge on Flow Energy
4.2. Impact of Gully Head on Flow Energy
4.3. Response of Sediment Yield on Flow Energy Consumption
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, T.; Fukuda, H.; Hu, Q.N. Analysis on traditional gully village’s sustainable development methods in Gully Region of Loess Plateau. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 216, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhong, L.N.; Zhao, W.W.; Ying, L.X. The influence of rainfall and land use patterns on soil erosion in multi-scale watersheds: A case study in the hilly and gully area on the Loess Plateau, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, G.G.; Fan, H.H.; Ji, Q.Q.; Li, A.B.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Feng, B.Y.; Yu, Y.H.; Ma, L.; Gao, J.E. Erosion-transportation processes influenced by spatial distribution of terraces in watershed in the Loess hilly-gully region (LHGR), China. Water 2022, 14, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Lyu, J.Q.; Yuan, W.N.; Zhou, X.W.; Mo, S.H.; Mu, D.R.; Luo, P.P. Detecting the quantitative hydrological response to changes in climate and human activities at temporal and spatial scales in a typical gully region of the Loess Plateau, China. Water 2022, 14, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.F.; Kitamura, T.; Wang, S.S.Y. Numerical simulation of head-cut with a two-layered bed. Int. J. Sediment. Res. 2005, 20, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.H.; Wang, W.L.; Zhu, B.C.; Guo, M.M. Experimental study of hydraulic characteristics on headcut erosion and erosional response in the tableland and gully regions of China. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 700–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.R.; Li, F.Y.; Dai, Z.Y.; Yang, X.; Cui, X.J.; Luo, L.H. Spatial variation of gully development in the loess plateau of China based on the morphological perspective. Earth Sci. Inform. 2020, 13, 1103–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.J.; Alonso, C.V.; Prasad, S.N.; Romkens, M.J.M. Experiments on headcut growth and migration in concentrated flows typical of upland areas. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 1911–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.K.; Tsujimoto, T.; Kitamura, T. Experimental investigations on different modes of headcut migration. J. Hydraul. Res. 2007, 45, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaimes, G.N.; Schultz, R.C. Assessing riparian conservation land management practice impacts on gully erosion in Iowa. Environ. Manag. 2012, 49, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaimes, G.N.; Tufekcioglu, M.; Schultz, R.C. Riparian land-use impacts on stream bank and gully erosion in agricultural watersheds: What we have learned. Water 2019, 11, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.J.; Alonso, C.V. Turbulent flow and bed pressure within headcut scour holes due to plane reattached jets. J. Hydraul. Res. 2006, 44, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.J.; Xiong, D.H.; Zhang, G.H.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Yang, D.; Xiao, L.; Dong, Y.F.; Su, Z.A.; Lu, X.N. Impacts of headcut height on flow energy, sediment yield and surface landform during bank gully erosion processes in the Yuanmou Dry-hot Valley region, southwest China. Earth Surf. Proc. Land 2018, 43, 2271–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.R.; Momm, H.J.; Rigby, J.R.; Bennett, S.J.; Bingner, R.L.; Dabney, S.M. An empirical investigation of gully widening rates in upland concentrated flows. Catena 2013, 101, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.J. Effect of slope on the growth and migration of headcuts in rills. Geomorphology 1999, 30, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.J.; Casalí, J. Effect of initial step height on headcut development in upland concentrated flows. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, C.V.; Bennett, S.J.; Stein, O.R. Predicting head cut erosion and migration in concentrated flows typical of upland areas. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 39-1–39-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, L.M.; Bennett, S.J.; Bingner, R.L.; Theurer, F.D.; Alonso, C.V. Simulating ephemeral gully erosion in AnnAGNPS. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, L.M.; Bennett, S.J.; Wells, R.R.; Alonso, C.V. Effect of soil stratification on the development and migration of headcuts in upland concentrated flows. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.R.; Alonso, C.V.; Bennett, S.J. Morphodynamics of headcut development and soil erosion in upland concentrated flows. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, R.B.; Poesen, J. Laboratory experiments on the influence of slope length on runoff, percolation and rill development. Earth Surf. Proc. Land 2010, 14, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.J.; Wells, R.R. Gully erosion processes, disciplinary fragmentation, and technological innovation. Earth Surf. Proc. Land 2019, 44, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babazadeh, H.; Ashourian, M.; Shafai-Bajestan, M. Experimental study of headcut erosion in cohesive soils under different consolidation types and hydraulic parameters. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashourian, M.; Shafaei Bejestan, M.; Babazade, H. Investigation of headcut erosion in cohesive soils. Water Resour. 2018, 45, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.F.; Xiong, D.H.; Su, Z.A.; Li, J.J.; Yang, D.; Zhai, J.; Shi, L.T. Critical topographic threshold of gully erosion in Yuanmou dry-hot valley in southwestern China. Phys. Geogr. 2013, 34, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.F.; Xiong, D.H.; Su, Z.A.; Li, J.J.; Yang, D.; Shi, L.T.; Liu, G.C. The distribution of and factors influencing the vegetation in a gully in the dry-hot valley of southwest China. Catena 2014, 116, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.F.; Wu, Y.Q.; Qin, W.; Guo, Q.K.; Yin, Z.; Duan, X.W. The gully erosion rates in the black soil region of northeastern China: Induced by different processes and indicated by different indexes. Catena 2019, 182, 104146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.A.; Xiong, D.H.; Dong, Y.F.; Li, J.J.; Yang, D.; Zhang, J.H.; He, G.X. Simulated headward erosion of bank gullies in the dry-hot valley region of southwest China. Geomorphology 2014, 204, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.A.; Xiong, D.H.; Dong, Y.F.; Zhang, B.J.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, X.Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, J.H.; Fan, J.R.; Fang, H.D. Hydraulic properties of concentrated flow of a bank gully in the dry-hot valley region of southwest China. Earth Surf. Proc. Land 2015, 40, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.A.; Xiong, D.H.; Dong, Y.F.; Yang, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, B.J.; Zheng, X.Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Shi, L.T. Influence of bare soil and cultivated land use types upstream of a bank gully on soil erosion rates and energy consumption for different gully erosion zones in the dry-hot valley region, Southwest China. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, S183–S202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Xiong, D.H.; Guo, M.; Su, Z.A.; Zhang, B.J.; Zheng, X.Y.; Fang, H.D. Impact of grass belt position on the hydraulic properties of runoff in gully beds in the Yuanmou dry-hot valley region of southwest China. Phys. Geogr. 2015, 36, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.J.; Xiong, D.H.; Su, Z.A.; Yang, D.; Dong, Y.F.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, S.; Shi, L.T. Effects of initial step height on the headcut erosion of bank gullies: A case study using a 3D photo-reconstruction method in the dry-hot valley region of southwest China. Phys. Geogr. 2016, 37, 409–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Ni, J.R.; Li, T.H. Headcut and bank Landslip in rill evolution. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 2002, 10, 115–125. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, C.; Zheng, F.L.; Zhang, X.C.J.; Xu, X.M.; Liu, G. A simulation of rill bed incision processes in upland concentrated flows. Catena 2018, 165, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Zheng, F.L.; Wilsond, G.V.; Zhang, X.C.J.; Xu, X.M. Apportioning contributions of individual rill erosion processes and their interactions on loessial hillslopes. Catena 2019, 181, 104099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudi, H.; Theo, V.A. Modelling gully erosion for a small catchment on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Catena 2003, 54, 131–146. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Li, P.; Hou, J.M.; Li, Z.B.; Ren, Z.P.; Cheng, S.D.; Xu, G.C.; Su, Y.Y.; Wang, F.C. Response of the meltwater erosion to runoff energy consumption on loessal slopes. Water 2018, 10, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.B.; Lu, K.X.; Ding, W.F. Study on the dynamic process of rill erosion of loess slope surface. Int. J. Sediment. Res. 2001, 16, 308–314. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Yao, W.Y.; Chen, J.N.; Ding, W.F.; Yang, J.F.; Li, L.; Yang, C.X. Experimental study on changeable characteristics of runoff energy in hillslope-gully slope erosion system with different grass coverage. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2005, 19, 13–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Li, X.G.; Li, Z.B. Experimental study on variable characteristics of runoff energy in convex composite slopes of Loessial soil. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 28, 71–76. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Soil Erosion by Water: Some Measures for Its Control on Cultivated Lands; UNESCO: Rome, Italy, 1956; pp. 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Che, X.L. Study of Distribution Characteristic and Evolution of Headward Erosion on Dongzhi Tableland of the Loess Gully Region; Northwest A&F University: Xianyang, China, 2012. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.M.; Chen, Z.X.; Wang, W.L.; Wang, T.C.; Shi, Q.H.; Kang, H.L.; Zhao, M.; Feng, L.Q. Spatiotemporal changes in flow hydraulic characteristics and soil loss during gully headcut erosion under controlled conditions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 4473–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Song, X.Y.; Shen, B.; Li, H.Y.; Meng, C.X. Influence of vegetation change on producing runoff and sediment in gully region of Loess Plateau. J. Northwest Sci-Tech Univ. Agric. For. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2006, 34, 117–120. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.X. The characteristics of hard rain and its distribution over the Loess Plateau. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1983, 38, 416–425. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Q.H.; Peng, X.D.; Zhao, L.S.; Shao, H.B.; Yang, Z. Effects of underground pore fissures on soil erosion and sediment yield on karst slopes. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 1922–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govers, G. Relationship between discharge, velocity and flow area for rills eroding loose, non-layered materials. Earth Surf. Proc. Land 1992, 17, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.H.; Liu, B.Y.; Liu, G.B.; He, X.W.; Nearing, M.A. Detachment of undisturbed soil by shallow flow. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Li, F.H.; Zhang, J.; Lei, T.W.; Li, J.; Chen, P.; Wang, X.F. Velocity of water flow along saturated loess slopes under erosion effects. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiechefu, G.C. The impact of velocity fluctuations and hydraulic flow conditions in small channel headcut erosion. In ASABE Annual International Meeting, Montreal, Canada; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Carson, M.A.; Kirkby, M.J. Hillslope Form and Process; Cambridge Univ. Press: Cambridge, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, D.M.; Bryan, R.B. The relationship of soil loss by interrill erosion to slope gradient. Catena 2000, 38, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.D.; She, D.L.; Yu, S.E.; Shao, G.C.; Chen, D. Rainfall intensity and slope gradient effects on sediment losses and splash from a saline-sodic soil under coastal reclamation. Catena 2015, 128, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.H. Experimental Study of Hydrodynamic Processes and Gully Head Morphological Evolution in the LOESS Yuan; Northwest A&F University: Xianyang, China, 2022. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Q.; Wang, W.; Feng, L. Response of the Headcut Erosion Process to Flow Energy Variation in the Loess Gully Region of China. Water 2022, 14, 3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193038
Shi Q, Wang W, Feng L. Response of the Headcut Erosion Process to Flow Energy Variation in the Loess Gully Region of China. Water. 2022; 14(19):3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193038
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Qianhua, Wenlong Wang, and Lanqian Feng. 2022. "Response of the Headcut Erosion Process to Flow Energy Variation in the Loess Gully Region of China" Water 14, no. 19: 3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193038
APA StyleShi, Q., Wang, W., & Feng, L. (2022). Response of the Headcut Erosion Process to Flow Energy Variation in the Loess Gully Region of China. Water, 14(19), 3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193038





