Hydraulically Controlled Bottom Flow in the Orkney Passage
Abstract
1. Introduction
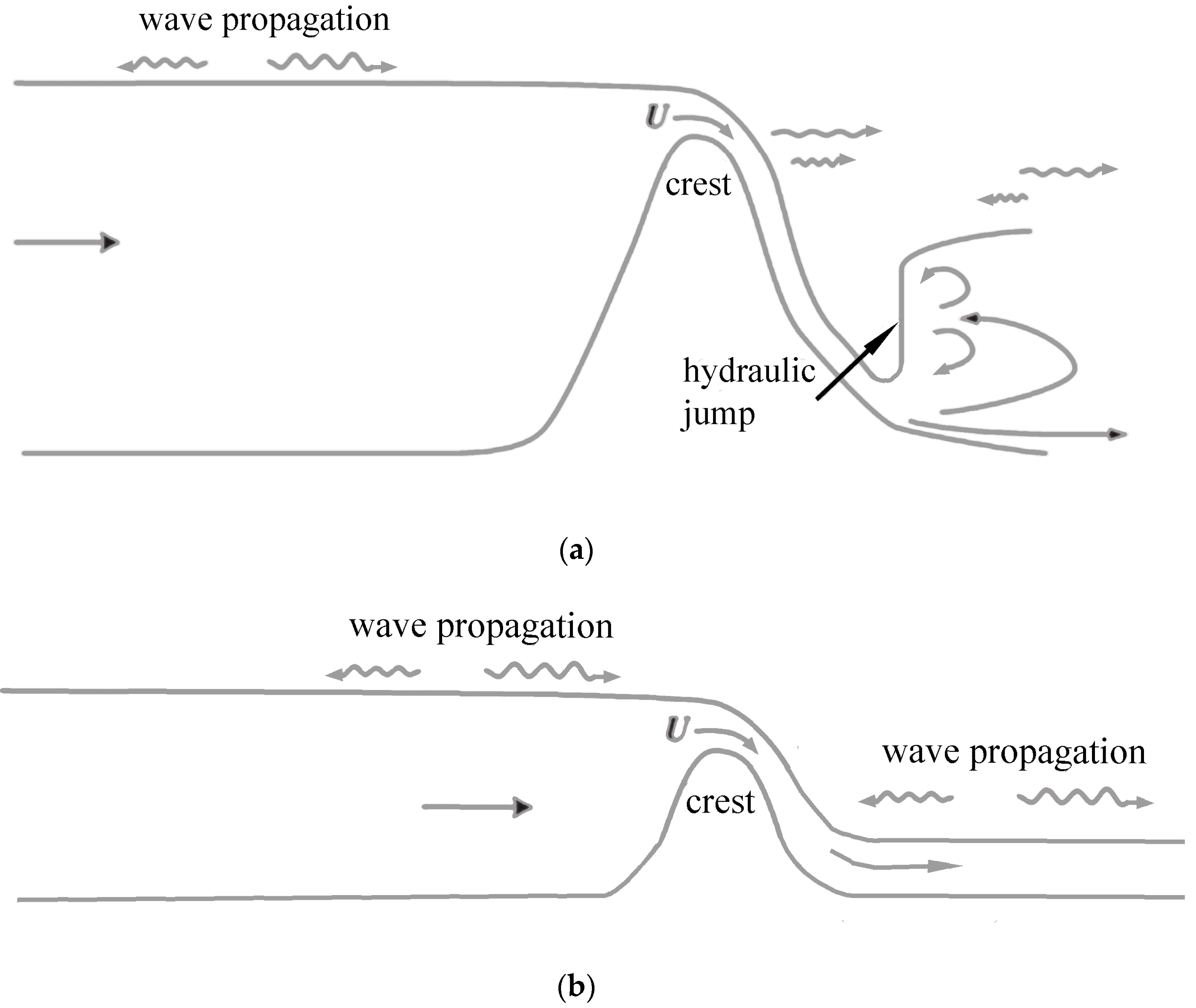
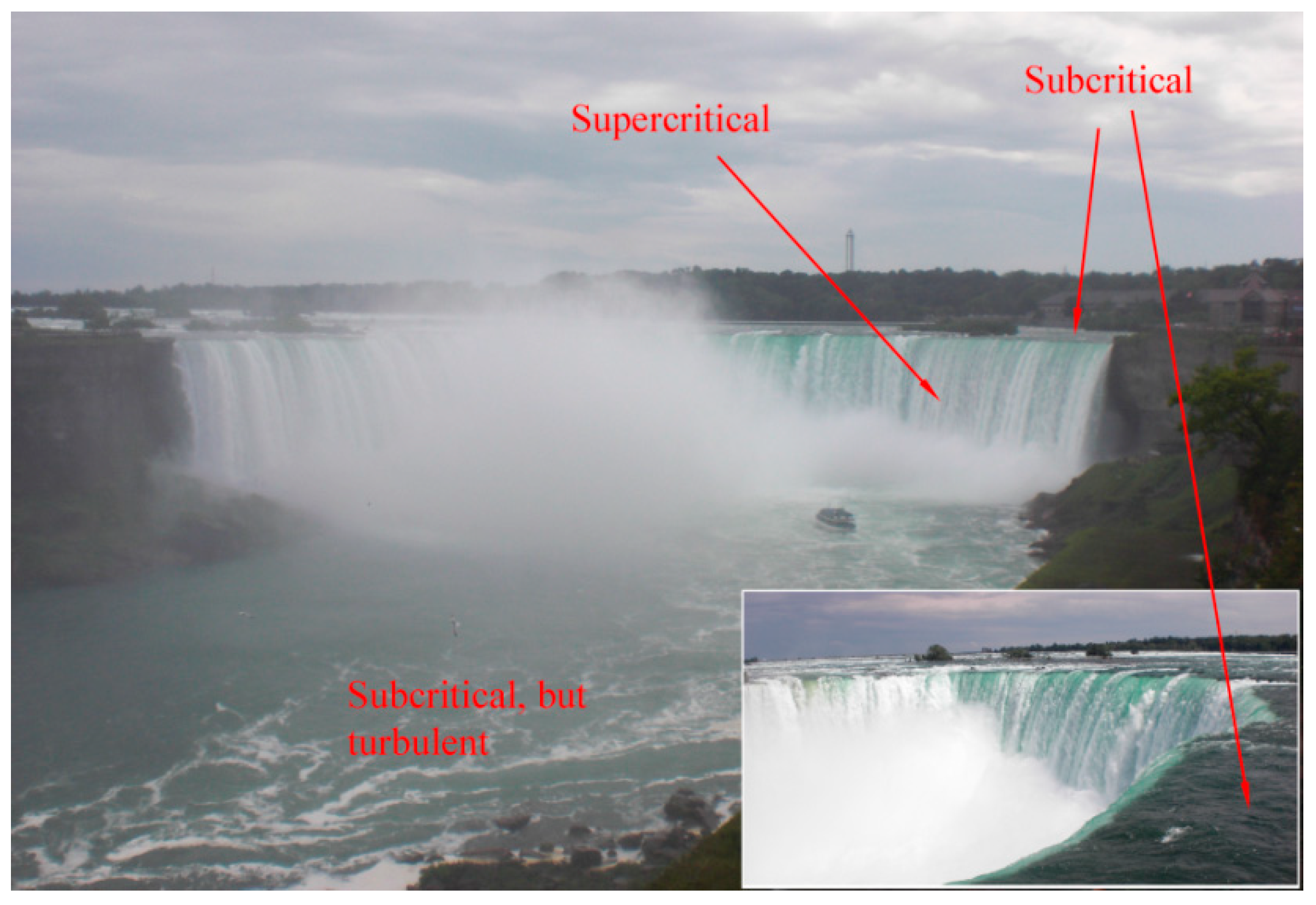
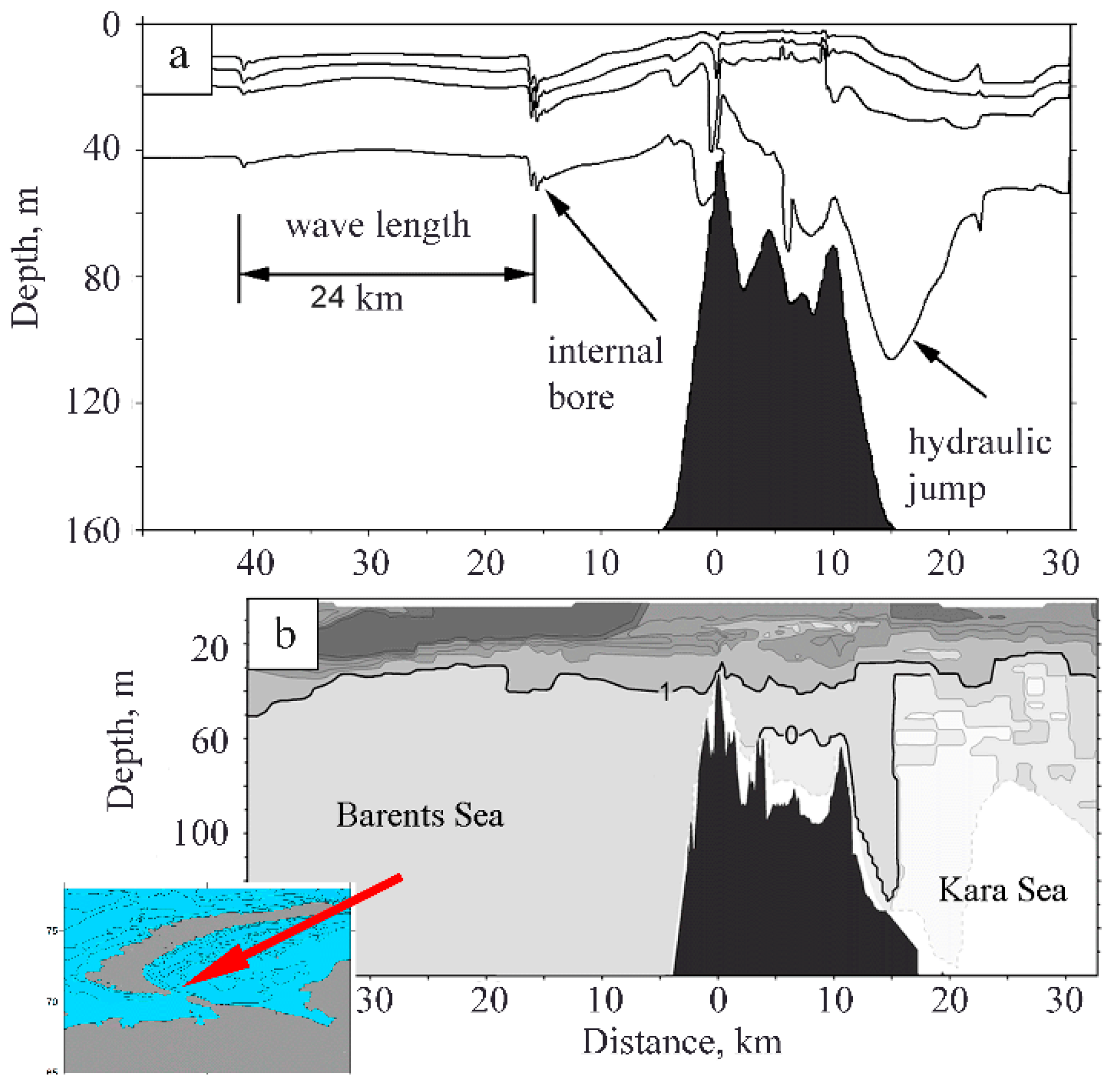
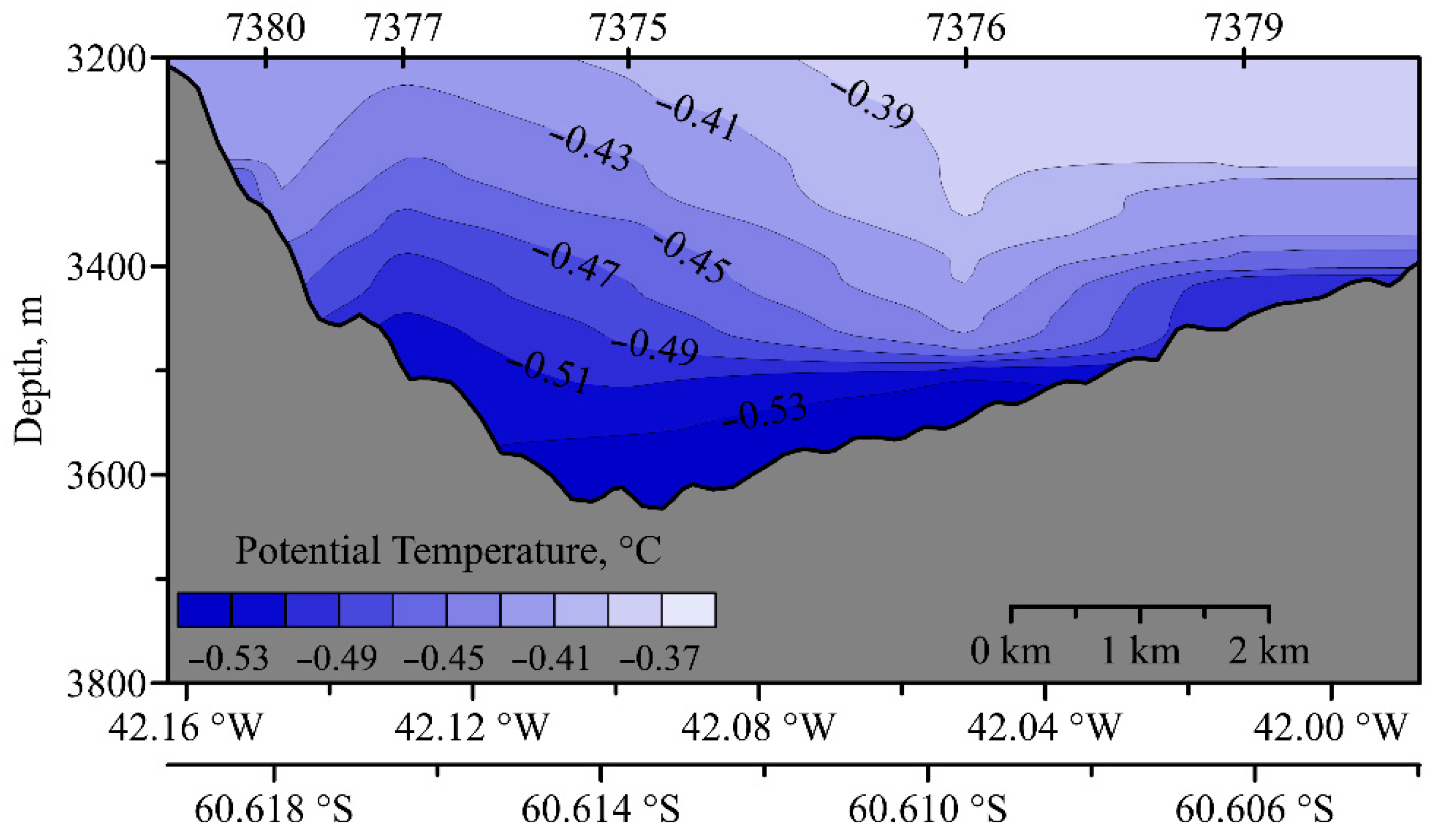
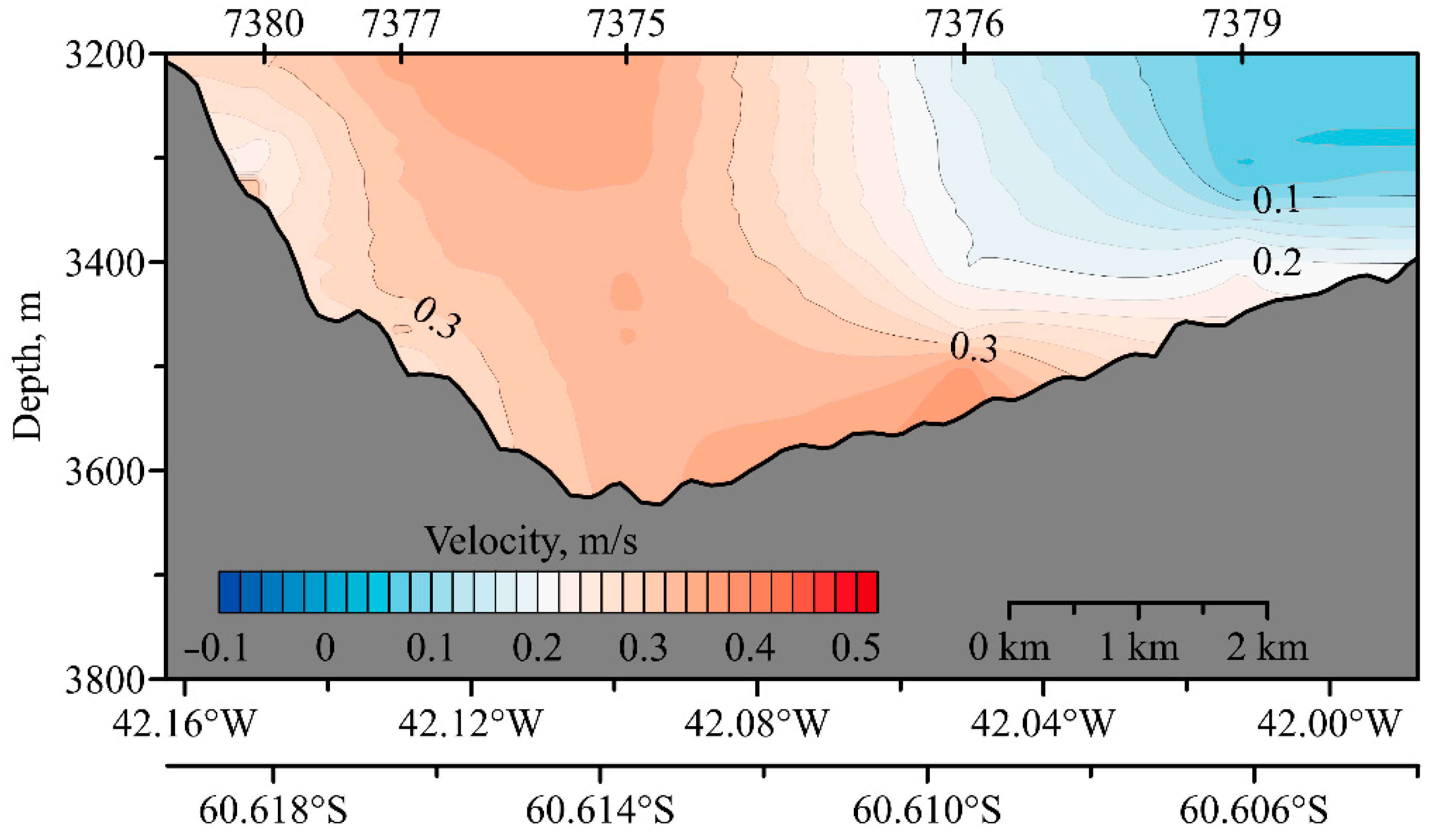
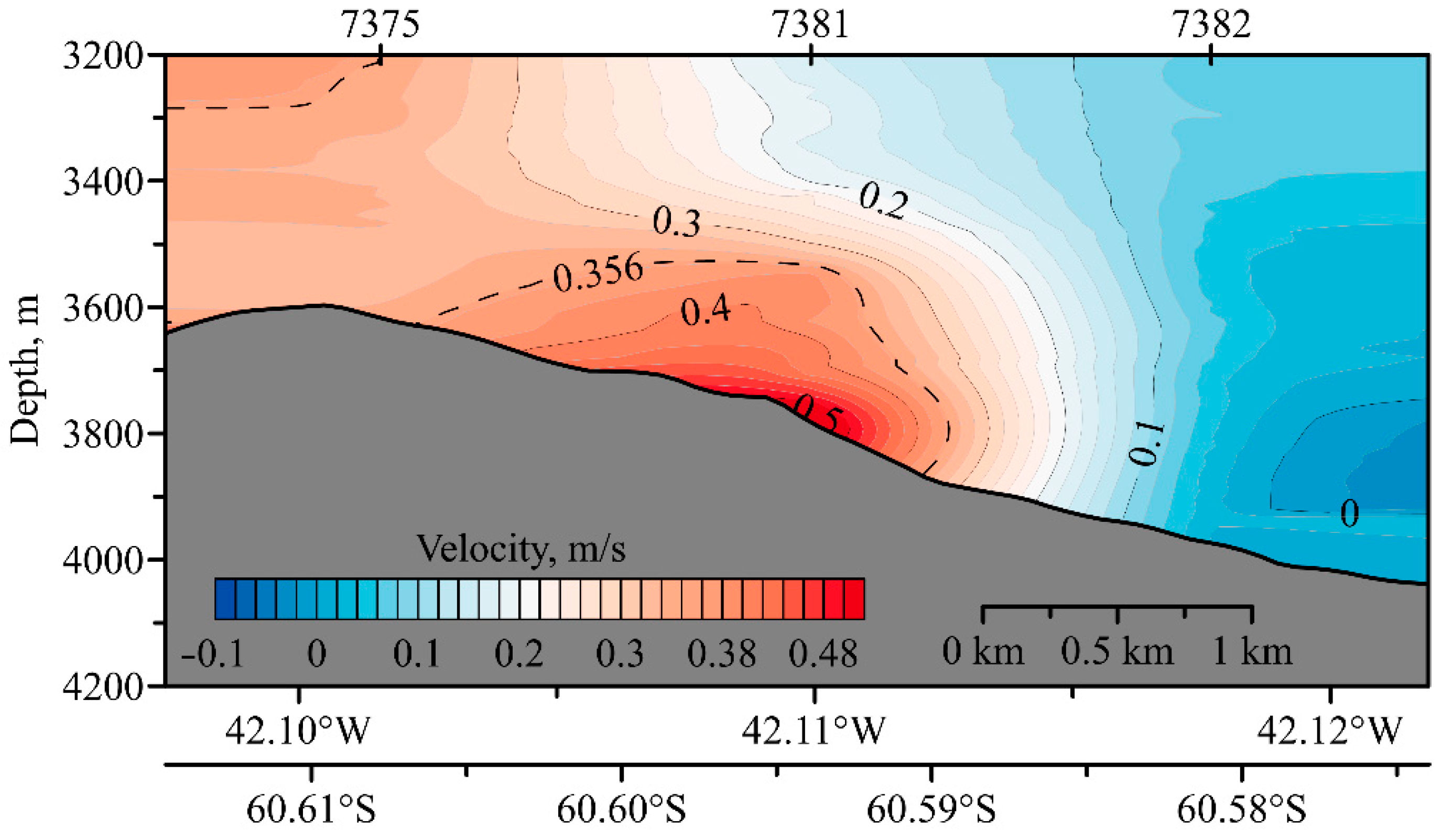
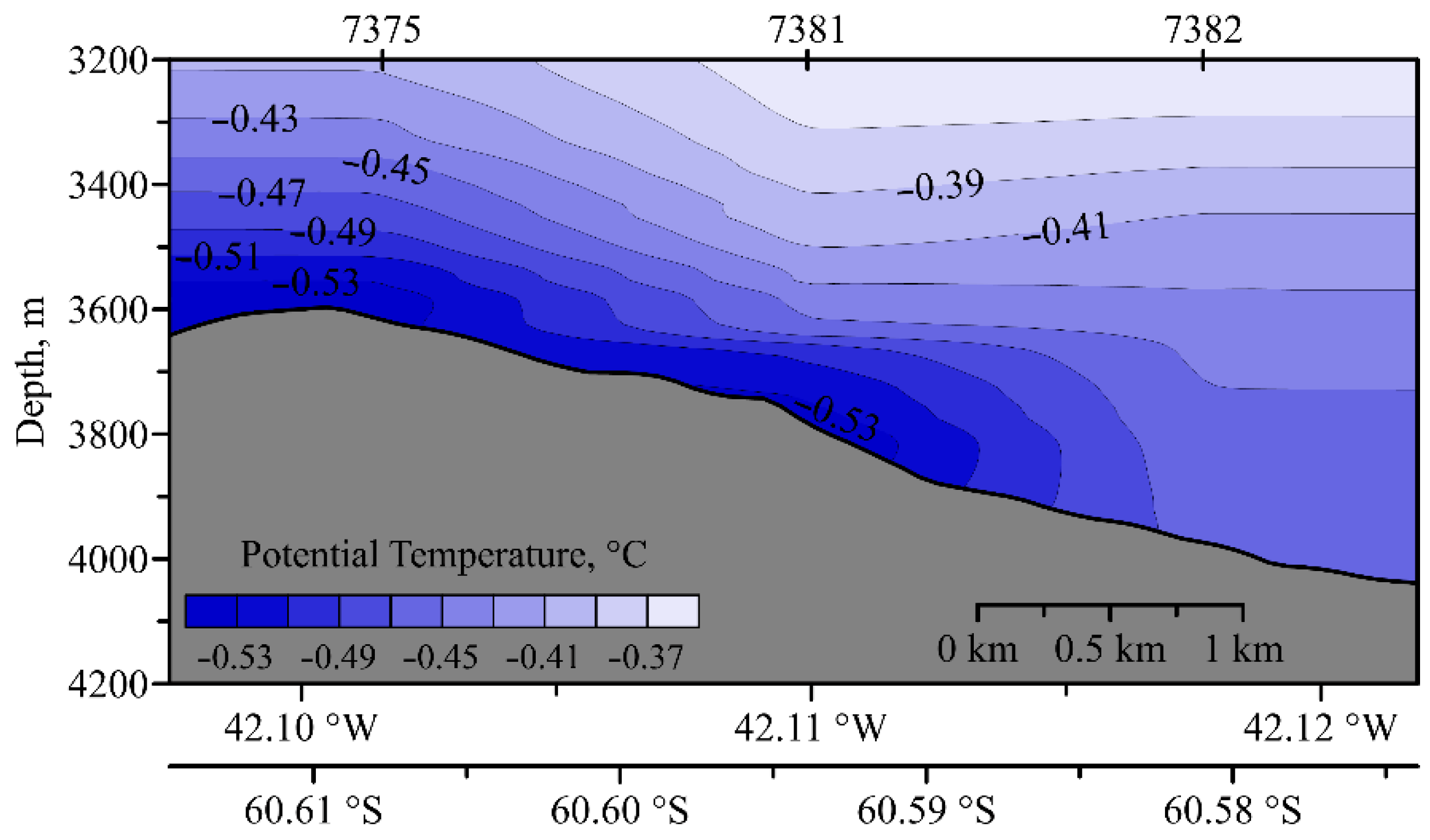
2. Hydraulic Control
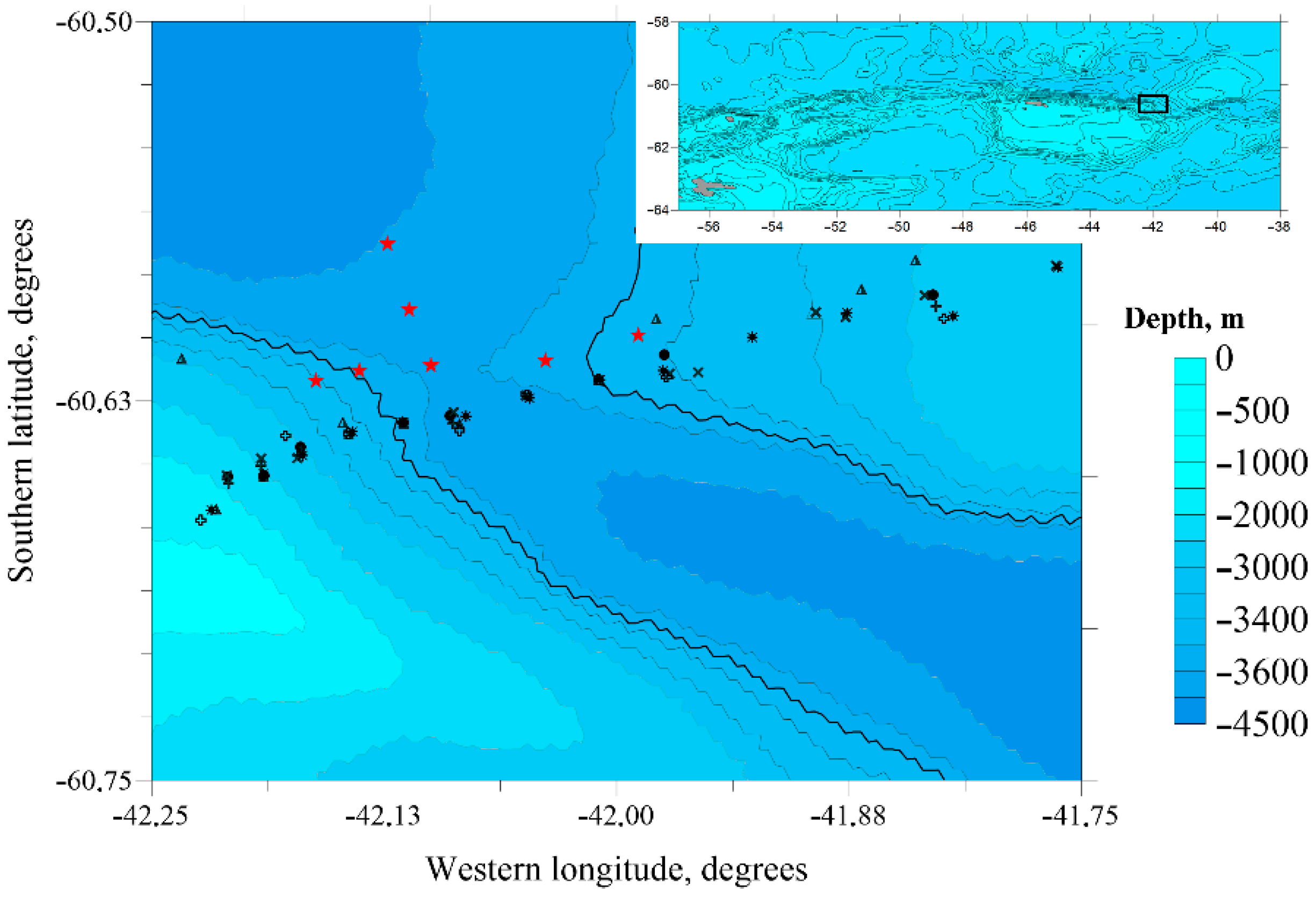
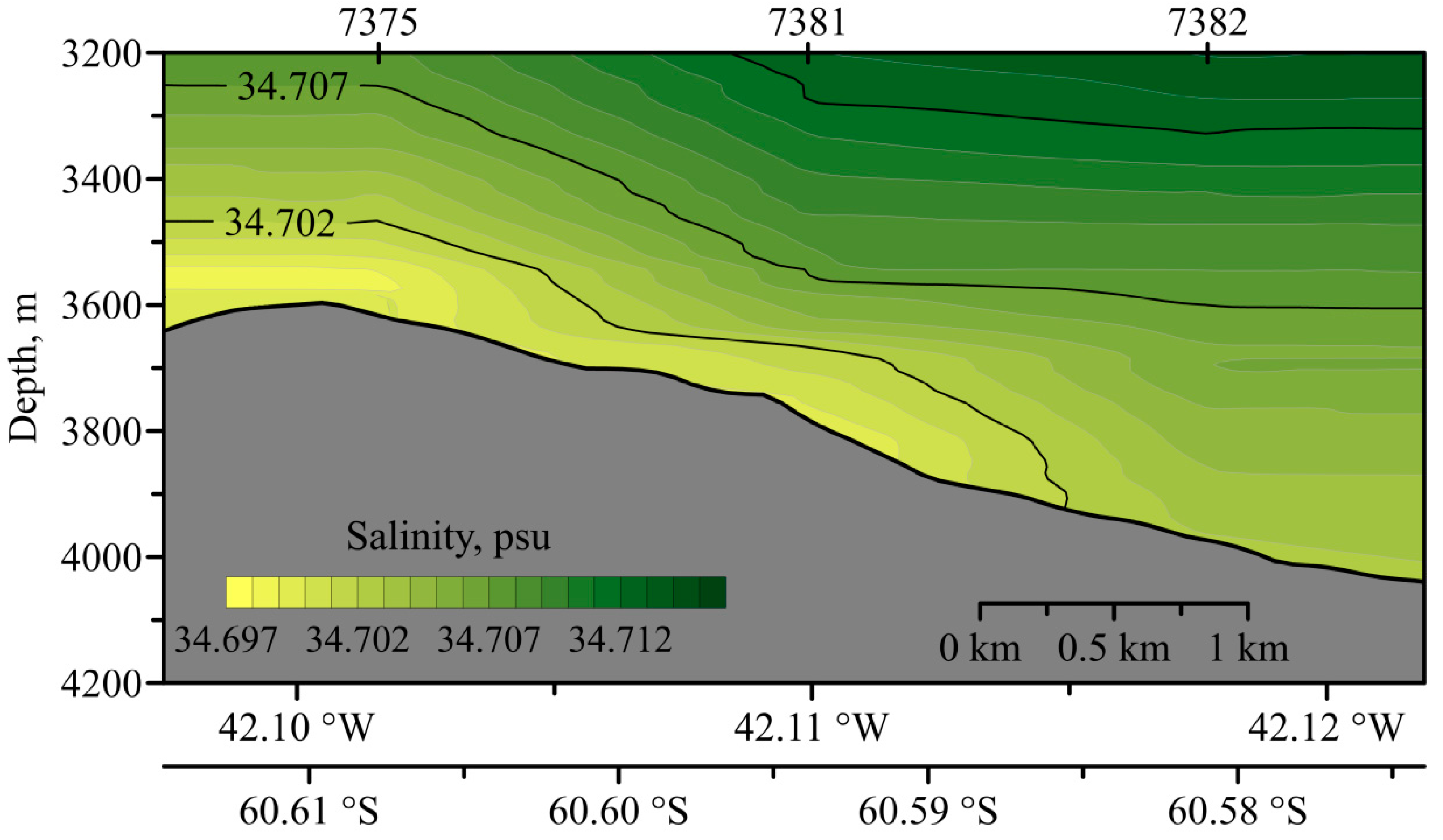
3. Data and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AABW | Antarctic bottom water |
| WSDW | Weddell Sea deep water |
| LADCP | Lowered acoustic Doppler current profiler |
| CTD | Conductivity, temperature, and depth profiler |
| Fr | Froude number |
| v | Meridional component of velocity |
| Reduced acceleration due to gravity | |
| H | Thickness of the flow |
| ρ = 1 g/cm3 | In situ density |
| g = 9.8 m s−1 | Acceleration due to gravity |
| Δρ | Density difference between layers |
References
- Vernet, M.; Geibert, W.; Hoppema, M.; Brown, P.J.; Haas, C.; Hellmer, H.H.; Jokat, W.; Jullion, L.; Mazloff, M.; Bakker, D.C.E.; et al. The Weddell Gyre, Southern Ocean: Present Knowledge and Future Challenges. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 623–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsen, E.P.; Meijers, A.J.S.; Polzin, K.L.; Garabato, A.C.N.; King, B.; Firing, Y.L.; Sallée, J.-B.; Sheen, K.L.; Gordon, A.L.; Huber, B.A.; et al. Stabilization of dense Antarctic water supply to the Atlantic Ocean overturning circulation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, M.P.; Gordon, A.L.; Garabato, A.C.N.; Abrahamsen, E.P.; Huber, B.A.; Jullion, L.; Venables, H.J. Synchronous intensification and warming of Antarctic Bottom Water outflow from the Weddell Gyre. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L03603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloyan, B.; Rintoul, S. The Southern Ocean Limb of the Global Deep Overturning Circulation*. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 143–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, A.H.; Johnson, G.C.; Bullister, J.L. Circulation, mixing and production of Antarctic Bottom Water. Prog. Oceanogr. 1999, 43, 55–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garabato, A.C.N.; McDonagh, E.L.; Stevens, D.P.; Heywood, K.J.; Sanders, R.J. On the export of Antarctic Bottom Water from the Weddell Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part II: Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2002, 49, 4715–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.L.; Visbeck, M.; Huber, B. Export of Weddell Sea deep and bottom water. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2001, 106, 9005–9017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, M.P.; Locarnini, R.A.; Van Scoy, K.A.; Watson, A.; Heywood, K.; King, B.A. On the sources of Weddell Gyre Antarctic Bottom Water. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2000, 105, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schodlok, M.P.; Hellmer, H.H.; Beckmann, A. On the transport, variability and origin of dense water masses crossing the South Scotia Ridge. Deep Sea Res. Part II: Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2002, 49, 4807–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, L.J.; Lundberg, P.A. Hydraulics of rotating strait and sill flow. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1991, 23, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, L.J.; Whitehead, J.A. Rotating Hydraulics: Nonlinear Topographic Effects in the Ocean and Atmosphere; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; p. 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, J.A.; Leetmaa, A.; Knox, R.A. Rotating hydraulics of strait and sill flows. Geophys. Fluid Dyn. 1974, 6, 101–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratantoni, D.M.; Zantopp, W.E.; Johns, E.; Miller, J.L. Updated bathymetry of the Anegada-Jungfern passage complex and implications for Atlantic inflow to the abyssal Caribbean Sea. J. Mar. Res. 1997, 55, 847–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armi, L.; Farmer, D.M. The flow of Mediterranean water through the Strait of Gibraltar. Prog. Oceanogr. 1988, 21, 1–105. [Google Scholar]
- Cenedese, C.; Whitehead, J.A.; Ascarelli, T.A.; Ohiwa, M. A Dense Current Flowing down a Sloping Bottom in a Rotating Fluid. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2004, 34, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenedese, C.; Adduce, C. A New Parameterization for Entrainment in Overflows. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2010, 40, 1835–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, E.G.; Frey, D.I.; Gladyshev, S.V.; Gladyshev, V.S. Hydrodynamics of the Bottom-Water Flow from the Arctic to the Atlantic through the Strait of Denmark. Izv. Atmospheric Ocean. Phys. 2020, 56, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fer, I.; Voet, G.; Seim, K.S.; Rudels, B.; Latarius, K. Intense mixing of the Faroe Bank Channel overflow. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L026042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, E.G.; Parrilla-Barrera, G.; Velarde, M.G.; Scherbinin, A.D. The Straits of Gibraltar and Kara Gates: A Comparison of internal tides. Oceanol. Acta 2003, 26, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, E.; Trulsen, K.; Velarde, M.G.; Vlasenko, V.I. Internal Tides in the Strait of Gibraltar. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2002, 32, 3193–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, E.G.; Paka, V.T.; Bakhanov, V.V. Strong internal tides in the Kara Gates Strait. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L16603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasenko, V.I. Nonlinear model for the generation of baroclinic tides over extensive inhomogeneities of bottom topography. Phys. Oceanogr. 1992, 3, 417–424. [Google Scholar]
- Visbeck, M. Deep Velocity Profiling Using Lowered Acoustic Doppler Current Profilers: Bottom Track and Inverse Solutions*. J. Atmospheric Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, E.G.; Tarakanov, R.Y.; Frey, D.I. Bottom Gravity Currents and Overflows in Deep Channels of the Atlantic. Observations, Analysis, and Modeling; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; 483p. [Google Scholar]
- Thurnherr, A.M.; Speer, K.G. Boundary Mixing and Topographic Blocking on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge in the South Atlantic*. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2003, 33, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurnherr, A.M.; Clément, L.; Laurent, L.S.; Ferrari, R.; Ijichi, T. Transformation and Upwelling of Bottom Water in Fracture Zone Valleys. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2020, 50, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morozov, E.G.; Frey, D.I.; Zuev, O.A.; Velarde, M.G.; Krechik, V.A.; Mukhametianov, R.Z. Hydraulically Controlled Bottom Flow in the Orkney Passage. Water 2022, 14, 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193088
Morozov EG, Frey DI, Zuev OA, Velarde MG, Krechik VA, Mukhametianov RZ. Hydraulically Controlled Bottom Flow in the Orkney Passage. Water. 2022; 14(19):3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193088
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorozov, Eugene G., Dmitry I. Frey, Oleg A. Zuev, Manuel G. Velarde, Viktor A. Krechik, and Rinat Z. Mukhametianov. 2022. "Hydraulically Controlled Bottom Flow in the Orkney Passage" Water 14, no. 19: 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193088
APA StyleMorozov, E. G., Frey, D. I., Zuev, O. A., Velarde, M. G., Krechik, V. A., & Mukhametianov, R. Z. (2022). Hydraulically Controlled Bottom Flow in the Orkney Passage. Water, 14(19), 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193088





