Quantitative Study of Climatic and Anthropogenic Contributions to Streamflow and Sediment Load in the Yangtze River, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
3. Methods
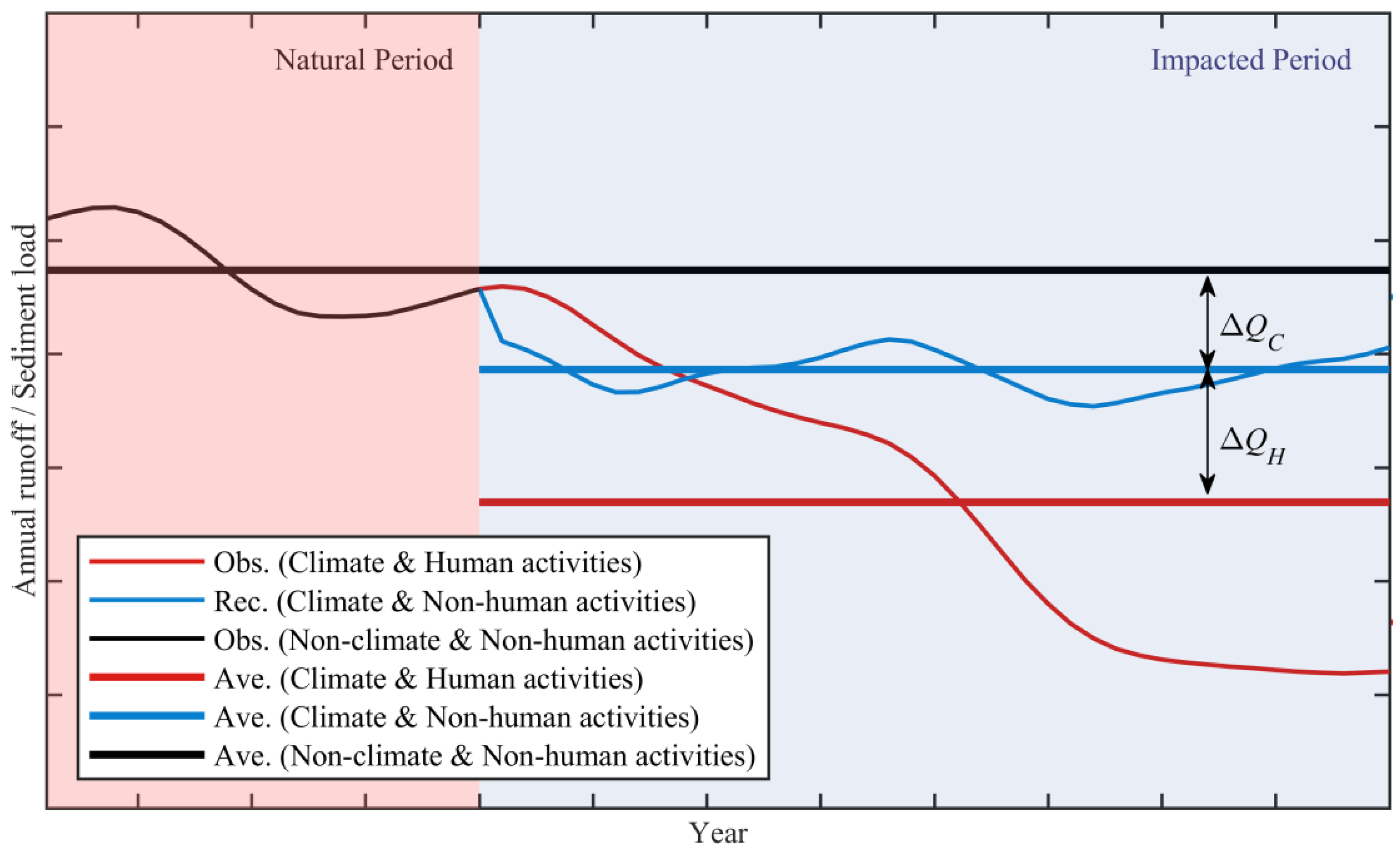
3.1. Division of Periods
3.2. Effects Assessment of Climate Change and Human Activities
3.3. Error Assessment of Regression-Based Predictions
4. Results
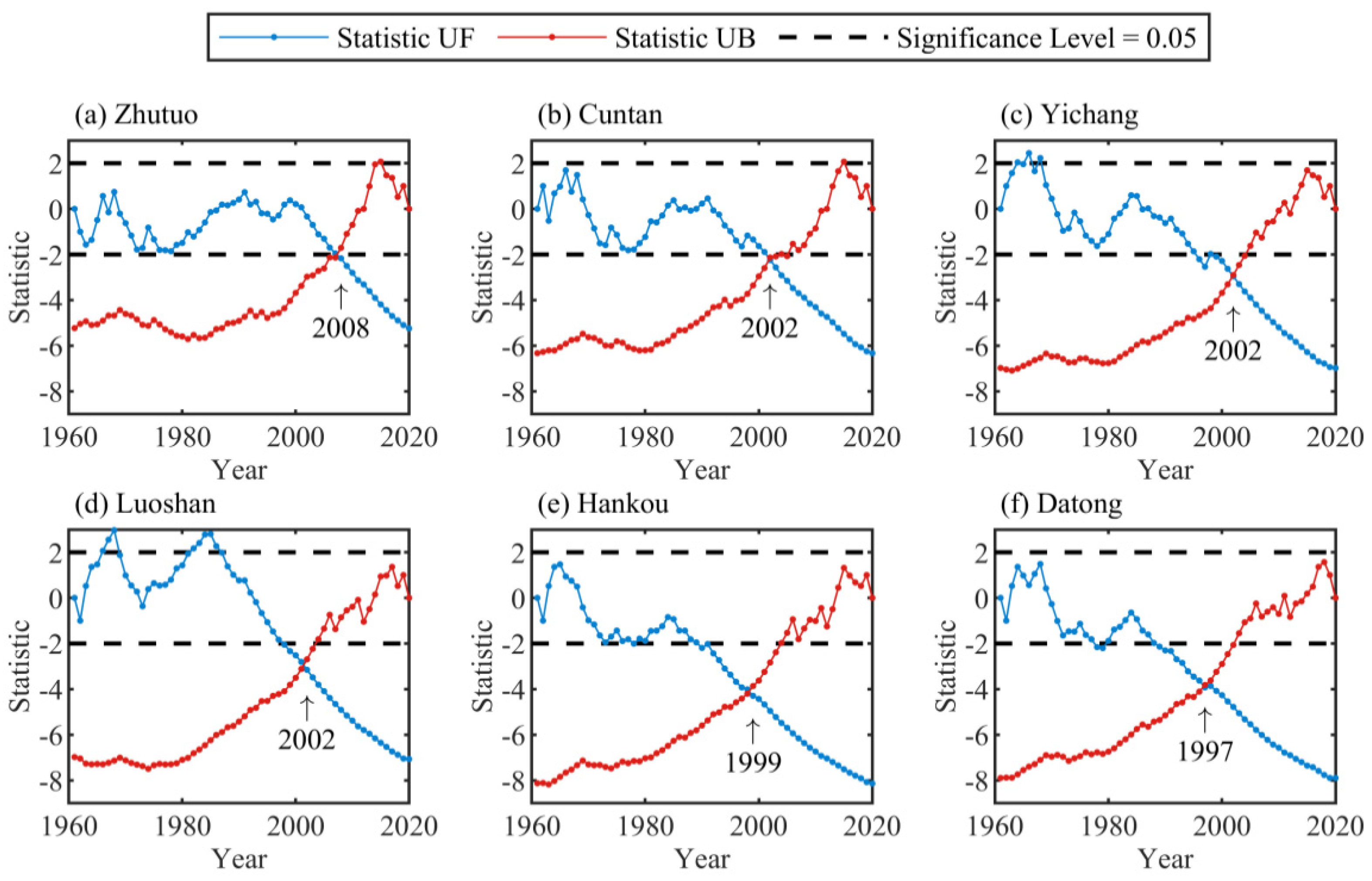
4.1. Periods Division by Abrupt Change Points
4.2. Changes in Annual Precipitation, Runoff, and Sediment Load
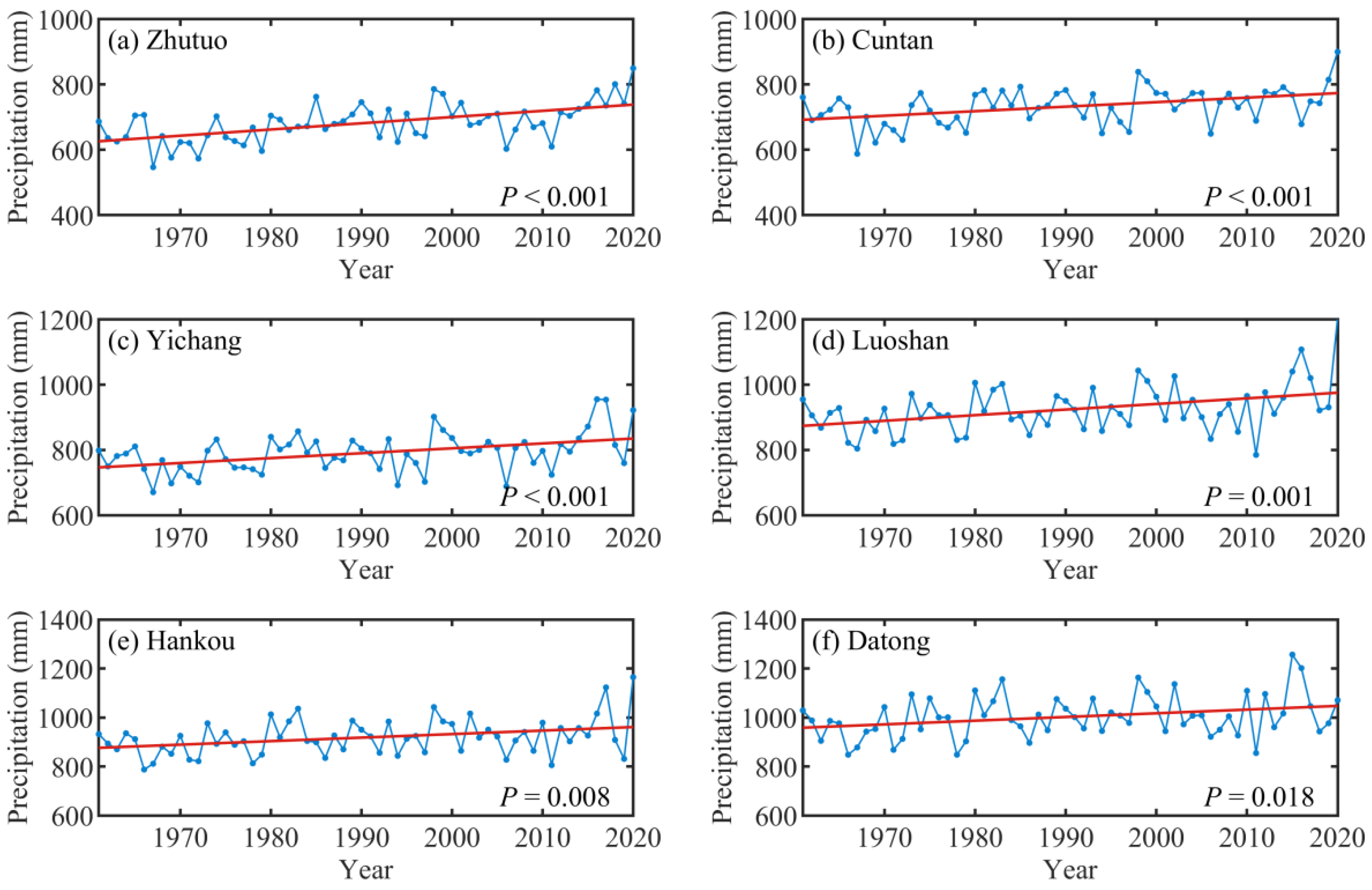
4.2.1. Variation Trend of Precipitation
4.2.2. Variation Trend of Runoff and Sediment Load
4.2.3. Relationships among Runoff, Sediment Load, and Precipitation
4.3. Quantitative Assessments of Climate Change and Human Activities
4.3.1. Effects of Climate Change and Human Activities on Runoff
4.3.2. Effects of Climate Change and Human Activities on Sediment Load
5. Discussion
5.1. Human Activities Involved in Runoff and Sediment Load Changes
5.2. Climate Change Involved in Runoff and Sediment Load
5.3. Evaluation of the Error of Regression Prediction
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iles, C.E.; Hegerl, G.C. Systematic change in global patterns of streamflow following volcanic eruptions. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Wang, F.; Tian, P.; Mu, X.-M.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G.-J.; Wu, Y.-P. Impact Assessment of Human Activities on Runoff and Sediment of Beiluo River in the Yellow River Based on Paired Years of Similar Climate. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.I.; Smerdon, J.E.; Seager, R.; Coats, S. Constraints on future changes in climate and the hydrologic cycle. Nature 2002, 419, 224. [Google Scholar]
- Salzmann, M. Global warming without global mean precipitation increase? Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Mu, X.; Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Gu, C. Impacts of Climate Variability and Human Activities on the Changes of Runoff and Sediment Load in a Catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 4724067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grams, P.E.; Schmidt, J.C.; Topping, D.J. The rate and pattern of bed incision and bank adjustment on the Colorado River in Glen Canyon downstream from Glen Canyon Dam, 1956–2000. GSA Bull. 2007, 119, 556–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Z.; Liu, J.T. Impacts of large dams on downstream fluvial sedimentation: An example of the Three Gorges Dam (TGD) on the Changjiang (Yangtze River). J. Hydrol. 2013, 480, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Guo, W. The variation and attribution analysis of the runoff and sediment in the lower reach of the Yellow River during the past 60 years. Water Supply 2021, 21, 3193–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaeda, T.; Rashid, H. The impacts of sediment released from dams on downstream sediment bar vegetation. J. Hydrol. 2012, 430–431, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Cai, S.; Ni, P.; Zhan, W. Impacts of climate change and human activities on the water discharge and sediment load of the Pearl River, southern China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Luo, X.; Temmerman, S.; Kirwan, M.; Bouma, T.; Xu, K.; Zhang, S.; Fan, J.; Shi, B.; Yang, H.; et al. Role of delta-front erosion in sustaining salt marshes under sea-level rise and fluvial sediment decline. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, 1990–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegel, R.L. Nile Delta Erosion. Science 1996, 272, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Chang, Y.; Dai, Z. Streamflow changes of the Changjiang (Yangtze) River in the recent 60 years: Impacts of the East Asian summer monsoon, ENSO, and human activities. Quat. Int. 2014, 336, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zou, X.; Gao, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Tang, D.; Wang, T.; Wu, X. Quantifying the anthropogenic and climatic contributions to changes in water discharge and sediment load into the sea: A case study of the Yangtze River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cui, B. Impacts of climate change/variability on the streamflow in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Qi, G.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, H.; Gao, X. Quantitative Assessment of the Contributions of Climate Change and Human Activities to Vegetation Variation in the Qinling Mountains. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 782287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Hessel, R.; Mu, X.; Maroulis, J.; Zhao, G.; Geissen, V.; Ritsema, C. Distinguishing the impacts of human activities and climate variability on runoff and sediment load change based on paired periods with similar weather conditions: A case in the Yan River, China. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Ni, J.; Borthwick, A.G.; Yang, L. A preliminary estimate of human and natural contributions to the changes in water discharge and sediment load in the Yellow River. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2011, 76, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, A.; Zhang, C.; Fu, G.; Wang, B.; Bao, Z.; Zheng, H. Assessments of Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Runoff with SWAT for the Huifa River Basin, Northeast China. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 2199–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Mu, X.; Jiao, J.; Gao, P.; Sun, W.; Li, E.; Wei, Y.; Huang, J. Assessing response of sediment load variation to climate change and human activities with six different approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhao, G.; Mu, X.; Tian, P.; Gao, P.; Sun, W. Quantifying the impacts of human activities on runoff and sediment load changes in a Loess Plateau catchment, China. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 3866–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Lü, H.; Sadeghi, A.M.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Ouyang, F.; Su, J.; Chen, R. Assessment on the Effect of Climate Change on Streamflow in the Source Region of the Yangtze River, China. Water 2017, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Zhu, C.; Wu, L.; Huang, L. Problems caused by the Three Gorges Dam construction in the Yangtze River basin: A review. Environ. Rev. 2013, 21, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Q. Variation of runoff and sediment inflows to the Three Gorges Reservoir: Impact of upstream cascade reservoirs. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. Impacts of Three Gorges Reservoir on the sedimentation regimes in the downstream-linked two largest Chinese freshwater lakes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Deng, J.; Chai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Li, S. Variation of the Water Level in the Yangtze River in Response to Natural and Anthropogenic Changes. Water 2019, 11, 2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Mei, X.; Dai, Z.; Gao, J.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Lou, Y. Hydromorphological processes of Dongting Lake in China between 1951 and 2014. J. Hydrol. 2018, 562, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.-C.; Zhang, X.-F.; Xu, Q.-X. Unprecedented sedimentation in response to emerging cascade reservoirs in the upper Yangtze River Basin. Catena 2022, 209, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Fagherazzi, S.; Mei, X.; Gao, J. Decline in suspended sediment concentration delivered by the Changjiang (Yangtze) River into the East China Sea between 1956 and 2013. Geomorphology 2016, 268, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Z.; Chu, A.; Stive, M.; Du, J.; Li, J. Is the Three Gorges Dam the cause behind the extremely low suspended sediment discharge into the Yangtze (Changjiang) Estuary of 2006? Hydrol. Sci. J. 2011, 56, 1280–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, S.L. Climatic and anthropogenic impacts on water discharge in the Yangtze river over the last 56 years (1956–2011). Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2014, 23, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Lu, X. Sediment load change in the Yangtze River (Changjiang): A review. Geomorphology 2014, 215, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.L.; Guo, J.L.; Hou, Y.K.; Xiong, L.H.; Hong, X.J. Prediction of future runoff change based on Budyko hypothesis in Yangtze River Basin. Adv. Water Sci. 2015, 26, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Singh, V.P.; Gu, X.; Chen, X. Evaluation of impacts of climate change and human activities on streamflow in the Poyang Lake basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 2562–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Dai, Z.; Wei, W.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Sheng, H. Secular bathymetric variations of the North Channel in the Changjiang (Yangtze) Estuary, China, 1880–2013: Causes and effects. Geomorphology 2017, 303, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Milliman, J.; Xu, K.; Deng, B.; Zhang, X.; Luo, X. Downstream sedimentary and geomorphic impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 138, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, S.; Xu, K.; Milliman, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, C. Human impacts on sediment in the Yangtze River: A review and new perspectives. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2018, 162, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Milliman, J.D.; Yang, Z.; Xu, H. Climatic and Anthropogenic Impacts on Water and Sediment Discharges from the Yangtze River (Changjiang), 1950–2005. In Large Rivers: Geomorphology and Management; John Wiley Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Du, J.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Chen, J. Runoff characteristics of the Changjiang River during 2006: Effect of extreme drought and the impounding of the Three Gorges Dam. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, L.; Liu, W.; Han, J.; Yang, Y. Influence of Large Reservoir Operation on Water-Levels and Flows in Reaches below Dam: Case Study of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mei, X.; Dai, Z.; van Gelder, P.H.A.J.M.; Gao, J. Linking Three Gorges Dam and downstream hydrological regimes along the Yangtze River, China. Earth Space Sci. 2015, 2, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Xu, K.; Milliman, J.D.; Yang, H.F.; Wu, C.S. Decline of Yangtze River water and sediment discharge: Impact from natural and anthropogenic changes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, J. Spatial patterns of scale effect on specific sediment yield in the Yangtze River basin. Geomorphology 2011, 130, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Singh, V.P.; Xu, C.-Y. Copula-based spatio-temporal patterns of precipitation extremes in China. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Fu, G.; He, R.; Yan, X.; Jin, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, A. Attribution for decreasing streamflow of the Haihe River basin, northern China: Climate variability or human activities? J. Hydrol. 2012, 460–461, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zeng, G.; Liang, J.; Huang, L.; Hua, S.; Li, F.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; He, X.; et al. Variation of water level in Dongting Lake over a 50-year period: Implications for the impacts of anthropogenic and climatic factors. J. Hydrol. 2015, 525, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, M.J.; Wüest, A.; Wehrli, B.; Landert, J.; Senn, D. Impact of a large tropical reservoir on riverine transport of sediment, carbon, and nutrients to downstream wetlands. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W12531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, K.; Milliman, J.D.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H. Yangtze sediment decline partly from Three Gorges Dam. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2006, 87, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Wang, S.; Fan, X. Channel change at Toudaoguai Station and its responses to the operation of upstream reservoirs in the upper Yellow River. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.Y. Review and prospect of 60-year soil and water conservation in Yangtze River Basin. Yangtze River 2010, 41, 26–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, L.; Zeng, C.; Wang, D.; Liu, D.; Wu, X. Variations of Runoff and Sediment Load in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River, China (1950-2013). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Milliman, J.; Li, P.; Xu, K. 50,000 dams later: Erosion of the Yangtze River and its delta. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2011, 75, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Smith, J.P.; Dai, S.; Gao, A.; Li, P. Impact of dams on Yangtze River sediment supply to the sea and delta intertidal wetland response. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2005, 110, F03006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Relationship between Waterway Depth and Low-Flow Water Levels in Reaches below the Three Gorges Dam. J. Waterw. Port Coastal Ocean Eng. 2019, 145, 04018032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Müller, B.; Pernet-Coudrier, B.; Singer, H.; Liu, H.; Qu, J.; Berg, M. Organic micropollutants in the Yangtze River: Seasonal occurrence and annual loads. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.J.; Zhou, P.X.; Mao, L.H. General Review on Effects of Soil and Water Conservation Measures on Water Resources in China. Prog. Geogr. 2006, 25, 49–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Milliman, J.D. Seasonal variations of sediment discharge from the Yangtze River before and after impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam. Geomorphology 2009, 104, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiqing, C.; Qiaoju, Z.; Erfeng, Z. In-channel sand extraction from the mid-lower Yangtze channels and its management: Problems and challenges. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2006, 49, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-M.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Y. Sediment flux sensitivity to climate change: A case study in the Longchuanjiang catchment of the upper Yangtze River, China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 60, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Li, C. Human impact on floods and flood disasters on the Yangtze River. Geomorphology 2001, 41, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.-J.; Chu, A.; Du, J.-Z.; Stive, M.; Hong, Y. Assessment of extreme drought and human interference on baseflow of the Yangtze River. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 24, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, E.; Liu, S.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Higgins, R.W.; et al. The atmospheric anomalies associated with the drought over the Yangtze River basin during spring 2011. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 5881–5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Liu, Z.; Dai, S.; Gao, Z.X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Luo, X.X.; Wu, C.S.; Zhang, Z. Temporal variations in water resources in the Yangtze River (Changjiang) over the Industrial Period based on reconstruction of missing monthly discharges. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W10516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
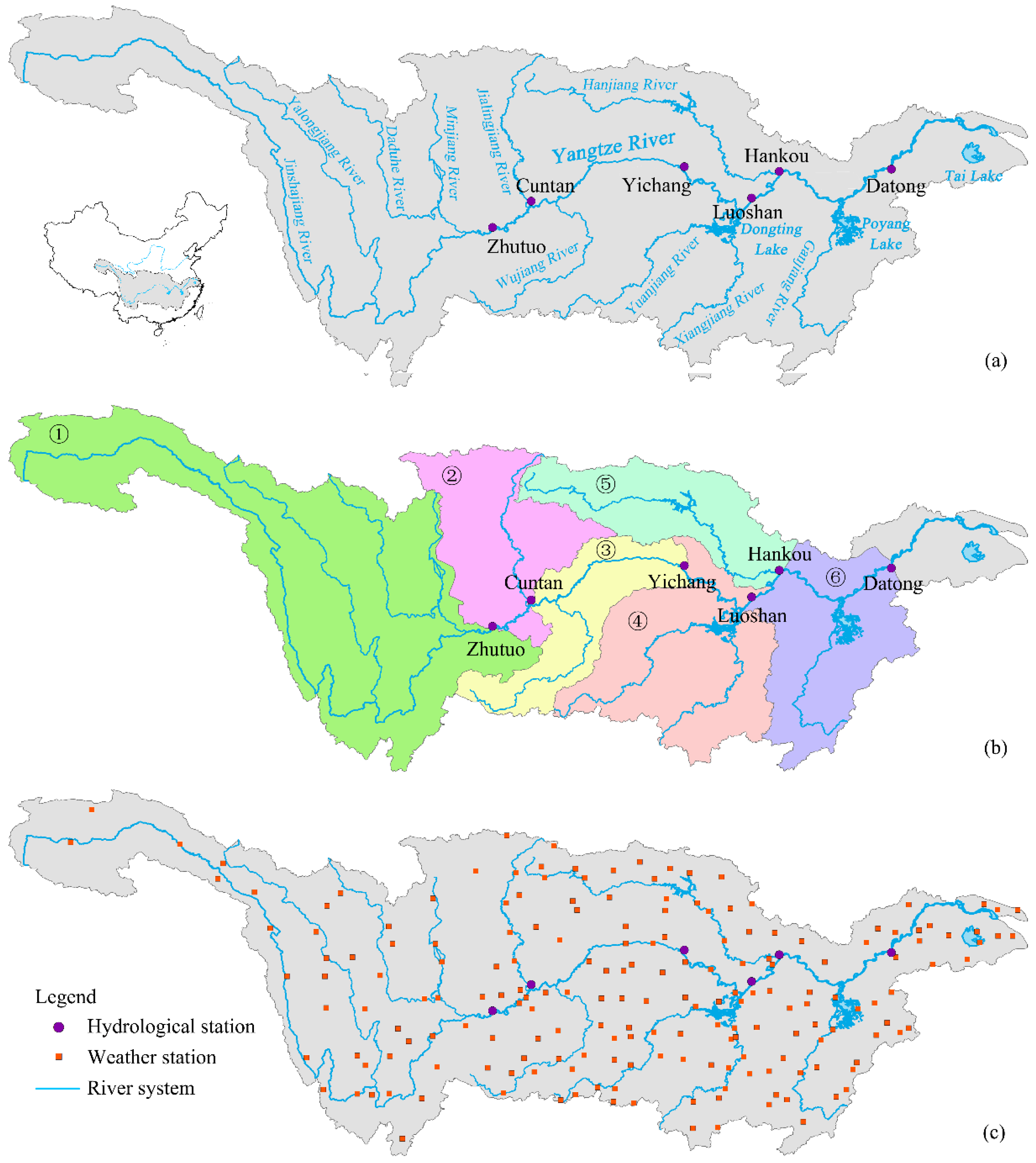

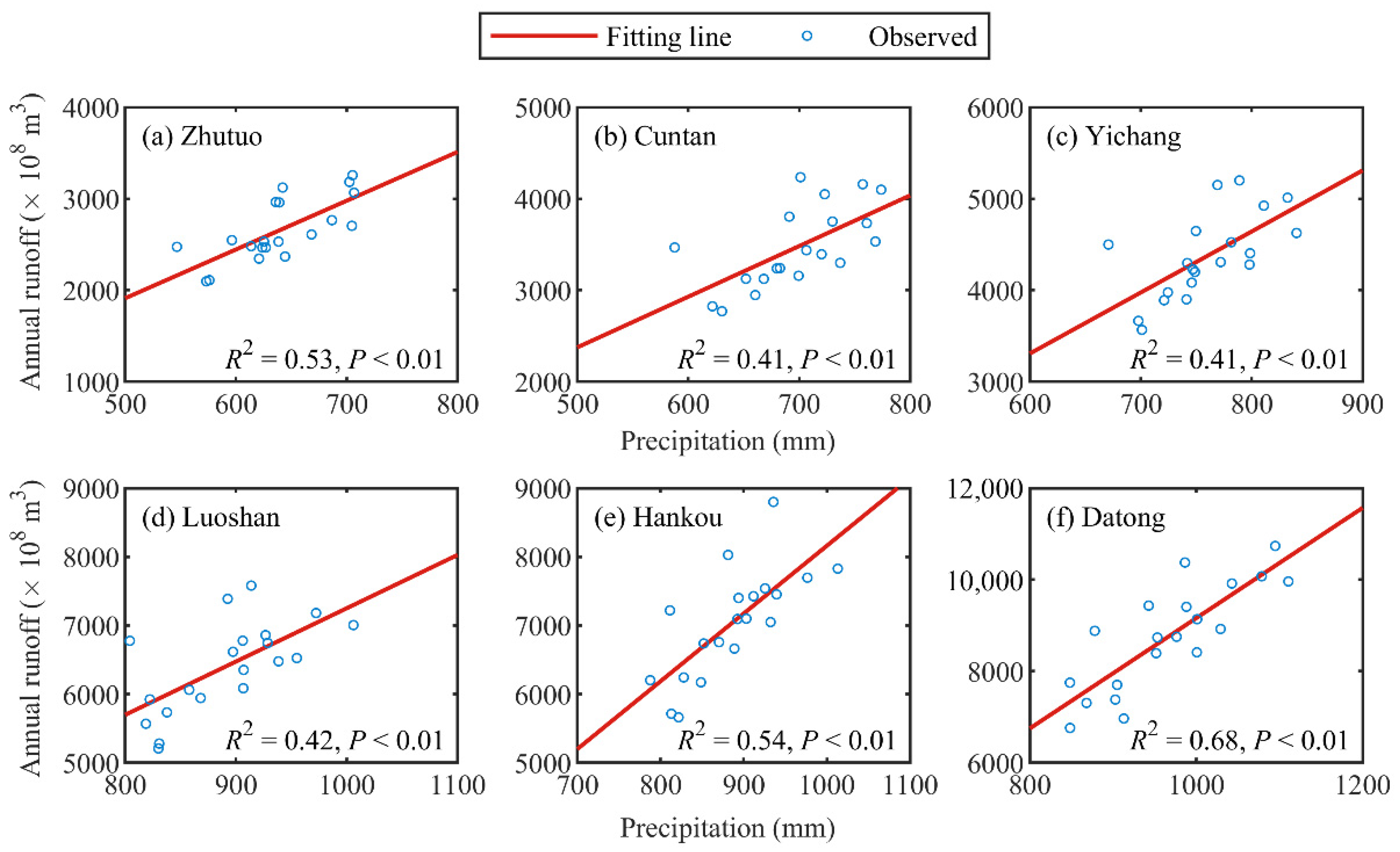
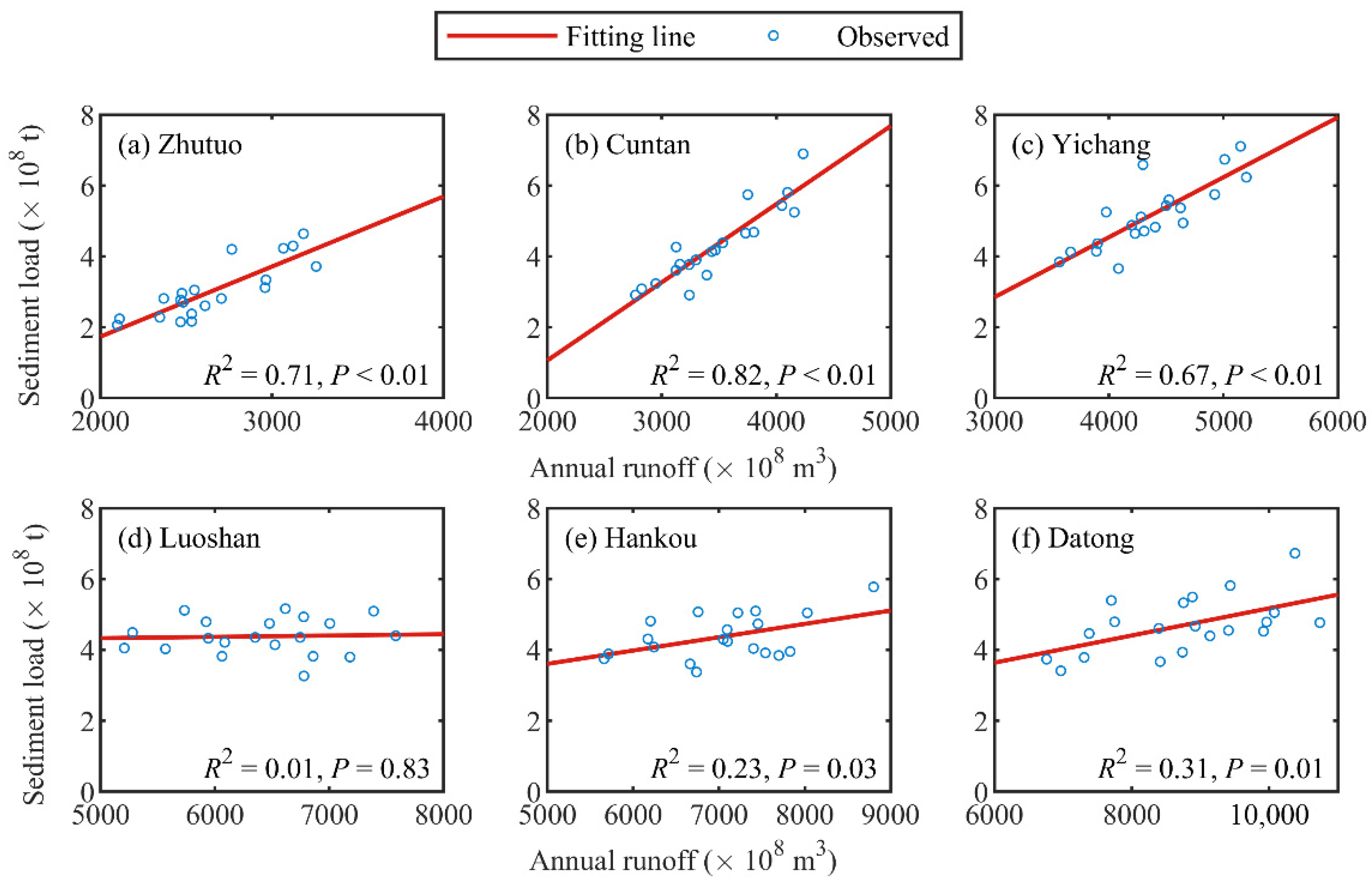
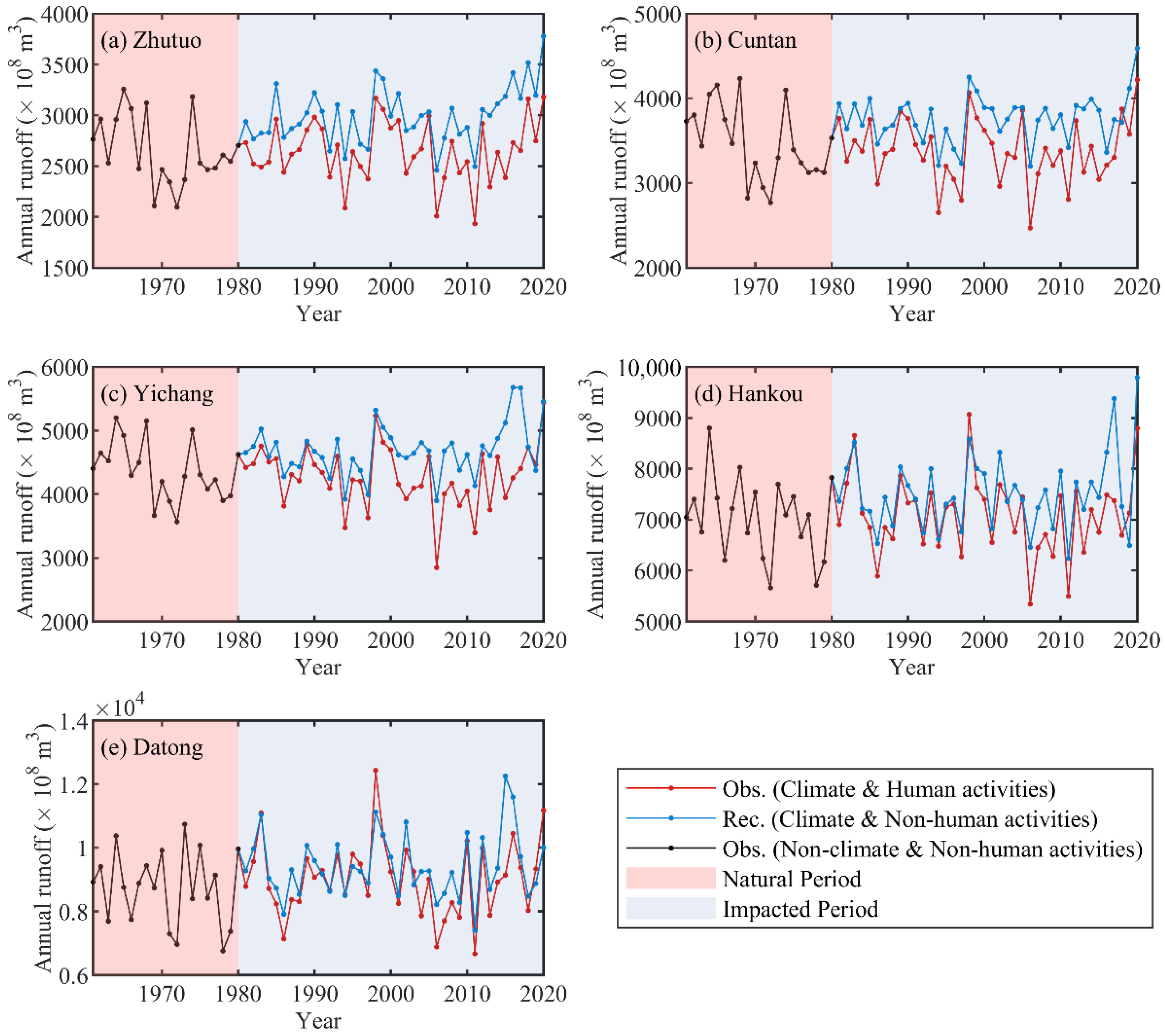
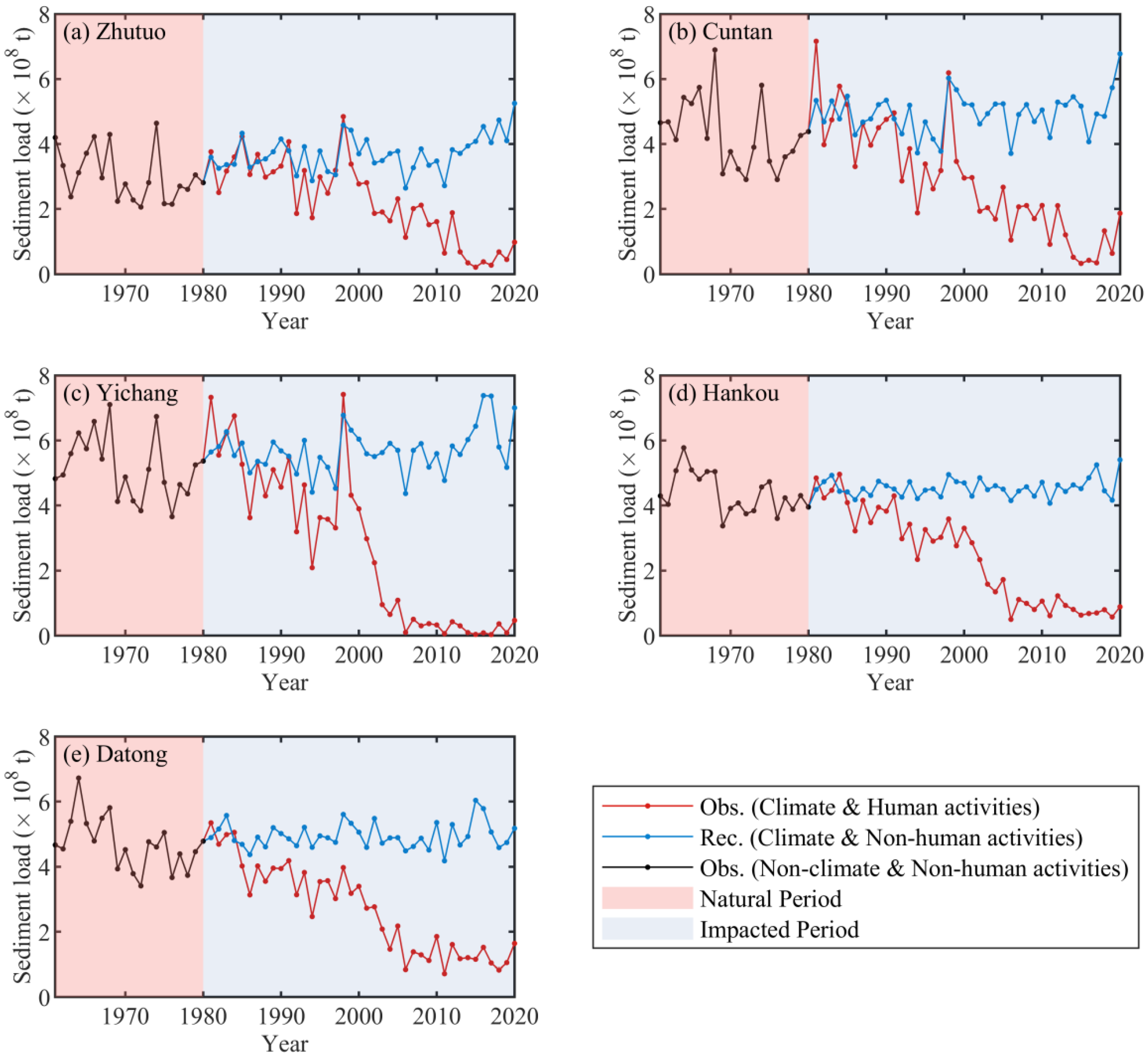
| Stations | Zhutuo | Cuntan | Yichang | Luoshan | Hankou | Datong |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drainage area (×104 km2) | 69.47 | 86.66 | 100.55 | 127 | 148.8 | 170.54 |
| Weather station | 41 | 18 | 21 | 40 | 24 | 31 |
| Location | Upper | Upper | Upper | Middle | Middle | Lower |
| Period | 1961–2020 | |||||
| Periods | Precipitation Variations (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhutuo | Cuntan | Yichang | Luoshan | Hankou | Datong | |
| 1981–2000 | 56 | 47 | 37 | 41 | 45 | 57 |
| 2001–2020 | 74 | 59 | 58 | 61 | 53 | 54 |
| 1981–2020 | 65 | 53 | 48 | 51 | 49 | 56 |
| Station | Runoff (×108 m3) | Sediment Load (×108 t) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1981–2000 | 2001–2020 | 1981–2020 | 1981–2000 | 2001–2020 | 1981–2020 | |||||||
| Zhutuo | 22 | (+0.8%) | −33 | (−1.2%) | −5 | (−0.2%) | 0.2 | (+5.7%) | −1.8 | (−58%) | −0.8 | (−26%) |
| Cuntan | −48 | (−1.4%) | −126 | (−3.6%) | −87 | (−2.5%) | −0.1 | (−3.1%) | −2.8 | (−65%) | −1.5 | (−34%) |
| Yichang | 12 | (+0.3%) | −198 | (−4.5%) | −93 | (−2.1%) | −0.4 | (−7.4%) | −4.6 | (−89%) | −2.5 | (−48%) |
| Luoshan | 110 | (+1.7%) | −159 | (−2.5%) | −25 | (−0.4%) | −0.4 | (−9.9%) | −3.4 | (−77%) | −1.9 | (−44%) |
| Hankou | 193 | (+2.7%) | −93 | (−1.3%) | 50 | (+0.7%) | −0.7 | (−16.4%) | −3.3 | (−75%) | −2.0 | (−46%) |
| Datong | 500 | (+5.7%) | 58 | (+0.7%) | 279 | (+3.2%) | −0.8 | (−18.0%) | −3.2 | (−68%) | −2.0 | (−43%) |
| Station | Runoff | Sediment Load | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression Equation | Coefficient | Regression Equation | Coefficient (×10−4) | |
| Zhutuo | 5.33·P − 754 | 5.33 | 1.98 × 10−3 Rr − 2.22 | 19.77 |
| Cuntan | 5.54·P − 393 | 5.54 | 2.21 × 10−3 Rr − 3.35 | 22.06 |
| Yichang | 6.67·P − 695 | 6.67 | 1.69 × 10−3 Rr − 2.23 | 16.92 |
| Luoshan | 7.77·P − 518 | 7.77 | 3.73 × 10−5 Rr + 4.14 | 0.37 |
| Hankou | 9.88·P − 1718 | 9.88 | 3.76 × 10−4 Rr + 1.73 | 3.76 |
| Datong | 12.06·P − 2897 | 12.06 | 3.84 × 10−4 Rr + 1.34 | 3.84 |
| Station | 1981–2000 | 2001–2020 | 1981–2020 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human Activities | Climate Change | Total Change | Human Activities | Climate Change | Total Change | Human Activities | Climate Change | Total Change | |
| Zhutuo | −279 | 301 | 22 | −426 | 394 | −33 | −353 | 347 | −5 |
| Cuntan | −306 | 258 | −48 | −452 | 326 | −126 | −379 | 292 | −87 |
| Yichang | −236 | 248 | 12 | −587 | 389 | −198 | −411 | 319 | −93 |
| Hankou | −247 | 440 | 193 | −616 | 522 | −93 | −431 | 481 | 50 |
| Datong | −184 | 684 | 500 | −598 | 656 | 58 | −391 | 670 | 279 |
| Station | 1981–2000 | 2001–2020 | 1981–2020 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human Activities | Climate Change | Total Change | Human Activities | Climate Change | Total Change | Human Activities | Climate Change | Total Change | |
| Zhutuo | −0.42 | 0.60 | 0.17 | −2.53 | 0.78 | −1.75 | −1.48 | 0.69 | −0.79 |
| Cuntan | −0.70 | 0.57 | −0.13 | −3.52 | 0.72 | −2.80 | −2.11 | 0.64 | −1.47 |
| Yichang | −0.80 | 0.42 | −0.38 | −5.25 | 0.66 | −4.59 | −3.03 | 0.54 | −2.49 |
| Hankou | −0.88 | 0.17 | −0.72 | −3.46 | 0.20 | −3.27 | −2.17 | 0.18 | −1.99 |
| Datong | −1.11 | 0.26 | −0.84 | −3.47 | 0.25 | −3.21 | −2.29 | 0.2 | −2.03 |
| Year | Observation | Prediction (m3·s−1) | Errors of Prediction (m3·s−1) | Relative Errors of Prediction (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P (mm) | Q (m3·s−1) | Regression of uneven year | Regression of even year | Uneven-year regression for even year | Uneven-year regression for uneven year | Even-year regression for even year | Even-year regression for uneven year | Uneven-year regression for even year | Uneven-year regression for uneven year | Even-year regression for even year | Even-year regression for uneven year | |
| 1971 | 573 | 2097 | 2579.8 | 2554.9 | 235 | 210 | 0.10 | 0.09 | ||||
| 1972 | 644 | 2368 | 2458.6 | 2290.8 | 362 | 194 | 0.17 | 0.09 | ||||
| 1973 | 702 | 3183 | 2639.7 | 2685.4 | 272 | 318 | 0.11 | 0.13 | ||||
| 1974 | 638 | 2531 | 2787.7 | 3008.0 | −395 | −175 | −0.12 | −0.05 | ||||
| 1975 | 627 | 2466 | 2624.8 | 2653.0 | 94 | 123 | 0.04 | 0.05 | ||||
| 1976 | 614 | 2481 | 2595.4 | 2588.9 | 130 | 123 | 0.05 | 0.05 | ||||
| 1977 | 668 | 2609 | 2561.9 | 2515.9 | 81 | 35 | 0.03 | 0.01 | ||||
| 1978 | 596 | 2547 | 2700.7 | 2818.4 | 92 | 209 | 0.04 | 0.08 | ||||
| 1979 | 705 | 2704 | 2517.4 | 2419.0 | −30 | −128 | −0.01 | −0.05 | ||||
| 1980 | 573 | 2097 | 2793.3 | 3020.1 | 89 | 316 | 0.03 | 0.12 | ||||
| AA ± K | / | −84 ± 284 | 2 ± 228 | 1 ± 246 | −37 ± 295 | −2 ± 10 | 1 ± 8 | 1 ± 9 | −1 ± 12 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chai, Y. Quantitative Study of Climatic and Anthropogenic Contributions to Streamflow and Sediment Load in the Yangtze River, China. Water 2022, 14, 3104. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193104
Qian H, Liu J, Yang Y, Liu Y, Chai Y. Quantitative Study of Climatic and Anthropogenic Contributions to Streamflow and Sediment Load in the Yangtze River, China. Water. 2022; 14(19):3104. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193104
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Honglu, Jinxin Liu, Yunping Yang, Yunjia Liu, and Yuanfang Chai. 2022. "Quantitative Study of Climatic and Anthropogenic Contributions to Streamflow and Sediment Load in the Yangtze River, China" Water 14, no. 19: 3104. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193104
APA StyleQian, H., Liu, J., Yang, Y., Liu, Y., & Chai, Y. (2022). Quantitative Study of Climatic and Anthropogenic Contributions to Streamflow and Sediment Load in the Yangtze River, China. Water, 14(19), 3104. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193104







