Analyzing the Reliability of Unstructured Data for Urban Rainfall Pattern Studies—A Case Study from Zhengzhou
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
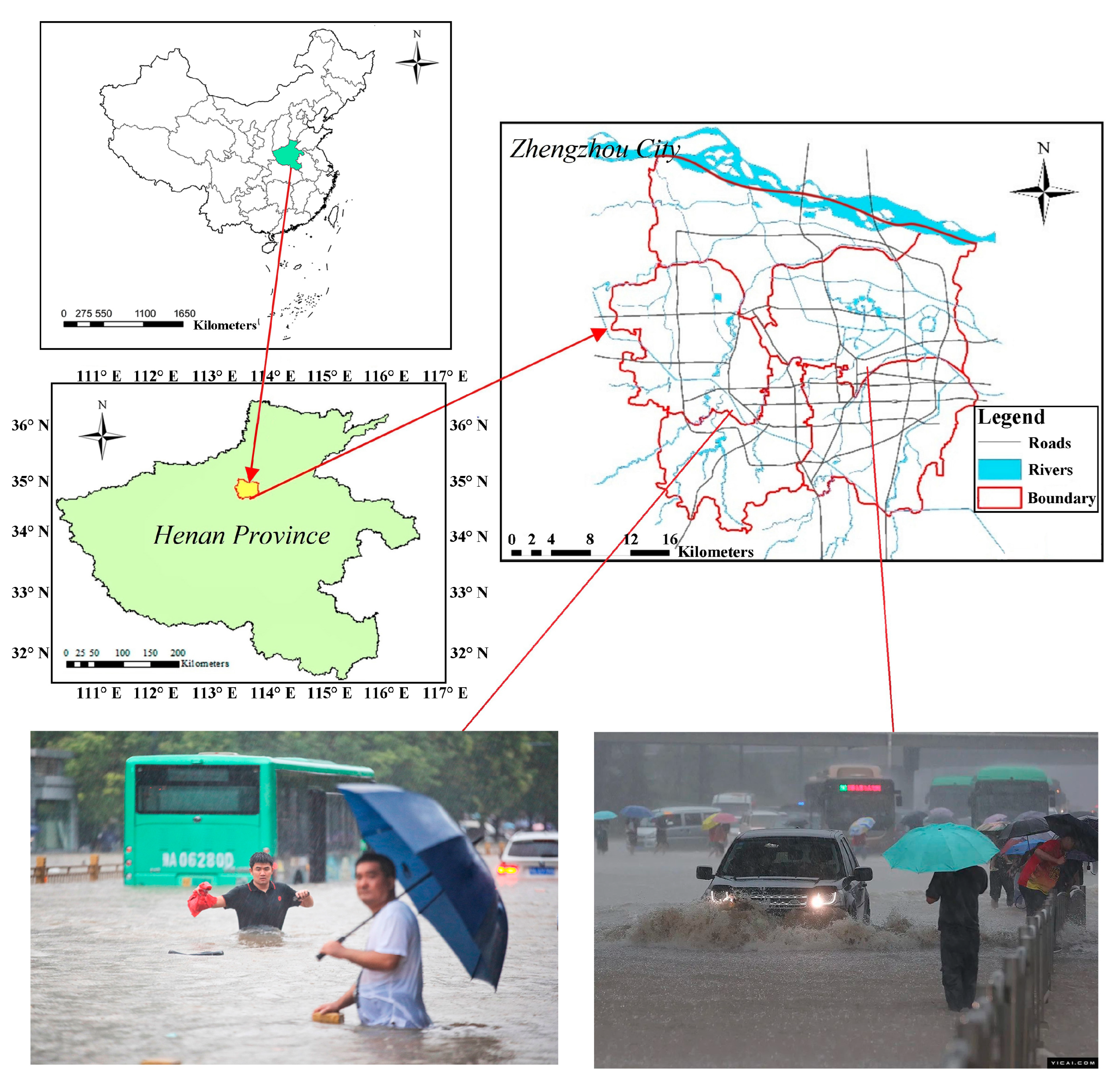
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. Rainfall
2.2.2. Unstructured Data
2.3. Methodology
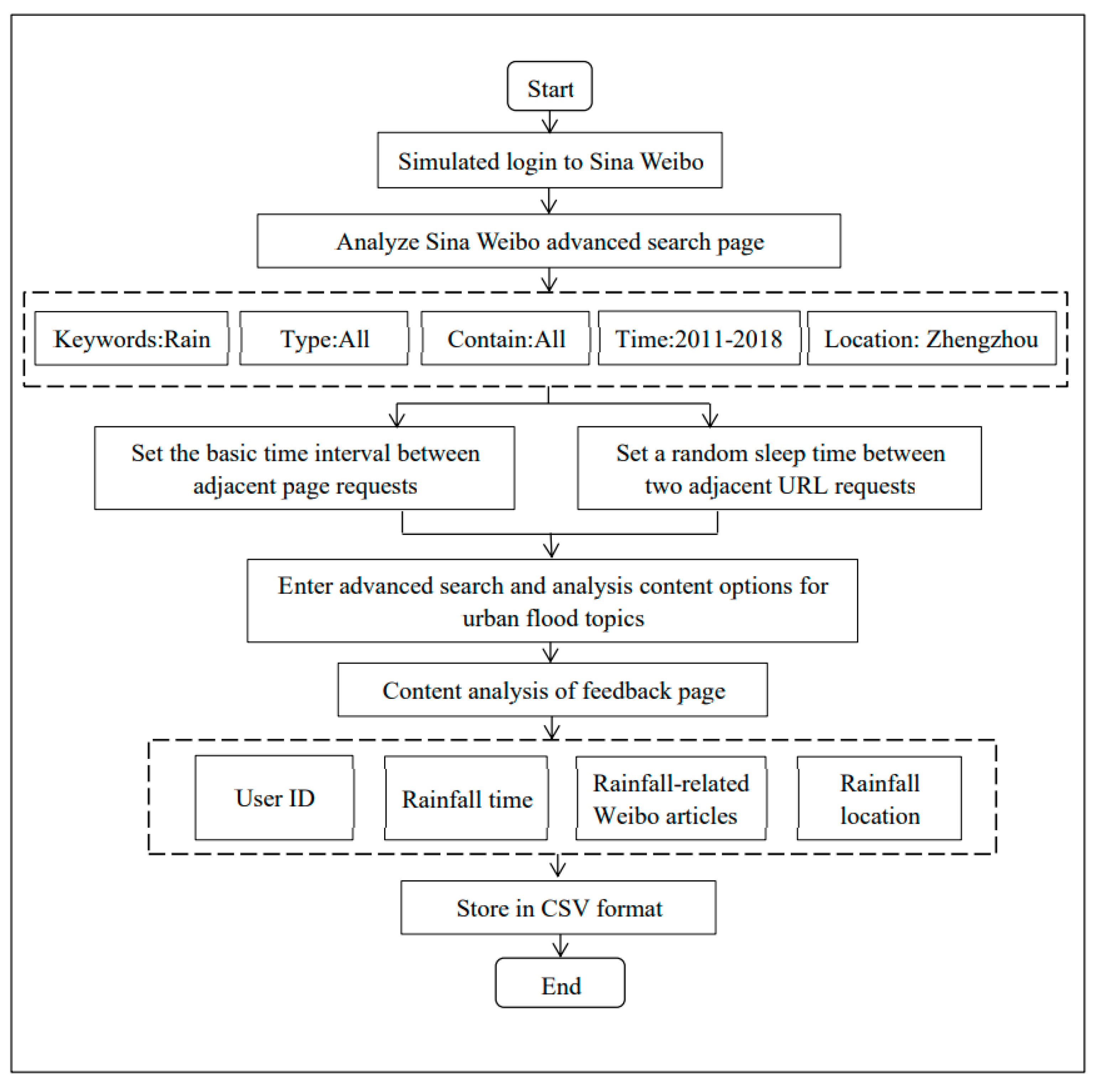
2.3.1. Unstructured Data Acquisition Method of the Rainfall Based on Web Crawler Technology
2.3.2. Correlation Analysis Method of the Unstructured Data and the Measured Rainfall Data
2.3.3. Rainfall Pattern Identification Method Based on the Fuzzy Recognition Method
3. Results
3.1. Calculation Results of Rain Patterns in Zhengzhou City Based on Unstructured Data
3.1.1. Result and Analysis of the Unstructured Data Crawling
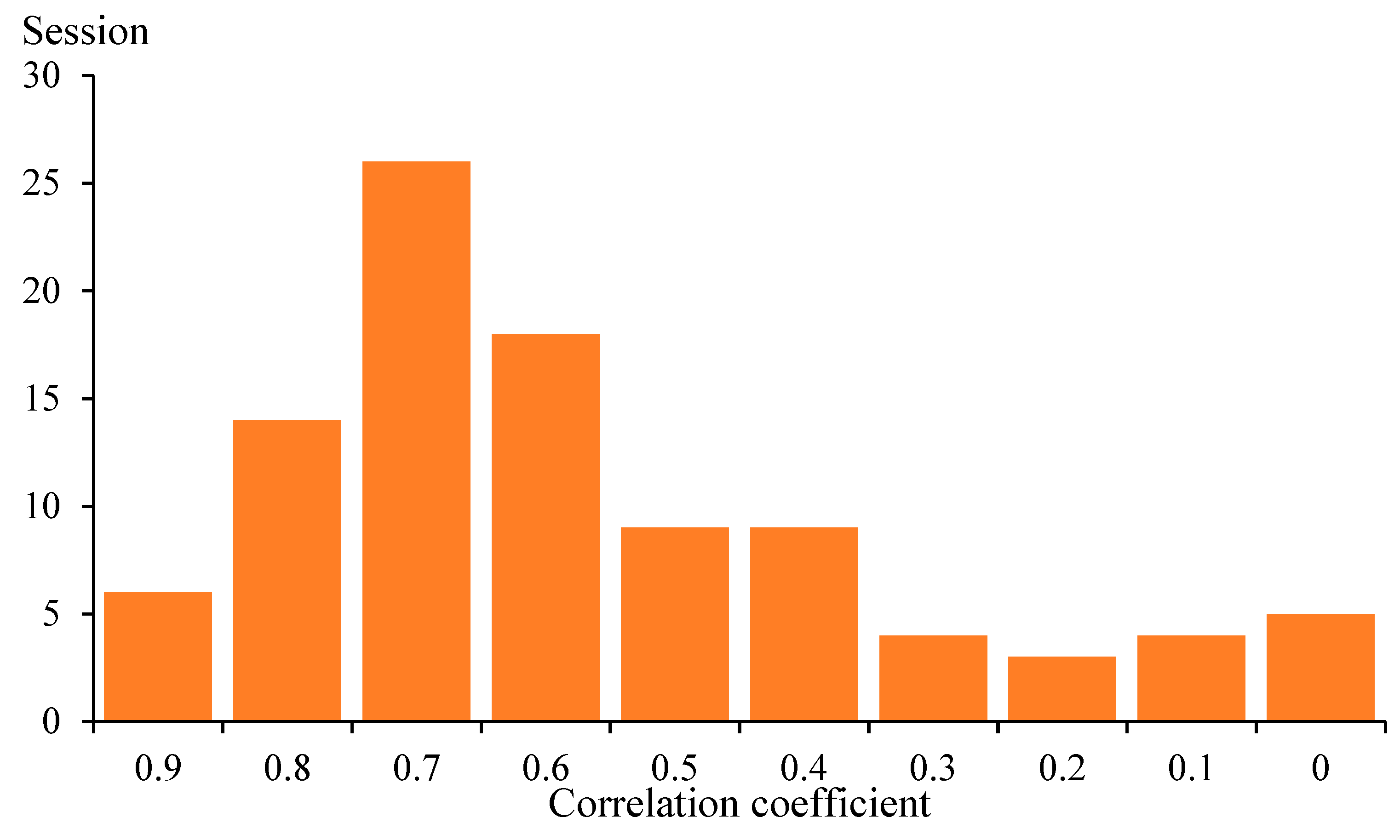
3.1.2. Correlation Analysis
3.1.3. Calculation Results of the Rain Pattern Analysis
3.2. Analysis of the Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sörensen, J.; Mobini, S. Pluvial, urban flood mechanisms and characteristics-Assessment based on insurance claims. J. Hydrol. 2017, 555, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viero, D.P. Modelling urban floods using a finite element staggered scheme with an anisotropic dual porosity model. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Ye, M.; Chang, L.; Chang, F. AI-based design of urban stormwater detention facilities accounting for carryover storage. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspersen, P.S.; Ravn, N.H.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Madsen, H.; Drews, M. Comparison of the impacts of urban development and climate change on exposing European cities to pluvial flooding. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 4131–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cullwell, R.K.; Klein, T. Upgrading Downtown Sewer Infrastructure in the Nation’s 7th Most Populous City. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2014, 78, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Lei, L.; Yu, B.; Ding, Q. The fundamental features of the extreme severe rain events in the recent 10 years in the Beijing area. Acta Meteorologica Sinica 2015, 73, 609–623. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Xiao, H.; Yang, H.; Ding, J.; Fu, D.; Guo, X.; Feng, L. Analysis of Dynamic Conditions and Hydrometeor Transport of Zhengzhou Superheavy Rainfall Event on 20 July 2021 Based on Optical Flow Field of Remote Sensing Data. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 45, 1384–1399. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Ma, B.; Wang, H.; Hu, C.; Lv, H.; Zhang, X. Identification of Sensitive Parameters of Urban Flood Model Based on Artificial Neural Network. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 2115–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Li, Q.; Du, F.; Jang, H. Study on design of rainstorm pattern based on short duration in Nanjing City. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2019, 30, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Tu, X.; Su, C.; Liu, M.; Yan, D.; Wu, Z. Research on the Critical Rainfall of Flash Floods in Small Watersheds Based on the Design of Characteristic Rainfall Patterns. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 3297–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Deng, C.; Li, H.; Ma, M.; Li, Y. Hydrological Environmental Responses of LID and Approach for Rainfall Pattern Selection in Precipitation Data-Lacked Region. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 3271–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Xue, Q.; Yu, X.; Zhang, B.; Yue, Y. Study of Rainfall Characteristics and Pattern in Changchun City. China Water Wastewater 2015, 31, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, S.; Ye, X.; Wang, F.; Zhu, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J. Applicability of Pilgrim & Cordery Rainstorm Pattern in Urban Drainage Calculation. Water Resour. Power 2018, 36, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Cen, G.; Shen, J.; Fan, R. Research on Rainfall Pattern of Urban Design Storm. Adv. Water Sci. 1998, 1998, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Yao, S.; Weng, Y.; Li, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q. New Method for Data Sampling on Urban Storm Intensity Formula. China Water Wastewater 2012, 28, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Aragao, R.; El-Diraby, T.E. Network analytics and social BIM for managing project unstructured data. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Sharma, A.; Masud, M.; Gaba, G.S.; Dhiman, G.; Ghafoor, K.Z.; AlZain, M.A. Urban Rain Flood Ecosystem Design Planning and Feasibility Study for the Enrichment of Smart Cities. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruijn, J.A.; de Moel, H.; Jongman, B.; de Ruiter, M.C.; Wagemaker, J.; Aerts, J. A global database of historic and real-time flood events based on social media. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, A.; Sahu, N.; Kumar, P.; Nayak, S.; Duan, W.; Avtar, R.; Behera, S. Advanced Rainfall Trend Analysis of 117 Years over West Coast Plain and Hill Agro-Climatic Region of India. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gong, C.; Fan, Y.; Li, X.; Liang, Y.; Hu, M. Spatio-Temporal Variation Assessment of Urban Waterlogging in Zhengzhou Using Social Media Data. J. China Hydrol. 2022, 42, 48–52+26. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Wu, Z. Research on Construction Method of Urban Simulated Rainfall Station Based on Sina Weibo Geographical Location Data. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 545, 012017. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Shen, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, M. Quantitative assessment of urban flood disaster vulnerability based on text data: Case study in Zhengzhou. Water Supply 2020, 20, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yan, D. Urban flood forecasting based on the coupling of numerical weather model and stormwater model: A case study of Zhengzhou city. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 39, 100985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, W.; Zhang, X.; Song, C.; Hu, D.; Liang, T. Annual precipitation analysis and forecasting–taking Zhengzhou as an example. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2020, 20, 1604–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Hua, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, M. Network Patterns of Zhongyuan Urban Agglomeration in China Based on Baidu Migration Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y. Design and Application of High Resolution Earthquake Catalogue Auto Update Program Based on Python Crawler Technology. Earthq. Res. China 2019, 35, 541–549. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, M.; Lu, Q. Study on clustering of micro-blog business enterprise users reputation based on web crawler. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Math. 2017, 8, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Han, T.; Zhang, C.; Yao, Y. Research and Construction of the Online Pesticide Information Center and Discovery Platform Based on Web Crawler. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 166, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElAraby, M.E.; Shams, M.Y. Face retrieval system based on elastic web crawler over cloud computing. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 11723–11738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Bindal, A.; Gautam, R.; Bhatia, R. Keyword query based focused Web crawler. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 125, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zou, T.; Lai, Y. Novel method for industrial sewage outfall detection: Water pollution monitoring based on web crawler and remote sensing interpretation techniques. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; You, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, D. Pearson correlation coefficient-based pheromone refactoring mechanism for multi-colony ant colony optimization. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 752–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Yang, D.; Guo, Y. Laser ultrasonic damage detection in coating-substrate structure via Pearson correlation coefficient. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 353, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Lu, T.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Peng, H.; Li, C.; Yang, S.; Yao, F. Research on a laser ultrasonic visualization detection method for human skin tumors based on pearson correlation coefficient. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 141, 107117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavinia, M.; Saleh, F.N.; Asadi, H. Effects of rainfall patterns on runoff and rainfall-induced erosion. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2019, 34, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhadi, A.; Soulis, E.D. Time-varying extreme rainfall intensity-duration-frequency curves in a changing climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2454–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, B.; Gong, Z. Real-time identification of urban rainstorm waterlogging disasters based on Weibo big data. Nat. Hazards 2018, 94, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Rainfall Pattern | Period | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| I | 30.4% | 26.1% | 17.4% | 13.0% | 8.7% | 4.3% |
| II | 3.8% | 7.7% | 11.5% | 23.1% | 30.8% | 23.1% |
| III | 5.0% | 20.0% | 35.0% | 25.0% | 10.0% | 5.0% |
| IV | 14.3% | 19.0% | 14.3% | 19.0% | 14.3% | 19.0% |
| V | 25.0% | 15.0% | 5.0% | 10.0% | 25.0% | 20.0% |
| VI | 22.2% | 11.1% | 16.7% | 27.8% | 16.7% | 5.6% |
| VII | 8.7% | 13.0% | 30.4% | 17.4% | 8.7% | 21.7% |
| Time Period | Session | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 July 2018 | 25 August 2017 | 5 June 2016 | 28 August 2015 | 1 May 2014 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 16.14 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.32 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | 0 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | 0.07 | 1.36 | 1.71 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 0.07 | 6.25 | 12.07 | 0 | 0 |
| 11 | 0.21 | 9.04 | 1.54 | 0 | 0 |
| 12 | 3.82 | 2.89 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 |
| 13 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 14 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0 | 0 | 2.14 |
| 15 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 |
| 16 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.57 | 0 |
| 17 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0 | 4.64 | 0 |
| 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.32 | 0 |
| 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 20 | 0 | 0 | 3.57 | 0 | 0 |
| 21 | 0 | 0 | 12.89 | 0 | 0 |
| 22 | 0 | 0 | 11.04 | 0 | 0 |
| 23 | 0 | 0 | 3.5 | 0 | 0 |
| Time Period | Session | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 July 2018 | 25 August 2017 | 5 June 2016 | 28 August 2015 | 1 May 2014 | |
| 0 | 13 | 6 | 645 | 10 | 12 |
| 1 | 3 | 6 | 100 | 5 | 7 |
| 2 | 1 | 3 | 19 | 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 5 | 1 | 12 | 2 | 2 |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 16 | 2 | 3 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 10 |
| 6 | 9 | 8 | 16 | 5 | 9 |
| 7 | 14 | 18 | 47 | 23 | 12 |
| 8 | 16 | 29 | 63 | 11 | 8 |
| 9 | 25 | 52 | 136 | 16 | 15 |
| 10 | 18 | 98 | 388 | 10 | 9 |
| 11 | 38 | 103 | 173 | 21 | 20 |
| 12 | 78 | 84 | 128 | 5 | 14 |
| 13 | 70 | 33 | 82 | 14 | 16 |
| 14 | 38 | 43 | 76 | 12 | 105 |
| 15 | 34 | 42 | 53 | 26 | 78 |
| 16 | 34 | 30 | 46 | 31 | 31 |
| 17 | 31 | 32 | 46 | 139 | 20 |
| 18 | 23 | 26 | 66 | 63 | 34 |
| 19 | 31 | 25 | 90 | 26 | 24 |
| 20 | 28 | 37 | 160 | 32 | 27 |
| 21 | 24 | 39 | 407 | 26 | 27 |
| 22 | 31 | 38 | 505 | 27 | 28 |
| 23 | 25 | 43 | 119 | 29 | 18 |
| Correlation Coefficient | Session | Rainfall Pattern | Rain Peak Type | Rainfall Peak Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8 | 26 August 2014 | III | single peak | Central |
| 0.8 | 27 August 2014 | III | Central | |
| 0.8 | 7 July 2015 | III | Central | |
| 0.8 | 22 July 2015 | III | Central | |
| 0.8 | 3 August 2015 | I | Front section | |
| 0.8 | 28 August 2015 | III | Central | |
| 0.8 | 7 June 2016 | II | Rear | |
| 0.8 | 25 August 2017 | III | Central | |
| 0.9 | 19 June 2014 | III | Central | |
| 0.9 | 29 July 2014 | II | Rear | |
| 0.9 | 5 June 2016 | III | Central | |
| 0.9 | 12 September 2016 | III | Central | |
| 0.9 | 22 May 2017 | I | Front section | |
| 0.8 | 19 April 2014 | IV | uniform rain pattern | No peak |
| 0.8 | 10 May 2014 | IV | No peak | |
| 0.8 | 19 April 2015 | IV | No peak | |
| 0.8 | 22 June 2017 | IV | No peak | |
| 0.8 | 1 May 2015 | VI | bimodal peak | Front and middle |
| 0.8 | 26 June 2015 | V | Front and back | |
| 0.9 | 6 October 2015 | VI | Front and middle |
| Session | Rainfall Pattern | Rain Peak Type | Rainfall Peak Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| 19 April 2014 | II | single peak | Rear |
| 26 August 2014 | III | Central | |
| 27 August 2014 | I | Front section | |
| 1 May 2015 | II | Rear | |
| 7 July 2015 | II | Rear | |
| 22 July 2015 | III | Central | |
| 28 August 2015 | III | Central | |
| 22 June 2017 | I | Front section | |
| 25 August 2017 | III | Central | |
| 19 June 2014 | II | Rear | |
| 6 October 2015 | III | Central | |
| 5 June 2016 | III | Central | |
| 12 September 2016 | III | Central | |
| 22 May 2017 | I | Front section | |
| 10 May 2014 | IV | uniform rain pattern | No peak |
| 19 April 2015 | VI | bimodal peak | Front and middle |
| 26 June 2015 | V | Front and back | |
| 3 August 2015 | VI | Front and middle | |
| 7 June 2016 | VI | Front and middle | |
| 29 July 2014 | VI | Front and middle |
| Session | Rain Pattern | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Weibo Data | Measured Data | ||
| Match | 10 May 2014 | IV | IV |
| 26 August 2014 | III | III | |
| 26 June 2015 | V | V | |
| 22 July 2015 | III | III | |
| 28 August 2015 | III | III | |
| 25 August 2017 | III | III | |
| 5 June 2016 | III | III | |
| 12 September 2016 | III | III | |
| 22 May 2017 | I | I | |
| Does not match | 19 April 2014 | IV | II |
| 27 August 2014 | III | I | |
| 19 April 2015 | IV | VI | |
| 1 May 2015 | VI | II | |
| 7 July 2015 | III | II | |
| 3 August 2015 | I | VI | |
| 7 June 2016 | II | VI | |
| 22 June 2017 | IV | I | |
| 19 June 2014 | III | II | |
| 29 July 2014 | II | VI | |
| 6 October 2015 | VI | III | |
| Rainfall Pattern | Matching Number | Mismatch Number | Total | Proportion of Rain Pattern | Proportion of Matching | Percentage of Mismatches | Matching Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
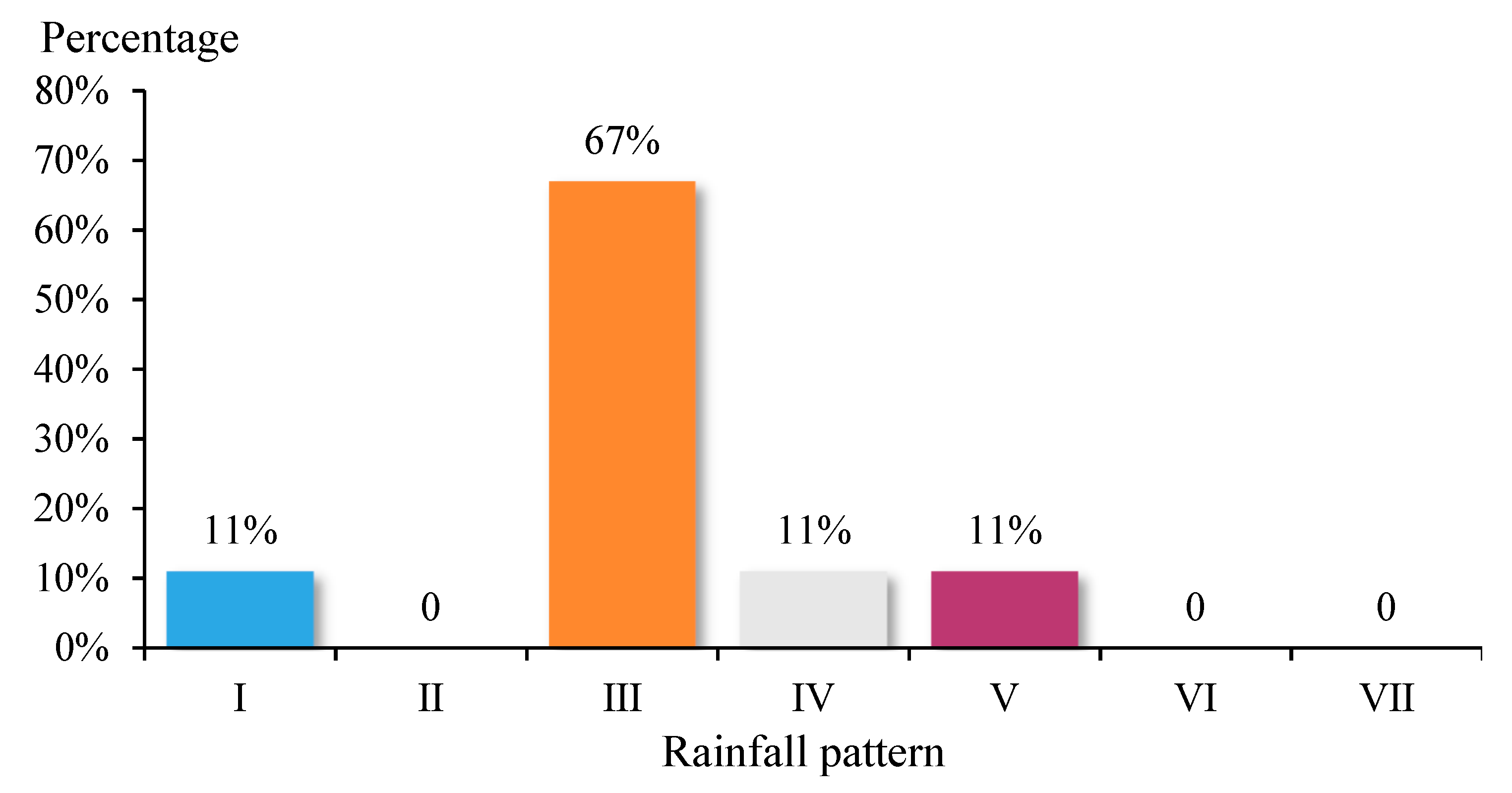
| I | 1 | 2 | 3 | 15% | 11% | 18% | 33% |
| II | 0 | 4 | 4 | 20% | 0% | 36% | 0% |
| III | 6 | 1 | 7 | 35% | 67% | 9% | 86% |
| IV | 1 | 0 | 1 | 5% | 11% | 0% | 100% |
| V | 1 | 0 | 1 | 5% | 11% | 0% | 100% |
| VI | 0 | 4 | 4 | 20% | 0% | 36% | 0% |
| VII | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0% | 0% | 0% | |
| Total | 9 | 11 | 20 | 100% | 100% | 100% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, C.; Niu, Z.; Ling, M.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Yan, D. Analyzing the Reliability of Unstructured Data for Urban Rainfall Pattern Studies—A Case Study from Zhengzhou. Water 2022, 14, 3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203316
Lv C, Niu Z, Ling M, Wu Z, Li Y, Yan D. Analyzing the Reliability of Unstructured Data for Urban Rainfall Pattern Studies—A Case Study from Zhengzhou. Water. 2022; 14(20):3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203316
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Cuimei, Zhaoying Niu, Minhua Ling, Zening Wu, Yang Li, and Denghua Yan. 2022. "Analyzing the Reliability of Unstructured Data for Urban Rainfall Pattern Studies—A Case Study from Zhengzhou" Water 14, no. 20: 3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203316
APA StyleLv, C., Niu, Z., Ling, M., Wu, Z., Li, Y., & Yan, D. (2022). Analyzing the Reliability of Unstructured Data for Urban Rainfall Pattern Studies—A Case Study from Zhengzhou. Water, 14(20), 3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203316





