Abstract
Continuous monitoring of drinking water quality is essential in terms of the levels of heavy metals and toxic substances, especially in developing countries like Pakistan. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate groundwater quality in residential areas of the Rajanpur District, Pakistan. Groundwater samples (n = 200) were collected from various sites in the study area and analyzed by in situ tests (pH, EC, TDS, temperature, and turbidity), and the concentration of 32 dissolved elements and ions was also analyzed. The results showed that higher concentrations of dissolved elements are the primary reason for poor drinking water quality. A few measured parameters (TDS~992 mg L−1 and EC~1921.15 µS/cm) exceeded the permissible limits of the World Health Organization (WHO, Geneva, Switzerland) in most of the samples. Elements that had higher values than the allowable limits in most of the samples were calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), bicarbonates (HCO3), sulfate (SO4), chlorides (Cl), manganese (Mn), and strontium (Sr), with average values of 113 mg L−1, 223 mg L−1, 282 mg L−1, 367 mg L−1, 175 mg L−1, 69 mg L−1, and 1291 mg L−1, respectively. The measured parameters that had no significant issues in terms of drinking water quality were aluminum (Al), nitrite (NO2), phosphate (PO4), pH, and turbidity. The levels of potentially toxic elements such as arsenic (As), lead (Pb), chromium (Cr), and copper (Cu) (average ~2.179 mg L−1, 1.659 mg L−1, 0.092 mg L−1, and 1.032 mg L−1, respectively) were found to be lower than the drinking water guideline values of the WHO. The statistical analysis revealed weak correlations possibly due to multiple sources and localized variations. The physicochemical analysis-based WQI values for all groundwater samples were much lower at the residential sampling locations and in industrial settings, indicating poor water quality. The elevation model indicated that as water moves in the aquifer in the general direction of west to southeast, it gets concentrated by mineral dissolution, with geogenic sources having a major impact on the hydrochemistry. Hence, regular monitoring of water quality is required through advanced technology to overcome groundwater deterioration issues. The quality of water is poor for drinking purposes and the health of the residents of the Rajanpur District may be at risk.
1. Introduction
World water resources have become indispensable and valuable because of the economic growth of the last decades and other factors such as climate change and hydrogeological characteristics, which have severely affected the conservation, protection, and management of natural resources [1,2,3,4,5]. Freshwater supplies are scarce worldwide, and the available resources are attenuating and getting polluted with time, making them insufficient to support an ever-growing human population [6,7,8]. It is projected that 50% of the world’s population may face water deficiency by 2025 [9]. There are several factors that determine the quality and chemistry of water resources, including mineral compositions of the underlying lithology, climatic setting, human activities, topography, hydrogeological setting, ionic exchanges, and weathering products [10,11,12,13,14,15,16].
Water quality and quantity go hand in hand according to the principles of water resource management. Water consumption and poor water quality are once again propelling the people of the world to pay more attention to water resources in the face of natural disasters, floods, water shortages, water pollution, and resulting illnesses in developing countries [17,18]. As the quality of water has a profound impact on human health, interest in water quality regulation has surged in recent years [19]. Groundwater resources have been under immense pressure because of rapid urbanization, quality degradation caused by natural factors, and anthropogenic addition of potentially toxic metals into groundwater [20,21,22]. Around one third of the world’s population utilizes groundwater for drinking purposes and another twenty percent for irrigation purposes, which puts a strain on available resources [23,24]. Drinking, irrigation, and recreational uses of water are determined largely by its physical, chemical, and biological properties [25].
A combination of improper wastewater treatment, water scarcity, and increased industrial activity in developing countries have contributed to a dramatic increase in heavy metal pollution in lakes, rivers, and other freshwater resources [26,27]. Heavy metal exposure can lead to the development of chronic and non-chronic diseases in humans due to the elevated levels of dissolved potentially toxic elements such as iron (Fe), nickel (Ni), manganese (Mn), copper (Cu), cadmium (Cd), arsenic (As), chromium (Cr), and lead (Pb) [28,29]. The significance of the effects on water use depends on both the severity and frequency of pollution events and the usefulness of groundwater resources [30,31]. Agricultural stability is being compromised by unregulated and uncontrolled use of groundwater, which is plummeting in quantity and quality, and as a result, Pakistan’s newborns suffer from water-borne diseases [32].
The identification of sources of groundwater pollution in some small areas can be difficult when monitoring data is limited; hence, a better way to manage groundwater pollution would be to identify the sources [33]. There is a lot of success in perpetuating and enhancing groundwater quality, but the existing knowledge is inadequate for water quality issues in residential areas of the Rajanpur District, Punjab, Pakistan. Rajanpur was selected due to its geographical location and proximity to the Indus River, which has a significant impact on groundwater quality. This study was designed to fill this knowledge gap by combining a spatial geographic information system (GIS) the Canadian water quality index (CCME), statistical techniques (principal component analysis (PCA)), correlation, and regression methods. The main objectives of this investigation were to: (1) assess groundwater quality in terms of dissolved elements (major, minor, and trace); (2) develop spatial distribution maps by using GIS tools; and (3) analyze quality according to water standards and guidelines in relation to human health. If the improvement of groundwater quality and future scenarios are not considered, this problem may become more serious. Hence, this study provides relevant information to residents and public authorities concerned with drinking water quality and the potential effects of contamination.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The city of Rajanpur lies between the Indus River and the Balochistan mountain ranges. The study area lies between the Sulaiman Mountains in the west and the Indus River in the east, to the extreme southwest direction of Punjab (28.43° N–29.82° N and 69.55° E–70.76° E; Figure 1). It is a narrow and long strip of land that lies on the eastern side of the Indus River [34]. As a result of the geographical and hydrological settings of the region, the mountains receive seasonal rainfall which becomes overland flow in the downstream areas and ultimately drains into the Indus River basin. Floods, as hill torrents, are triggered by this situation seasonally almost every year. This study focused on the Rajanpur area which is greatly dependent on groundwater resources, and the quality of groundwater is changing due to human activities and the aquifer characteristics. The study area has a subtropical desert climate with an average annual rainfall of 224.5 mm and an average annual temperature of 30 °C. The main land uses in the study area are residential (urban and rural) and agricultural.
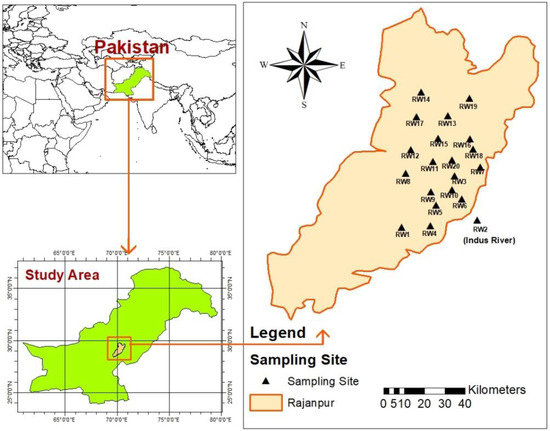
Figure 1.
Location map showing sampling sites in the study area.
2.2. Pre-Field Methods
A field survey of the study area was conducted before the water sampling. Topographic maps were reviewed to select housing colonies and agricultural land for water sampling, keeping in view the general land use and potential contamination in the area. In the present study, accurate analytical data was ensured in terms of the quality of work, adequacy, and reliability. The analytical measurements were performed in controlled conditions in the laboratory.
2.3. Sample Collection
Groundwater sources in residential areas were the focus of this study and a total of 20 sampling locations were selected for detailed analysis. As per World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines [35], samples were taken from the study sites for physicochemical analysis from residential, semi-urban settings, as well as industrial and agricultural areas. Hence, ten water samples were collected from each site in sanitized precleaned plastic bottles (600 mL) for analytical analysis of dissolved elements (e.g., metals, major ions). The water sampling included water derived from hand pumps and motorized water pumps, as well as tap water from the local water supply. Sampling included sites such as public places (e.g., railway station, Masajid, school) and housing colonies. One sample was collected from the main irrigation canal flowing through the city. Cultivated area sampling included the direct supply of water from tube wells for irrigation in the cotton and sugar cane fields. In situ testing included measurements of the pH, electrical conductivity (EC), total dissolved solids (TDS), temperature, and turbidity levels of the water samples. All of the samples were labeled and stored in an icebox and transported to the laboratory for analytical measurements. Aesthetic parameters like color, smell, and taste were also recorded at the sites using corresponding standard methods of field testing. Field observations and relevant data were recorded on field data sheets, including sampling location coordinates for the GIS analysis.
2.4. Analytical Techniques
Samples were transported to the Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources (PCRWR) laboratory in Islamabad for analytical measurements. Chemical analysis of major, minor, and trace metals was conducted following the standard methods described in the APHA, 23rd edition and the NSDWQ [36,37]. The detection limits in milligrams per liter and measurement uncertainty for various elements are given in Table 1.

Table 1.
Laboratory detection limits and relevant details for selected constituents.
The instruments that were used in the analytical measurements included an atomic absorption spectrometer (Model: AAS Vario 6 Analytical Jena Germany), ion chromatographer, and a mass spectrometer. Aesthetic and physical parameters were analyzed by comparing their values with WHO guidelines and Pak-EPA standards (NEQS). A digital meter was used for testing pH (Model: Martini Mi 180), while a conductivity meter (Model: Jenway 470) was used to determine TDS and EC. Moreover, arsenic concentration was determined by using the atomic absorption spectrometer with a single-element hollow cathode lamp and the combustion of air–acetylene. The measurements of elements including chromium, zinc, copper, manganese, cadmium, lead, and all others were determined using ICP-OES (Inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry). Alkalinity, along with bicarbonate and carbonate concentrations, were determined by titration with hydrochloric acid (HCl) and methyl orange and phenolphthalein as indicators.
2.5. Spatial Analysis
Spatial analysis requires the use of geographic information systems (GIS) to map the chemical evolution of groundwater to show the spatial distribution of different major and minor ions and trace elements. ArcGIS version 10.5 was used to create various spatial distribution maps. Analytical laboratory data was arranged on an MS Excel spreadsheet which contained sample ID, longitude, latitude, and laboratory results. The data on groundwater quality was processed, analyzed, and interpreted using distribution maps. The spatial analysis helped understand the chemical evolution of groundwater to show the distribution of measured major and minor ions and trace elements.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Brief methodology of sampling, analytical techniques and the statistical analysis depicted in the Figure 2. Statistical analysis for the principal component of different metals was carried out on Minitab 18. The PCA was performed to determine the principal components (PCs) from sampling points and to assess local variations in groundwater and possible sources of heavy metals. Correlation and regression analysis was also carried out, and the water quality index of the Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME) was determined.
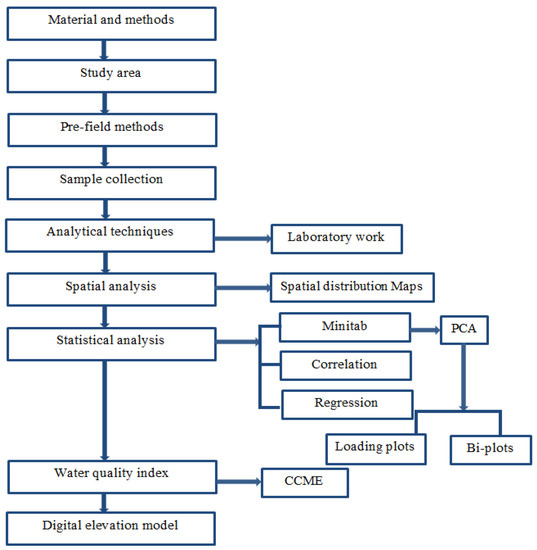
Figure 2.
Flow chart showing the general methodology.
3. Results
3.1. Physico-Chemical Parameters
The pH level of the drinking water was determined to be compliant with the WHO [34] guidelines, ranging between 6.9 and 8.2. Standard values of TDS and EC are divided into categories as follows: less than 300 mg L−1 is excellent, from 300 mg L−1 to 600 mg L−1 is good, between 600 mg L−1 and 900 mg L−1 is fair, from 900 mg L−1 to 1200 mg L−1 is poor, and higher than 1200 mg L−1 is unacceptable [38]. In the present study, values of TDS in the water samples varied from 150 to 3732 mg L−1. According to this, the RW7, RW1, RW19, RW16, and RW15 sampling locations fall into the category of unacceptable, and RW8, RW5, RW13, RW14, RW9, RW17, RW6, and RW3 fall into good. The highest value was recorded at the RW7 sampling location, which corresponded to the water sample collected from the residential area. The EC detected was very high—with values ranging between 6020 µS cm and 2070 µS cm, including both agricultural and residential areas—for the following sites (in increasing order): RW7 > RW2 > RW1 > RW18 > RW20 > RW19 > RW16 > RW15. The EC values detected at other locations ranged between 1825 µS cm and 1160 µS cm, and they were measured at the following sites (in increasing order): RW12 > RW8 > RW5 > RW9 > RW13 > RW14 > RW3 > RW17 > RW6. A statistical summary of all physical parameters is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Statistical summary of the physical parameters measured in the field.
3.2. Chemical Parameters
Water samples were collected for the evaluation of various major and trace elements. Major elements include alkalinity, bicarbonates, carbonates, hardness, P, N, Na, K, Ca, Mg, Cl, and SO4. Minor and trace elements include As, Al, Co, Cd, Cu, Cr, Mo, Mn, Pb, Ni, Sr, F, and Zn. A discussion of the variations in concentration and spatial distribution patterns is given in below in the subsections.
3.2.1. Major Elements
Present data showed that values ranged between 22 and 461 mg L−1 for Ca. The highest value was recorded in the water sample at the RW7 location, which was taken from the residential area. Magnesium values varied from 10 to 109 mg L−1 with an average value of 113.15 mg L−1, and sodium values ranged between 18 mg L−1 and 820 mg L−1. The bicarbonate concentration ranged from 92 to 452 mg L−1. The sulfate (SO4) values ranged from 34 mg L−1 to 933 mg L−1 and the concentrations were detected in the order of RW7 > RW19 > RW20 > RW18 > RW16 at the sampling locations. The concentration of chloride ranged from 20 to 1296 mg L−1 in the water samples. The high values at the sampling locations were detected in the order of RW7 > RW1 > RW18 > RW20 > RW19 > RW16 > RW8. In this study, potassium and phosphate values were slightly higher than the permissible levels (Figure 3).
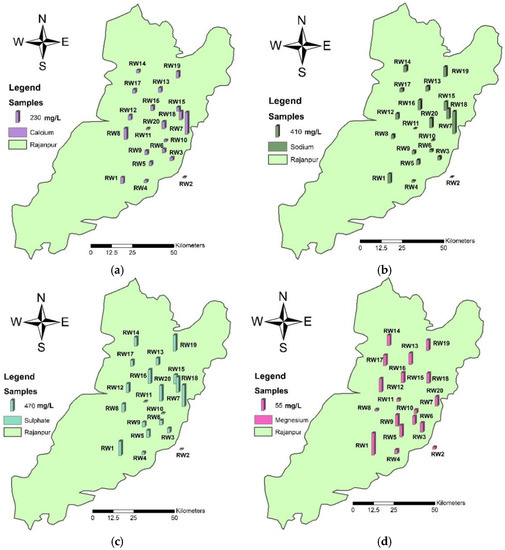
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution maps of (a) calcium, (b) sodium, (c) sulfate, and (d) magnesium showing the concentration of elements at the location sites in the study area.
3.2.2. Trace Elements
Only two samples (RW1 and RW9) were above the acceptable levels for arsenic, but the levels were only slightly higher. The concentration of dissolved Al in water in the near-neutral pH range is commonly 1–50 mg L−1 but upsurges up to 500–1000 mg L−1 in highly acidic water or water rich in biological material have also been observed [35]. In the present data, only two samples (RW2 & RW11) registered higher levels that fall in the category of acidic water. The concentration of manganese reported in the present data was from the below detection limit to 404.6 mg L−1 and the values were found in increasing order at RW1 > RW4 > RW3 > RW13. The results showed that nitrates, nitrites, and chromium had low values in water samples from the study area (Figure 4).
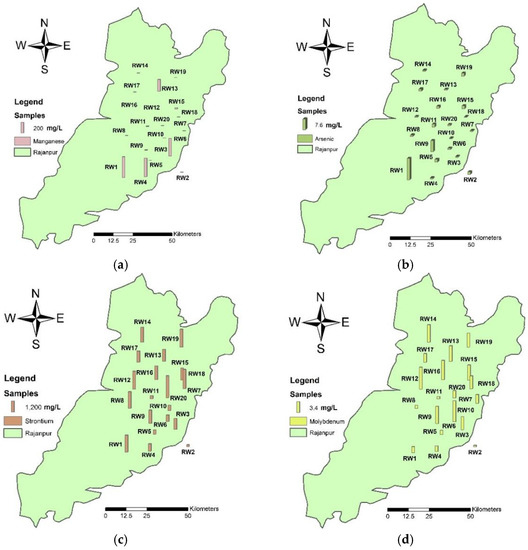
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution maps of (a) strontium, (b) arsenic, (c) manganese, and (d) molybdenum showing the concentration of elements at the location sites in the study area of Rajanpur.
The concentration of molybdenum generally does not register higher levels in freshwater bodies. In this study, molybdenum was reported to be between 0.2 and 6.76 mg L−1, which is within the permissible limit. There is no health risk due to the copper, cobalt, nickel, and cadmium concentrations found in the study area. Strontium concentration ranged between 207 mg L−1 and 2487.76 mg L−1 with an average of 1291.845 mg L−1, with 70% of sampling locations registering values above the allowable limits of drinking water. The USEPA [39] scheduled strontium on the CCL 3 (USEPA Contaminant Candidate List 3) to consider possible and additional future regulations. The pollutant competitor list is a catalog of unregulated impurities which are not exposed to any declared or proposed public drinking water guidelines and public water frameworks [40].
3.3. Water Quality Index
The water is undrinkable if values of WQI are less than 44 according to the CCME water quality index method. These values indicate that 50.5% of samples are “unfit” for drinking and 45.5% are “poor” according to the drinking water quality standards. This study examined the potential of using the CCME WQI calculated from various types of numeric water elements at the sampling locations to check water quality.
3.4. Principal Component Analysis
In the present study, concentration levels above the permissible limits set by the WHO make a cluster (Figure 5). The values are plotted in the quadrant on the positive side of PC1 and negative side of PC2. Parameters that are near each other show a strong correlation and other variables which are plotted away from each other are weakly related, except those that are plotted diametrically opposite to each other, indicating a negative correlation. Most major nutrients (Ca, Na, S, and Cl) and physical parameters (conductivity, TDS, and hardness) are clustered together with the large loading lines. Most minor nutrients such as Co, Mo, Sr, and Mn, and other major nutrients are also grouped together. No significant concerns are noted for Al, Cr, pH, and turbidity, which are shown on the negative side of the PCs. In the loading plot, the positive loadings specify a measured variable and its correlation to other parameters, in which an increase in one parameter may increase the other and vice versa, due to the common origin source. The directions of the lines and their nearness indicate how correlated nutrients are grouped. The length of the loadings on the principal components plot indicates the degree of a variable in terms of its concentration or values. Major nutrients that reduce water quality are grouped in clusters that are plotted along the PC1 and PC2 values in Figure 5a. Clusters are indicative of hydrological settings and common origin sources of the determined parameters. The shaded regions of the plot are locations that indicate extreme values plotting away from the main clusters. Locations RW11 and RW2 are the canal waters, location RW7 is from the residential area near the industrial site, and RW1 is an agricultural site. An arrow shows a trend of water quality changing from marginally fit water to very poor-quality water (Figure 5) in the study area.
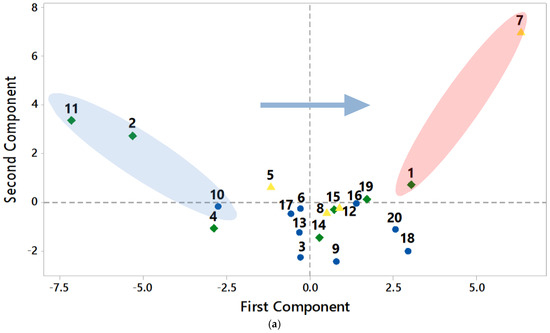
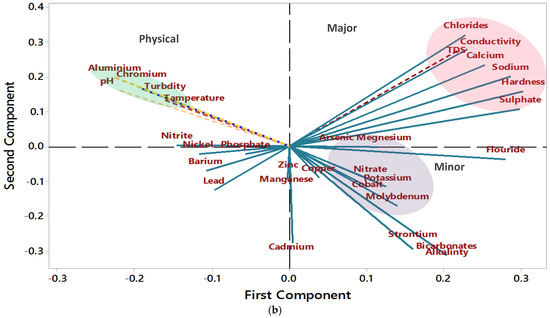
Figure 5.
PCA graphs (a,b) show negative and positive trends of samples and parameters. In graph (a) public places are denoted by a yellow color, agriculture by a green color, and residential areas by a blue color. Shaded circular regions in various colors in the plots indicate the main clusters of measured variables concentration changes and the sampling locations which are based on the land use and anthropogenic activities in the study area.
3.5. Correlation and Regression Analysis
Correlation analysis and principal component analysis result in a notable correlation between major elements. Correlation coefficients between metals showed positive correlations for Ni-Cu (r = 0.52), Zn-Cu (r = 0.44), HCO3−-Mo (r = 0.58), PO43−-Al (r = 0.46), Mn-Ar (r = 0.43), PO43−-Cu (r = 0.61), Mg-Mo (r = 0.45), HCO3−-Sr (r = 0.76), Mg-Sr (r = 0.50), PO43−-Zn (r = 0.52), Ca-Cl (r = 0.92), Ca-Na (r = 0.85), Cl-Na (r = 0.89), K-NO3- (r = 0.62), and SO4-F (r = 0.77). Correlation coefficients between metals showed negative correlations for Sr-Al (r = −0.40), Al-HCO3− (r = −0.54), Ni-Cd (r = −0.41), and NO2−-SO42− (r = −0.40).
Results obtained from linear regression showed high values for twelve elements (Figure 6). Regression for levels of metals showed a strong correlation for HCO3-Sr (R2 = 0.5761), F-SO4 (R2 = 0.589), Na-Ca (0.7225), and Ar-Mg (0.4105). The correlation coefficients between metals and physical elements showed a strong relationship between Cl and conductivity (R2 = 0.7783), and between hardness and Ca (0.8684). These results indicate that metals showing a strong correlation might have a similar pollution source, which could be agricultural operations or other anthropogenic activities. However, more research is required to fully determine the physicochemical processes involved in metal bindings, mobilization, and the fate of chemicals in the study area (Table 3).
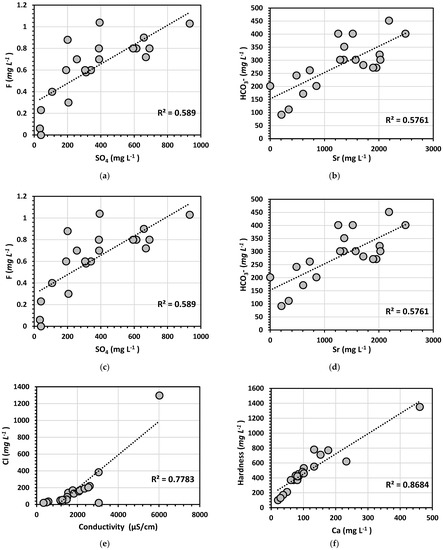
Figure 6.
Scatter plots (a) F-SO4; (b) HCO3−Sr; (c) Cl-conductivity; (d) hardness-Ca; (e) Ar-Mg; and (f) Ca-Na showing variations in relationships among the measured parameters in water samples taken from the study area.

Table 3.
Pearson correlations between different elements.
3.6. Digital Elevation Model
Groundwater quality determination processes can be complicated because they reflect biochemical interactions on scales that are not easily observed. To characterize the natural mechanism, an understanding of the water flow and transport routes in a region is required [41]. In this study, a simple digital elevation model (DEM) was utilized to understand and interpret the general flow conditions. The map of the Indus River near the Rajanpur District indicates that the quality of water changes from marginal to poor in various directions (Figure 7). In addition, the DEM provided a basic understanding of the possible hydrological flow on a larger scale in connection to the terrain characteristics (i.e., stream, slants, curve) of the study area as water moves from the elevated area on the western side to the downstream areas in the southeast direction. As groundwater moves towards the lower elevation areas, it dissolves various nutrients and becomes concentrated. Finally, it joins the Indus River which is the main water body controlling regional drainage and flow directions. The arrow indicates the water flow direction, which depends on the local geography shown by contours of various elevation values. Hence, the DEM indicated that geological features, hydrological features, and other factors (mountains, floods) are the main determinants of the spatial variation in elemental concentrations in the area.
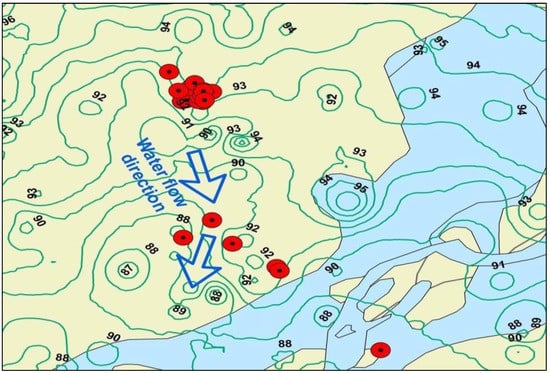
Figure 7.
The DEM shows the direction of water in the sampling area and the adjoining Indus River.
4. Discussion
A previous study reported that most of the residents of Jampur (a tehsil in the Rajanpur District) and Rajanpur are drinking polluted water, which is detrimental and dangerous, and also reported several hotspots in terms of metal and chemical contamination [42,43,44]. Aesthetic and physical attributes examined in this study such as the turbidity, odor, and taste of the water were not objectionable in most of the samples. The turbidity of the two samples that were collected from the surface water (river and canal) was high (muddy waters). The pH values of all samples were within permissible limits as per the WHO standards [45]. About 98.5% of the water samples were within the permissible limits of alkalinity and only 2.5% showed high alkalinity. Toor and Tahir [46] reported that arsenic levels are low in the southern areas of Punjab and the present study registered values in agreement with their findings.
Overall, 35% of the water samples that are observed in the spatial distribution maps have high values of Ca. The highest value of sulfate was detected in the sample from residential areas. Elements such as Ca, Mg, and Na are accountable for significant vital functions in the human body. It was previously reported that momentary exposure to extraordinary groupings of Ca does not cause health-related ramifications, yet long-term exposure might prompt hypercalcemia, calcification of the urinary tract and in kidneys [47]. Groundwater usually contains more minerals and salts than surface water, especially in areas rich in sodium minerals or areas with seawater intrusion [48]. The values of carbonates and bicarbonates were also within permissible limits. The highest concentrations of almost all the major elements were detected in a residential sample, RW7. Chloride levels are found in a wide variety of concentrations in natural waters.
The content of chloride usually increases with the addition of minerals [35]. Water is fit for consumption when it contains some trace elements and heavy metals, but when those constituents surpass the levels considered safe for consumption by humans, the water becomes unfit or possibly toxic [49,50]. Depending on their type, use, and amount, metals and trace metals can cause serious health problems, and most of them are generally toxic [51,52]. Chemical stability, a broad variety of sources, difficulties in remediation, poor degradation, bioaccumulation, and severe toxicity make trace elements one of the most dangerous contaminants in water [53,54]. Humans are mostly exposed to As, Al, Cd, Hg, and Pb due to their widespread use in manufacturing and industrial operations in the modern economy. The release of potentially toxic substances in water can result in a variety of health problems, including cancer, intellectual disabilities, neurological conditions, cardiovascular diseases, kidney problems, bone problems, Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease [55,56,57,58]. The level of As and Al increased in the two samples, but not significantly. The results show that nitrates, nitrites, and Cr do not have significant health impacts in the study area.
According to the values of the water quality index, water seems to be hard and contaminated with heavy metals in the area of study. The WQI is a powerful tool for indicating water quality. The study area of the Rajanpur District is impacted and stressed by geological factors, climatic factors, chemical parameters, and anthropogenic activities [59].
According to principal component analysis, the major nutrients that reduce water quality are grouped into clusters on the PC1 and PC2 biplot. Elements and parameters that exceeded the allowable limits are Ca, Na, sulfate, chlorides, Co, Mn, Sr, TDS, and hardness. The residents of the Rajanpur District are mainly dependent on agriculture for their livelihood, which significantly impacts groundwater quality. Water movement (seasonal floods) and excess use of fertilizers are mainly responsible for degrading the water quality. In any case, industrial waste discharge is currently a less contributing factor, but that might change soon as the population of the study area is rising. Elements that pose no environmental issues are Al, pH, turbidity, temperature, Cr, nitrite, and phosphate. Depending on the elemental pair some correlations are very weak; there may be independent varying sources that contribute to the weak correlation between the elements [60].
In this study, a DEM was utilized to extract information for mapping the Indus River near the Rajanpur District, which indicates that water moves from west to southeast for about 50 km. The quality of water changes from marginal to very poor along the flow direction as water becomes enriched in dissolved nutrients. A gradual addition of elements raises the dissolved contents of the water, and this depends upon the residence time, aquifer material characteristics, and anthropogenic inputs. Geogenic sources are the main contributing factor, followed by agricultural activities that affect the hydrogeochemistry of the study area. Hence, continuous monitoring of water quality is required to ensure a clean water supply in developing countries [61,62].
There is a need for more research work on the major nutrients in this area. There is a need for extensive hydrological study in order to understand the aquifer hydrogeochemistry and groundwater flow dynamics. However, we do not know about the general health impacts of poor-quality water on the people of this area because this study concentrated on the assessment of groundwater quality parameters.
5. Conclusions
It is concluded that the overall quality of water is poor in the residential and agricultural areas of Rajanpur. Most of the population is consuming contaminated water due to the elevated levels of metals and ions in the area. Spatial variation maps showed that levels of major elements were mostly high, increasing the salt level and resulting in poor-quality water. Some trace elements showed very high levels at a few places because of geographical locations and land use practices. The principal component analysis identified the sources and the factors accountable for variations in water quality. WQI values indicated that water quality in the greater part of the sampled sites in the region is exceptionally poor or close to poor. The digital elevation model determined that as water moves through the aquifer it dissolves salts and becomes concentrated. The geographical setting, seasonal flooding cycles, and climatic conditions in this area are mainly accountable for the variations in physicochemical parameters and high metal content. Agricultural activities, anthropogenic activities, and some industrial activities are also responsible for the poor groundwater quality. This study highlights the importance of continuous monitoring of heavy metal levels in groundwater through advanced technology, as water shortage and consumption of poor-quality water are impacting the living standards of people.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.S. and Q.u.Z.; Data curation, A.M. and K.A.; Methodology, A.M. and K.S.; Software, K.S., B.S. and A.H.; Writing—original draft, K.A., Q.u.Z. and A.M.; Writing—review and editing, Q.u.Z., F.U.H., B.S. and K.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the efforts of the Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources (PCRWR) for their assistance in laboratory analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ayandiran, T.A.; Fawole, O.O.; Dahunsi, S.O. Water quality assessment of bitumen polluted Oluwa river, South-Western Nigeria. Water Resour. Ind. 2018, 19, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadiati, M.; Rajabi Yami, Z.; Eskandari, E.; Nakhaei, M.; Kisi, O. Application of artificial intelligence models for prediction of groundwater level fluctuations: Case study (Tehran-Karaj alluvial aquifer). Environ. Monitt. Assess. 2022, 194, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wu, J.; Qian, H. Hydrochemical appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and the major influencing factors: A case study in and around Hua County, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh, H.P.; Linh, N.K.; Linh, N.T.; Linh PT, N.; Linh, T.K.; Mai TT, N.; Nam, D.V. Why is freshwater important to humanity? 2022; preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghfam, S.; Bagheri, A.; Razzagh, S.; Nadiri, A.A.; Vadiati, M.; Senapathi, V.; Sekar, S. Hydrochemical analysis of seawater intrusion by graphical techniques in coastal aquifers to delineate vulnerable areas. In Groundwater Contamination in Coastal Aquifers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, C.B.; Lee, Y.H.; Park, J.C.; Kang, H.M.; Hagiwara, A.; Lee, J.S. Effects of metal-polluted seawater on life parameters and the induction of oxidative stress in the marine rotifer Brachionus koreanus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 225, 108576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Paul, M.; Bhoumik, N.; Hassan, M.; Alam, M.; Aktar, Z. Heavy metal pollution assessment in the groundwater of the Meghna Ghat industrial area, Bangladesh, by using water pollution indices approach. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Progress on Household Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2000–2017: Special Focus on Inequalities; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Tripathi, V.R.; Garg, S.K. Physicochemical and microbiological assessment of recreational and drinking waters. Environ. Monitt Assess. 2012, 184, 2691–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbueri, J.C. Assessment of the quality of groundwaters proximal to dumpsites in Awka and Nnewi metro-polises: A comparative approach. Int. J. Energ. Water Res. 2018, 2, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofinlade, W.S.; Daramola, S.O.; Olabode, O.F. Hydrochemical and statistical modeling of groundwater quality in two constrasting geological terrains of southwestern Nigeria. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 4, 1405–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, M.P. Hydrogeochemical analysis and evaluation of surface water quality of Pratapgarh district, Uttar Pradesh, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgbenu, C.N.; Egbueri, J.C. The hydrogeochemical signatures, quality indices and health risk assessment of water resources in Umunya district, southeast Nigeria. Appli. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Vasa, S.K.; Li, P. Evaluation of groundwater quality, Peddavagu in Central Telangana (PCT), South India: An insight of controlling factors of fluoride enrichment. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 4, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, M.G.; Uddin, S.M.; Haque, A.B.M.H. Assessment of hydro-geochemistry and groundwater quality of Rajshahi City in Bangladesh. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 4663–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A.; Azam, M.; Saboor, A. Water Quality Status of Upper KPK and Northern Areas of Pakistan; Publication No. 142-2010; Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources, Water Resources Research Centre, Peshawar, Ministry of Science and Technology: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ochilova, N.R.; Muratova, G.S.; Karshieva, D.R. The Importance of Water Quality and Quantity in Strengthening the Health and Living Conditions of the Population. Cent. Asian J. Med. Nat. Sci. 2021, 2, 399–402. [Google Scholar]
- Memon, M.; Soomro, M.S.; Akhtar, M.S.; Memon, K.S. Drinking water quality assessment in Southern Sindh (Pakistan). Environ. Monitt Assess. 2011, 177, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, P.; Saxena, A.; Singh, D.S.; Verma, D. Impact of rapid urbanization on water quality index in groundwater fed Gomati River, Lucknow, India. Curr. Sci. 2018, 114, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Y.; Dilawar, A.; Ullah, S.F.; Akhter, G.; Martinez-Carvajal, H.; Hussain, M.B.; Aslam, A.Q. Modelling the spatial distribution of arsenic in water and its correlation with public health, central Indus Basin, Pakistan. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2016, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stefanakis, A.I.; Zouzias, D.; Marsellos, A. Groundwater pollution: Human and natural sources and risks. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 4, 82–102. [Google Scholar]
- Vincy, M.; Brilliant, R.; Pradeepkumar, A. Hydrochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater for drinking and irrigation purposes: A case study of Meenachil River Basin, Western Ghats, Kerala, India. Environ. Monitt. Assess. 2015, 187, 4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zektser, I.S.; Everett, L.G. Groundwater Resources of the World and Their Use; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Egbueri, J.C. Water quality appraisal of selected farm provinces using integrated hydrogeochemical, multivariate statistical, and microbiological technique. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 5, 997–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, L.; Jun, B.M.; Flora, J.R.; Park, C.M.; Yoon, Y. Removal of heavy metals from water sources in the developing world using low-cost materials: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 229, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häder, D.P.; Banaszak, A.T.; Villafañe, V.E.; Narvarte, M.A.; González, R.A.; Helbling, E.W. Anthropogenic pollution of aquatic ecosystems: Emerging problems with global implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Javed, S.; Ullah, S.; Fatima, S.H.; Zaidi, F.; Khan, M.S. Bayesian spatial analysis and prediction of groundwater contamination in Jhelum city (Pakistan). Environ Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbueri, J.C. Heavy metals pollution source identification and probabilistic health risk assessment of shallow groundwater in Onitsha, Nigeria. Anal. Lett. 2020, 53, 1620–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.S.; Sunitha, B.; Rambabu, R.; Rao, P.V.; Rao, P.S.; Spandana, B.D.; Marghade, D. Quality and degree of pollution of groundwater, using PIG from a rural part of Telangana State, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Rosin, K.G. Ground Water Vulnerability Assessment–Challenges and Opportunities; Division of Environmental Sciences, Indian Agricultural Research Institute: Delhi, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hashmi, I.; Farooq, S.; Qaiser, S. Chlorination and water quality monitoring within a public drinking 15 water supply in Rawalpindi Cantt (Westridge and Tench) area, Pakistan. Environ. Monitt. Assess. 2009, 158, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Taani, A.A.; Nazzal, Y.; Howari, F.M. Groundwater scarcity in the Middle East. In Global Groundwater; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 163–175. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Zuo, R.; Ni, P.; Xue, Z.; Xu, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D. Application of a genetic algorithm to groundwater pollution source identification. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.S.; Roy, S.D.; Ghaffari, M.A.; Choudhary, B.A.; Uzair, M.; Ijaz, A.S.; Khan, T.R. Survey of ethno-medicinal weeds of district rajhan pur, Punjab, Pakistan. Indian. Res. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 1, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Manganese in Drinking-Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; No. WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/104; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; Rice, E.W., Ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Dil, A.S.; Qazi, I.A.; Baig, M.A.; Khan, E.A.; Tahir, A. National Standards for Drinking Water Quality (NSDWQ); Government of Pakistan, Pakistan Environmental Protection Agency: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2008. Available online: https://mocc.gov.pk/SiteImage/Misc/files/Drinking%20Water%20Quality%20Standares%20MAY%202007.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2018).
- WHO. Aluminium in Drinking-Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality (No. WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/53); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Drinking Water Contaminant Candidate List 3-Draft. 2008. Available online: https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2008/02/21/E8-3114/drinking-water-contaminant-candidate-list-3-draft (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- O’Donnell, A.J.; Lytle, D.A.; Harmon, S.; Vu, K.; Chait, H.; Dionysiou, D.D. Removal of strontium from drinking water by conventional treatment and lime softening in benchscale studies. Water Res. 2016, 103, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, U.; Josset, L.; Russo, T. A snapshot of the world’s groundwater challenges. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2020, 45, 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, H.M.; Abbas, I.; Sohl, M.A.; Shehzadi, R.; Ramay, S.M.; Imran, M.; Sohl, M.N. Appraisal of drinking water quality of tehsil Jampur, Pakistan. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 52, 4641–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Chand, S.; Rafique, H.M. Predicting the spatial distribution of sulfate concentration in groundwater of Jampur-Pakistan using geostatistical methods. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 28195–28204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, M.; Sultana, N.; Jamil, M.; Ashraf, R. Investigation of portable groundwater quality and health risk assessment of selected trace metals in flood affected areas of district Rajanpur, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. An. Ch. 2016, 3, 1000183. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: First Addendum to the Fourth Edition; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Toor, I.A.; Tahir, S.N.A. Study of arsenic concentration levels in Pakistani drinking water. Polish J. Environ. Studies. 2009, 18, 907–912. [Google Scholar]
- Azizullah, A.; Khattak, M.N.K.; Richter, P.; Häder, D.P. Water pollution in Pakistan and its impact on public health—A review. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samantara, M.K.; Padhi, R.K.; Sowmya, M.; Kumaran, P.; Satpathy, K.K. Heavy metal contamination, major ion chemistry and appraisal of the groundwater status in coastal aquifer, Kalpakkam, Tamil Nadu, India. GW. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 5, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyer, C.M.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Carpio, E.A.; García, P.A.; Stengel, C.; Berg, M. Arsenic, manganese and aluminum contamination in groundwater resources of Western Amazonia (Peru). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 1437–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewoyin, O.O.; Kayode, O.T.; Omeje, O.; Odetunmibi, O.A. Risk assessment of heavy metal and trace elements contamination in groundwater in some parts of Ogun state. Cogent Engr. 2019, 6, 1632555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adepoju-Bello, A.A.; Alabi, O.M. Heavy metals: A review. Nig. J. Pharm. 2005, 37, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Peng, W.; Cheng, C. Source estimating of heavy metals in shallow groundwater based on UNMIX Model: A case study. BioTechnology 2016, 45, 756–762. [Google Scholar]
- Barzegar, R.; Asghari Moghaddam, A.; Adamowski, J.; Nazemi, A.H. Assessing the potential origins and human health risks of trace elements in groundwater: A case study in the Khoy plain, Iran. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2019, 41, 981–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momodu, M.A.; Anyakora, C.A. Heavy metal contamination of ground water: The Surulere case study. Res. J. Environ Earth Sci. 2010, 2, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.Y.; Qian, H. Human health risk assessment for chemical pollutants in drinking water source in Shizuishan City, Northwest China. Sci. Inf. Database 2011, 8, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Prüss-Ustün, A.; Vickers, C.; Haefliger, P.; Bertollini, R. Knowns and unknowns on burden of disease due to chemicals: A systematic review. Environ. Health 2011, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.P.; Wang, S.W.; Kao, Y.H.; Chen, J.S. Health risk assessment of groundwater arsenic pollution in southern Taiwan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogilo, J.K.; Onditi, A.O.; Salim, A.M.; Yusuf, A.O. Assessment of levels of heavy metals in paints from interior walls and indoor dust from residential houses in Nairobi City County, Kenya. Chem. Sci. Int. J. 2017, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaa, B.; Elbeltagi, A.; Boudibi, S.; Chaffaï, H.; Islam, A.R.M.; Kulimushi, L.C.; Wong, Y.J. Water quality index modeling using random forest and improved SMO algorithm for support vector machine in Saf-Saf river basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 48491–48508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Karunanidhi, D.; Subramani, T.; Srinivasamoorthy, K. Sources and consequences of groundwater contamination. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicology. 2021, 80, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.J.; Shimizu, Y.; He, K.; Nik Sulaiman, N.M. Comparison among different ASEAN water quality indices for the assessment of the spatial variation of surface water quality in the Selangor river basin, Malaysia. Environ. Monitt. Assess. 2020, 192, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.J.; Shimizu, Y.; Kamiya, A.; Maneechot, L.; Bharambe, K.P.; Fong, C.S.; Nik Sulaiman, N.M. Application of artificial intelligence methods for monsoonal river classification in Selangor river basin, Malaysia. Environ. Monitt. Assess. 2021, 193, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).