Controlling Biofilm Growth and Its Antibiotic Resistance in Drinking Water by Combined UV and Chlorination Processes
Abstract
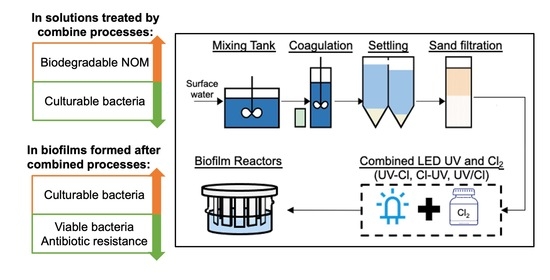
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Degradation of Organics
3.2. Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance Control
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Qi, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhou, W. Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Drinking Water and Biofilms: The Correlation with the Microbial Community and Opportunistic Pathogens. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waak, M.B.; LaPara, T.M.; Hallé, C.; Hozalski, R.M. Occurrence of Legionella Spp. in Water-Main Biofilms from Two Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7630–7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Knibbe, W.-J.; Feng, C.; Liu, W.; Medema, G.; van der Meer, W. Potential Impacts of Changing Supply-Water Quality on Drinking Water Distribution: A Review. Water Res. 2017, 116, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingender, J.; Flemming, H.-C. Biofilms in Drinking Water and Their Role as Reservoir for Pathogens. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douterelo, I.; Calero-Preciado, C.; Soria-Carrasco, V.; Boxall, J.B. Whole Metagenome Sequencing of Chlorinated Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 2080–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J.; Su, C.; Zhou, J.; Xu, L.; Qian, Y.; Chen, H. Effects and Mechanisms of Ultraviolet, Chlorination, and Ozone Disinfection on Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Secondary Effluents of Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, M.; Wang, L.; Niu, F.; Yang, D.; Zhang, G. Evaluation Survey of Microbial Disinfection Methods in UV-LED Water Treatment Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Choi, Y.-J. The Effects of UV Disinfection on Drinking Water Quality in Distribution Systems. Water Res. 2010, 44, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, B.; Lu, Y.; Mei, Y.; Shen, L. Advances in Application of Ultraviolet Irradiation for Biofilm Control in Water and Wastewater Infrastructure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torkzadeh, H.; Cates, E.L. Biofilm Growth under Continuous UVC Irradiation: Quantitative Effects of Growth Conditions and Growth Time on Intensity Response Parameters. Water Res. 2021, 206, 117747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Chen, Y.; Hu, J. Application of UVC and UVC Based Advanced Disinfection Technologies for the Inactivation of Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Elimination of Horizontal Gene Transfer Activities: Opportunities and Challenges. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Wen, G.; Cao, R.; Zhao, H.; Xu, X.; Xia, Y.; Wu, G.; Lin, W.; Wang, J.; Huang, T. Simultaneously Enhance the Inactivation and Inhibit the Photoreactivation of Fungal Spores by the Combination of UV-LEDs and Chlorine: Kinetics and Mechanisms. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ye, C.; Guo, L.; Chen, C.; Kong, X.; Chen, Y.; Shu, L.; Wang, P.; Yu, X.; Fang, J. Assessment of the UV/Chlorine Process in the Disinfection of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa: Efficiency and Mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 9221–9230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, J.Y. Effect of DNA Sizes and Reactive Oxygen Species on Degradation of Sulphonamide Resistance Sul1 Genes by Combined UV/Free Chlorine Processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsyth, J.E.; Zhou, P.; Mao, Q.; Asato, S.S.; Meschke, J.S.; Dodd, M.C. Enhanced Inactivation of Bacillus Subtilis Spores during Solar Photolysis of Free Available Chlorine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12976–12984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hessler, C.M.; Xue, Z.; Seo, Y. The Role of Extracellular Polymeric Substances on the Sorption of Natural Organic Matter. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Geng, J.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, L.; Xu, K. Inactivation of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Municipal Wastewater Effluent by Chlorination and Sequential UV/Chlorination Disinfection. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyara, A.M.; Torvinen, E.; Veijalainen, A.-M.; Heinonen-Tanski, H. The Effect of UV and Combined Chlorine/UV Treatment on Coliphages in Drinking Water Disinfection. Water 2016, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shekhawat, S.S.; Kulshreshtha, N.M.; Vivekanand, V.; Gupta, A.B. Impact of Combined Chlorine and UV Technology on the Bacterial Diversity, Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Disinfection by-Products in Treated Sewage. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 339, 125615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, H.M.; Payne, S.J.; Gagnon, G.A. Sequential UV- and Chlorine-Based Disinfection to Mitigate Escherichia coli in Drinking Water Biofilms. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, L.; Xiao, H.; Shen, F.; Deng, S.; Zhang, S.; He, J.; Song, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Effects of Disinfection Efficiency on Microbial Communities and Corrosion Processes in Drinking Water Distribution Systems Simulated with Actual Running Conditions. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 88, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Xing, X.; Hu, C.; Wang, H.; Lyu, L. Effect of Sequential UV/Free Chlorine Disinfection on Opportunistic Pathogens and Microbial Community Structure in Simulated Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, J.P.; Malley Jr., J.P.; Willoughby, S.A. Effects of UV Irradiation on Organic Matter. J. AWWA 2000, 92, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosińska, A.; Rakocz, K. The Influence UV/Chlorination Process on Changes of Biodegradable Fraction in Water. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Ng, T.-W.; Chen, H.; Chow, A.T.; Liu, S.; Wong, P.K. Formation of Assimilable Organic Carbon (AOC) during Drinking Water Disinfection: A Microbiological Prospect of Disinfection Byproducts. Environ. Int. 2020, 135, 105389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Jafari, I.; Zhong, Y.; Chee, M.J.; Hu, J. Degradation of Organics and Formation of DBPs in the Combined LED-UV and Chlorine Processes: Effects of Water Matrix and Fluorescence Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasiri, M.; Sano, D.; Suzuki, S. Understanding Human Health Risks Caused by Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria (ARB) and Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARG) in Water Environments: Current Knowledge and Questions to Be Answered. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 2016–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, S.; Yu, X. Exposure to Mutagenic Disinfection Byproducts Leads to Increase of Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8188–8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ateia, M.; Awfa, D.; Yoshimura, C. Regrowth of Bacteria after Light-Based Disinfection—What We Know and Where We Go from Here. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gunawan, C.; Barraud, N.; Rice, S.A.; Harry, E.J.; Amal, R. Understanding, Monitoring, and Controlling Biofilm Growth in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8954–8976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, J.R.; Stefan, M.I.; Shaw, P.-S.; Lykke, K.R. Determination of the Quantum Yields of the Potassium Ferrioxalate and Potassium Iodide–Iodate Actinometers and a Method for the Calibration of Radiometer Detectors. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2011, 222, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AWWA. AWWARF Water Industry Database: Utility Profiles. In American Water Works Association; American Water Works Association Research Foundation: Denver, CO, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Micó, P.; García-Ballesteros, S.; Mora, M.; Vicente, R.; Amat, A.M.; Arques, A. EEMlab: A Graphical User-Friendly Interface for Fluorimetry Experiments Based on the DrEEM Toolbox. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2019, 188, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.R.; Stedmon, C.A.; Graeber, D.; Bro, R. Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Multi-Way Techniques. PARAFAC. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 6557–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, K.R.; Stedmon, C.A.; Wenig, P.; Bro, R. OpenFluor—An Online Spectral Library of Auto-Fluorescence by Organic Compounds in the Environment. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 658–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, C.; Hu, X. Treatment of NOM Fractions of Reservoir Sediments: Effect of UV and Chlorination on Formation of DBPs. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 154, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, F.J.; Núñez, L.A. Characterization of Aquatic Humic Substances. Water Environ. J. 2011, 25, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Shao, Y.; Gao, N.; Deng, Y.; Li, L.; Deng, J.; Tan, C. Characterization of Algal Organic Matters of Microcystis Aeruginosa: Biodegradability, DBP Formation and Membrane Fouling Potential. Water Res. 2014, 52, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platikanov, S.; Tauler, R.; Rodrigues, P.M.S.M.; Antunes, M.C.G.; Pereira, D.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G. Factorial Analysis of the Trihalomethane Formation in the Reaction of Colloidal, Hydrophobic, and Transphilic Fractions of DOM with Free Chlorine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, J. Photoelectrocatalytic Degradation of Organics and Formation of Disinfection Byproducts in Reverse Osmosis Concentrate. Water Res. 2020, 168, 115105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X. Formation Potential of Disinfection By-Products after Coagulation of Algal Matters. Master’s thesis, The University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, K.R.; Hambly, A.; Singh, S.; Henderson, R.K.; Baker, A.; Stuetz, R.; Khan, S.J. Organic Matter Fluorescence in Municipal Water Recycling Schemes: Toward a Unified PARAFAC Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2909–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, T.S.; Osburn, C.; Shields, M.R.; Yvon-Lewis, S.; Young, J.; Guo, L.; Zhou, Z. Deepwater Horizon Oil in Gulf of Mexico Waters after 2 Years: Transformation into the Dissolved Organic Matter Pool. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9288–9297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Guo, L. Variations in Colloidal DOM Composition with Molecular Weight within Individual Water Samples as Characterized by Flow Field-Flow Fractionation and EEM-PARAFAC Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1657–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stedmon, C.A.; Thomas, D.N.; Granskog, M.; Kaartokallio, H.; Papadimitriou, S.; Kuosa, H. Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter in Baltic Coastal Sea Ice: Allochthonous or Autochthonous Origins? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7273–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Boyer, J.N.; Jaffé, R. Evaluating the Distribution of Terrestrial Dissolved Organic Matter in a Complex Coastal Ecosystem Using Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 66, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence Excitation−Emission Matrix Regional Integration to Quantify Spectra for Dissolved Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulman, D.M.; Remucal, C.K. Role of Reactive Halogen Species in Disinfection Byproduct Formation during Chlorine Photolysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9629–9639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shin, H.-S.; Hur, J. Estimating the Concentration and Biodegradability of Organic Matter in 22 Wastewater Treatment Plants Using Fluorescence Excitation Emission Matrices and Parallel Factor Analysis. Sensors 2014, 14, 1771–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Qu, F.; Sun, L.; Liang, H.; Han, Z.; Chang, H.; Shao, S.; Li, G. Relationship between Soluble Microbial Products (SMP) and Effluent Organic Matter (EfOM): Characterized by Fluorescence Excitation Emission Matrix Coupled with Parallel Factor Analysis. Chemosphere 2015, 121, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Xie, P.; Wang, Z.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Wiesner, M.R. Comparative Study on the Pretreatment of Algae-Laden Water by UV/Persulfate, UV/Chlorine, and UV/H2O2: Variation of Characteristics and Alleviation of Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling. Water Res. 2019, 158, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-L.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Du, Y.; Hu, H.-Y. Degradation of Natural Organic Matter by UV/Chlorine Oxidation: Molecular Decomposition, Formation of Oxidation Byproducts and Cytotoxicity. Water Res. 2017, 124, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsvetanova, Z.; Tsvetkova, I.; Najdenski, H. Antimicrobial Resistance of Heterotrophic Bacteria in Drinking Water-Associated Biofilms. Water 2022, 14, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim[otilde]es, L.C.; Azevedo, N.; Pacheco, A.; Keevil, C.W.; Vieira, M.J. Drinking Water Biofilm Assessment of Total and Culturable Bacteria under Different Operating Conditions. Biofouling 2006, 22, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernard, L.; Schäfer, H.; Joux, F.; Courties, C.; Muyzer, G.; Lebaron, P. Genetic Diversity of Total, Active and Culturable Marine Bacteria in Coastal Seawater. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yao, S.; Lin, K.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, C. Removal of Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Control of Horizontal Transfer Risk by UV, Chlorination and UV/Chlorination Treatments of Drinking Water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, D.E.; Kim, S. Fate of Tetracycline Resistance in Synthetic Livestock Carcass Leachate for Two Years. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 187, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Chen, Y.; Feng, L.; Wan, K.; Li, J.; Feng, M.; Yu, X. Effect of the Ultraviolet/Chlorine Process on Microbial Community Structure, Typical Pathogens, and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Reclaimed Water. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 16, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Chiang, T.Y.; Zhu, X.; Hu, J. Controlling Biofilm Growth and Its Antibiotic Resistance in Drinking Water by Combined UV and Chlorination Processes. Water 2022, 14, 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223643
Chen Y, Li Y, Yang S, Chiang TY, Zhu X, Hu J. Controlling Biofilm Growth and Its Antibiotic Resistance in Drinking Water by Combined UV and Chlorination Processes. Water. 2022; 14(22):3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223643
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yiwei, Yizhen Li, Shaolun Yang, Tsung Yen Chiang, Xiaoying Zhu, and Jiangyong Hu. 2022. "Controlling Biofilm Growth and Its Antibiotic Resistance in Drinking Water by Combined UV and Chlorination Processes" Water 14, no. 22: 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223643
APA StyleChen, Y., Li, Y., Yang, S., Chiang, T. Y., Zhu, X., & Hu, J. (2022). Controlling Biofilm Growth and Its Antibiotic Resistance in Drinking Water by Combined UV and Chlorination Processes. Water, 14(22), 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223643