Accurate Monitoring of Algal Blooms in Key Nearshore Zones of Lakes and Reservoirs Using Binocular Video Surveillance System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
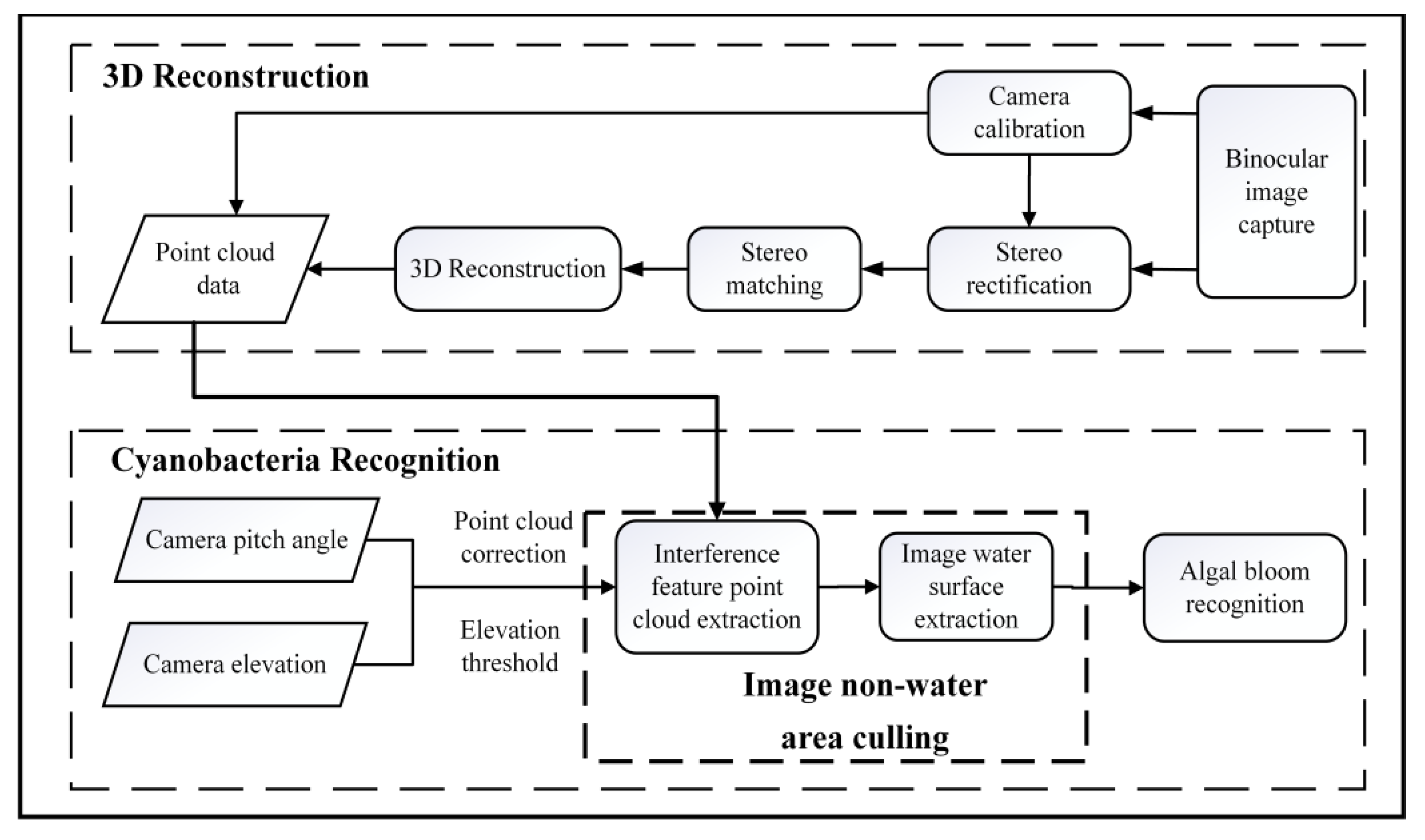
2.1. Basic Principle of Algal Extraction Based on a Video Image
2.2. Binocular Image Data Acquisition in Key Nearshore Zones of Lakes and Reservoirs
2.3. Accurate Extraction of Algal Blooms Based on Binocular Images
2.3.1. Binocular Stereo Vision 3D Point Cloud Acquisition
- Step 1: Image acquisition
- Step 2: Camera calibration
- Step 3: Image correction
- Step 4: Stereo matching
- Step 5: 3D reconstruction
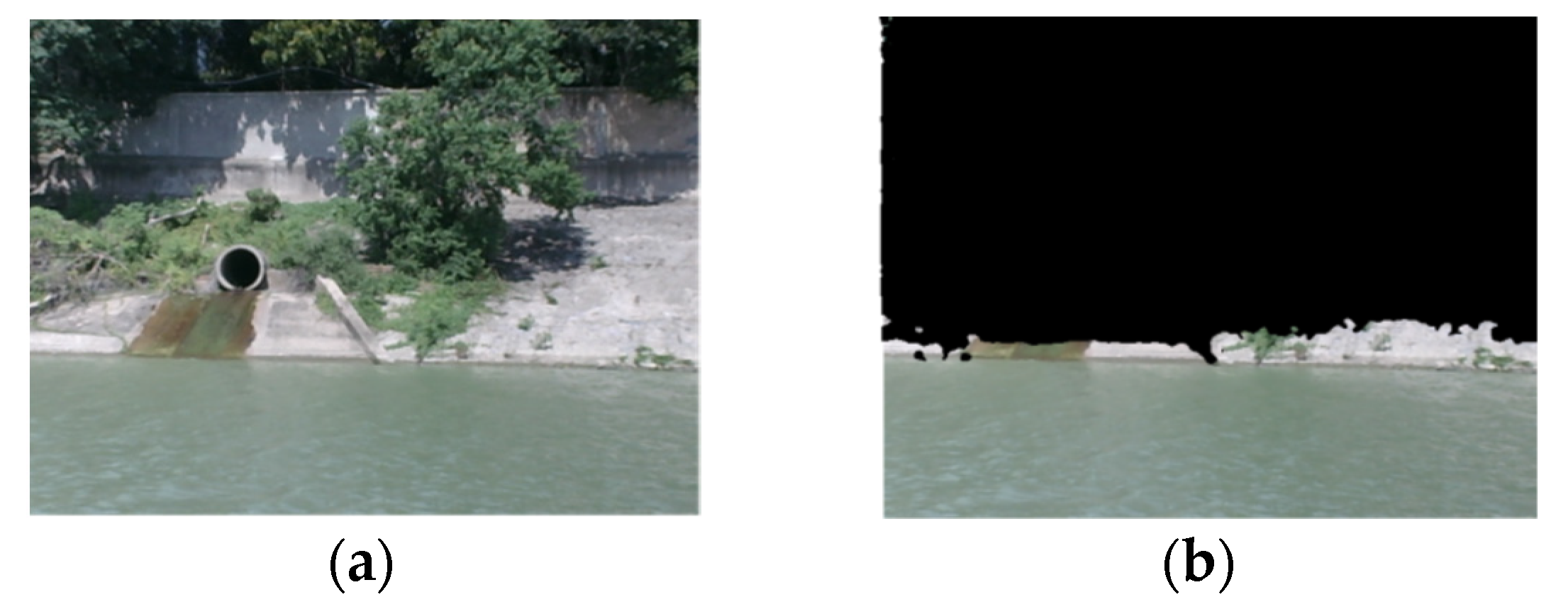
2.3.2. Separation of Water Region and Non-Water Region
- (1)
- Non-water region identification in 3D point clouds
- (2)
- Obtaining the pixel coordinates of the non-water regions
- (3)
- Deletion of non-water regions in the left image
2.3.3. Accurate Identification of Algal Blooms
2.4. Precision Evaluation
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brooks, B.W.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Howard, M.D.; Johnson, M.-V.V.; Morton, S.L.; Perkins, D.A.; Reavie, E.D.; Scott, G.I.; Smith, S.A.; Steevens, J.A. Are harmful algal blooms becoming the greatest inland water quality threat to public health and aquatic ecosystems? Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, C.S. Cyanobacterial water-blooms. Adv. Bot. Res. 1987, 13, 67–143. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Erik, J.; Jens-Christian, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, T.; Wang, P.; Shingirai, N.; et al. From unusual suspect to serial killer: Cyanotoxins boosted by climate change may jeopardize African megafauna. Innov. Amst. 2021, 2, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Duan, H.; Xie, H.; Ding, X.; Jiao, Y. Design and development of a web-based interactive twin platform for watershed management. Trans. GIS 2022, 26, 1299–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgersen, C.; Faux, R.N.; McIntosh, B.A.; Poage, N.J.; Norton, D.J. Airborne thermal remote sensing for water temperature assessment in rivers and streams. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieling, A. Satellite remote sensing for water erosion assessment: A review. CATENA 2006, 65, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon-Torres, A.; Ross, L.G.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Watson, A.I. The application of SPOT multispectral imagery for the assessment of water quality in Lake Patzcuaro, Mexico. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1992, 13, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Cai, X.; Biradar, C.M.; Platonov, A.; Dheeravath, V.; Goldlshleger, N.; Ben Dor, E.; Alchanatis, V.; Vithanage, J.; Markandu, A.; et al. Water productivity mapping using remote sensing data of various resolutions to support “more crop per drop”. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2009, 3, 033557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Villa, P.; Martinelli, A. Application of Remote Sensing in Water Resource Management: The Case Study of Lake Trasimeno, Italy. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 3885–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, P.O.; Holzman, M.; Degano, M.; Faramiñán, A.; Rivas, R.; Bayala, M. Spatial variability of the green water footprint using a medium-resolution remote sensing technique: The case of soybean production in the Southeast Argentine Pampas. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 142963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Rosa, S.; Hernández, W.; Williams, S.; Armstrong, R. Water Quality Anomalies following the 2017 Hurricanes in Southwestern Puerto Rico: Absorption of Colored Detrital and Dissolved Material. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Qin, B. Monitoring water quality using proximal remote sensing technology. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.; Schaeffer, B.; Darling, J.A.; Urquhart, E.A.; Johnston, J.M.; Ignatius, A.R.; Myer, M.H.; Loftin, K.A.; Werdell, P.J.; Stumpf, R.P. Satellite monitoring of cyanobacterial harmful algal bloom frequency in recreational waters and drinking water sources. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 80, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, J.; Alonso, C.A.; García, A. Remote sensing as a tool for monitoring water quality parameters for mediterranean lakes of European Union water framework directive (WFD) and as a system of surveillance of cyanobacterial harmful algae blooms (SCyanoHABs). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 181, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jim, G.; Chuanmin, H.; Gary, B.; Stephanie, K. Ocean Color Satellites Show Extensive Lines of Floating Sargassum in the Gulf of Mexico. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 3619–3625. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Taylor, C.; Carder, K.L.; Kelble, C.; Johns, E.; Heil, C.A. Red tide detection and tracing using MODIS fluorescence data: A regional example in SW Florida coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edward, S.; Frédéric, F.; Rafael, A.; Baptista, P.; Heygster, G.; Lubac, B.; Raucoules, D.; Almeida, P.L.; Bergsma, E.W.J.; Capo, S.; et al. Monitoring Beach Topography and Nearshore Bathymetry Using Spaceborne Remote Sensing: A Review. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2212. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Lee, Z.; Ma, R.; Yu, K.; Li, D.; Shang, S. Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) observations of cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu Lake, China. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2010, 115, C04002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W. Satellite-Observed Algae Blooms in China’s Lake Taihu. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2011, 89, 201–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Hu, C.; Visser, P.M.; Ma, R. Diurnal changes of cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu Lake as derived from GOCI observations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 1711–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Brookes, J.D.; Hall, N.S.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, H.; et al. The persistence of cyanobacterial (Microcystis spp.) blooms throughout winter in Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Duan, H.; Loiselle, S.; Zhang, M.; Xu, J. A novel MODIS algorithm to estimate chlorophyll a concentration in eutrophic turbid lakes. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Loiselle, S.; Li, J.; Hu, M. A MODIS-Based Novel Method to Distinguish Surface Cyanobacterial Scums and Aquatic Macrophytes in Lake Taihu. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaire, T.; Tiit, K.; Alo, L.; Sepp, M.; Paavel, B.; Noges, T. First Experiences in Mapping Lake Water Quality Parameters with Sentinel-2 MSI Imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 640. [Google Scholar]
- Yuji, S.; Akihiro, M.; Akihiro, M.; Ono, S.; Ito, A. A Simple Red Tide Monitoring Method using Sentinel-2 Data for Sustainable Management of Brackish Lake Koyama-ike. Japan. Water 2019, 11, 1044. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Shi, X.; Chen, N.; Zhang, M. Spatial-temporal variations of the in-situ growth rate of bloom-forming cyanobacteria and their environmental factors in Lake Chaohu, China. J. Lake Sci. 2021, 33, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, N.; Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, Y.; Cai, H.; et al. The proposal, practice and preliminary application of land-based (ground-based, shore-based) remote sensing of water environment. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2021, 25, 2163–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Deepak, R.M.; Abhishek, K.; Lakshmish, R.; Boddula, V.K.; Das, M.C.; Page, B.P.; Weber, S.J. CyanoTRACKER: A cloud-based integrated multi-platform architecture for global observation of cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms. Harmful Algae 2020, 96, 101828. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.; Wan, N.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, G.; Ceng, Q.; Luo, J.; Chen, Y.; Qi, T. Discussions and practices on the framework of monitoring system in eutrophic lakes and reservoirs. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 1396–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Duan, H.; Wan, N.; Gao, R.; Huang, J.; Xue, K.; Peng, Z.; Xiao, P. Design and practice of a platform for monitoring, early-warning and simulation of algal blooms in Lake Chaohu. J. Lake Sci. 2022, 34, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Xiao, P.; Zhang, X.; Duan, H.; Qiu, Y. Real-time monitoring of cyanobacterial blooms dynamics around Lake Chaohu based on video surveillance images. J. Lake Sci. 2022, 34, 1840–1853. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Yan, X.; Fang, S.; Du, Y.; Xue, B.; Yu, K.; Wang, C. Monitoring Cyanobacteria Bloom in Dianchi Lake Based on Ground-Based Multispectral Remote-Sensing Imaging: Preliminary Results. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Yu, G.; Sun, S.; Dou, Y.; Li, H.; Qiao, Z. Monitoring Water Quality of the Haihe River Based on Ground-Based Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Water 2022, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Sun, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G. A ground-based remote sensing system for high-frequency and real-time monitoring of phytoplankton blooms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Experiment ID | Original Image | MI | MV | BV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment_01 |  |  |  |  |
| Experiment_02 |  |  | 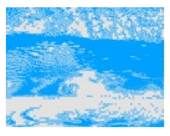 |  |
| Experiment_03 |  |  | 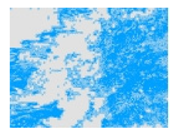 |  |
| Experiment_04 |  |  |  |  |
| Experiment_05 |  |  |  |  |
 algal area
algal area  algae-free areas).
algae-free areas).| Experiment ID | Original Image | MI | MV | BV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment_01 |  | 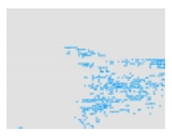 | 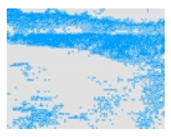 |  |
| Experiment_02 |  |  |  |  |
| Experiment_03 |  |  |  |  |
 algal area
algal area  algae-free area).
algae-free area).| Experiment ID | MI | MV | BV | DV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment_01 | 25% | 43% | 27% | 16 % |
| Experiment_02 | 36% | 51% | 40% | 11% |
| Experiment_03 | 9% | 48% | 19% | 29% |
| Experiment_04 | 37 % | 65% | 41% | 24% |
| Experiment_05 | 22% | 38 % | 26% | 12% |
| Experiment ID | MI | MV | BV | DV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment_01 | 5% | 30% | 8% | 22% |
| Experiment_02 | 9% | 46% | 13% | 33% |
| Experiment_03 | 1% | 16% | 6% | 10% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Xia, C.; Xie, H.; Wang, X.; Qiu, Y. Accurate Monitoring of Algal Blooms in Key Nearshore Zones of Lakes and Reservoirs Using Binocular Video Surveillance System. Water 2022, 14, 3728. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223728
Liu J, Xia C, Xie H, Wang X, Qiu Y. Accurate Monitoring of Algal Blooms in Key Nearshore Zones of Lakes and Reservoirs Using Binocular Video Surveillance System. Water. 2022; 14(22):3728. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223728
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jia, Chunlin Xia, Hui Xie, Xiaodong Wang, and Yinguo Qiu. 2022. "Accurate Monitoring of Algal Blooms in Key Nearshore Zones of Lakes and Reservoirs Using Binocular Video Surveillance System" Water 14, no. 22: 3728. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223728
APA StyleLiu, J., Xia, C., Xie, H., Wang, X., & Qiu, Y. (2022). Accurate Monitoring of Algal Blooms in Key Nearshore Zones of Lakes and Reservoirs Using Binocular Video Surveillance System. Water, 14(22), 3728. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223728







