A Dam Construction Event Recorded by High-Resolution Sedimentary Grain Size in an Outflow-Controlled Lake (Hulun Lake, China)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area

2.2. Sampling
2.3. Experiments and Methods
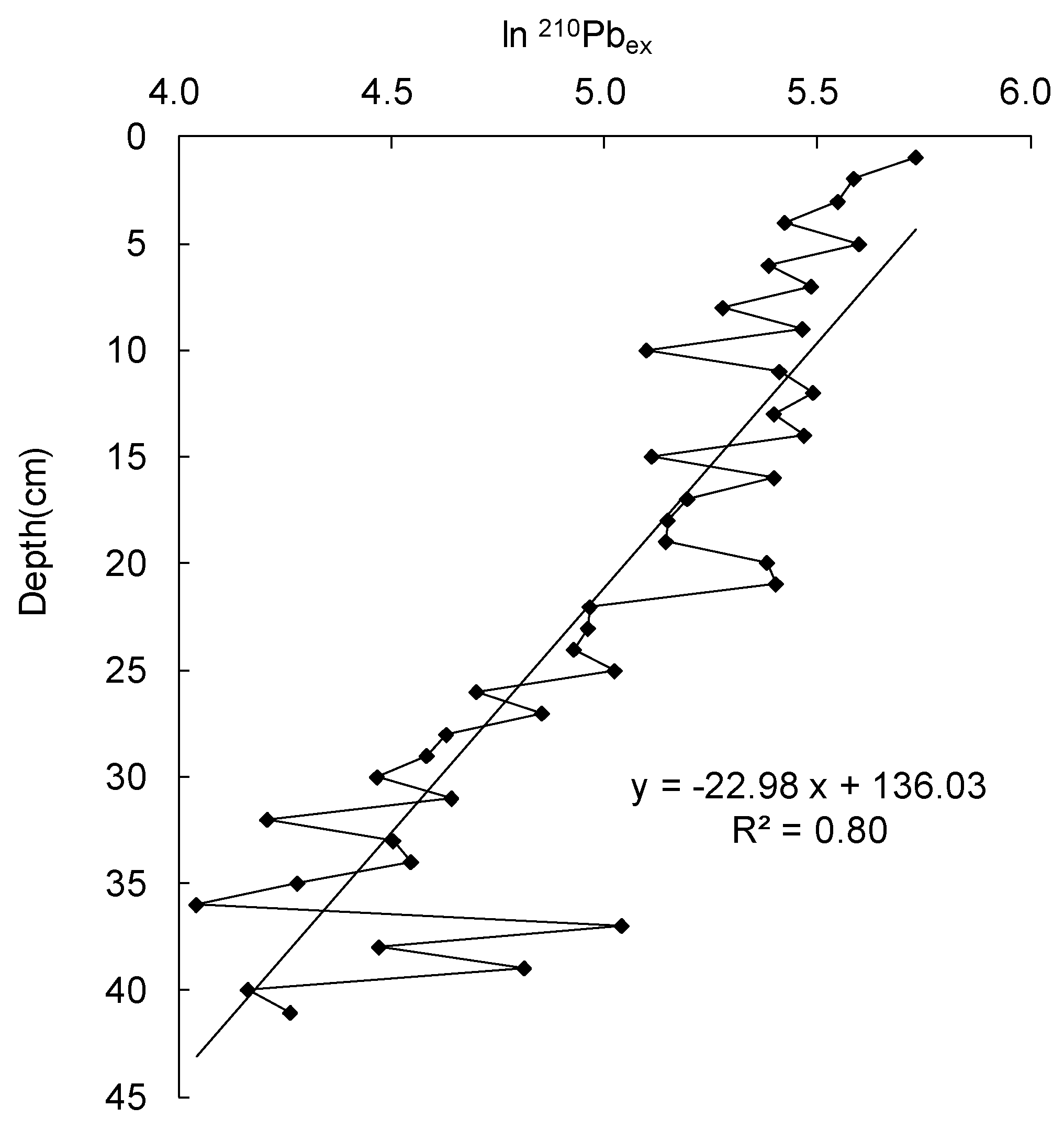
2.3.1. Sediment Core Chronology
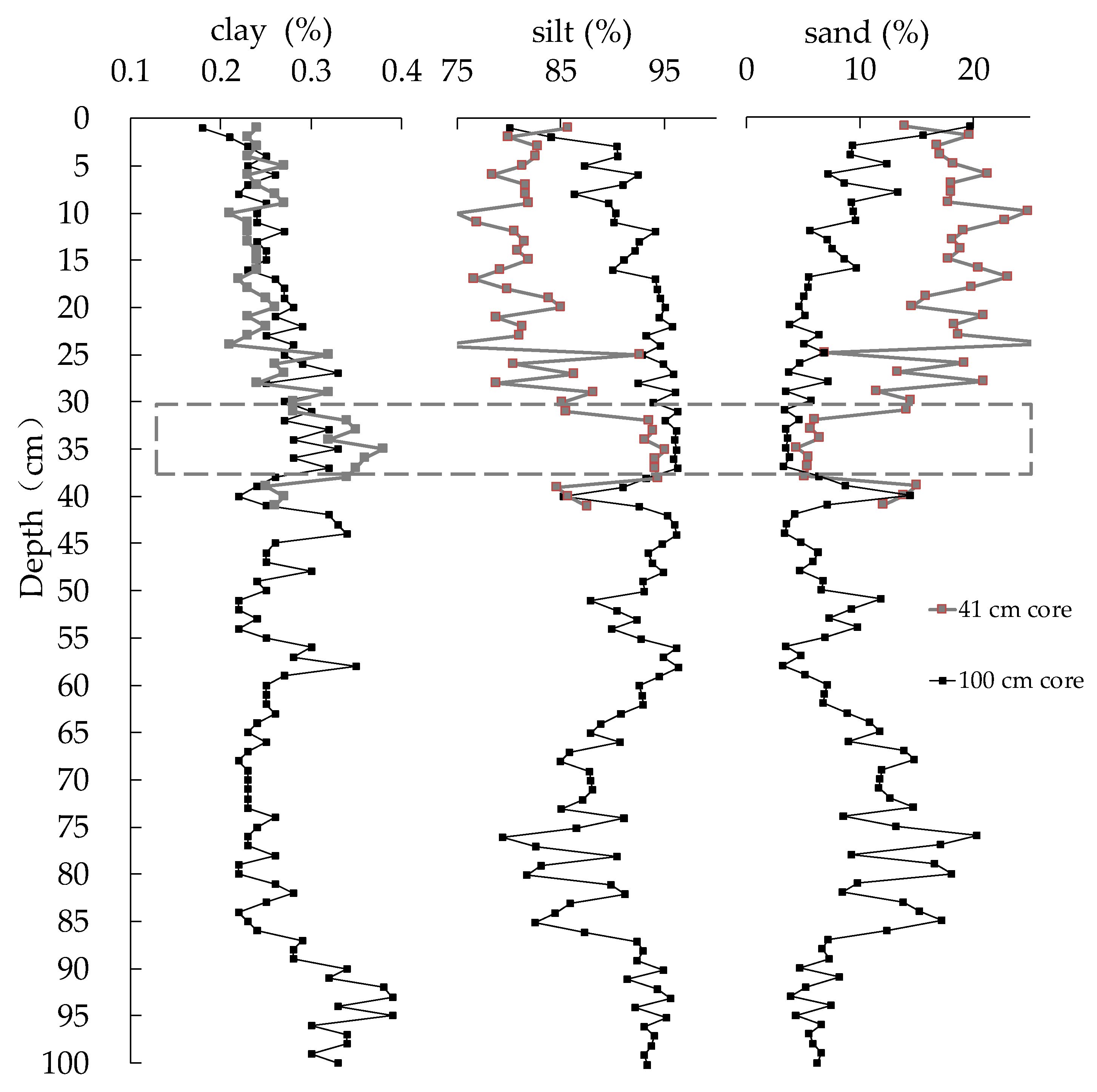
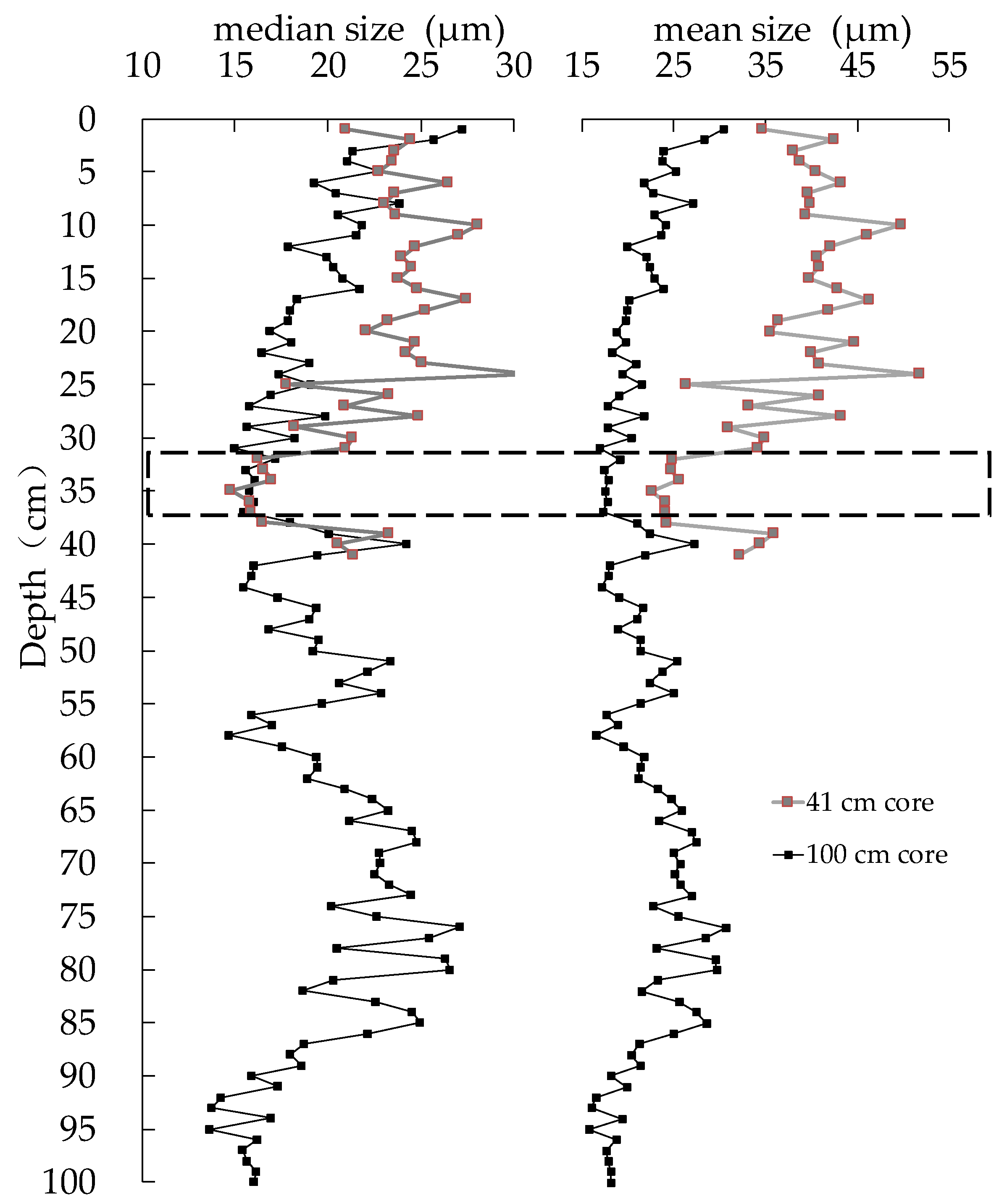
2.3.2. Grain Size of the Sediment Core
3. Results
3.1. Sediment Core Chronology
3.2. Characteristics of the Profile Distribution of Sediment Grain Size in Hulun Lake
4. Discussion
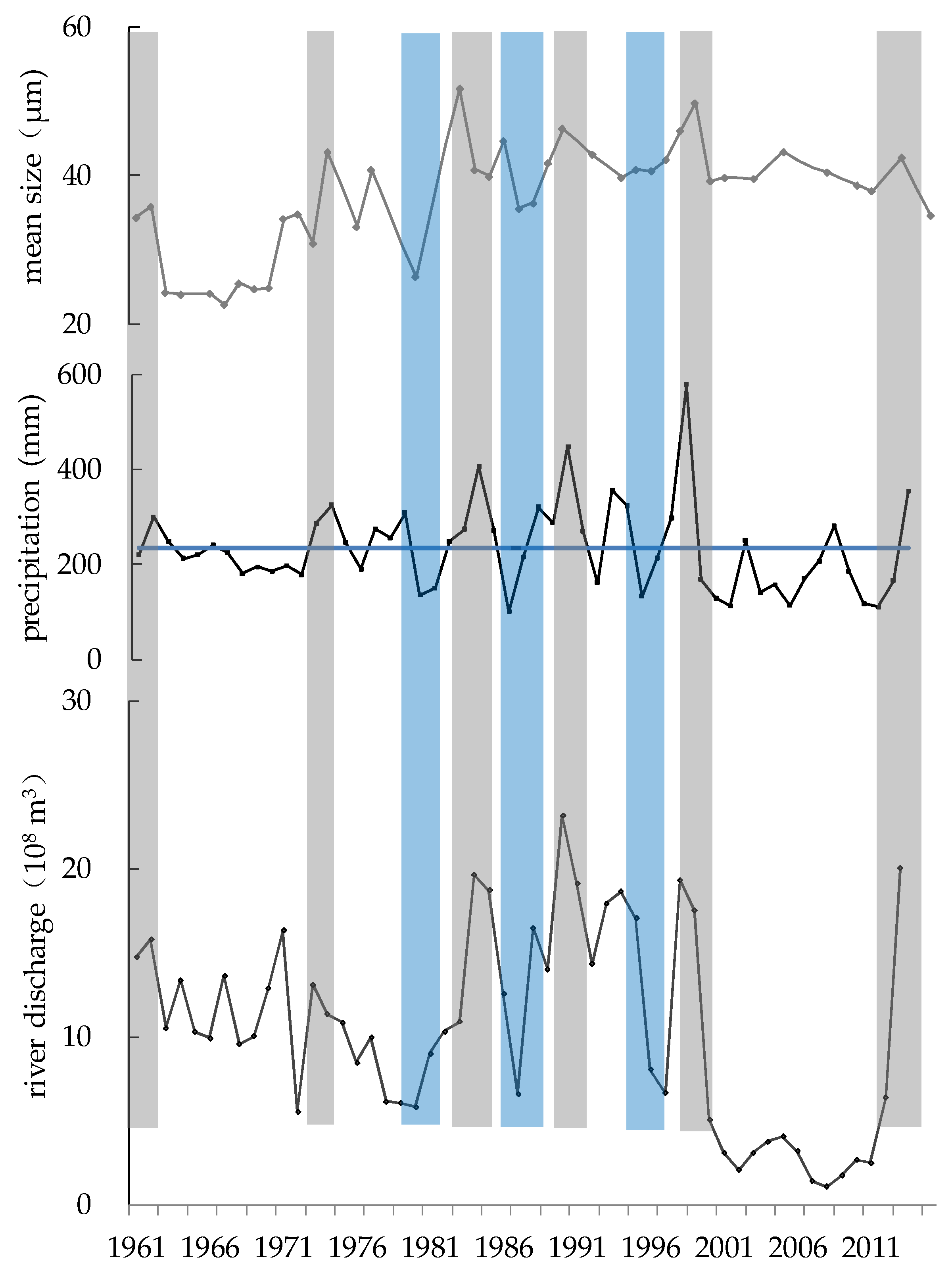
4.1. The Relationship between Precipitation and Sedimentary Grain Size
4.2. The Relationship between River Discharge and Sedimentary Grain Size
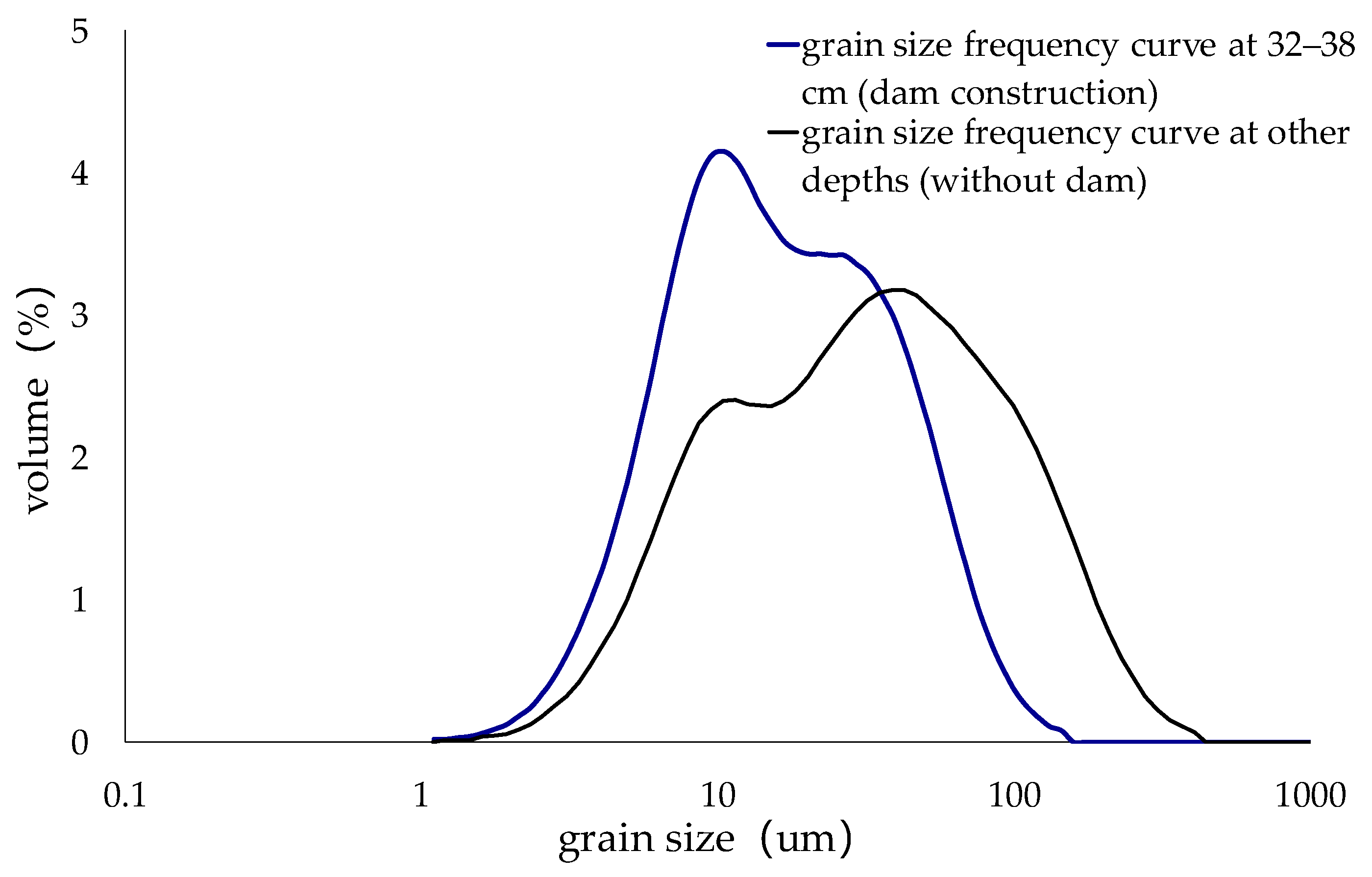
4.3. A Dam Construction Event Recorded by Sedimentary Grain Size
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Espinoza-Encinas, I.R.; Israde-Alcántara, I.; Domínguez-Vázquez, G.; Zárate-del Valle, P.F.; Huerta-Magaña, C.G. A 15,000-yr paleo-environmental record from Lake Chapala, west-central Mexico. J. Paleolimnol. 2022, 68, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.R.; Holmes, J.A.; Leng, M.J.; Sloane, H.; Horne, D.J. Effects of cleaning methods upon preservation of stable isotopes and trace elements in shells of Cyprideis torosa (Crustacea, Ostracoda): Implications for palaeoenvironmental reconstruction. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2018, 189, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Zeng, H. Sediment record of abrupt environmental changes in Lake Chenpu, upper reaches of Yellow River Basin, north China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 73, 6355–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, P.; Achyuthan, H.; Geethanjali, K.; Kumar, P.; Chopra, S. Late Pleistocene Paleoflood Deposits Identified by Grain Size Signatures, Parsons Valley Lake, Nilgiris, Tamil Nadu. J. Geol. Soc. India 2018, 91, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Tian, F.; Yang, J. Comparison of grain-size distributions between nearshore sections and a deep-water sediment core from Dali Lake, North China, and inferred Holocene lake-level changes. J. Paleolimnol. 2016, 56, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, M.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Song, L.; Huang, X.; Chen, F. Holocene record of eolian activity from Genggahai Lake, northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahm, W.-H.; Lee, G.H.; Yang, D.-Y.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kashiwaya, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Sakaguchi, A. A 60-year record of rainfall from the sediments of Jinheung Pond, Jeongeup, Korea. J. Paleolimnol. 2009, 43, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colman, S.M.; Baucom, P.C.; Bratton, J.F.; Cronin, T.M.; McGeehin, J.P.; Willard, D.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Vogt, P.R. Radiocarbon Dating, Chronologic Framework, and Changes in Accumulation Rates of Holocene Estuarine Sediments from Chesapeake Bay. Quat. Res. 2002, 57, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.A.; Wan, G.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhang, F.; Huang, R. Environmental records of lake sediments at different time scales: Sediment grain size as an example. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2004, 47, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Bierman, P.; Lini, A.; Thompson Davis, P.; Southon, J. Reconstructing lake and drainage basin history using terrestrial sediment layers: Analysis of cores from a postglacial lake in New England, USA. J. Paleolimnol. 2002, 28, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Kao, S.-J.; Dai, M. The role of mega dams in reducing sediment fluxes: A case study of large Asian rivers. J. Hydrol. 2012, 464–465, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-P.; Zhang, M.-J.; Li, Y.-T.; Fan, Y.-Y. Trend and dynamic cause of sediment particle size on the adjacent continental shelf of the Yangtze Estuary. China Ocean Eng. 2016, 30, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, E.B.; Pasternack, G.B.; Gray, A.B.; Goñi, M.; Woolfolk, A.M. Particle size characterization of historic sediment deposition from a closed estuarine lagoon, Central California. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 126, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chuai, X.; Yang, L.; Zhao, H. Climatic warming and overgrazing induced the high concentration of organic matter in Lake Hulun, a large shallow eutrophic steppe lake in northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 431, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Wang, S.; Appel, E.; Ji, L. Environmental mechanism of magnetic susceptibility changes of lacustrine sediments from Lake Hulun, China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2000, 43, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.; Xiao, J.; Chang, Z.; Zhai, D.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Itoh, S.; Lomtatidze, Z. Holocene climate changes in the mid-high-latitude-monsoon margin reflected by the pollen record from Hulun Lake, northeastern Inner Mongolia. Quat. Res. 2010, 73, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Chang, Z.; Wen, R.; Zhai, D.; Itoh, S.; Lomtatidze, Z. Holocene weak monsoon intervals indicated by low lake levels at Hulun Lake in the monsoonal margin region of northeastern Inner Mongolia, China. Holocene 2009, 19, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.J.; Jiang, F.Y.; Zhao, H.W.; Zhang, Z.B.; Sun, L. Annals of Hulun Lake; Jilin Literature and History Publishing House: Jilin, China, 1989. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wen, R.; Xiao, J.; Chang, Z.; Zhai, D.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Itoh, S. Holocene precipitation and temperature variations in the East Asian monsoonal margin from pollen data from Hulun Lake in northeastern Inner Mongolia, China. Boreas 2010, 39, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L. Environment and Climate Evolution Recorded in Sediment of Hulun Lake since Middle-Late Holocene. Ph.D. Thesis, Environment Group, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2017. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Glew, J.R.; Smol, J.P.; Last, W.M. Sediment core collection and extrusion. In Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments; Last, W.M., Smol, J.P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 73–105. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaswamy, S.; Lal, D.; Martin, J.M.; Meybeck, M. Geochronology of lake sediments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1971, 11, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, J.A.; Edgington, D.N. Determination of recent sedimentation rates in Lake Michigan using Pb-210 and Cs-137. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1975, 39, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, P.G.; Nolan, P.J.; Giford, D.W.; Godfrey, M.J.; Oldfeld, F.; Anderson, N.J.; Battarbee, R.W. 210Pb dating by low background gamma counting. Hydrobiologia 1986, 143, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, P.G.; Oldfield, F. Applications of lead-210 to sedimentation studies. In Uranium-Series Disequilibrium: Application to Earth, Marine, Environmental Sciences; Ivanovich, M., Harmon, R.S., Eds.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1992; pp. 731–778. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, J.C.; McHenry, J.R. Application of Radioactive Fallout Cesium-137 for Measuring Soil Erosion and Sediment Accumulation Rates and Patterns: A Review. J. Environ. Qual. 1990, 19, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, T.J.; Mikkelsen, O.A.; Møller, A.L.; Pejrup, M. Deposition and mixing depths on some European intertidal mudflats based on 210Pb and 137Cs activities. Cont. Shelf Res. 2000, 20, 1569–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Fang, N.Q.; Wang, Q.; Nie, H.G.; Qing, Z.L. Magnetic susceptibility of lacustrine sediments and its environmental significance: Evidence from Napahai lake, northwestern Yunnan, China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2002, 22, 413–419. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, H.; Zhang, R.; Wang, G.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wu, J.; Wu, L. A Dam Construction Event Recorded by High-Resolution Sedimentary Grain Size in an Outflow-Controlled Lake (Hulun Lake, China). Water 2022, 14, 3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233878
Gao H, Zhang R, Wang G, Fan Y, Zhu X, Wu J, Wu L. A Dam Construction Event Recorded by High-Resolution Sedimentary Grain Size in an Outflow-Controlled Lake (Hulun Lake, China). Water. 2022; 14(23):3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233878
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Hongbin, Rui Zhang, Gang Wang, Yanru Fan, Xinfeng Zhu, Junfeng Wu, and Li Wu. 2022. "A Dam Construction Event Recorded by High-Resolution Sedimentary Grain Size in an Outflow-Controlled Lake (Hulun Lake, China)" Water 14, no. 23: 3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233878
APA StyleGao, H., Zhang, R., Wang, G., Fan, Y., Zhu, X., Wu, J., & Wu, L. (2022). A Dam Construction Event Recorded by High-Resolution Sedimentary Grain Size in an Outflow-Controlled Lake (Hulun Lake, China). Water, 14(23), 3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233878











