A Paleolimnological Perspective on Arctic Mountain Lake Pollution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
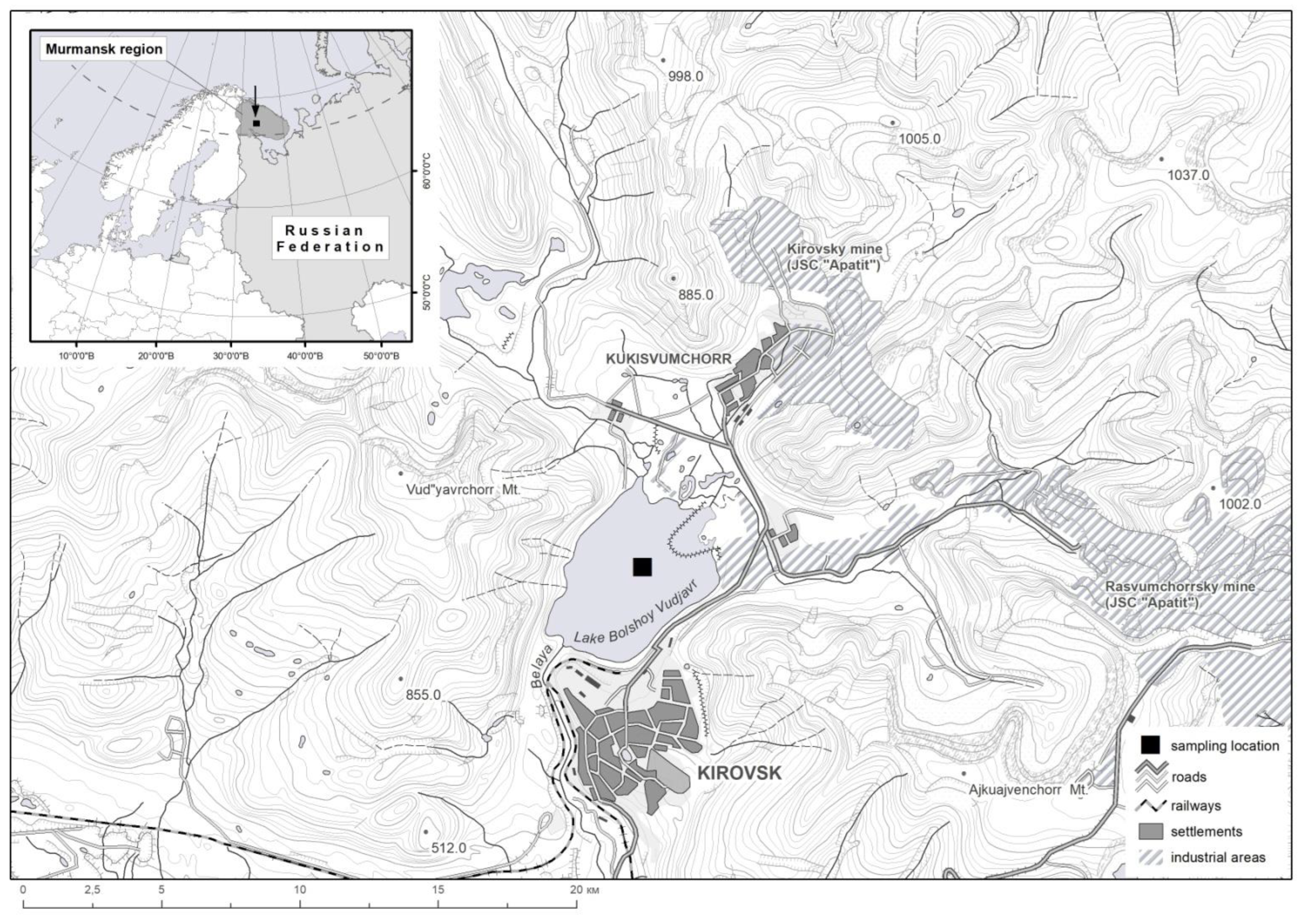
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Geological Structure
2.3. Morphometric and Hydrological Characteristics of the Lake
2.4. History of Development and Anthropogenic Activity
2.5. Research Methods, Sampling and Analysis of Sediments
2.5.1. Sediment Sampling
2.5.2. Granulometric Analysis of Sediments
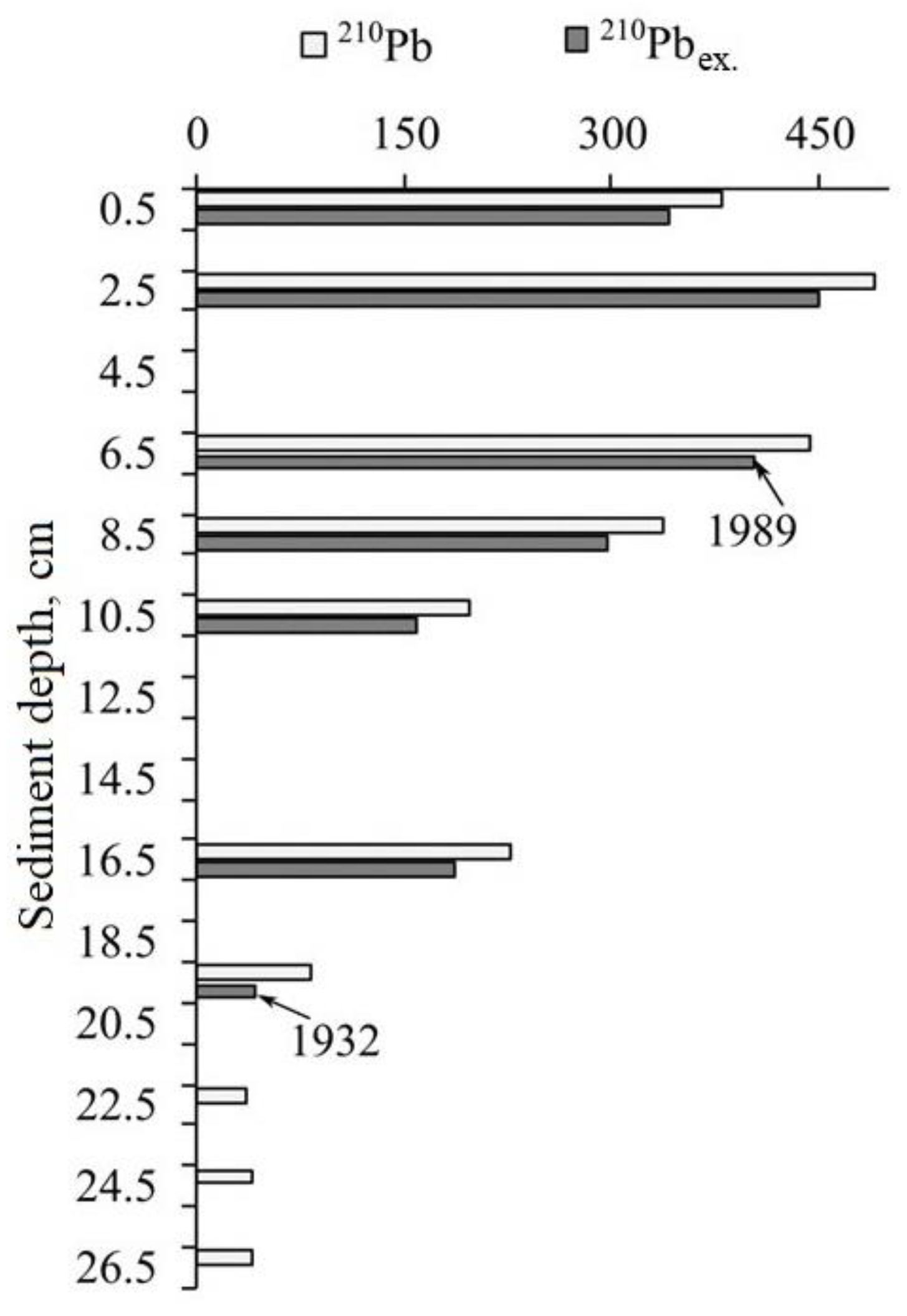
2.5.3. Sediment Dating
2.5.4. Determination of Loss on Ignition
2.5.5. Chemical Analysis of Elements
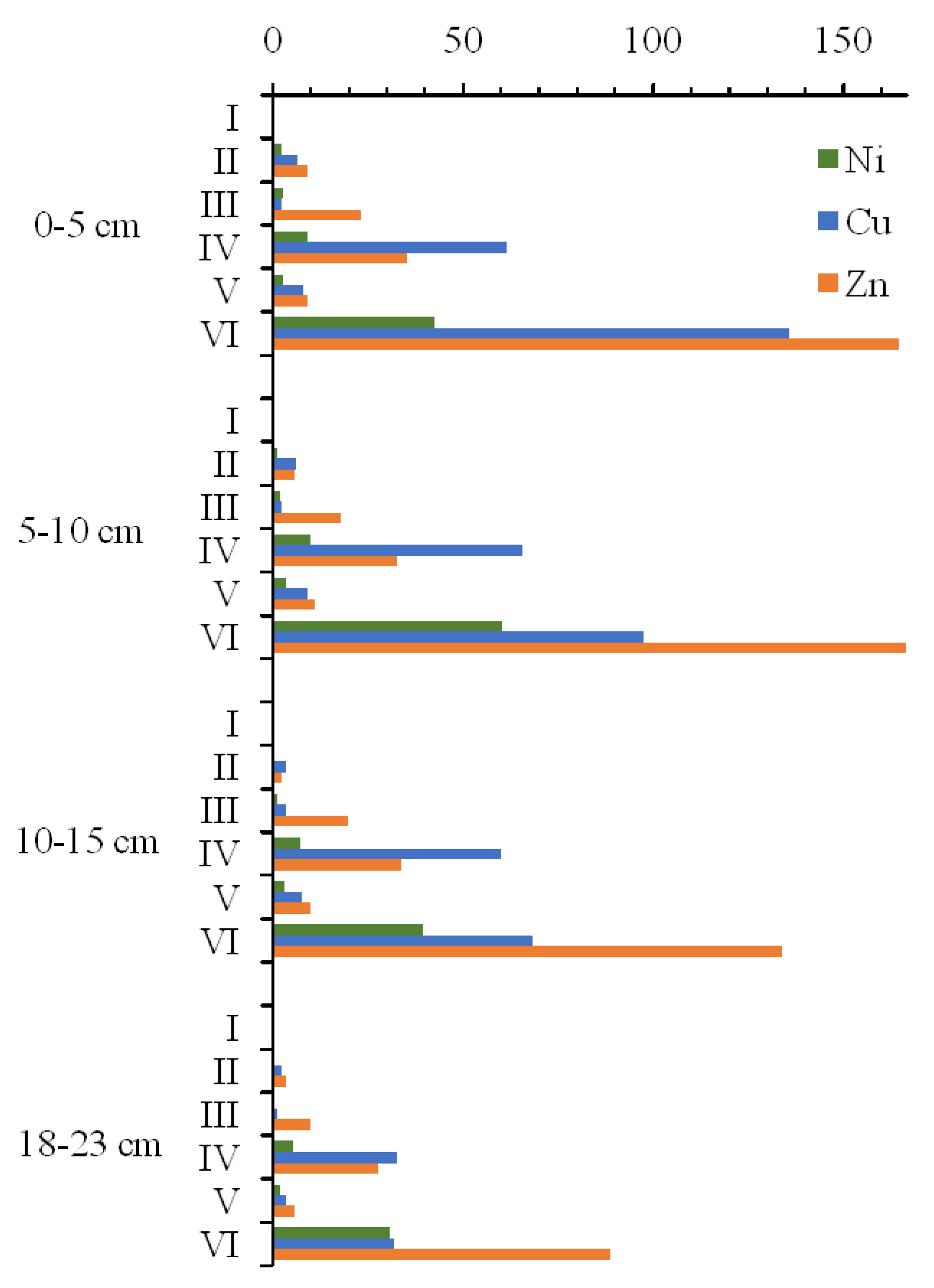
2.5.6. Determining the Chemical Fractions of Elements
- -
- Water-soluble fractions (reagent H2O).
- -
- Available (exchangeable) fractions (reagent NH4CH3COO, pH 4.8). The elements can desorb in case of changing of pH or ionic composition of water.
- -
- Fractions bound to Fe and Mn hydroxides (reagents 0.04 M NH2OH+HCl in 25% CH3COOH). Iron and manganese oxides exist in sediments as nodules, concretions, cement between particles. They are excellent scavengers for metals. The fraction is thermodynamically unstable under anoxic conditions (low Eh).
- -
- Fractions bound to organic matter (reagents 0.02 M HNO3 + 30% H2O2 and 3.2 M NH4CH4COO in 20% HNO3). Trace metals may be associated to various forms of organic matter. The complexation ability of humic substances in natural ecosystems is studied previously [71]. Organic matter can be degraded under oxidizing conditions leading to a release of trace metals in water.
- -
- Acid-soluble (residual) fractions (reagent HNO3); the most stable (mineral) fraction. The metals are associated with residual compound and not available to living organism. Dissolution of the fraction is possible only under a very strong anthropogenic impact on the reservoir.
- -
- Mineral (silicate) fractions obtained by deducting the combined concentration of all the above fractions from the total concentrations. The metals bounded with the crystal structure of silicate minerals are not expected to be released in water over a reasonable time span under the conditions normally encountered in nature.
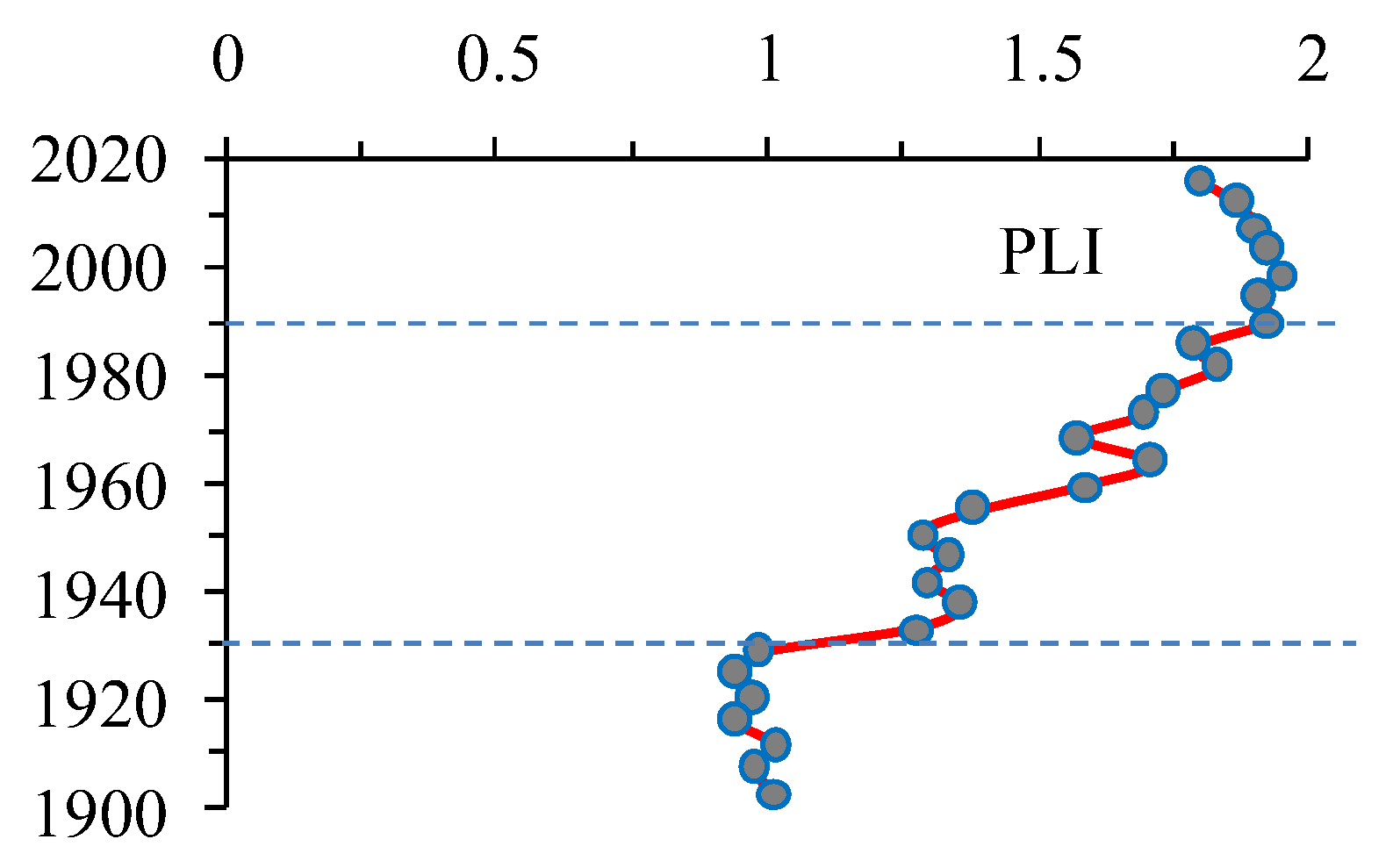
2.5.7. Intensity of Lake Pollution
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Granulometric Composition of Sediments
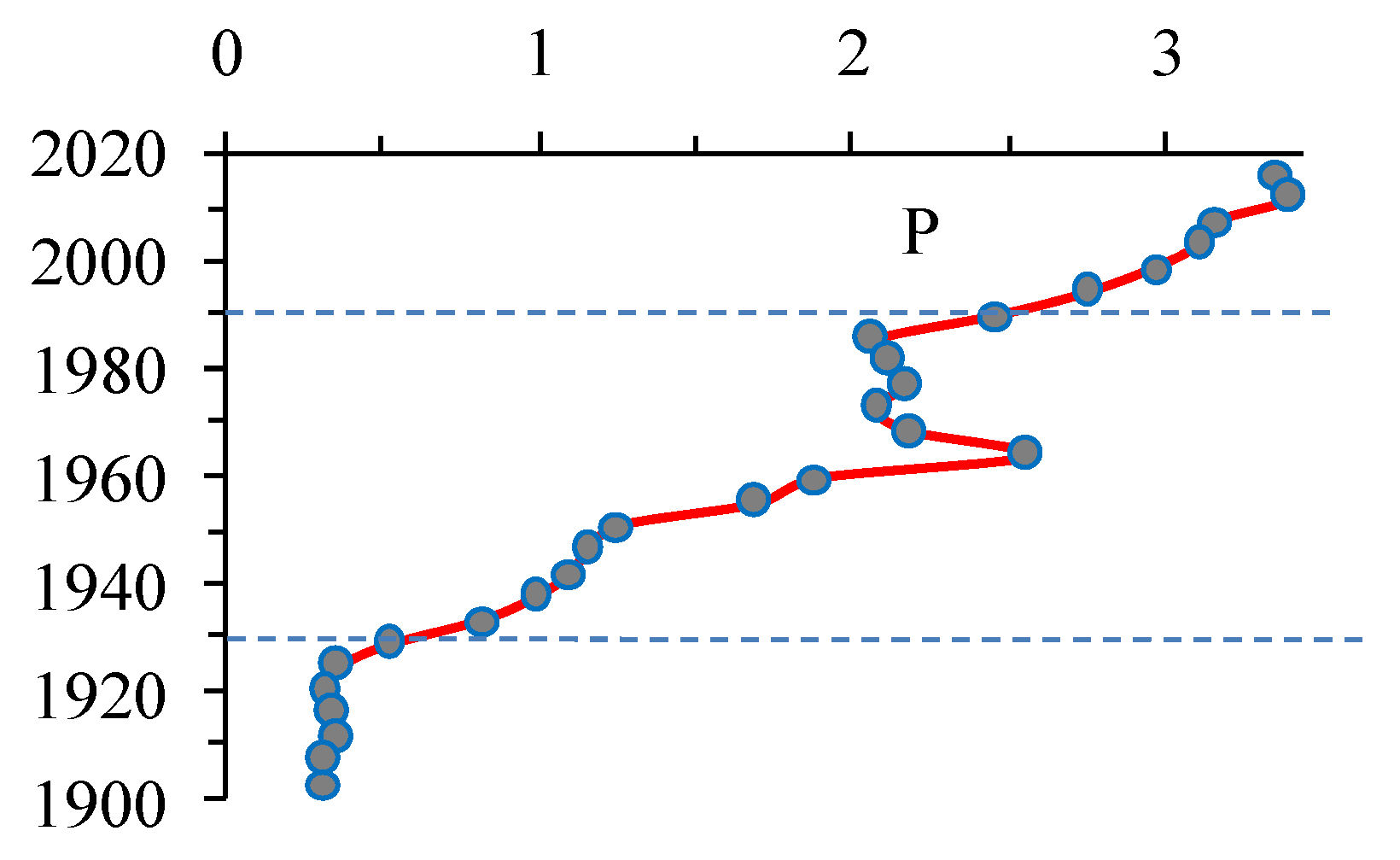
3.2. Dating of Sediments
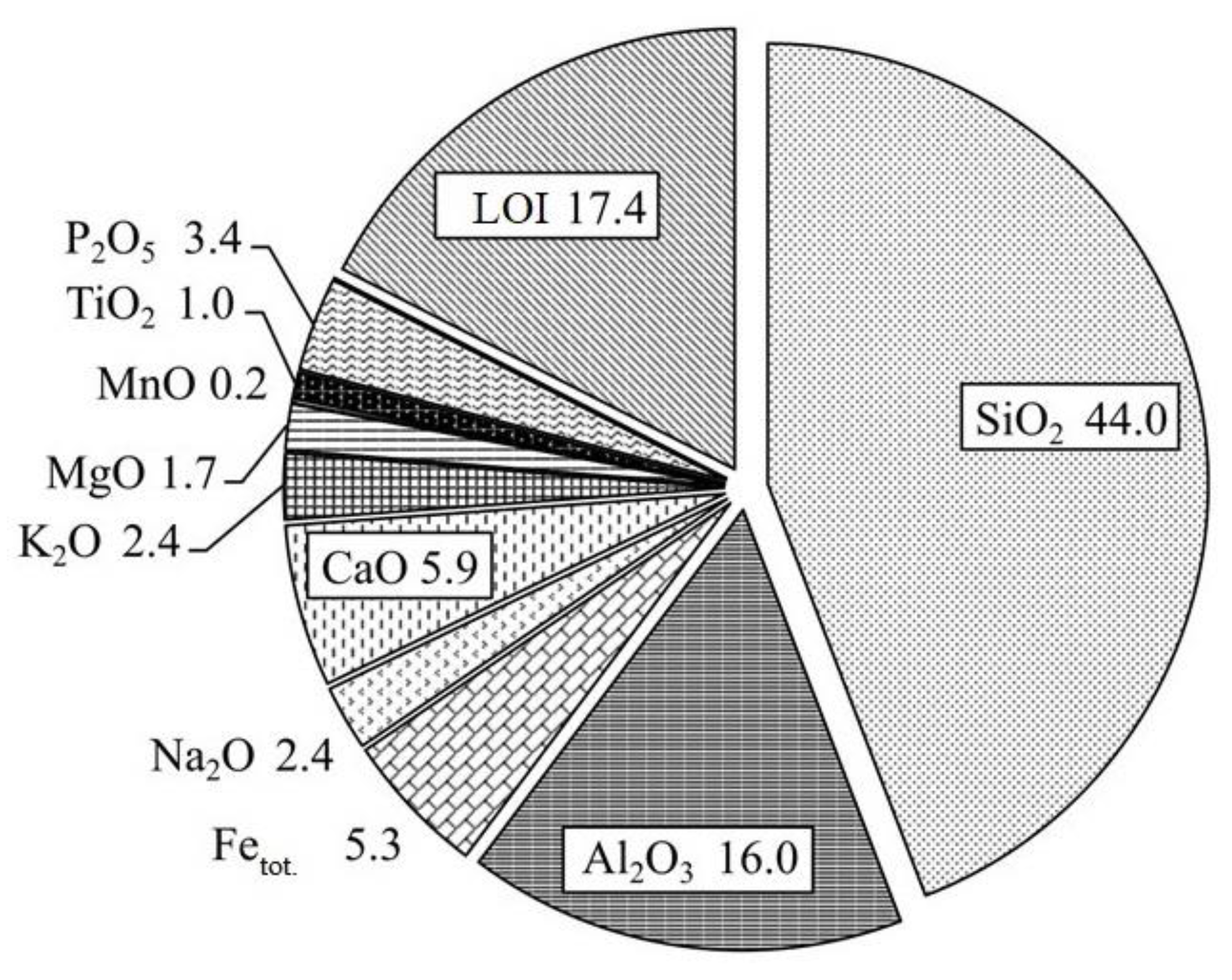
3.3. The Main Rock-Forming Elements
3.4. Trace Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals
3.5. Rare Earth Elements (REE)
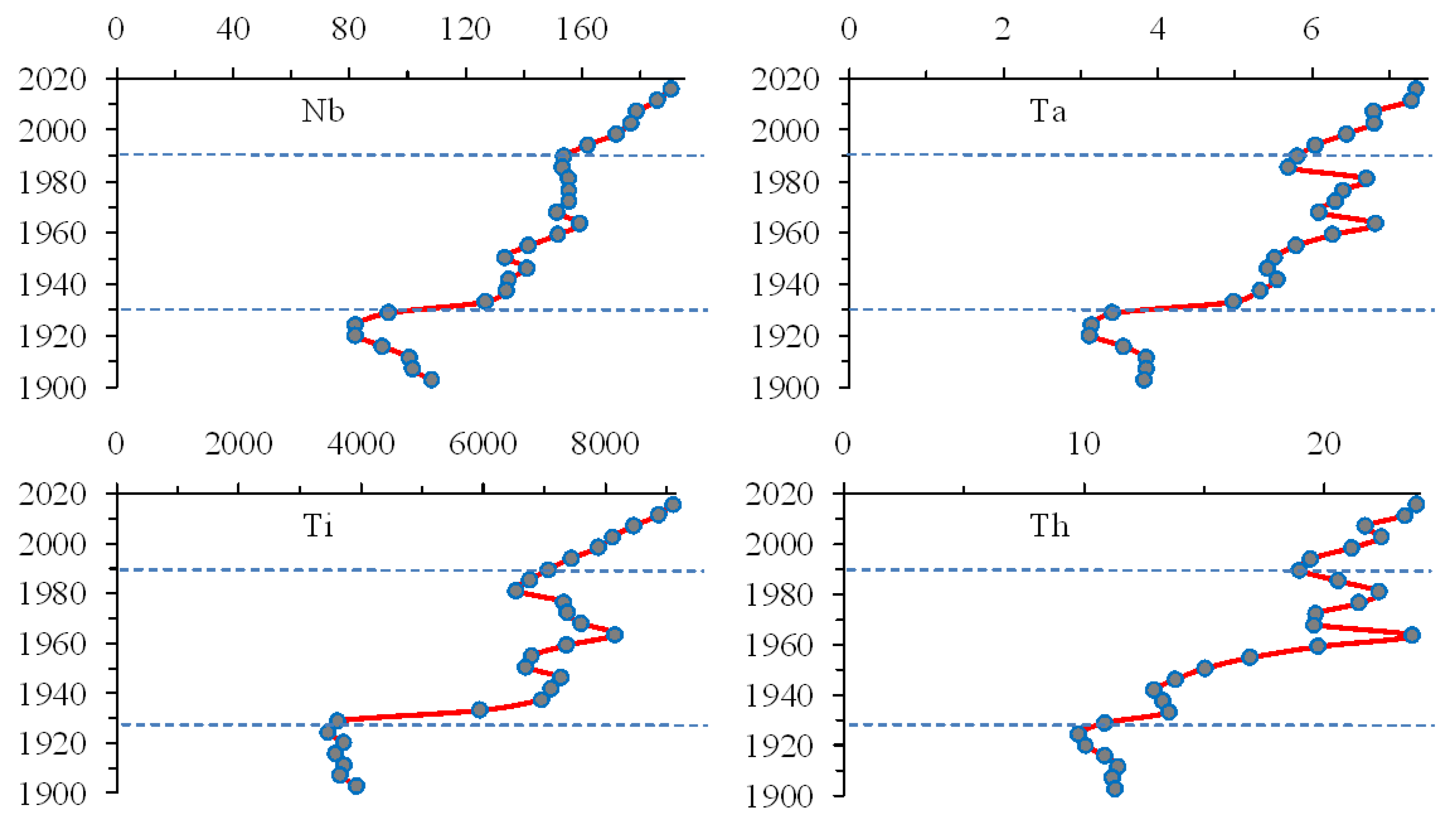
3.6. Trace Elements That Reduce the Content throughout the Sediment Core
3.7. Trace Elements That Reduce the Content in the Upper Sediment Layers
3.8. Trace Elements That Increasethe Content in the Upper Sediment Layers
3.9. Trace Element Fractions in Sediments
3.10. Anthropogenic Load on the Lake
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delile, H.; Blichert-Toft, J.; Goiran, J.-P.; Keay, S.; Albarède, F. Lead in ancient Rome’s city waters. Proceed. NAS USA 2014, 111, 6594–6599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renberg, I.; Wik-Persson, M.; Emteryd, O. Pre-industrial atmospheric lead contamination detected in Swedish lake sediments. Nature 1994, 368, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renberg, I.; Bindler, R.; Brännvall, M.L. Using the historical atmospheric lead-deposition record as a chronological marker in sediment deposits in Europe. Holocene 2001, 11, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.; Schulte, L. Reconstruction of mining activities in the Western Alps during the past 2500 years from natural archives. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killick, D.; Fenn, T. Archaeometallurgy: The study of preindustrial mining and metallurgy. Annu. Rev. Anthropol. 2012, 41, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Cortizas, A.; López-Merino, L.; Bindler, R.; Mighall, T.; Kylander, M. Early atmospheric metal pollution provides evidence for Chalcolithic/Bronze Age mining and metallurgy in Southwestern Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545–546, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McConnell, J.R.; Wilson, A.I.; Stohl, A.; Arienzo, M.M.; Chellman, N.J.; Eckhardt, S.; Thompson, E.M.; Pollard, A.M.; Steffensen, J.P. Lead pollution recorded in Greenland ice indicates European emissions tracked plagues, wars, and imperial expansion during antiquity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5726–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durali-Mueller, S.; Brey, G.P.; Wigg-Wolf, D.; Lahaye, Y. Roman lead mining in Germany: Its origin and development through time deduced from lead isotope provenance studies. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2007, 34, 1555–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, J.C. Mining in the later Roman Empire and beyond: Continuity or disruption? J. Rom. Stud. 1989, 79, 84–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Cortizas, A.; López-Merino, L.; Bindler, R.; Mighall, T.; Kylander, M. Atmospheric Pb pollution in N Iberia during the late Iron Age/Roman times reconstructed using the high-resolution record of La Molina mire (Asturias, Spain). J. Paleolimnol. 2013, 50, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preunkert, S.; McConnell, J.R.; Hoffmann, H.; Legrand, M.; Wilson, A.I.; Eckhardt, S.; Stohl, A.; Chellman, N.J.; Arienzo, M.N.; Friedrich, R. Lead and antimony in basal ice from Col du Dome (French Alps) dated with radiocarbon: A record of pollution during antiquity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 4953–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shotyk, W.; Krachler, M. Atmospheric deposition of silver and thallium since 12370 14C years BP recorded by a Swiss peat bog profile, and comparison with lead and cadmium. J. Environ. Monit. 2004, 6, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, D.; Shotyk, W.; Appleby, P.G.; Cheburkin, A.K.; Kramers, J.D. Atmospheric Pb deposition since the Industrial Revolution recorded by five Swiss peat profiles: Enrichment factors, fluxes, isotopic composition, and sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1340–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabanov, A.V.; Kalinina, T.A.; Kiselev, A.A.; Krasnobaev, A.I. Giant in the Khibiny; Ore and Metals: Moscow, Russia, 1999; 287p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kashulin, N.A.; Denisov, D.B.; Sandimirov, S.S.; Dauvalter, V.A.; Kashulina, T.G.; Malinovsky, D.N.; Vandysh, O.I.; Ilyashuk, B.P.; Kudryavtseva, L.P. Anthropogenic Changes in the Water Systems of the Khibiny Mountains (Murmansk Region); KSC RAS: Apatity, Russia, 2008; 282p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dauvalter, V.; Moiseenko, T.; Kudryavtseva, L.; Sandimirov, S. Accumulation of heavy metals in Lake Imandra because of its pollution with industrial waste. Water Resour. 2000, 27, 279–287. [Google Scholar]
- Yuoguy, V.S.; Dauvalter, V.A. Characteristic of bottom sediments of Lakes Bolshoy and Malyi Vudjavr. In The Quaternary in All of Its Variety. Basic Issues, Results, and Major Trends of Further Research, Proceedings of the VII All-Russian Quaternary Conference, Apatity, Russia, September 12–17, 2011; Korsakova, O.P., Kolka, V.V., Eds.; RAS: Saint-Petersburg, Russia, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 333–336. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Denisov, D.B.; Dauvalter, V.A.; Kashulin, N.A.; Kagan, L.Y. Long-term Changes of Diatom Assemblages in Subarctic Lakes under the Anthropogenic Influence (According to the Data of Diatom Analysis). Inland Water Biol. 2006, 1, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Denisov, D.B. Changes in the Hydrochemical Composition and Diatomic Flora of Bottom Sediments in the Zone of Influence of Metal Mining Production (Kola Peninsula). Water Resour. 2007, 34, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriano, D. Trace Elements in the Terrestrial Environment; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kashulin, N.A.; Dauvalter, V.A.; Denisov, D.B.; Valkova, S.A.; Vandysh, O.I.; Terentjev, P.M.; Kashulin, A.N. Selected aspects of the current state of freshwater resources in the Murmansk Region, Russia. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2017, 52, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.; Mariani, M.; Saunders, K.M.; Maher, W.A.; Harrison, J.J.; Fletcher, M.-S.; Zawadzki, A.; Heijnis, H.; Haberle, S.G. How significant is atmospheric metal contamination from mining activity adjacent to the Tasmanian Wilderness World Heritage Area? A spatial analysis of metal concentrations using air trajectories models. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denisov, D.B.; Kashulin, N.A.; Terentjev, P.M.; Valkova, S.A. Modern trends in the biota of freshwater ecosystems in the Murmansk Region. Proceed. Murm. St. Techn. Univer. 2009, 12, 525–538. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Terentjev, P.M.; Kashulin, N.A.; Zubova, E.M. The role of the European smelt Osmeruseperlanus (Linnaeus) in the structure of the ichthyofauna of the lake basin Imandra (Murmansk region). Proceed. Zoolog. Inst. 2017, 321, 228–243. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Moiseenko, T.I.; Gashkina, N.A.; Dinu, M.I.; Kremleva, T.A.; Khoroshavin, V.Y. Water Chemistry of Arctic Lakes under Airborne Contamination of Watersheds. Water 2020, 12, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, S.A.; Appleby, P.G.; Dauvalter, V.; Traaen, T.S. Trace Metal Pollution in Eastern Finnmark, Norway and Kola Peninsula, Northeastern Russia as Evidences by Studies of Lake Sediment; NIVA-Report 41/1996; NIVA: Oslo, Norway, 1996; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Dauvalter, V.A.; Terentiev, P.M.; Denisov, D.B.; Udachin, V.N.; Filippova, K.A.; Borisov, A.P. Reconstruction of pollution of the territory of the Rybachy Peninsula of the Murmansk region with heavy metals. Proceed. Fersman Sci. Sess. Geolog. Inst. KSC RAS 2018, 15, 441–444. [Google Scholar]
- Köck, G.; Muir, D.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.; Talbot, C.; Gantner, N.; Moser, D. Bathymetry and Sediment Geochemistry of Lake Hazen (Quttinirpaaq National Park, Ellesmere Island, Nunavut). Arctic 2012, 65, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalan, J.; Curtis, C.J.; Kernan, M. Remote European mountain lake ecosystems: Regionalisation and ecological status. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 2419–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovieva, N.; Jones, V.J.; Nazarova, L.; Brooks, S.J.; Birks, H.J.B.; Grytnes, J.-A.; Appleby, P.G.; Kauppila, T.; Kondratenok, B.; Renberg, I.; et al. Palaeolimnological evidence for recent climatic change in lakes from the northern Urals, arctic Russia. J. Paleolimn. 2005, 33, 463–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovieva, N.; Tarasov, P.E.; MacDonald, G. Quantitative reconstruction of Holocene climate from the Chuna Lake pollen record, Kola Peninsula, northwest Russia. Holocene 2005, 15, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, K.K.; Mariani, M.; Fletcher, M.-S.; Schneider, L.; Aquino-Lopez, M.A.; Gadd, P.S.; Heijnis, H.; Saunders, K.M.; Zawadzki, A. The impacts of intensive mining on terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems: A case of sediment pollution and calcium decline in cool temperate Tasmania, Australia. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, J.M.; Brown, J.E.; Ferguson, C.L.; Bixby, R.J.; Delay, N.T. Sediment record of mining legacy and water quality from a drinking-water reservoir, Aztec, New Mexico, USA. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvalter, V.A.; Denisov, D.B.; Slukovskii, Z.I. Impact of Wastewaters from Apatite–Nepheline Production on the Biogeochemical Processes in an Arctic Mountain Lake. Geochem. Int. 2022, 60, 1014–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuge, R.; Paveley, C.F.; Holdham, M.T. Heavy metal contamination in the Tanat Valley, North Wales. Environ. Geochem. Health 1989, 11, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, A.J.; Elrick, K.A.; Robbins, J.A.; Cook, R.B. A summary of the effects of mining and related activities on the sediment-trace element geochemistry of Lake Coeur d’Alene, Idaho, USA. J. Geochem. Explor. 1995, 52, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, A.J.; Elrick, K.A.; Robbins, J.A.; Cook, R.B. Effect of mining and related activities on the sediment trace element geochemistry of Lake Coeur d’Alene, Idaho, USA part II: Subsurface sediments. Hydrol. Process. 1995, 9, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M. Environmental Contamination of Heavy Metals in Soils, Plants, Waters and Sediments in the Vicinity of Metalliferous Mine in Korea. Unpublished. Ph.D Thesis, University of London, London, UK, 1995; pp. 189–317. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, M.C. Heavy metal contamination of soils and waters in and around the Imcheon Au–Ag mine, Korea. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.C.; Thornton, I. Heavy metal contamination of soils and plants in the vicinity of a lead-zinc mine, Korea. Appl. Geochem. 1996, 11, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.C.; Thornton, I. Environmental contamination and seasonal variation of metals in soils, plants and waters in the paddy fields around a Pb–Zn mine in Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 198, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langman, J.B.; Ali, J.D.; Child, A.W.; Wilhelm, F.M.; Moberly, J.G. Sulfur Species, Bonding Environment, and Metal Mobilization in Mining-Impacted Lake Sediments: Column Experiments Replicating Seasonal Anoxia and Deposition of Algal Detritus. Minerals 2020, 10, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.G.; Chon, H.-T.; Jung, M.C. Heavy metal contamination in the vicinity of the Daduk Au–Ag–Pb–Zn mine in Korea. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrington, G.; Alloway, B. The transfer and fate of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn from two historic metalliferous mine sites in the UK. Appl. Geochem. 1994, 9, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestana, M.H.D.; Formoso, M.L.; Teixeir, E.C. Heavy metals in stream sediments from copper and gold mining areas in southern Brazil. J. Geochem. Explor. 1997, 58, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, I. Geochemical aspects of heavy metal pollution and agriculture in England and Wales. Ref. Book Minist. Agric. Fish. Food 1980, 326, 105–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Leavitt, P.R.; Moser, K.A. Effects of a century of mining and industrial production on metal contamination of a model saline ecosystem, Great Salt Lake, Utah. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouzekri, S.; El Fadili, H.; El Hachimi, M.L.; El Mahi, M.; El Lotfi, M. Assessment of trace metals contamination in sediment and surface water of quarry lakes from the abandoned Pb mine Zaida, High Moulouya-Morocco. Environ. Develop. Sustain. 2020, 22, 7013–7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvalter, V.; Moiseenko, T.; Rodyushkin, I. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in Imandra Lake, Murmansk Area. Geochem. Int. 1999, 37, 325–331. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, C.A.; Abbott, M.B. A paleolimnological perspective on industrial-era metal pollution in the central Andes, Peru. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2008, 393, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fersman, A.E. Our Apatite; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1968; 136p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Yakovenchuk, V.N.; Ivanyuk, G.Y.; Pakhomovsky, Y.A.; Men’shikov, Y.P. Khibiny; Laplandia Minerals: Apatity, Russia, 2005; p. 468. [Google Scholar]
- Arzamastsev, A.A.; Arzamastseva, L.V.; Shamatrina, A.M.; Travin, A.V.; Belyatsky, B.V.; Antonov, A.V.; Larionov, A.N.; Rodionov, N.V.; Sergeev, S.A. Duration of formation of magmatic system of polyphase paleozoic alkaline complexes of the Central Kola: U-Pb, Rb-Sr, Ar-Ar data. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2007, 413, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kola Ecological Center. To Prevent the Resumption of the Conflict in the Khibin. Available online: https://www.change.org/ (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Kanygina, A.V. Hydrobiological and Hydrochemical Study of Bolshoy and Maly Vudjavr Lakes; Kola Research Base of Academy of Sciences of USSR: Apatity, Russia, 1939; 206p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradova, A.A.; Kotova, E.I.; Topchaya, V.Y. Atmospheric transport of heavy metals to the regions of the North of the European territory of Russia. Geogr. Natl. Resour. 2017, 1, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvalter, V.A. Geochemistry of Lakes in a Zone Impacted by an Arctic Iron-Producing Enterprise. Geochem. Int. 2020, 58, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregurek, D.; Melcher, F.; Pavlov, V.A.; Reimann, C.; Stumpf, E.F. Mineralogy and mineral chemistry of snow filter residues in the vicinity of the nickel-copper processing industry, Kola Peninsula, NW Russia. Miner. Petrol. 1999, 65, 87–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L. Sediment sampling in different aquatic environments: Statistical aspects. Water Resour. Res. 1984, 20, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L. Determination of characteristic values for physical and chemical lake sediment parameters. Water Resour. Res. 1981, 17, 1625–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taft, R.A.; Jones, C. Sediment Sampling Guide and Methodologies; Ohio Environmental Protection Agency: Columbus, OH, USA, 2001; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- Dauvalter, V.A. Geoecology of Lake Sediments; Murmansk St. Techn. Univer.: Murmansk, Russia, 2012; 242p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Slukovskii, Z.I. Background concentrations of heavy metals and other chemical elements in the sediments of small lakes in the south of Karelia, Russia. Proceed. Murm. St. Techn. Univer. 2020, 23, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control—a sedimentological approach. Water Resear. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, B.S.; Joshi, S.R. An evaluation of the CIC model of 210Pb dating of sediments. Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 1989, 14, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, R.L. Rapid Determination of Lead-210 and Polonium-210 in Environmental Samples by Deposition on Nickel. Anal. Chem. 1966, 38, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, F.; Nematollahi, M.J.; Keshavarzi, B. Heavy metals fractionation in surface sediments of Gowatr bay-Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaren, R.G.; Crawford, D.W. Studies on soil copper 1. the fractionation of copper in soils. J. Soil Sci. 1973, 24, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ure, A.M.; Quevauviller, P.; Muntau, H.; Griepink, B. Speciation of Heavy Metals in Soils and Sediments. An Account of the Improvement and Harmonization of Extraction Techniques Undertaken Under the Auspices of the BCR of the Commission of the European Communities. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1993, 51, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzeva, A.; Slukovskii, Z.; Dauvalter, V.; Denisov, D. Trace element fractions in sediments of urbanised lakes of the arctic zone of Russia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subetto, D.A. Bottom Sediments of Lakes: Paleolimnological Reconstructions; Rus. St. Pedag. Univer.: Saint-Petersburg, Russia, 2009; 343p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Strakhovenko, V.D. Geochemistry of Sediments of Small Continental Lakes in Siberia. Dr. Sci. Thesis, Novosibirsk St. Univer., Novosibirsk, Russia, 2011; 24p. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Dauvalter, V. Impact of mining and refining on the distribution and accumulation of nickel and other heavy metals in sediments of subarctic lake Kuetsjärvi, Murmansk region, Russia. J. Environ. Monit. 2003, 5, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognerud, S.; Norton, S.A.; Dauvalter, V. Heavy Metal Pollution in Lake Sediments in the Border Areas between Russia and Norway; NIVA-Report 522/93; NIVA: Oslo, Norway, 1993; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Rognerud, S.; Hongve, D.; Fjeld, E.; Ottesen, R.T. Trace metal concentrations in lake and overbank sediments in southern Norway. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slukovskii, Z.; Medvedev, M.; Siroezhko, E. Long-range transport of heavy metals as a factor of the formation of the geochemistry of sediments in the southwest of the Republic of Karelia, Russia. J. Elementol. 2020, 25, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidov, I.N.; Shelekhova, T.S. Diatomites of Karelia (Features of Formation, Distribution, Prospects of Use); Karelian Research Centre of RAS: Petrozavodsk, Russia, 2006; 89p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kashulin, N.A.; Sandimirov, S.S.; Dauvalter, V.A.; Kudryavtseva, L.P.; Terentyev, P.M.; Denisov, D.B.; Vandysh, O.I.; Korolova, I.M.; Valkova, S.A.; Kashulina, T.G. Annotated Ecological Catalogue of Lakes of the Murmansk Region: The Central and Southwest Areas of the Murmansk Region (Basins of the Barents Sea, the White Sea and the Bothnia Gulf of the Baltic Sea); KSC RAS: Apatity, Russia, 2013; 298p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Moiseenko, T.; Dauvalter, V.; Rodyushkin, I. Geochemical Migration and Covariation of Elements in the Imandra Lake, Barents Region; Research Report TULEA; Univer. Techn.: Luleå, Sweden, 1996; Volume 22, 108p. [Google Scholar]
- Moiseenko, T.I.; Dauvalter, V.A.; Rodyushkin, I.V. Geochemical Migration of Elements in Subarctic Freshwater Body (on the Example of the Imandra Lake); KSC RAS: Apatity, Russia, 1997; 127p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Slukovskii, Z.I.; Guzeva, A.V.; Dauvalter, V.A. Rare earth elements in surface lake sediments of Russian arctic: Natural and potential anthropogenic impact to their accumulation. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 142, 105325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V. Rare earth elements: A review of applications, occurrence, exploration, analysis, recycling, and environmental impact. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 1285–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaulina, T.V.; Afanasieva, E.N.; Il’chenko, V.L.; Nerovich, L.I.; Lialina, L.M.; Nitkina, E.A.; Mokrushina, O.D. Litsa Uranium-Ore District; GEOS: Moscow, Russia, 2021; 136p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Krasotkin, I.S.; Voytekhovsky, Y.L.; Leskov, A.L.; Udobina, V.S. Abandoned molybdenite mine Takhtarvumchorr. Proceed. Fersman Sci. Sess. Geolog. Inst. KSC RAS 2005, 2, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Slukovskii, Z.I.; Dauvalter, V.A. Features of Pb, Sb, Cd accumulation in sediments of small lakes in the south of the Republic of Karelia. Proceed. Karelian SC RAS 2020, 4, 75–94. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slukovskii, Z.; Dauvalter, V.; Guzeva, A.; Denisov, D.; Cherepanov, A.; Siroezhko, E. The Hydrochemistry and Recent Sediment Geochemistry of Small Lakes of Murmansk, Arctic Zone of Russia. Water 2020, 12, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krachler, M.; Zheng, J.; Koerner, R.; Zdanowicz, C.; Fisher, D.; Shotyk, W. Increasing atmospheric antimony contamination in the northern hemisphere: Snow and ice evidence from Devon Island, Arctic Canada. J. Environ. Monit. 2006, 7, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudovich, Y.E.; Ketris, M.P. Toxic Trace Elements in Fossil Coals; Ural Branch RAS: Yekaterinburg, Russia, 2005; 648p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Teng, Y.; Ni, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Lin, X.; Huang, Y. Environmental geochemistry and ecological risk of vanadium pollution in Panzhihua mining and smelting area, Sichuan, China. Chin. J. Geochem. 2006, 25, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia, J.A.; Rodriguez, R.; Armienta, A. Aquifer Vulnerability Zoning, an Indicator of Atmospheric Pollutants Input? Vanadium in the Salamanca Aquifer, Mexico. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 185, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slukovskii, Z.I. Accumulation level and fractions of heavy metals in sediments of small lakes of the urbanized area (Karelia). Vestn. St. Petersburg Univer. Earth Sci. 2020, 65, 171–192. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shpirt, M.Y.; Rashevsky, V.V. Trace Elements of Fossil Fuels; Kuchkovo Pole: Moscow, Russia, 2010; 348p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Denisov, D.; Terentjev, P.; Valkova, S.; Kudryavtzeva, L. Small Lakes Ecosystems under the Impact of Non-Ferrous Metallurgy (Russia, Murmansk Region). Environments 2020, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinogradova, A.A.; Ivanova, Y.A. Pollution of central Karelia environment under long-range atmospheric transport of anthropogenic pollutants. Izv. RAS Geogr. Ser. 2013, 5, 98–108. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pacyna, J.M.; Pacyna, E.G. An assessment of global and regional emissions of trace metals to the atmosphere from anthropogenic sources worldwide. Environ. Rev. 2001, 9, 269–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvalter, V.A. Chalcophile elements (Hg, Cd, Pb, and As) in bottom sediments of water bodies of the White Sea catchment area on the Kola Peninsula. Geochem. Int. 2006, 44, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvalter, V.A.; Kashulin, N.A. Biogeochemical Features of the Distribution of Chalcophilic Elements (Hg, Cd, Pb, As) in Water Bodies of the North of the European Part of Russia; Murmansk St. Techn. Univ.: Murmansk, Russia, 2015; 136p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Starodymova, D.P.; Shevchenko, V.P.; Kokryatskaya, N.M.; Aliev, R.A.; Bychkov, A.Y.; Zabelina, S.A.; Chupakov, A.V. Geochemistry of bottom sediments of a small lake (drainage area of Lake Onega, Arkhangelsk region). Succes. Mod. Natl. Sci. 2016, 9, 172–177. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, V. The elimination of lead in gasoline. Ann. Rev. Energy Environ. 1995, 20, 301–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvalter, V.A.; Kashulin, N.A. Mercury pollution of Lake Imandra sediments, Murmansk Region, Russia. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2018, 12, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slukovskii, Z.I.; Dauvalter, V.A.; Denisov, D.B.; Siroezhko, E.V.; Cherepanov, A.A. Geochemistry features of sediments of small urban arctic Lake Komsomolskoye, Murmansk region. IOP Confer. Series: Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 467, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

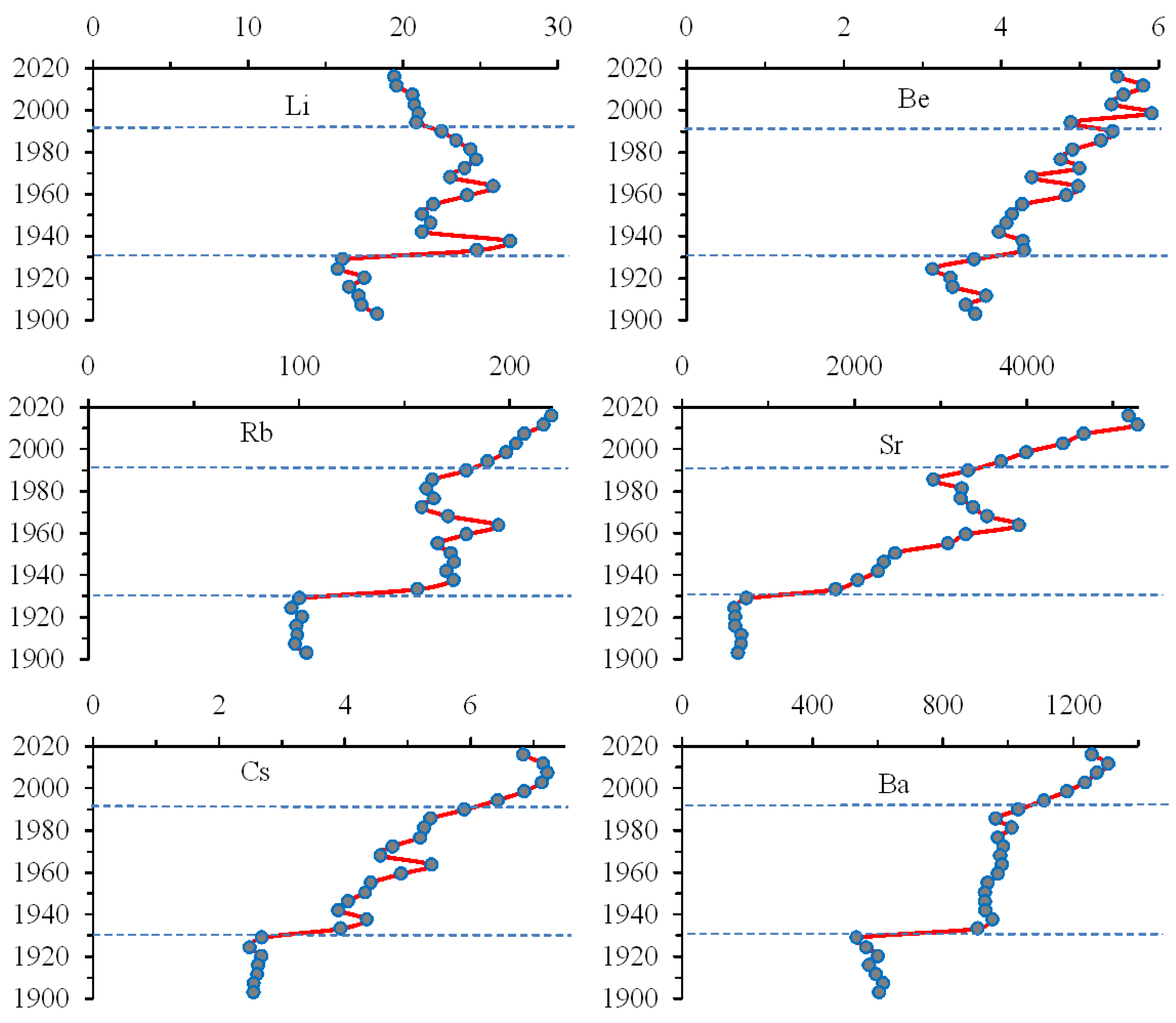

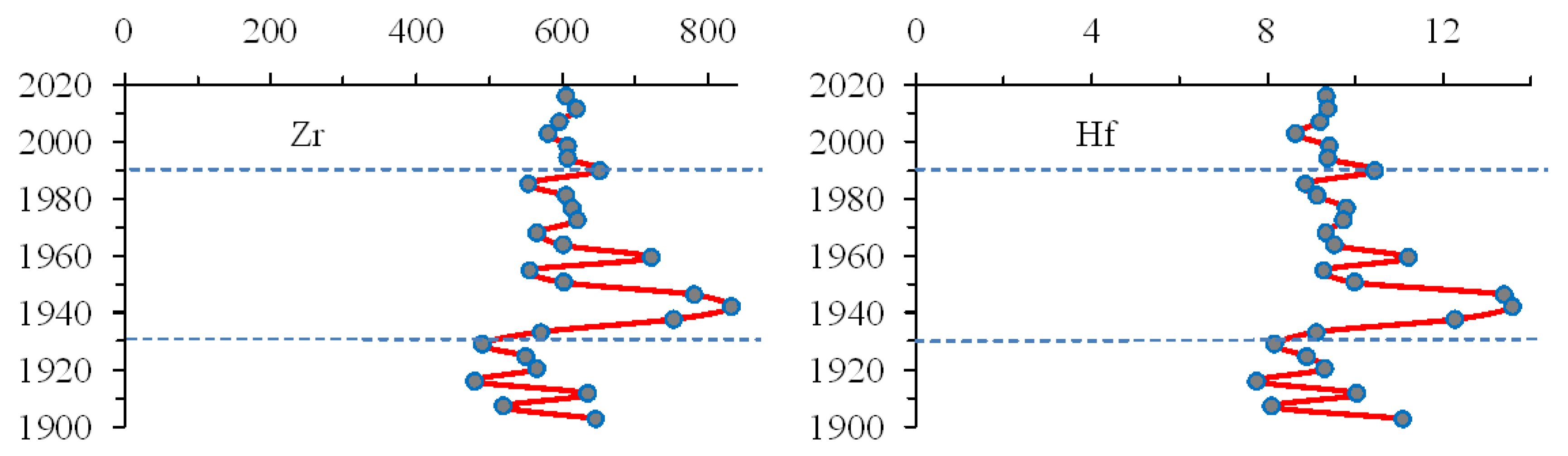

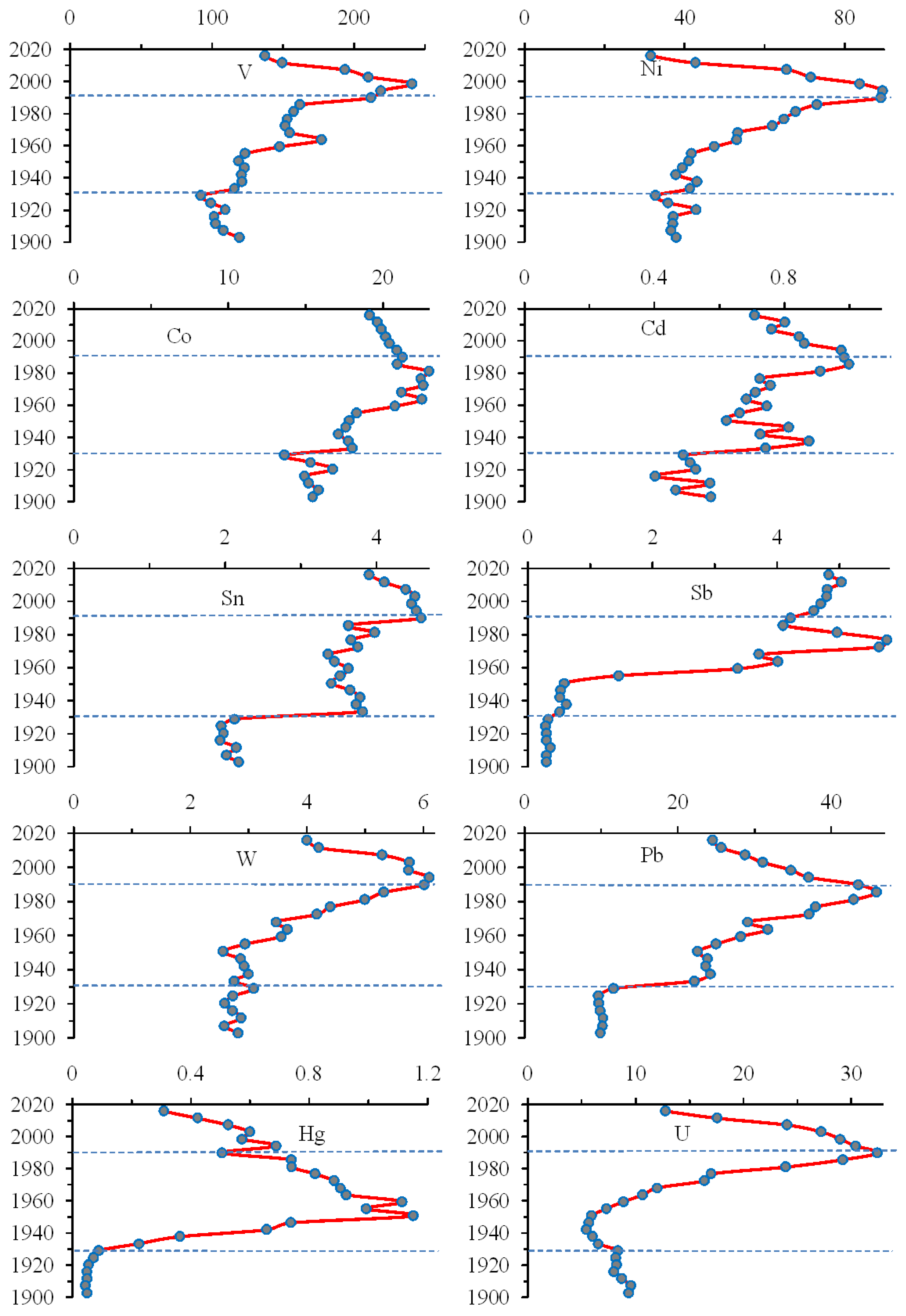
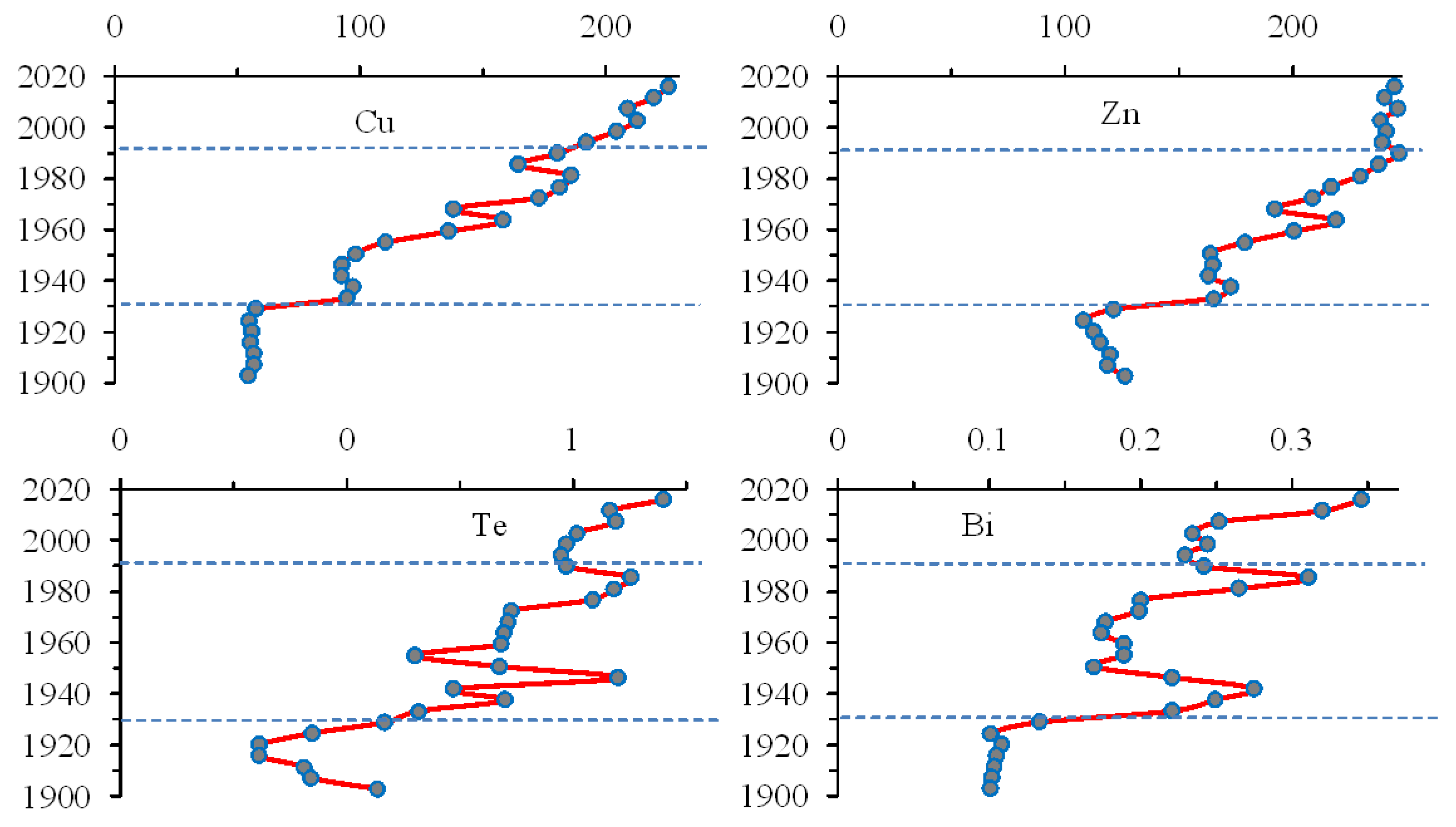
| Elements | Apatite Ore1 | Tailings1 | Bolshoy Vudjavr | Imandra1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–1 cm | 26–27 cm | 0–1 cm | 18–19 cm | |||
| LOI | – | – | 14.08 | 18.36 | 29.33 | 13.69 |
| SiO2 | 26.6 | 39.8 | 37.68 | 51.09 | 69.43 | 75.27 |
| Al2O3 | 12.1 | 17.7 | 15.87 | 16.35 | 9.51 | 9.98 |
| Fe2O3 | 6.49 | 8.14 | 5.74 | 4.45 | 6.41 | 3.99 |
| Na2O | 6.23 | 9.74 | 3.48 | 1.95 | 0.95 | 1.77 |
| CaO | 24 | 9.72 | 9.68 | 2.77 | 2.98 | 2.31 |
| K2O | 2.83 | 4.28 | 3.65 | 1.67 | 1.01 | 1.07 |
| MgO | 1.27 | 1.52 | 1.41 | 1.82 | 0.80 | 1.72 |
| MnO | 0.188 | 0.247 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.92 | 0.14 |
| TiO2 | 3.01 | 4.07 | 1.33 | 0.62 | 0.46 | 0.41 |
| Element | Apatite Ore 1 | Tailings1 | Bolshoy Vudjavr | Imandra1 | Rybachy2 | Severnoye3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–1 cm | 26–27 cm | 0–1 cm | 18–19 cm | 0–1 cm | 26–27 cm | 0–1 cm | 37–39 cm | |||
| Li | 4.41 | 6.45 | 19.46 | 18.34 | 15.1 | 13.4 | 13.2 | 8.70 | 12.63 | 5.07 |
| Be | 3.21 | 6.39 | 5.48 | 3.67 | 1.84 | 0.75 | 1.30 | 1.49 | 0.64 | 0.49 |
| P | 73759 | 16093 | 33590 | 3213 | – | – | – | – | 3488 | 1128 |
| Sc | 2.52 | 0.76 | 9.15 | 17.05 | 2.62 | 7.96 | 4.91 | 5.22 | 12.18 | 9.76 |
| Ti | 719 | 1011 | 9109 | 3932 | – | – | 1733 | 1362 | 1257 | 479 |
| V | 261 | 303 | 137 | 119 | 94.5 | 109 | 63.1 | 53.5 | 528 | 40 |
| Cr | 32.8 | 33.7 | 47.31 | 87.79 | 94.9 | 112 | 61.5 | 51.1 | 58.49 | 34.77 |
| Mn | 234 | 400 | 1624 | 964 | – | – | 1932 | 203 | 174 | 114 |
| Co | 19.6 | 17.6 | 19.15 | 15.43 | 29.6 | 16.3 | 40.0 | 3.98 | 20.08 | 13.85 |
| Ni | 13.4 | 9.38 | 32 | 38 | 1751 | 59 | 127 | 24 | 171 | 27 |
| Cu | 79.1 | 101 | 225 | 55 | 429 | 96 | 370 | 38 | 111 | 25 |
| Zn | 47 | 71 | 245 | 126 | 132 | 78 | 148 | 56 | 416 | 64 |
| Ga | 26.4 | 39.9 | 27.57 | 64.44 | 27.7 | 30.8 | 7.52 | 5.90 | – | – |
| As | 2.80 | 0.86 | 3.78 | 6.11 | 19.1 | 9.1 | 6.28 | 1.89 | – | – |
| Rb | 68 | 90 | 220 | 104 | 49.8 | 37.4 | 32.4 | 18.7 | 19.28 | 3.83 |
| Sr | 13900 | 3710 | 5186 | 652 | 941 | 187 | 153 | 169 | 157 | 53 |
| Y | 161 | 72.9 | 104 | 30 | 40 | 21 | 17 | 36 | 10 | 11 |
| Zr | 317 | 584 | 606 | 645 | 163 | 123 | 53 | 45 | 26 | 11 |
| Nb | 168 | 288 | 191 | 108 | 36 | 8.5 | 5.4 | 3.7 | 3.0 | 1.2 |
| Mo | 6 | 6.53 | 8 | 10 | 24 | 11.4 | 6.1 | 11.4 | 8.3 | 23.5 |
| Cd | 0.36 | 0.081 | 0.71 | 0.57 | 1.29 | 0.34 | 0.50 | 0.45 | 1.18 | 0.30 |
| Sn | <24 | <24 | 3.90 | 2.17 | 16.30 | 13.50 | 32.1 | 0.61 | 7.11 | 0.80 |
| Sb | 85 | 70 | 4.82 | 0.29 | – | – | 0.50 | 0.138 | 2.68 | 0.09 |
| Cs | – | – | 6.84 | 2.55 | – | – | 1.98 | 0.91 | 0.83 | 0.25 |
| Ba | 603 | 1100 | 1257 | 606 | 685 | 486 | 198 | 169 | 258 | 78 |
| La | 1285 | 280 | 535 | 89 | 136 | 57 | 29 | 70 | 26 | 20 |
| Ce | 2130 | 460 | 779 | 153 | 236 | 81 | 50 | 98 | 39 | 27 |
| Pr | 190 | 44 | 79.2 | 15.4 | 24.8 | 13.6 | 6.6 | 15.6 | 5.1 | 4.9 |
| Nd | 640 | 154 | 283 | 54 | 95 | 53 | 25 | 62 | 19 | 19 |
| Sm | 81.3 | 21.6 | 43.6 | 9.0 | 13.6 | 7.7 | 5.17 | 11.63 | 3.23 | 3.31 |
| Eu | 24.6 | 7.1 | 12.21 | 2.38 | 3.91 | 1.83 | 1.08 | 2.41 | 0.75 | 0.71 |
| Gd | 98.1 | 26.8 | 34.8 | 7.0 | 14.10 | 7.25 | 3.84 | 8.92 | 2.73 | 2.78 |
| Tb | 8.16 | 2.51 | 4.61 | 1.07 | 1.46 | 0.86 | 0.56 | 1.31 | 0.36 | 0.38 |
| Dy | 33.1 | 11.4 | 22.17 | 5.69 | 8.68 | 4.11 | 2.98 | 6.78 | 1.74 | 1.92 |
| Ho | 5.33 | 1.96 | 3.70 | 0.99 | 1.43 | 0.69 | 0.53 | 1.11 | 0.31 | 0.36 |
| Er | 11.40 | 4.64 | 9.09 | 2.96 | 3.45 | 1.96 | 1.73 | 3.36 | 0.87 | 1.04 |
| Tm | 1.22 | 0.545 | 1.06 | 0.39 | 0.32 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.38 | 0.12 | 0.13 |
| Yb | 6.04 | 2.79 | 5.55 | 2.44 | 2.57 | 1.76 | 1.34 | 2.62 | 0.69 | 0.88 |
| Lu | 0.61 | 0.309 | 0.61 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.35 | 0.10 | 0.12 |
| Hf | 0.73 | 0.328 | 9.35 | 11.08 | 4.36 | 4.10 | 1.69 | 1.34 | 0.59 | 0.31 |
| Ta | 0.61 | 0.173 | 7.34 | 3.82 | 2.12 | 0.64 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.23 | 0.06 |
| W | <24 | 34.5 | 4.00 | 2.82 | 38.10 | 31.4 | 0.78 | 0.33 | 8.70 | 1.00 |
| Hg | 0.051 | 0.024 | 0.308 | 0.050 | 0.282 | 0.034 | – | – | – | – |
| Tl | – | – | 0.12 | 0.19 | – | – | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.49 | 0.29 |
| Pb | 2.66 | 2.99 | 24.6 | 9.9 | 28.0 | 4.5 | 82.0 | 10.7 | 44.0 | 6.3 |
| Bi | – | – | 0.35 | 0.10 | – | – | 0.98 | 0.058 | 0.24 | 0.07 |
| Th | 13.7 | 14.9 | 23.8 | 11.3 | 8.0 | 7.9 | 4.7 | 6.4 | 2.3 | 1.2 |
| U | 2.76 | 3.25 | 12.8 | 9.4 | 8.0 | 15.1 | 44 | 190 | 77 | 204 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dauvalter, V.; Slukovskii, Z.; Denisov, D.; Guzeva, A. A Paleolimnological Perspective on Arctic Mountain Lake Pollution. Water 2022, 14, 4044. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14244044
Dauvalter V, Slukovskii Z, Denisov D, Guzeva A. A Paleolimnological Perspective on Arctic Mountain Lake Pollution. Water. 2022; 14(24):4044. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14244044
Chicago/Turabian StyleDauvalter, Vladimir, Zakhar Slukovskii, Dmitry Denisov, and Alina Guzeva. 2022. "A Paleolimnological Perspective on Arctic Mountain Lake Pollution" Water 14, no. 24: 4044. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14244044
APA StyleDauvalter, V., Slukovskii, Z., Denisov, D., & Guzeva, A. (2022). A Paleolimnological Perspective on Arctic Mountain Lake Pollution. Water, 14(24), 4044. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14244044







