Residues of Selected Anticonvulsive Drugs in Surface Waters of the Elbe River Basin (Czech Republic)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Sample Collection and Sampling Sites
2.3. Sample and Calibration Standards Preparation
2.4. Instrumentation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
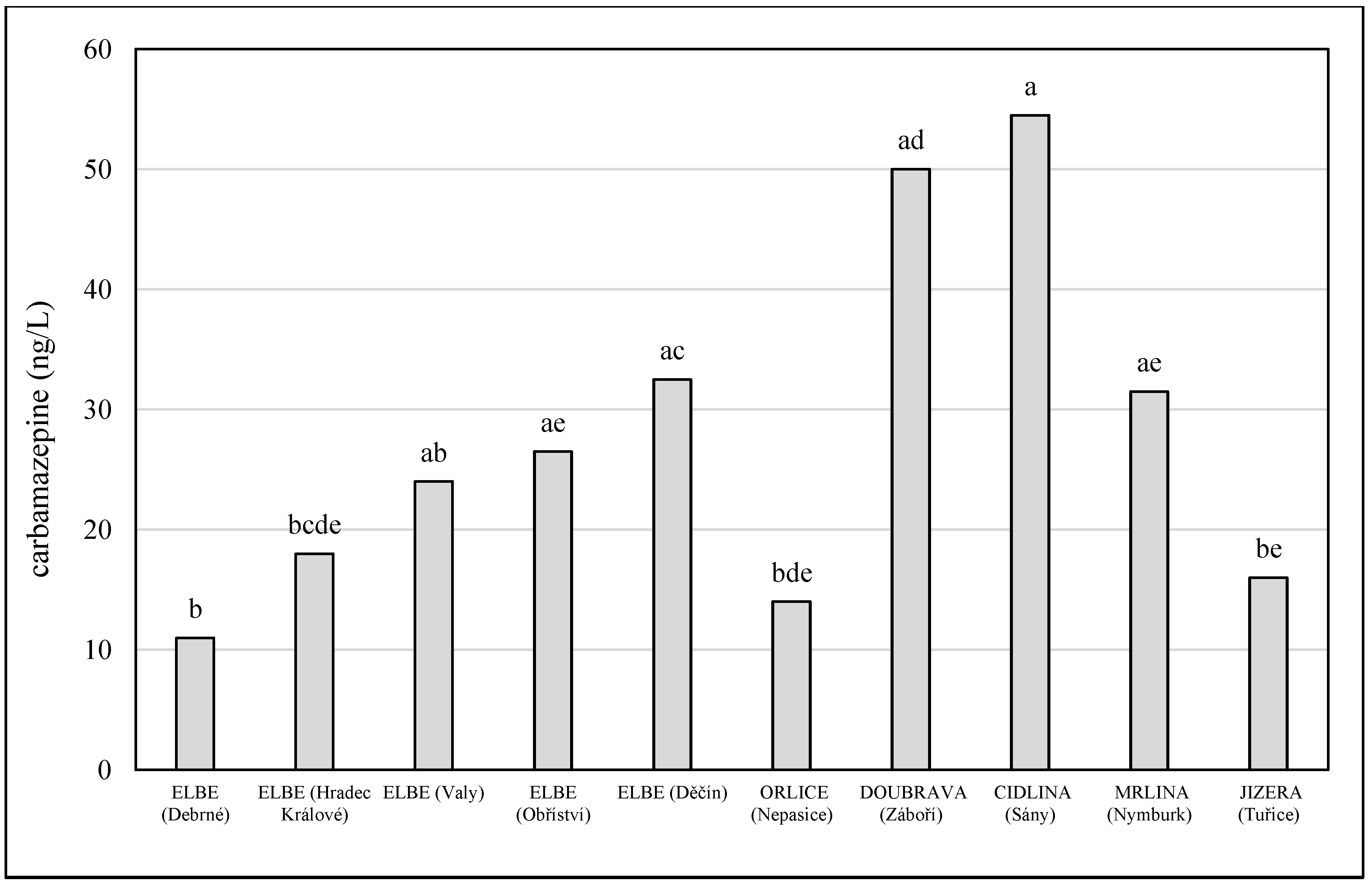
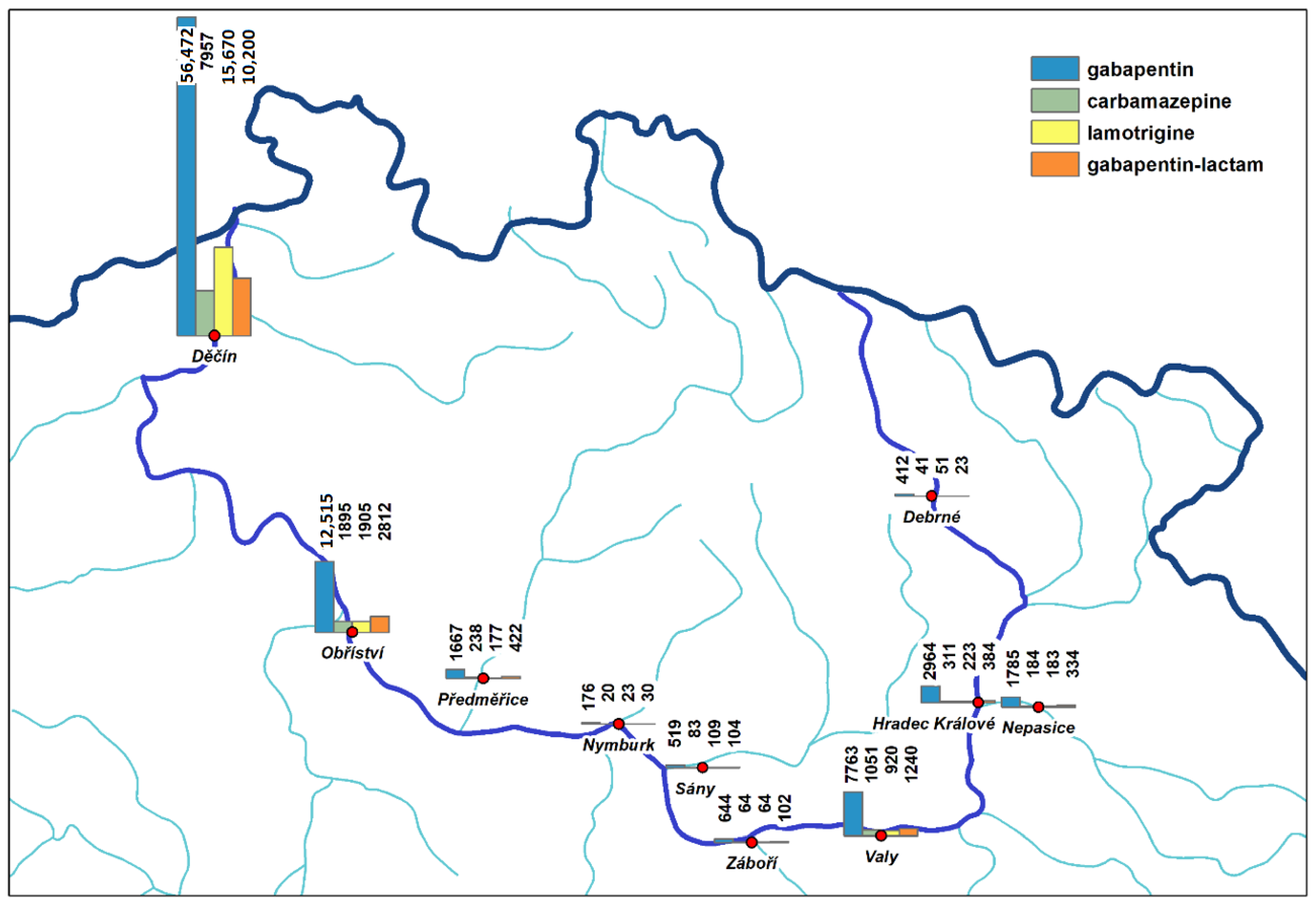
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grunze, H.C.R. Anticonvulsants in bipolar disorder. J. Ment. Health. 2010, 19, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, H.; Feuerstein, T.J. Novel anticonvulsant drugs. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 113, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcagno, E.; Durando, P.; Valdes, M.E.; Franchioni, L.; Bistoni, M.D. Effects of carbamazepine on cortisol levels and behavioral responses to stress in the fish Jenynsia multidentata. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 158, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallego-Rios, S.E.; Penuela, G.A.; Martinez-Lopez, E. Updating the use of biochemical biomarkers in fish for the evaluation of alterations produced by pharmaceutical products. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 88, 103756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.; Haddad, S.P.; Luek, A.; Scott, W.C.; Saari, G.N.; Kristofco, L.A.; Connors, K.A.; Rash, C.; Rasmussen, J.B.; Chambliss, C.K.; et al. Bioaccumulation and trophic dilution of human pharmaceuticals across trophic positions of an effluent-dependent wadeable stream. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B. 2014, 369, 20140058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabicova, K.; Grabic, R.; Fedorova, G.; Vojs Stanova, A.; Blaha, M.; Randak, T.; Brooks, B.W.; Zlabek, V. Water reuse and aquaculture: Pharmaceutical bioaccumulation by fish during tertiary treatment in a wastewater stabilization pond. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comoretto, L.; Chiron, S. Comparing pharmaceutical and pesticide loads into a small Mediterranean river. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 349, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, S.G.; Catala, M.; Maroto, R.R.; Gil, J.L.R.; de Miguel, A.G.; Valcarcel, Y. Pollution by psychoactive pharmaceuticals in the Rivers of Madrid metropolitan area (Spain). Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calza, P.; Medana, C.; Padovano, E.; Giancotti, V.; Minero, C. Fate of selected pharmaceuticals in river waters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 2262–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovko, O.; Kumar, V.; Fedorova, G.; Randak, T.; Grabic, T. Seasonal changes in antibiotics, antidepressants/psychiatric drugs, antihistamines and lipid regulators in a wastewater treatment plant. Chemosphere. 2014, 111, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, C.M.G.; Helbling, D.E. Widespread micropollutant monitoring in the Hudson River estuary reveals spatiotemporal micropollutant clusters and their sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6187–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, E.; Hernandez, F.; Ibaneza, M.; Rico, A.; Pitarch, E.; Bijlsma, L. Occurrence and ecological risks of pharmaceuticals in a Mediterranean river in Eastern Spain. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 106004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreozzi, R.; Marotta, R.; Paxeus, N. Pharmaceuticals in STP effluents and their solar photodegradation in aquatic environment. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevre, N.; Coutu, S.; Margot, J.; Wynn, H.K.; Bader, H.P.; Scheidegger, R.; Rossi, L. Substance flow analysis as a tool for mitigating the impact of pharmaceuticals on the aquatic system. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2995–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busetti, F.; Ruff, M.; Linge, K.L. Target screening of chemicals of concern in recycled water. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2015, 1, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagheri, H.; Afkhamib, A.; Noroozic, A. Removal of pharmaceutical compounds from hospital wastewaters using nanomaterials: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. Res. 2016, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorova, G.; Grabic, R.; Grabicova, K.; Turek, J.; Nguyen, T.V.; Randak, T.; Brooks, B.W.; Zlabek, V. Water reuse for aquaculture: Comparative removal efficacy and aquatic hazard reduction of pharmaceuticals by a pond treatment system during a one year study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, B.; Gameiro, C.; Matos, A.R.; Figueiredo, A.; Silva, M.S.; Cordeiro, C.; Cacador, I.; Reis-Santos, P.; Fonseca, V.; Cabrita, M.T. First screening of biocides, persistent organic pollutants, pharmaceutical and personal care products in Antarctic phytoplankton from Deception Island by FT-ICR-MS. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langass, S.; Aliakseyeva, N.; Gooch, G.; Lopman, E.; Nilsson, S.; Timmerman, J. Working paper-environmental information in transboundary river basin policy-making and management. Selected European case studies. Mantra East 2002, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Mayo, A.L.; Ritter, D.J.; Bruthans, J.; Tingey, D. Contributions of commercial fertilizer, mineralized soil nitrate, and animal and human waste to the nitrate load in the Upper Elbe River Basin, Czech Republic. HydroResearch 2019, 1, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, R.M. An evaluation of some record reconstruction techniques. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, D.G.; Vecchia, A.V.; Dahl, A.L. Evaluation of Drainage-Area Ratio Method Used to Estimate Streamflow for the Red River of the North Basin, North Dakota and Minnesota; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe, U.; Ludwig, D.P.W.D.; Klauber, J. Arzneiverordnungs-Report 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Panayiotopoulos, C.P. Atlas of Epilepsies; Springer: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gurke, R.; Roßler, M.; Marx, C.; Diamond, S.; Schubert, S.; Oertel, R.; Fauler, J. Occurrence and removal of frequently prescribed pharmaceuticals and corresponding metabolites in wastewater of a sewage treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Dinsdale, R.M.; Guwy, A.J. The occurrence of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, endocrine disruptors and illicit drugs in surface water in South Wales, UK. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3498–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Dinsdale, R.M.; Guwy, A.J. Illicit drugs and pharmaceuticals in the environment–forensic applications of environmental data, Part 2: Pharmaceuticals as chemical markers of faecal water contamination. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 156, 1778–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Dinsdale, R.M.; Guwy, A.J. The removal of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, endocrine disruptors and illicit drugs during wastewater treatment and its impact on the quality of receiving waters. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 43, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferencik, M. Výskyt a možnosti snížení vnosu znečišťujících látek–pesticidů a léčiv ve vodárenské nádrži Vrchlice. Agromanuál 2020, 15, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Katuri, J.V.P.; Ekkundi, V.S.; Nagarajan, K. A simple and expedient procedure for the preparation of gabapentin lactam (2-aza-spiro[4,5]decan-3-one). Org. Process Res. Dev. 2016, 20, 1828–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajda, F.J.E.; Eadie, M.J. Seminar in epilptology the clinical pharmacology of traditional antiepileptic drugs. Epileptic Disord. 2014, 16, 395–408. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.A.; Oh, S.O.; Park, P.W.; Park, J.Y. Effect of probenecid on the pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine in healthy subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 61, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Geissen, S.U.; Gal, C. Carbamazepine and diclofenac: Removal in wastewater treatment plants and occurrence in water bodies. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenker, A.; Cicero, M.R.; Prestinaci, F.; Bottoni, P.; Carere, M. Bioaccumulation and biomagnification potential of pharmaceuticals with a focus to the aquatic environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caracciolo, A.B.; Topp, E.; Grenni, P. Pharmaceuticals in the environment: Biodegradation and effects on natural microbial communities: A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 106, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ter Laak, T.; van der Aa, M.; Houtman, C.; Stoks, P.; van Wezel, A. Temporal and spatial trends of pharmaceuticals in the Rhine. RIWA Rep. 2010, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Skocovska, M.; Ferencik, M.; Svoboda, M.; Svobodova, Z. Residues of selected sulphonamides, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics-antipyretics in surface water of the Elbe river basin (Czech Republic). Vet. Med. 2021, 66, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonja, B.; Pérez, S.; Barceló, D. Human metabolite lamontrigine-n2-glucuronide is the principal source of lamotrigine-derived compounds in wastewater treatment plants and surface water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Writer, J.H.; Ferrer, I.; Barber, L.B.; Thurman, E.M. Widespread occurrence of neuro-active pharmaceuticals and metabolites in 24 Minnesota rivers and wastewaters. Sci. Total. Environ. 2013, 461–462, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sörengård, M.; Campos-Pereira, H.; Ullberg, M.; Lai, F.Y.; Golovko, O.; Ahrens, L. Mass loads, source apportionment, and risk estimation of organic micropollutants from hospital and municipal wastewater in recipient catchments. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Qian, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Xu, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y. The assessment of the eco-toxicological effect of gabapentin on early development of zebrafish and its antioxidant systém. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 22777–22784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Li, X.; Jia, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Yu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y. A transcriptomics-based analysis of the toxicity mechanisms of gabapentin to zebrafish embryos at realistic environmental concentrations. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, X.; Jia, D.; Du, S.; Zhu, R.; Zhou, W.; Pan, S.; Zhang, Y. Toxicity of gabapentin-lactam on the early developmental stage of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.S.; Oliveira, R.; Lisboa, C.A.; Pinto, J.M.; Sousa-Moura, D.; Camargo, N.S.; Perillo, V.; Oliveira, M.; Grisolia, C.K.; Domingues, I. Chronic effects of carbamazepine on zebrafish: Behavioral, reproductive and biochemical endpoints. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galus, M.; Kirischian, N.; Higgins, S.; Purdy, J.; Chow, J.; Rangaranjan, S.; Li, H.; Metcalfe, C.; Wilson, J.Y. Chronic, low concentration exposure to pharmaceuticals impacts multiple organ systems in zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 132–133, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.H.; Li, P.; Rodina, M.; Randak, T. Effect of human pharmaceutical carbamazepine on the quality parameters and oxidative stress in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) spermatozoa. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Delivery [kg/year] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Gabapentin | Carbamazepine | Lamotrigine |
| 2011 | 8420 | 5465 | 1366 |
| 2012 | 9333 | 5171 | 1426 |
| 2013 | 10,429 | 5959 | 1472 |
| 2014 | 10,429 | 4807 | 1472 |
| 2015 | 13,141 | 4643 | 1589 |
| 2016 | 13,746 | 4328 | 1678 |
| 2017 | 14,360 | 4215 | 1705 |
| 2018 | 14,558 | 3929 | 1779 |
| 2019 | 16,127 | 3736 | 1806 |
| 2020 | 15,390 | 3540 | 1866 |
| rs | 0.9848 | −0.9636 | 0.997 |
| p value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Localities | Gabapentin | Gabapentin-Lactam | Carbamazepine | Lamotrigine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elbe (Debrné) | −0.455 | −0.6862 | −0.946 | −0.587 |
| Elbe (Hradec Králové) | −0.288 | −0.9062 | −0.885 | −0.707 |
| Elbe (Valy) | 0.063 | −0.7461 | −0.787 | −0.778 |
| Elbe (Obříství) | 0.049 | −0.4471 | −0.658 | −0.573 |
| Elbe (Děčín) | −0.029 | −0.2853 | −0.685 | −0.593 |
| Orlice (Nepasice) | −0.203 | −0.6877 | −0.968 | −0.670 |
| Doubrava (Záboří) | −0.028 | −0.8511 | −0.844 | −0.843 |
| Cidlina (Sány) | −0.140 | −0.6154 | −0.818 | −0.705 |
| Mrlina (Nymburk) | −0.846 | −0.9161 | −0.865 | −0.848 |
| Jizera (Tuřice) | 0.132 | −0.4472 | −0.656 | −0.330 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferencik, M.; Blahova, J.; Schovankova, J.; Siroka, Z.; Svobodova, Z.; Kodes, V.; Stepankova, K.; Lakdawala, P. Residues of Selected Anticonvulsive Drugs in Surface Waters of the Elbe River Basin (Czech Republic). Water 2022, 14, 4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14244122
Ferencik M, Blahova J, Schovankova J, Siroka Z, Svobodova Z, Kodes V, Stepankova K, Lakdawala P. Residues of Selected Anticonvulsive Drugs in Surface Waters of the Elbe River Basin (Czech Republic). Water. 2022; 14(24):4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14244122
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerencik, Martin, Jana Blahova, Jana Schovankova, Zuzana Siroka, Zdenka Svobodova, Vit Kodes, Karla Stepankova, and Pavla Lakdawala. 2022. "Residues of Selected Anticonvulsive Drugs in Surface Waters of the Elbe River Basin (Czech Republic)" Water 14, no. 24: 4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14244122








