Abstract
New construction practices for roller compacted concrete (RCC) overlays and stepped chutes are changing the step geometry from a traditional square-edge, vertical face to a 45° beveled face. A large-scale 3(H):1(V) (i.e., θ = 18.4°) stepped chute model was tested with a 45° beveled face step with a height (h) of 152 mm. Results were compared to data on square-edge, vertical face steps previously obtained. The distance to the inception point of free-surface aeration normalized by the surface roughness was reduced approximately 25% for the same Froude number defined in terms of roughness height. An existing inception point relationship for vertical face steps was adjusted with a best fit correction factor to predict the free-surface inception point for this chute slope and beveled face angle. Relative flow depths, mean air concentration, and energy loss data showed similar general trends for vertical face and beveled face steps, but the depths and air concentrations for beveled face steps were slightly higher for equal values of relative free-surface inception point, Li/L, and relative step height (e.g., h/dc). Energy loss at the free-surface inception point ranged from approximately 20 to 40% of total head for both step types. Additional research is needed to determine the generalized effects of the bevel angle and the chute slope on flow properties. This research is expected to be used by field engineers for the design of stepped chutes with beveled face steps.
1. Introduction
Like roads, bridges, and buildings, dams are affected over time by structural deterioration, sedimentation of reservoirs, and changes in land use that can alter hydrology associated with the dam. Rehabilitation of these dams is often necessary. One option commonly used for embankment dam rehabilitation is a roller compacted concrete (RCC) overlay that armors the top and downstream slope of an existing dam. Typical construction methods produce a stepped chute that helps to dissipate flow energy. Material cost-savings and shorter construction schedules are advantages of RCC stepped chutes, and designers and contractors are constantly in search of more cost-effective ways while also maintaining a safe performance of the structure. RCC is typically placed in horizontal lifts with traditional earthwork equipment and compacted with vibratory rollers, which naturally produces a stepped profile. While forms are not required for placement of RCC, forms allow for better compaction along the step edge. In addition, aesthetic appeal of a finished concrete step aids the acceptance of these structures when located in residential communities. A finished step edge also improves long-term resistance to weathering. Placement with constructed vertical forms can be costly and time-consuming, but the characteristics of RCC also enable construction of a beveled geometry (e.g., 45° angle) using slip forms that move with the placement. This provides an attractive result and is economical to construct, so it is becoming widely implemented in the United States even though little is known about the impact the step shape has on the hydraulic performance of the stepped chute. A chute constructed with beveled face steps is illustrated in Figure 1.
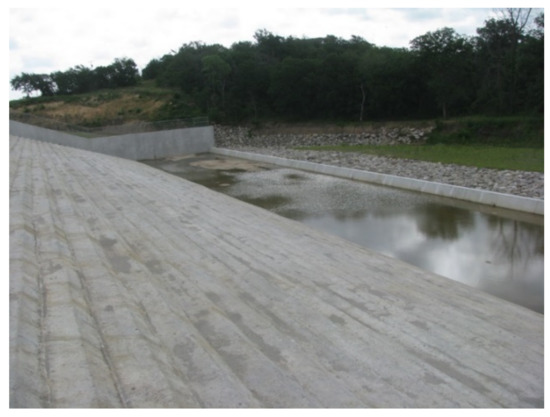

Figure 1.
Constructed RCC beveled face stepped chute at Caney Coon Site 2 in Oklahoma (photo courtesy of USDA-NRCS).
Researchers have examined the effects that step height, step geometry, and step appurtenances have on the development of the free-surface inception point, aerated flow depth, and overall hydraulic performance of stepped chutes. Physical models of traditional stepped chutes (e.g., squared cornered, vertical face step) have been widely tested [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. These studies have produced relationships defining the free-surface inception point, velocity profiles, clear and aerated flow depths, mean air concentration, and energy coefficient. Other researchers [4,12,13,14,15,16] expanded studies on stepped chutes to include unique step appurtenances (e.g., steps with vanes, wedge-shaped steps, steps with circular burlings, and pooled steps). In addition, some studies report the effects of non-standard step configurations (e.g., micro- and macro-roughness) [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. Steps with 20 mm chamfers on the corner of square steps, which is similar to the fully beveled face step that contractors are using today but leaves a partial vertical face, was specifically studied [23]. In this study, e.g., [23], the chamfer step data shifted the free-surface inception point location downstream as compared to the traditional squared-edge vertical face stepped chute, especially for flow conditions well into the skimming flow regime; thus, concluding the step edge shape has substantial effects on the free-surface inception point location. When these data were compared [26], the free-surface inception point data were noted to be in reasonable agreement for steeper chute slopes (e.g., θ = 53°). Three sizes of triangular wedged blocks placed in the cavity of the step were also examined [23]. These configurations moved the free-surface inception point upstream by approximately one step when compared to the traditional squared-edge vertical face steps. For smaller flows, the triangular step wedges extended the range of nappe and/or transition flow conditions and delayed the onset of skimming flow; these steps also caused undulations and chaotic behavior of the free-surface that seemed related to the early inception of aeration [23]. Another close study [25] to the study described herein investigated the use of angled vanes on the inclined step for fish passage. Researchers found the inclined step without the vanes exhibited the lowest energy dissipation for the configurations tested.
Because beveled face steps are commonly constructed for stepped chutes in the U.S. and little is known about the effect of this step shape, the objective of this study is to continue to build on previous research, e.g., ref. [6,8,10] by examining the physical effects of beveled face steps on the development of the free-surface inception point and other design parameters including flow depth, velocity profiles, and mean air concentration. This research is relevant to contemporary design and construction practices for stepped chutes.
2. Materials and Methods
Tests were conducted in the same 2-dimensional flume [10], with a width of 1.8 m and a total drop height of 5.6 m and a chute slope of 18.4° (e.g., 3(H):1(V)). Key facility information [10] is reproduced here with additional details added that relate to this specific set of tests. The original flume design was based on Froude similitude recommendations [2,3]. To minimize scale effects, Reynolds numbers, R ≥ 105, were maintained for all discharges tested as shown in Table 1. It is recommended the results of this study be applied for scales 10:1 or larger to minimize scale effects. The entrance of the flume consisted of a 3 m long broad-crested concrete weir with an equivalent roughness height of 0.46 mm [27]. The flume was initially provided with concrete vertical face steps with a height of 304 mm. For this specific study, the steps were reduced to a height of 152 mm with a 45° beveled face. These steps were constructed of wood with 152 mm by 152 mm, 45° triangular wooden inserts in the step cavities. Figure 2 is a schematic of the stepped chute test facility with beveled face steps installed.

Table 1.
Test parameters.
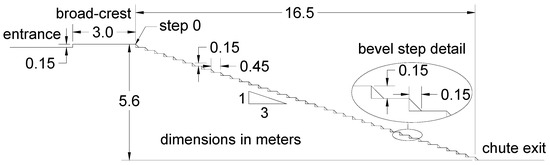
Figure 2.
Schematic of a stepped chute model with beveled face steps.
Flow was delivered to the test flume from a vegetated gravity-flow channel that was supplied by five 0.46 m diameter siphons drawing from the adjacent Lake Carl Blackwell. Discharge was monitored at the broad-crested weir of the flume by (1) a combination of a gage well and manually operated point gage and (2) a string potentiometer coupled with a computerized data acquisition system. A series of nine test flows were conducted with unit discharges (q) ranging between 0.16 to 1.84 m3/(s·m). All flows with exception of the smallest test flow (0.16 m3/(s·m)) were classified as skimming flow [2]. The smallest test flow was classified as nappe or transition flow. Table 1 summarizes the unit discharges, q; critical flow depth, dc; step height to critical flow depth ratio, h/dc; Reynolds number, R; and flow description. The free-surface inception point was noted for each test flow summarized in Table 1, and tests were repeated as needed to obtain flow depth and air–water flow measurements.
For each test, the location of free-surface inception point was recorded through written notations and digital photography, with the same standardization method in reporting as previous studies, e.g., [6,8,10]. Flow depths, y, upstream of the free-surface inception point, were measured for five of the nine test flows at even number steps starting at step zero (e.g., downstream crest edge), using a manually operated point gage attached to a movable carriage system. Air–water flow properties including flow depth, air concentration, and velocity along the centerline of the flume downstream of the free-surface inception point for these five test flows were measured with an RBI dual-tipped fiber optic probe (RBI Instrumentation, Meylan, France). Details to the sampling rate, signal response time, time of measurement and number of bubbles processed for the fiber optic probe were the same as those in other studies, e.g., [10,28]. The air–water flow measurements were used to calculate the clear-water flow depth, ycw, and the mean air concentration, Cmean, for the aerated region downstream of the free-surface inception point. Measurements were not made in the tailwater zone for these tests; the tailwater level was adjusted to keep the hydraulic jump at the toe of the slope contained within a stilling basin to reduce erosion of the exit channel.
3. Free-Surface Inception Point
Classical research on the turbulent boundary layer development and identification of the free-surface inception point for smooth chutes are outlined in several studies, e.g., [29,30,31]. A widely accepted empirical relationship for defining the free-surface inception point for smooth chutes was developed [32], and this relationship was expanded upon for application to steep, vertical face stepped chutes (θ > 30°) with ogee-crested weir entrance conditions in other studies, e.g., [1,2]. Studies, e.g., ref. [6,10], report that the relationship defined in studies, e.g., ref. [1,2], overestimated the length to the free-surface inception point for moderate sloped, vertical face stepped chutes (10° ≤ θ ≤ 30°) with broad-crested weir entrances. A similar overestimation of Li by the relationship [1] was reported in another study [23], but none of these studies suggested that the difference in crest geometries was a significant factor. The following free-surface inception point relationships with skimming flow conditions (0.035 ≤ h/dc ≤ 1.1) were developed in previous studies, e.g., [6,10]:
where θ = chute slope, F* = Froude number defined in terms of roughness height: F* = q/[g(sinθ)ks3]0.5, q = unit discharge, g = gravitational constant, ks = the surface roughness = hcos(θ), and h = step height. These relationships were validated with several independent studies. Defining the Li is key to the empirical design relationships for moderate-sloped (10° ≤ θ ≤ 30°) stepped chutes with traditional vertical step face in skimming flow conditions (0.035 ≤ h/dc ≤ 1.1) [10]. It was unknown if Equations (1) and (2) were applicable to beveled face steps.
In this study, the surface roughness, ks, is defined differently for vertical and beveled face steps. For the vertical face step, the surface roughness is defined as ks = hcos(θ) with h equal to the vertical step height. For the unique beveled face step in this study, the surface roughness is defined as ks = [(z − 1)/z]hcos(θ) where z = 1/tan(θ) for 45° beveled face steps. For this study with a chute slope of 18.4°, the surface roughness can be written as ks = (2/3)hcos(θ). Figure 3 provides photographs of a stepped chute with vertical (e.g., Figure 3a) and beveled face steps (e.g., Figure 3b) illustrating ks, h, and θ. One should note for stepped chutes with beveled face steps, the surface roughness definition is unique for each bevel angle.
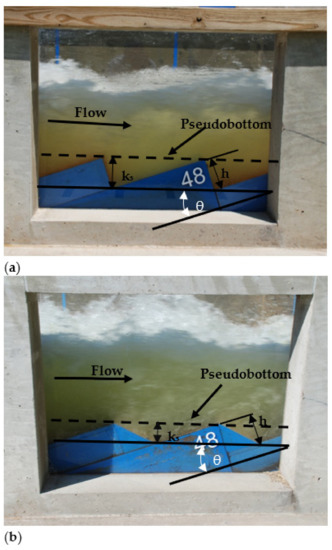
Figure 3.
Skimming flow in a stepped chute model on a 3(H):1(V) slope (θ = 18.4°) with (a) traditional vertical face steps where ks = hcos(θ) and (b) 45° beveled face steps where ks = 2/3hcos(θ) defined for this chute slope. Note photographs are oriented along the chute slope.
4. Results
The visually observed free-surface inception point was recorded for each test flow. Table 2 summarizes the observed distances from the downstream edge of the broad-crested weir to the free-surface inception point, Li, and Li/ks. For consistency with studies, e.g., [6,10], Li was defined as the streamwise distance from the downstream edge of the spillway crest to the point where “white water” first appeared across the full width of the free surface of the stepped chute. Figure 4 compares Equation (1) and observed Li/ks for the tested beveled face steps (h = 152 mm) and vertical face steps for multiple heights tested [6]. The vertical face step data shown in Figure 4 include all step heights tested [6] whereas for this study, only one beveled face step height, h = 152 mm, was tested. For all tested flows, Equation (1) overestimated Li/ks for the beveled face steps by approximately 25% for the same Froude number defined in terms of roughness height. The scatter for beveled and vertical face step data is similar. Some of the scatter at the lower values of F* may be due to limited measurement resolution producing large variation on a percentage basis.

Table 2.
Observed inception point location relative to step location, distance to the free-surface inception point, Li, and free-surface inception point to surface roughness ratio, Li/ks.
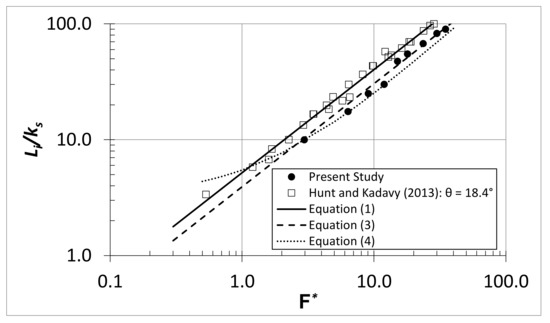
Figure 4.
Visually observed free-surface inception point (Li) normalized by the step roughness (ks) for a vertical face step (ks = h cos(θ)) from [6] and beveled face step (ks = (2/3) h cos(θ)) as compared to predicted Li/ks using Equations (1), (3) and (4).
As shown in Figure 4, the free-surface inception point for the beveled face step is shifted upstream approximately 25% compared to the vertical face step with the same Froude number defined in terms of roughness height, F*. Since the slopes of the trendlines for the beveled face step and vertical face step are similar, a best fit correction factor is added to Equation (1), producing Equation (3).
where Cf = 0.76. The correlation coefficient, R2, for the best fit was 0.99.
Equation (3) accurately predicts the location of the inception point for the beveled face step for the range of F* tested for a bevel angle of 45 degrees. For other bevel angles additional correction factors may be required.
The difference in Li/ks for beveled and vertical face steps may be explained by observations recorded through videography and photography in this study and previous studies [10]. In review of the video, e.g., [10], the circulation pattern was observed to be more circular within the cavity of the vertical face step (e.g., Figure 5a) and more elongated within the cavity of the beveled face step (e.g., Figure 5b) for the present study. Figure 5 provides photographs of these circulation patterns. For beveled face steps, the flow remains attached to the pseudobottom for small relative step heights, h/dc. As h/dc increases (due to reduced unit discharge and critical flow depth) and approaches transition to nappe flow conditions, the water surface becomes more undular.
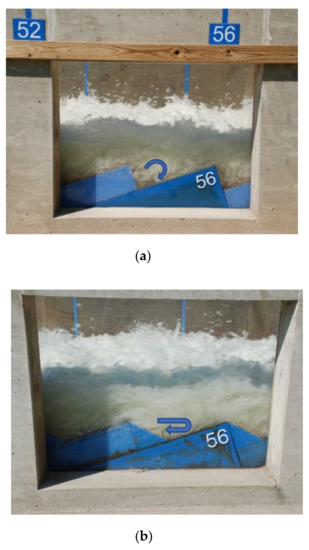
Figure 5.
Observed circulation patterns in stepped chutes with (a) vertical face steps and (b) beveled face steps.
Figure 6 illustrates important mechanics of the flow over beveled steps. Flow separates cleanly from the tip of vertical steps for all practical chute slopes, but beveled face steps have a smaller difference between the angle of the beveled face and the prevailing flow direction that makes it possible near the nappe flow transition for flow to remain attached to the bevel and across the tread in parallel alignment with it. At low unit discharges, the flow may also remain attached to the next bevel, making a sharp turn over the step tip, which produces a corresponding undular water surface. However, at higher unit discharges and velocities, the parallel alignment of the flow and the tread can cause a clean separation from the next step tip. This flow pattern is not stable from one step to the next; attachment to one bevel and its flowing tread leads to detachment from the next bevel. It also seems possible for the flow to detach from one bevel, skip over the next step cavity, and attach to the subsequent bevel. In this configuration, alternate step cavities will experience attached flow and separated flow, although it is uncertain whether a water filled cavity could be maintained over the step at which the flow is not attached. Regardless, there is the potential for strong undular flows that will affect streamlines near the floor and near the water surface, as shown in Figure 6. Strong centripetal acceleration of the flow is needed to maintain these flow structures. If it cannot be provided or if the flow skips too far (jumping several steps at once), there is potential for early onset of aeration. This is most likely to occur for a flow rate that is not much larger than that required to transition from nappe to skimming flow. More research is needed to examine this phenomenon closely for other chute slopes and bevel angles.
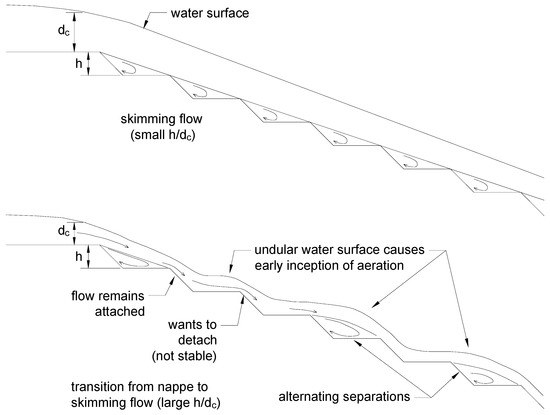
Figure 6.
Flow pattern possibilities for beveled face stepped chutes.
The observations made in this study are consistent with tests [23] having triangular wedge blocks inserted that partially filled the cavity and prolonged nappe and/or transition flow. In the study, e.g., [23], undulations, chaotic behaviors, and irregular ejections of fluid associated with early onset of aeration were reported. The study, e.g., [23] offers an empirical relationship for Li/ks for stepped chutes on a 45° slope with triangular wedges partially filling the step cavities:
Equation (4) is applicable for skimming flow conditions. Figure 4 shows this relationship is in reasonable agreement with the beveled face step data obtained from the present study, despite the different chute slopes. More research is recommended to determine the general effects of beveled faced steps on the development of the free-surface inception point, as Equations (3) and (4) are specific to the chute slope and bevel angle for which they were developed.
Figure 7 compares the flow properties upstream (e.g., y) and downstream (e.g., ycw, Cmean, and y90) of the free-surface inception point and the relative energy loss, ΔH/Ho, for this present study and the previous study on vertical face steps [10] in relation to the flow distance down the slope normalized by the length to the inception point. y90 is the characteristic flow depth with 90% air concentration. Even though data were collected for both nappe and skimming flow conditions, for ease of comparison Figure 7 includes only skimming flow data. Data in the air-entrained region were not collected for the flowrate corresponding to h/dc = 0.22 for the beveled face steps due to damage to the fiber optic probe system during testing. Figure 7a shows that the relative flow depth, y/dc, decreases rapidly for both beveled and vertical face steps from the crest to L/Li = 1.0, the location of the free-surface inception point. For L/Li > 1.0, the relative clear water flow depth, ycw/dc, approaches a constant value that depends on the relative step height, h/dc. The values of ycw/dc for beveled steps tend to be slightly larger than the vertical face steps. When L/Li > 2.0, Cmean approaches a constant value that depends on h/dc for beveled and vertical face steps (Figure 7b). A similar trend for vertical face steps was observed in previous studies [10,33]. Cmean for L/Li > 2.0 ranged from 0.28 ≤ Cmean ≤ 0.40 for the beveled stepped chute tested. Cmean for the beveled face steps is slightly larger than that of the vertical face steps. Similar to vertical face steps, the normalized bulked flow depth, y90/dc, approaches a constant value that depends on h/dc for L/Li > 2.0 for beveled face steps, as shown in Figure 7c, and values of y90/dc are consistently larger for beveled face steps. Figure 7d shows for both step types that the relative energy loss, ΔH/Ho, increases rapidly from about 20 to 40% from the free-surface inception point, L/Li = 1.0, to nearly a constant value of about 80% as uniform flow is reached near the toe of the stepped chute. Relative energy loss is the ratio of the total energy loss from the crest to the measurement location, ΔH, to the total energy at the crest referenced to the measurement location step surface, Ho. For the calculation of the specific energy, H, the influence of the air concentration on the energy coefficient was considered negligible for these slopes, as per [34]. There is more scatter in the energy loss data for the beveled face steps, but the mean values and trends agree well with the vertical face steps.
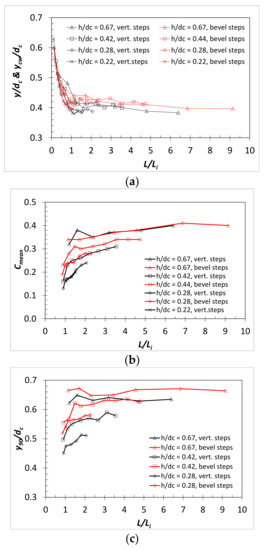
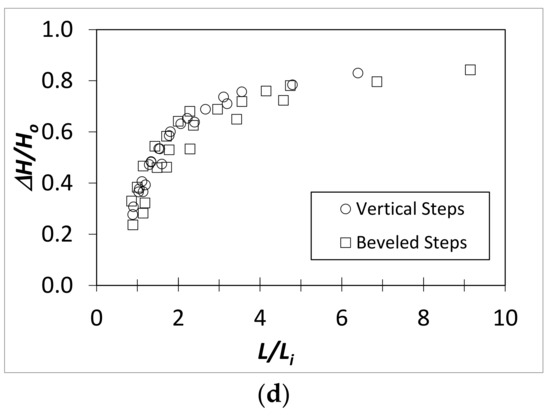
Figure 7.
Comparisons of (a) relative flow depths (y/dc, ycw/dc), (b) mean air concentration, Cmean, (c) y90/dc, and (d) relative energy loss, ΔH/Ho, for vertical and beveled face steps.
For the study on vertical face steps, e.g., [10], Li is key in the development of empirical design relationships for the stepped chute parameters shown in Figure 7. These relationships may be used for rough estimates for the design parameters for beveled face stepped chutes. To do so, Equation (3) should be used to determine Li for stepped chutes on a 3(H):1(V) slope with 45° beveled steps.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Chutes constructed with slip-formed, beveled steps are becoming common in the embankment dam rehabilitation industry as a more practical and economical solution than vertical-edge forms for compacting the RCC step edge. While RCC does not absolutely require forms or vertical edges, the aesthetics of RCC in embankment dam rehabilitation is important to residential communities where many of these dams are located, so some type of cleanly constructed edge is desirable. A finished edge can also improve long-term durability. When beveled face steps are used, testing shows the distance to the inception point of free-surface aeration normalized by the surface roughness is reduced approximately 25% for the same Froude number defined in terms of roughness height as compared to vertical face steps. A fitted correction factor was developed to adjust the vertical face step inception point relationship for applications with beveled face steps. For stepped chutes operating in the skimming flow range, y/dc, ycw/dc, y90/dc, Cmean, and ΔH/Ho showed similar general trends for both beveled and vertical face steps. All relative flow depths and the mean air concentration were slightly higher for the beveled face steps when compared to vertical face steps at equal values of L/Li and h/dc. For instance, relative flow depth, y/dc, decreased rapidly from the spillway crest to the free-surface inception point, L/Li = 1.0, then approached a constant value downstream from the free-surface inception point. Cmean approached a constant value for L/Li > 2.0. Energy loss for both step types ranges from approximately 20 to 40% of total head near L/Li = 1.0 and increases to a limit of about 80% as uniform flow is achieved. The results of this study are specific to the tested configuration with a 3(H):1(V) chute slope and 45° bevel angle for the step face. For other configurations, more research is needed to determine generalized effects beveled face steps have on the developing free-surface inception point and resulting profiles of flow depth, mean air concentration, and energy loss.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.L.H. and K.C.K.; methodology, S.L.H. and K.C.K.; formal analysis, S.L.H., K.C.K., T.L.W. and D.W.M.; investigation, S.L.H., K.C.K., T.L.W. and D.W.M.; resources, S.L.H.; data curation, S.L.H. and K.C.K.; writing—original draft preparation, S.L.H., K.C.K., T.L.W. and D.W.M.; writing—review and editing, S.L.H., K.C.K., T.L.W. and D.W.M.; visualization, S.L.H., K.C.K., T.L.W. and D.W.M.; supervision, S.L.H.; project administration, S.L.H.; funding acquisition, S.L.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by U.S. Congressional Appropriations to the United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. The project number for this research is 3072-13000-011-000-D.
Data Availability Statement
Some of the data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer. Mention of trade names or commercial products in this publication is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
| Notation | |
| A | area; |
| Cf | correction factor to the free-surface inception point for beveled face steps; |
| Cmean | mean air concentration; |
| dc | critical flow depth; |
| F* | Froude number defined in terms of roughness height: q/[g(sinθ)ks3]0.5; |
| g | gravitational constant; |
| h | step height; |
| h/dc | step height to critical flow depth ratio; |
| H | specific energy (e.g., ); |
| Hcrest | total drop height from the weir crest to the measurement location step surface; |
| Ho | total energy at the crest relative to the measurement location step surface (e.g., Ho = Hcrest + 1.5dc); |
| ks | the surface roughness = hcos(θ) for vertical face steps and = [(z − 1)/z]hcos(θ) for beveled face steps; |
| L | length from the downstream edge of the broad-crested weir to the point of interest; |
| L/Li | normalized length; |
| Li | characteristic length from the downstream edge of the broad-crested weir to the surface inception point; |
| q | unit discharge; |
| R | Reynolds number = q/vk; |
| vk | kinematic viscosity; |
| V | mean velocity; |
| v | velocity for an incremental area in the velocity profile; |
| y | flow depth, normal coordinate from pseudobottom; |
| ycw | equivalent clear water flow depth; |
| y90 | characteristic flow depth where the air concentration is 90%; |
| z | 1/tan(θ) for 45° beveled face steps; |
| α | energy coefficient, ; |
| ΔA | incremental area; |
| ΔH | total energy loss, ΔH = Ho − H; |
| ΔH/Ho | relative energy loss, (e.g., ΔH/Ho = 1 − (H/Ho)); |
| θ | chute slope; |
| Acronyms | |
| H | horizontal; |
| NRCS | Natural Resources Conservation Service; |
| RCC | roller compacted concrete; |
| USDA | United States Department of Agriculture; |
| V | vertical. |
References
- Chanson, H. Hydraulics of skimming flows over stepped channels and spillways. IAHR J. Hydraul. Res. 1994, 32, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chanson, H. The Hydraulics of Stepped Chutes and Spillways; A. A. Balkema Publishers: Steenwijk, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Boes, R.M.; Hager, W.H. Two-phase flow characteristics of stepped spillways. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2003, 129, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, C. An Experimental Study of Free-Surface Aeration on Embankment Stepped Chutes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Meireles, I.; Matos, J. Skimming flow in the nonaerated region of stepped spillways over embankment dams. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2009, 135, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, S.L.; Kadavy, K.C. Inception point for embankment dam stepped spillways. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2013, 139, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, S.L.; Kadavy, K.C. Estimated splash and training wall height requirements for stepped chutes applied to embankment dams. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2017, 143, 06017018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, S.L.; Kadavy, K.C. Inception point for stepped chute designs with multiple sections of different step heights. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2021, 147, 06021001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Gulliver, J.S.; Zhu, D. Application of displacement height and surface roughness length to determination boundary layer development length over stepped spillway. Water 2014, 6, 3888–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunt, S.L.; Kadavy, K.C.; Hanson, G.J. Simplistic design methods for moderate-sloped stepped chutes. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chanson, H. Hydraulics of the developing flow region of stepped spillways. I: Physical modeling and boundary layer development. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Relvas, A.T.; Pinheiro, A.N. Inception point and air concentration in flows on stepped chutes lined with wedge-shaped concrete blocks. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2008, 134, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bung, D.B.; Schlenkhoff, A. Self-aerated skimming flow on embankment stepped spillways—The effect of additional micro-roughness on energy dissipation and oxygen transfer. In Proceedings of the 1st IAHR European Congress, Edinburgh, Scotland, 4–6 May 2010; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Felder, S.; Chanson, H. Air-water flows and free-surface profiles on a non-uniform stepped chute. J. Hydraul. Res. IAHR 2014, 52, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felder, S.; Chanson, H. Effects of step pool porosity upon flow aeration and energy dissipation on pooled stepped spillways. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felder, S.; Chanson, H. Simple design criterion for residual energy on embankment dam stepped spillways. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 142, 04015062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephenson, D. Stepped energy dissipators. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Hydraulics for High Dams, IAHR, Beijing, China, 15–18 November 1988; pp. 1228–1235. [Google Scholar]
- André, S. High Velocity Aerated Flow on Stepped Chutes with Macro-Roughness Elements. Ph.D. Thesis, Communication LCH20, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- André, S.; Matos, J.; Boillat, J.L.; Schleiss, A.J. Energy dissipation and hydrodynamic forces of aerated flow over macro-roughness linings for overtopped embankment dams. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Hydraulics of Dams and River Structures, Tehran, Iran, 26–28 April 2004; Yazdandoost, F., Attari, J., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 2004; pp. 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, C.A.; Chanson, H. Hydraulic design of stepped spillways and downstream energy dissipators for embankment dams. Dam Eng. 2007, 17, 223–243. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, C.A.; Takahashi, M.; Chanson, H. An experimental study of effects of step roughness in skimming flows on stepped chutes. J. Hydraul. Res. 2008, 46, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zare, H.K.; Doering, J.C. Inception point of air entrainment and training wall characteristics of baffles and sills on stepped spillways. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2012, 138, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chanson, H. Effects of step and cavity shapes and aeration and energy dissipation performances of stepped chutes. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daneshfaraz, R.; Aminvash, E.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Ghaderi Am Kriqi, A.; Najibi, A.; Ricardo, A.M. Laboratory investigation of hydraulic parameters on inclined drop equipped with fishway elements. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshfaraz, R.; Aminvash, E.; Ghaderi, A.; Kuriqi, A.; Abraham, J. Three-dimensional investigation of hydraulic properties of vertical drop in the presence of step and grid dissipators. Symmetry 2021, 13, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meireles, I.; Renna, F.; Matos, J.; Bombardelli, F.A. Skimming, nonaerated flow on stepped spillways over roller compacted concrete dams. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2012, 138, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, V.T. Open-Channel Hydraulics; McGraw-Hill, Book Company, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, S.L.; Kadavy, K.C. Lesson learned in stepped chute instrumentation. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2021, 37, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, E. Entrainment of air in swiftly flowing water. Civil Eng. 1939, 9, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Halbronn, G. Etude de la mise en régime des écoulements sur les ouvrages à forte pente. Houille Blanche 1952, 38, 347–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauer, W.J. Turbulent boundary layer on steep slopes. Trans. Am. Soc. Civil Eng. 1954, 119, 1212–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, I.R.; Ackers, P.; Loveless, J. General method for critical point on spillways. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1983, 109, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, M.; Hager, W.H. Self-entrainment of air on stepped spillways. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2011, 37, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Ohtsu, I. Aerated flow characteristics of skimming flow over stepped chutes. J. Hydr. Res. 2012, 50, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).