Comparative Analysis of Developed Rainfall Intensity–Duration–Frequency Curves for Erbil with Other Iraqi Urban Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Collection
2.2. Precipitation Duration Reduction Formula
2.3. Frequency Distribution and the Development of IDF Curves
2.3.1. Gumbel Distribution
2.3.2. Log-Pearson Type III
2.4. Derivation of IDF Empirical Formula
2.5. Goodness of Fit
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Amri, N.S.; Subyani, A.M. Generation of rainfall intensity duration frequency (IDF) curves for ungauged sites in arid region. Earth Syst. Environ. 2017, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Salehi, S.; Mosavi, A.; Nabipour, N.; Shamshirband, S.; Ghamisi, P. Spatial analysis of seasonal precipitation over Iran: Co-variation with climate indices. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dupont, B.; Allen, D.L. Revision of the Rainfall-Intensity Duration Curves for the Commonwealth of Kentucky; University of Kentucky Transportation Center: Lexington, KY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Koutsoyiannis, D.; Kozonis, D.; Manetas, A. A mathematical framework for studying rainfall intensity-duration-frequency relationships. J. Hydrol. 1998, 206, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, F.C. Generalized rainfall-duration-frequency relationships. J. Hydraul. Div. 1969, 95, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-L. Rainfall intensity-duration-frequency formulas. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1983, 109, 1603–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershfield, D.M. Estimating the probable maximum precipitation. J. Hydraul. Div. 1961, 87, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.; Frederick, R.; Tracey, R. Precipitation frequency atlas of the conterminous western United States (by states). US Natl. Weather Serv. NOAA Atlas 1973, 2, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Nhat, L.M.; Tachikawa, Y.; Takara, K. Establishment of intensity-duration-frequency curves for precipitation in the monsoon area of Vietnam. Annu. Disaster Prev. Res. Inst. 2006, 49b, 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.P.; Zhang, L. IDF curves using the Frank Archimedean copula. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2007, 12, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.H.R.; Kwon, H.-H.; Kim, Y.-T. A local-regional scaling-invariant Bayesian GEV model for estimating rainfall IDF curves in a future climate. J. Hydrol. 2018, 566, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wendi, D.; Kim, D.E.; Liong, S.-Y. Deriving intensity–duration–frequency (IDF) curves using downscaled in situ rainfall assimilated with remote sensing data. Geosci. Lett. 2019, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kristvik, E.; Johannessen, B.G.; Muthanna, T.M. Temporal Downscaling of IDF Curves Applied to Future Performance of Local Stormwater Measures. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noor, M.; Ismail, T.; Shahid, S.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Dewan, A. Evaluating intensity-duration-frequency (IDF) curves of satellite-based precipitation datasets in Peninsular Malaysia. Atmos. Res. 2021, 248, 105203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ombadi, M.; Nguyen, P.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.-L. Developing Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) Curves From Satellite-Based Precipitation: Methodology and Evaluation. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 7752–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schardong, A.; Simonovic, S.P.; Gaur, A.; Sandink, D. Web-Based Tool for the Development of Intensity Duration Frequency Curves under Changing Climate at Gauged and Ungauged Locations. Water 2020, 12, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinerowska-Bords, K. Development of local IDF-formula using controlled random search method for global optimization. Acta Geophys. 2015, 63, 232–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krvavica, N.; Rubinić, J. Evaluation of Design Storms and Critical Rainfall Durations for Flood Prediction in Partially Urbanized Catchments. Water 2020, 12, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khalaf, H. Predicting Short-Duration, High-Intensity Rainfall in Saudi Arabia. Master’s Thesis, King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shaikh, A. Rainfall Frequency Studies for Saudi Arabia. Master’s Thesis, Civil Engineering Department King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- AlHassoun, S.A. Developing an empirical formulae to estimate rainfall intensity in Riyadh region. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2011, 23, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elsebaie, I.H. Developing rainfall intensity–duration–frequency relationship for two regions in Saudi Arabia. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2012, 24, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deger, İ.; Yuce, M. Rainfall Intensity-Duration-Frequency Analysis for the City of Gaziantep. In Proceedings of the International Civil Engineering and Architecture Conference, Trabzon, Turkey, 17–20 April 2019; pp. 760–766. [Google Scholar]
- Şen, Z. Annual daily maximum rainfall-based IDF curve derivation methodology. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 3, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadadin, N.A. Rainfall intensity-duration-frequency relationship in the Mujib Basin in Jordan. J. Appl. Sci. 2005, 5, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamaamin, Y.A. Developing of Rainfall Intensity-Duration-Frequency Model for Sulaimani City. J. Zankoy Sulaimani 2017, 19, p10634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, I.F.; Saeed, Y.N. Analysis of Rainfall Data for a Number of Stations in Northern Iraq. Al-Rafidain Eng. J. AREJ 2020, 25, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, E.S.; Mohamedmeki, M.Z. Analysis of rainfall intensity-duration-frequency (IDF) curves of Baghdad city. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Chennai, India, 16–17 September 2020; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; p. 012066. [Google Scholar]
- Jalee, L.A.; Farawn, M.A. Developing rainfall intensity-duration-freqency relationship for Basrah City. Kufa J. Eng. 2013, 5, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Majeed, A.R.; Nile, B.K.; Al-Baidhani, J.H. Selection of suitable PDF model and build of IDF curves for rainfall in Najaf city, Iraq. Proc. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1973, 012184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakheel, A.A. Drawing curves of the rainfall intensity duration frequency (IDF) and assessment equation intensity rainfall for Nasiriyah city, Iraq. Univ. Thi-Qar J. 2017, 12, 63–82. [Google Scholar]
- Nanekely, M.; Scholz, M.; Al-Faraj, F. Strategic framework for sustainable management of drainage systems in semi-arid cities: An Iraqi case study. Water 2016, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mustafa, A.M.; Muhammed, H.; Szydłowski, M. Extreme rainfalls as a cause of urban flash floods; a case study of the Erbil-Kurdistan region of Iraq. Acta Sci. Pol. Form. Circumiectus 2019, 18, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Szydłowski, M. The impact of spatiotemporal changes in land development (1984–2019) on the increase in the runoff coefficient in Erbil, Kurdistan Region of Iraq. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mustafa Andam, S.M. The analysis of the influence of urbanisation on the runoff coefficient using remote sensing, GIS and hydrological modelling in Erbil-Kurdistan Region of Iraq. In Proceedings of the 6th IAHR Europe Congress, Warsaw, Poland, 15–18 February 2021; pp. 454–455. [Google Scholar]
- Szydłowski, M.; Mikos-Studnicka, P.; Zima, P.; Weinerowska-Bords, K.; Hakiel, J.; Kalinowska, D. Stormwater and snowmelt runoff storage control and flash flood hazard forecasting in the urbanized coastal basin. In Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium Water Management and Hydraulic Engineering, Brno, Czech Republic, 8–10 September 2015; pp. 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Shareef, M.E.; Abdulrazzaq, D.G. River Flood Modelling For Flooding Risk Mitigation in Iraq. Civ. Eng. J. 2021, 7, 1702–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdistan Region Statistics Office. Report of the Expectation of Kurdistan Region Population from 2009–2020; Kurdistan Region Statistics Office: Erbil-Kurdistan Region, Iraq, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ramaseshan, S. Urban hydrology in different climatic conditions. In Lecture Notes of the International Course on Urban Drainage in Developing Countries; Regional Engineering College: Warangal, India, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Acar, R.; Senocak, S. Modelling of Short Duration Rainfall (SDR) Intensity Equations for Ankara, Turkey. In Proceedings of the BALWOIS 2008, Ohrid, Republic of Macedonia, 27–31 May 2008; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Oyebande, L. Deriving rainfall intensity-duration-frequency relationships and estimates for regions with inadequate data. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1982, 27, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raiford, J.; Aziz, N.; Khan, A.; Powell, D. Rainfall depth-duration-frequency relationships for South Carolina, North Carolina, and Georgia. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 3, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbel, E.J. Statistics of Extremes; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Gumbel, E.J. The Return Period of Flood Flows. Ann. Math. Stat. 1941, 12, 163–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotz, S.; Nadarajah, S.A. Extreme Value Distributions: Theory and applications; World Scientific: Singapore, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nadarajah, S. The exponentiated Gumbel distribution with climate application. Environmetrics 2006, 17, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.; Ghose, D.K. Flood Frequency Analysis for Menace Gauging Station of Mahanadi River, India. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. A 2021, 102, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantaray, S.; Sahoo, A. Estimation of flood frequency using statistical method: Mahanadi River basin, India. H2Open J. 2020, 3, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.L.S.; Ng, J.L.; Huang, Y.F.; Ang, C.K. Assessment of the best probability distribution method in rainfall frequency analysis for a tropical region. Malays. J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, V.T.; Maidment, D.R.; Larry, W.; Mays. Applied Hydrology; Tata McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Salman, S.A.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.; Rahman, N.B.A.; Wang, X.; Chung, E.-S. Unidirectional trends in daily rainfall extremes of Iraq. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 134, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ansari, N. Management of water resources in Iraq: Perspectives and prognoses. Engineering 2013, 5, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Ansari, N. Topography and climate of Iraq. J. Earth Sci. Geotech. Eng. 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
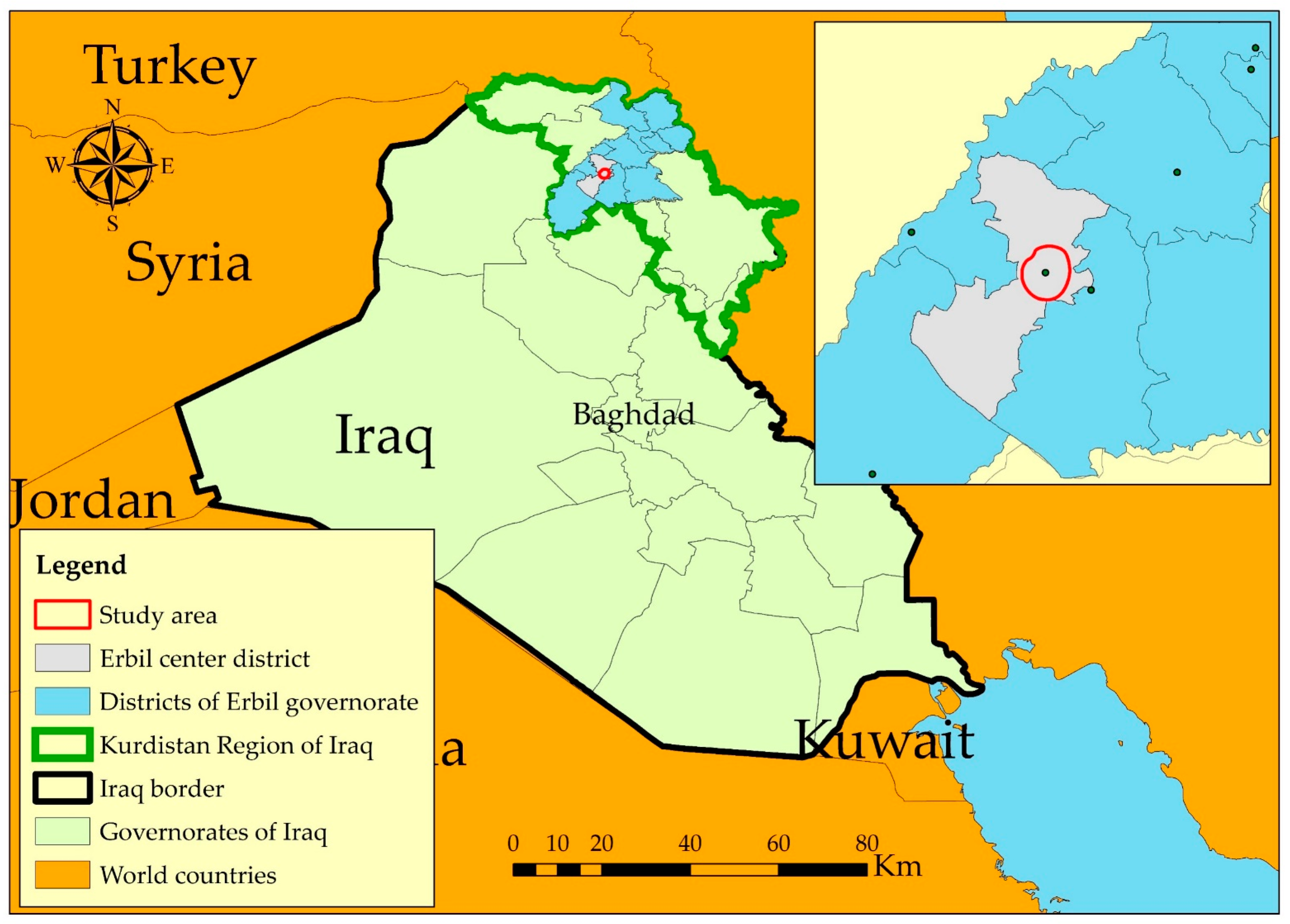

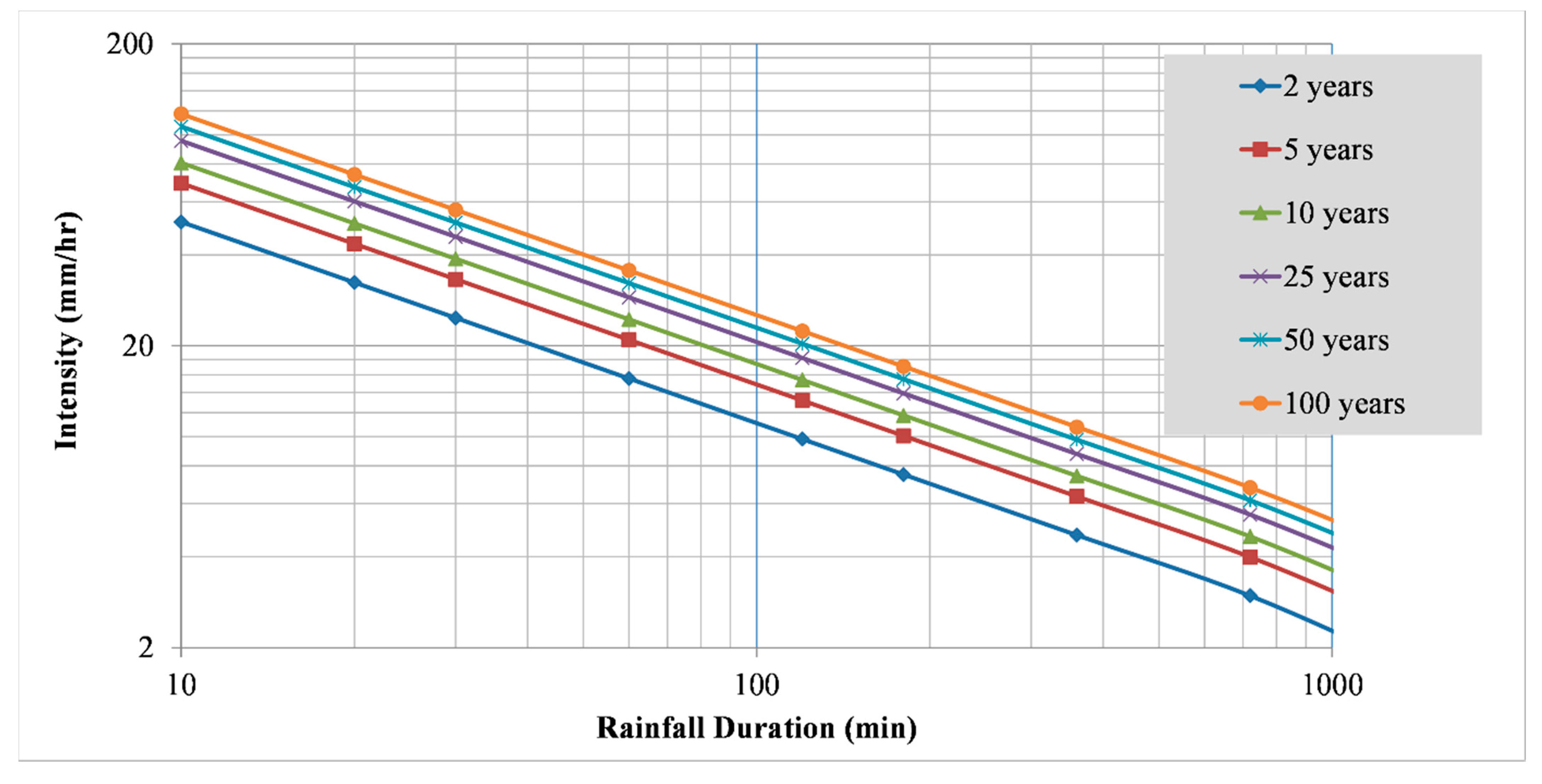

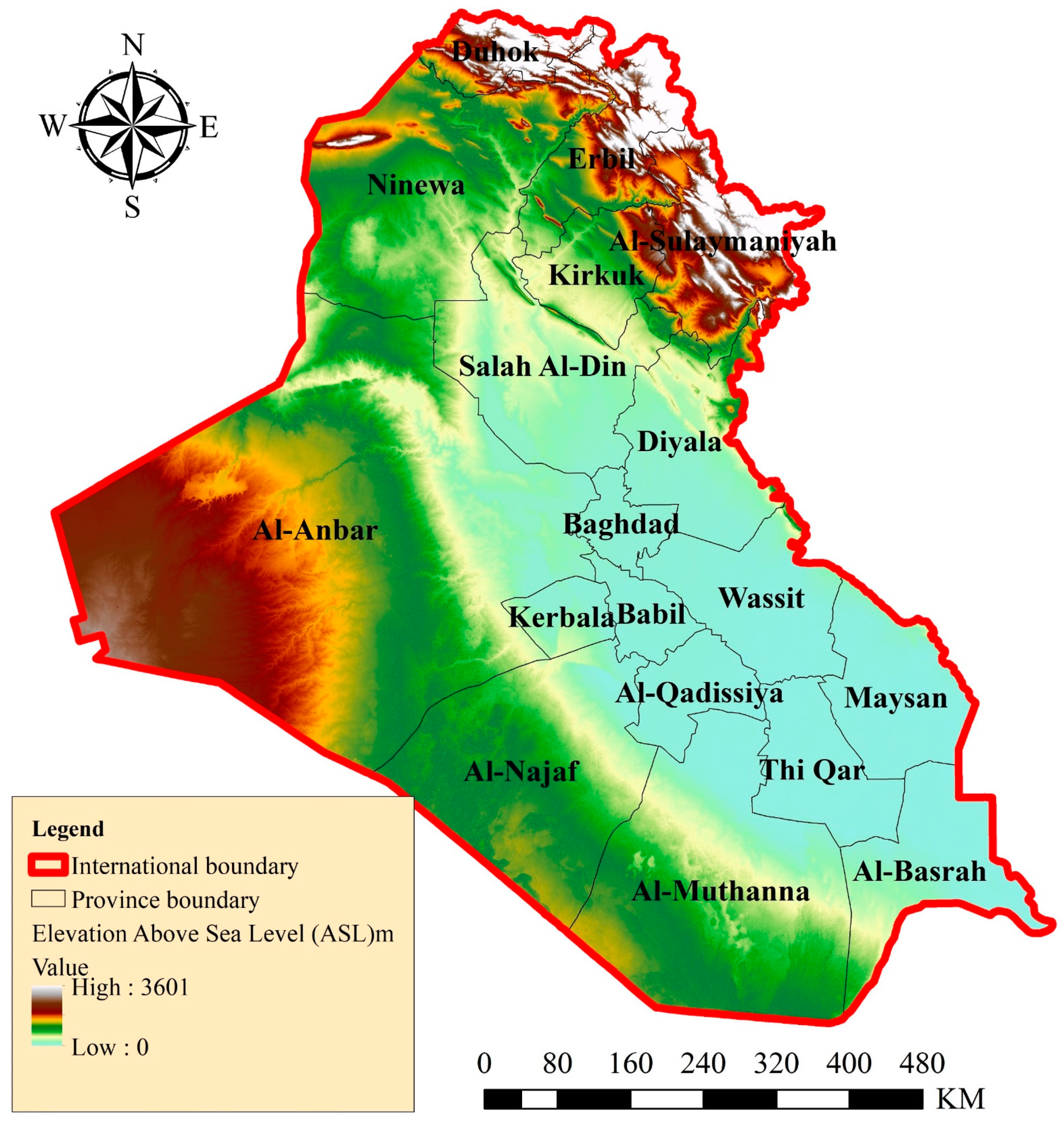

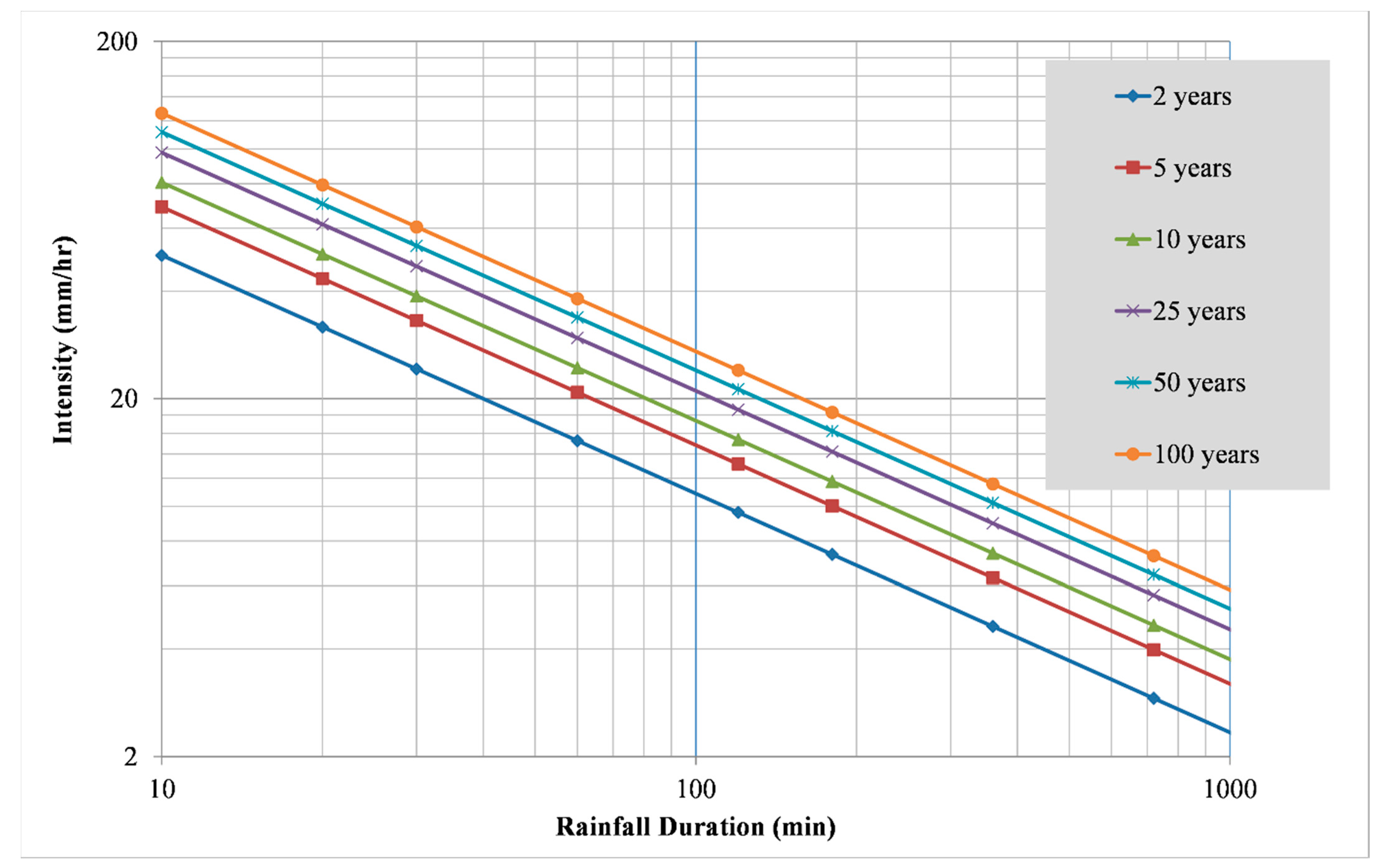
| No. | Year | 24 h Precipitation (mm) | No. | Year | 24 h Precipitation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1980 | 57.6 | 21 | 2000 | 46.4 |
| 2 | 1981 | 40.9 | 22 | 2001 | 48.3 |
| 3 | 1982 | 38.1 | 23 | 2002 | 59.2 |
| 4 | 1983 | 32.9 | 24 | 2003 | 41.4 |
| 5 | 1984 | 42.7 | 25 | 2004 | 40.6 |
| 6 | 1985 | 72.7 | 26 | 2005 | 34 |
| 7 | 1986 | 73.6 | 27 | 2006 | 103.9 |
| 8 | 1987 | 31.8 | 28 | 2007 | 38 |
| 9 | 1988 | 37.2 | 29 | 2008 | 41 |
| 10 | 1989 | 48.4 | 30 | 2009 | 28.2 |
| 11 | 1990 | 35.8 | 31 | 2010 | 33.8 |
| 12 | 1991 | 62.4 | 32 | 2011 | 67 |
| 13 | 1992 | 79 | 33 | 2012 | 29.4 |
| 14 | 1993 | 57.9 | 34 | 2013 | 71.8 |
| 15 | 1994 | 41.7 | 35 | 2014 | 51 |
| 16 | 1995 | 75.7 | 36 | 2015 | 55.8 |
| 17 | 1996 | 23.9 | 37 | 2016 | 42.4 |
| 18 | 1997 | 35.8 | 38 | 2017 | 31.4 |
| 19 | 1998 | 36.8 | 39 | 2018 | 47.7 |
| 20 | 1999 | 28.3 |
| 10 min | 20 min | 30 min | |||||||
| = 9.121 | = 3.326 | = 11.492 | = 4.190 | = 13.155 | = 4.796 | ||||
| Tr (years) | K | K | K | ||||||
| 2 | −0.164 | 8.576 | 51.454 | −0.164 | 10.805 | 32.414 | −0.164 | 12.368 | 24.736 |
| 5 | 0.719 | 11.513 | 69.080 | 0.719 | 14.506 | 43.518 | 0.719 | 16.605 | 33.210 |
| 10 | 1.305 | 13.459 | 80.757 | 1.305 | 16.958 | 50.874 | 1.305 | 19.412 | 38.824 |
| 25 | 2.044 | 15.918 | 95.506 | 2.044 | 20.055 | 60.165 | 2.044 | 22.957 | 45.915 |
| 50 | 2.592 | 17.742 | 106.451 | 2.592 | 22.353 | 67.060 | 2.592 | 25.588 | 51.176 |
| 100 | 3.137 | 19.552 | 117.313 | 3.137 | 24.634 | 73.903 | 3.137 | 28.199 | 56.398 |
| 60 min | 120 min | 180 min | |||||||
| = 16.574 | = 6.043 | = 20.882 | = 7.614 | = 23.904 | = 8.715 | ||||
| K | K | K | |||||||
| 2 | −0.164 | 15.583 | 15.583 | −0.164 | 19.633 | 9.817 | −0.164 | 22.475 | 7.492 |
| 5 | 0.719 | 20.921 | 20.921 | 0.719 | 26.359 | 13.180 | 0.719 | 30.174 | 10.058 |
| 10 | 1.305 | 24.458 | 24.458 | 1.305 | 30.815 | 15.407 | 1.305 | 35.274 | 11.758 |
| 25 | 2.044 | 28.924 | 28.924 | 2.044 | 36.442 | 18.221 | 2.044 | 41.716 | 13.905 |
| 50 | 2.592 | 32.239 | 32.239 | 2.592 | 40.619 | 20.309 | 2.592 | 46.497 | 15.499 |
| 100 | 3.137 | 35.529 | 35.529 | 3.137 | 44.763 | 22.382 | 3.137 | 51.241 | 17.080 |
| 360 min | 720 min | 1440 min | |||||||
| = 30.117 | = 10.981 | = 37.945 | = 13.835 | = 42.638 | = 16.877 | ||||
| K | K | K | |||||||
| 2 | −0.164 | 28.316 | 4.719 | −0.164 | 35.676 | 2.973 | −0.164 | 39.870 | 1.661 |
| 5 | 0.719 | 38.016 | 6.336 | 0.719 | 47.898 | 3.991 | 0.719 | 54.779 | 2.282 |
| 10 | 1.305 | 44.442 | 7.407 | 1.305 | 55.994 | 4.666 | 1.305 | 64.655 | 2.694 |
| 25 | 2.044 | 52.559 | 8.760 | 2.044 | 66.220 | 5.518 | 2.044 | 77.131 | 3.214 |
| 50 | 2.592 | 58.582 | 9.764 | 2.592 | 73.809 | 6.151 | 2.592 | 86.388 | 3.599 |
| 100 | 3.137 | 64.560 | 10.760 | 3.137 | 81.340 | 6.778 | 3.137 | 95.576 | 3.982 |
| 10 min | 20 min | 30 min | ||||||||
| = 9.121 | = 3.326 | = 11.492 | = 4.190 | = 13.155 | = 4.796 | |||||
| Tr (years) | K | |||||||||
| 2 | −0.073 | 0.924 | 8.399 | 50.393 | 1.025 | 10.582 | 31.745 | 1.083 | 12.113 | 24.226 |
| 5 | 0.852 | 1.060 | 11.477 | 68.861 | 1.160 | 14.460 | 43.380 | 1.219 | 16.552 | 33.105 |
| 10 | 1.319 | 1.128 | 13.436 | 80.613 | 1.229 | 16.928 | 50.783 | 1.287 | 19.377 | 38.755 |
| 25 | 1.890 | 1.212 | 16.291 | 97.745 | 1.312 | 20.525 | 61.575 | 1.371 | 23.495 | 46.991 |
| 50 | 2.280 | 1.269 | 18.582 | 111.495 | 1.369 | 23.412 | 70.237 | 1.428 | 26.801 | 53.601 |
| 100 | 2.640 | 1.322 | 20.983 | 125.898 | 1.422 | 26.437 | 79.311 | 1.481 | 30.263 | 60.525 |
| 60 min | 120 min | 180 min | ||||||||
| = 16.574 | = 6.043 | = 20.882 | = 7.614 | = 23.904 | = 8.715 | |||||
| K | ||||||||||
| 2 | −0.073 | 1.184 | 15.262 | 15.262 | 1.284 | 19.228 | 9.614 | 1.343 | 22.011 | 7.337 |
| 5 | 0.852 | 1.319 | 20.855 | 20.855 | 1.420 | 26.275 | 13.138 | 1.478 | 30.078 | 10.026 |
| 10 | 1.319 | 1.388 | 24.414 | 24.414 | 1.488 | 30.760 | 15.380 | 1.547 | 35.211 | 11.737 |
| 25 | 1.890 | 1.471 | 29.602 | 29.602 | 1.572 | 37.297 | 18.648 | 1.630 | 42.694 | 14.231 |
| 50 | 2.280 | 1.528 | 33.767 | 33.767 | 1.629 | 42.543 | 21.272 | 1.688 | 48.700 | 16.233 |
| 100 | 2.640 | 1.581 | 38.129 | 38.129 | 1.682 | 48.039 | 24.020 | 1.740 | 54.991 | 18.330 |
| 360 min | 720 min | 1440 min | ||||||||
| = 30.117 | = 10.981 | = 37.945 | = 13.835 | = 42.638 | = 16.877 | |||||
| 2 | −0.073 | 1.443 | 27.732 | 4.622 | 1.543 | 34.940 | 2.912 | 1.644 | 44.022 | 1.834 |
| 5 | 0.852 | 1.579 | 37.896 | 6.316 | 1.679 | 47.746 | 3.979 | 1.779 | 60.156 | 2.506 |
| 10 | 1.319 | 1.647 | 44.363 | 7.394 | 1.747 | 55.894 | 4.658 | 1.848 | 70.422 | 2.934 |
| 25 | 1.890 | 1.731 | 53.791 | 8.965 | 1.831 | 67.773 | 5.648 | 1.931 | 85.388 | 3.558 |
| 50 | 2.280 | 1.788 | 61.358 | 10.226 | 1.888 | 77.306 | 6.442 | 1.989 | 97.400 | 4.058 |
| 100 | 2.640 | 1.841 | 69.284 | 11.547 | 1.941 | 87.293 | 7.274 | 2.041 | 109.982 | 4.583 |
| Region | Parameter | Gumbel Method | LPT III Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Erbil | 234.020 | 212.790 | |
| 0.200 | 0.228 | ||
| 0.681 | 0.667 | ||
| Sulaymaniyah | 288.4 | ||
| 0.191 | |||
| 0.666 | |||
| Baghdad | 9.074 | 7.044 | |
| 0.318 | 0.422 | ||
| 0.667 | 0.667 | ||
| Nasiriyah | 8.283 | 7.565 | |
| 0.301 | 0.350 | ||
| 0.674 | 0.674 | ||
| Basrah | 7.95 | ||
| 0.298 | |||
| 0.667 |
| Chi Square () | ||
|---|---|---|
| Return Periods (Year) | Gumbel Method | LPT III Method |
| 2 | 0.255 | 0.095 |
| 5 | 0.023 | 0.092 |
| 10 | 0.080 | 0.103 |
| 25 | 0.037 | 0.049 |
| 50 | 0.006 | 0.0002 |
| 100 | 0.167 | 0.098 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kareem, D.A.; M Amen, A.R.; Mustafa, A.; Yüce, M.I.; Szydłowski, M. Comparative Analysis of Developed Rainfall Intensity–Duration–Frequency Curves for Erbil with Other Iraqi Urban Areas. Water 2022, 14, 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030419
Kareem DA, M Amen AR, Mustafa A, Yüce MI, Szydłowski M. Comparative Analysis of Developed Rainfall Intensity–Duration–Frequency Curves for Erbil with Other Iraqi Urban Areas. Water. 2022; 14(3):419. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030419
Chicago/Turabian StyleKareem, Dalshad Ahmed, Aumed Rahman M Amen, Andam Mustafa, Mehmet Ishak Yüce, and Michał Szydłowski. 2022. "Comparative Analysis of Developed Rainfall Intensity–Duration–Frequency Curves for Erbil with Other Iraqi Urban Areas" Water 14, no. 3: 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030419
APA StyleKareem, D. A., M Amen, A. R., Mustafa, A., Yüce, M. I., & Szydłowski, M. (2022). Comparative Analysis of Developed Rainfall Intensity–Duration–Frequency Curves for Erbil with Other Iraqi Urban Areas. Water, 14(3), 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030419








