Impacts of Flood Disturbance on the Dynamics of Basin-Scale Swimming Fish Migration in Mountainous Streams
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
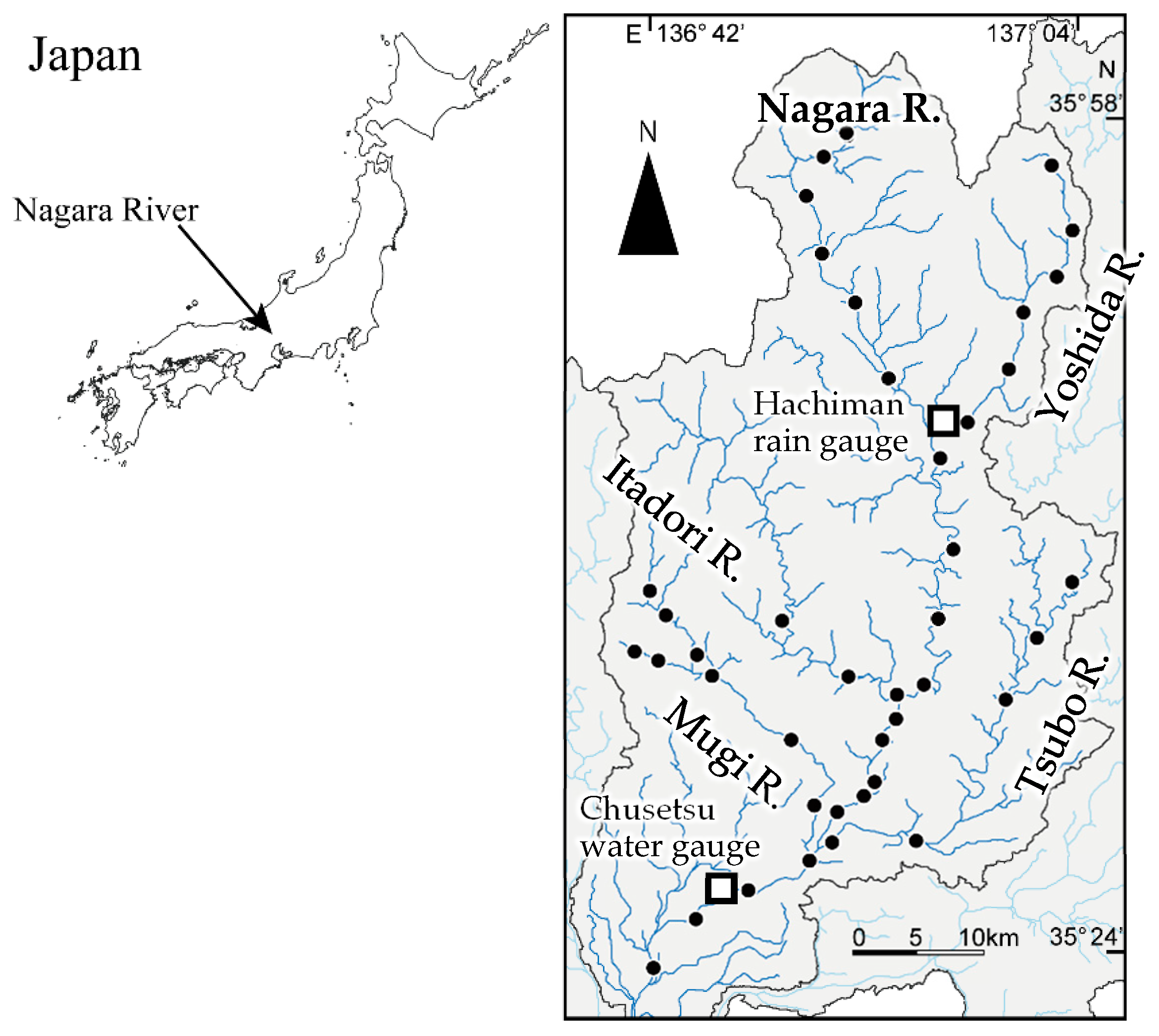
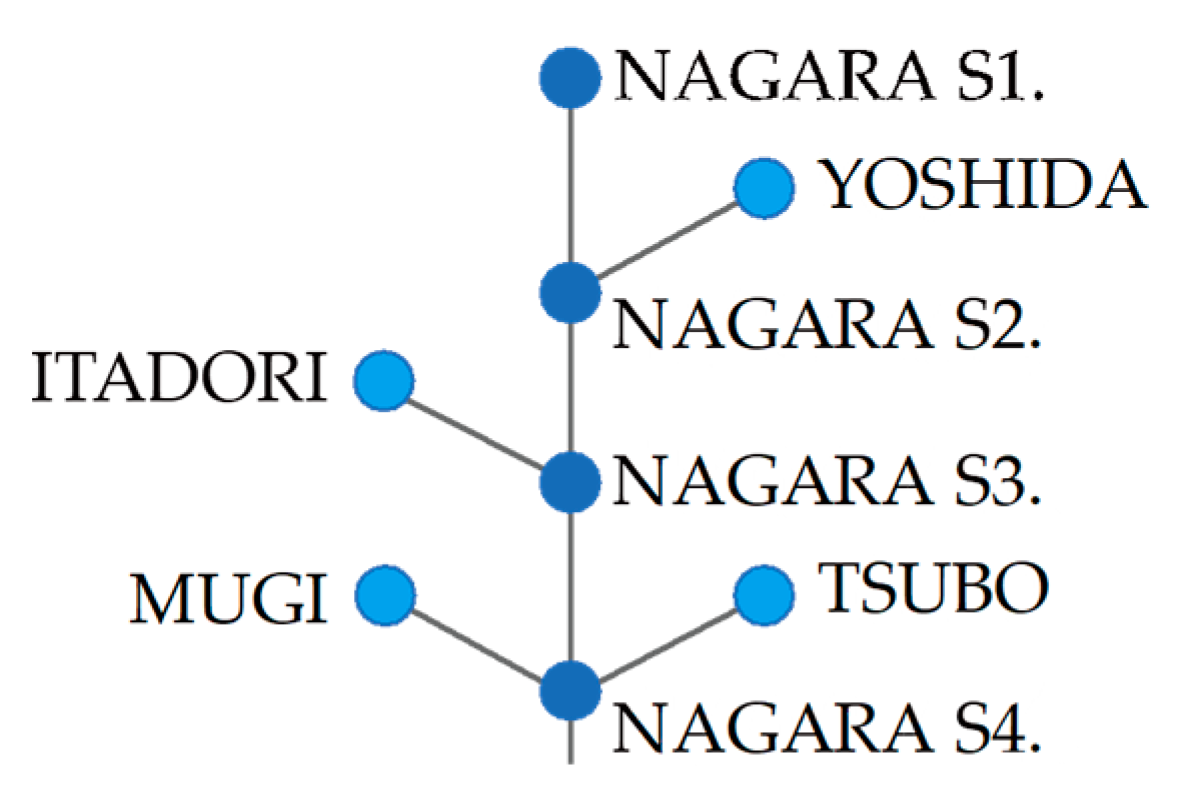
2.1. Study River
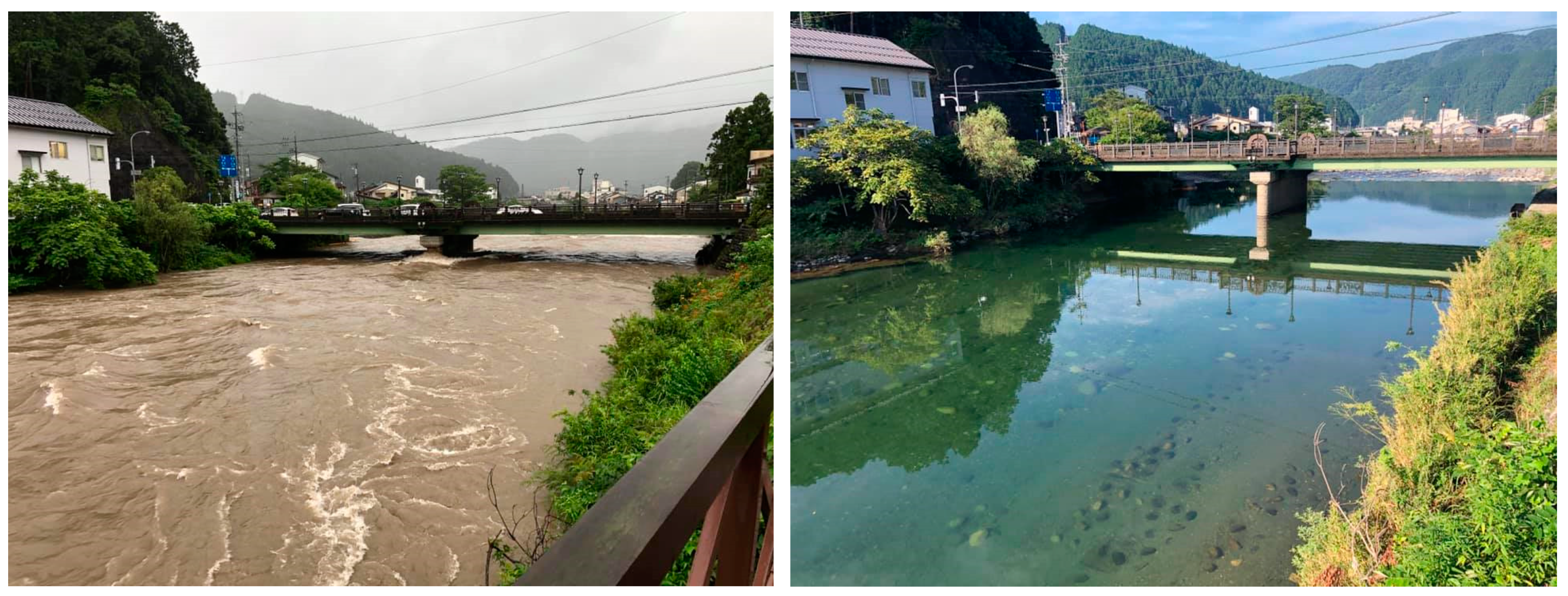
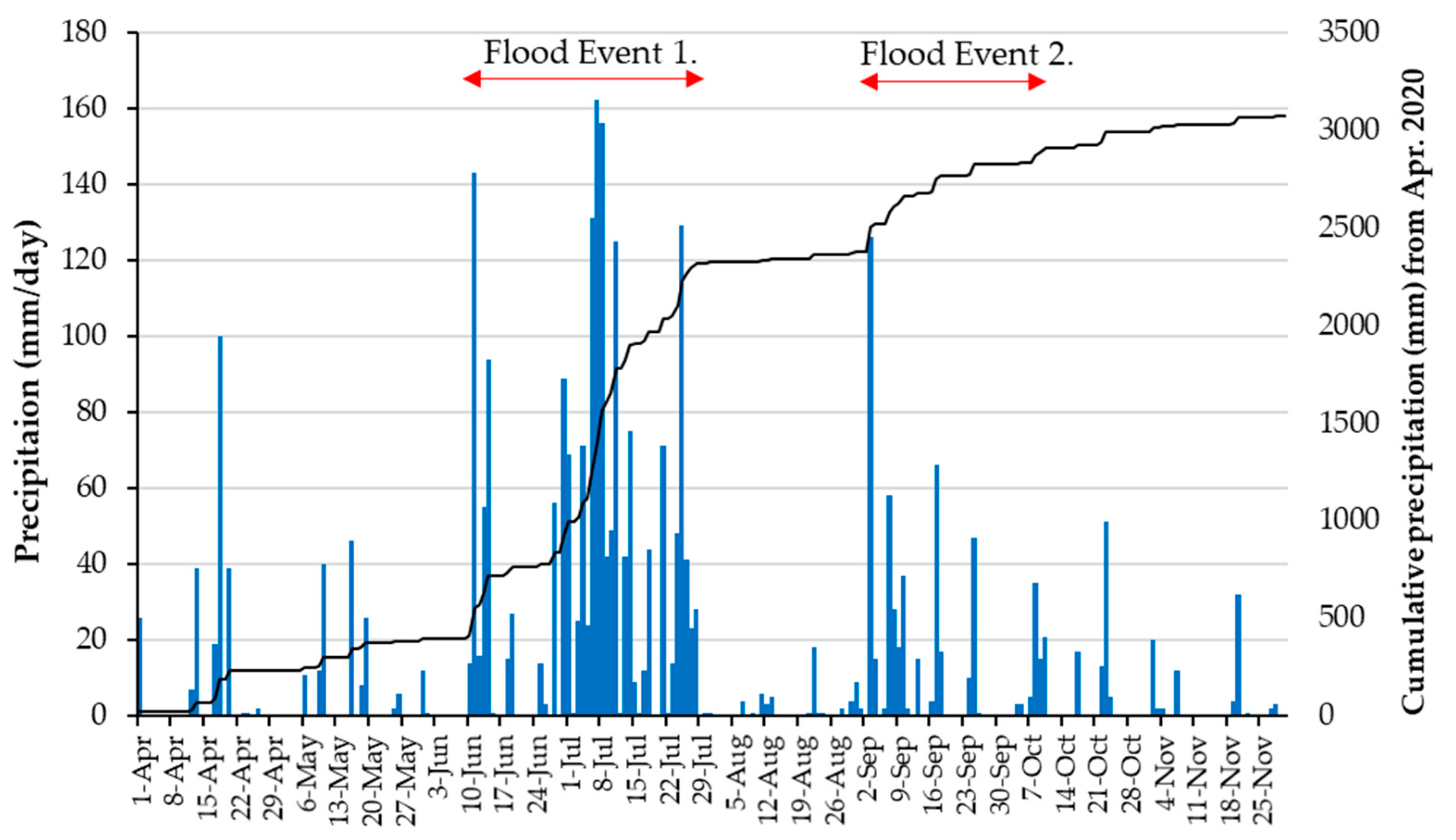
2.2. Flood Events
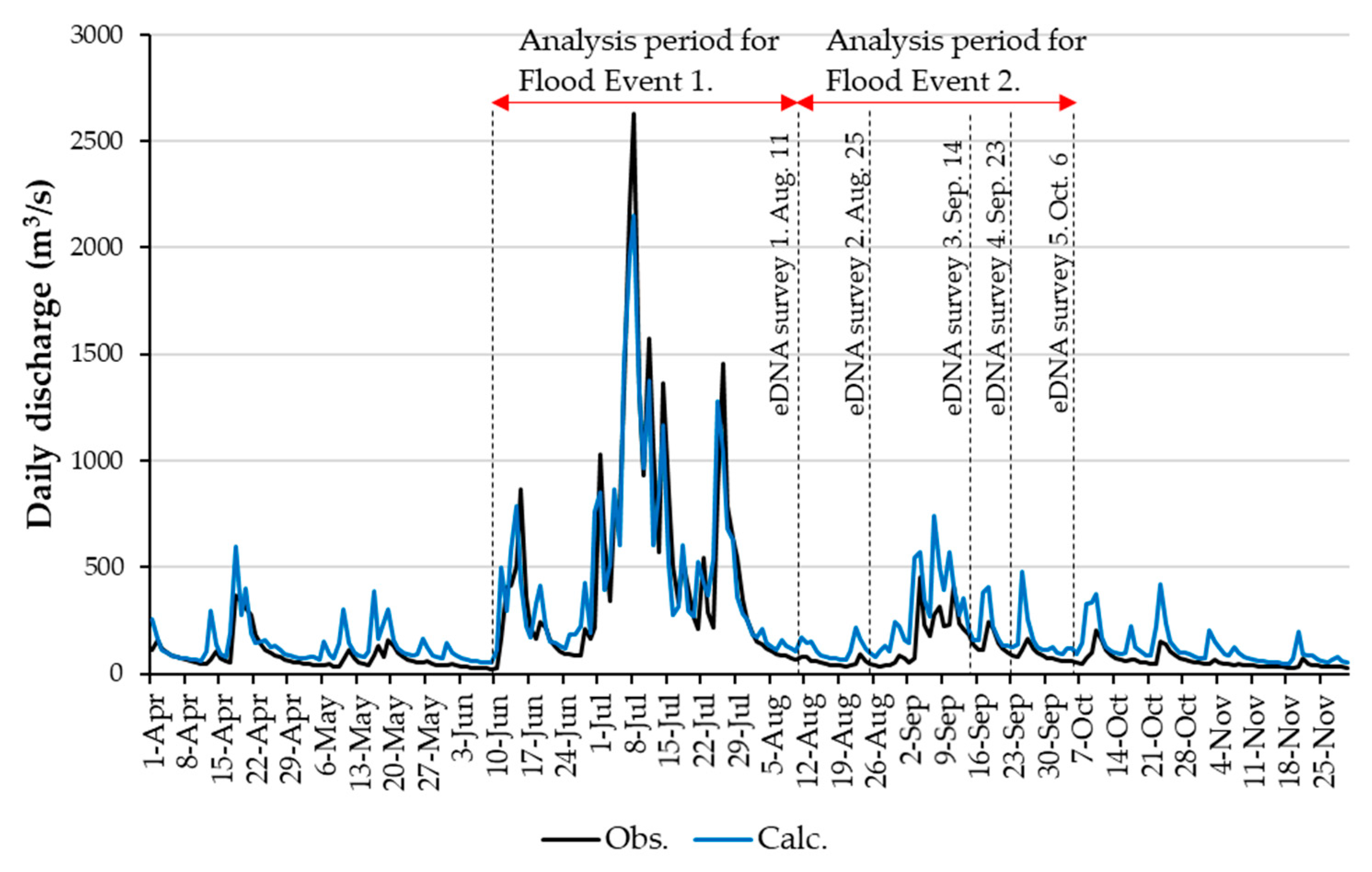
2.3. eDNA Sampling
2.4. DNA Filtration, Extraction, and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.5. Rainfall–Runoff–Inundation Model
2.6. Hydrologic Index of Flood Magnitude
2.7. Analysis
3. Results
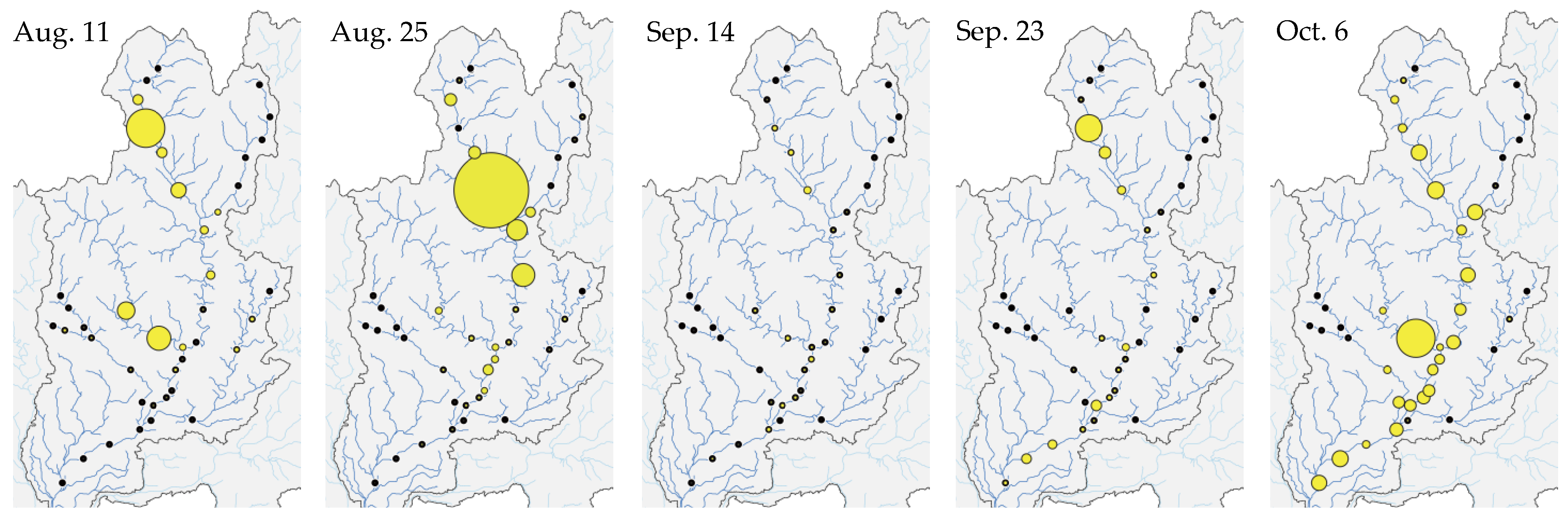
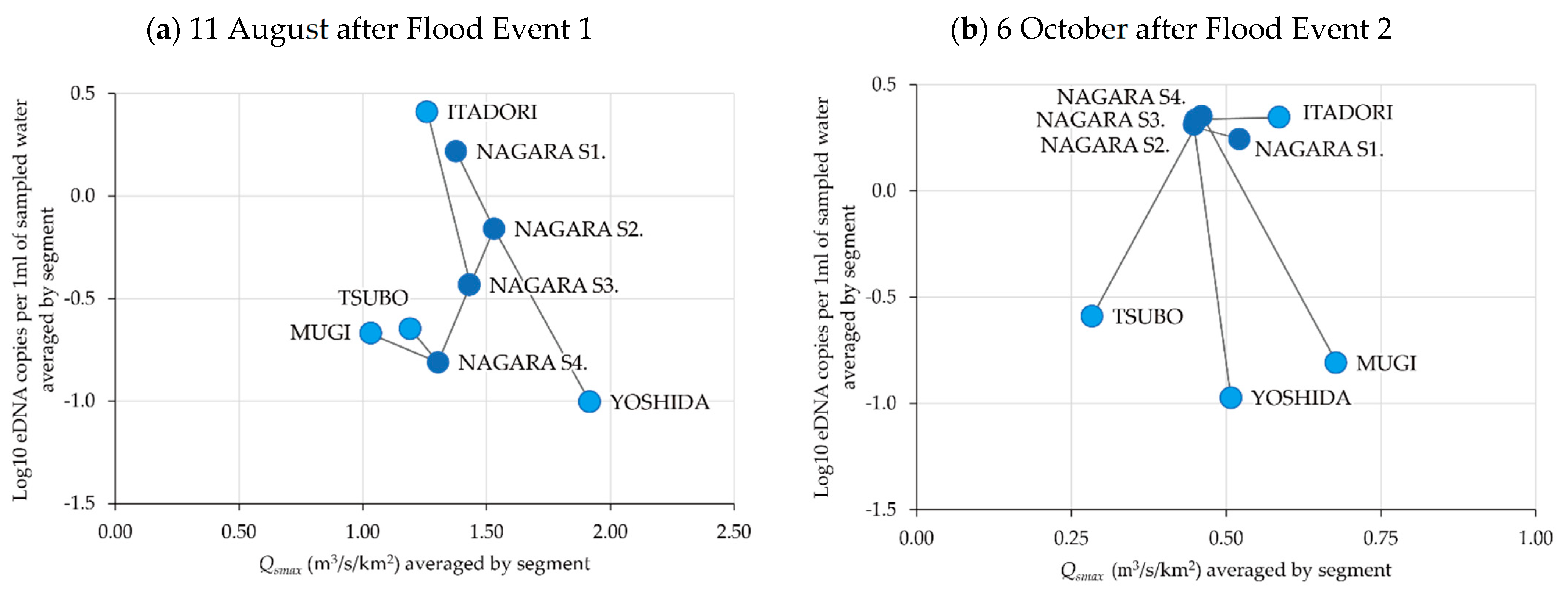
3.1. Spatiotemporal Change in eDNA Concentrations of P. altivelis
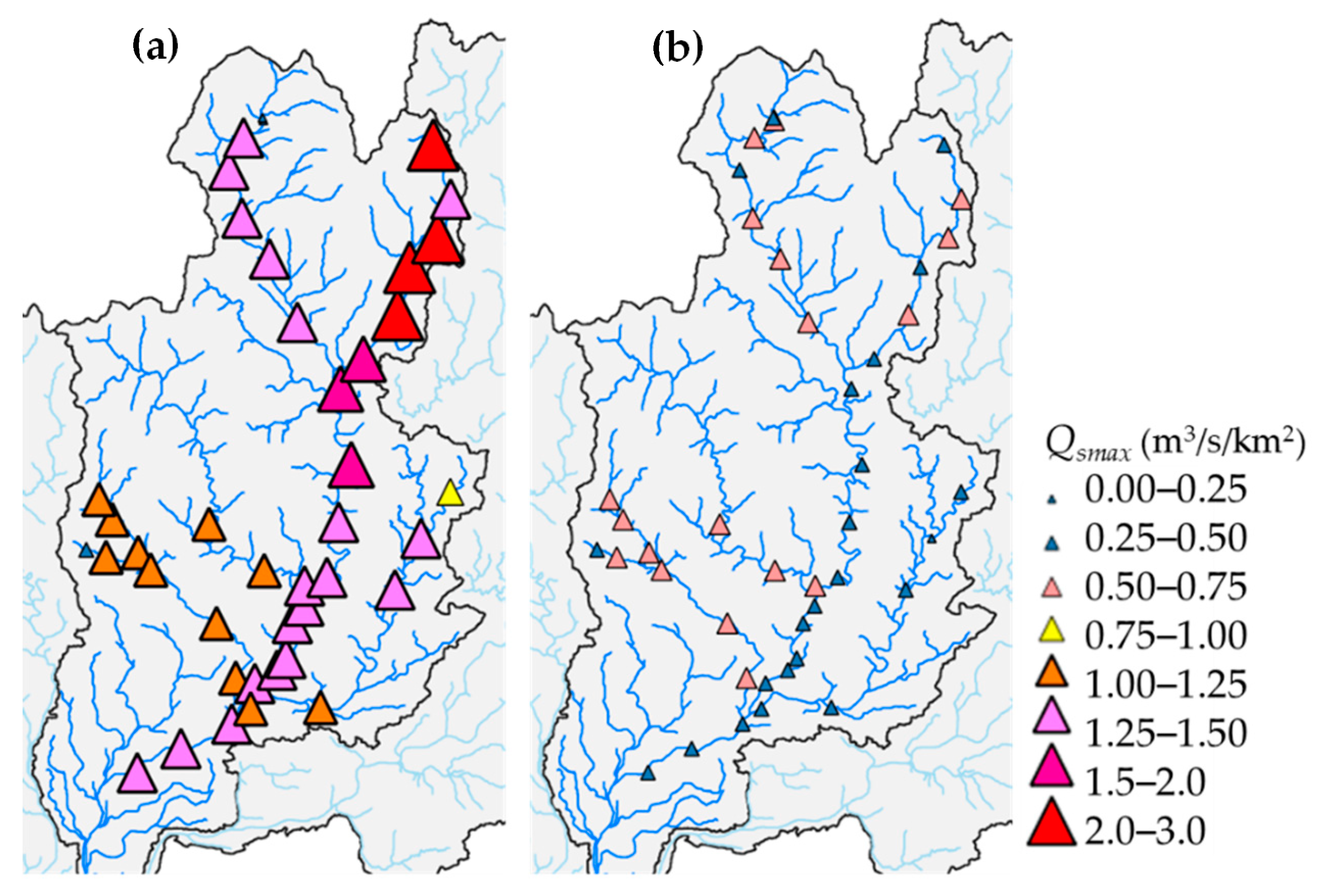
3.2. RRI Model Calculation Results
3.3. Flood Magnitude Index
3.4. Relationship between eDNA Concentration and Flood Magnitude Index
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poff, N.L.; Allan, J.D.; Bain, M.B.; Karr, J.R.; Prestegaard, K.L.; Richter, B.D.; Sparks, R.E.; Stromberg, J.C. The natural flow regime. BioScience 1997, 47, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resh, V.H.; Brown, A.V.; Covich, A.P.; Gurtz, M.E.; Li, H.W.; Minshall, G.W.; Reice, S.R.; Sheldon, A.L.; Wallace, J.B.; Wissmar, R.C. The role of disturbance in stream ecology. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1988, 7, 433–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytle, D.A.; Poff, N.L. Adaptation to natural flow regimes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, F.J.; Johnson, S.L.; Gregory, S.V.; Acker, S.A. Flood disturbance in a forested mountain landscape: Interactions of land use and floods. BioScience 1998, 48, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.J.; Humphries, P.; Lake, P.S. Fish recruitment on floodplains: The roles of patterns of flooding and life history characteristics. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2003, 60, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, W.J. Fish faunal structure in an Ozark stream: Stability, persistence and a catastrophic flood. Copeia 1986, 1986, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, P.S. Disturbance, patchiness, and diversity in streams. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2000, 19, 573–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, A.M.; Robertson, A.L.; McDermott, M.J.; Klaar, M.J.; Brown, L.E. Major flood disturbance alters river ecosystem evolution. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedell, J.R.; Reeves, G.H.; Hauer, F.R.; Stanford, J.A.; Hawkins, C.P. Role of refugia in recovery from disturbances: Modern fragmented and disconnected river systems. Environ. Manag. 1990, 14, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.S.; Herricks, E.E. Fish use of stage-specific fluvial habitats as refuge patches during a flood in a low-gradient Illinois stream. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 1540–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwo, H.O.; Huang, Y.S.; Ueda, H. Site fidelity of and habitat use by the Formosan landlocked salmon (Oncorhynchus masou formosanus) during typhoon season in Chichiawan Stream, Taiwan as assessed by nano-tag radio telemetry. Zool. Stud. 2009, 48, 460–467. [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi, I.; Kanazawa, Y.; Tanaka, Y. The fishermen were right: Experimental evidence for tributary refuge hypothesis during floods. Zool. Sci. 2013, 30, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamoto, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Takahara, T.; Honjo, M.N.; Kawabata, Z.I. Surveillance of fish species composition using environmental DNA. Limnology 2012, 13, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, H.; Minamoto, T. The use of environmental DNA of fishes as an efficient method of determining habitat connectivity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 62, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Inui, R.; Akamatsu, Y.; Kanno, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Takahara, T.; Minamoto, T. Environmental DNA analysis for estimating the abundance and biomass of stream fish. Freshw. Biol. 2017, 62, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.A.; Turner, C.R.; Jerde, C.L.; Renshaw, M.A.; Chadderton, W.L.; Lodge, D.M. Environmental conditions influence eDNA persistence in aquatic systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, J.B.; Sunday, J.M.; Rogers, S.M. Predicting the fate of eDNA in the environment and implications for studying biodiversity. Proc. R. Soc. B 2019, 286, 20191409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilliod, D.S.; Laramie, M.B.; MacCoy, D.; Maclean, S. Integration of eDNA-based biological monitoring within the US Geological Survey’s National Streamgage Network. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2019, 55, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GIAHS Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems. Available online: https://www.fao.org/giahs/giahsaroundtheworld/en/ (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Mouri, G.; Shinoda, S.; Oki, T. Estimating Plecoglossus altivelis altivelis migration using a mass balance model expressed by hydrological distribution parameters in a major limpid river basin in Japan. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 2808–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, I.; Iguchi, K.I. High growth performance in the early ontogeny of an amphidromous fish, Ayu Plecoglossus altivelis altivelis, promoted survival during a disastrous river spate. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, M.; Sugimoto, A.; Marui, A.; Azuma, N. Field experiment on the critical swimming speed of natural fingering sweetfish (Plecoglossus altivelis altivelis) during initial period of upstream river migration. J. JSCE 2021, 9, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, H.; Minamoto, T.; Matsuura, J.; Sakurai, S.; Tsuji, S.; Motozawa, H.; Hongo, M.; Sogo, Y.; Kakimi, N.; Teramura, I.; et al. A simple method for preserving environmental DNA in water samples at ambient temperature by addition of cationic surfactant. Limnology 2017, 18, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainfall-Runoff-Inundation (RRI) Model. Available online: https://www.pwri.go.jp/icharm/research/rri/index.html (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Lehner, B.; Verdin, K.; Jarvis, A. New global hydrography derived from spaceborne elevation data. Eos Trans. AGU 2008, 89, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HydroSHEDS. Available online: https://www.hydrosheds.org/ (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Ishizaki, H.; Matsuyama, H. Distribution of the annual precipitation ratio of radar/raingauge-analyzed precipitation to AMeDAS across Japan. SOLA 2018, 14, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D.; Baumgartner, J.V.; Braun, D.P.; Powell, J. A spatial assessment of hydrologic alteration within a river network. Regul. Rivers Res. Manag. 1998, 14, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olden, J.D.; Poff, N.L. Redundancy and the choice of hydrologic indices for characterizing streamflow regimes. River Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Kato, Y.; Takagi, T.; Onoda, Y.; Kayaba, Y. Turbid water induces refuge behaviour of a commercially important ayu: A field experiment for interstream movement using multiple artificial streams. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2018, 27, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, M.; Maruya, Y.; Kojima, T.; Matsuoka, D.; Nakagawa, Y.; Kawahara, S.; Araki, F. Flood frequency analysis and impact assessment for climate change in the Nagara River basin. J. JSCE 2020, 8, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]


| Explanation | Value | Determination |
|---|---|---|
| Manning’s roughness in river channel | 0.030 | Default value |
| Manning’s roughness on slope cells | 0.500 | By calibration |
| Soil depths (m) | 1.000 | By calibration |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harada, M.; Nagayama, S. Impacts of Flood Disturbance on the Dynamics of Basin-Scale Swimming Fish Migration in Mountainous Streams. Water 2022, 14, 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040538
Harada M, Nagayama S. Impacts of Flood Disturbance on the Dynamics of Basin-Scale Swimming Fish Migration in Mountainous Streams. Water. 2022; 14(4):538. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040538
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarada, Morihiro, and Shigeya Nagayama. 2022. "Impacts of Flood Disturbance on the Dynamics of Basin-Scale Swimming Fish Migration in Mountainous Streams" Water 14, no. 4: 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040538
APA StyleHarada, M., & Nagayama, S. (2022). Impacts of Flood Disturbance on the Dynamics of Basin-Scale Swimming Fish Migration in Mountainous Streams. Water, 14(4), 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040538






