Effect of Different Sowing Methods on Water Use Efficiency and Grain Yield of Wheat in the Loess Plateau, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Field Management
2.2. Measurements
2.2.1. Soil Moisture
2.2.2. Evapotranspiration (ET), Precipitation, and Water Use Efficiency (WUE)
2.2.3. Yield and Yield Components
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Water Storage
3.2. Correlation between Yield Formation and Field Water Consumption
3.3. Water Use Efficiency (WUE) and Yield Components
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Yield Components and Contribution of Water Sources
4. Discussion
4.1. Wheat Grain Yield and Yield Components
4.2. Wheat Yield Formation and Water
4.3. Water Impact on Wheat Yield
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, W.; Cai, D.; Lv, J.; Jiang, G.; Huang, J.; Gao, J.; Hartmanne, R.; Gabrielset, D. Effects of conservation tillage practices on winter wheat water-use efficiency and crop yield on the Loess Plateau, China. Agri. Water Manag. 2007, 87, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Hao, M.; Wu, Y. Potential impacts of climate change on carbon dynamics in a rain-fed agroecosystem on the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 577, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.Z.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Y.; Hu, X.; Cai, H.; Gu, B. Effects of limited irrigation on yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat in the Loess Plateau of China. Agri. Water Manag. 2002, 55, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, A.; Sun, M.; Xue, L.; Deng, Y.; Wang, P.; Lei, M.; Lin, W.; Yang, Z.; Gao, Z. Spatio-temporal dynamics in soil water storage reveals effects of nitrogen inputs on soil water consumption at different growth stages of winter wheat. Agri. Water Manag. 2019, 216, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungria, M.; Franchini, J.C.; Brandão-Junior, O.; Kaschuk, G.; Souza, R.A. Soil microbial activity and crop sustainability in a long-term experiment with three soil-tillage and two crop-rotation systems. Appl. Soil Ecology. 2009, 42, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, D.; Cheng, S.; Huang, X. Combined effects of runoff and soil erodibility on available nitrogen losses from sloping farmland affected by agricultural practices. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 176, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, T.; Derpsch, R.; Kassam, A. Overview of the global spread of conservation agriculture. In Sustainable Development of Organic Agriculture; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 75–90. Available online: http://journals.openedition.org/factsreports/1941 (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Jiang, C.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Dong, X. Quantifying changes in multiple ecosystem ser-vices during 2000–2012 in the Loess Plateau, China, as a result of climate variability and ecological restoration. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 97, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Xu, X. Effects of large-scale climate anomalies on trends in seasonal precipitation over the Loess Plateau of China from 1961 to 2016. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, Z.; He, G.; Dai, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, S.; Luo, L.; Sadras, V.O.; Hoogmoed, M.; Malhi, S.S. Tailoring NPK fertilizer application to precipitation for dryland winter wheat in the Loess Plateau. Field Crop. Res. 2017, 209, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Chen, D. Nitrogen fertilizer use in China—Contributions to food production, impacts on the environment and best management strategies. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2002, 63, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.C.; Asseng, S. Productivity, sustainability, and rainfall-use efficiency in Australian rainfed Mediterranean agricultural systems. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2005, 56, 1123–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.L.; Li, D.D.; Jing, Q.; Cai, J.; Jiang, D.; Cao, W.X.; Dai, T.B. Effects of nitrogen applications on soil nitrogen balance and nitrogen utilization of winter wheat in a rice-wheat rotation. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 127, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarotto, C.; Ferro, N.D.; Piccoli, I.; Polese, R.; Morari, F. Conservation agriculture and cover crop practices to regulate water, carbon and nitrogen cycles in the low-lying Venetian plain. Catena 2018, 167, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, P.W.; Kaspar, T.C. Soil compaction and root growth: A review. Agron. J. 1994, 86, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Garrido, R.; Madejón, E.; León-Camacho, M.; Girón, I.; Moreno, F.; Murillo, J.M. Reduced tillage as an alternative to no-tillage under Mediterranean conditions: A case study. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 140, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.L.; Aparicio, V.; Cerda, A. Soil physical quality changes under different management systems after 10 years in the Argentine humid pampa. Solid Earth 2015, 6, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noor, H.; Wang, Q.; Islam, M.A.; Sun, M.; Lin, W.; Ren, A.X.; Feng, Y.; Yu, S.B.; Fida, N.; Dong, S.F.; et al. Effects of sowing methods and nitrogen rates on photosynthetic characteristics, yield and quality of winter wheat. Photosynthetica 2021, 59, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; He, P.; Wei, J.; Cui, R.; Sun, J.; Qiu, S.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, W. Use of controlled-release urea to improve yield, nitrogen utilization, and economic return and reduce nitrogen loss in wheat-maize crop rotations. Agronomy 2021, 11, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymbek, A.; Saunikov, E.; Kenenbayev, S.; Perovic, V.; Ramazanova, S. Protein content changes in wheat grain as influenced by nitrogen fertilization. Agrochim. Pisa 2017, 61, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yu, N.; Camberato, J.J.; Gao, J.; Liu, P.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J. Crop production kept stable and sustainable with the decrease of nitrogen rate in North China Plain: An economic and environmental assessment over 8 years. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Palta, J.A.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.L.; Deng, X.P. Nitrogen fertilization improved water-use efficiency of winter wheat through increasing water use during vegetative rather than grain filling. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 197, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhu, H.; Dang, T.; Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Hao, M.; Li, Y.; Syers, J.K. Winter wheat grain yield associated with precipitation distribution under long-term nitrogen fertilization in the semiarid Loess Plateau in China. Geoderma 2012, 189, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, C.; Yu, H.; Cao, B.; Tian, S.; Liao, Y.; Siddique, K.H.M. Wheat yield improvements in China: Past trends and future directions. Field Crop. Res. 2015, 177, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slafer, G.A. Genetic basis of yield as viewed from a crop physiologist’s perspective. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2003, 142, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadras, V.O.; Slafer, G.A. Environmental modulation of yield components in cereals: Heritabilities reveal a hierarchy of phenotypic plasticities. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 127, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, D.R.; Lu, K. A correlation and path-coefficient analysis of components of crested wheatgrass seed production. Agron. J. 1959, 51, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Singh, M.; Sharma, K.C. Correlation and path coefficient analysis among flag leaf area, yield and yield attributes in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Cereal Res. Commun. 1979, 7, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, D.; Qu, H.; Ma, W. Identifying the limiting factors driving the winter wheat yield gap on smallholder farms by agronomic diagnosis in North China Plain. J. Integr. Agri. 2019, 18, 1701–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, A.; Aydin, F. Effect of water stress at various growth stages on some quality characteristics of winter wheat. J. Agron. Crop. Sci. 2004, 190, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddaiu, G.; Iocola, I.; Farina, R.; Orsini, R.; Iezzi, G.; Roggero, P.P. Long term effects of tillage practices and N fertilization in rainfed Mediterranean cropping systems: Durum wheat, sunflower and maize grain yield. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 77, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Z. Meta-analysis of no-tillage effect on wheat and maize water use efficiency in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Ren, A.; Gao, Z.; Wang, P.; Mo, F.; Xue, L.; Lei, M. Long-term evaluation of tillage methods in fallow season for soil water storage, wheat yield and water use efficiency in semiarid southeast of the loess plateau. Field Crops Res 2018, 218, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Dai, J.; Li, Q. Soil water storage and winter wheat productivity affected by soil surface management and precipitation in dryland of the Loess Plateau. China. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 171, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Lyu, W.; Wang, X.; Cheng, K.; Mao, H.; Zhang, X. Reasonable fertilization improves the conservation tillage benefit for soil water use and yield of rain-fed winter wheat: A case study from the Loess Plateau, China. Field Crops Res. 2019, 242, 107589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D. Water use efficiency and optimal supplemental irrigation in a high yield wheat field. Field Crops Res. 2017, 217, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, D. Effects of supplemental irrigation on water consumption characteristics, grain yield and water use efficiency in winter wheat under different soil moisture conditions at seeding stage. Acta Agron. Sin. 2017, 43, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Shan, L.; Zhang, H.; Turner, N.C. Improving agricultural water use efficiency in arid and semiarid areas of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Khan, S.; Sun, M.; Anwar, S.; Ren, A.; Gao, Z.; Lin, W.; Xue, J.; Yang, Z.; Deng, Y. Effects of tillage practices on water consumption and grain yield of dryland winter wheat under different precipitation distribution in the loess plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 191, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, J.; Griepentrog, H.W.; Kristensen, L. Suppression of weeds by spring wheat Triticum aestivum increases with crop density and spatial uniformity. J. Appl. Ecol. 2001, 38, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Blanco, I.A.; Rajaram, S.; Kronstad, W.E. Agronomic potential of synthetic hexaploid wheat-derived populations. Crop. Sci. 2001, 41, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, X.; Shao, Y.; Feng, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, T. Grain number responses to pre-anthesis dry matter and nitrogen in improving wheat yield in the Huang-Huai Plain. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Wei, T.; Yang, Z.; Cai, T.; Zhang, P.; Ding, R.; Jia, Z. Photosynthetic characteristics and grain yield of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in response to fertilizer, precipitation, and soil water storage before sowing under the ridge and furrow system: A path analysis. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 272, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochman, Z. Effect of water stress with phasic development on yield of wheat grown in a semi-arid environment. Field Crops Res. 1982, 5, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhe, A.A.; Barnes, R.T.; Six, J.; Marín-Spiotta, E. Role of soil erosion in biogeochemical cycling of essential elements: Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2018, 46, 521–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, X.C.; Feng, Y.Q.; Labzovskii, L. Challenging the land degradation in China’s Loess Plateau: Benefits, limitations, sustainability, and adaptive strategies of soil and water conservation. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 127, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, C.H.; Dijkstra, T.; Wasowski, J.; Meng, X.M. Loess geohazards research in China: Advances and challenges for mega engineering projects. Eng. Geol. 2019, 251, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.D.; Lowery, B. Effect of three conservation tillage practices on soil temperature and thermal properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, B.; Shen, H.; Arkebauer, T.J.; Walters, D.T. Effect of previous crop residue on soil surface carbon dioxide flux in maize. Soil Sci. 2007, 172, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueschen, W.E. Tillage, row spacing, and planting date effects on soybean following corn or wheat. J. Prod. Agric. 1992, 5, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Prueger, J.H. Microclimate effects of crop residues on biological processes. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1996, 54, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, A.L.; Schepers, J.; Olson, R.A.; Power, J.F. Irrigated corn yield and nitrogen accumulation response in a comparison of no-till and conventional till: Tillage and surface-residue variables. Agron. J. 1998, 90, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xin, X.; Zhu, A.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W. Effects of tillage and residue managements on organic C accumulation and soil aggregation in a sandy loam soil of the North China Plain. CATENA 2017, 156, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagger, M.G.; Denton, H.P. Crop and tillage rotations: Grain yield, residue cover, and soil water. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; McKyes, E. Reflectance of light from the soil surface in relation to tillage practices, crop residues and the growth of corn. Soil Tillage Res. 1993, 26, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; McLaughlin, N.; Zhang, X.; Xu, M.; Liang, A. Effect of tillage and crop residue on soil temperature following planting for a Black soil in Northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Donk, S.J.; Martin, D.L.; Irmak, S.; Melvin, S.R.; Petersen, J.L.; Davison, D.R. Crop residue cover effects on evaporation, soil water content, and yield of deficit-irrigated corn in west-central Nebraska. Trans. ASABE 2010, 53, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.M.; Hoyt, G.D. Changes to the soil environment under conservation tillage. Horttechnology 1999, 9, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Bala, G.; Duffy, P.B. Biogeophysical impacts of cropland management changes on climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, A.L.; Wilhelm, M.; Davin, E.L.; Thiery, W.; Seneviratne, S.I. Can climate-effective land management reduce regional warming? J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 2269–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Li, Y.; Nie, J.; Wang, C.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; She, H.; Liu, X.; Ruan, R. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and planting density on the leaf photosynthetic characteristics, agronomic traits and grain yield in common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum M.). Field Crop. Res. 2018, 219, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, H.; Min, S.; Khan, S.; Lin, W.; Ren, A.; Yu, S.; Ullah, S.; Yang, Z.; Gao, Z. Different sowing methods increasing the yield and quality of soil water consumption of dryland winter wheat on the loess plateau of china. Appl. Ecol. Env. Res. 2020, 18, 8285–8308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijay, S.; Sharma, R.K.; Jaspreet, K.; Jat, M.L.; Martin, K.L.; Yadvinder, S.; Varinderpal, S.; Chandna, P.; Choudhary, O.P.; Gupta, R.K.; et al. Assessment of the nitrogen management strategy using an optical sensor for irrigated wheat. J. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 31, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Shao, S.; Cui, W.; Xiong, F. Novel insights into the effect of nitrogen on storage protein biosynthesis and protein body development in wheat caryopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2259–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zörb, C.; Ludewig, U.; Hawkesford, M.J. Perspective on wheat yield and quality with reduced nitrogen supply. Trends Plant. Sci. 2018, 23, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mullen, R.W.; Freeman, K.W.; Raun, W.R.; Johnson, G.V.; Stone, M.L.; Solie, J.B. Identifying an in-season response index and the potential to increase wheat yield with nitrogen. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Lu, F.; Yan, P.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X. Elucidating population establishment associated with N management and cultivars for wheat production in China. Field Crop. Res. 2014, 163, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, J.; Dong, H.; Kong, X. High plant density inhibits vegetative branching in cotton by altering hormone contents and photosynthetic production. Field Crop. Res. 2019, 230, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregersen, P.L.; Culetic, A.; Boschian, L.; Krupinska, K. Plant senescence and crop productivity. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 82, 603–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Li, W.; Eneji, A.E.; Zhang, D. Nitrogen rate and plant density effects on yield and late-season leaf senescence of cotton raised on a saline field. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 126, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Kamran, M.; Xie, J.; Meng, X.; Han, Q.; Liu, T.; Han, J. Shoot and root traits of summer maize hybrid varieties with higher grain yields and higher nitrogen use efficiency at low nitrogen application rates. Peer J. 2019, 7, e7294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitonyo, O.M.; Sadras, V.O.; Zhou, Y.; Denton, M.D. Nitrogen supply and sink demand modulate the patterns of leaf senescence in maize. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 225, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Zhao, Q.; Dai, J.; Tian, L.; Dong, H. Effects of reduced nitrogen rate on cotton yield and nitrogen use efficiency as mediated by application mode or plant density. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 218, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, Z.; Shao, M.; Dyckmans, J. Effects of nitrogen nutrition and water deficit on net photosynthetic rate and chlorophyll fluorescence in winter wheat. J. Plant Physiol. 2000, 156, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
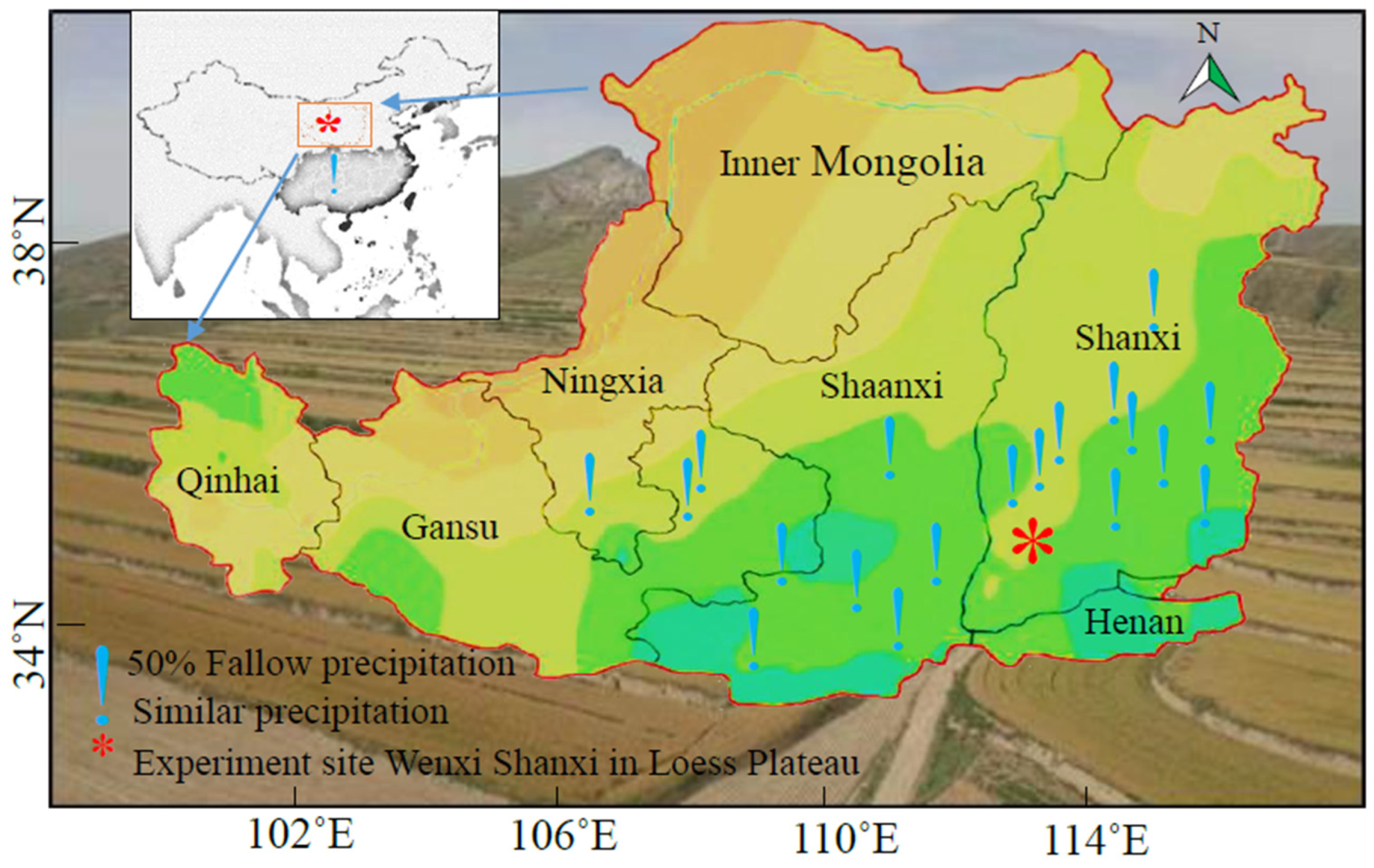



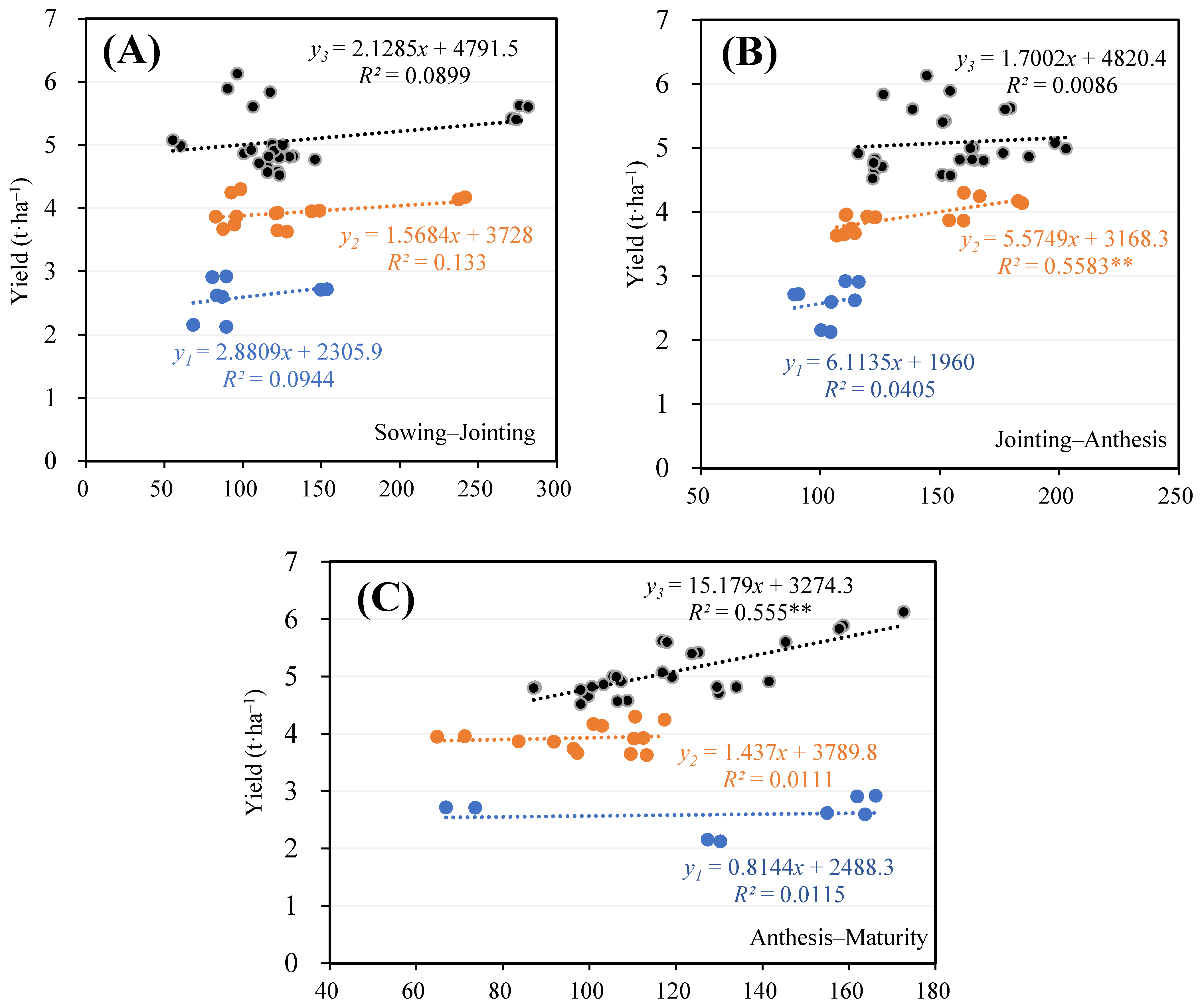
| Year | Organic Matter (g·kg−1) | Total N (g·kg−1) | Alkali-Hydrolysis N (mg·kg−1) | Available Phosphorus (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012–2013 | 8.63 | 0.71 | 32.89 | 15.73 |
| 2013–2014 | 9.18 | 0.70 | 39.32 | 16.62 |
| 2014–2015 | 9.55 | 0.68 | 37.65 | 17.64 |
| 2015–2016 | 8.54 | 0.67 | 32.79 | 19.23 |
| 2016–2017 | 9.62 | 0.69 | 32.22 | 15.28 |
| 2017–2018 | 8.07 | 0.69 | 33.42 | 16.26 |
| Sowing Methods | Tillers (104 ha−1) | Grain Number per Spike | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | Yield (t·ha−1) | Evapotranspiration (mm) | Water Use Efficiency (WUE; kg·h−1·mm−1) | Precipitation Use Efficiency (PUE; kg·h−1·mm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009–2010 DS | 407.71 a | 20.38 c | 36.14 c | 2714.96 b | 311.98 c | 8.70 a | 8.10 b |
| 2012–2013 DS | 300.25 d | 20.37 c | 36.46 c | 2140.25 d | 310.17 c | 6.90 d | 6.24 d |
| 2012–2013 FS | 341.50 c | 22.29 b | 38.81 b | 2608.30 c | 354.10 b | 7.37 c | 7.61 c |
| 2012–2013 WS | 350.25 b | 23.17 a | 40.67 a | 2915.32 a | 362.43 a | 8.04 b | 8.50 a |
| Mean | 349.93 | 21.55 | 38.02 | 2594.71 | 334.67 | 7.75 | 7.61 |
| 2009–2010 FS | 427.18 c | 21.70 f | 39.04 c | 3639.82 f | 344.88 d | 10.55 f | 10.87 b |
| 2009–2010 WS | 453.72 b | 23.78 e | 42.08 a | 3923.57 c | 354.37 c | 11.07 e | 11.71 a |
| 2010–2011 DS | 401.04 e | 26.22 c | 40.51 b | 3705.67 e | 301.65 g | 12.28 a | 6.93 f |
| 2011–2012 DS | 485.50 a | 24.33 d | 35.44 d | 4155.60 b | 525.20 a | 7.91 g | 6.17 g |
| 2013–2014 DS | 386.65 f | 27.55 b | 39.12 c | 3866.73 d | 334.05 e | 11.58 c | 8.15 d |
| 2014–2015 DS | 417.00 d | 27.48 b | 39.14 c | 3956.22 c | 325.22 f | 12.16 b | 7.66 e |
| 2016–2017 DS | 452.12 b | 33.36 a | 35.66 d | 4274.00 a | 373.02 b | 11.46 d | 10.52 c |
| Mean | 431.89 | 26.35 | 38.71 | 3931.66 | 365.48 | 11.00 | 8.86 |
| 2010–2011 FS | 446.58 k | 28.24 g | 40.59 c,d | 4588.15 h | 340.81 j | 13.46 c | 8.58 i |
| 2010–2011 WS | 481.08 h | 28.38 f,g | 42.58 a | 4794.56 g | 361.01 i | 13.28 c | 8.97 h |
| 2011–2012 WS | 603.00 b | 26.56 h | 37.15 f | 5412.04 d | 549.04 b | 9.86 h | 8.04 k |
| 2011–2012 FS | 616.50 a | 26.74 h | 38.63 e | 5612.45 c | 575.02 a | 9.76 h | 8.34 j |
| 2013–2014 FS | 454.41 j | 28.31 f,g | 41.04 b,c | 4575.40 h | 379.48 f | 12.06 f | 9.65 f |
| 2013–2014 WS | 466.00 i | 29.63 e | 41.55 b | 4818.74 f,g | 409.82 c | 11.76 g | 10.16 e |
| 2014–2015 FS | 488.33 f,g | 28.79 f | 40.30 d | 4806.55 f,g | 380.16 f | 12.64 e | 9.30 g |
| 2014–2015 WS | 522.98 c | 29.72 e | 41.01 b,c | 4999.96 e | 391.54 e | 12.77 d,e | 9.68 f |
| 2015–2016 DS | 425.75 l | 34.78 d | 39.06 e | 4812.00 f,g | 371.90 h | 12.94 d | 12.44 c |
| 2015–2016 WS | 484.50 g,h | 36.23 b | 39.11 e | 5719.08 b | 396.09 d | 14.44 b | 14.79 b |
| 2015–2016 FS | 493.25 e,f | 37.80 a | 41.26 b | 6009.75 a | 408.60 c | 14.71 a | 15.54 a |
| 2016–2017 WS | 496.25 e | 35.57 c | 33.12 h | 4892.00 f | 390.33 e | 12.53 e | 12.04 d |
| 2016–2017 FS | 503.36 d | 35.54 c | 34.21 g | 5032.00 e | 376.52 g | 13.36 c | 12.38 c |
| Mean | 498.61 | 31.25 | 39.20 | 5082.51 | 410.02 | 12.58 | 10.76 |
| ANOVA | |||||||
| Sowing (S) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Year (Y) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| S × Y | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Sowing Methods | Tillers | Number per Spike | 1000-Grain Weight | Simulation Equation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS | 0.676 ** | 0.661 * | 0.634 * | Y = 5.694 × Y1 + 111.949 × Y3 − 3653.974, R2 = 0.999 |
| FS | 0.626 ** | 0.641 ** | −0.700 ** | Y = 4.558 × Y1 + 42.942 × Y2 + 831.857, R2 = 0.999 |
| WS | 0.540 ** | 0.375 * | −0.088 | Y = 8.836 × Y1 + 111.52 × Y2 + 93.9 × Y3 − 6489.48, R2 = 0.999 |
| Sowing Methods | Yield Composition | Fallow Precipitation | Soil Water Consumption Sowing–Jointing | Precipitation Sowing–Jointing | Soil Water Consumption Jointing–Anthesis | Precipitation Jointing–Anthesis | Soil Water Consumption Anthesis–Maturity | Precipitation of Anthesis–Maturity | Simulation Equation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS | Tillers | 0.869 ** | 0.951 ** | 0.869 ** | −0.698 ** | 0.869 ** | −0.199 | −0.869 ** | Y1 = 1.345 × X6 − 2.108 × X7 + 489.556, R2 = 0.999 |
| Grain number per ear | −0.551 * | −0.338 | −0.551 * | 0.765 ** | −0.551 * | 0.949 ** | 0.551 * | Y2 = 0.064 × X6 + 19.014, R2 = 0.999 | |
| 1000-grain weight | −0.585 * | −0.370 | −0.585 * | 0.779 ** | −0.585 * | 0.944 ** | 0.585 * | Y3 = 0.097 × X6 + 34.21, R2 = 0.999 | |
| FS | Tillers | 0.012 | −0.033 | 0.812 ** | 0.665 ** | −0.611 ** | 0.939 ** | −0.483 * | Y1 = 0.267 × X4 + 1.513 × X6 + 326.621, R2 = 0.999 |
| Grain number per ear | −0.112 | −0.785 ** | 0.368 | 0.242 | 0.120 | −0.167 | 0.069 | Y2 = 0.01 × X1 − 0.097 × X2 − 0.1 × X6 − 0.131 × X7 + 38.279, R2 = 0.999 | |
| 1000-grain weight | −0.212 | 0.360 | −0.869 ** | −0.730 ** | 0.259 | −0.470 * | 0.356 | Y3 = −0.058 × X3 + 0.051 × X6 + 41.543, R2 = 0.98 | |
| WS | Tillers | 0.345 * | 0.630 ** | 0.819 ** | 0.524 ** | 0.629 ** | −0.482 ** | −0.559 ** | Y1 = 0.375 × X1 + 0.97 × X3 + 0.732 × X5 + 355.131, R2 = 0.999 |
| Grain number per ear | −0.872 ** | −0.099 | −0.478 ** | −0.949 ** | 0.311 * | 0.253 | 0.695 ** | Y2 = 0.053 × X3 − 0.039 × X4 − 0.021 × X5 − 0.077 × X6 + 44.642, R2 = 0.99 | |
| 1000-grain weight | 0.605 ** | −0.708 ** | −0.211 | 0.269 * | −0.822 ** | 0.451 ** | 0.160 | Y3 = 0.017 × X1 + 0.061 × X3 − 0.051 × X5 + 0.051 × X7 + 37.26, R2 = 0.999 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noor, H.; Sun, M.; Lin, W.; Gao, Z. Effect of Different Sowing Methods on Water Use Efficiency and Grain Yield of Wheat in the Loess Plateau, China. Water 2022, 14, 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040577
Noor H, Sun M, Lin W, Gao Z. Effect of Different Sowing Methods on Water Use Efficiency and Grain Yield of Wheat in the Loess Plateau, China. Water. 2022; 14(4):577. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040577
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoor, Hafeez, Min Sun, Wen Lin, and Zhiqiang Gao. 2022. "Effect of Different Sowing Methods on Water Use Efficiency and Grain Yield of Wheat in the Loess Plateau, China" Water 14, no. 4: 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040577
APA StyleNoor, H., Sun, M., Lin, W., & Gao, Z. (2022). Effect of Different Sowing Methods on Water Use Efficiency and Grain Yield of Wheat in the Loess Plateau, China. Water, 14(4), 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040577







