Ion Exchange to Capture Iron after Real Effluent Treatment by Fenton’s Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ion Exchange Resin and Chemicals
2.2. Experimental Procedures
2.2.1. Fenton’s Reaction
2.2.2. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.2.3. Ion Exchange Continuous Experiments
2.3. Analytical Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
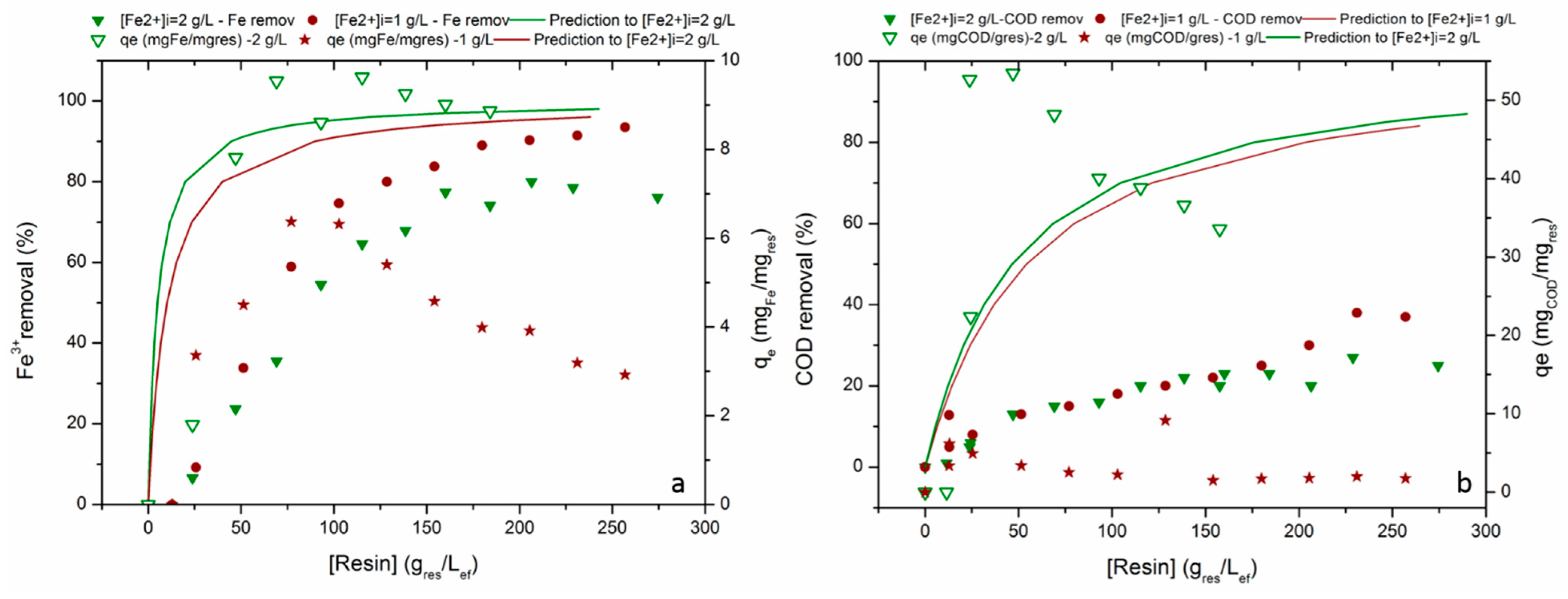
3.1. Adsorption Equilibrium Isotherms
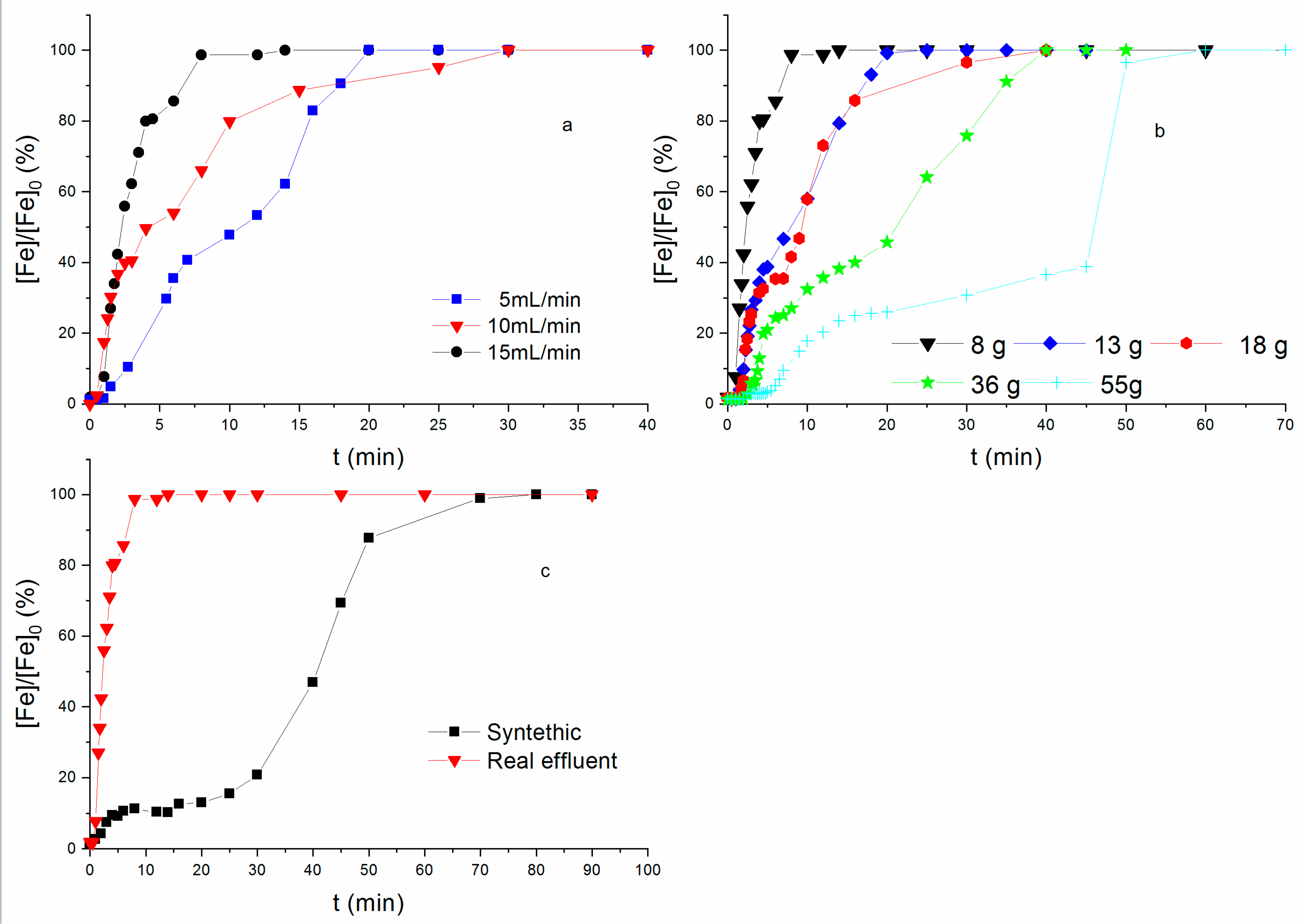
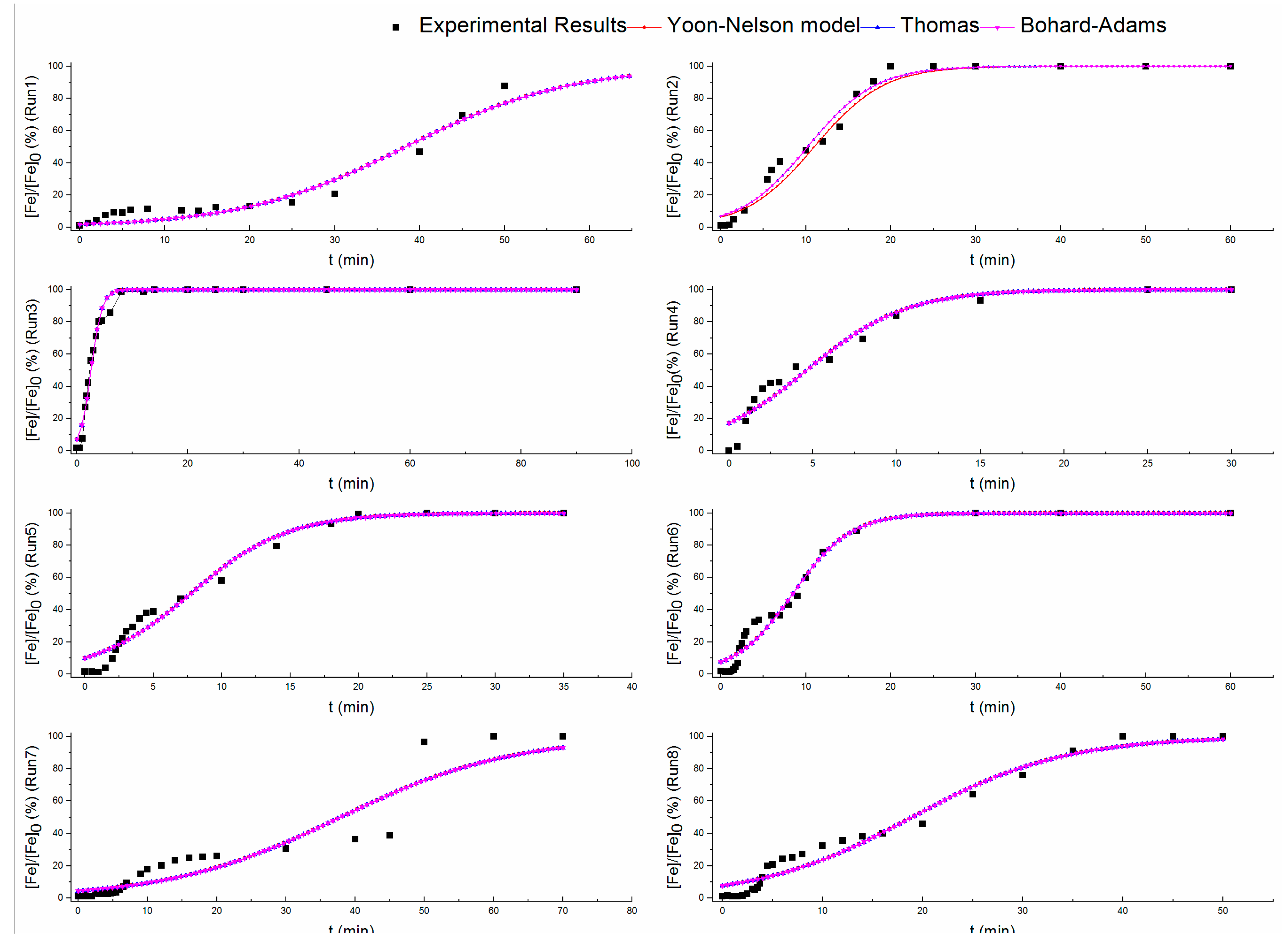
3.2. Analysis of Fe3+ Sorption in Continuous Process
3.3. Amberlite@HPR1100 Regeneration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lucas, M.S.; Dias, A.A.; Sampaio, A.; Amaral, C.; Peres, J.A. Degradation of a textile reactive Azo dye by a combined chemical-biological process: Fenton’s reagent-yeast. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallard, H.; De Laat, J. Kinetic modeling of Fe(III)/H2O2 oxidation reactions in dilute aqueous solution using atrazine as a model organic compounds. Water Res. 2000, 34, 3107–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, E.; Gomes, J.; Quina, M.J.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M.; Martins, R.C. Detoxification of Olive Mill Wastewaters by Fenton’s Process. Catalysts 2018, 8, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, S.; Aneggi, E.; Goi, D. Catalytic activity of metals in heterogeneous Fenton-like oxidation of wastewater contaminants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2405–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.S.F.; Alves, A.; Madeira, L.M. Paraquat removal from water by oxidation with Fento’s reagent. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 175, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, M.I.; Ali, M.E.M. Fenton’s peroxidation and coagulation processes for the treatment of combined industrial and domestic wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, E.; Fernandes, E.; Gomes, J.; Castro-Silva, S.; Martins, R.C. Olive oil extraction industry wastewater treatment by coagulation and Fenton’s process. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 39, 101818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, F.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J.; Madeira, L.M. Influence of the characteristics of carbon materials on their behavior as heterogeneous Fenton catalysts for the elimination of the azo dye Orange II from aqueous solutions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 103, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.N.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, G.S.; Wang, P. A review on Fenton-like processes for organic wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 762–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volesky, B. Detoxification of metal-bearing effluents: Biosorption for the nextcentury. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 59, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.J.M.; Reis, P.M.; Martins, R.C.; Gando-Ferreira, L.M.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M. Iron recovery from the Fenton’s treatment of winery effluent using an ion-exchange resin. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 242, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostroski, I.C.; Barros, M.A.S.D.; Silva, E.A.; Dantas, J.H.; Arroyo, P.A.; Lima, O.C.M. A comparative study for the ion exchange of Fe(III) and Zn(II) on zeolite NaY. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Ghani, N.T.; Hefny, M.; El-Chagbaby, G.A.F. Removal of lead from aqueous solution using low cost abundantly available adsorbents. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marañón, E.; Suárez, F.; Alonso, F.; Fernández, Y.; Sastre, H. Preliminary study of iron removal from hydrochloric pickling liquor by ion exchange. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 2782–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üstün, G.E.; Solmaz, S.K.A.; Birgül, A. Regeneration of industrial district wastewater using a combination of Fenton process and ion exchange—A case study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 52, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Víctor-Ortega, J.M.; Ochando-Pulido, A.; Martínez-Ferez, A. Thermodynamic and kinetic studies on iron removal by means of a novel strong-acid cation exchange resin for olive mill effluent reclamation. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 86, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.G.M.; Moreira, F.C.; Cechinel, M.A.P.; Mazur, L.-P.; Ulson de Souza, A.A.; Souza, S.M.A.G.U.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Vilar, V.J.P. Integration of Fenton’s reaction-based processes and cation exchange processes in textile wastewater treatment as a strategy for water reuse. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 272, 111082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Anber, M.; Al-Anber, Z.A. Utilization of natural zeolite as ion-exchange and sorbent material in the removal of iron. Desalination 2008, 225, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Zhang, L.; Keane, M.A. Removal of iron from aqueous solutions by ion exchange with a Na-Y zeolite. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2001, 36, 1509–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, P.C.; Bhosle, A.B. Bioremoval of some metals by living algae Spirogyra sp. and Spirullina sp. from aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2012, 6, 571–576. [Google Scholar]
- García-Rodríguez, O.; Bañuelos, J.A.; Godínez, L.A.; Valdez, H.C.A.; Zamudio, E.; Ramírez, V.; Rodríguez-Valdez, F.J. Iron Supported on Ion Exchange Resin as Source of Iron for Fenton Reagent: A Heterogeneous or a Homogeneous Fenton Reagent Generation? Int. J. Chem. React. 2017, 15, 20170026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Víctor-Ortega, J.M.; Ochando-Pulido, A.; Martínez-Ferez, A. Iron removal and reuse from Fenton-like pretreated olive mill wastewater with novel strong-acid cation exchange resin fixed-bed column. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 36, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K. Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2313–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, S.H.; Ismail, I.M.; Mostafa, T.M.; Sulaymon, A.H. Biosorption of Heavy Metals: A Review. J. Chem. Sci. Technol. 2014, 3, 74–102. [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich, H. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Temkin, M.J.; Pyzhev, V. Recent modifications to Langmuir isotherms. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 1940, 12, 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Turiel, E.; Perez-Conde, C.; Martin-Esteban, A. Assessment of the cross-reactivity and binding sites characterisation of a propazine-imprinted polymer using the Langmuir-Freundlich isotherm. Analyst 2003, 128, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpleby, R.J.; Baxter, S.C.; Chen, Y.; Shah, R.N.; Shimizu, K.D. Characterization of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers with the Langmuir- Freundlich Isotherm. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 4584–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, A.; Clesceri, I.; Eaton, A. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 16th ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Domingues, E.; Assunção, N.; Gomes, J.; Lopes, D.V.; Frade, J.R.; Quina, M.J.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M.; Martins, R.C. Catalytic Efficiency of Red Mud for the Degradation of Olive Mill Wastewater through Heterogeneous Fenton’s Process. Water 2019, 11, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millar, G.J.; Schot, A.; Couperthwaite, S.J.; Shilling, A.; Nuttall, K.; Bruyn, M. Equilibrium and column studies of iron exchange with strong acid cation resin. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, K.S.; Dash, P.K.; Sarangi, D.; Chaudhury, G.R.; Misra, V.N. Treatment of wastewater containing Pb and Fe using ion-exchange techniques. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 892. [Google Scholar]
- Senthil Kumar, P.; Gayathri, R. Adsorption of Pb2+ ions from aqueous solutions onto bael tree leaf powder: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics study. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2009, 4, 381–399. [Google Scholar]
- Bulai, P.; Cioanca, E. Iron removal from wastewater using chelating resin Purolite S930. TEHNOMUS J. 2011, 18, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodaifa, G.; Ochando-Pulido, J.M.; Alami, S.B.D.; Rodríguez-Vives, S.; Martínez-Férez, A. Kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of iron adsorption onto olivestones. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 49, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivan, E.; Altun, T. The study of various parameters affecting the ion exchange of Cu2+, Zn2+, Ni2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ from aqueous solution on Dowex 50W synthetic resin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 134, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Appereance a | Amber, translucent, spherical beads |
| Copolymer, Matrix a | Styrene-divinylbenzene, Gel |
| Functional group a | Sulfonic acid |
| Ionic Form as Shipped a | Na+ |
| Particle diameter a (µm) | 585 ± 5 |
| Surface area b (m2/g) | 0.673 |
| Average pore diameter b (nm) | 2.595 |
| Pore volume b (cm3/g) | 0.0004 |
| Real density b (g/cm3) | 1.227 |
| Parameter | Before Fenton Process | After Fenton Process |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 4.8 ± 0.3 | 3–3.4 |
| COD (g O2 L−1) | 50.4 ± 5 | 17.5–22.5 |
| BOD5 (mg O2 L−1) | 8000 ± 800 | 770–1100 |
| Biodegradability (BOD5/COD) (%) | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 44 |
| [Fe3+] (g L−1) | 0 | ~2 |
| Langmuir | Freundlich | Temkin | Langmuir–Freundlich | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL (L m g−1) | qmax (mg g−1) | R2 | KF (mg1−(1/n) L1/n/g) | nF | R2 | A (L g−1) | B (J mol−1) | R2 | Qm (mg g−1) | Ka (L m g−1) | n | R2 | |
| Fe3+ | 0.02 | 10.09 | 0.87 | 2.37 | 0.20 | 0.77 | 0.30 | 1.71 | 0.81 | 9.66 | 0.02 | 1 | 0.84 |
| COD | 0.01 | 47.35 | 0.80 | 18.65 | 0.10 | 0.71 | 2.29 | 4.92 | 0.72 | --- | -- | --- | |
| Run | Q (mL min−1) | m (g) | q (mg g−1) | τ (min) | tst (min) | FSB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 (iron solut.) | 8.0 | 9.84 | 0.39 | 5.68 | 0.015 |
| 2 | 5 | 8.0 | 9.80 | 0.78 | 13.25 | 0.026 |
| 3 | 10 | 8.0 | 9.80 | 0.26 | 4.49 | 0.021 |
| 4 | 15 | 8.0 | 9.86 | 0.39 | 5.30 | 0.021 |
| 5 | 10 | 13.0 | 9.77 | 0.78 | 14.34 | 0.065 |
| 6 | 10 | 18.0 | 9.86 | 1.18 | 16.17 | 0.044 |
| 7 | 10 | 55.0 | 9.78 | 3.76 | 68.04 | 0.040 |
| 8 | 10 | 36.0 | 9.78 | 2.43 | 43.69 | 0.076 |
| Model | Parameter | Run | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||
| Bohard-Adams | kba (L mg−1 min) | 0.052 | 0.126 | 0.508 | 0.169 | 0.142 | 0.147 | 0.041 | 0.065 |
| qba (mg g−1) | 22.85 | 5.24 | 0.46 | 2.11 | 3.79 | 4.15 | 22.82 | 10.94 | |
| R2 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.90 | 0.96 | |
| RMSE | 1.78 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 1.72 | 0.10 | |
| Thomas | kth (mL min−1 mg) | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.51 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.07 |
| qth (mg g−1) | 47.93 | 12.77 | 3.18 | 5.80 | 9.66 | 10.60 | 47.31 | 23.64 | |
| R2 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.90 | 0.96 | |
| RMSE | 1.78 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 1.72 | 0.10 | |
| Yoon and Nelson | kyn (min−1) | 0.10 | 0.25 | 1.02 | 0.34 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0.13 |
| τh (min) | 38.35 | 10.22 | 2.55 | 4.64 | 7.72 | 8.48 | 37.85 | 18.91 | |
| R2 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.90 | 0.96 | |
| RMSE | 1.78 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 1.72 | 0.10 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Domingues, E.; Fernandes, E.; Vaz, T.; Gomes, J.; Castro-Silva, S.; Martins, R.C.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.; Ferreira, L.M. Ion Exchange to Capture Iron after Real Effluent Treatment by Fenton’s Process. Water 2022, 14, 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050706
Domingues E, Fernandes E, Vaz T, Gomes J, Castro-Silva S, Martins RC, Quinta-Ferreira R, Ferreira LM. Ion Exchange to Capture Iron after Real Effluent Treatment by Fenton’s Process. Water. 2022; 14(5):706. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050706
Chicago/Turabian StyleDomingues, Eva, Eryk Fernandes, Telma Vaz, João Gomes, Sergio Castro-Silva, Rui C. Martins, Rosa Quinta-Ferreira, and Licínio M. Ferreira. 2022. "Ion Exchange to Capture Iron after Real Effluent Treatment by Fenton’s Process" Water 14, no. 5: 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050706
APA StyleDomingues, E., Fernandes, E., Vaz, T., Gomes, J., Castro-Silva, S., Martins, R. C., Quinta-Ferreira, R., & Ferreira, L. M. (2022). Ion Exchange to Capture Iron after Real Effluent Treatment by Fenton’s Process. Water, 14(5), 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050706










