Lessons Learnt from the Application of MCDA Sorting Methods to Pipe Network Rehabilitation Prioritization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Methodology Description
2.2. MCDA Sorting Methods
2.2.1. Types of Methods
2.2.2. Pseudo-Criterion Model
- : , in this situation there is no significant advantage to differentiate the two actions, meaning that is indifferent to according to a specific criterion .
- : , in this situation, there is a significant advantage of over , meaning that is strictly preferred to according to a specific criterion .
- : , in this situation represents a zone of ambiguity meaning that the advantage of over is a little large to fulfil over an indifference between and , but this advantage is not necessary to fulfil over the strict preference in favor of . In that case, is weakly preferred to .
2.2.3. Prioritization Categories
2.2.4. FlowSort Method
2.2.5. ELECTRE TRI-B and ELECTRE TRI-C Methods Family
- λ-outranking:
- λ-preference:
- λ-indifference:
- λ-incomparability:
2.2.6. Eliciting Technical Parameters
2.3. Affinity Propagation Clustering
3. Case Study
4. Methodology Application
4.1. Definition of the Assessment Criteria
4.1.1. Available Data and Criteria Establishment
4.1.2. Remaining Useful Life
4.1.3. Minimum Velocity Performance Index
4.1.4. Maximum Velocity Performance Index
4.1.5. Number of Pipe Bursts in the Last 10 Years
4.1.6. Consumption Satisfaction in Case of Water Service Disruption
4.1.7. Pipe Material
4.1.8. Maximum Pressure-Head Levels
4.2. Selection of the Assessment Criteria
4.3. Application of the Aggregation Methods and Sensitivity Analysis
4.3.1. ELECTRE TRI-C
4.3.2. FlowSort (Central Profiles)
4.4. Elaboration of Final Recommendations
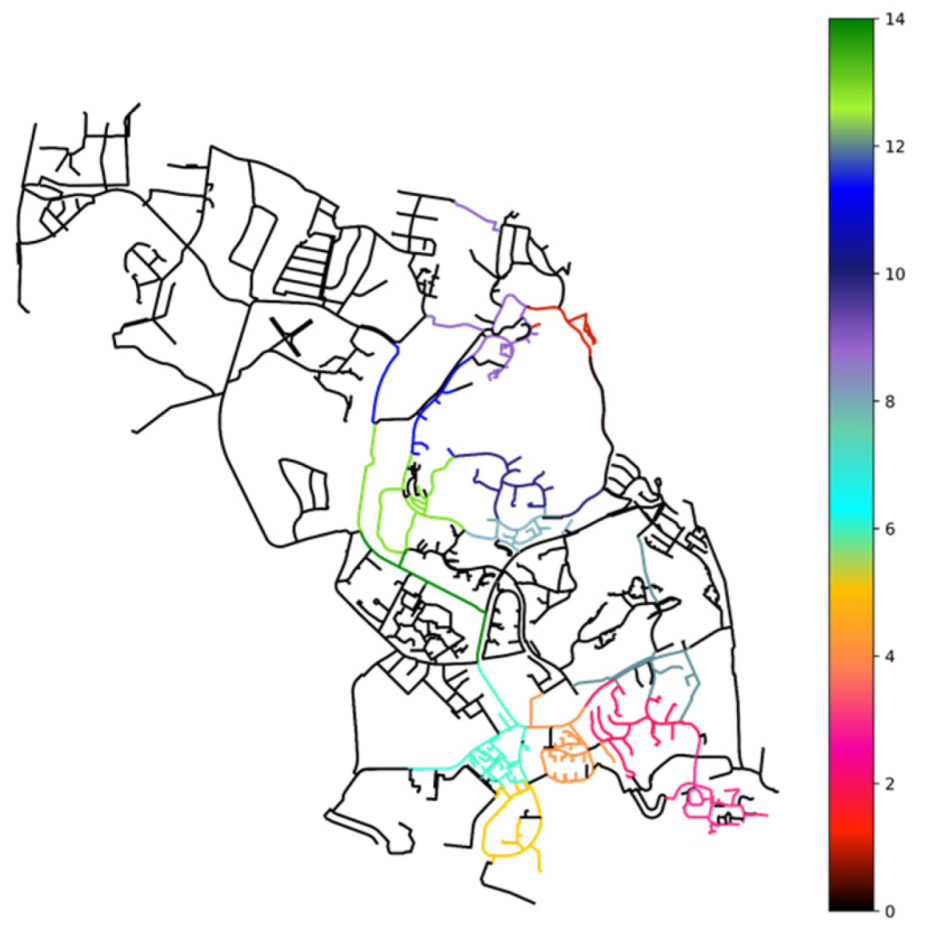
4.5. Affinity Propagation Clustering
5. Results Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clark, R.M.; Sivaganesan, M.; Selvakumar, A.; Sethi, V. Cost Models for Water Supply Distribution Systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2002, 128, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, A.; Tafuri, A.N. Rehabilitation of Aging Water Infrastructure Systems: Key Challenges and Issues. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2012, 18, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, R.; Alegre, H.; Matos, J.S. Highlights of key international water infrastructure asset management initiatives, and trends, challenges and developments in Portugal. Water Policy 2017, 19, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriço, N.; Covas, D.; Almeida, C. Multi-criteria decision analysis in urban water asset management. Urban Water J. 2021, 18, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, O.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Hamam, Y.; Page, P.R.; Adedeji, K.B.; Piller, O. Solving management problems in water distribution networks: A survey of approaches and mathematical models. Water 2019, 11, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scholten, L. Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis for Water Supply Infrastructure Planning under Uncertainty. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Covas, D.; Cabral, M.; Pinheiro, A.; Marchionni, V.; Antunes, S.; Lopes, N.; Mamouros, L.; Brôco, N. Custos de Construção de Infraestruturas Associadas ao Ciclo Urbano da Água; ERSAR: Lisbon, Portugal, 2018; pp. 133–142. ISBN 978-972-98996-4-5.
- Wang, J.J.; Jing, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.F.; Zhao, J.H. Review on multi-criteria decision analysis aid in sustainable energy decision-making. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2263–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B. Paradigms and Challenges. In Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis: State of the Art Surveys; Figueira, J., Greco, S., Ehrgott, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 3–24. ISBN 0-387-23081-5. [Google Scholar]
- Baur, R.; Le Gauffre, P.; Sægrov, S. Multi-criteria decision support for annual rehabilitation programmes in drinking water networks. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2003, 3, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.; Han, J.; Koo, J. Decision method for rehabilitation priority of water distribution system using ELECTRE method. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 2369–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten, L.; Scheidegger, A.; Reichert, P.; Mauer, M.; Lienert, J. Strategic rehabilitation planning of piped water networks using multi-criteria decision analysis. Water Res. 2014, 49, 124–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tscheikner-Gratl, F.; Egger, P.; Rauch, W.; Kleidorfer, M. Comparison of multi-criteria decision support methods for integrated rehabilitation prioritization. Water 2017, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida-Dias, J.; Figueira, J.R.; Roy, B. Electre Tri-C: A multiple criteria sorting method based on characteristic reference actions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 204, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nemery, P.; Lamboray, C. Flow sort: A flow-based sorting method with limiting or central profiles. Top 2008, 16, 90–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macary, F.; Dias, J.A.; Figueira, J.R.; Roy, B. A Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis Model Based on ELECTRE TRI-C for Erosion Risk Assessment in Agricultural Areas. Environ. Model. Assess. 2014, 19, 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumpos, M.; Figueira, J.R. A multicriteria outranking approach for modeling corporate credit ratings: An application of the ELECTRE TRI-NC method. Omega 2019, 82, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadziński, M.; Tervonen, T.; Rui Figueira, J. Robust multi-criteria sorting with the outranking preference model and characteristic profiles. Omega 2015, 55, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zopounidis, C.; Doumpos, M. PREFDIS: A multicriteria decision support system for sorting decision problems. Comput. Oper. Res. 2000, 27, 779–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biluca, J.; de Aguiar, C.R.; Trojan, F. Sorting of suitable areas for disposal of construction and demolition waste using GIS and ELECTRE TRI. Waste Manag. 2020, 114, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhooshiarzanagh, P.; Abi-Zeid, I. A disaggregation approach for indirect preference elicitation in Electre TRI-nC: Application and validation. J. Multi Criteria Decis. Anal. 2021, 28, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrazin, R.; De Smet, Y.; Rosenfeld, J. An extension of PROMETHEE to interval clustering. Omega 2018, 80, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükbay, F.; Sürücü, E. Corporate sustainability performance measurement based on a new multicriteria sorting method. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2019, 26, 664–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özpeynirci, Ö.; Özpeynirci, S.; Mousseau, V. An interactive approach for inverse multiple criteria sorting problem. J. Multi Criteria Decis. Anal. 2021, 28, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafi, A.; Werey, C. Aide à la décision multicritère pour la hiérarchisation de tronçons d’assainissement dans le cadre d’une gestion patrimoniale. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2009, 36, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaka, A.; Nemery, P. Assigning machines to incomparable maintenance strategies with ELECTRE-SORT. Omega 2014, 47, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greco, S.; Kadziński, M.; Mousseau, V.; Słowiński, R. Robust ordinal regression for multiple criteria group decision: UTA GMS-GROUP and UTADIS GMS-GROUP. Decis. Support Syst. 2012, 52, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriço, N.; Covas, D.I.C.; Céu Almeida, M.; Leitão, J.P.; Alegre, H. Prioritization of rehabilitation interventions for urban water assets using multiple criteria decision-aid methods. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zopounidis, C.; Doumpos, M. Multicriteria classification and sorting methods: A literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 138, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, J.; Greco, S.; Roy, B.; Słowiński, R. An Overview of ELECTRE Methods and their Recent Extensions. J. Multi Criteria Decis. Anal. 2013, 20, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, E.; Navarro, J.; Olmedo, R. Characterization of the Effectiveness of Several Outranking-Based Multi-Criteria Sorting Methods. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2018, 17, 1047–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailly, D.; Abi-Zeid, I.; Pepin, S. A multi-criteria classification approach for identifying favourable climates for tourism. J. Multi Criteria Decis. Anal. 2014, 21, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, P.A.; Ishizaka, A.; Martínez, L. Multiple-criteria decision-making sorting methods: A survey. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 183, 115368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brans, J.P. L’ingénièrie de la décision; Elaboration d’instruments d’aide à la décision. La méthode PROMETHEE. In L’Aide à la Décision: Nature, Instruments et Perspectives d’Avenir; Nadeau, R., Landry, M., Eds.; Presses de l’Université Laval: Québec, QC, Canada, 1982; pp. 183–213. [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka, A.; Nemery, P. Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis: Methods and Software; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-119-97407-9. [Google Scholar]
- Brans, J.P.; Vincke, P. Note—A Preference Ranking Organisation Method. Manage. Sci. 1985, 31, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papathanasiou, J.; Ploskas, N. Multiple Criteria Decision—Aid Methods (Mcda); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 57–76. ISBN 978-3-319-91646-0. [Google Scholar]
- Brans, J.P.; Vincke, P.; Mareschal, B. How to select and how to rank projects: The PROMETHEE method. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1986, 24, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.; Mousseau, V. Eliciting multi-criteria preferences: ELECTRE models. Int. Ser. Oper. Res. Manag. Sci. 2018, 261, 349–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B. The outranking approach and the foundations of electre methods. Theory Decis. 1991, 31, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousseau, V. Eliciting Information Concerning the Relative Importance of Criteria. In Advances in multicriteria analysis; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 17–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bana e Costa, C.A.; Vansnick, J.C. MACBETH—An interactive path towards the construction of cardinal value functions. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 1994, 1, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.; Mousseau, V.; Figueira, J.; Clímaco, J. An aggregation/disaggregation approach to obtain robust conclusions with ELECTRE TRI. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 138, 332–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doumpos, M.; Zopounidis, C. Preference disaggregation and statistical learning for multicriteria decision support: A review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 209, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somisetti, V.S.S.; Palla, S.H. Efficient Clustering of Water Distribution Network Using Affinity Propagation. Ingénierie Des Systèmes D′information 2020, 25, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, B.J.; Dueck, D. Clustering by passing messages between data points. Science 2007, 315, 972–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dueck, D.; Frey, B.J. Non-metric affinity propagation for unsupervised image categorization. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Computer Vision, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 14–21 October 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriço, N.; Ferreira, B. Data and Information Systems Management for the Urban Water Infrastructure Condition Assessment. Front. Water 2021, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, L.; Woo, H.; Tryby, M.; Shang, F.; Janke, R.; Haxton, T. EPANET 2.2 User Manual; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2020.
- Klise, K.A.; Bynum, M.; Moriarty, D.; Murray, R. A software framework for assessing the resilience of drinking water systems to disasters with an example earthquake case study. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 95, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, S. Performance in Water Distribution—A System Approach; Research Studies Press Ltd.: Baldock, UK; ISBN 0863802192.
- Coelho, S.; Alegre, H. Indicadores do Desempenho de Sistemas de Saneamento Básico; LNEC: Lisboa, Portugal, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Caetano, J.; Regina, C.; Monteiro, L.; Covas, D. Using hydraulic and water quality models as decision support tools in a water utility. In Proceedings of the 14th International CCWI Conference (Computing and Control for the Water Industry), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 7–9 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- D’Ercole, M.; Righetti, M.; Raspati, G.S.; Bertola, P.; Ugarelli, R.M. Rehabilitation planning of water distribution network through a reliability-based risk assessment. Water 2018, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, B.J.M.; Shamir, U.; Marks, D.H. Water distribution reliability: Simulation methods. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1988, 114, 276–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Creaco, E.; Franchini, M. Fast network multi-objective design algorithm combined with an a posteriori procedure for reliability evaluation under various operational scenarios. Urban Water J. 2012, 9, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puust, R.; Kapelan, Z.; Savic, D.A.; Koppel, T. A review of methods for leakage management in pipe networks. Urban Water J. 2010, 7, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ERSAR. Water and Waste Services Quality Assessment Guide: 2nd Generation of the Assessment System; ERSAR: Lisbon, Portugal, 2017; ISBN 978-989-8360-11-3.














| Generalized Criterion | Definition | Parameters to Fix | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1: Usual criterion |  | - | |
| Type 2: U-shape criterion |  | ||
| Type 3: V-shape criterion |  | ||
| Type 4: Level criterion |  | ||
| Type 5: V-shape with indifference criterion |  | ||
| Type 6: Gaussian criterion |  | ||
| Parameter | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | 1 | 95 | 60 | |
| 20 | 1 | 2 | 98 | 40 | |
| 50 | 0 | 3 | 100 | 30 | |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | |
| Preference direction | Max | Min | Max | Max | Min |
| Scenarios | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Scenario 2 | 30 | 20 | 30 | 10 | 10 |
| Scenario 3 | 40 | 10 | 40 | 5 | 5 |
| Method | Scenarios | High Priority (€) | Intermediate Priority (€) | Low Priority (€) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELECTRE TRI-C | Scenario 1 | 1.96 M | 3.42 M | 5.59 M |
| Scenario 2 | 3.46 M | 3.34 M | 4.17 M | |
| Scenario 3 | 3.46 M | 4.30 M | 3.22 M | |
| FlowSort | Scenario 1 | 38 k | 9.73 M | 1.20 M |
| Scenario 2 | 179 k | 9.03 M | 1.77 M | |
| Scenario 3 | 698 k | 8.47 M | 1.80 M |
| Cluster ID | Percentage of WDN Length (%) | Cost (k€) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.5 | 108 |
| 2 | 2.8 | 184 |
| 3 | 2.3 | 143 |
| 4 | 2.7 | 191 |
| 5 | 2.0 | 255 |
| 6 | 3.5 | 604 |
| 7 | 0.2 | 17 |
| 8 | 1.6 | 111 |
| 9 | 2.4 | 154 |
| 10 | 2.1 | 133 |
| 11 | 1.6 | 364 |
| 12 | 2.4 | 167 |
| 13 | 2.7 | 511 |
| 14 | 1.3 | 520 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caetano, J.; Carriço, N.; Covas, D. Lessons Learnt from the Application of MCDA Sorting Methods to Pipe Network Rehabilitation Prioritization. Water 2022, 14, 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050736
Caetano J, Carriço N, Covas D. Lessons Learnt from the Application of MCDA Sorting Methods to Pipe Network Rehabilitation Prioritization. Water. 2022; 14(5):736. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050736
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaetano, João, Nelson Carriço, and Dídia Covas. 2022. "Lessons Learnt from the Application of MCDA Sorting Methods to Pipe Network Rehabilitation Prioritization" Water 14, no. 5: 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050736
APA StyleCaetano, J., Carriço, N., & Covas, D. (2022). Lessons Learnt from the Application of MCDA Sorting Methods to Pipe Network Rehabilitation Prioritization. Water, 14(5), 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050736








