Reverse Osmosis Membrane Combined with Ultrasonic Cleaning for Flue Gas Desulfurization Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
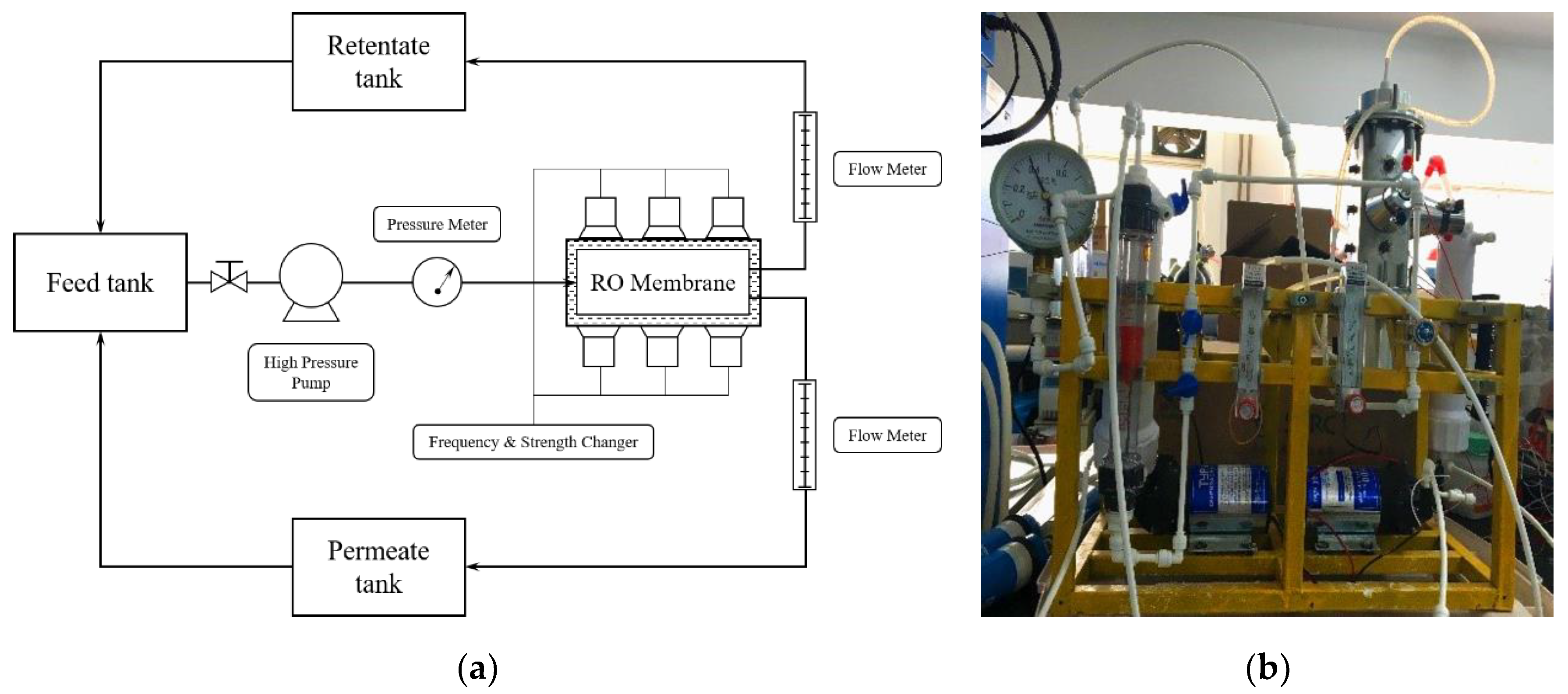
2.2. Design of Laboratory-Scale Membrane System with Ultrasonic Cleaning
2.3. Optimization Experiments for RO Membrane Operation
2.4. Optimization Experiments for Ultrasound Generation Conditions
2.5. Ultrasonic Cleaning Performance of RO Membrane after Actual FGD Wastewater Treatment
2.6. Analytical Methods for Evaluation Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Operating Conditions on Membrane Performance
3.2. Effect of Frequency and Intensity on Membrane Cleaning
3.3. Treatment of Actual FGD Wastewater and Ultrasonic Cleaning of the Fouled Membrane
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Statistical Review of World Energy 2021. Available online: https://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/business-sites/en/global/corporate/pdfs/energy-economics/statistical-review/bp-stats-review-2021-full-report.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- Han, X.; Zhang, D.; Yan, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, J. Process development of flue gas desulphurization wastewater treatment in coal-fired power plants towards zero liquid discharge: Energetic, economic and environmental analyses. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Jiao, Y.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Wei, Y. Insight into the magnetic lime coagulation-membrane distillation process for desulfurization wastewater treatment: From pollutant removal feature to membrane fouling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Chen, N.; Yan, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Karellas, S. Thermodynamic analysis and life cycle assessment of supercritical pulverized coal-fired power plant integrated with No.0 feedwater pre-heater under partial loads. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 1106–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez, E.; Baeza, J.A.; Gabriel, D.; Guisasola, A. Treatment of real flue gas desulfurization wastewater in an autotrophic biocathode in view of elemental sulfur recovery: Microbial communities involved. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wales, M.D.; Gebremichael, E.; Wang, X.; Perea, E.; Jayaweera, P.; Jayaweera, I. Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) Wastewater Treatment Using Polybenzimidazole (PBI) Hollow Fiber (HF) Membranes. Membranes 2021, 11, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuangchen, M.; Jin, C.; Gongda, C.; Weijing, Y.; Sijie, Z. Research on desulfurization wastewater evaporation: Present and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingerich, D.B.; Grol, E.; Mauter, M.S. Fundamental challenges and engineering opportunities in flue gas desulfurization wastewater treatment at coal fired power plants. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 909–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, V.; Branca, T.A.; Rosito, F.; Lucca, C.; Vivas, B.P.; Delmiro, V.M. Sustainable Reverse Osmosis application for wastewater treatment in the steel industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 130, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenten, I.G.; Khoiruddin. Reverse osmosis applications: Prospect and challenges. Desalination 2016, 391, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Dong, J.; Sun, C.; Chen, G. Removal of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) from Municipal Waste Water with Integrated Membrane Systems, MBR-RO/NF. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Huang, W.; Han, H.; Xu, C. Review on treatment technology of salt wastewater in coal chemical industry of China. Desalination 2020, 493, 114640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.X.; Rahardianto, A.; Gu, H.; Christofides, P.D.; Cohen, Y. Novel design and operational control of integrated ultrafiltration—Reverse osmosis system with RO concentrate backwash. Desalination 2016, 382, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvador Cob, S.; Beaupin, C.; Hofs, B.; Nederlof, M.M.; Harmsen, D.J.H.; Cornelissen, E.R.; Zwijnenburg, A.; Genceli Güner, F.E.; Witkamp, G.J. Silica and silicate precipitation as limiting factors in high-recovery reverse osmosis operations. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423–424, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Badrelzaman, M.; Darwish, N.N.; Darwish, N.A.; Hilal, N. Reverse osmosis desalination: A state-of-the-art review. Desalination 2019, 459, 59–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alsarayreh, A.A.; Al-Obaidi, M.A.; Farag, S.K.; Patel, R.; Mujtaba, I.M. Performance evaluation of a medium-scale industrial reverse osmosis brackish water desalination plant with different brands of membranes. A simulation study. Desalination 2021, 503, 114927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, G.E.; Schmid, J. Feasibility study of brackish water desalination in the Egyptian deserts and rural regions using PV systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2002, 43, 2641–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.V.; Cheng, C.-M.; Butalia, T.S.; Weavers, L.K. Forward Osmosis–Membrane Distillation Process for Zero Liquid Discharge of Flue Gas Desulfurization Wastewater. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 5130–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Vanoppen, M.; van Agtmaal, J.M.C.; Cornelissen, E.R.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Verliefde, A.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Picioreanu, C. Cost of fouling in full-scale reverse osmosis and nanofiltration installations in the Netherlands. Desalination 2021, 500, 114865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conidi, C.; Macedonio, F.; Ali, A.; Cassano, A.; Criscuoli, A.; Argurio, P.; Drioli, E. Treatment of Flue Gas Desulfurization Wastewater by an Integrated Membrane-Based Process for Approaching Zero Liquid Discharge. Membranes 2018, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.C.-T.; Lee, D.-J.; Huang, C. Membrane Fouling Mitigation: Membrane Cleaning. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 858–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Amy, G.; Cho, J.; Yoon, Y.; Moon, S.-H.; Kim, I.S. Cleaning strategies for flux recovery of an ultrafiltration membrane fouled by natural organic matter. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3301–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddeo, V.; Borea, L.; Belgiorno, V. Sonochemical control of fouling formation in membrane ultrafiltration of wastewater: Effect of ultrasonic frequency. J. Water Process. Eng. 2015, 8, e92–e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siavash Madaeni, S.; Mohamamdi, T.; Kazemi Moghadam, M. Chemical cleaning of reverse osmosis membranes. Desalination 2001, 134, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnajjar, H.; Tabatabai, A.; Alpatova, A.; Leiknes, T.; Ghaffour, N. Organic fouling control in reverse osmosis (RO) by effective membrane cleaning using saturated CO2 solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 264, 118410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamdi, M.A.; Alhadidi, A.; Ghaffour, N. Membrane backwash cleaning using CO2 nucleation. Water Res. 2019, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Park, S.G.; Lee, J.E.; Kang, S.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Quyen, V.T.K.; Kim, H.S. Steam cleaning for control of membrane fouling in ceramic membrane system. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 138, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimkhani, A.; Zhang, W.; Marhaba, T. Ceramic membrane defouling (cleaning) by air Nano Bubbles. Chemosphere 2016, 146, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, M.H.C.; Zimmerman, W.B. Membrane defouling using microbubbles generated by fluidic oscillation. Water Supply 2019, 19, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayarathne, H.N.P.; Jeong, S.; Jang, A. Chemical-free scale inhibition method for seawater reverse osmosis membrane process: Air micro-nano bubbles. Desalination 2019, 461, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Huang, Y.; Sun, C.; Xiaozhen, L.; Bentian, X.; Wang, Z. Study on ultrasonic techniques for enhancing the separation process of membrane. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 55, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghapour Aktij, S.; Taghipour, A.; Rahimpour, A.; Mollahosseini, A.; Tiraferri, A. A critical review on ultrasonic-assisted fouling control and cleaning of fouled membranes. Ultrasonics 2020, 108, 106228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thombre, N.V.; Gadhekar, A.P.; Patwardhan, A.V.; Gogate, P.R. Ultrasound induced cleaning of polymeric nanofiltration membranes. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 62, 104891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Ladewig, B.P. A review of reverse osmosis membrane fouling and control strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, H.; Amer, E.H.; Ibrahim, K.A. Effect of operating conditions on salt concentration at the wall of RO membrane. Desalination 2015, 357, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gur-Reznik, S.; Koren-Menashe, I.; Heller-Grossman, L.; Rufel, O.; Dosoretz, C.G. Influence of seasonal and operating conditions on the rejection of pharmaceutical active compounds by RO and NF membranes. Desalination 2011, 277, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Hafez, A.; Shaaban, A.; Abdelmonem, N.; Hanafy, M. Removal of Reactive Dyes from Dye-house Effluent Using Nanofiltration Membrane. Egypt. Soc. Chem. Eng. 2011, 37, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Goosen, M.F.A.; Sablani, S.S.; Al-Maskari, S.S.; Al-Belushi, R.H.; Wilf, M. Effect of feed temperature on permeate flux and mass transfer coefficient in spiral-wound reverse osmosis systems. Desalination 2002, 144, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Li, S.; Ghaffour, N. Evaluation of different cleaning strategies for different types of forward osmosis membrane fouling and scaling. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 596, 117731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.; Stevens, G.; Kentish, S. The effect of feed pH on the performance of a reverse osmosis membrane. Desalination 2010, 261, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskooki, A.; Shahraki, M.H.; Mohamadi, M. Effects of various frequencies and powers of ultrasound on cleaning of flat sheet membrane during and after microfiltration. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 57, 5376–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Chai, X.; Fujii, N. Ultrasound enhanced cross-flow membrane filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 1999, 17, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamminen, M.O.; Walker, H.W.; Weavers, L.K. Mechanisms and factors influencing the ultrasonic cleaning of particle-fouled ceramic membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 237, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Zhao, S.; Liang, H. Mechanisms for the enhancement of ultrafiltration and membrane cleaning by different ultrasonic frequencies. Desalination 2010, 263, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Che Lah, N.F.; Ismail, S.; Ooi, B.S. Membrane Antifouling Methods and Alternatives: Ultrasound Approach. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2012, 41, 318–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefi-Oskoui, S.; Khataee, A.; Safarpour, M.; Orooji, Y.; Vatanpour, V. A review on the applications of ultrasonic technology in membrane bioreactors. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.Y.; Guo, N.; Teh, C.Y.; Hay, J.X.W. Advances in Ultrasound Technology for Environmental Remediation; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lamminen, M.O.; Walker, H.W.; Weavers, L.K. Cleaning of particle-fouled membranes during cross-flow filtration using an embedded ultrasonic transducer system. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 283, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Cho, H.; Shin, Y.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S.; Koo, J. Comparison of fouling propensity and physical cleaning effect in forward osmosis, reverse osmosis, and membrane distillation. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 24532–24541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaeni, S.S.; Sasanihoma, A.; Zereshki, S. Chemical cleaning of reverse osmosis membrane fouled by sugar solution. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 5, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Ion | Initial Concentration (mg/L) | Permeate Concentration before Cleaning (mg/L) | Rejection before Cleaning (%) | Permeate Concentration after Cleaning (mg/L) | Rejection after Cleaning (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2333.90 | 119.86 | 94.86% | 94.86 | 95.94% | |
| 2400.00 | 120.20 | 94.99% | 70.41 | 97.07% | |
| 2499.90 | 119.11 | 95.24% | 69.34 | 97.23% | |
| 48.32 | 2.50 | 94.83% | 1.46 | 96.98% | |
| 53.87 | 2.73 | 94.93% | 1.56 | 97.10% | |
| 59.55 | 2.61 | 95.62% | 1.47 | 97.53% | |
| 792.70 | 43.60 | 94.50% | 26.32 | 96.68% | |
| 806.74 | 43.60 | 94.60% | 25.04 | 96.90% | |
| 836.51 | 42.77 | 94.89% | 24.33 | 97.09% | |
| 1350.00 | 83.97 | 93.78% | 66.69 | 95.06% | |
| 1388.48 | 85.15 | 93.87% | 67.84 | 95.11% | |
| 1440.30 | 84.33 | 94.14% | 54.46 | 96.22% | |
| 309.58 | 18.82 | 93.92% | 15.06 | 95.14% | |
| 320.63 | 19.10 | 94.04% | 14.60 | 95.45% | |
| 350.67 | 18.22 | 94.80% | 13.62 | 96.12% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Li, T.; Dou, X.; Meng, L.; Xu, S. Reverse Osmosis Membrane Combined with Ultrasonic Cleaning for Flue Gas Desulfurization Wastewater Treatment. Water 2022, 14, 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060875
Chen X, Li T, Dou X, Meng L, Xu S. Reverse Osmosis Membrane Combined with Ultrasonic Cleaning for Flue Gas Desulfurization Wastewater Treatment. Water. 2022; 14(6):875. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060875
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xingyu, Tianxin Li, Xiaomin Dou, Linglong Meng, and Shuiyang Xu. 2022. "Reverse Osmosis Membrane Combined with Ultrasonic Cleaning for Flue Gas Desulfurization Wastewater Treatment" Water 14, no. 6: 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060875
APA StyleChen, X., Li, T., Dou, X., Meng, L., & Xu, S. (2022). Reverse Osmosis Membrane Combined with Ultrasonic Cleaning for Flue Gas Desulfurization Wastewater Treatment. Water, 14(6), 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060875





