Partitioning and Availability of Metals from Water Suspended Sediments: Potential Pollution Risk Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Sample Analysis
2.3.1. Water and Sediments Samples
2.3.2. Characterization of Suspended Sediments and Dissolved Phase
Scanning Electron Microscopy
X-ray Diffraction
Chemical Analysis
Element Characterization
Radiological Characterization
2.4. Distribution Coefficient (kd)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Potential Pollution Risk Assessment
2.6.1. Contamination Factor (Cf)
2.6.2. Enrichment Factor (Ef)
2.6.3. Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo)
2.6.4. Metal Availability Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Bulk Water Quality
3.2. Mineral Composition of the Suspended Particulate Matter
3.3. Morphology and Elemental Composition
3.4. Partitioning of Chemical Species
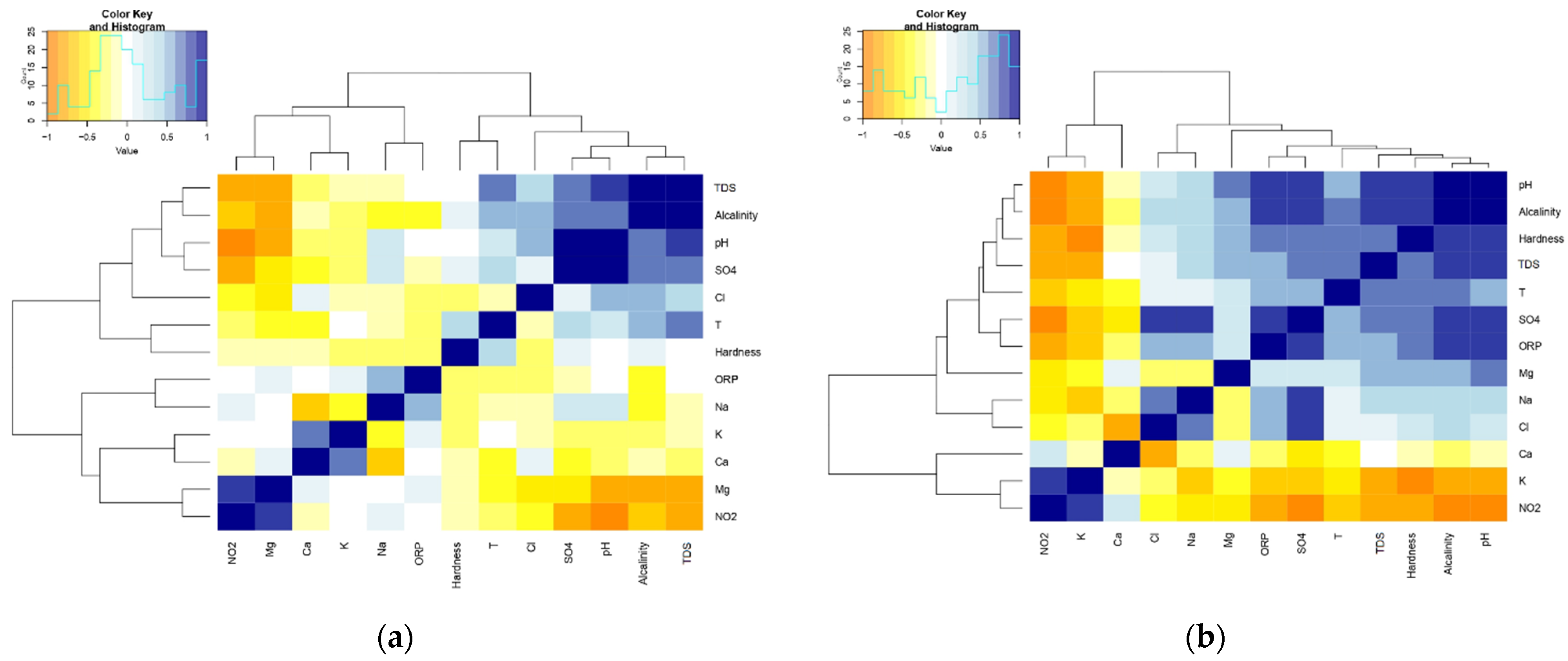
3.4.1. Physicochemical Parameters
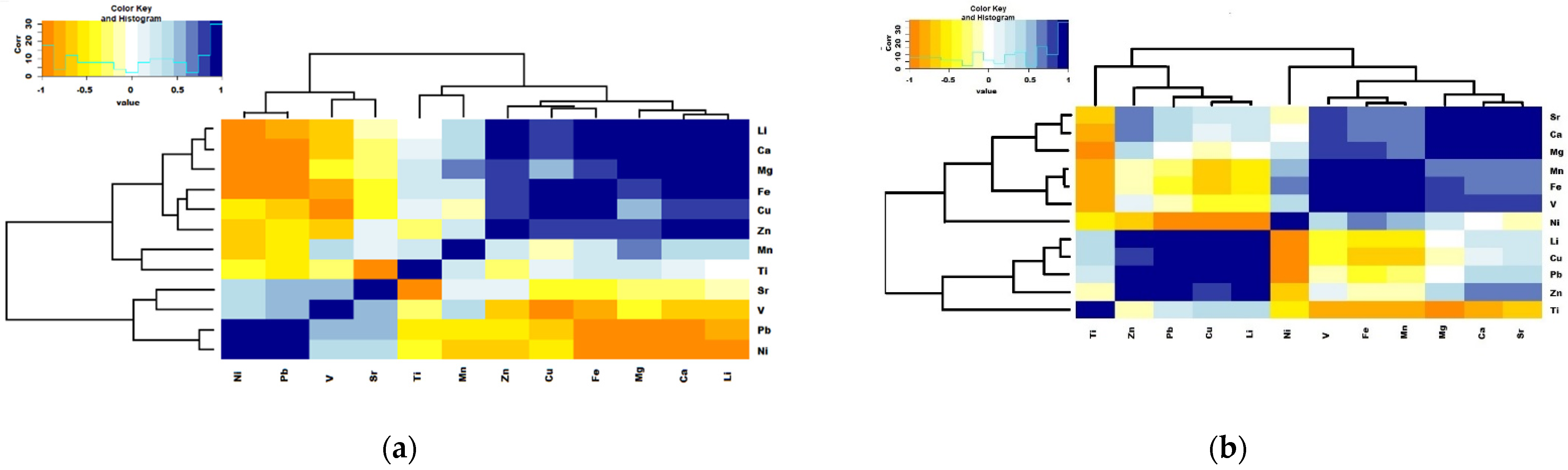
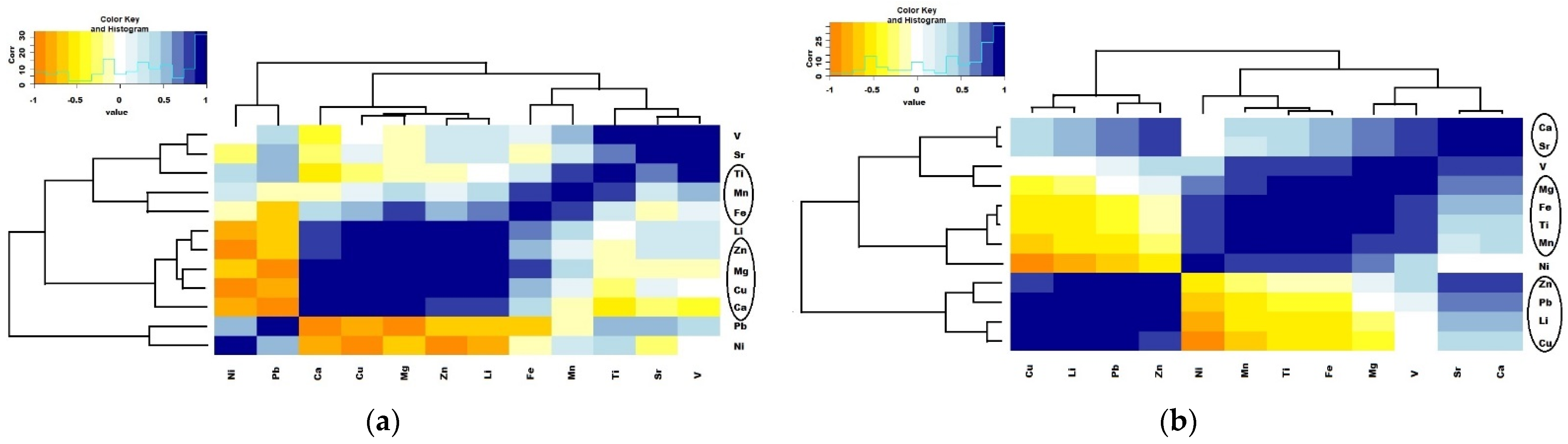
3.4.2. Particle Composition
3.5. Isotopic Determination
3.6. Potential Pollution Risk
4. Discussion
Potential Pollution Risk
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Islam, M.K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, M.; Robles, S.; Avilés, J.; Nuño, C.; Vivas, S.; Bonada, N.; Prat, N.; Alba Tercedor, J.; Casas, J.; Guerrero, C.; et al. Calidad de Las Aguas de Los Ríos Mediterráneos del Proyecto GUADALMED; Características Físico-Químicas; Limnetica: Madrid, Spain, 2002; pp. 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Sophocleous, M. Interactions between groundwater and surface water: The state of the science. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.Y.; Wong, D.W. An adaptive inverse-distance weighting spatial interpolation technique. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Fernández, A.C.; Páez-Osuna, F.; Urrutia-Fucugauchi, J.; Preda, M. 210Pb geochronology of sediment accumulation rates in Mexico City Metropolitan Zone as recorded at Espejo de los Lirios lake sediments. Catena 2005, 61, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrans, L.; Jani, Y.; Burlakovs, J.; Klavins, M.; Hogland, W. Chemical speciation of metals from marine sediments: Assessment of potential pollution risk while dredging, a case study in southern Sweden. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.A.; Antoine, J. Evaluation of the elemental pollution status of Jamaican surface sediments using enrichment factor, geoaccumulation index, ecological risk and potential ecological risk index. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 157, 111288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloaguen, T.V.; Motta, P.N.S.D.; Couto, C.F. A grain-size correction for metal pollution indexes in river sediments. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2020, 36, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, P.; Krishnakumar, S.; Silva, J.D.; Pradhap, D.; Vidyasakar, A.; Radhakrishnan, K.; Godson, P.S.; Arumugam, K.; Magesh, N.S. Elemental concentration and potential ecological risk assessment of reef associated surface sediments of Appa Island, Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve, Southeast coast of India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 128, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, T.C.C.; Roddaz, M.; Moquet, J.-S.; Handt Delgado, H.; Calves, G.; Bayon, G. Controls on the geochemistry of suspended sediments from large tropical South American rivers (Amazon, Orinoco and Maroni). Chem. Geol. 2019, 522, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.L.S.; Saikia, B.K.; da Boit, K.; Pinto, D.; Tutikian, B.F.; Silva, L.F.O. River dynamics and nanopaticles formation: A comprehensive study on the nanoparticle geochemistry of suspended sediments in the Magdalena River, Caribbean Industrial Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viers, J.; Dupré, B.; Gaillardet, J. Chemical composition of suspended sediments in World Rivers: New insights from a new database. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 853–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabaux, F.; Bourdon, B.; Riotte, J. Chapter 3 U-Series Geochemistry in Weathering Profiles, River Waters and Lakes. In Radioactivity in the Environment; Porcelli, D., Krishnaswami, S., Cochran, J.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 13, pp. 49–104. [Google Scholar]
- Looi, L.J.; Aris, A.Z.; Yusoff, F.M.; Isa, N.M.; Haris, H. Application of enrichment factor, geoaccumulation index, and ecological risk index in assessing the elemental pollution status of surface sediments. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA. Handbook of Parameter Values for the Prediction of Radionuclide Transfer in Terrestrial and Freshwater Environments; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2010; p. 200. [Google Scholar]
- Ani, E.-C.; Wallis, S.; Kraslawski, A.; Agachi, P.S. Development, calibration and evaluation of two mathematical models for pollutant transport in a small river. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batley, G.E.; Simpson, S. Sediment Quality Guidelines. In Encyclopedia of Aquatic Ecotoxicology; Férard, J.-F., Blaise, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1015–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, N.; Allan, I.J.; Carter, J.E.; House, W.A.; Parker, A. Pesticides and other micro-organic contaminants in freshwater sedimentary environments—A review. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 159–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alan, M.; Kara, D. Comparison of a new sequential extraction method and the BCR sequential extraction method for mobility assessment of elements around boron mines in Turkey. Talanta 2019, 194, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemati, K.; Bakar, N.K.A.; Abas, M.R.; Sobhanzadeh, E. Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor, Malaysia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-López, R.; Álvarez-Valero, A.M.; Nieto, J.M. Changes in mobility of toxic elements during the production of phosphoric acid in the fertilizer industry of Huelva (SW Spain) and environmental impact of phosphogypsum wastes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Cortés, M.; Reyes-Cortés, I.A.; Espino Valdez, S.; Rentería-Villalobos, M.; Burillo Montúfar, J.C.; Montero-Cabrera, M.E. Origen y distribución de la radiactividad natural en la zona norte de la cuenca de Chihuahua, México. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geológicas 2012, 29, 659–675. [Google Scholar]
- Ferríz, H. Uranium mineralization in the San Marcos volcanic center Chihuahua, Mex. In Proceedings of the Uranium Deposits in Volcanic Rocks, El Paso, TX, USA, 2–5 April 1984; pp. 197–216. [Google Scholar]
- INEGI. Compendio de Información Geográfica Municipal; INEGI: Aguascalientes City, Mexico, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rentería-Villalobos, M.; Cortés, M.R.; Mantero, J.; Manjón, G.; García-Tenorio, R.; Herrera, E.; Montero-Cabrera, M.E. Uranium in the Surrounding of San Marcos-Sacramento River Environment (Chihuahua, Mexico). Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burillo Montufar, J.C.; Reyes Cortés, M.; Reyes Cortés, I.A.; Espino Valdez, M.S.; Hinojosa de la Garza, O.R.; Nevárez Ronquillo, D.P.; Herrera Peraza, E.; Rentería Villalobos, M.; Montero Cabrera, M.E. Uranium-series isotopes transport in surface, vadose and ground waters at San Marcos uranium bearing basin, Chihuahua, Mexico. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOM-014-SSA1-1993. Sanitary Procedures for the sampling of water for human use and consumption in public and private water supply systems. (Procedimientos Sanitarios para el muestreo de agua para uso y consumo humano en sistemas de abastecimiento de agua públicos y privados). Official Mexican Standard. Enviromental Health. Mexico, H.a.A.D., Ed.; DOF, Diario Oficial de la Federación, Secretaria de Economía: Mexico City, Mexico, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- NMX-AA-072-SCFI-2001. In Water Analysis—Determination of Total Hardness in Natural, Wastewaters and Wastewaters Treated—Test Method; DOF, Diario Oficial de la Federación, Secretaría de Economía: Mexico City, Mexico, 2001; pp. 1–14.
- NMX-AA-073-SCFI-2001. In Water Analysis—Determination of Total Chlorine in Natural Water, Wastewaters and Wastewaters Treated—Test Method; DOF, Diario Oficial de la Federación, Secretaria de Economía: Mexico City, Mexico, 2001; pp. 1–13.
- NMX-AA-036-SCFI-2001. In Water Analysis—Determination of Acidity and Total Alkalinity in Natural, Drinking, Wastewaters and Treated Wastewaters; Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial, Secretaria de Economía: Mexico City, Mexico, 2001; pp. 1–22.
- Hach Company. Procedures Manual, DR/2010 Spectrophotometer: Photometric, Titration, and Microbiological Procedures, 3rd ed.; Hach Company: Loveland, CO, USA, 2000; p. 874. [Google Scholar]
- NMX-AA-051-SCFI-2001. In Water Analisis—Determination of Metals By Atomic Absorption in Natural, Drinking, Wastewaters and Wastewaters Treated—Test Method; DOF, Diario Oficial de la Federación, Secretaria de Economía: Mexico City, Mexico, 2001; pp. 1–47.
- Mondal, P.; Schintu, M.; Marras, B.; Bettoschi, A.; Marrucci, A.; Sarkar, S.K.; Chowdhury, R.; Jonathan, M.P.; Biswas, J.K. Geochemical fractionation and risk assessment of trace elements in sediments from tide-dominated Hooghly (Ganges) River Estuary, India. Chem. Geol. 2020, 532, 119373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Moreno, S.M.; Gázquez, M.J.; Pérez-López, R.; Bolivar, J.P. Validation of the BCR sequential extraction procedure for natural radionuclides. Chemosphere 2018, 198, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degueldre, C.; Kline, A. Study of thorium association and surface precipitation on colloids. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 264, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabaux, F.; Riotte, J.; Dequincey, O. U-Th-Ra Fractionation during Weathering and River Transport. In Uranium Series Geochemistry: Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry; Bourdon, B., Henderson, G.M., Lundstrom, C.C., Turner, S.P., Eds.; Mineralogical Society of America: Chantilly, VA, USA, 2003; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kynčlová, P.; Hron, K.; Filzmoser, P. Correlation Between Compositional Parts Based on Symmetric Balances. Math. Geosci. 2017, 49, 777–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SAS. Statistical Analysis System Users’ Guide; Statistical Analysis System Institute, Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Boente, C.; Martín-Méndez, I.; Bel-Lán, A.; Gallego, J.R. A novel and synergistic geostatistical approach to identify sources and cores of Potentially Toxic Elements in soils: An application in the region of Cantabria (Northern Spain). J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 208, 106397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarvainen, T.; Sapon, S.; Jarva, J. Applying heatmaps in interpretation of geochemical baseline data on urban soils in Finland. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 205, 106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; Filzmoser, P.; Garrett, R.G. Factor analysis applied to regional geochemical data: Problems and possibilities. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M. The Importance of Enrichment Factor (EF) and Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo) to Evaluate the Soil Contamination. J. Geol. Geophys. 2016, 5, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.A.; Tolosa, C.A.; Tack, F.M.G.; Verloo, M.G. Characterization of Selected Element Concentrations and Enrichment Ratiosin Background and Anthropogenically Impacted Roadside Areas. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnick, R.L. Earth’s Continental Crust. In Encyclopedia of Geochemistry: A Comprehensive Reference Source on the Chemistry of the Earth; White, W.M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 392–418. [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. Composition of the Continental Crust. Treatise Geochem. 2003, 3, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, G.F. An assessment of aluminum and iron in normalisation and enrichment procedures for environmental assessment of marine sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Peng, X.; Liu, B.; Min, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, J.; Wu, Z. Aluminum distribution heterogeneity and relationship with nitrogen, phosphorus and humic acid content in the eutrophic lake sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.; Jumbo-Flores, D.; González-Merizalde, M.; Bermeo-Flores, S.A. Niveles de Metales Pesados En Sedimentos de La Cuenca Del Río Puyango, Ecuador. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2016, 32, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, F.; Zhang, C.; Qu, L.; Song, Q.; Ji, X.; Mei, K.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M. A comprehensive analysis and source apportionment of metals in riverine sediments of a rural-urban watershed. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 121230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimann, C.; Filzmoser, P.; Hron, K.; Kynčlová, P.; Garrett, R.G. A new method for correlation analysis of compositional (environmental) data—A worked example. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, G.; Leitão, P.; Pinto, L.; Jauch, E.; Fernandes, L.; Neves, R. Development and validation of a morphological model for multiple sediment classes. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2017, 32, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, E.; Wang, W.; Sun, M. Mineral composition and particle size distribution of river sediment and loess in the middle and lower Yellow River. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2020, 36, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-García, C.G. Reconstrucción Histórica de la Contaminación Por Arsénico, Plomo y Uranio en Los Sedimentos de Las Represas San Marcos y Luis L. León, en Chihuahua; Original Research; Centro de Investigación en Materiales Avanzados, CIMAV: Chihuahua, Mexico, 2014; p. 148. [Google Scholar]
- Telfeyan, K.; Breaux, A.; Kim, J.; Cable, J.E.; Kolker, A.S.; Grimm, D.A.; Johannesson, K.H. Arsenic, vanadium, iron, and manganese biogeochemistry in a deltaic wetland, southern Louisiana, USA. Mar. Chem. 2017, 192, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.F.; El Zokm, G.M.; Okbah, M.A. Risk assessment and chemical fractionation of selected elements in surface sediments from Lake Qarun, Egypt using modified BCR technique. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ondoño, E.; Bacchetta, G.; Lallena, A.M.; Navarro, F.B.; Ortiz, I.; Jiménez, M.N. Use of BCR sequential extraction procedures for soils and plant metal transfer predictions in contaminated mine tailings in Sardinia. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 172, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.G.; Shi, J.B.; He, B.; Liu, J.F.; Liang, L.N.; Jiang, G.B. Speciation of heavy metals in marine sediments from the East China Sea by ICP-MS with sequential extraction. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruder-Hubscher, V.; Lagarde, F.; Leroy, M.J.F.; Coughanowr, C.; Enguehard, F. Application of a sequential extraction procedure to study the release of elements from municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 451, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, Ş.; Aydın, Z.; Tokalıoğlu, Ş. Fractionation of metals in street sediment samples by using the BCR sequential extraction procedure and multivariate statistical elucidation of the data. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 132, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, T.; Kübeck, C. Uranium in groundwater–a synopsis based on a large hydrogeochemical data set. Water Res. 2018, 129, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priestley, S.C.; Payne, T.E.; Harrison, J.J.; Post, V.E.A.; Shand, P.; Love, A.J.; Wohling, D.L. Use of U-isotopes in exploring groundwater flow and inter-aquifer leakage in the south-western margin of the Great Artesian Basin and Arckaringa Basin, central Australia. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 98, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noli, F.; Kazakis, N.; Vargemezis, G.; Ioannidou, A. The uranium isotopes in the characterization of groundwater in the Thermi-Vasilika region, northern Greece. Isot. Env. Health Stud. 2016, 52, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Tomita, J.; Sakaguchi, A.; Ohtsuka, Y.; Hoshi, M.; Apsalikov, K. Uranium isotopes in well water samples as drinking sources in some settlements around the Semipalatinsk Nuclear Test Site, Kazakhstan. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2010, 284, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reyes, E.; Marques, L.S. Uranium series disequilibria in ground waters from a fractured bedrock aquifer (Morungaba Granitoids–Southern Brazil): Implications to the hydrochemical behavior of dissolved U and Ra. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2008, 66, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmond, J.K.; Ivanovich, M. Uranium-series mobilization and surface hydrology. In Uranium-Series Disequilibrium: Applications to Earth, Marine, and Environmental Science; Ivanovich, M., Harmon, R.S., Eds.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1992; pp. 259–289. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Jian, X.; Shang, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Fu, H. Underestimated heavy metal pollution of the Minjiang River, SE China: Evidence from spatial and seasonal monitoring of suspended-load sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 760, 142586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, E.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, E.; Yang, F.; Wei, C.; Shen, J. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal pollution and ecological risk in lake sediment by combining total concentration and chemical partitioning. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, J.G.A. Sediment quality criteria in use around the world. Limnology 2002, 3, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorfi, S.; Maleki, R.; Jaafarzadeh, N.; Ahmadi, M. Pollution load index for heavy metals in Mian-Ab plain soil, Khuzestan, Iran. Data Brief 2017, 15, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Cai, A.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Wu, T.; Pan, B.; Song, N.; Li, F.; Lu, M. Heavy metals in the riverbed surface sediment of the Yellow River, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 24768–24780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiman, U.; Mahmood, A.; Waheed, S.; Malik, R.N. Enrichment, geo-accumulation and risk surveillance of toxic metals for different environmental compartments from Mehmood Booti dumping site, Lahore city, Pakistan. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 2229–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahra, A.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Malik, R.N.; Ahmed, Z. Enrichment and geo-accumulation of heavy metals and risk assessment of sediments of the Kurang Nallah—Feeding tributary of the Rawal Lake Reservoir, Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varol, M. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillardet, J.; Viers, J.; Dupré, B. 7.7—Trace Elements in River Waters. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 195–235. [Google Scholar]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupré, B.; Allègre, C.J. Geochemistry of large river suspended sediments: Silicate weathering or recycling tracer? Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 4037–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Han, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X. Chemical weathering inferred from riverine water chemistry in the lower Xijiang basin, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4749–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Yin, J.; Zhu, L. Risk assessment for sediment associated heavy metals using sediment quality guidelines modified by sediment properties. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 115844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, L.C.; da Silva Júnior, J.B.; dos Santos, I.F.; de Carvalho, V.S.; de Santana Santos, A.; Hadlich, G.M.; Ferreira, S.L.C. Assessment of toxicity of metals in river sediments for human supply: Distribution, evaluation of pollution and sources identification. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Variable | Components | kd | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coarse Particles | Fine Particles | Coarse Particles | Fine Particles | |||
| PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | |||
| Surface level | ||||||
| Fe | 0.284 | −0.006 | 0.302 | 0.05 | 9.0 × 102 | 7.4 × 102 |
| Mg | 0.284 | −0.034 | 0.301 | −0.002 | 1.3 × 101 | 2.0 × 101 |
| Ca | 0.284 | −0.016 | 0.302 | 0.038 | 9.9 × 100 | 2.6 × 101 |
| Mn | 0.284 | 0.011 | 0.296 | 0.098 | 1.1 × 104 | 5.1 × 103 |
| Pb | 0.279 | 0.253 | 0.302 | −0.052 | 5.2 × 101 | 1.7 × 102 |
| V | 0.275 | 0.072 | 0.278 | −0.109 | 1.7 × 102 | 2.4 × 102 |
| Ni | 0.207 | −0.937 | −0.042 | 0.73 | 2.5 × 102 | 2.3 × 102 |
| Ti | 0.283 | 0.097 | 0.302 | 0.045 | - | - |
| Sr | 0.284 | −0.022 | 0.301 | 0.09 | 1.0 × 101 | 3.3 × 101 |
| Cu | 0.284 | 0.062 | 0.302 | 0.059 | 7.1 × 101 | 3.0 × 102 |
| Li | 0.281 | 0.182 | 0.302 | 0.045 | 6.8 × 101 | 3.1 × 102 |
| Zn | 0.284 | 0.029 | 0.301 | 0.088 | 4.3 × 101 | 1.5 × 102 |
| U * | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Autocorrelation | 12.36 | 0.53 | 10.89 | 1.73 | ||
| Variance (%) | 95.1 | 4.1 | 83.8 | 13.3 | ||
| Accumulated variance (%) | 95.1 | 99.2 | 83.8 | 97.1 | ||
| Deep level | ||||||
| Fe | 0.289 | 0.086 | 0.281 | 0.141 | 2.6 × 102 | 3.9 × 103 |
| Mg | 0.289 | 0.076 | 0.281 | −0.145 | 6.8 × 100 | 9.4 × 101 |
| Ca | 0.287 | 0.145 | 0.281 | 0 | 5.7 × 100 | 3.7 × 101 |
| Mn | 0.288 | 0.122 | 0.279 | 0.248 | 7.7 × 103 | 1.0 × 105 |
| Pb | 0.279 | −0.163 | 0.276 | −0.268 | 1.4 × 101 | 1.3 × 102 |
| V | 0.135 | −0.924 | 0.266 | −0.655 | 5.1 × 101 | 8.2 × 102 |
| Ni | 0.283 | −0.017 | 0.27 | 0.049 | 1.5 × 102 | 5.5 × 102 |
| Ti | 0.287 | 0.114 | 0.272 | 0.512 | ||
| Sr | 0.289 | 0.053 | 0.281 | −0.128 | 2.9 × 100 | 2.0 × 101 |
| Cu | 0.289 | 0.053 | 0.279 | 0.225 | 3.5 × 101 | 1.3 × 102 |
| Li | 0.288 | 0.053 | 0.281 | 0.079 | 2.5 × 101 | 1.2 × 102 |
| Zn | 0.288 | 0.096 | 0.281 | 0.13 | 3.2 × 101 | 1.3 × 102 |
| U * | 8.7 × 100 | 2.3 × 101 | ||||
| Autocorrelation | 11.89 | 0.91 | 12.61 | 0.25 | ||
| Variance (%) | 91.5 | 7 | 97 | 1.9 | ||
| Accumulated variance (%) | 91.5 | 98.5 | 97 | 98.9 | ||
| Coarse | Coarsesum * | Fine | Finesum * | Dissolved 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 238U | 45 | 65 | 125 | 197 | 5.3 |
| 26–57 | 16–90 | 90–152 | 78–482 | 2–9.7 | |
| 234U | 87 | 111 | 142 | 320 | 30 |
| 44–159 | 30–171 | 100–189 | 175–471 | 10–70 | |
| 232Th | nm a | 74 | 49 | 79 | nm |
| 18–104 | 31–74 | 43–133 | |||
| 230Th | nm | 64 | 169 | 78 | nm |
| 7–92 | 101–246 | 43–160 | |||
| 234U/238U | 2.1 | 1.7 | 1.2 | 2.1 | 6.3 |
| 1.2–3.0 | 1.5–1.9 | 0.8–1.5 | 1–3.5 | 1.5–10.5 | |
| 230Th/232Th | - | 0.8 | 3.6 | 1.0 | - |
| 0.4–1.0 | 2.3–5.0 | 0.8–1.2 | |||
| 232Th/238U | - | 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.6 | - |
| 1.0–1.3 | 0.2–0.8 | 0.1–1.0 | |||
| 230Th/238U | - | 0.9 | 1.5 | 0.6 | - |
| 0.4–1.2 | 0.7–2.7 | 0.1–1.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabral-Lares, M.; Rentería-Villalobos, M.; Mendieta-Mendoza, A.; Ortíz-Caballero, Z.; Montero-Cabrera, E.; Vioque, I. Partitioning and Availability of Metals from Water Suspended Sediments: Potential Pollution Risk Assessment. Water 2022, 14, 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060980
Cabral-Lares M, Rentería-Villalobos M, Mendieta-Mendoza A, Ortíz-Caballero Z, Montero-Cabrera E, Vioque I. Partitioning and Availability of Metals from Water Suspended Sediments: Potential Pollution Risk Assessment. Water. 2022; 14(6):980. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060980
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabral-Lares, Magaly, Marusia Rentería-Villalobos, Aurora Mendieta-Mendoza, Ziury Ortíz-Caballero, Elena Montero-Cabrera, and Ignacio Vioque. 2022. "Partitioning and Availability of Metals from Water Suspended Sediments: Potential Pollution Risk Assessment" Water 14, no. 6: 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060980
APA StyleCabral-Lares, M., Rentería-Villalobos, M., Mendieta-Mendoza, A., Ortíz-Caballero, Z., Montero-Cabrera, E., & Vioque, I. (2022). Partitioning and Availability of Metals from Water Suspended Sediments: Potential Pollution Risk Assessment. Water, 14(6), 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060980







