Abstract
The discharge exponent is a general index used to evaluate the hydraulic performance of emitters, which is affected by emitters’ structural parameters. Accurately estimating the effect of change in structural parameters on the discharge exponent is critical for the design and optimization of emitters. In this research, the response surface methodology (RSM) and two machine learning models, the artificial neural network (ANN) and support vector regression (SVR), are used to predict the discharge exponent of tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitters. The input parameters consist of the number of channel units (N), channel depth (D), tooth angle (α), tooth height (H) and channel width (W). The applied models are assessed through the coefficient of determination (R2), root-mean-square error (RMSE) and mean absolute error (MAE). The analysis of variance shows that tooth height had the greatest effect on the discharge exponent. Statistical criteria indicate that among the three models, the SVR model has the highest prediction accuracy and the best robustness with an average R2 of 0.9696, an average RMSE of 0.0037 and an average MAE of 0.0031. The SVR model can quickly and accurately simulate the discharge exponent of emitters, which is conducive to the rapid design of the emitter.
1. Introduction
With the growth of the population, the rapid development of social economy and global warming, the shortage of water resources is becoming more and more serious [1,2]. Therefore, improving the utilization rate of water resources and saving water resources are very important for the development of human beings. At present, agriculture is the field that consumes the most water resources [3], so water-saving irrigation technology has been advocated around the world to improve the utilization rate of agricultural water and achieve the purpose of water saving. Drip irrigation is an efficient and energy-saving irrigation technology, which has been widely used all over the world [4,5]. The drip irrigation emitter is the core component of drip irrigation systems, which determines the water supply for and uniformity of each crop, so the performance of entire drip irrigation systems is ultimately reflected by the performance of drip irrigation emitters. Hydraulic performance is a major standard to measure the irrigation quality of emitters [6,7,8]. The relationship between the discharge and pressure of emitters can be expressed according to the following empirical formula [9]:
where kd is the discharge coefficient, x is the discharge exponent, Q is the emitter discharge (L/h), and P is the working pressure (kPa).
Q = kd Px
The discharge exponent reflects the sensitivity of the discharge of emitters to the pressure change, and its value is between 0 and 1. The larger the discharge exponent, the more sensitive the emitter discharge is to the change of pressure. In theoretical analyses and engineering applications, the discharge exponent has been used as one of the indicators to evaluate the hydraulic performance of emitters [10,11]. Labyrinth channel emitters are widely used due to their simple structure and low manufacturing cost [12]. Labyrinth channel units with different shapes lead to different hydraulic performances of emitters, and a labyrinth channel with the same shape, but different structural parameters, also leads to different hydraulic performances of the emitters. Therefore, accurately evaluating the relationship between the structure of the labyrinth channel emitter and its discharge exponent is very important for its design and optimization.
At present, the commonly used emitter discharge exponent prediction method needs to design a single factor or multi-factor orthogonal test first, and then make predictions according to the established linear or nonlinear regression equations between the emitter structure parameters and the emitter discharge exponent. Li et al. [13] found that tooth-shaped spacing had a significant effect on the emitter’s discharge exponent. Niu et al. [14] studied the influence of the angle of the tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitter on its performance, and found that the angle was negatively correlated with the discharge exponent. Al-Alamoud et al. [15] reported that the width and length of flow path, channel unit number, height, and spacing had a positive correlation with the hydraulic performance of the emitters. Yang et al. [16] discussed the influence of structural parameters on the hydraulic performance emitters by a numerical simulation, and found that the channel depth was positively correlated with the discharge exponent, while the channel height was negatively correlated with the discharge exponent. The tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitter is one of the most common emitters on the market, and many researchers studied the relationship between its structure and its discharge exponent; however, as far as we know, most of the current studies only discuss the independent influences of each factor, but do not consider the interactive influences between the factors. This is because if the interactive influence between the factors is considered, the number of orthogonal tests will increase exponentially with the increase in factors, so the interactive influence is usually ignored. However, if the response surface method is used for experimental designs, the number of experiments is far fewer than that of the orthogonal test method, while considering the interactions between the factors, which greatly reduces the experimental time and cost [17,18,19]. In addition, when analyzing the experimental results, RSM can describe the influence relationship between independent variables and dependent variables through a three-dimensional response surface map and contour map, making the results more intuitive and clear. Therefore, in this study, the RSM is used to study the influence of the structural parameters on the discharge exponent of the tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitter.
In recent years, machine learning methods have been greatly expanded to solve multivariate, nonlinear and prediction problems, and they have been widely used in various fields, such as finance, education, medicine, construction, agriculture, e-commerce, robotics, information search and weather forecasting [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. At present, the application of machine learning in agriculture mainly lies in the soil parameter prediction, crop yield prediction, detection of pests and weeds, intelligent harvesting, intelligent irrigation and livestock management [30,31,32,33,34,35]. In intelligent irrigation, some scholars applied machine learning methods to predict the hydraulic performance of drip irrigation emitters. Li et al. [36] obtained the relationship between the path area and length of the fractal path and the discharge coefficient of the fractal flow path emitter by using a support vector machine. Guo et al. [37] employed the support vector machine to predict the discharge of a two-way mixed-flow emitter, and the model inputs were the emitter’s structure parameters and working pressure. The work concluded that the average relative error between the predicted value of the support vector machine model and the actual value was 1.91%. Lavanholi et al. [38] used the structural parameters of the trapezoidal labyrinth channel emitter and the working pressure as the inputs of the artificial neural network model, and the discharge as the output. The results showed that the maximum relative error of the predicted results was 9.5%. Mattar et al. [39] compared the prediction results of the artificial neural network model and the gene expression programming model for the emitter discharge variation and manufacturer’s coefficient of variation, and the structural parameters of the tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitter, water temperature and working pressure were used as the model inputs. They found out that the artificial neural network model was better than the gene expression programing model. Seyedzadeh et al. [40] applied the artificial neural network, neuro-fuzzy sub-clustering, neuro-fuzzy c-means clustering, and least-squares support-vector machine to predict the drip irrigation tape’s discharge with working pressure, water temperature, discharge coefficient, discharge exponent and nominal discharge as the model inputs. The results revealed that the least-squares support-vector machine model had the lowest error. The above literature review confirms the feasibility of machine learning methods in predicting the hydraulic performance of emitters, such as the discharge, discharge coefficient, manufacturing coefficient error, and discharge variation. However, there is no literature on predicting the discharge exponent of drip irrigation emitters. Hence, the machine learning methods (artificial neural network (ANN) and support vector regression (SVR)) are used to establish the models for predicting the discharge exponent of tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitters, with their structural parameters as the model inputs in this study, and compared these with the results predicted by the traditional RSM model. The predicted performance of the three models (RSM, ANN, and SVR) was evaluated via a statistical comparison between the discharge exponent obtained from the models and the experimental measured results.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Geometry of the Drip Irrigation Emitter
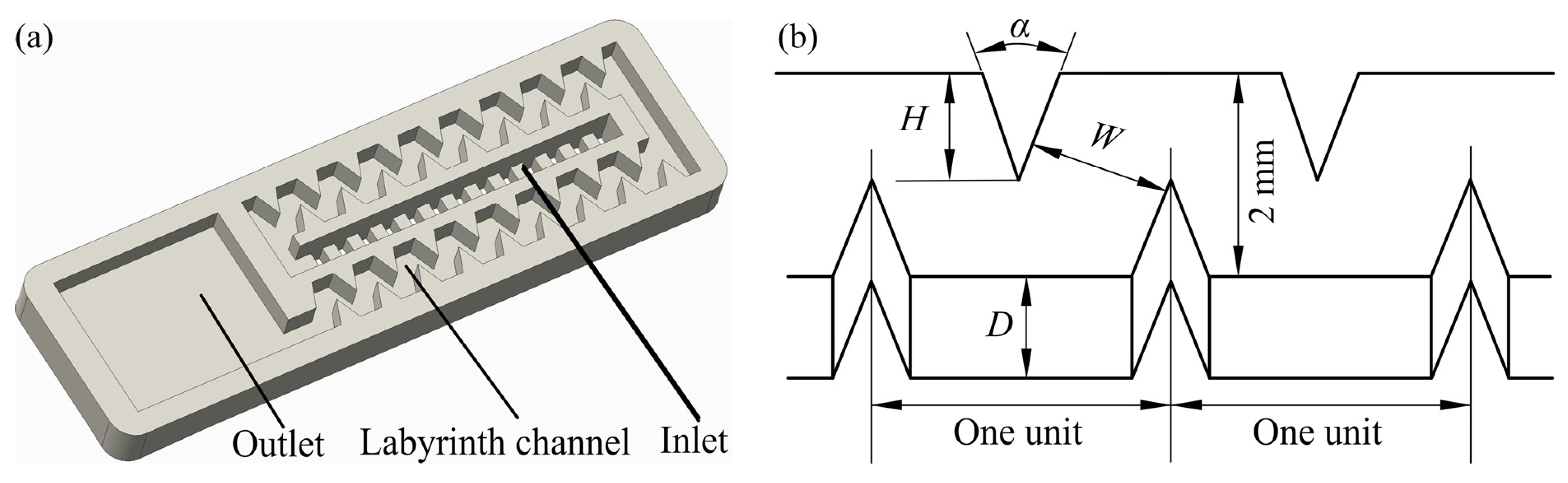
The physical model of the tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitter studied in this paper and its tooth-shaped structure is shown in Figure 1. The five structural parameters of the tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitter (i.e., number of channel units (N), channel depth (D), tooth angle (α), tooth height (H) and channel width (W)) are extracted for the parametric design.
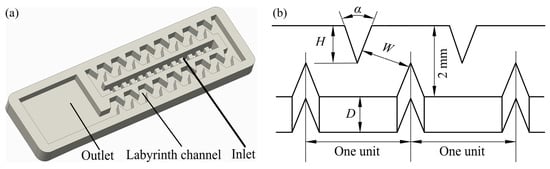
Figure 1.
Physical model and structural parameters of the tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitter. (a) Physical model and (b) structural parameters of the tooth-shaped labyrinth channel unit. N indicates the number of channel units, D indicates the channel depth, α indicates the tooth angle, H indicates the tooth height, and W indicates the channel width.
2.2. Experiment Layout and Procedures
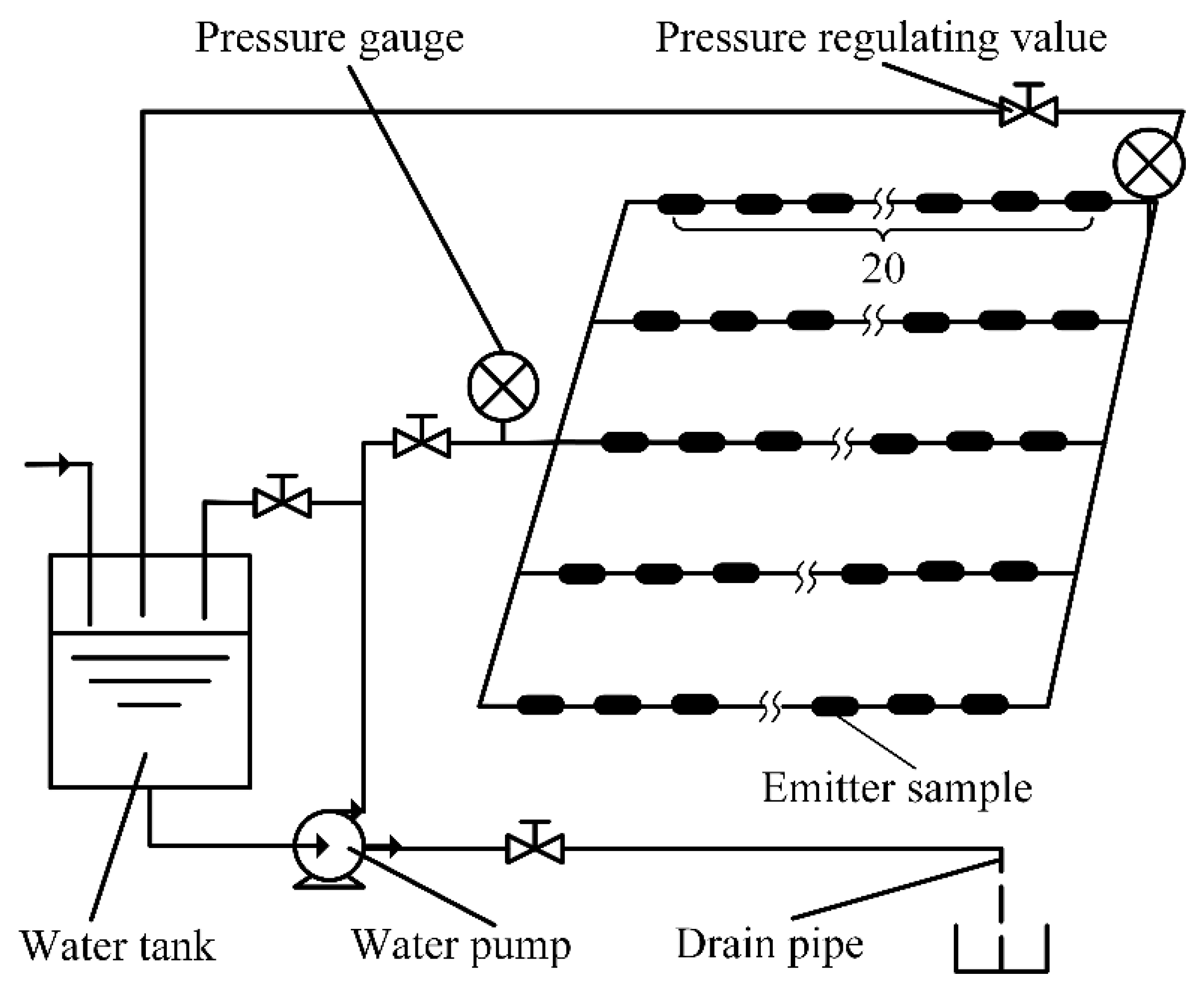
The hydraulic performance experimental platform of the drip irrigation emitter layout is shown in Figure 2. The tap water was used as experimental water. The 3D-printing method was used to manufacture the emitter samples. A total of 5 drip irrigation tapes were installed on the hydraulic performance experimental platform, and 20 emitter samples were installed on each drip irrigation tape, so a total of 100 emitter samples was installed on the hydraulic performance experimental platform.
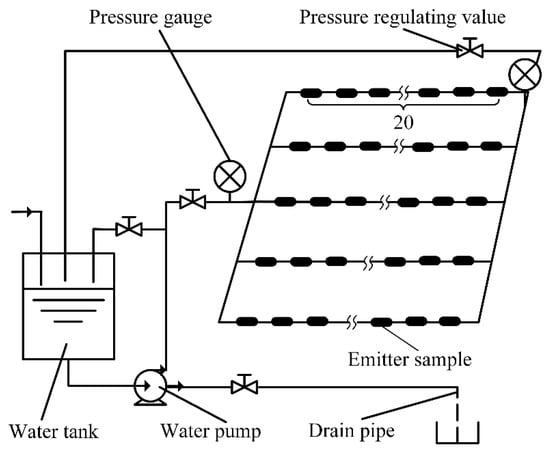
Figure 2.
Layout of the hydraulic performance experimental platform.
In this study, the discharge of each emitter model was measured under the water pressures (P) of 10 kPa, 20 kPa, 30 kPa, 40 kPa, 50 kPa, 60 kPa, 70 kPa, 80 kPa, 90 kPa, and 100 kPa. The test for each emitter model was repeated four times. The average value of the four tests was taken as the discharge of each emitter model at each pressure condition. At each pressure stage, an already-weighed measuring cup was placed under each sample to measure the discharge, and after 5 min, the measuring cup was removed for weighing. The emitter discharge (Q) was calculated as follows:
where j is the number of emitter samples, k is the number of tests, T is the measure time (min), mjkT is the total weight of the water within the time T and empty measuring cup (g), and mjk is the weight of the empty measuring cup (g).
2.3. Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
In this study, the effect of the five structural parameters of the emitter and their interaction on its discharge exponent was studied by the response surface methodology (RSM) applying the Box–Behnken Design (BBD). The factor variables (dependent variables) were the number of channel units (N, 12–20), channel depth (D, 0.8–1.2 mm), tooth angle (α, 30–60°), tooth height (H, 0.8–1.2 mm), and channel width (W, 0.6–1.0 mm), and the response variable (independent variable) was the emitter discharge exponent. The code and levels of the factor variables are listed in Table 1. According to the statistical requirements of the Box–Behnken experimental design, a total run of 45 experiments was carried out, and the experimental design and results are shown in Table 2.

Table 1.
Levels and code of the five structural factors.

Table 2.
The coded and actual values of the structural factors.
The mathematical relationship between the emitter discharge exponent and structural parameters is described by the quadratic polynomial equation below:
where y is the predicted response; x1, x2, x3, x4, and x5 are the independent variables; β0 is the model regression intercept; β1, β2, β3, β4, and β5 are the linear regression coefficients; β12, β13, β14, β15, β23, β24, β25, β34, β35, and β45 are the interaction regression coefficients; and β11, β22, β33, β44, and β55 are the quadratic regression coefficients.
y = β0 + β1 x1 + β2 x2 + β3 x3 + β4 x4 + β5 x5 + β12 x1 x2 + β13 x1 x3 + β14 x1 x4 + β15 x1 x5 + β23 x2 x3 + β24 x2 x4 + β25 x2 x5 + β34 x3 x4 + β35 x3 x4 + β45 x4 x5 + β11 x12 + β22 x22+ β33 x132+ β44 x42+ β55 x52
2.4. Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
The artificial neural network (ANN) is a mathematical model or computational model established by imitating the structure and function of a biological neural network. The neuron is the core component and the most basic unit of the artificial neural network. Neurons form the input layer, the output layer, and the hidden layer. Each neuron in a hidden layer is connected with the neurons in the previous layer and the next layer through weights to form a complete neural network. The input layer is mainly used to obtain input information, that is, independent variables. The input layer data is weighted and transferred to the hidden layer. Then, the hidden layer uses the activation function to process the data and transmits the hidden layer information to the output layer. Finally, the model processing results (the dependent variables) are output through the output layer. The effective parameters that affect the accuracy of an ANN model include the number of hidden layers, the number of neurons in each hidden layer, the activation function, the learning rate, the learning rate optimization algorithm, the momentum term, and the number of iterations. The activation functions mainly include sigmoid, tanh, relu, and linear activation functions. Commonly used learning rate optimization algorithms include stochastic gradient descent (SGD), the limited-memory Broyden—Fletcher–Goldfarb–Shanno (LBFGS) algorithm, and adaptive moment estimation (Adam). In the present study, the input layer has five neurons, which are the number of channel units (N), channel depth (D), tooth angle (α), tooth height (H), and channel width (W). The output layer has only one neuron, which is the discharge exponent (x). The tanh function and Adam algorithm were selected as the activation function and the learning rate optimization algorithm, respectively. The Bayesian optimization method is employed for optimizing the number of hidden layers, the number of neurons in each hidden layer, the learning rate, the momentum term, and the number of iterations. The k-fold cross-validation approach is an effective way to avoid model overfitting. Therefore, a 5-fold cross-validation approach was used for data division in this study. In order to eliminate the influence of the difference in the value range among the indicators, the standardization of data was carried out.
2.5. Support Vector Regression (SVR)
The support vector machine is a machine learning method that implements classification or regression by constructing one or a set of hyperplanes in a high-dimensional space, where the method used for regression is called support vector regression (SVR). The kernel function is used in an SVR model to solve a linearly inseparable problem. Since the kernel function is one of the important factors affecting the accuracy of the SVR model, it is particularly important to choose an appropriate kernel function for the SVR model. At present, the kernel functions of the SVR model are mainly divided into four types, namely, the linear, polynomial, radial basis function (RBF), and sigmoid. In addition, after the kernel function is selected, the hyperparameters also affect the performance of the SVR model, such as gamma, C, and epsilon, so the selection of the hyperparameters is also a key step in SVR modeling. In this study, the radial basis function (RBF) was selected as the kernel function. Similarly, the Bayesian optimization method was employed for hyperparameters optimization, the standardization of data was carried out, and a 5-fold cross-validation approach was used for data division.
2.6. Indices for Evaluating Modeling Accuracy
The coefficient of determination (R2), the root-mean-square error (RMSE), and the mean absolute error (MAE) were employed to evaluate the accuracy of the RSM, ANN, and SVR models in the present study.
where Mi and Ei are the discharge exponents of the No. i drip irrigation emitter measured via the hydraulic performance experiment and estimated via the applied estimation models, respectively; is the average discharge exponents measured via the hydraulic performance experiment; and N is the total number of measured discharge exponents.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. RSM Modeling
3.1.1. Statistical Analysis of Experimental Results
Design-Expert software was employed to process and analyze the experimental data. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted to check whether the RSM model fits the overall data and identify the degree of influence of the independent variables on the dependent variables. The ANOVA results of the response models of the discharge exponent are presented in Table 3. From Table 3, it can be observed that the significant value (p-value) of the regression model item is less than 0.01, while the p-value of the lack-of-fit item is greater than 0.05; in other words, the regression model is extremely significant and its lack-of-fit item is not significant, indicating that the regression model is reasonable and effective. The adequacy of the regression model was evaluated by the value of R2. For a good fit of a model, the value of R2 should be greater than 0.80, and the closer the value of R2 is to 1, the better the model fit. The value of R2 of the RSM model was 0.9851, indicating that the fitness of the model of discharge exponent was quite good. The adequate precision (AP) was used to measure the signal-to-noise ratio, its value of the regression model was 27.807, which was greater than 4, indicating that this model can be used to navigate the design space. The coefficient of variance (C.V. %) of the discharge exponent regression model was only 0.84%, which was much lower than 10%, indicating that the model had good reliability and precision. These statistical results show that the predicted values of the discharge exponential response surface model are in good agreement with the measured values.

Table 3.
ANOVA for the response of the discharge exponent.
The p-value is an indicator used to access the intensity of the influence of independent variables on dependent variables. When the p-value of a factor is less than 0.05, it can be considered that the influence of the factor on the response variable is significant, and the lower the p-value, the greater the influence of the factor. According to Table 3, in the linear term, excluding the number of channel units (N), the channel depth (D), tooth angle (α), tooth height (H), and channel width (W) all had extremely significant influences on the discharge exponent. In the interaction term, the interaction between the number of channel units and the tooth height (N × H), the interaction between the channel depth and the tooth height (D × H), and the interaction between the tooth height and the channel width (H × W) had extremely significant influences on the discharge exponent, while the remaining interaction factors had no significant influence. In the square term, the square term of the tooth height (H2) and the square term of channel width (W2) had extremely significant influences on the discharge exponent, while the other square terms had no significant influence on the discharge exponent. Moreover, it can be observed that the linear term, square term of the tooth height, and its interaction term with other structural factors all had a significant effect on the discharge exponent, indicating that the tooth height was a key factor affecting the discharge exponent of the tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitters.
It can be observed from Table 3 that the factors that have a significant effect are ranked in order of their effect on the discharge exponent, according to the F-value of each factor, which is as follows: square term of the tooth height (H2) > tooth height (H) > channel width (W) > tooth angle (α) > square term of channel width (W2) > interaction between the channel depth and the tooth height (D × H) > channel depth (D) > interaction between the number of channel units and the tooth height (N × H) > interaction between the tooth height and the channel width (H × W).
The relationship between the discharge exponent and the structural factors can be written based on the ANOVA regression coefficients of the BBD model as:
x = 1.75049 + 5.90729 × 10−3 × N − 0.041229 × D +7.83333 × 10−5 × α − 2.31267 × H − 0.34817 × W − 2.81250 × 10−4 × N × D + 4.16667 × 10−6 × N × α − 7.96875 × 10−3 × N × H + 2.50000 × 10−4 × N × W − 3.66667 × 10−4 × D × α + 0.15313 × D × H + 7.50000 × 10−3 × D × W + 6.66667 × 10−5× α × H − 1.10000 × 10−3 × α × W + 0.19125 × H × W + 5.76823 × 10−5 × N2 − 0.039010 × D2 + 7.58333 × 10−6 ×α2 + 1.01849 × H2 + 0.14557 × W2
3.1.2. The Interactive Effects on the Discharge Exponent
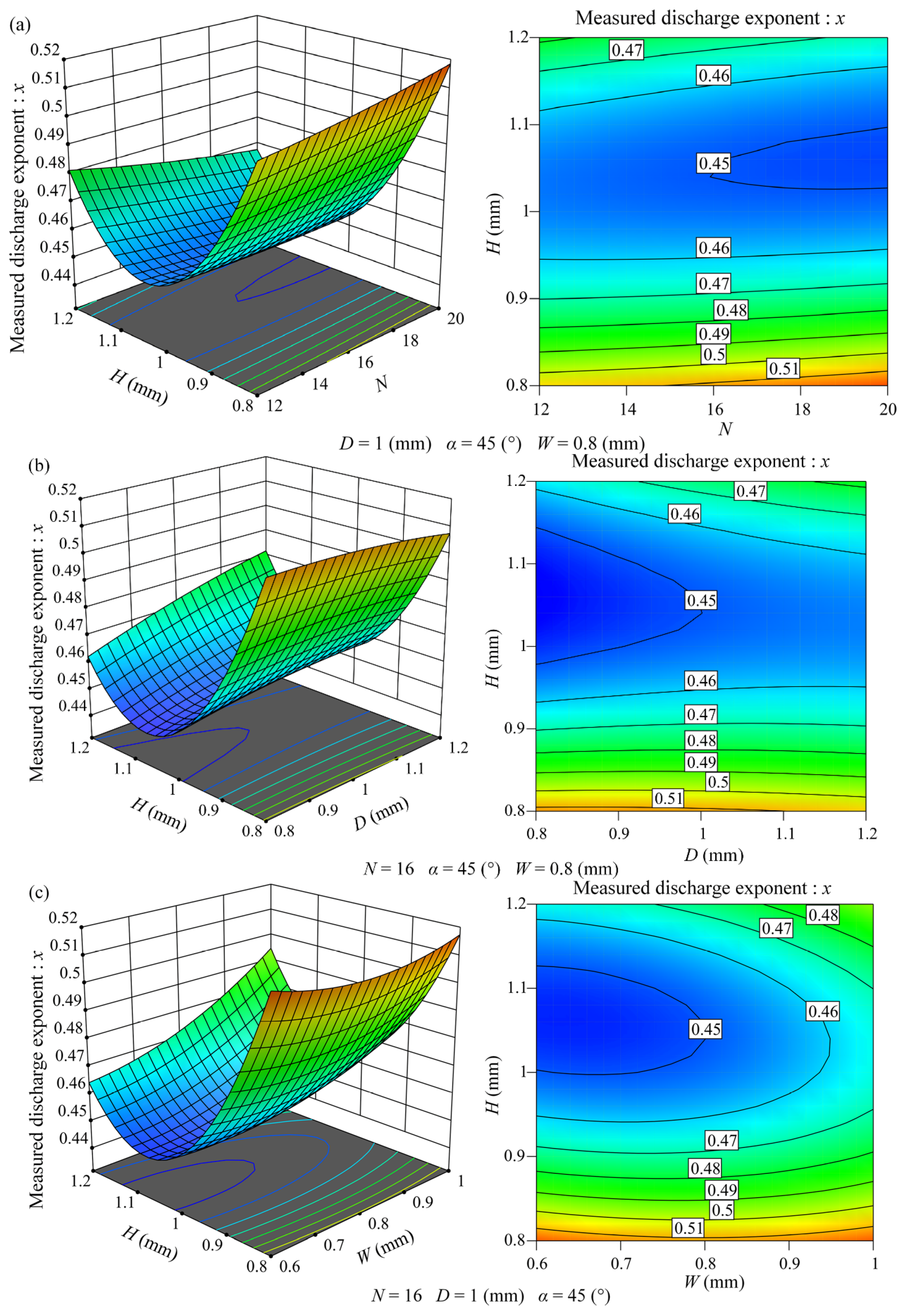
The interactions between the variables on the discharge exponent, which has a significant influence, are illustrated in Figure 3. When the interaction between two structural variables on the discharge exponent was studied, the other three structural variables were at center levels.
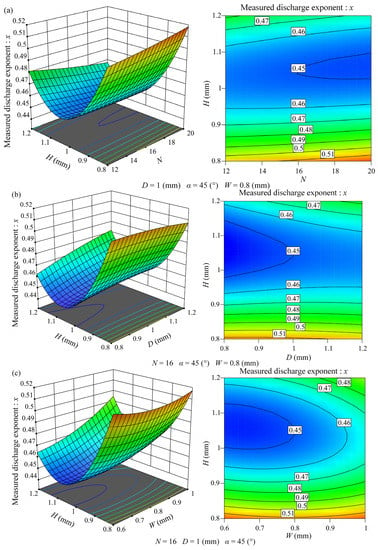
Figure 3.
3D response surface plots and contour plots. (a) Interaction between the number of channel units and the tooth height (N × H); (b) interaction between the channel depth and the tooth height (D × H); and (c) interaction between the tooth height and the channel width (H × W).
The three-dimensional response surface plot and the contour plot of the interactions between the tooth height and the number of channel units, channel depth, and channel width (N × H, D × H, H × W) on the discharge exponent are shown in Figure 3a–c, respectively. It can be observed from Figure 3 that when the number of channel units, the channel depth, or the channel width changes, the variation range of the discharge exponent with the increase in the tooth height is affected by the changes in the other three structural factors, but the variation trend of the discharge exponent with the increase in the tooth height is same, which first decreased and then increased. However, when the tooth height took different values, the variation trends of the discharge exponent with the increase in the other three structural factors were different. By comparing the variation range of the discharge exponent with the change of tooth height in the three figures, it can be observed that, no matter what, the values of the other three structural factors are the discharge exponent when the tooth height is 1.2 mm, which is significantly smaller than that when the tooth height is 0.8 mm, indicating that moderately increasing the tooth height can reduce the discharge exponent of the tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitters, but excessively increasing the tooth height is not conducive to reducing the discharge exponent of the tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitters.
Figure 3a displays that when the tooth height exceeds 0.95 mm, the discharge exponent decreases with the increase in the number of channel units, whereas when the tooth height is less than 0.95 mm, the discharge exponent increases with the increase in the number of channel units. Figure 3b shows that when the tooth height exceeds 0.9 mm, the discharge exponent increases with the increase in the channel depth, but when the tooth height is less than 0.9 mm, the discharge exponent slightly decreases with the increase in the channel depth. Figure 3c depicts that when the tooth height exceeds 0.95 mm, the discharge exponent increases with the increase in the channel width. When the tooth height is less than 0.95 mm, the discharge exponent first decreases and then increases with the increase in the channel width, but the variation range of the discharge exponent with the change of the channel width is very small, indicating that when the tooth height is small, the change of channel width can not significantly affect the discharge exponent.
3.2. ANN Modeling
The hyperparameters of the ANN model were optimized using the Bayesian optimization method based on the average R2 of 5-fold cross-validation. The optimization results show that, compared to the ANN model that has a single hidden layer and double hidden layer, the ANN model with 3 hidden layers has better prediction results, and the number of neurons of three hidden layers is four, six, and four, respectively. After modeling the data with the ANN model with the three hidden layers, the Bayesian optimization results show that the model with hyperparameter values, such as learning rate = 0.0143, momentum term = 0.6, and the number of iterations = 6000, results in the predicted discharge exponent that is closest to the measured discharge exponent.
The 5-fold cross-validation results of the ANN model with the optimal hyperparameters are shown in Table 4. From Table 4, it can be observed that the average R2 is 0.9496, indicating that the estimated value from the ANN model was in good agreement with the measured value obtained from the experiment. The values of the average RMSE and MAE were also small, which were 0.0048 and 0.0036, respectively, indicating that the error between the estimated value and the measured value was small. Moreover, the five values of R2, RMSE, and MAE of the 5-fold cross-validation were all relatively close, indicating that the established ANN model had good robustness. Based on the above analysis, it can be concluded that the established ANN model has a high accuracy when predicting the discharge exponent of tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitters.

Table 4.
Values of the evaluation indices of the 5-fold cross validation for the ANN model.
3.3. SVR Modeling
Based on the SVR model with the kernel function of RBF, the Bayesian optimization results show that when gamma is 0.01203, C is 522.001, and epsilon is 0.0001; the value of average R2 of 5-fold cross-validation is the largest. The values of the R2, RMSE, and MAE statistical indices for the best SVR model are listed in Table 5.

Table 5.
Values of the evaluation indices of the 5-fold cross-validation for the SVR model.
As can be observed in Table 5, the established SVR model with the average R2, the average RMSE, and the average MAE of 0.9696, 0.0037, and 0.0031 had a high correlation between the predicted values and the measured values. In addition, the ranges of the R2 value, RMSE value, and MAE value in the 5-fold cross-validation for the established SVR model were 0.9552~0.9863, 0.0028~0.0046, and 0.0026~0.0038, respectively. Furthermore, it can be observed that the changes of the three indices are minor, which demonstrates that the SVR model has high robustness. The above results determine that the established SVR model has an excellent prediction capability to simulate the discharge exponent of the tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitters.
3.4. Comparison of the Applied Models
In order to compare the 5-fold cross-validation results of the ANN and SVR models, the R2, RSME, and MAE values of the RSM model, according to the data of the 5-fold cross-validation approach, were calculated, and the results are presented in Table 6.

Table 6.
Values of the evaluation indices of the 5-fold cross-validation for the RSM model.
A comparison of the results presented in Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6 shows that the average R2 for the SVR model is closer to one than that produced by the ANN and RSM models. The average RMSE in the RSM model (0.0055) was 1.15 times the value produced by the ANN model (0.0048), and 1.49 times that produced by the SVR model (0.0037). The average MAE in the RSM model (0.0046) was 1.28 times that produced by the ANN model (0.0036), and 1.48 times that produced by the SVR model. The results reveal that the prediction accuracy of the SVR model is greater than the ANN and RSM models, and the prediction accuracy of the ANN model is greater than the RSM model.
Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6 determine that the maximum difference of R2 in the 5-fold cross-validation is 0.0686 in the ANN model, 0.0311 in the SVR model, and 0.0791 in the RSM model, respectively. It can be observed that the maximum difference of R2 of RSM model is 1.15 times that produced by ANN model, and 2.54 times that produced by SVR model; therefore, the robustness of the RSM model is worse than the ANN and SVR models, and the robustness of the SVR model is the best.
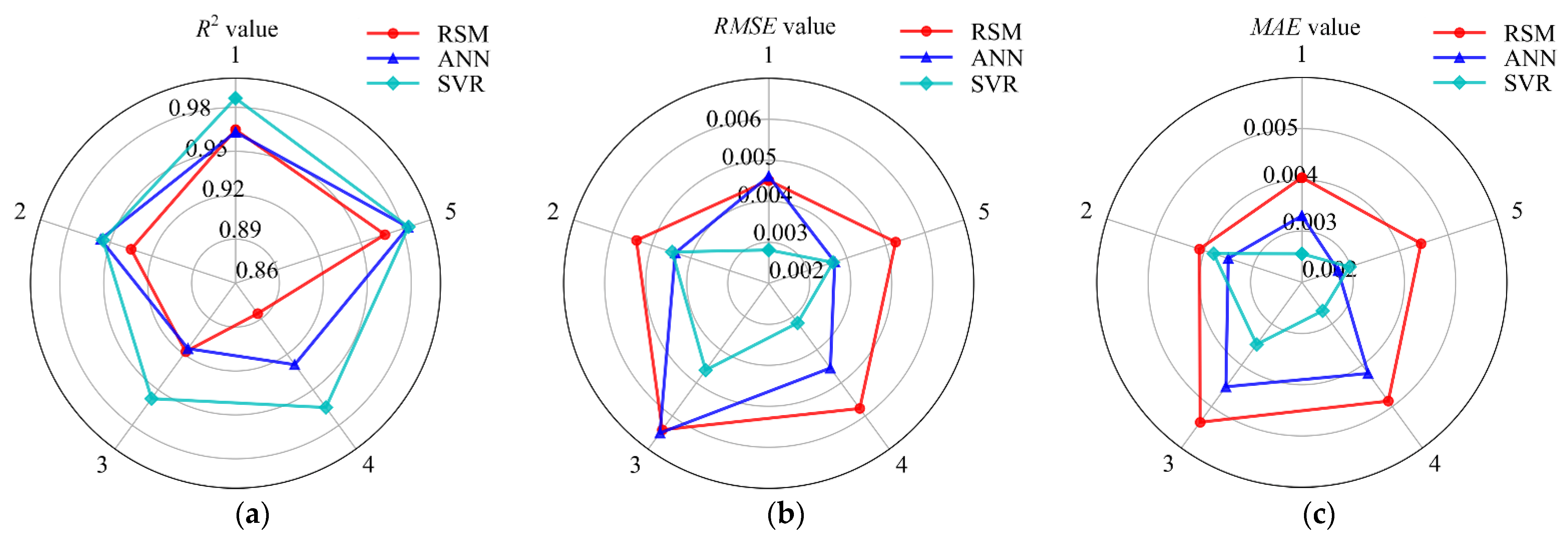
The radar diagrams of 5-fold cross-validation for the three estimation models in terms of R2, RSME, and MAE are illustrated in Figure 4. From an observation of Figure 4a, the 5 R2 values of the SVR model are all greater than 0.95, which are all greater than the corresponding values of the RSM model. Although the ANN model performed slightly better than the SVR model in the second-fold cross-validation, the other four values of the SVR model were greater than that of the ANN model. Comparing the five R2 values of the ANN and RSM models, it was found that the RSM model performed slightly better than the ANN model in the first and third fold of the cross-validation, but the results of the other three-fold cross-validations were lower than those of the ANN model. For the RMSE estimated metric (Figure 4b), the comparison results of the three models were completely consistent with the R2 estimated metric comparison results. In Figure 4c, it can be observed that, for the MAE term, the five values in the SVR and ANN models are all larger than those of the RSM model. The MAE values of the SVR model were lower than that of the ANN model in the second-fold cross-validation and fifth-fold cross-validation, but the other three-fold cross-validation results were better than the ANN model. Overall, in the radar diagram, the RMSE and MAE values of the SVR model had the smallest area and R2 value had the largest area, thus the prediction performance of the SVR model was the best among the three models, and the ANN model was second only to the SVR model.
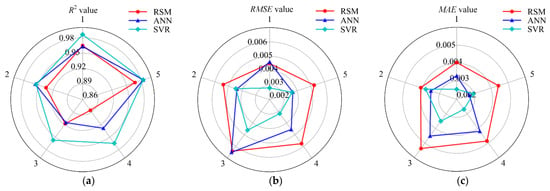
Figure 4.
Radar diagrams of the 5-fold cross-validation for the three estimation models in terms of R2, RMSE, and MAE. (a) R2, (b) RMSE, and (c) MAE.
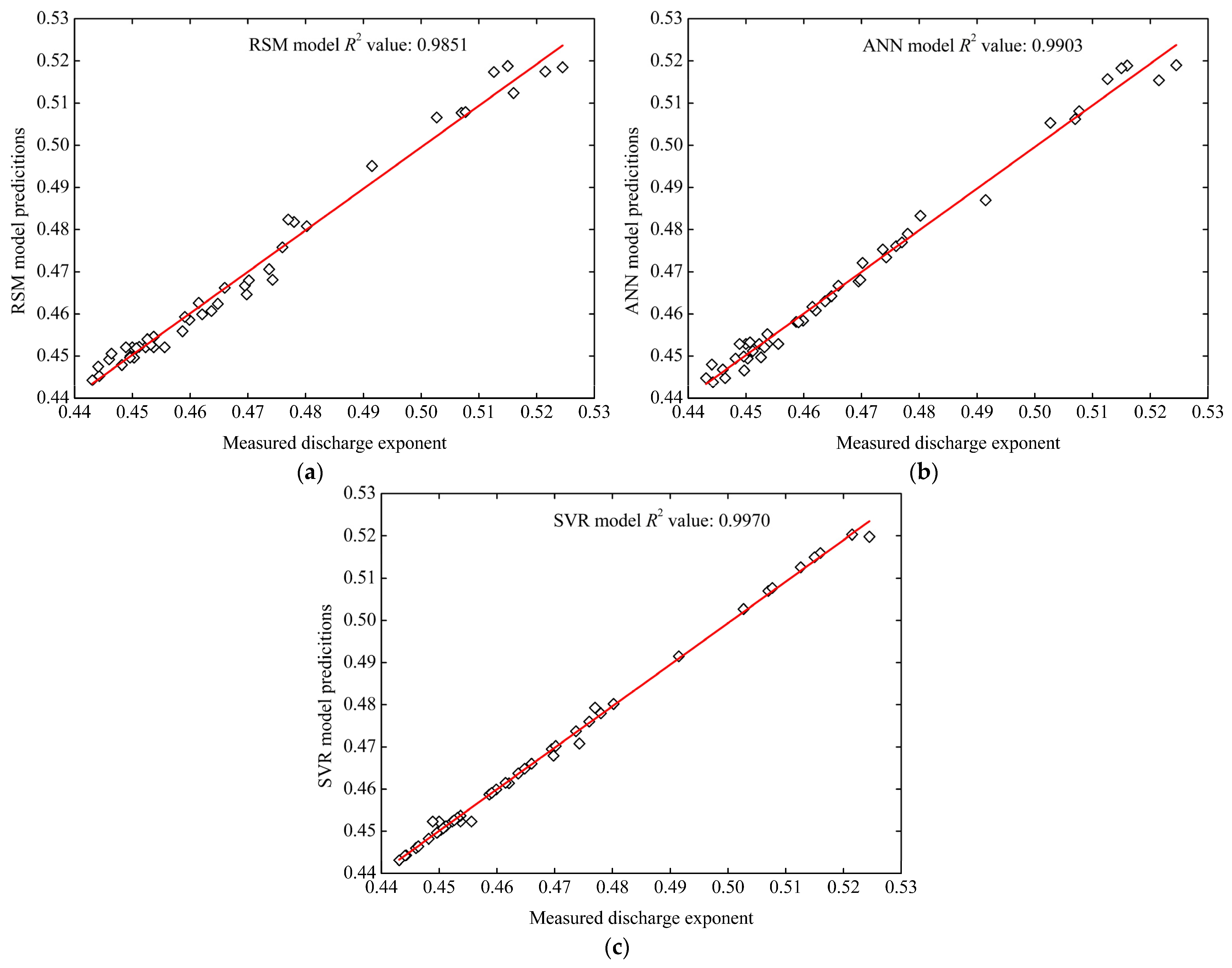
Figure 5 shows the linear dependency relationship between the predicted values of the 3 models and all 45 experiment measured values. According to Figure 5, an R2 value of 0.9851 for all the data was produced by the RSM model, and the R2 values of the ANN and SVR models were 0.9903 and 0.9970, respectively. Thus, the values of R2 demonstrated that the linear fitting relationship between the predicted results of the three models and the experimental results were all good, but among the three models, the predicted results of the SVR model were the most approximate to the experimental results, and the second was the ANN model.
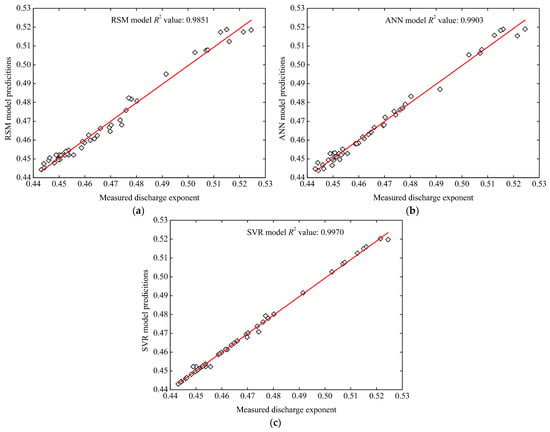
Figure 5.
Comparison of the RSM, ANN, and SVR performances for all data sets. (a) RSM model, (b) ANN model, and (c) SVR model.
The comparison results between the measured discharge exponent from 45 experiments and the predicted discharge exponent from three models are listed in Table 7. The relative error, which refers to the ratio of the deviation between the predicted value and experimental value to the experimental value, was used to describe the prediction error between the experimental value and the predicted value in this study. From Table 7, it can be observed that the range of the relative error between the experiment measured values and predicted values for the RSM, ANN, and SVR models are 0~1.3072%, 0~1.1697%, and 0~0.8961%, respectively. The results clearly demonstrate that the SVM model leads to the smallest relative error compared to the ANN and RSM models. Furthermore, the mean relative error between the experiment measured values and predicted values for RSM was 0.4825%, and increased by 27.24% and 315.59%, compared to that for the ANN (0.3792%) and SVR (0.1161%) models, respectively. In summary, the predicted value of the SVR model was more similar to the actual measured value, so the SVR approach performed extremely well in predicting the discharge exponent of tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitters.

Table 7.
Experimental result comparisons of the RSM, ANN, and SVR model predictions.
4. Discussion
Some scholars studied the influence of the same structural variable on the discharge exponent of a drip irrigation emitter, but they obtained different influence laws. On the one hand, this may be caused by the different value ranges of the studied structural parameter; on the other hand, it may also be caused by the interactive influence between the structural parameters, that is, the influence law of a structural factor on the discharge exponent may be affected by the value of other structural factors [16]. If there is a significant interactive influence between the structural variables, but this influence is ignored in the research and analysis, a one-sided conclusion will be drawn. Therefore, in order to fully and accurately understand the influence of the structure on the discharge exponent of the emitters, the interactive influence between the structural parameters must be considered. At present, most of the influence laws between structural factors and the discharge exponent of emitters studied by scholars are obtained without considering the interactive influence between the factors. The interactive influence between the structural factors of the tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitter was studied using the RSM model in this paper. The statistical analysis results show that for the tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitter, the interaction between the number of channel units and the tooth height, the interaction between the channel depth and the tooth height, and the interaction between the tooth height and the channel width all have extremely significant effects on the discharge exponent (Table 3). The results of the interaction analysis show that when the tooth height takes the maximum value (1.2 mm) and minimum value (0.8 mm) of the research range, the influence laws of the discharge exponent with the increase in the number of channel units, the channel depth, or the channel width are obviously different, and even displays the opposite trend for the number of channel units is (Figure 3). The above analysis and discussion fully reveal that the interactive effects between the factors cannot be ignored in the study of the influence of the structural factors on the emitters’ discharge exponents.
Many researchers used the prediction mechanism of machine learning models to predict irrigation needs, for example, Adeyemi et al. [41] used the machine learning method to predict the temporal soil moisture fluxes based on past soil moisture, precipitation, and climatic measurements, and Ahmadi et al. [42] used the machine learning method to estimate evapotranspiration based on climate parameters. These studies helped to improve irrigation decisions and refine the construction of smart irrigation systems. However, the final execution component of the irrigation decision is the drip irrigation emitters, and the performance of the emitters determines whether the implementation of irrigation decisions can reach the theoretical level; therefore, realizing the performance prediction of the drip irrigation emitters is crucial to the development of intelligent irrigation. By applying machine learning techniques to drip irrigation emitters’ performance predictions, once the machine learning model is successfully trained, whenever a new design for the structure of an emitter is proposed, its hydraulic performance can be quickly and accurately presented by the machine learning model. In this study, two machine learning models, ANN and SVR, were used to predict the discharge exponent of emitters, which is an under-researched area. In addition, the prediction results of the two machine learning models are compared with the results predicted by the traditional RSM model. The compared results indicate that the SVR model has the best robustness and accuracy among the three models. However, the discharge exponent prediction model established in this study is based on laboratory data. The actual field irrigation situation is more complicated than the laboratory situation, so future work involves testing the discharge exponent prediction model in field conditions. In addition, further research needs to be carried out in relation to different terrains, different crops, and different climatic conditions.
5. Conclusions
The hydraulic performance of drip irrigation emitters is very important for drip irrigation systems, and the discharge exponent is an important standard to evaluate the hydraulic performance of drip irrigation emitters. In this study, the response surface methodology (RSM) and machine learning models (artificial neural network (ANN) and support vector regression (SVR)) were used to predict the change of discharge exponents of tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitters due to structural parameters. The structural parameters were the number of channel units (N), the channel depth (D), the tooth angle (α), the tooth height (H), and the channel width (W). The response surface methodology results demonstrate that the tooth height is the most important parameter for determining the discharge exponent of a tooth-shaped labyrinth channel emitter in the range of this study. The discharge exponent showed a non-linear trend with the increase in the tooth height, which first decreased and then increased. Moreover, the value of the tooth height affected the influence law of the channel depth, channel width, and the number of channel units on the discharge exponent. The prediction accuracy of the developed ANN model and SVM model was compared with the RSM model; the comparison results show that the SVR model is better than the ANN model, and the two machine learning models show a better prediction performance than the traditional RSM model. In addition, the mean relative error between the experiment measured values and predicted values for the three models were 0.4825%, 0.3792%, and 0.01161%, respectively, which exhibited that the predicted discharge exponent of the SVR model was closest to the experiment measured value. The findings of this study show that the SVR model can predict the discharge exponent of emitters accurately and reliably, as well as save time and cost when it comes to conducting the experiments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.C.; methodology, X.C.; investigation, X.C. and K.H.; data curation, X.C.; writing—original draft preparation, X.C.; writing—review and editing, X.C. and Z.W.; supervision, Z.W.; funding acquisition, Z.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Plan of China, grant number 2017YFD0201504-2.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kourgialas, N.N. A critical review of water resources in Greece: The key role of agricultural adaptation to climate-water effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, L.; Saito, H.; Saefuddin, R.; Simunek, J. Evaluation of subsurface drip irrigation designs in a soil profile with a capillary barrier. Water 2021, 13, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christias, P.; Mocanu, M. A machine learning framework for olive farms profit prediction. Water 2021, 13, 3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattar, M.A.; Alamoud, A.I. Artificial neural networks for estimating the hydraulic performance of labyrinth-channel emitters. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 114, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, N.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Long, J. Influence of flushing pressure, flushing frequency and flushing time on the service life of a labyrinth-channel emitter. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 172, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Ren, S.; Xu, W. Hydraulic characterizations of tortuous flow path drip irrigation emitter. J. Hydrodyn. 2006, 18, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.; Wei, Z.; Tang, Y.; Lu, B. Numerical and experimental study on hydraulic performance of emitters with arc labyrinth channels. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2007, 56, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, N.; Zhou, B. Simulation and verification of hydraulic performance and energy dissipation mechanism of perforated drip irrigation emitters. Water 2021, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.; Karmeli, D. Trickle irrigation design parameters. Trans. ASABE 1974, 17, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmeli, D.; Keller, J. Trickle Irrigation Design; Rain Bird Sprinkler Manufacturing Corp.: Glendora, CA, USA, 1975; 133p. [Google Scholar]
- ASABE. EP-458: Field Evaluation of Microirrigation Systems; ASABE: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.; Lu, B. New method of hydraulic performance evaluation on emitters with labyrinth channels. J. Irrig. Drainage Eng.-ASCE 2011, 137, 811–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, J.; Alam, M.; Zhao, Y. Influence of geometrical parameters of labyrinth flow path of drip emitters on hydraulic and anti-clogging performance. Trans. ASABE. 2006, 49, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.; Yu, L.; Wu, P.; Fan, X.; Zhang, L. Influence of angle of labyrinth channels on anti-clogging performance of emitter. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2009, 40, 51–67, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Al-Alamoud, A.I.; Mattar, M.A.; Ateia, M.I. Impact of water temperature and structural parameters on the hydraulic labyrinth-channel emitter performance. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2014, 12, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.D.; Gong, S.H.; Wang, H.T.; Mo, Y. Numerical simulation of hydraulic performance of tooth-form channel of labyrinth emitter. J. Drain. Irrig. Mach. Eng. 2019, 38, 71–76, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Moghaddam, T.B.; Soltani, M.; Karim, M.R.; Baaj, H. Optimisation of asphalt and modifier contents for polyethylene terephthalate modified asphalt mixtures using response surface methodology. Measurement 2015, 74, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danmaliki, G.I.; Saleh, T.A.; Shamsuddeen, A.A. Response surface methodology optimisation of adsorptive desulfurization on nickel/activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, H.; Farhudi, Z.; Behroozi-Khazaei, N. Multi-objective optimisation of savory leaves drying in continuous infrared-hot air dryer by response surface methodology and desirability function. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 168, 105112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Lv, S. Financial credit risk prediction in internet finance driven by machine learning. Neural. Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 8359–8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, J.; Mohan, S. Machine learning in gifted education: A demonstration using neural networks. Gifted. Child. Q. 2019, 63, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacEachern, S.; Forkert, D. Machine learning for precision medicine. Genome 2021, 64, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshtegar, B.; Bagheri, M.; Yaseen, Z.M. Shear strength of steel fiber-unconfined reinforced concrete beam simulation: Application of novel intelligent model. Compos. Struct. 2019, 212, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Jain, A.; Gupta, P.; Chowdary, V. Machine learning applications for precision agriculture: A comprehensive review. IEEE Access 2020, 9, 4843–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, L.; Wu, P.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yao, C. Hydraulic performance and parameter optimisation of a microporous ceramic emitter using computational fluid dynamics, artificial neural network and multi-objective genetic algorithm. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 189, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassan, S.; Xi, C.; Gupta, P.; Jhanjhi, N.; Raza, H. A smart comparative analysis for secure electronic websites. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2021, 30, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, J.; Ocampo, R.; Gross, D.; Tavakoli, M. Intelligent robotics incorporating machine learning algorithms for improving functional capacity evaluation and occupational rehabilitation. J. Occup. Rehabil. 2020, 30, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, H.; Pan, B.; Law, R. Machine learning in internet search query selection for tourism forecasting. J. Travel Res. 2020, 60, 1213–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Diao, L.; Zang, Z.; Che, H.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X. A Machine-Learning Approach Combining Wavelet Packet Denoising with Catboost for Weather Forecasting. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, S.; Fulton, J.; Klopfenstein, A.; Douridas, N.; Shearer, S. Integration of high resolution remotely sensed data and machine learning techniques for spatial prediction of soil properties and corn yield. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 153, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlingaryan, A.; Sukkarieh, S.; Whelan, B. Machine learning approaches for crop yield prediction and nitrogen status estimation in precision agriculture: A review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 151, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, A.; Goyal, M.; Gupta, D.; Khanna, A.; Hassanien, A.E.; Pandey, H.M. An optimized dense convolutional neural network model for disease recognition and classification in corn leaf. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 151, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, L.; Zhang, J.; Whiting, M.; Karkee, M.; Zhang, Q. Determination of key canopy parameters for mass mechanical apple harvesting using supervised machine learning and principal component analysis (PCA). Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 193, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, P.K.; Kumar, S.; Jaiswal, A.; Prasad, M.; Gandomi, A.H. Towards precision agriculture: IoT-enabled intelligent irrigation systems using deep learning neural network. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 17479–17491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, R.; Smith, D.; Rawnsley, R.; Bishop-Hurley, G.; Hills, J.; Timms, G.; Henry, D. Dynamic cattle behavioural classification using supervised ensemble classifiers. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 111, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Ren, S.; Lei, X.; Wu, X.; Guan, X. Effects of fractal flow path designing and its parameters on emitter hydraulic performance. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2007, 43, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Bai, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhou, W.; Cheng, P. Establishment and validation of flow rate prediction model for drip irrigation emitter based on support vector machine. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 74–82, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lavanholi, R.; de Camargo, A.P.; Bombardelli, W.W.A.; Frizzone, J.A.; Ait-Mouheb, N.; da Silva, E.A.; de Oliveira, F.C. Prediction of pressure-discharge curves of trapezoidal labyrinth channels from nonlinear regression and artificial neural networks. J. Irrig. Drainage Eng-ASCE 2020, 146, 4020018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattar, M.A.; Alamoud, A.I.; Al-Othman, A.A.; Elansary, H.O.; Farah, A.H.H. Hydraulic performance of labyrinth-channel emitters: Experimental study, ANN, and GEP modeling. Irrig. Sci. 2020, 38, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedzadeh, A.; Maroufpoor, S.; Maroufpoor, E.; Shiri, J.; Bozorg-Haddad, O.; Gavazi, F. Artificial intelligence approach to estimate discharge of drip tape irrigation based on temperature and pressure. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 228, 105905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, O.; Grove, I.; Peets, S.; Domun, Y.; Norton, T. Dynamic neural network modelling of soil moisture content for predictive irrigation scheduling. Sensors 2018, 18, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, F.; Mehdizadeh, S.; Mohammadi, B.; Pham, Q.B.; Doan, T.N.C.; Vo, N.D. Application of an artificial intelligence technique enhanced with intelligent water drops for monthly reference evapotranspiration estimation. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).