An Operational Model for Remote Estimating Absorption of Optical Activity Constituents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets Used
2.2. Construction of the TAA Model
2.3. Accuracy Assessment
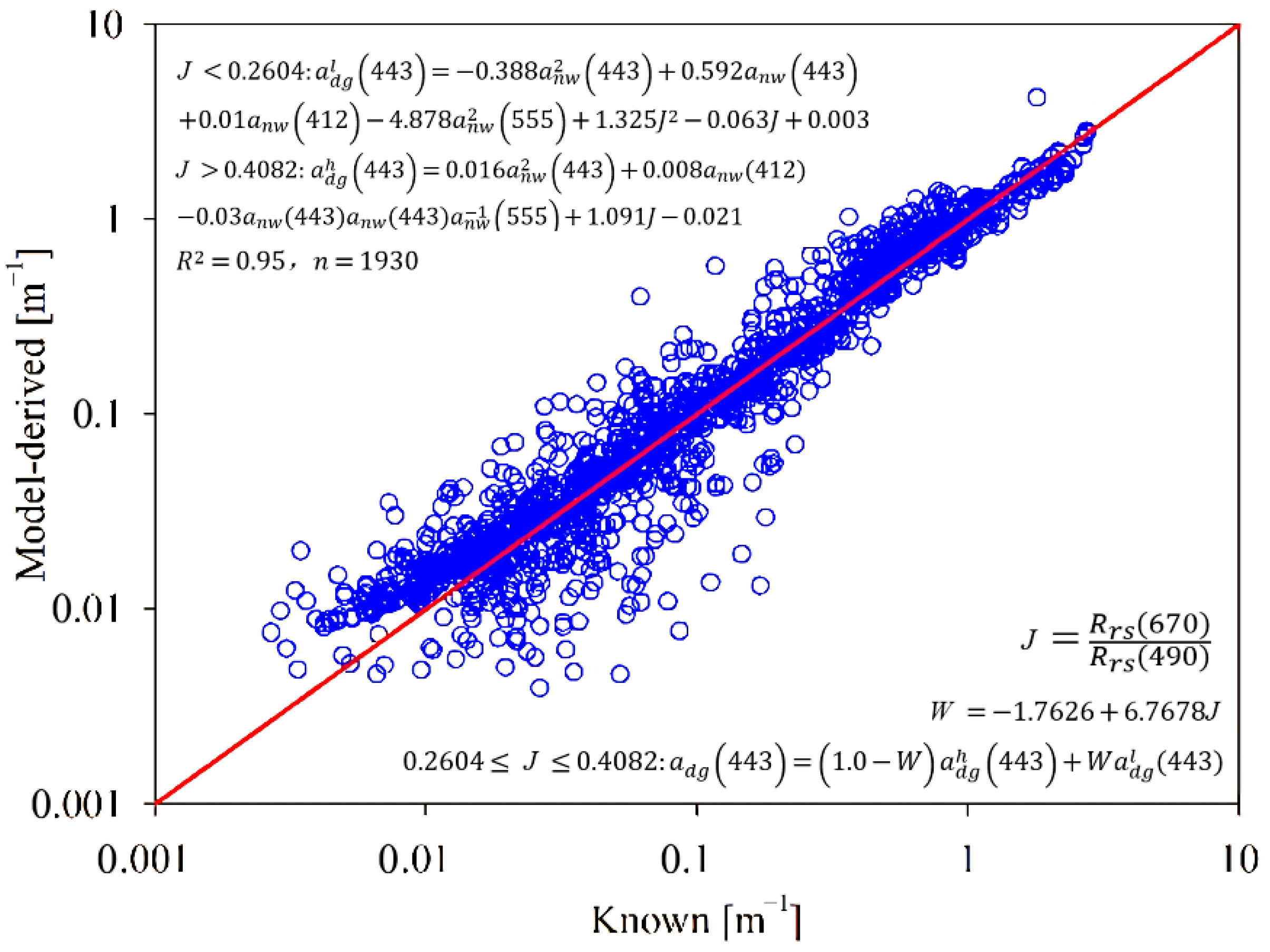
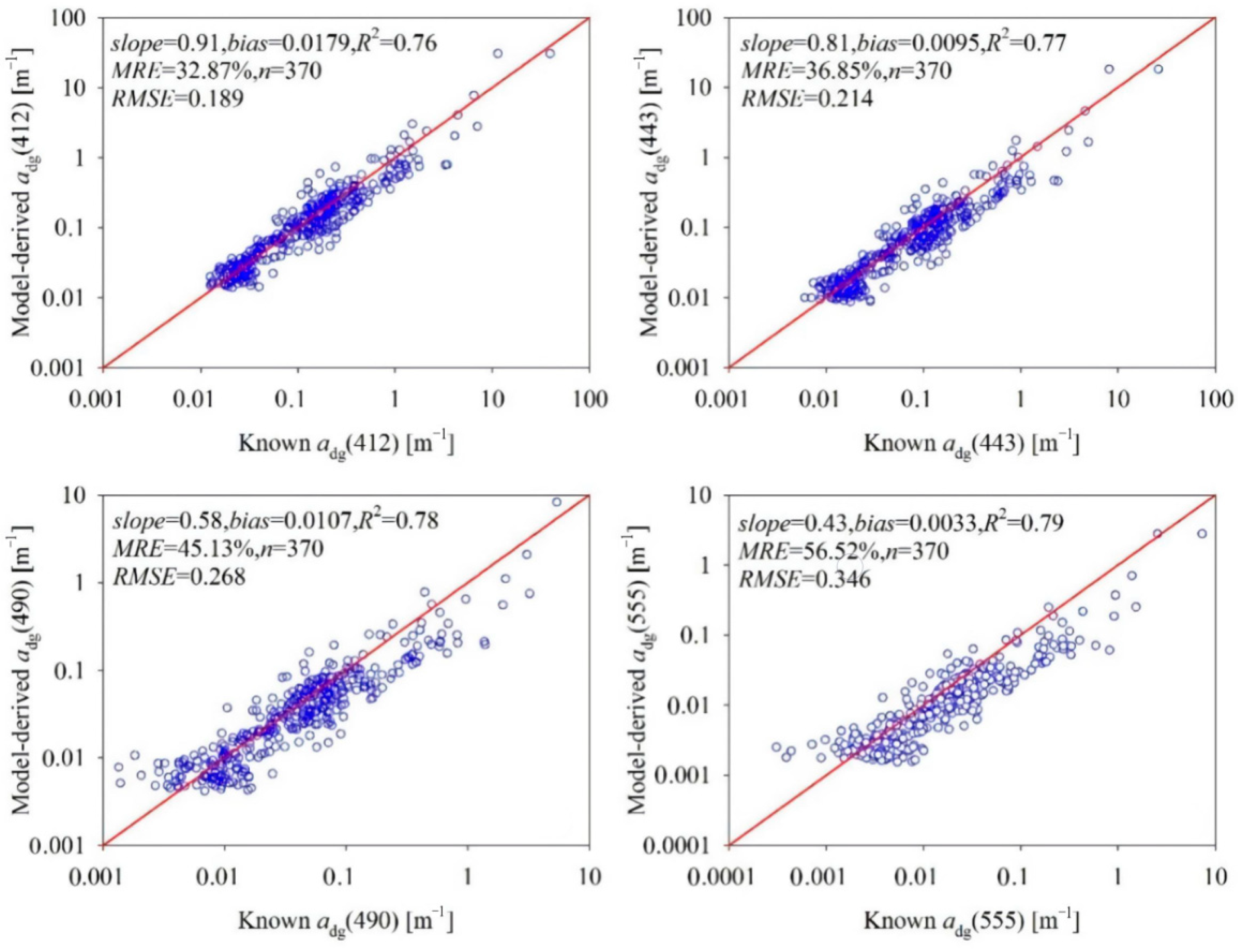
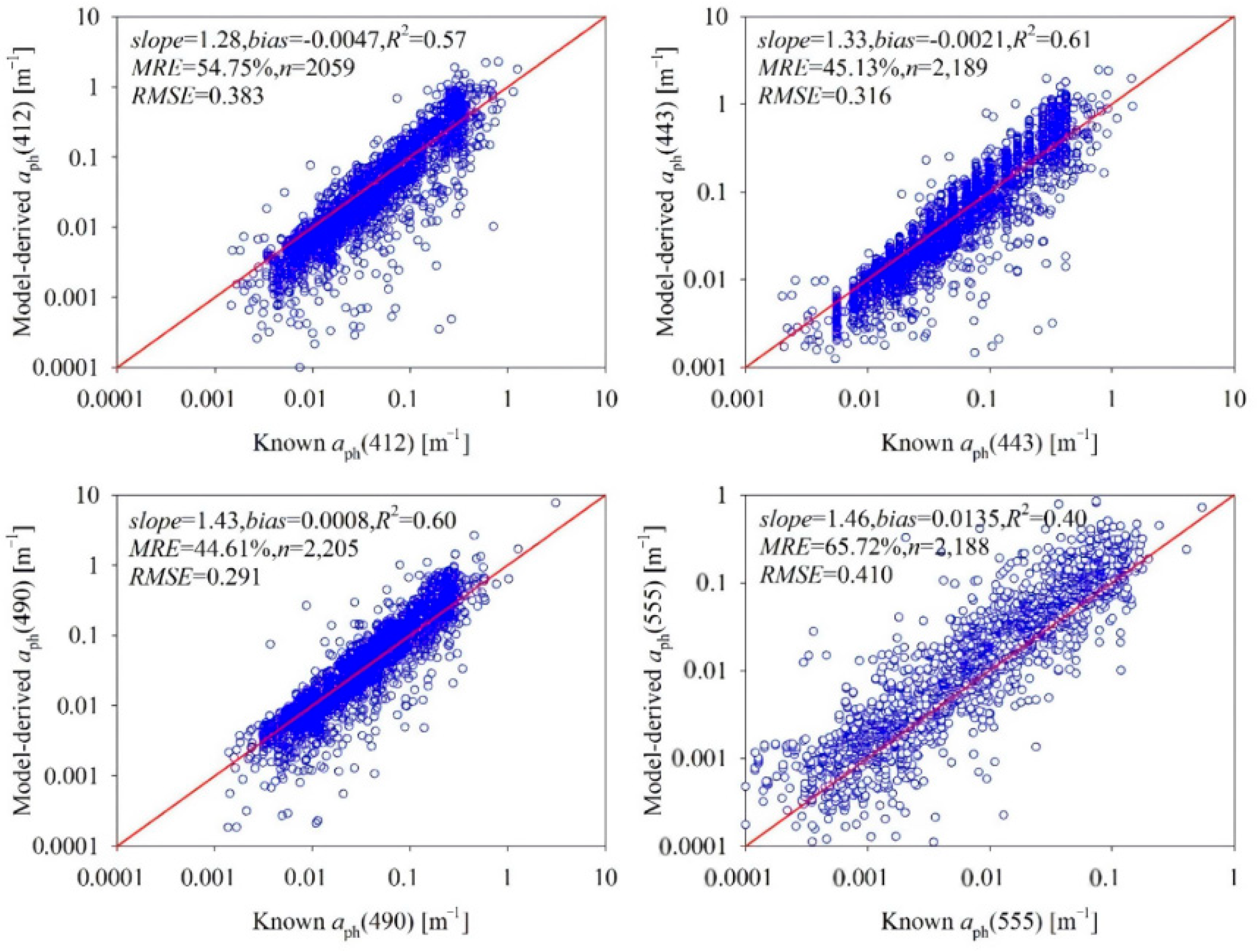
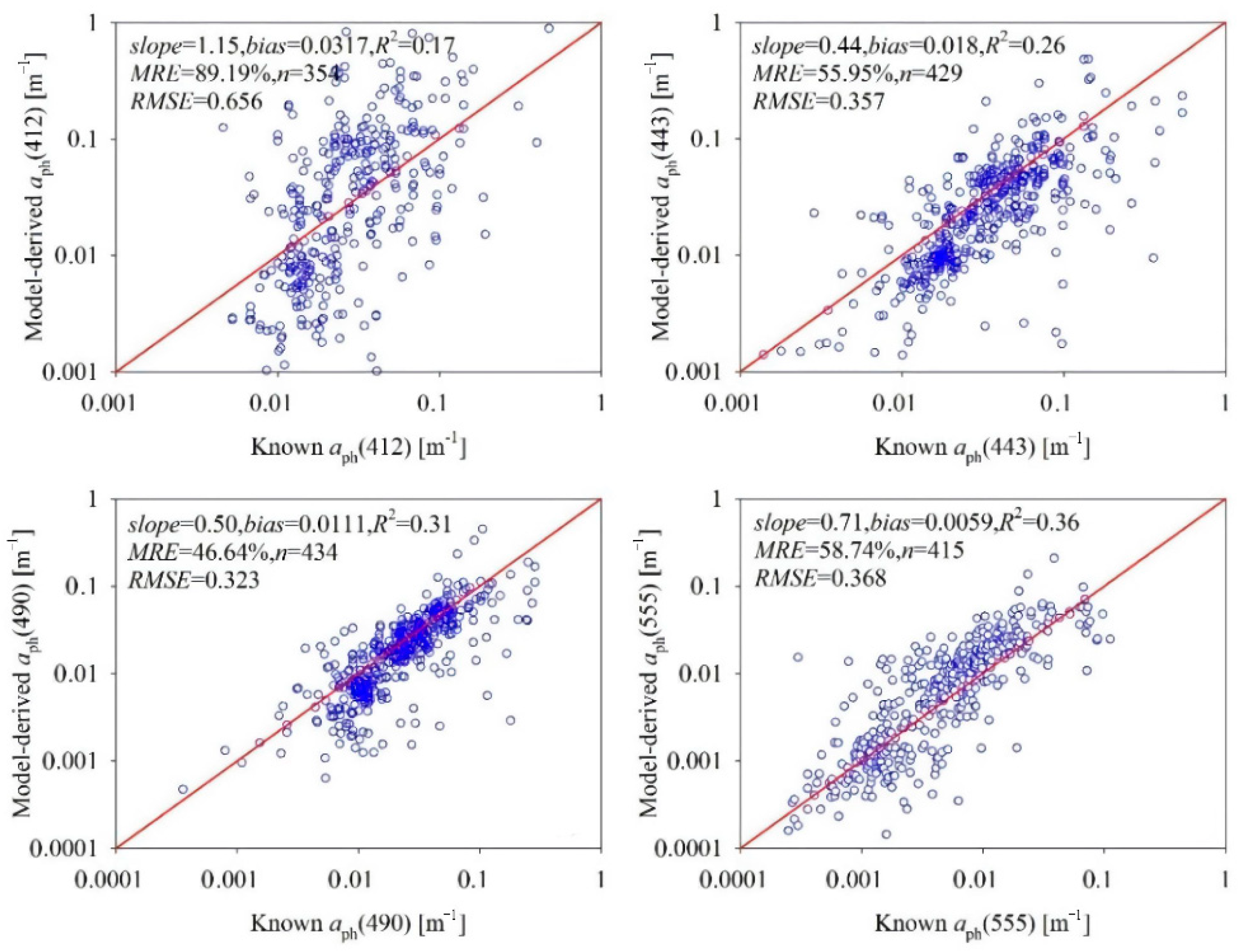
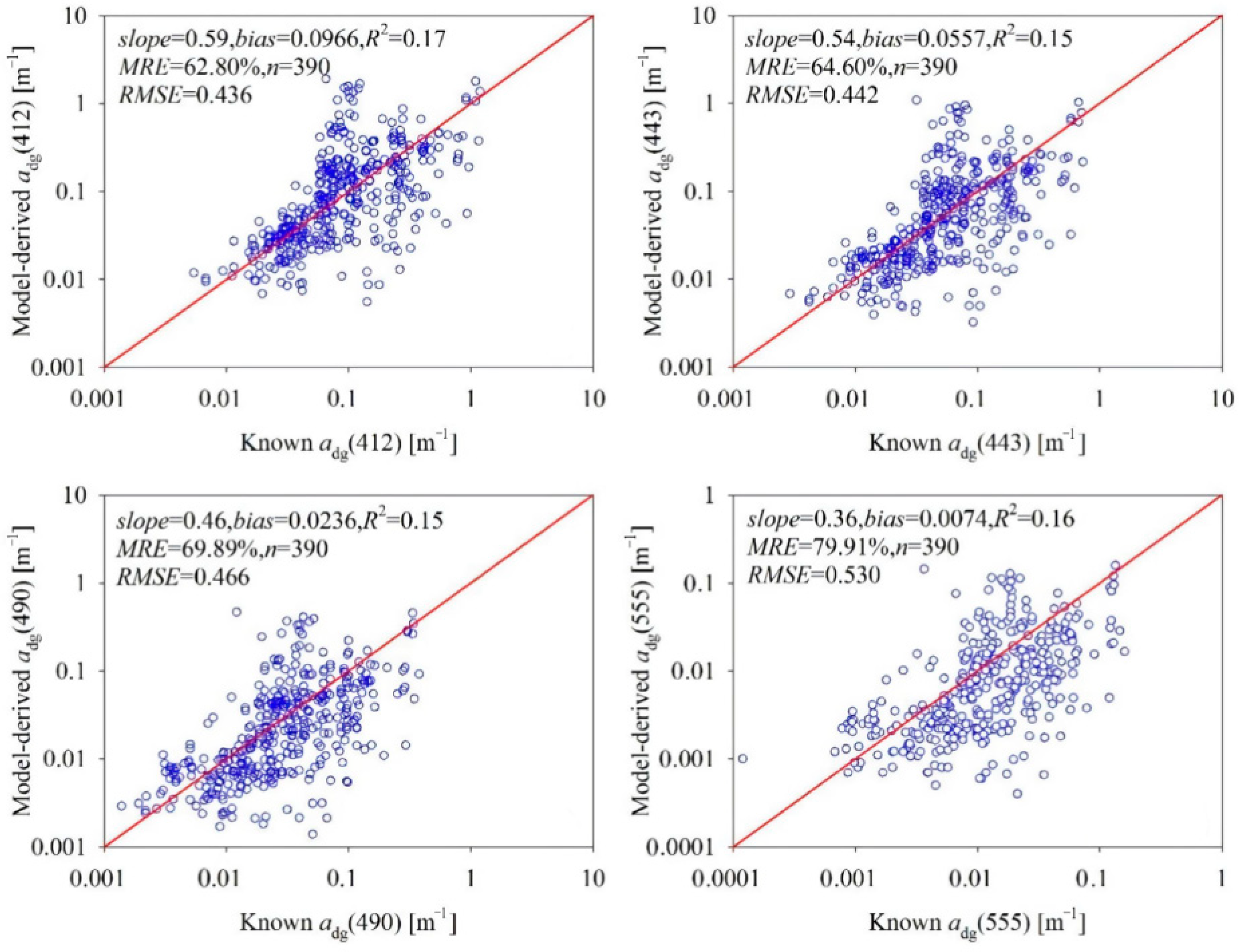
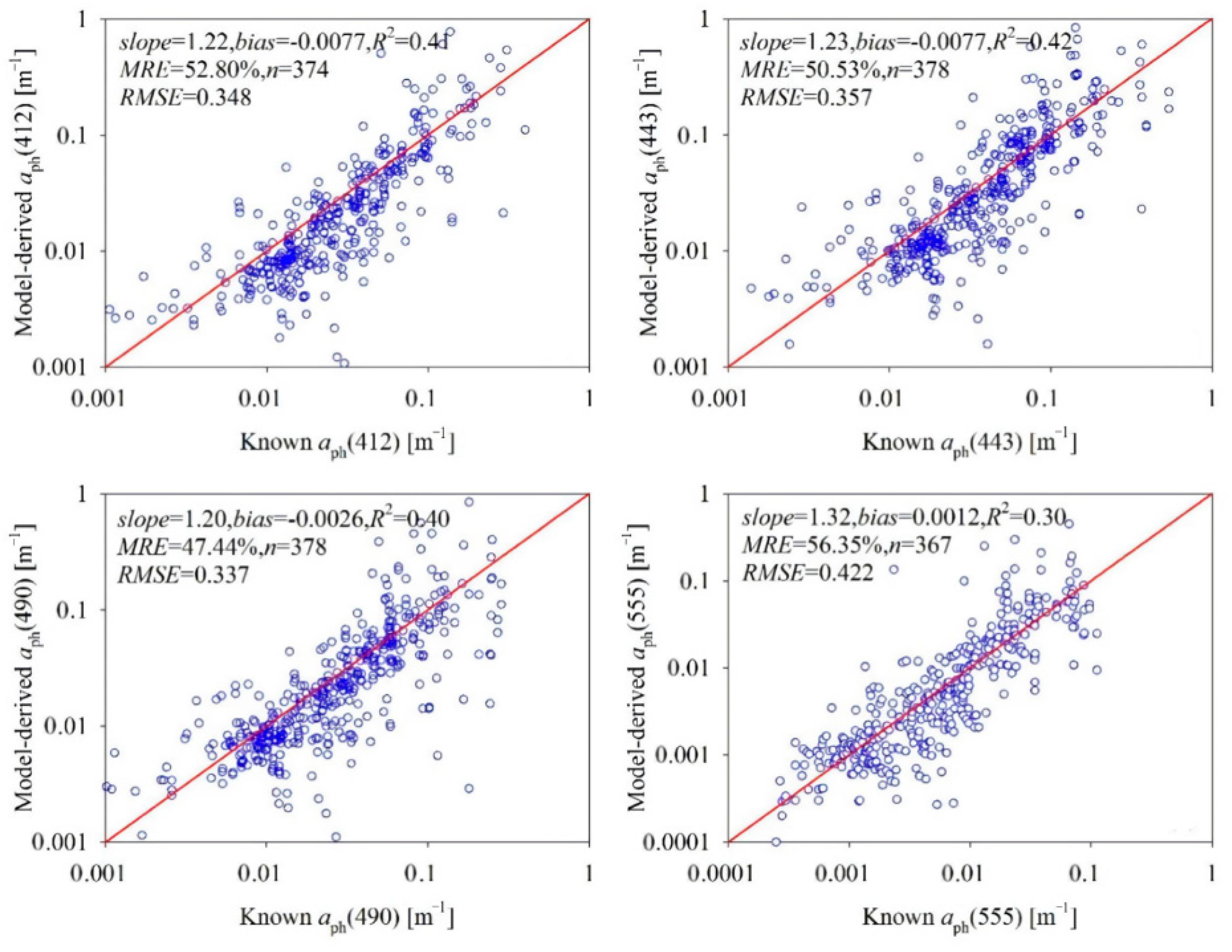
3. Results
3.1. Model Initialization
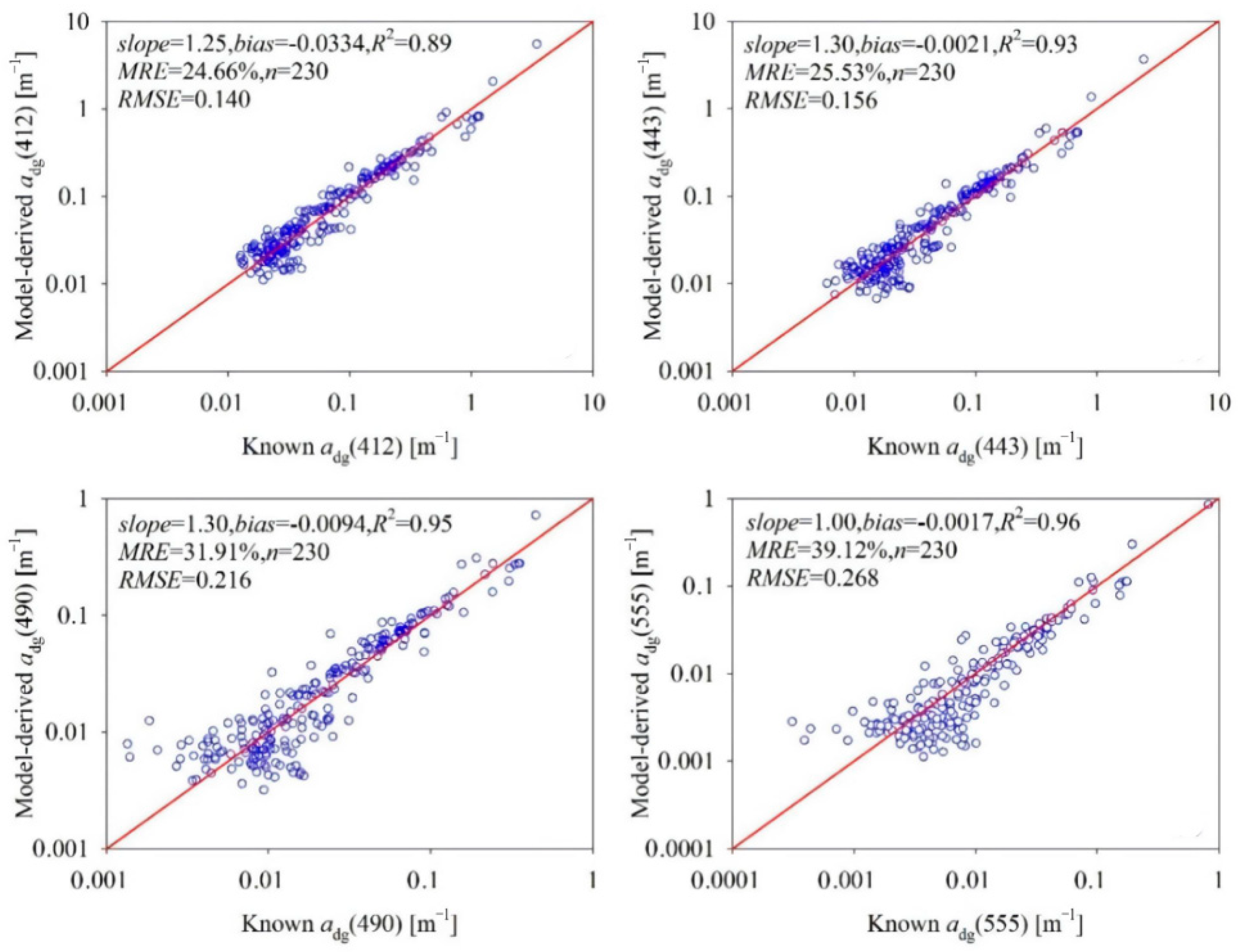
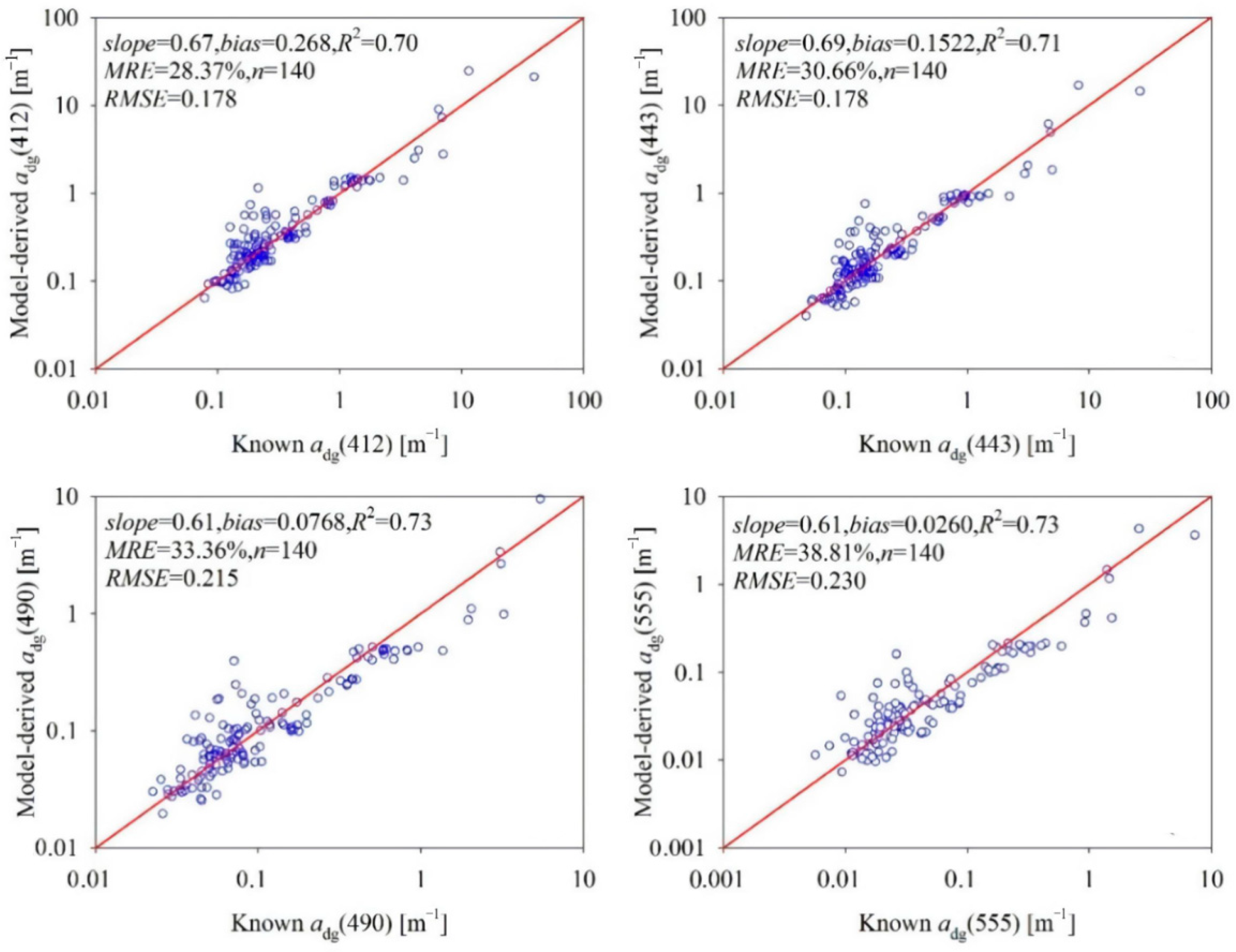
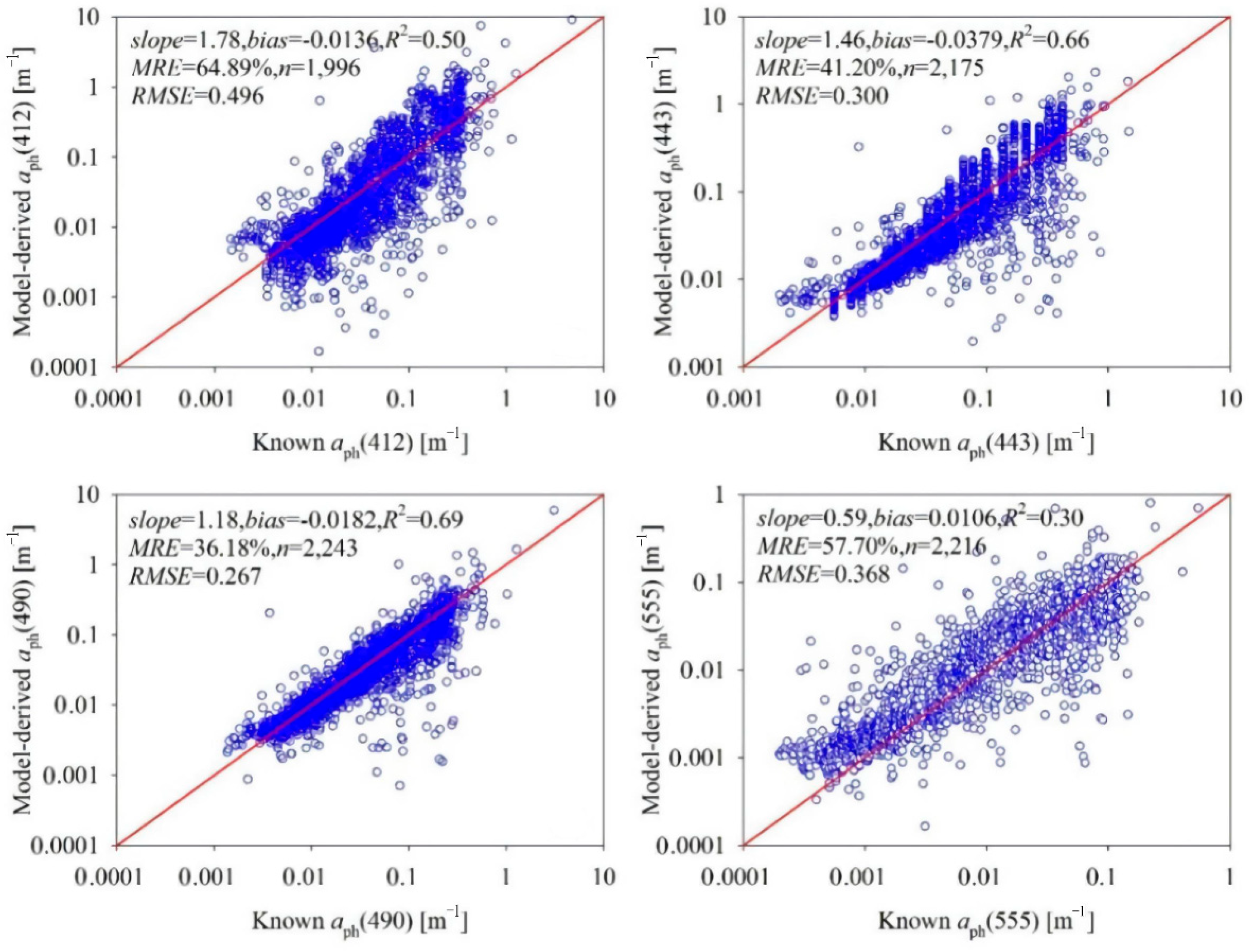
3.2. Model Evaluation
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with the QAA Model Performance
4.2. Accuracy Evaluation of the Satellite-Derived Products
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; He, X.; Liu, Z.; Xu, N.; Ma, L.; Xing, Q.; Hu, X.; Pan, D. An approach to cross-calibrating multi-mission satellite data for the open ocean. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; He, X.; Xing, X.; Xing, Q.; Liu, Z.; Pan, D. An Inherent Optical Properties Data Processing System for Achieving Consistent Ocean Color Products from Different Ocean Color Satellites. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 125, e2019JC015811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carder, K.L.; Chen, F.R.; Lee, Z.P.; Hawes, S.K.; Cannizzaro, J.P. MODIS Ocean Science Team: Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document. ATBD 19 Case 2 Chlorophyll-a. 2003, Version 7. Available online: http://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/atbd/atbd_mod19.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2022).
- Garver, S.A.; Siegel, D.A. Inherent optical property inversion of ocean color spectral and its biogeochemical interpretation. 1. time series from the Sargasso Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1997, 102, 18607–18625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.P.; Carder, K.L.; Arnone, R. Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: A multi-band quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 5755–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doerffer, R.; Schiller, H. The MERIS Case 2 water algorithm. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Maritorena, S. Bio-optical properties of oceanic waters: A reappraisal. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2001, 106, 7163–7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnard, A.H.; Zaneveld, J.R.V.; Pegau, W.S. In situ determination of the remotely sensed reflectance and the absorption coefficient: Closure and inversion. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 5108–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobley, C.D. Light and Water: Radiative Transfer in Natural Waters; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- IOCCG. Remote sensing of inherent optical properties: Fundamentals, tests of algorithms, and applications. In Reports of the International Ocean Colour Coordinating Group No.5; IOCCG: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Cui, T.; Quan, W. A neural network-based four-band model for estimating the total absorption coefficients from the global oceanic and coastal waters. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Stramski, D.; Reynolds, R.A. Evaluation of the QAA algorithm for estimating the inherent optical properties from remote sensing reflectance in Arctic waters. In Proceedings of the Ocean Sciences Meeting, Portland, OR, USA, 22–26 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Smyth, T.J.; Moore, G.F.; Hirata, T.; Aiken, J. Semi-analytical model for the derivation of ocean color inherent optical properties: Description, implementation, and performance assessment. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 8116–8132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lee, Z.; Hu, C.; Wei, J. Improving satellite data products for open oceans with a scheme to correct the residual errors in remote sensing reflectance. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 3866–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werdell, P.J.; Bailey, S.W. The SeaWiFS Bio-Optical Archive and Storage System (SeaBASS): Current Architecture and Implementation; Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Werdel; Bailey, S.W. An improved bio-optical data set for ocean color algorithm development and satellite data product variation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, P. New models for retrieving and partitioning the colored dissolved organic matter in the global ocean: Implications for remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1501–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Son, S.; Harding, L.W., Jr. Retrieval of diffuse attenuation coefficient in the Chesapeake Bay and turbid ocean regions for satellite ocean color applications. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2009, 114, C10011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, E.A. Mathematical Methods for Oceanographers: An Introduction; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hooker, S.B.; Lazin, G.; Zibordi, G.; McLean, S. An Evaluation of Above- and In-Water Methods for Determining Water-Leaving Radiances. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 486–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Hu, C.; Shang, S.; Du, K.; Lewis, M.; Arnone, R.; Brewin, R. Penetration of UV-visible solar radiation in the global oceans: Insights from ocean color remote sensing. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 4241–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Z.P.; Werdell, P.J.; Arnone, R. An Update of the Quasi-Analytical Algorithm (QAA_V5). IOCCG Software Report 2009. Available online: https://www.ioccg.org/groups/Software_OCA/QAA_v5.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2022).
- Bailey, S.W.; Werdell, P.J. A multi-sensor approach for the on-orbit validation of ocean color satellite data products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Feng, L.; Lee, Z. Uncertainties of SeaWiFS and MODIS remote sensing reflectance: Implications from clear water measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 133, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdell, P.J.; Franz, B.A.; Bailey, S.; Feldman, G.C.; Boss, E.; Brando, V.; Dowell, M.; Hirata, T.; Lavender, S.; Lee, Z.; et al. Generalized ocean color inversion model for retrieving marine inherent optical properties. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 2019–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Dataset | a(λ) | Min. | Max. | Median | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IOCCG dataset n = 1000 | aph(443) | 0.005 | 0.416 | 0.056 | 0.115 | 0.518 |
| adg(443) | 0.004 | 2.642 | 0.153 | 0.497 | 0.628 | |
| NOMAD dataset n = 930 | aph(443) | 0.002 | 1.457 | 0.033 | 0.059 | 0.089 |
| adg(443) | 0.003 | 0.902 | 0.044 | 0.087 | 0.126 | |
| WFS dataset n = 230 | aph(443) | 0.008 | 0.684 | 0.025 | 0.050 | 0.072 |
| adg(443) | 0.006 | 0.900 | 0.039 | 0.088 | 0.134 | |
| YCE dataset n = 140 | aph(443) | 0.009 | 0.680 | 0.081 | 0.680 | 0.102 |
| adg(443) | 0.048 | 8.168 | 0.147 | 0.359 | 0.824 | |
| Synchronized dataset n = 437 | aph(443) | 0.001 | 0.540 | 0.034 | 0.053 | 0.065 |
| adg(443) | 0.003 | 1.250 | 0.055 | 0.105 | 0.146 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Z.; Yin, S.; Yuan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, N.; Meng, B.; Zhou, B. An Operational Model for Remote Estimating Absorption of Optical Activity Constituents. Water 2022, 14, 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071154
Yu Z, Yin S, Yuan X, Zhou Y, Wang N, Meng B, Zhou B. An Operational Model for Remote Estimating Absorption of Optical Activity Constituents. Water. 2022; 14(7):1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071154
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Zhifeng, Shoujing Yin, Xiaohong Yuan, Yaming Zhou, Nan Wang, Bin Meng, and Bin Zhou. 2022. "An Operational Model for Remote Estimating Absorption of Optical Activity Constituents" Water 14, no. 7: 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071154
APA StyleYu, Z., Yin, S., Yuan, X., Zhou, Y., Wang, N., Meng, B., & Zhou, B. (2022). An Operational Model for Remote Estimating Absorption of Optical Activity Constituents. Water, 14(7), 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071154





