Water Footprint Assessment of Rainfed Crops with Critical Irrigation under Different Climate Change Scenarios in SAT Regions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Climate
2.2. Data Acquisition
Climate Data
2.3. Estimation of Water Balance in a Watershed Using SWAT
2.4. Estimation of Crop Yields in Different Climate Change Scenarios
2.5. Water Footprint (WF) Assessment
2.5.1. Green Water Footprint
2.5.2. Blue Water Footprint
2.5.3. Water Footprints for Climate Change Scenarios
3. Results
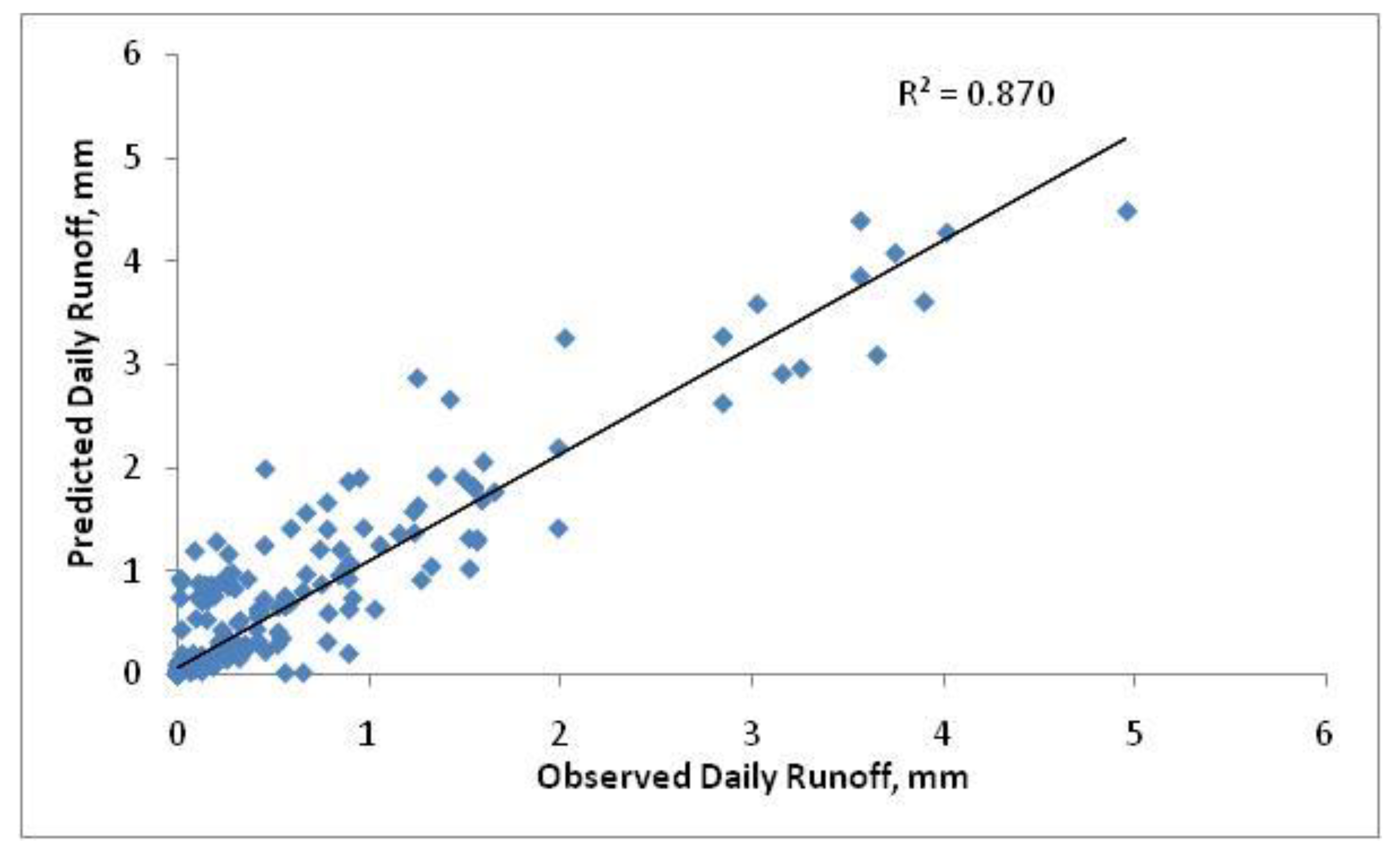
3.1. SWAT Calibration and Validation
3.2. Water Balance
3.3. Water Footprint of Rainfed Crops
3.3.1. Base Period (1994–2013)
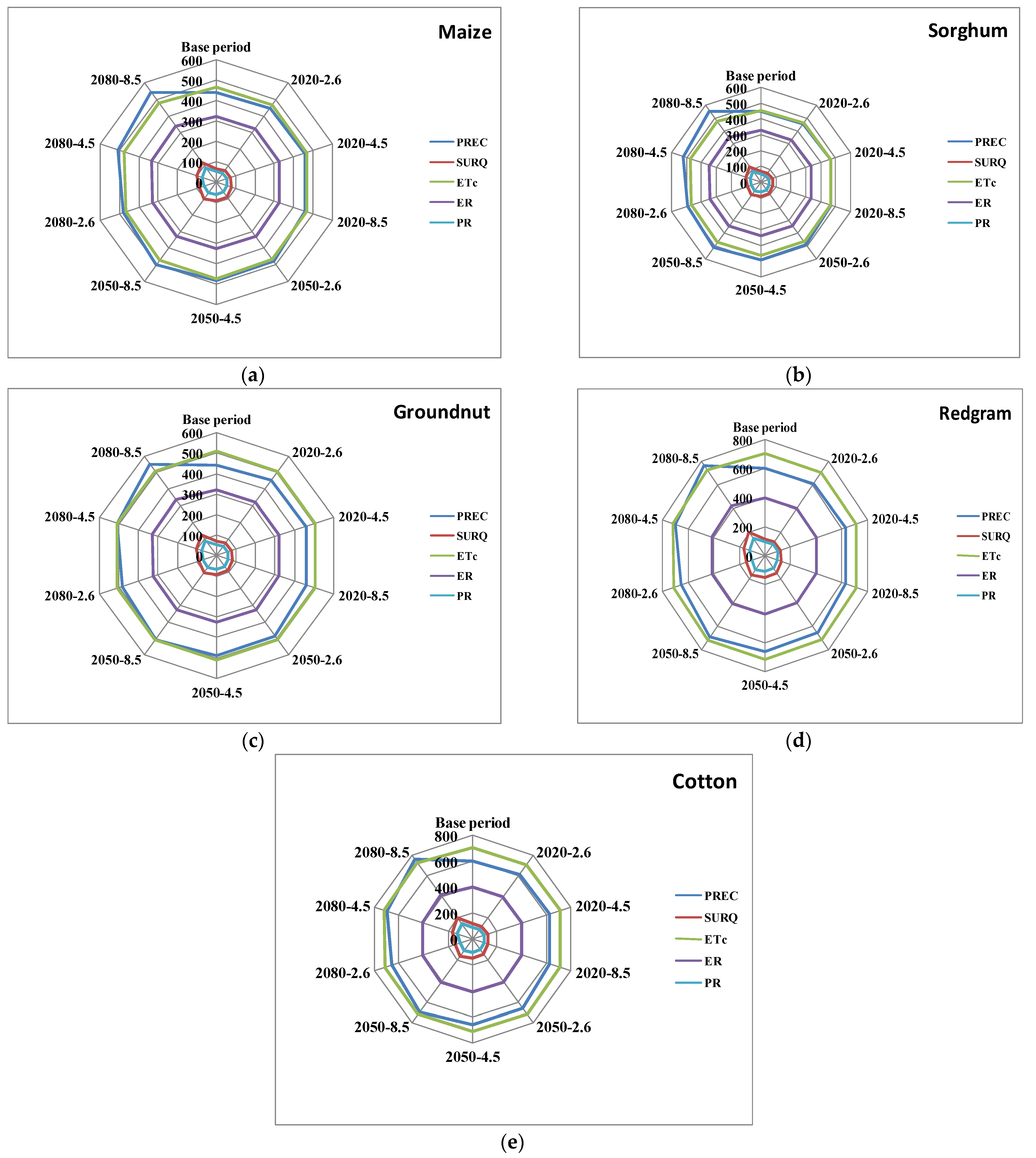
3.3.2. Green and Blue Water Footprints of Rainfed Crops under Different Climate Change (CC) Scenarios
Maize
Sorghum
Groundnut
Redgram
Cotton
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The World Economical Forum 2021. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/ (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Four billion people facing severe water scarcity. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1500323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agricultural Statistics at a Glance 2020. Available online: https://eands.dacnet.nic.in/PDF/Agricultural%20Statistics%20at%20a%20Glance%20-%202020%20(English%20version).pdf (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- Rockström, J.; Karlberg, L.; Wani, S.P.; Barron, J.; Hatibu, N.; Oweis, T.; Bruggeman, A.; Farahani, J.; Qiang, Z. Managing water in rainfed agriculture—The need for a paradigm shift. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, K.S.; Ricart, S.; Maruthi, V.; Pankaj, P.K.; Krishna, T.S.; Reddy, A.A. Economic assessment of water harvesting plus supplemental irrigation for improving water productivity of a pulse–cotton based integrated farming system in Telangana, India. Irrig. Drain. John Wiley Sons 2020, 69, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fraiture, C.; Wichelns, D. Satisfying future water demands for agriculture. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Mekonnen, M.M. Reply to Ridoutt and Huang: From water footprint assessment to policy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wani, S.P.; Dixin, Y.; Li, Z.; Dar, W.D.; Chander, G. Enhancing agricultural productivity and rural incomes through sustainable use of natural resources in the Semi Arid Tropics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 92, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.S.; Kumar, M.; Maruthi, V.; Ravi Kumar, N.; Maheswari, M.; Sikka, A.K.; Lakshminarayana, P.; Vijayalakshmi, U.B.; Reddy, Y.V.K. ATLAS on Climate Change Impacts on Crop Water Balance of Cotton (Gossypium herbaceum) and Maize (Zea mays L.) in Telangana; ICAR: Hyderabad, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- McCartney, M.; Smakhtin, V. Water storage in an era of climate change: Addressing the challenge of increasing rainfall variability. Blue Pap. 2010, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldaya, M.M.; Llamas, M. Water Footprint Analysis for the Guadiana River Basin; UNESCO-IHE: Delft, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Geng, Y.; Sarkis, J.; Fujita, T.; Okadera, T.; Xue, B. Regional water footprint evaluation in China: A case of Liaoning. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 442, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Chapagain, A.K. The water footprints of Morocco and the Netherlands: Global water use as a result of domestic consumption of agricultural commodities. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 64, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampman, D.A.; Hoekstra, A.Y.; Krol, M.S. The water footprint of India. Value Water Res. Rep. Ser. 2008, 32, 1–152. [Google Scholar]
- Van Oel, P.; Mekonnen, M.; Hoekstra, A. The external water footprint of the Netherlands: Geographically-explicit quantification and impact assessment. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 69, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulsink, F.; Hoekstra, A.Y.; Booij, M.J. The water footprint of Indonesian provinces related to the consumption of crop products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ercin, E.; Mekonnen, M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. The Water Footprint of Switzerland (Value of Water Research Report; No. 57), Unesco-IHE Institute for Water Education. 2012. Available online: https://waterfootprint.org/media/downloads/Report57-WaterFootprintSwitzerland_1.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2022).
- Shrestha, S.; Pandey, V.P.; Chanamai, C.; Ghosh, D.K. Green, Blue and Grey Water Footprints of Primary Crops Production in Nepal. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 5223–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Chapagain, A.K. Water footprints of nations: Water use by people as a function of their consumption pattern. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 21, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, H. Spatially explicit assessment of global consumptive water uses in cropland: Green and blue water. J. Hydrol. 2010, 384, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. The green, blue and grey water footprint of crops and derived crop products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1577–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Chapagain, A.K.; Mekonnen, M.M.; Aldaya, M.M. The Water Footprint Assessment Manual: Setting the Global Standard; Routledge: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Mang, S.; Cai, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Innes, J.L. Integrated watershed management: Evolution, development and emerging trends. J. For. Res. 2016, 27, 967–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thornton, P.K.; Jones, P.G.; Alagarswamy, G.; Andresen, J.; Herrero, M. Adapting to climate change: Agricultural system and household impacts in East Africa. Agric. Syst. 2010, 103, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, K.; Son, M.; Hong, S.; An, S.; Part, S. Method to assess water footprint, a case study for white radishes in Korea. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2017, 5, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, F.; Azari, M.; Dastorani, M.T. Spatial optimization of soil and water conservation practices using coupled SWAT model and evolutionary algorithm. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.K.; Rajput, T.B.S. Rainfall effectiveness for different crops in canal command areas. J. Agrometeorol. 2008, 10, 328–332. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, A.; Mani, A.; Devi, M.U.; Reddy, M.D. Blue and green water quantification for sustainable water resources management in Kothakunta sub-watershed, Andhra Pradesh. Indian J. Soil Conserv. 2013, 41, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Mali, S.S.; Singh, D.; Sarangi, A.; Khanna, M.; Parihar, S.; Das, D. Variability mapping of crop evapotranspiration for water footprint assessment at basin level. Indian J. Soil Conserv. 2015, 43, 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bocchiola, D. Impact of potential climate change on crop yield and water footprint of rice in the Po valley of Italy. Agric. Syst. 2015, 139, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Lu, F.; Hou, B.; Li, B. Assessment of Potential Climate Change Effects on the Rice Yield and Water Footprint in the Nanliujiang Catchment, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harmonized World Soil Database Version 1.1 March. 2009. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/aq361e/aq361e.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper-56: Rome, Italy, 1998; p. 300. [Google Scholar]
- Doorenbos, J.; Pruitt, W.O. Crop water requirements, FAO irrigation and drainage paper 24. Land Water Dev. Div. FAO Rome 1977, 144, 214. [Google Scholar]
- Venu Gopal, R.C.; Vanishree, K. Telangana Vyavsayam Professor Jayashankar Telangana State Agricultural University 2019. Available online: https://pjtsau.edu.in/Vyavasayam.html (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- USDA. Irrigation water requirements. Agr. Soil Manag. 1967, 59, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, B.R.; Rao, K.; Vittal, K.; Ramakrishna, Y.; Amarasinghe, U. Estimating the potential of rainfed agriculture in India: Prospects for water productivity improvements. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzaz, F.A.; Sombroek, W.G. (Eds.) Global Climate Change and Agricultural Production: Direct and Indirect Effects of Changing Hydrological, Pedological, and Plant Physiological Processes; Food & Agriculture Org.: Rome, Italy, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, K.; Maruthi, V.; Kumar, M.; Pankaj, P.; Reddy, A.; Umesha, B. Enhancing economic water productivity under on farm reservoirs in diversified rainfed cropping systems. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2017, 11, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobin, A.; Kersebaum, K.C.; Eitzinger, J.; Trnka, M.; Hlavinka, P.; Takáč, J.; Kroes, J.; Ventrella, D.; Marta, A.D.; Deelstra, J.; et al. Variability in the Water Footprint of Arable Crop Production across European Regions. Water 2017, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Crop | Kc_Ini | Kc_mid | Kc_end | Date of Sowing | Length of Crop Growing Period (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maize | 0.3 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 05-July | 120 |
| Sorghum | 0.3 | 1 | 0.55 | 05-July | 115 |
| Groundnut | 0.4 | 1.15 | 0.6 | 10-July | 120 |
| Cotton | 0.35 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 15-July | 180 |
| Redgram | 0.3 | 1 | 0.5 | 10-July | 120 |
| Maize | Sorghum | Groundnut | Redgram | Cotton | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETc (mm) | ER (mm) | ETc (mm) | ER (mm) | ETc (mm) | ER (mm) | ETc (mm) | ER (mm) | ETc (mm) | ER (mm) | |
| Base period | 464.57 | 321.93 | 455.20 | 331.88 | 508.09 | 319.74 | 455.33 | 352.98 | 705.55 | 401.62 |
| 2020-2.6 | 465.63 | 322.62 | 462.63 | 332.14 | 510.16 | 319.92 | 456.82 | 353.24 | 707.13 | 401.70 |
| 2020-4.5 | 466.72 | 323.90 | 463.74 | 333.92 | 511.09 | 321.74 | 457.62 | 354.84 | 708.59 | 402.15 |
| 2020-8.5 | 467.68 | 325.73 | 464.25 | 334.95 | 512.88 | 322.61 | 458.12 | 356.65 | 709.14 | 403.12 |
| 2050-2.6 | 469.87 | 329.26 | 467.25 | 339.32 | 516.76 | 326.83 | 461.58 | 360.64 | 713.67 | 407.80 |
| 2050-4.5 | 473.55 | 330.54 | 468.76 | 340.86 | 517.61 | 327.57 | 462.18 | 361.62 | 714.37 | 408.96 |
| 2050-8.5 | 474.16 | 332.66 | 470.47 | 342.64 | 521.77 | 330.44 | 464.32 | 364.33 | 718.95 | 413.33 |
| 2080-2.6 | 471.59 | 331.99 | 469.69 | 341.02 | 518.72 | 328.59 | 462.07 | 362.08 | 715.73 | 409.46 |
| 2080-4.5 | 475.70 | 334.16 | 470.50 | 345.60 | 521.09 | 331.43 | 463.48 | 365.68 | 718.01 | 413.83 |
| 2080-8.5 | 478.37 | 339.06 | 476.18 | 350.48 | 532.72 | 338.06 | 470.31 | 370.97 | 728.29 | 421.82 |
| Maize (t/ha) | Sorghum (t/ha) | Groundnut (t/ha) | Redgram (t/ha) | Cotton (t/ha) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfed | 30 mm | 50 mm | Rainfed | 30 mm | 50 mm | Rainfed | 30 mm | 50 mm | Rainfed | 30 mm | 50 mm | Rainfed | 30 mm | 50 mm | |
| Base period | 1.50 | 2.20 | 4.20 | 1.00 | 1.76 | 2.98 | 1.30 | 2.70 | 4.80 | 0.80 | 1.51 | 2.60 | 0.90 | 2.40 | 4.50 |
| 2020-2.6 | 1.53 | 2.29 | 4.51 | 1.02 | 1.84 | 3.17 | 1.34 | 2.90 | 5.19 | 0.82 | 1.62 | 2.80 | 0.93 | 2.58 | 4.87 |
| 2020-4.5 | 1.56 | 2.39 | 4.74 | 1.05 | 1.91 | 3.35 | 1.36 | 2.99 | 5.49 | 0.85 | 1.66 | 2.94 | 0.98 | 2.66 | 5.17 |
| 2020-8.5 | 1.60 | 2.51 | 4.98 | 1.09 | 2.05 | 3.61 | 1.39 | 3.17 | 5.85 | 0.87 | 1.76 | 3.14 | 0.99 | 2.80 | 5.51 |
| 2050-2.6 | 1.65 | 2.62 | 5.25 | 1.12 | 2.11 | 3.92 | 1.44 | 3.29 | 6.27 | 0.90 | 1.82 | 3.39 | 1.01 | 2.92 | 5.91 |
| 2050-4.5 | 1.70 | 2.76 | 5.56 | 1.16 | 2.21 | 4.19 | 1.49 | 3.41 | 6.63 | 0.92 | 1.89 | 3.65 | 1.04 | 3.04 | 6.33 |
| 2050-8.5 | 1.74 | 2.86 | 6.05 | 1.18 | 2.31 | 4.42 | 1.52 | 3.59 | 7.05 | 0.94 | 1.98 | 3.88 | 1.06 | 3.21 | 6.78 |
| 2080-2.6 | 1.76 | 2.94 | 6.42 | 1.20 | 2.35 | 4.73 | 1.55 | 3.68 | 7.58 | 0.95 | 2.04 | 4.09 | 1.08 | 3.27 | 7.09 |
| 2080-4.5 | 1.80 | 3.05 | 6.97 | 1.21 | 2.46 | 5.00 | 1.58 | 3.84 | 7.98 | 0.98 | 2.11 | 4.32 | 1.10 | 3.39 | 7.50 |
| 2080-8.5 | 1.83 | 3.15 | 7.30 | 1.24 | 2.51 | 5.20 | 1.61 | 3.92 | 8.47 | 1.00 | 2.18 | 4.58 | 1.13 | 3.52 | 8.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reddy, K.S.; Maruthi, V.; Pankaj, P.K.; Kumar, M.; Pushpanjali; Prabhakar, M.; Reddy, A.G.K.; Reddy, K.S.; Singh, V.K.; Koradia, A.K. Water Footprint Assessment of Rainfed Crops with Critical Irrigation under Different Climate Change Scenarios in SAT Regions. Water 2022, 14, 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14081206
Reddy KS, Maruthi V, Pankaj PK, Kumar M, Pushpanjali, Prabhakar M, Reddy AGK, Reddy KS, Singh VK, Koradia AK. Water Footprint Assessment of Rainfed Crops with Critical Irrigation under Different Climate Change Scenarios in SAT Regions. Water. 2022; 14(8):1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14081206
Chicago/Turabian StyleReddy, Konda Sreenivas, Vegapareddy Maruthi, Prabhat Kumar Pankaj, Manoranjan Kumar, Pushpanjali, Mathyam Prabhakar, Artha Gopal Krishna Reddy, Kotha Sammi Reddy, Vinod Kumar Singh, and Ashishkumar Kanjibhai Koradia. 2022. "Water Footprint Assessment of Rainfed Crops with Critical Irrigation under Different Climate Change Scenarios in SAT Regions" Water 14, no. 8: 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14081206
APA StyleReddy, K. S., Maruthi, V., Pankaj, P. K., Kumar, M., Pushpanjali, Prabhakar, M., Reddy, A. G. K., Reddy, K. S., Singh, V. K., & Koradia, A. K. (2022). Water Footprint Assessment of Rainfed Crops with Critical Irrigation under Different Climate Change Scenarios in SAT Regions. Water, 14(8), 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14081206






