The Occurrence of Catastrophic Multiple-Fatality Flash Floods in the Eastern Mediterranean Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Sources
2.2. Database Evaluation
2.3. Database Structure and Analysis
3. Results
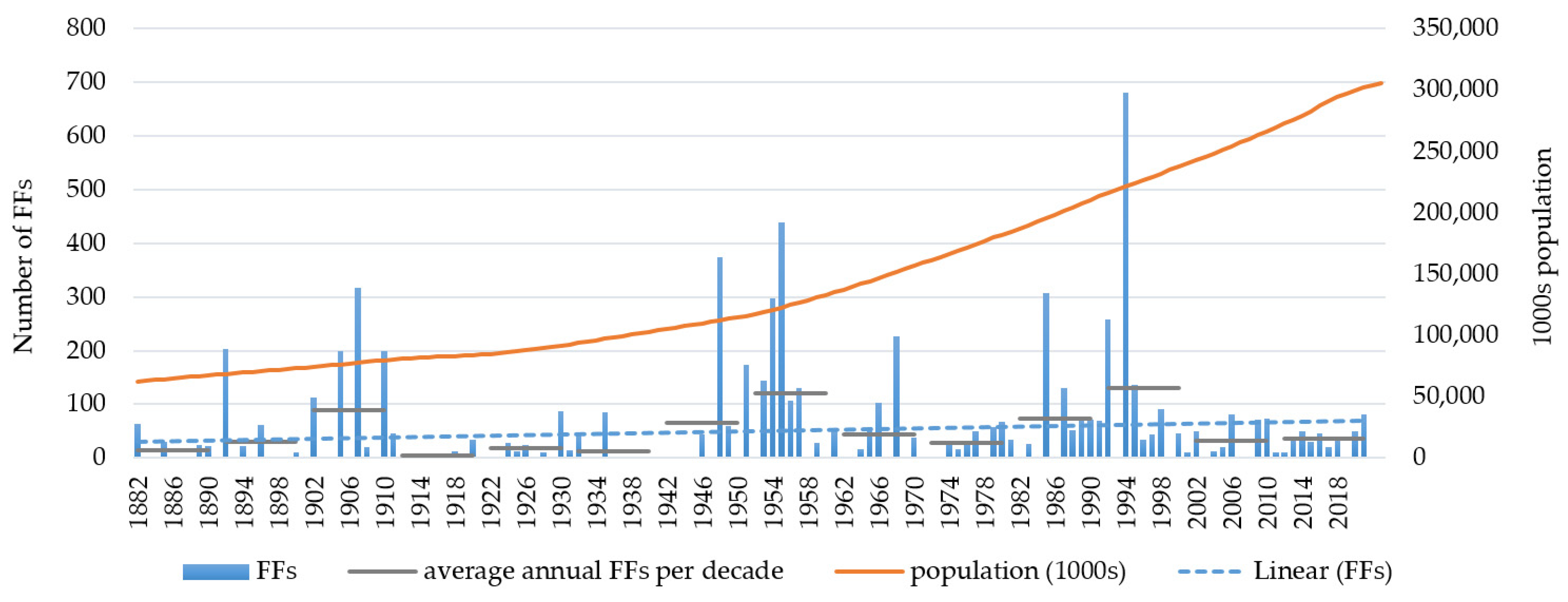
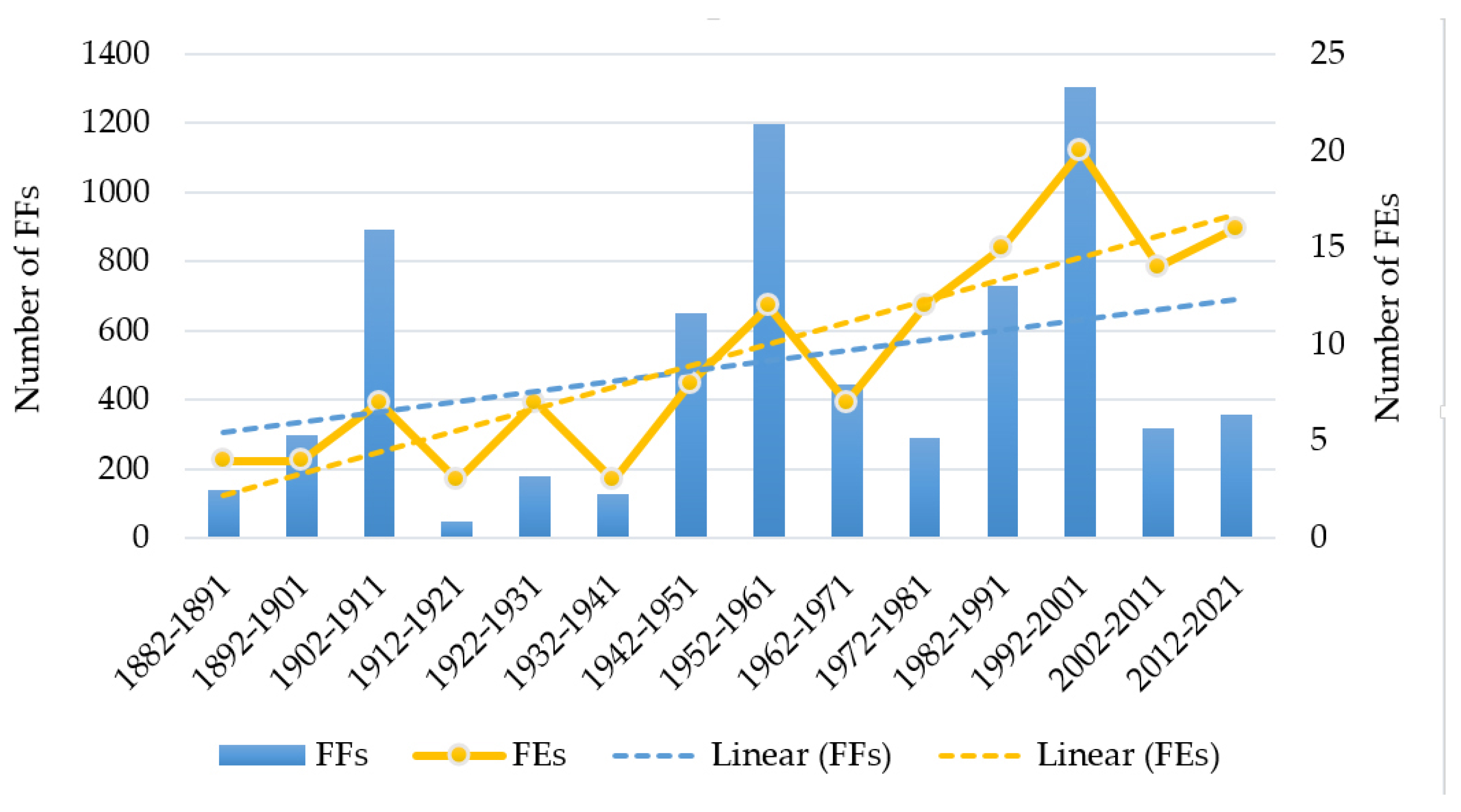
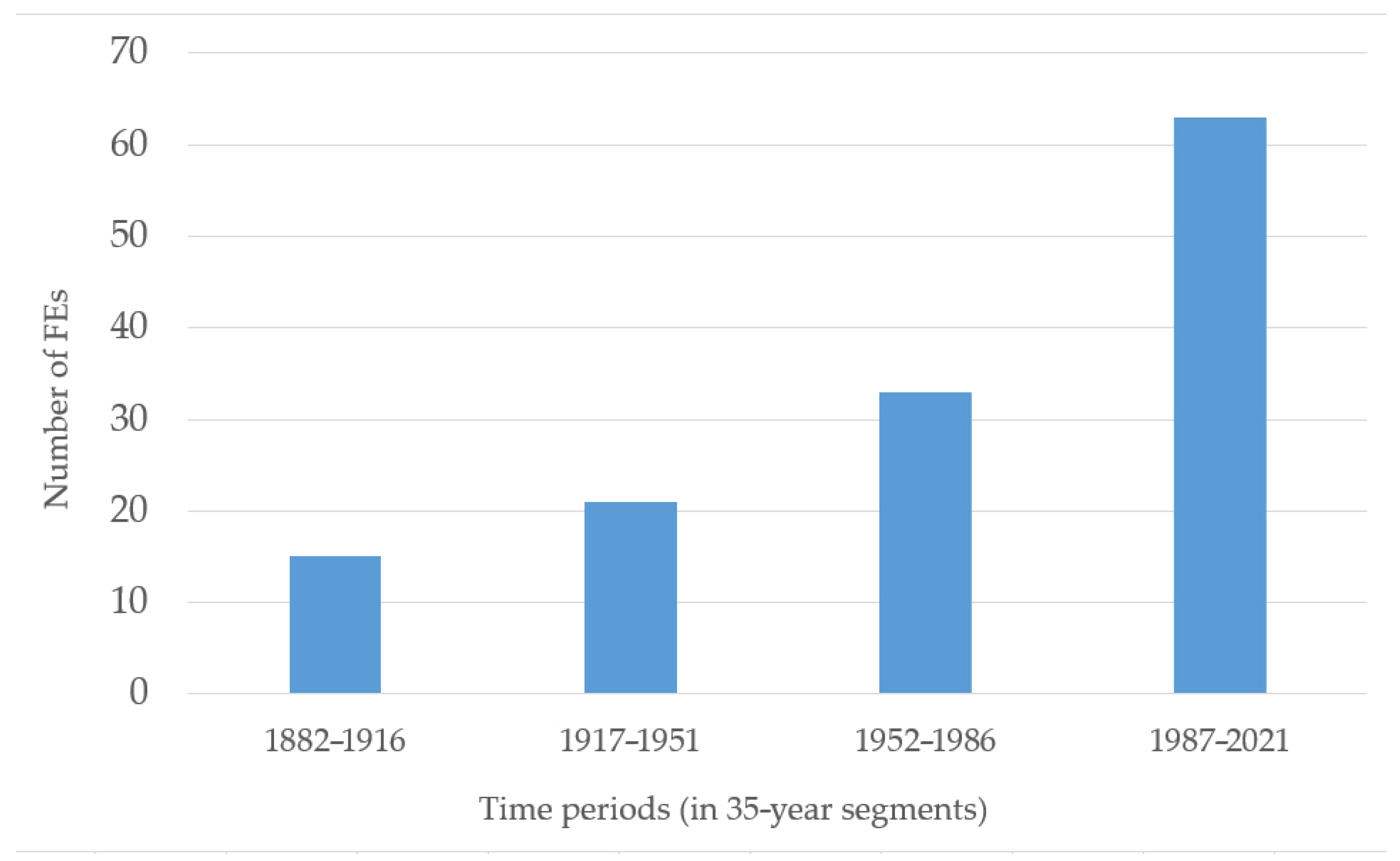
3.1. Temporal Evolution
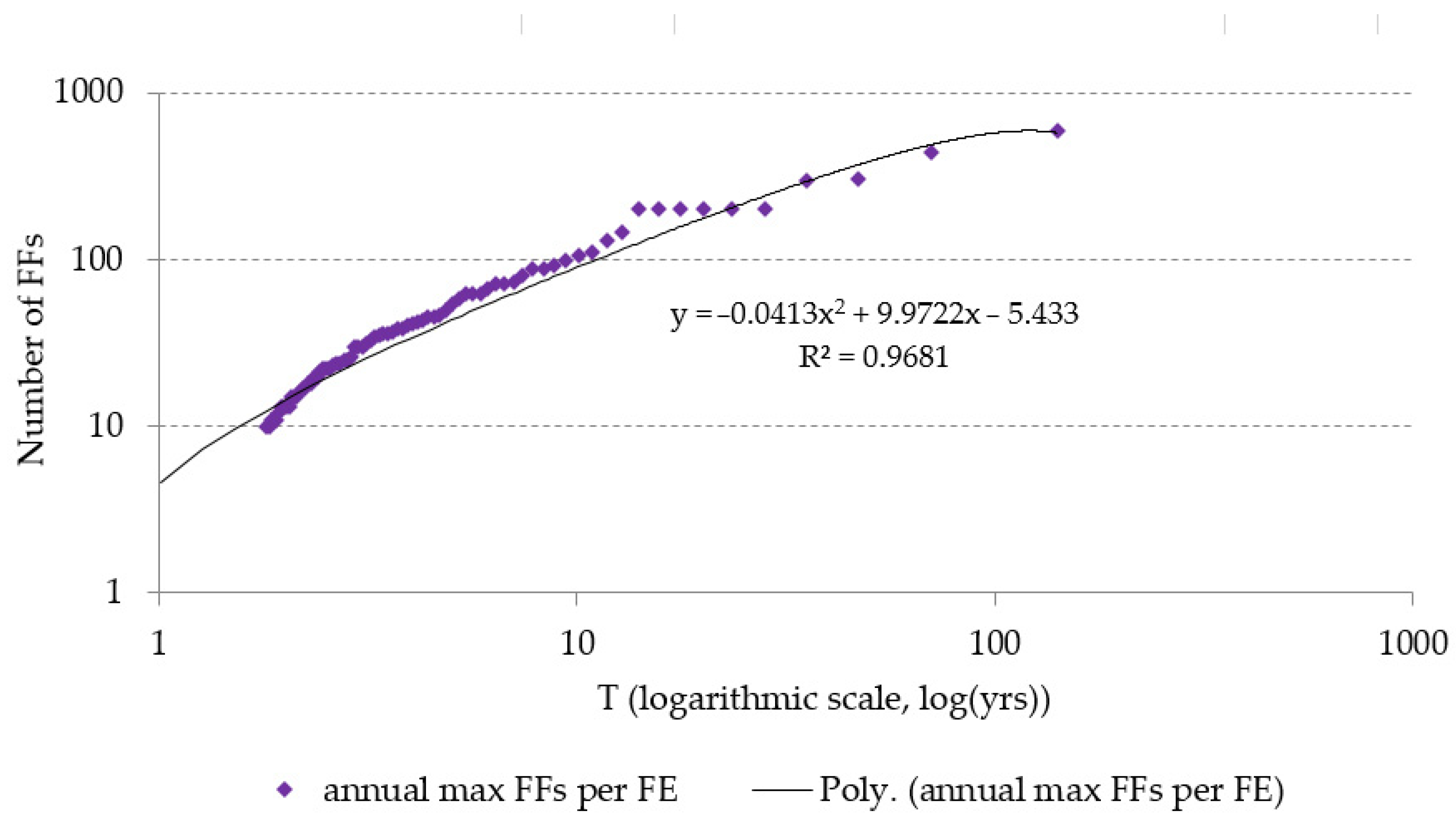
3.2. Return Period of Flash Flood Events with Ten or More Fatalities
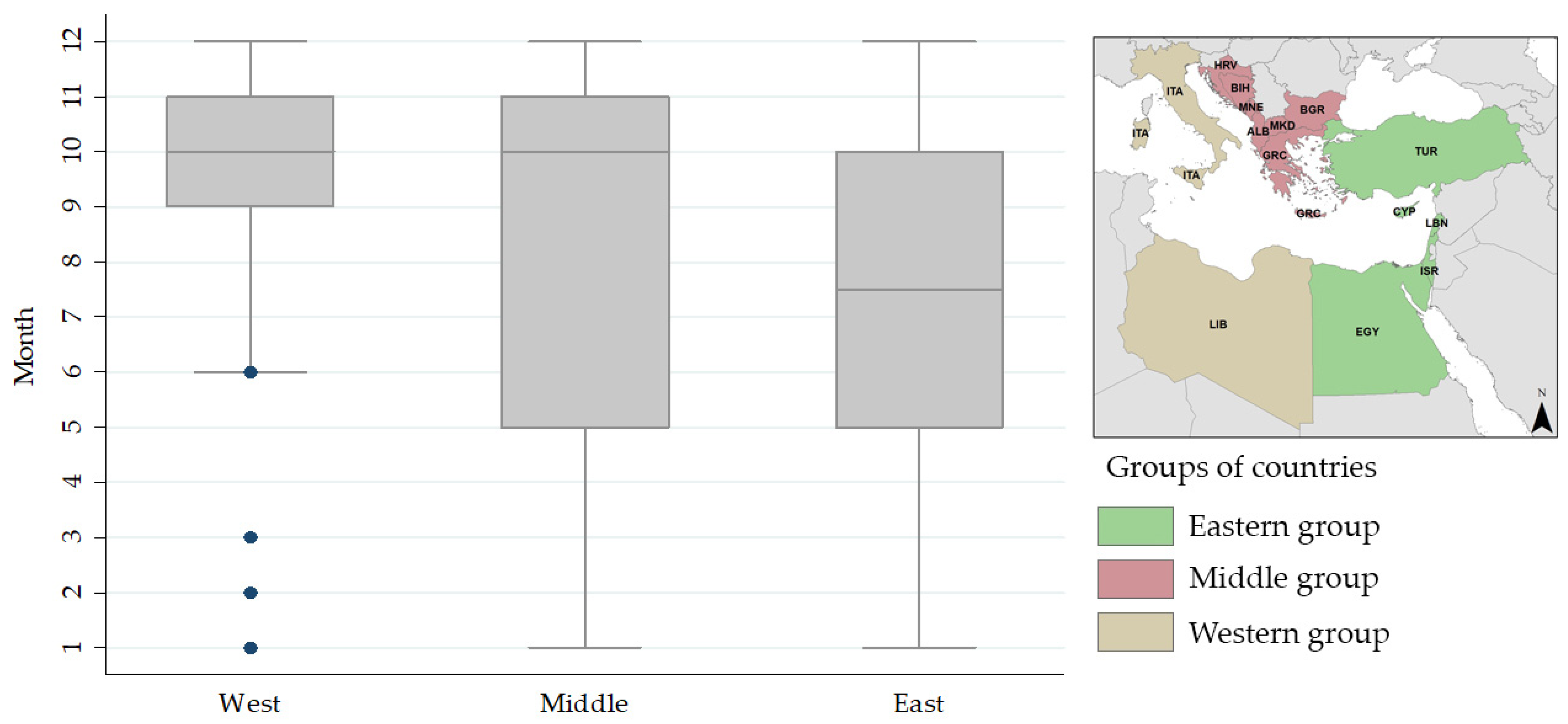
3.3. Seasonal Distribution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morrison, A.; Westbrook, C.J.; Noble, B.F. A review of the flood risk management governance and resilience literature. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dordi, T.; Henstra, D.; Thistlethwaite, J. Flood risk management and governance: A bibliometric review of the literature. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2022, 15, e12797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, E.C.; Thorne, C.R. Drivers of future urban flood risk. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2020, 378, 20190216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arduino, G.; Reggiani, P.; Todini, E. Recent advances in flood forecasting and flood risk assessment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 9, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanchetta, A.D.L.; Coulibaly, P. Recent Advances in Real-Time Pluvial Flash. Water 2020, 12, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delrieu, G.; Ducrocq, V.; Gaume, E.; Nicol, J.; Payrastre, O.; Yates, E.; Kirstetter, P.E.; Andrieu, H.; Ayral, P.A.; Bouvier, C.; et al. The catastrophic flash-flood event of 8–9 September 2002 in the Gard Region, France: A first case study for the Cévennes-Vivarais Mediterranean Hydrometeorological Observatory. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaume, E.; Livet, M.; Desbordes, M.; Villeneuve, J.P. Hydrological analysis of the river Aude, France, flash flood on 12 and 13 November 1999. J. Hydrol. 2004, 286, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, K.; Coates, L.; van den Honert, R.; Gissing, A.; Bird, D.; Dimer de Oliveira, F.; D’Arcy, R.; Smith, C.; Radford, D. Exploring the circumstances surrounding flood fatalities in Australia—1900–2015 and the implications for policy and practice. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 76, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakakis, M.; Andreadakis, E.; Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Spyrou, N.I.; Gogou, M.E.; Deligiannakis, G.; Katsetsiadou, N.K.; Antoniadis, Z.; Melaki, M.; Georgakopoulos, A.; et al. An integrated approach of ground and aerial observations in flash flood disaster investigations. The case of the 2017 Mandra flash flood in Greece. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 33, 290–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinet, F.; Lumbroso, D.; Defossez, S.; Boissier, L. A comparative analysis of the loss of life during two recent floods in France: The sea surge caused by the storm Xynthia and the flash flood in Var. Nat. Hazards 2012, 61, 1179–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwall, W. Europe’s deadly floods leave scientists stunned. Sciene 2021, 373, 372–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekete, A.; Sandholz, S. Here comes the flood, but not failure? Lessons to learn after the heavy rain and pluvial floods in germany 2021. Water 2021, 13, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucci, O.; Aceto, L.; Bianchi, C.; Brázdil, R.; Diakakis, M.; Inbar, M.; Kahraman, A.; Kılıç, O.; Krahn, A.; Kreibich, H.; et al. FFEM-DB “Database of Flood Fatalities from the Euro-Mediterranean region”. Sci. Data 2021, 9, 166. [Google Scholar]
- Petrucci, O.; Aceto, L.; Bianchi, C.; Bigot, V.; Br, R.; Pereira, S.; Kahraman, A.; Kılıç, Ö.; Kotroni, V.; Llasat, M.C.; et al. Flood Fatalities in Europe, 1980–2018: Variability, Features, and Lessons to Learn. Water 2019, 11, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinet, F.; Cherel, J.P.; Weiss, K.; Lewandowski, M.; Boissier, L. La mortalité liée aux inondations en région méditerranéenne française (1980–2020). LHB Hydrosci. J. 2022, 108, 2097022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruntfest, E. Long term social and economic impacts of extreme floods. In US-Italy Research Workshop on the Hydrometeorology, Impacts, and Management of Extreme Floods, Perugia, Italy; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1995; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Skouloudis, A.; Tsalis, T.; Nikolaou, I.; Evangelinos, K.; Filho, W.L. Small & medium-sized enterprises, organizational resilience capacity and flash floods: Insights from a literature review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Yang, L.; Toloo, S.; Wang, Z.; Tong, S.; Sun, X.; Crompton, D.; FitzGerald, G.; Huang, C. The long-term physical and psychological health impacts of flooding: A systematic mapping. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 165–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krichene, H.; Geiger, T.; Frieler, K.; Willner, S.N.; Sauer, I.; Otto, C. Long-term impacts of tropical cyclones and fluvial floods on economic growth–Empirical evidence on transmission channels at different levels of development. World Dev. 2021, 144, 105475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, D.; Werritty, A.; Ball, T.; Black, A. Environmental vulnerability and resilience: Social differentiation in short- and long-term flood impacts. Trans. Inst. Br. Geogr. 2020, 46, 102–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordbeck, R.; Löschner, L.; Pelaez Jara, M.; Pregernig, M. Exploring Science–Policy Interactions in a Technical. Water 2019, 11, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahraman, A.; Kendon, E.J.; Chan, S.C.; Fowler, H.J. Quasi-Stationary Intense Rainstorms Spread Across Europe Under Climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL092361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J. What Makes a Catastrophic Flood? And Is Climate Change Causing More of Them? New York Times, 22 March 2019; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Zittis, G.; Almazroui, M.; Alpert, P.; Ciais, P.; Cramer, W.; Dahdal, Y.; Fnais, M.; Francis, D.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Howari, F.; et al. Climate Change and Weather Extremes in the Eastern Mediterranean and Middle East. Rev. Geophys. 2022, 60, e2021RG000762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, R.; Emanuel, K. Climate change and hurricane-like extratropical cyclones: Projections for North Atlantic polar lows and medicanes based on CMIP5 models. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González-Alemán, J.J.; Pascale, S.; Gutierrez-Fernandez, J.; Murakami, H.; Gaertner, M.A.; Vecchi, G.A. Potential Increase in Hazard From Mediterranean Hurricane Activity With Global Warming. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, S.T.; Ashley, W.S. Flood fatalities in the United States. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkman, S.N.; Kelman, I. An analysis of the causes and circumstances of flood disaster deaths. Disasters 2005, 29, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terti, G.; Ruin, I.; Anquetin, S.; Gourley, J.J. A situation-based analysis of flash flood fatalities in the United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.; Diakakis, M.; Deligiannakis, G.; Zêzere, J.L. Comparing flood mortality in Portugal and Greece (Western and Eastern Mediterranean). Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2017, 22, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.; Zêzere, J.L.; Quaresma, I.; Santos, P.P.; Santos, M. Mortality Patterns of Hydro-Geomorphologic Disasters. Risk Anal. 2016, 36, 1188–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brázdil, R.; Chroma, K.; Dolák, L.; Řehoř, J.; Rezníchova, L.; Zahradníček, P.; Dobrovolný, P. Fatalities associated with the severe weather conditions in the Czech Republic, 2000–2019. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 21, 1355–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, K.; Demant, D.; Peden, A.E.; Hagger, M.S. A systematic review of human behaviour in and around floodwater. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 47, 101561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, L.; Borga, M.; Preciso, E.; Gaume, E. Characterisation of selected extreme flash floods in Europe and implications for flood risk management. J. Hydrol. 2010, 394, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Borga, M.; Morin, E.; Delrieu, G. Analysis of flash flood regimes in the North-Western and South-Eastern Mediterranean regions. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diakakis, M.; Deligiannakis, G.; Andreadakis, E.; Katsetsiadou, K.N.; Spyrou, N.I.; Gogou, M.E. How different surrounding environments influence the characteristics of flash flood-mortality: The case of the 2017 extreme flood in Mandra, Greece. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2020, 13, e12613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha-Sapir, D.; Below, R.; Hoyois, P. EM-DAT: The CRED/OFDA International Disaster Database; Brussels, Belgium. 2021. Available online: https://www.carismand.eu/resources/em-dat-the-credofda-international-disaster-database.html (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Brakenridge, G.R. Global Active Archive of Large Flood Events; Boulder, CO, USA. 2021. Available online: https://floodobservatory.colorado.edu/Archives/index.html (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Paprotny, D.; Morales-nápoles, O.; Jonkman, S.N. HANZE: A pan-European database of exposure to natural hazards and damaging historical floods since 1870. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Environment Agency. Flood Phenomena. European Past Floods; European Environment Agency: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Toto, E.; Massabo, M. Historical Collection of Disaster Loss Data in Albania; Savona, Italy. 2014. Available online: https://www.undrr.org/publication/historical-collection-disaster-loss-data-albania (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Bogdani, M.; Selenica, A. Catastrophic floods and their risk in the rivers of Albania. In Destructive Water: Water Caused Natural Disasters, Their Abatement and Control; Leavesley, G., Lins, H., Nobilis, F., Parker, R., Schneider, V., Ven de Van, F., Eds.; IAHS Publications: Wallingford, UK, 1997; pp. 83–85. [Google Scholar]
- GIZ. Preliminary Flood Risk Assessment for the Drin/Drim-Buna/Bojana River Basin; Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit: Bonn, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ACAPS. Floods in Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina; ACAPS: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- FloodList Floodlist Website. Available online: https://floodlist.com (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Kundzewicz, Z.W. Changes in Flood Risk in Europe, 1st ed.; Kundzewicz, Z.W., Ed.; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 9780203098097. [Google Scholar]
- Vidmar, A.; Globevnik, L.; Koprivšek, M.; Sečnik, M.; Zabret, K.; Durović, B.; Anzeljc, D.; Kastelic, J.; Kobold, M.; Sušnik, M.; et al. The Bosna River floods in May 2014. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 2235–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EU ECHO. Floods-Spring and Summer 2005. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/echo/files/civil_protection/floods_2005.htm (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Bonacci, O.; Ljubenkov, I. Changes in flow conveyance and implication for flood protection, Sava River, Zagreb. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačić, T. Analysis of Short-Term Rainfall Characteristics Related to the Pluvial Floods in the City of Zagreb; University of Zagreb: Zagreb, Croatia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Polignosi Floods. Available online: http://www.polignosi.com/cgibin/hweb?-A=9171&-V=limmata (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- WDD. Preliminary Flood Risk Assessment Final Report; WDD: Lefkosia, Cyprus, 2011; Volume 70. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.; Kantoush, S.A.; Sumi, T. Integrated Management of Flash Flood in Wadi System of Egypt: Disaster Prevention and Water Harvesting. Annu. Disaster Prev. Res. Inst. Kyoto Univ. 2015, 58, 485–496. [Google Scholar]
- El Afandi, G.; Morsy, M. Developing an early warning system for flash flood in Egypt: Case study Sinai Peninsula. In Flash Floods in Egypt; Negm, A.M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- El Gohary, R. Environmental Flash Flood Management in Egypt. In Flash Floods in Egypt; Negm, A.M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 85–105. [Google Scholar]
- IFRC. Emergency Plan of Action (EPoA), Egypt: Flash Floods; Mena. 2020. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/egypt/egypt-flash-floods-emergency-plan-action-epoa-final-report-dref-n-mdreg015 (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Negm, A.M. Flash Floods in Egypt; Negm, A.M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 9783030296346. [Google Scholar]
- The New York Times Article Archive. New York Times. 2022, p. 1. Available online: https://archive.nytimes.com/www.nytimes.com/ref/membercenter/nytarchive.html (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Omran, E.S.E. Egypt’s Sinai desert cries: Flash flood hazard, vulnerability, and mitigation. In Flash Floods in Egypt; Negm, A.M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 215–236. [Google Scholar]
- UN DHA. Egypt-Floods Nov 1994, UNDHA Situation Reports 1–4; UN DHA: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Saber, M.; Abdrabo, K.I.; Habiba, O.M.; Kantosh, S.A.; Sumi, T. Impacts of triple factors on flash flood vulnerability in Egypt: Urban growth, extreme climate, and mismanagement. Geoscience 2020, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papagiannaki, K.; Lagouvardos, K.; Kotroni, V. A database of high-impact weather events in Greece: A descriptive Atmospheric impact analysis for the period 2001–2011. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakakis, M.; Deligiannakis, G. Flood fatalities in Greece: 1970–2010. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2017, 10, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakakis, M. An inventory of flood events in Athens, Greece, during the last 130 years. Seasonality and spatial distribution. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2014, 7, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbar, M. Natural Hazards in Israel, 1948–2004: A Temporal and Spatial Analysis Author (s): Moshe Inbar Contemporary Israeli Geopraphy/תננמז תב תילארשי היפרגואג & lrm; ( 2004-ד " סשת ). In Contemporary Israeli Geography; Maos, J.O., Inbar, M., Shmueli, D.F., Eds.; Natural Hazards: Haifa, Israel, 2004; pp. 139–146. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/23712691 (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- APAT. Annuario Dei Dati Ambientali 2004; APAT: Roma, Italy, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Aronica, G.T.; Brigandi, G.; Morey, N. Flash floods and debris flow in the city area of Messina, north-east part of Sicily, Italy in October 2009: The case of the Giampilieri catchment. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccini, F.; Paliaga, G.; Piana, P.; Sacchini, A.; Watkins, C. The Bisagno stream catchment (Genoa, Italy) and its major floods: Geomorphic and land use variations in the last three centuries. Geomorphology 2016, 273, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucci, O.; Pasqua, A.A. Historical climatology of storm events in the mediterranean: A case study of damaging hydrological events in Calabria, Southern Italy. In Advances in Natural and Technological Hazards Research; Diodato, N., Bellocchi, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 39, pp. 249–268. ISBN 9789400779488. [Google Scholar]
- Gaume, E.; Borga, M.; Llasat, M.C.; Maouche, S.; Lang, M.; Diakakis, M. Mediterranean extreme floods and flash floods. In The Mediterranean Region under Climate Change: A Scientific Update; Sabrié, M.-L., Gibert-Brunet, E., Mourier, T., Eds.; IRD Editions: Marseille, France, 2016; pp. 133–145. [Google Scholar]
- Suwaydan, M.T. Abu Ali River Floods and Their Control in Tripoli, Lebanon; American University of Beirut: Tripoli, Libya, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- UNISDR. South Eastern Europe Disaster Risk Mitigation and Adaptation Initiative; UNISDR: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Malevski, I. Natural Hazards in the Republic of Macedonia with Special Emphasis on Flood and Earthquake in Skopje in 2016. Геoграфски Разгледи 2017, 50, 53–69. [Google Scholar]
- Yüksek, Ö.; Kankal, M.; Üçüncü, O. Assessment of big floods in the Eastern Black Sea Basin of Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 797–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haltas, I.; Yildirim, E.; Oztas, F.; Demir, I. A comprehensive flood event specification and inventory: 1930–2020 Turkey case study. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 56, 102086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uluatam, S.S. Risk reduction of environmental pollution and water resources problem for sustainable development. In Risk reduction: Chemicals and energy into the 21st Century; Richardson, M., Ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 1996; p. 612. [Google Scholar]
- Koç, G.; Petrow, T.; Thieken, A.H. Analysis of the most severe flood events in Turkey (1960-2014): Which triggering mechanisms and aggravating pathways can be identified? Water 2020, 12, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaymaz, I. The Lost Streams of Ankara: A Case Study of Bentderesi. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ballar, Z. Stormwater Management in Cities as a Climate Change Adaptation Strategy: Case of Halkapınar District. Master’s Thesis, Izmir Institute of Technology, Izmir, Turkey, 2019. Available online: https://gcris.iyte.edu.tr/bitstream/11147/9668/1/10308479.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Gürer, I. Flood Disasters and Preventative Measures in Turkey. J. Nat. Disaster Sci. 1998, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Burn, D.H. Evaluation of regional flood frequency analysis with a region of influence approach. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 2257–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavers, D.A.; Villarini, G. Atmospheric rivers and flooding over the central United States. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 7829–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibull, W. A Statistical Distribution Function of Wide Applicability. J. Appl. Mech. 1951, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinet, F.; Bigot, V.; Petrucci, O.; Papagiannaki, K.; Llasat, M.C.; Kotroni, V.; Boissier, L.; Aceto, L.; Grimalt, M.; Pasqua, A.A.; et al. Mapping Flood-Related Mortality in the Mediterranean Basin. Results from the MEFF v2.0 DB. Water 2019, 11, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, L.K.; Vogel, R.M. Reliability, return periods, and risk under nonstationarity. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 6381–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakakis, M. Flood seasonality in Greece and its comparison to seasonal distribution of flooding in selected areas across southern Europe. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2017, 10, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv, B.; Dayan, U.; Kushnir, Y.; Roth, C.; Enzel, Y. Regional and global atmospheric patterns governing rainfall in the southern Levant. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima, I.M.; Wallace, J.M. On the seasonality of the Hadley Cell. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionello, P. (Ed.) The Climate of the Mediteerranean Region. From the Past to the Future; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 9780124160422. [Google Scholar]
- Nastos, P.T.; Zerefos, C.S. Decadal changes in extreme daily precipitation in Greece. Adv. Geosci. 2008, 16, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koutroulis, A.G.; Tsanis, I.K.; Daliakopoulos, I.N. Seasonality of floods and their hydrometeorologic characteristics in the island of Crete. J. Hydrol. 2010, 394, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Sáenz, J.; Zorita, E. Analysis of wintertime atmospheric moisture transport and its variability over southern Europe in the NCEP reanalyses. Clim. Res. 2003, 23, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostertagová, E. Modelling using polynomial regression. Procedia Eng. 2012, 48, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoyois, P.; Guha-sapir, D. Three Decades of Floods in Europe: A Preliminary Analysis of EMDAT Data; Centre for Research on the Epidimiology of Disasters: Brussels, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Diakakis, M. Have flood mortality qualitative characteristics changed during the last decades? The case study of Greece. Environ. Hazards 2016, 15, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Country * | International Databases | Other Sources | Number of Fes ** with >10FFs *** | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM-DAT | DFO | FFEM-DB | HANZE-E | EPF | |||
| ALB | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Toto and Massabo [42] a Bogdani and Selenica [43] c GIZ [44] b | 2 | ||
| BIH | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ACAPS [45] f Floodlist.com [46] f Kundzewicz [47] d Vidmar [48] c | 3 | ||
| BGR | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | EU ECHO [49] d Floodlist.com [46] f | 3 | |
| HRV | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Bonacci & Ljubenkov [50] c Kovačić, T. [51] c | 1 | ||
| CYP | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Polignosi [52] b WDD [53] a | 2 |
| EGY | ✓ | ✓ | Abdel-Fattah et al. [54] c El Afandi & Morsy [55] c El Gohary [56] c IFRC [57] d Negm [58] c New York Times [59] e Omran [60] c UN DHA [61] f Saber et al. [62] c | 14 | |||
| GRC | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | IERSD/NOA catalogs a Papagiannaki et al. [63] c Diakakis and Deligiannakis [64] c Diakakis [65] c floodlist.com [46] f | 12 |
| ISR | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Inbar [66] a floodlist.com [46] f | 3 | ||
| ITA | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | APAT [67] b Aronica et al. [68] c floodlist.com [46] f Faccini et al. [69] c New York Times [59] e Petrucci & Pasqua [70] c | 51 |
| LBN | ✓ | ✓ | Gaume [71] c New York Times [59] e Suwaydan [72] c | 2 | |||
| LBY | ✓ | ✓ | Floodlist.com [46] f New York Times [59] | 1 | |||
| MNE | ✓ | ✓ | Floodlist.com [46] f UN/ISDR [73] d | 1 | |||
| MKD | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Floodlist.com [46] f Malevski [74] c | 2 | ||
| TUR | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | EBSB [75] a Haltas et al. [76] c Uluatam [77] c TAAB Database (Koç et al. [78]) a New York Times [59] e Kaymaz [79] c Ballar [80] c Gürer [81] c | 35 | |
| Total events (1882–2021) = 132 | |||||||
| Event Magnitude | Number of Events | This Study | Difference (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DFO a | 10 fatalities | 41 | 64 | 56% |
| ≥20 fatalities | 19 | 29 | 53% | |
| ≥50 fatalities | 7 | 11 | 57% | |
| ≥100 fatalities | 3 | 3 | 0% | |
| EM-DAT b | ≥10 fatalities | 70 | 125 | 79% |
| ≥20 fatalities | 39 | 67 | 72% | |
| ≥50 fatalities | 22 | 33 | 50% | |
| ≥100 fatalities | 10 | 16 | 60% | |
| EPF c | ≥10 fatalities | 36 | 46 | 28% |
| ≥20 fatalities | 19 | 22 | 16% | |
| ≥50 fatalities | 8 | 9 | 13% | |
| ≥100 fatalities | 1 | 1 | 0% | |
| FFEM-DB d | ≥10 fatalities | 38 | 46 | 21% |
| ≥20 fatalities | 12 | 19 | 58% | |
| ≥50 fatalities | 4 | 8 | 100% | |
| ≥100 fatalities | 0 | 1 | - | |
| HANZE-E e | ≥10 fatalities | 59 | 66 | 12% |
| ≥20 fatalities | 30 | 39 | 30% | |
| ≥50 fatalities | 14 | 18 | 29% | |
| ≥100 fatalities | 8 * | 7 * | −13% * |
| Class | FFs Number | Corresponding Percentiles | Number of Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
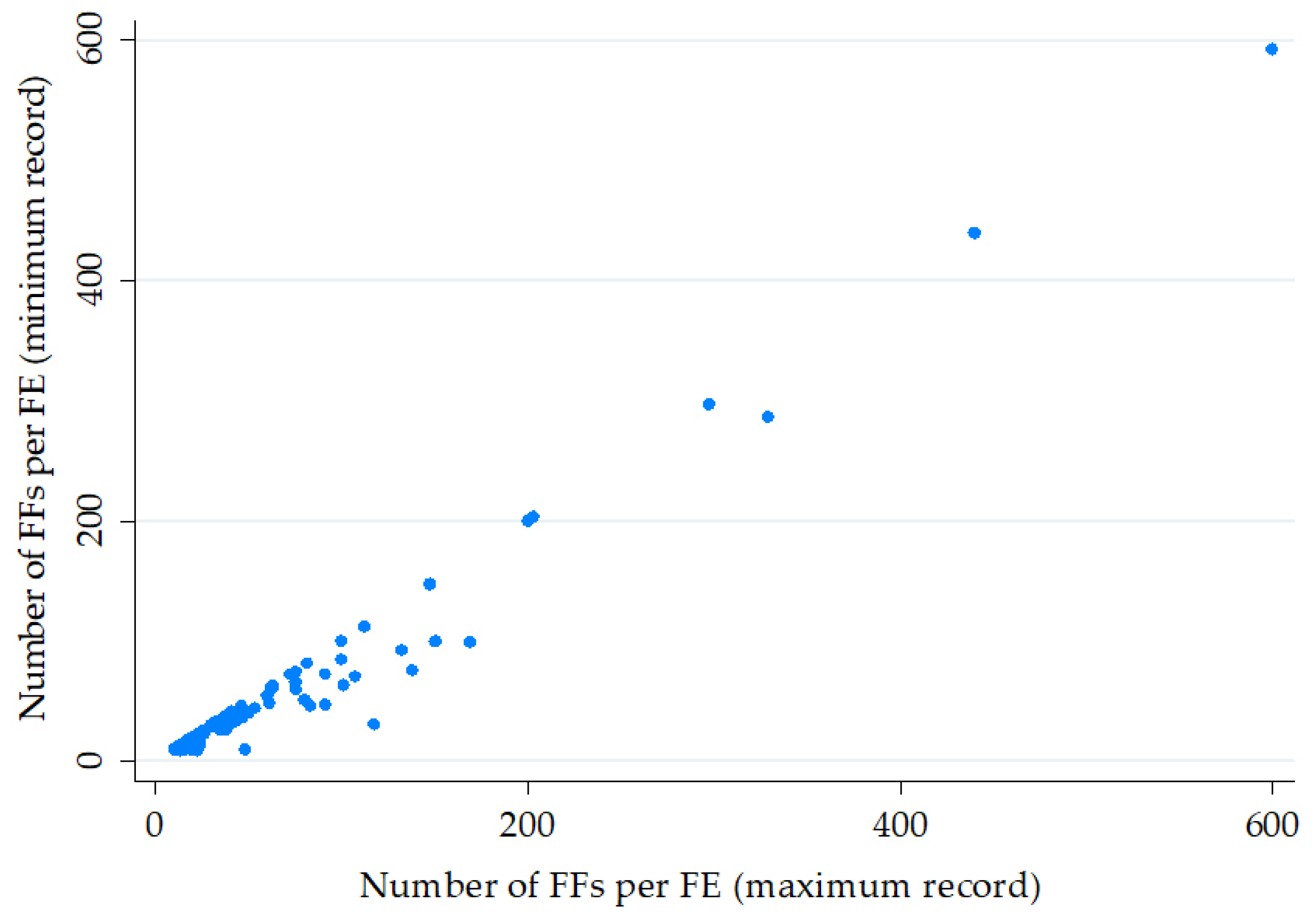
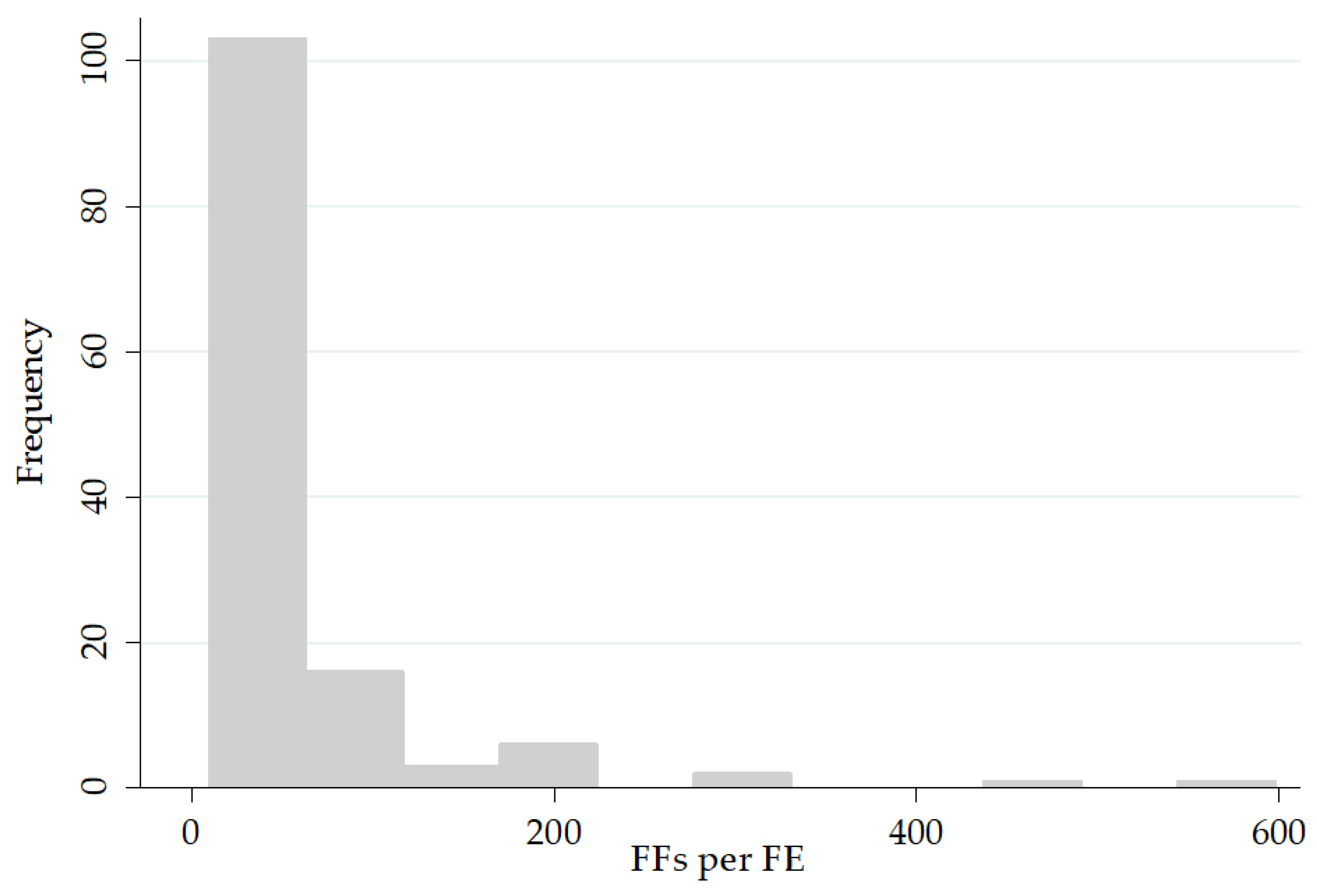
| FI1—Low | 10–22 | Minimum—50th | 67 |
| FI2—Moderate | 23–82 | 50th–85th | 45 |
| FI3—High | >82 | >85th | 20 |
| Flood Impact Magnitude Class (FI Index) | Return Period | Probability of Occurrence in a Single Year |
|---|---|---|
| FI1 | 1 event in 1.56 years | 0.641 |
| FI2 | 1 event in 2.78 years | 0.360 |
| FI3 | 1 event in 9.11 years | 0.110 |
| Flood Impact Magnitude Class (FI Index) | Study Area Segmentation | Return Period | Probability of Occurrence in a Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| FI1 | Western | 1 event in 3.38 years | 0.296 |
| Middle | 1 event in 6.61 years | 0.151 | |
| Eastern | 1 event in 3.5 years | 0.286 | |
| FI2 | Western | 1 event in 5.44 years | 0.184 |
| Middle | 1 event in 11.81 years | 0.085 | |
| Eastern | 1 event in 5.43 years | 0.184 | |
| FI3 | Western | 1 event in 16.39 years | 0.061 |
| Middle | 1 event in 40.38 years | 0.025 | |
| Eastern | 1 event in 15.31 years | 0.065 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diakakis, M.; Papagiannaki, K.; Fouskaris, M. The Occurrence of Catastrophic Multiple-Fatality Flash Floods in the Eastern Mediterranean Region. Water 2023, 15, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15010119
Diakakis M, Papagiannaki K, Fouskaris M. The Occurrence of Catastrophic Multiple-Fatality Flash Floods in the Eastern Mediterranean Region. Water. 2023; 15(1):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15010119
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiakakis, Michalis, Katerina Papagiannaki, and Meletis Fouskaris. 2023. "The Occurrence of Catastrophic Multiple-Fatality Flash Floods in the Eastern Mediterranean Region" Water 15, no. 1: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15010119
APA StyleDiakakis, M., Papagiannaki, K., & Fouskaris, M. (2023). The Occurrence of Catastrophic Multiple-Fatality Flash Floods in the Eastern Mediterranean Region. Water, 15(1), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15010119








