Water-Rock Action Analysis and Quality Evaluation of Shallow Groundwater in Rural Areas: A Case Study of Suzhou City, Northern Anhui, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. Data Analysis Methods
3. Results
Descriptive Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
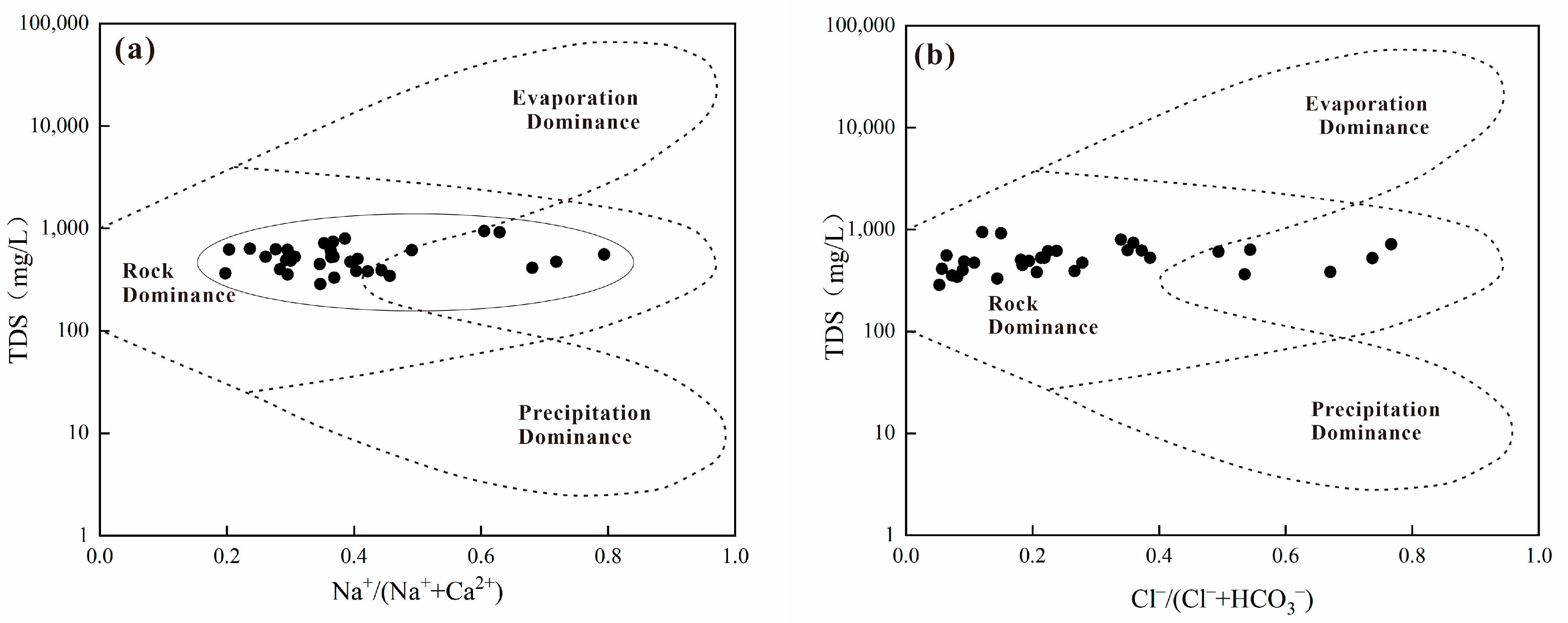
4.1. Water Chemistry Type and Water–Rock Action Analysis
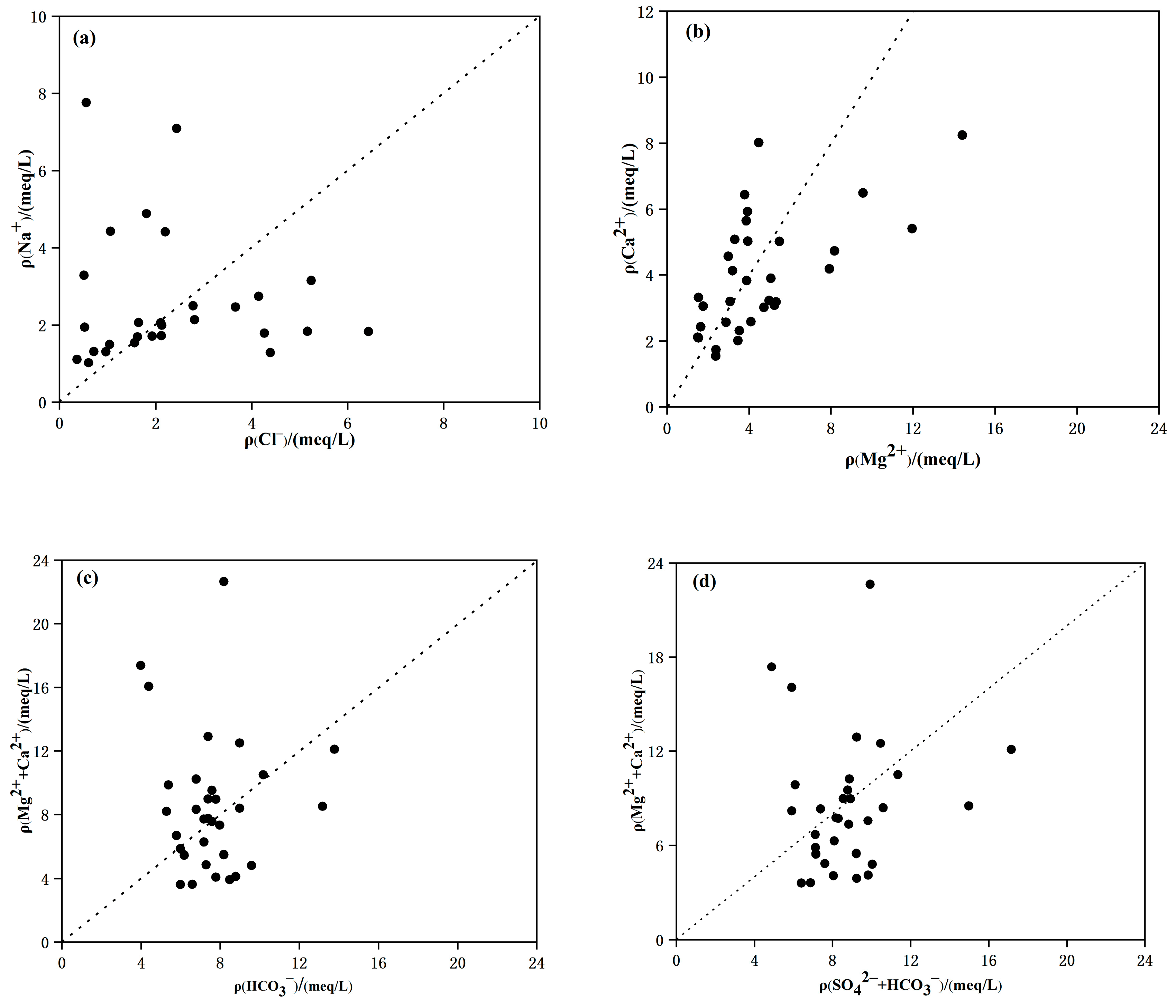
4.2. Ion Ratio Analysis
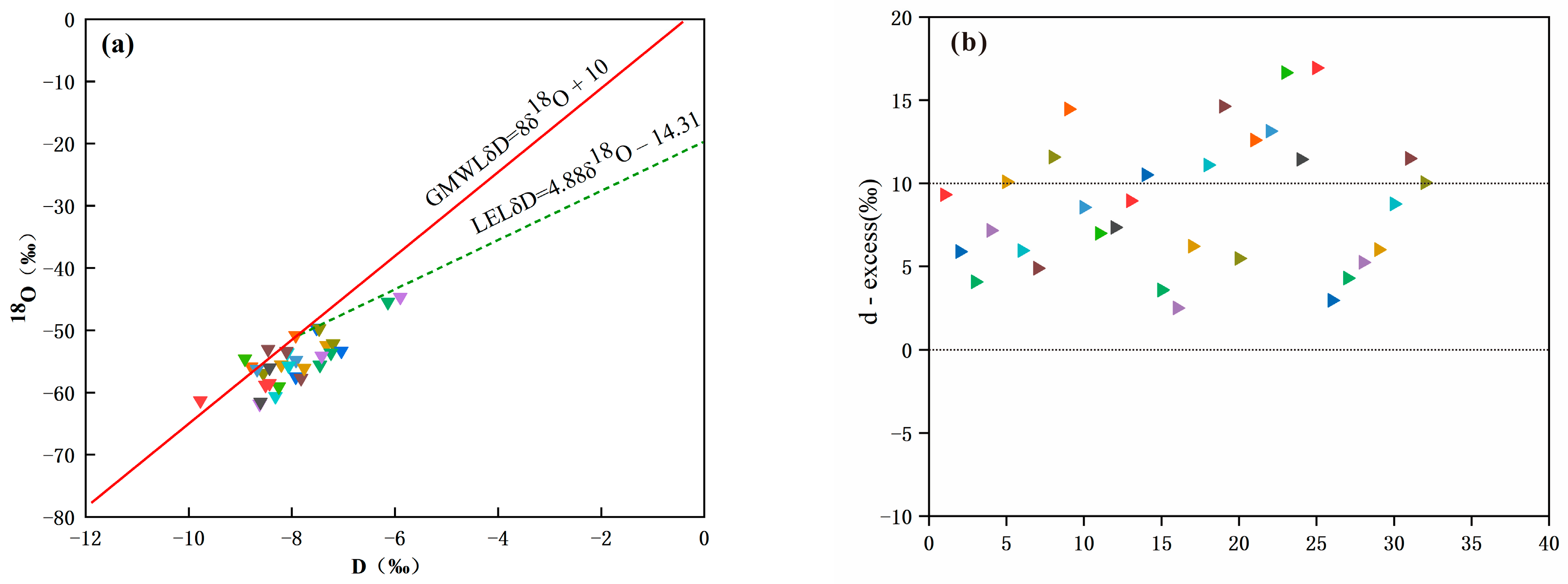
4.3. Hydrogeochemical Processes
4.4. Water Quality Assessment
4.4.1. Water Quality for Drinking
4.4.2. Irrigation-Water Quality Assessment
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The contents of conventional ions in the study area changed to HCO3− > Cl− > Ca2+ > K+ + Na+ > SO42− > Mg2+; cations are dominated by K+ + Na+ and Ca2+, and anions are dominated by HCO3− and Cl−. The hydrochemical types in the study area are mainly HCO3-Ca-type, HCO3-Mg-type, and HCO3-Na-type.
- (2)
- The hydrochemical fraction of shallow groundwater in the study area is mainly influenced by rock weathering and controlled by the process of water–rock interaction. Silicate weathering plays a major role in hydrogeochemical processes, while Mg2+ and Ca2+ are dominated by the dissolution of silicate minerals and carbonate minerals, where ion exchange most likely has occurred, with evaporation dominating the research area.
- (3)
- Our results for the drinking-water quality evaluation showed that the concentrations of all major ions were within the maximum expected range defined by (WHO 1997) and conformed to the national drinking-water hygiene standards. Regarding the results shown in the USSL and Wilcox diagrams, the high salt and alkali contents of the water samples collected from the study area indicate that the groundwater is suitable for irrigating plants with strong salt tolerance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbasnia, A.; Yousefifi, N.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nabizadeh, R.; Radfard, M.; Yousefifi, M.; Alimohammadi, M. Evaluation of groundwater quality using water quality index and its suitability for assessing water for drinking and irrigation purposes: Case study of Sistan and Baluchistan province (Iran). Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2019, 25, 988–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Wu, J. Groundwater quality and associated health risks in a semi-arid region of south India: Implication to sustainable groundwater management. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 191–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowing, J.; Walker, D.; Parkin, G.; Forsythe, N.; Haile, A.T.; Ayenew, D.A. Can shallow groundwater sustain small-scale irrigated agriculture in sub-Saharan Africa? Evidence from N-W Ethiopia. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalhor, K.; Ghasemizadeh, R.; Rajic, L.; Alshawabkeh, A. Assessment of groundwater quality and remediation in karst aquifers: A review. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.P. Hydrochemical characteristics and influencing factors of shallow groundwater in siyang area, jiangsu province. Geoscience 2014, 28, 1329–1336. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jasechko, S.; Perrone, D.; Befus, K.M.; Cardenas, M.B.; Ferguson, G.; Gleeson, T.; Luijendijk, E.; McDonnell, J.J.; Taylor, R.G.; Wada, Y.; et al. Global aquifers dominated by fossil groundwaters but wells vulnerable to modern contamination. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Parihar, R.D.; Sharma, A.; Bakshi, P.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Bali, A.S.; Karaouzas, I.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.K.; Gyasi-Agyei, Y.; et al. Global evaluation of heavy metal content in surface water bodies: A meta-analysis using heavy metal pollution indices and multivariate statistical analyses. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Ko, J.; Hwang, S. Evaluation of Water Quality Variation and Sediment of a Shallow Artificial Lake (Lake llgam) in Located the Metropolitan Area. J. Ecol. Environ. 2003, 36, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, T.T.K.; Giao, N.T. Analysis of Surface Water Quality in Upstream Province of Vietnamese Mekong Delta Using Multivariate Statistics. Water 2022, 14, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerselvam, B.; Ravichandran, N.; Kaliyappan, S.P.; Karuppannan, S.; Bidorn, B. Quality and Health Risk Assessment of Groundwater for Drinking and Irrigation Purpose in Semi-Arid Region of India Using Entropy Water Quality and Statistical Techniques. Water 2023, 15, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Qin, Z.; Huang, L. Evaluating Temporal and Spatial Variation in Nitrogen Sources along the Lower Reach of Fenhe River (Shanxi Province, China) Using Stable Isotope and Hydrochemical Tracers. Water 2018, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres Lopez, S.; delos Angeles Barrionuevo, M.; Rodriguez-Labajos, B. Water accounts in decision-making processes of urban water management: Benefits, limitations and implications in a real implementation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Q.; Wang, X.X.; Chen, X. Chemical characteristics and water quality evaluation of groundwater on the east coast of Laizhou Bay. Environ. Prot. Circ. Econ. 2020, 40, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.W.; Deng, Z.B.; Li, L.P.; Wen, J.X.; Cao, Y.F. Patial pattern and convergence of the development level of China’s water ecological civilization. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 1282–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.Y.; Chen FLi, Y.Y.; Tang, S.N.; Yu, L.L.; Yang, Y. Compiling background and ideas of The Action Plan for Comprehensive Treatment of Groundwater Overexploitation in North China. China Water Resour. 2020, 13, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Huang, D.J. Development of Sustainable Utilization of Water Resources in Northern Areas of Anhui Province. J. Bengbu Coll. 2014, 3, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; Li, E.K.; Guo, X.W.; Du, K. Evaluation Method for Status and Potential of Mine Water Resources Development and Utilization. Yellow River 2021, 43, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, G.S.; Zhou, J.N.; Li, Y.Z.; Jiang, C.J. Comprehensive water quality evaluation of typical areas in the belly of Lixia River based on entropy weight method. Water Resour. Power 2021, 39, 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Gui, H.; Li, C.; Wang, C.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Y. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Quality Assessment of Shallow Groundwater in Poultry Farming Sites in Suzhou City, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 4071–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Saleh, H.N.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Mahvi, A.H.; Ghadrpoori, M.; Suleimani, H. Data on water quality index for the groundwater in rural area Neyshabur County, Razavi province, Iran. Data Brief 2017, 15, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, F.B.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Dehghani, M.H.; Yousefi, M. Data on assessment of groundwater quality with application of ArcGIS in Zanjan, Iran. Data Brief 2018, 18, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, J. Groundwater as a geologic agent: An overview of the causes, processes, and manifestations. Hydrogeol. J. 1999, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.H.; Su, X.S.; Hou, G.C.; Lin, X.Y.; Liu, F.T. Distribution law of groundwater hydrochemical type in the ordos cretaceous artesi an basin. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2007, 2, 288–292. [Google Scholar]
- Yousafzai, A.; Eckstein, Y.; Dahl, P.S. Hydrochemical signatures of deep groundwater circulation in a part of the Himalayan foreland basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 59, 1079–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Wu, X.; Mu, W.P.; Fu, R.Z. Hydrogeo-Chemical Characterization and Suitability Assessment of Ground-water in an Agro-Pastoral Area, Ordos Basin, NW China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cai, W.T.; Li, Y.Z.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Geng, T.T.; Bian, C.; Zhao, M.; Cai, Y.M. Major Ionic Features and Their Possible Controls in the Water of the Niyang River Basin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 4537–4545. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.Q.; Dong, S.G.; Zhang, M.W. Hydrochemical characteristics and causes of shallow groundwater in Siziwangqi, Inner Mongolia. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2020, 34, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.L.; Zhu, W.H.; Zhong, Z.S. Fundamentals of Hydrogeochemistry; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1993; pp. 94–123. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.W.; Xu, D.Q.; Yin, X.X.; Xie, W.P.; Zeng, W. Analysis on hydrochemistry and its control factors in the concealed coal mining area in North China: A case study of dominant inrush aquifers in Suxian mining area. J. China Coal Soc. 2017, 42, 996–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, H. Isotopic Vaiations in Meteoric Waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.Q.; Gui, H.R.; Yu, H.; Wang, M.C.; Fang, H.X.; Wang, C.L.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.R.; Huang, Y.H. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Water Quality Evaluation of Rivers in Northern Anhui Province, China. Water 2020, 12, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Y.; Gui, H.R.; Chen, J.Y.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C.Z.; Guo, Y. Hydrochemical Process and Quality Assessment of Surface Water Around Fuli Abandoned Quarries Area, Northern Anhui Province, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Meng, X.Y. Appraising Groundwater Quality and Health Risks from Contamination in a Semiarid Region of Northwest China. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, F.M. Significance of carbonates in irrigation waters. Soil Sci. 1950, 69, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaghi, F.; Delgosha, F.; Razzaghmanesh, M.; Myers, B. Introducing a water quality index for assessing water for irrigation purposes: A case study of the Ghezel Ozan River. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 589, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, A.A.; El-Horiny, M.M.; Atwia, M.G.; Gemail, K.S.; Koike, K. Assessment of groundwater and soil quality degradation using multivariate and geostatistical analyses, Dakhla Oasis, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 142, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | Na+ + K+ /(mg/L) | Ca2+ /(mg/L) | Mg2+ /(mg/L) | Cl− /(mg/L) | SO42− /(mg/L) | HCO3− /(mg/L) | δ2H /(‰) | δ18O /(‰) | TDS /(mg/L) | EC /(μs/cm) | pH | Water Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30.48 | 100.71 | 47.36 | 155.68 | 55.63 | 450.62 | −58.78 | −8.51 | 622 | 1277 | 7.3 | Ca-HCO3 |
| 2 | 42.95 | 118.56 | 47.19 | 228.34 | 33.73 | 328.83 | −57.5 | −7.92 | 631 | 1295 | 7.35 | Ca-HCO3 |
| 3 | 58.63 | 76.66 | 46.64 | 98.68 | 53.43 | 438.44 | −55.58 | −7.46 | 471 | 1072 | 7.33 | Ca-HCO3 |
| 4 | 57.51 | 128.78 | 45.46 | 129.95 | 99.63 | 414.09 | −61.83 | −8.62 | 626 | 1342 | 7.03 | Ca-HCO3 |
| 5 | 73.88 | 100.45 | 65.79 | 186.06 | 55.75 | 621.13 | −55.55 | −8.2 | 797 | 1760 | 7.15 | Ca-HCO3 |
| 6 | 41 | 77.93 | 60.83 | 75.18 | 54.54 | 474.98 | −60.6 | −8.32 | 529 | 1105 | 7.24 | Mg-HCO3 |
| 7 | 35.16 | 51.35 | 34.64 | 37.11 | 46.04 | 377.55 | −57.7 | −7.82 | 330 | 684 | 7.41 | Ca-HCO3 |
| 8 | 39.78 | 64.01 | 36.92 | 57.5 | 43.42 | 438.44 | −56.87 | −8.56 | 449 | 928 | 7.22 | Ca-HCO3 |
| 9 | 46.83 | 113.05 | 46.41 | 75.48 | 57.03 | 462.80 | −55.83 | −8.79 | 528 | 1095 | 7.08 | Ca-HCO3 |
| 10 | 48.18 | 51.68 | 49.17 | 74.64 | 63.84 | 353.19 | −54.82 | −7.92 | 390 | 805 | 7.57 | Mg-HCO3 |
| 11 | 45.72 | 46.28 | 42.42 | 18.76 | 54.51 | 365.37 | −59.06 | −8.26 | 343 | 699 | 7.76 | Mg-HCO3 |
| 12 | 48.42 | 60.45 | 56.81 | 58.28 | 37.77 | 450.62 | −61.51 | −8.61 | 503 | 1032 | 7.35 | Mg-HCO3 |
| 13 | 64.19 | 94.53 | 98.12 | 147.12 | 88.82 | 450.62 | −58.51 | −8.43 | 738 | 1505 | 7.25 | Mg-HCO3 |
| 14 | 86.91 | 129.89 | 114.77 | 437.78 | 73.14 | 267.94 | −49.66 | −7.52 | 524 | 748 | 7.36 | Mg-Cl |
| 15 | 43.94 | 64.53 | 59.77 | 183.29 | 29.99 | 322.74 | −45.48 | −6.13 | 604 | 1258 | 7.38 | Mg-HCO3 |
| 16 | 41.94 | 61.63 | 62.92 | 151.43 | 29.05 | 414.09 | −44.65 | −5.9 | 527 | 1089 | 7.4 | Mg-HCO3 |
| 17 | 69.09 | 108.19 | 143.53 | 465.57 | 43.02 | 243.58 | −52.41 | −7.33 | 717 | 1062 | 7.35 | Mg-Cl |
| 18 | 164.19 | 83.64 | 95.06 | 86.58 | 162.14 | 840.35 | −53.61 | −8.09 | 917 | 1902 | 7.02 | Na-HCO3 |
| 19 | 113.7 | 63.74 | 63.9 | 64.25 | 86.56 | 803.81 | −57 | −8.46 | 943 | 1930 | 6.86 | Na-HCO3 |
| 20 | 102.16 | 91.32 | 35.97 | 78.06 | 106.96 | 462.80 | −52.13 | −7.2 | 612 | 1260 | 7.05 | Na-HCO3 |
| 21 | 102.85 | 34.72 | 28.69 | 37.78 | 50.12 | 535.88 | −50.81 | −7.93 | 472 | 965 | 7.34 | Na-HCO3 |
| 22 | 179.35 | 40.31 | 41.56 | 19.92 | 49.42 | 499.34 | −56.28 | −8.68 | 554 | 1135 | 7.28 | Na-HCO3 |
| 23 | 40.41 | 82.57 | 38.41 | 68.4 | 40.81 | 487.16 | −54.6 | −8.91 | 490 | 1000 | 7.2 | Ca-HCO3 |
| 24 | 50.25 | 101.72 | 39.69 | 99.84 | 77.16 | 548.06 | −56.01 | −8.43 | 617 | 1280 | 7.25 | Ca-HCO3 |
| 25 | 76.7 | 30.88 | 28.61 | 18.2 | 35.93 | 517.61 | −61.26 | −9.77 | 411 | 850 | 7.25 | Na-HCO3 |
| 26 | 26.08 | 41.97 | 18.46 | 13.02 | 13.62 | 401.91 | −53.33 | −7.04 | 285 | 576 | 7.48 | Ca-HCO3 |
| 27 | 129.05 | 164.74 | 172.93 | 591.96 | 83.84 | 499.34 | −53.65 | −7.24 | 384 | 686 | 6.97 | Mg-Cl |
| 28 | 45.77 | 160.29 | 53.72 | 367.58 | 71.07 | 548.06 | −54.12 | −7.42 | 364 | 727 | 6.83 | Ca-HCO3 |
| 29 | 24.36 | 48.66 | 19.76 | 21.71 | 12.59 | 474.98 | −56.06 | −7.76 | 355 | 740 | 7.26 | Ca-HCO3 |
| 30 | 36.28 | 42.35 | 18.12 | 55.48 | 19.89 | 365.37 | −55.73 | −8.06 | 380 | 785 | 7.43 | Ca-HCO3 |
| 31 | 31.11 | 61.12 | 21.24 | 34.43 | 21.86 | 584.59 | −53.34 | −8.01 | 486 | 998 | 7.02 | Ca-HCO3 |
| 32 | 30.81 | 66.42 | 18.52 | 25.45 | 15.67 | 444.53 | −49.72 | −7.47 | 398 | 820 | 7.1 | Ca-HCO3 |
| Min | 24.36 | 30.88 | 18.12 | 13.02 | 12.59 | 124.66 | −61.83 | −9.77 | 285 | 576 | 6.83 | / |
| Max | 179.35 | 164.74 | 172.93 | 591.96 | 162.14 | 840.35 | −44.65 | −5.9 | 943 | 1930 | 7.76 | / |
| Mean | 63.37 | 80.1 | 54.79 | 130.11 | 55.22 | 465.28 | −58.78 | −8.51 | 531.16 | 1075.31 | 7.25 | / |
| CV (%) | 0.61 | 0.43 | 0.64 | 1.08 | 0.56 | 0.27 | −0.07 | −0.09 | 0.31 | 0.32 | 0.03 | / |
| Parameters | Groundwater Samples | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Min (‰) | Max (‰) | Mean (‰) | |
| δD | −61.83 | −44.65 | −58.78 |
| δ18O | −9.77 | −5.90 | −8.51 |
| d-excess | 2.52 | 16.93 | 8.71 |
| Major Ions | Unit | Samples | WHO (1997) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | Desirable | Permissible | ||
| Na+ | mg/L | 23.48 | 178.49 | 62.42 | 50.00 | 200 |
| K+ | mg/L | 0.26 | 1.60 | 0.95 | 100.00 | 200 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 30.88 | 164.74 | 80.10 | 75.00 | 200 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 18.12 | 172.93 | 54.79 | 30.00 | 150 |
| F− | mg/L | 0.11 | 1.63 | 0.64 | 0.6-0.9 | 1.5 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 13.02 | 591.96 | 130.11 | 250.00 | 600 |
| SO42− | mg/l | 12.59 | 162.14 | 55.22 | 200.00 | 600 |
| HCO3− | mg/L | 124.66 | 840.35 | 465.28 | 200.00 | 600 |
| pH | / | 6.83 | 7.76 | 7.25 | 7.0–8.5 | 6.5–9.2 |
| TDS | mg/L | 285 | 943 | 531.16 | 500.00 | 1500 |
| EC | mg/L | 576 | 1930 | 1075.31 | 750.00 | 1500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, H.; Xu, J.; Xu, J.; Han, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Shu, Y. Water-Rock Action Analysis and Quality Evaluation of Shallow Groundwater in Rural Areas: A Case Study of Suzhou City, Northern Anhui, China. Water 2023, 15, 2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112006
Gao L, Zhao J, Zhao H, Xu J, Xu J, Han S, Wang L, Wang X, Shu Y. Water-Rock Action Analysis and Quality Evaluation of Shallow Groundwater in Rural Areas: A Case Study of Suzhou City, Northern Anhui, China. Water. 2023; 15(11):2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112006
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Li, Jingyu Zhao, Hongtao Zhao, Jiying Xu, Jiewei Xu, Shuxin Han, Ling Wang, Xiaoyue Wang, and Yonglie Shu. 2023. "Water-Rock Action Analysis and Quality Evaluation of Shallow Groundwater in Rural Areas: A Case Study of Suzhou City, Northern Anhui, China" Water 15, no. 11: 2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112006
APA StyleGao, L., Zhao, J., Zhao, H., Xu, J., Xu, J., Han, S., Wang, L., Wang, X., & Shu, Y. (2023). Water-Rock Action Analysis and Quality Evaluation of Shallow Groundwater in Rural Areas: A Case Study of Suzhou City, Northern Anhui, China. Water, 15(11), 2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112006







