Fish Size Structure as an Indicator of Fish Diversity: A Study of 40 Lakes in Türkiye
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
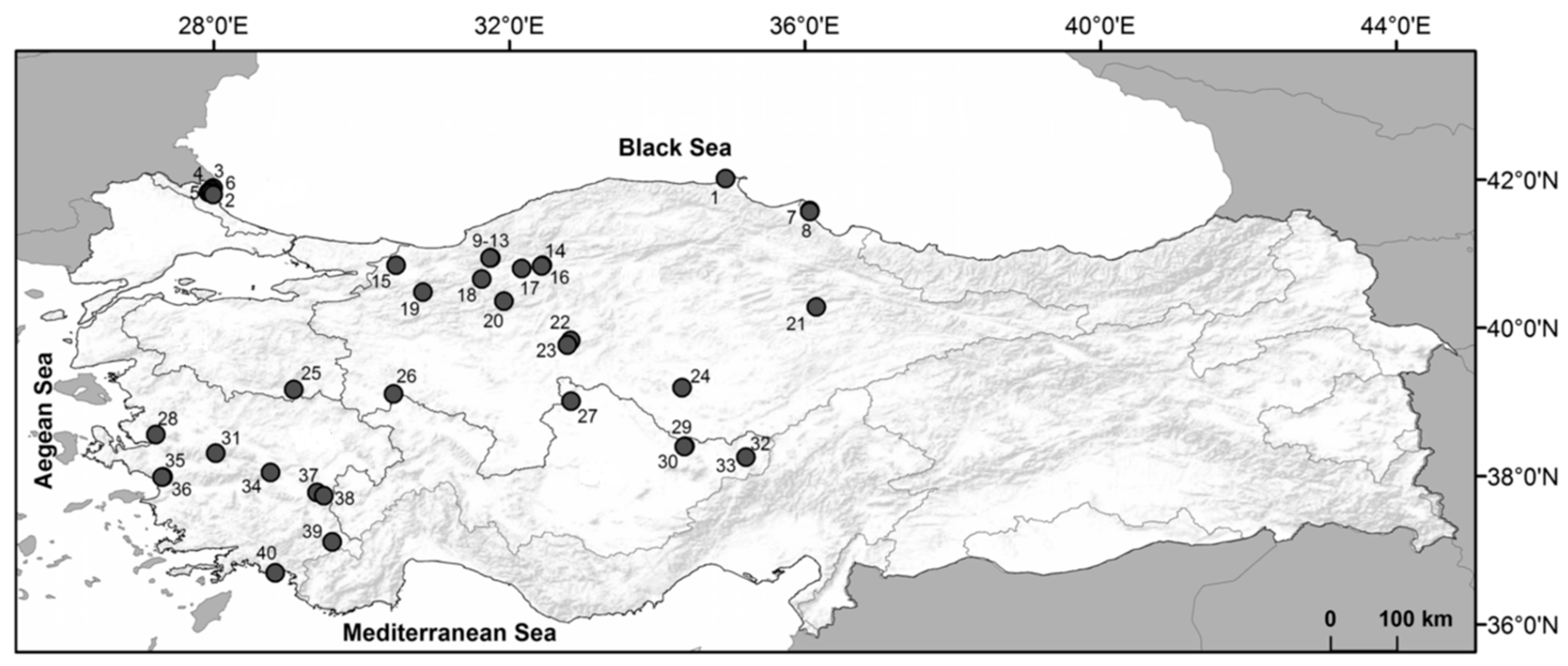
2.1. Study Area
| Variables | Median | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude (Lat) | 36°70′ | 42°01′ | |
| Longitude (Lon) | 27°22′ | 36°16′ | |
| Altitude (Alt, m) | 982 | 0.3 | 1423 |
| Air temperature annual average (Temp, °C) | 11.2 | 8.3 | 17.7 |
| Seasonality (Season, °C) | 19.2 | 15.8 | 22.4 |
| Precipitation total annual (Precip) | 611 | 355 | 1017 |
| Lake area (Area, ha) | 12.0 | 0.1 | 635 |
| Maximum depth (Depth, m) | 3.3 | 0.6 | 15.2 |
| Secchi depth (Sec, m) | 1.0 | 0.3 | 4.1 |
| Plant Volume Inhabited (PVI, %) | 6.9 | 0.0 | 79.9 |
| Chlorophyll a (Chl-a, µg/L) | 16.5 | 4.7 | 181.1 |
| Total phosphorous (TP, µg/L) | 72 | 18 | 402 |
| Total nitrogen (TN, µg/L) | 964 | 264 | 3250 |
| Salinity (Sal, ‰) | 0.30 | 0.06 | 14.50 |
| Species richness (number of fish species) | 3.5 | 1 | 11 |
| Shannon–Wiener diversity index (fish) | 0.62 | 0 | 1.9 |
| Fish (number of fish per net per night) | 53 | 1.5 | 1425 |
| Fish (gram fish per net per night) | 1119 | 116 | 4177 |
| Piscivorous fish proportion of total biomass | 0 | 0 | 0.9 |
2.2. Fish Survey
2.3. Statistical Analyses
| H’ | nSP | Lat | Lon | Alt | Area | Depth | Sec | Chl-a | TP | TN | Sal | PVI | Precip | Temp | Season | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H’ | 0.65 | 0.25 | −0.06 | −0.49 | 0.26 | −0.30 | −0.06 | −0.10 | 0.09 | −0.08 | 0.24 | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.30 | −0.54 | |
| nSP | 0.000 | 0.31 | −0.07 | −0.66 | 0.60 | −0.40 | −0.01 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.25 | −0.08 | 0.52 | −0.29 | |
| Lat | 0.133 | 0.059 | 0.09 | −0.32 | −0.02 | −0.27 | 0.28 | −0.38 | −0.08 | −0.54 | −0.11 | 0.26 | 0.01 | −0.07 | −0.36 | |
| Lon | 0.734 | 0.663 | 0.602 | 0.24 | −0.07 | −0.10 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.26 | −0.04 | 0.19 | 0.37 | −0.41 | −0.34 | 0.38 | |
| Alt | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.044 | 0.144 | −0.32 | 0.42 | −0.09 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.06 | −0.49 | −0.07 | −0.03 | −0.80 | 0.51 | |
| Area | 0.116 | 0.000 | 0.924 | 0.690 | 0.045 | −0.25 | −0.11 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.22 | 0.35 | 0.22 | 0.00 | 0.42 | 0.03 | |
| Depth | 0.062 | 0.012 | 0.099 | 0.545 | 0.008 | 0.128 | −0.57 | 0.03 | −0.26 | −0.07 | −0.35 | −0.55 | 0.22 | −0.43 | 0.07 | |
| Sec | 0.722 | 0.961 | 0.081 | 0.415 | 0.573 | 0.487 | 0.000 | −0.39 | −0.20 | −0.29 | 0.23 | 0.48 | 0.04 | 0.08 | −0.01 | |
| Chl-a | 0.545 | 0.803 | 0.018 | 0.246 | 0.370 | 0.075 | 0.843 | 0.013 | 0.71 | 0.74 | 0.21 | 0.09 | −0.29 | 0.14 | 0.33 | |
| TP | 0.596 | 0.300 | 0.624 | 0.113 | 0.693 | 0.106 | 0.107 | 0.213 | 0.000 | 0.56 | 0.16 | 0.32 | −0.23 | 0.04 | 0.23 | |
| TN | 0.631 | 0.943 | 0.000 | 0.820 | 0.710 | 0.185 | 0.671 | 0.075 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.21 | 0.07 | −0.13 | 0.26 | 0.29 | |
| Sal | 0.138 | 0.015 | 0.500 | 0.239 | 0.001 | 0.030 | 0.028 | 0.161 | 0.198 | 0.330 | 0.196 | 0.14 | −0.25 | 0.43 | 0.10 | |
| PVI | 0.753 | 0.130 | 0.105 | 0.022 | 0.661 | 0.185 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.585 | 0.047 | 0.685 | 0.392 | −0.18 | 0.21 | 0.10 | |
| Precip | 0.187 | 0.644 | 0.935 | 0.010 | 0.849 | 0.993 | 0.174 | 0.808 | 0.078 | 0.162 | 0.419 | 0.118 | 0.282 | 0.09 | −0.69 | |
| Temp | 0.067 | 0.001 | 0.676 | 0.035 | 0.000 | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.649 | 0.407 | 0.813 | 0.114 | 0.007 | 0.194 | 0.579 | −0.37 | |
| Season | 0.000 | 0.072 | 0.025 | 0.016 | 0.001 | 0.879 | 0.672 | 0.963 | 0.039 | 0.167 | 0.076 | 0.563 | 0.548 | 0.000 | 0.019 |
3. Results
| (Intercept) | H’ | Lat | Lon | Alt | Precip | Area | Depth | Sec | PVI | TP | TN | Sal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD excl. H’ | −0.7775 | −0.0293 | 0.0764 | −0.0003 | 0.0017 | 0.1060 | −0.1354 | 0.2351 | −0.1819 | −0.1895 | 0.3911 | −0.0740 | |
| Rel. import. | 0.28 | 0.56 | 0.62 | 0.98 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.30 | 0.27 | ||
| AICc: 70.0; | Adj. R2: 0.22; | ||||||||||||
| SD incl. H’ | −1.6612 | 2.7494 | −0.0251 | 0.0514 | −0.0001 | 0.0009 | 0.1378 | 0.0973 | 0.7644 | −0.2292 | −0.3127 | 0.6002 | −0.2005 |
| Rel. import. | 1.00 | 0.28 | 0.42 | 0.18 | 0.91 | 0.27 | 0.19 | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.47 | 0.54 | 0.19 | |
| AICc: 54.6; | Adj. R2: 0.56; | ||||||||||||
| (Intercept) | H’ | Lat | Lon | Alt | Precip | Area | Depth | Sec | PVI | TP | TN | Sal | |
| nSC excl. H’ | 1.331 | 0.0356 | 0.0036 | −0.0006 | 0.0000 | 0.1966 | −0.0916 | −0.1731 | 0.0135 | −0.0855 | −0.0265 | −0.1315 | |
| Rel. import. | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.99 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.62 | ||
| AICc: 270.9; | Adj. pseudo R2: −0.16; | ||||||||||||
| nSC incl. H’ | 1.034 | 2.2934 | 0.0378 | −0.0202 | 0.0002 | −0.0007 | 0.2407 | 0.0714 | −0.2222 | −0.0249 | −0.2168 | 0.1043 | −0.2277 |
| Rel. import. | 1.00 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.54 | 0.41 | 0.98 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.37 | 0.21 | 0.79 | |
| AICc: 252.5; | Adj. pseudo R2: 0.28; | ||||||||||||
| (Intercept) | Lat | Lon | Alt | Precip | Area | Depth | Sec | PVI | TP | TN | Sal | ||
| Geom. length | 17.7879 | 0.4004 | −0.0957 | 0.0031 | 0.0001 | −1.0663 | −2.3956 | −6.6931 | 0.2815 | −0.5769 | −4.4252 | −0.2741 | |
| Rel. import. | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.70 | 0.20 | 0.49 | 0.24 | 0.56 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.80 | 0.46 | ||
| AICc: 225.7; | Adj. R2: 0.28 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, J.H.; Gillooly, J.F.; Allen, A.P.; Savage, V.M.; West, G.B. Toward a metabolic theory of ecology. Ecology 2004, 85, 1771–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, G.; Ebenman, B.; Emmerson, M.; Montoya, J.M.; Olesen, J.M.; Valido, A.; Warren, P.H. Body size in ecological networks. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roos, A.M.; Persson, L.; McCauley, E. The influence of size-dependent life-history traits on the structure and dynamics of populations and communities. Ecol. Lett. 2003, 6, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roos, A.M.; Persson, L. Size-dependent life-history traits promote catastropic collapses of the top predators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12907–12912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trebilco, R.; Baum, J.K.; Salomon, A.K.; Dulvy, N.K. Ecosystem ecology: Size-based constraints on the pyramids of life. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucet, S.; Boix, D.; López-Flores, R.; Badosa, A.; Quintana, X.D. Size and species diversity of zooplankton communities in fluctuating Mediterranean salt marshes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 67, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucet, S.; Boix, D.; Quintana, X.D.; Jensen, E.; Nathansen, L.W.; Trochine, C.; Meerhoff, M.; Gascón, S.; Jeppesen, E. Factors influencing zooplankton size structure at contrasting temperatures in coastal shallow lakes: Implications for effects of climate change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 1697–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Chang, C.Y.; García-Comas, C.; Gong, G.-C.; Hsieh, C.H. Increasing zooplankton size diversity enhances the strength of top-down control on phytoplankton through diet niche partitioning. J. Anim. Ecol. 2013, 82, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Comas, C.; Sastri, A.R.; Ye, L.; Chang, C.-Y.; Lin, F.-S.; Su, M.-S.; Gong, G.-C.; Hsieh, C.-H. Prey size diversity hinders biomass trophic transfer and predator size diversity promotes it in planktonic communities. Proc. R. Soc. B 2016, 283, 20152129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucet, S.; Tavşanoğlu, Ü.N.; Özen, A.; Levi, E.E.; Bezirci, G.; Çakıroğlu, A.İ.; Jeppesen, E.; Svenning, J.C.; Ersoy, Z.; Beklioğlu, M. Size-based interactions across trophic levels in food webs of shallow Mediterranean lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2017, 62, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucet, S.; Arranz, I.; Mehner, T.; Argillier, C.; Beklioğlu, M.; Benejam, L.; Boll, T.; Holmgren, K.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Svenning, J.-C.; et al. Size diversity and species diversity relationships in fish assemblages of Western Palearctic lakes. Ecography 2018, 40, 1064–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucet, S.; Pédron, S.; Mehner, T.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Argillier, C.; Winfield, I.J.; Volta, P.; Emmrich, M.; Hesthagen, T.; Holmgren, K.; et al. Fish diversity in European lakes: Geographical factors dominate over anthropogenic pressures. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Meerhoff, M.; Holmgren, K.; González-Bergonzoni, I.; Teixeira-de Mello, F.; Declerck, S.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Bjerring, R.; Conde-Porcuna, J.M.; et al. Impacts of climate warming on lake fish community structure and potential effects on ecosystem function. Hydrobiologia 2010, 646, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, G.R.; Pope, K.L. Relationship between lake-record weights of fishes and reservoir area and growing season. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2004, 24, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Jensen, J.P.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L. Trophic structure, species richness and biodiversity in Danish lakes: Changes along a phosphorus gradient. Freshw. Biol. 2000, 45, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.D.; Abell, R.; Hogan, Z.; Revenga, C.; Taylor, B.W.; Welcomme, R.L.; Winemiller, K.; Allan, J.D.; Hogan, Z.E.B.; Taylor, B.W.; et al. Overfishing of inland water. Bioscience 2005, 55, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmrich, M.; Pédron, S.; Brucet, S.; Winfield, I.J.; Jeppesen, E.; Volta, P.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Holmgren, K.; Hesthagen, T.; Mehner, T. Geographical patterns in the size structure of European lake fish communities along abiotic and biotic gradients. J. Biogeogr. 2014, 41, 2221–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, D. Temperature and organism size: A biological law for ectotherms? Adv. Ecol. Res. 1994, 25, 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Post, D.M.; Pace, M.L.; Hairston, N.G. Ecosystem size determines food-chain length in lakes. Nature 2000, 405, 1047–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, R.H.; Wilson, E.O. The Theory of Island Biogeography; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, L. Food consumption and competition between age classes in a perch Perca fluviatilis population in a shallow eutrophic lake. Oikos 1983, 40, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, F.; Halpern, B.S. Low functional redundancy in coastal marine assemblages. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safi, K.; Cianciaruso, M.V.; Loyola, R.D.; Brito, D.; Armour-Marshall, K.; Diniz-Filho, J.A.F. Understanding global patterns of mammalian functional and phylogenetic diversity. Proc. R. Soc. B 2011, 366, 2536–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart-Smith, R.D.; Bates, A.E.; Lefcheck, J.S.; Duffy, J.E.; Baker, S.C.; Thomson, R.J.; Stuart-Smith, J.F.; Hill, N.A.; Kininmonth, S.J.; Airoldi, L.; et al. Integrating abundance and functional traits reveals new global hotspots of fish diversity. Nature 2013, 501, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strayer, D.L.; Dudgeon, D. Freshwater biodiversity conservation: Recent progress and future challenges. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2010, 9, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balian, E.V.; Segers, H.; Martens, K.; Lévéque, C. The Freshwater Animal Diversity Assessment: An overview of the results. In Freshwater Animal Diversity Assessment; Developments in Hydrobiology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 627–637. [Google Scholar]
- Abell, R.; Thieme, M.L.; Revenga, C.; Bryer, M.; Kottelat, M.; Bogutskaya, N.; Coad, B.; Mandrak, N.; Balderas, S.C.; Bussing, W.; et al. Freshwater Ecoregions of the World: A New Map of Biogeographic Units for Freshwater Biodiversity Conservation. Bioscience 2008, 58, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2020. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World Map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beklioğlu, M.; Bucak, T.; Levi, E.E.; Erdoğan, Ş.; Özen, A.; Filiz, N.; Bezirci, G.; Çakıroğlu, A.İ.; Tavşanoğlu, Ü.N.; Gökçe, D.; et al. Influences of climate and nutrient enrichment on the multiple trophic levels of Turkish shallow lakes: A space-for-time substitution approach. Inland Waters 2020, 10, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boll, T.; Levi, E.E.; Bezirci, G.; Özuluğ, M.; Tavşanoğlu, Ü.N.; Ҫakıroğlu, A.I.; Özcan, S.; Brucet, S.; Erik Jeppesen, E.; Beklioğlu, M. Fish assemblage and diversity in lakes of western and central Turkey: Role of geo-climatic and other environmental variables. Hydrobiologia 2016, 771, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, E.E.; Çakıroğlu, A.İ.; Bucak, T.; Odgaard, B.V.; Davidson, T.A.; Jeppesen, E.; Beklioğlu, M. Similarity between contemporary vegetation and plant remains in the surface sediment in Mediterranean lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2014, 59, 724–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olin, M.; Malinen, T.; Ruuhijärvi, J. Gillnet catch in estimating the density and structure of fish community—Comparison of gillnet and trawl samples in a eutrophic lake. Fish. Res. 2009, 96, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmrich, M.; Winfield, I.J.; Guillard, J.; Rustadbakken, A.; Vergès, C.; Volta, P.; Jeppesen, E.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Brucet, S.; Holmgren, K.; et al. Strong correspondence between gillnet catch per unit effort and hydroacoustically derived fish biomass in stratified lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 2436–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, X.D.; Brucet, S.; Boix, D.; López-Flores, R.; Gascón, S.; Badosa, A.; Sala, J. A nonparametric method for the measurement of size diversity with emphasis on data standardization. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2008, 6, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmrich, M.; Brucet, S.; Ritterbusch, D.; Mehner, T. Size spectra of lake fish assemblages: Responses along gradients of general environmental factors and intensity of lake-use. Freshw. Biol. 2011, 56, 2316–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullagh, P.; Nelder, J.A. Generalized Linear Models; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Heinzl, H.; Mittlböck, M. Pseudo R-squared measures for Poisson regression models with over- or underdispersion. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2003, 44, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, A.B.; Anderson, D.R.; Burnham, K.P. Estimation of long-term trends and variation in avian survival probabilities using random effects models. J. Appl. Stat. 2002, 29, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, K. MuMIn Package. Multi-Model Inference, R Package Version 1.43.15. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MuMIn (accessed on 11 May 2019).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Badosa, A.; Boix, D.; Brucet, S.; López-Flores, R.; Gascón, S.; Quintana, X.D. Zooplankton taxonomic and size diversity in Mediterranean coastal lagoons (NE Iberian Peninsula): Influence of hydrology, nutrient composition, food resource availability and predation. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 71, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchey, O.L.; Belgrano, A. Body-size distributions and size-spectra: Universal indicators of ecological status? Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farré, M.; Tuset, V.M.; Maynou, F.; Recasens, L.; Lombarte, A. Geometric morphology as an alternative for measuring the diversity of fish assemblages. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 29, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombarte, A.; Gordoa, A.; Whitfield, A.K.; James, N.C.; Tuset, V.M. Ecomorphological analysis as a complementary tool to detect changes in fish communities following major perturbations in two South African estuarine systems. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2012, 94, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleuter, D.; Daufresne, M.; Veslot, J.; Mason, N.W.H.; Lanoiselée, C.; Brosse, S.; Beauchard, O.; Argillier, C. Geographic isolation and climate govern the functional diversity of native fish communities in European drainage basins. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, S.M.; Olsen, E.M.; Vøllestad, L.A. Seasonal mortality and the effect of body size: A review and an empirical test using individual data on brown trout. Funct. Ecol. 2008, 22, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, D.J.; Mittelbach, G.G.; Cornell, H.V.; Field, R.; Guégan, J.-F.; Hawkins, B.A.; Kaufman, D.M.; Kerr, J.T.; Oberdorff, T.; O’Brien, E.; et al. Predictions and tests of climate-based hypotheses of broad-scale variation in taxonomic richness. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, K.; Appelberg, M. Size structure of benthic freshwater fish communities in relation to environmental gradients. J. Fish Biol. 2000, 57, 1312–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, N.; Yu, J.; Gutierrez, M.F.; Teixeira de Mello, F.; Tavsanoglu, Ü.N.; Çakiroglu, I.; He, H.; Meerhoff, M.; Brucet, S.; Liu, Z.; et al. Salinity shapes food webs in lakes: Implications for increasing aridity with climate change. Inland Waters 2021, 11, 476–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, S.; Romo, S.; Villena, M.-J.; Martínez, S. Fish communities and food web interactions in some shallow Mediterranean lakes. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506–509, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Kanstrup, E.; Petersen, B.; Eriksen, R.B.; Hammershøj, M.; Mortensen, E.; Jensen, J.-P.; Have, A. Does the impact of nutrients on the biological structure and function of brackish and freshwater lakes differ? Hydrobiologia 1994, 275, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innal, D.; Erk’akan, F. Effects of exotic and translocated fish species in the inland waters of Turkey. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2006, 16, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, A.; Randhir, T.O. Climatic change impacts on the ecohydrology of Mediterranean watersheds. Clim. Chang. 2012, 114, 319–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boll, T.; Erdoğan, Ş.; Aslan Bıçkı, Ü.; Filiz, N.; Özen, A.; Levi, E.E.; Brucet, S.; Jeppesen, E.; Beklioğlu, M. Fish Size Structure as an Indicator of Fish Diversity: A Study of 40 Lakes in Türkiye. Water 2023, 15, 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122147
Boll T, Erdoğan Ş, Aslan Bıçkı Ü, Filiz N, Özen A, Levi EE, Brucet S, Jeppesen E, Beklioğlu M. Fish Size Structure as an Indicator of Fish Diversity: A Study of 40 Lakes in Türkiye. Water. 2023; 15(12):2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122147
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoll, Thomas, Şeyda Erdoğan, Ümmühan Aslan Bıçkı, Nur Filiz, Arda Özen, Eti Ester Levi, Sandra Brucet, Erik Jeppesen, and Meryem Beklioğlu. 2023. "Fish Size Structure as an Indicator of Fish Diversity: A Study of 40 Lakes in Türkiye" Water 15, no. 12: 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122147
APA StyleBoll, T., Erdoğan, Ş., Aslan Bıçkı, Ü., Filiz, N., Özen, A., Levi, E. E., Brucet, S., Jeppesen, E., & Beklioğlu, M. (2023). Fish Size Structure as an Indicator of Fish Diversity: A Study of 40 Lakes in Türkiye. Water, 15(12), 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122147








