Hydrochemical Characteristics and Human Health Risk Assessment of Surface Water in the Danjiang River Source Basin of the Middle Route of China’s South-to-North Water Transfer Project
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
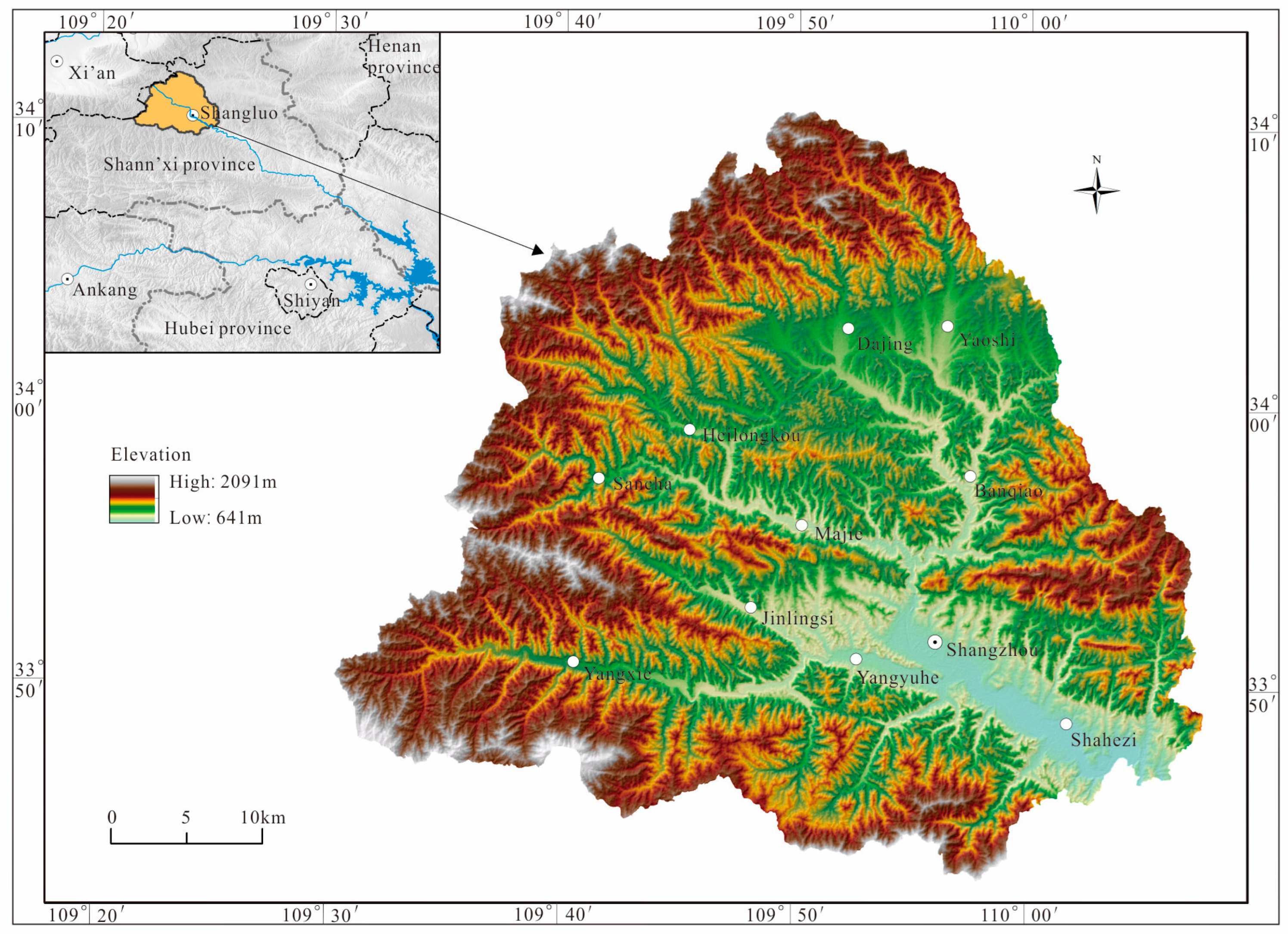
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Research Methods
| Parameter | Meaning | Unit | Values for Different Age Groups | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children | Adult Males | Adult Females | |||
| DRf | Reference dose | mg/kg·d | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| IR | Ingestion rate | L/d | 1.8 | 2.79 | 2.20 |
| BW | Average body weight | kg | 25.9 | 63.8 | 56.5 |
| AT | Average exposure time | d | 2190 | 10,950 | 10,950 |
| ED | Exposure duration | a | 6 | 30 | 30 |
| EF | Exposure frequency | d/a | 365 | 365 | 365 |
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics
3.2. Spatial Variability Characteristics of Hydrochemistry
3.3. Water Quality and Health Risk Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Influencing Factors of Main Ions
4.2. Source of Main Ions
4.2.1. Sources of Ca2+, Mg2+, and HCO3−
4.2.2. Sources of Na+, K+, Cl−, and NO3−
4.3. Water Environment Quality
4.3.1. Influence of Human Activities on Water Environmental Quality
4.3.2. Health Risk Assessment
4.4. Uncertainty Analysis
5. Conclusions
- 1.
- The surface water in the Danjiang River source basin is characterized by a low mineralization and slightly alkaline environment. The average concentration of cation equivalents is in the order of Ca2+ > Mg2+ > Na+ > K+, with Ca2+ and Mg2+ being the dominant cations. The average concentration of anions is in the order of HCO3− > SO42− > NO3− > Cl−, with HCO3− and SO42− being the dominant anions. The hydrochemisty of the water is characterized as HCO3− Ca·Mg type.
- 2.
- Our comprehensive study based on Gibbs diagrams, ion ratio coefficients, and factor analysis shows that the solutes in the water of the Danjiang River are mainly controlled by rock weathering, while agricultural activities and urban domestic sewage discharge also have certain impacts on the chemical components of the river water.
- 3.
- The results of the single-factor evaluation method and the entropy weight comprehensive index method show that the surface water quality in the Danjiang River source basin meets the Class I water quality standards. Overall, the water quality characteristics of the tributaries are better than the mainstream sections, and the upstream sections are better than those of the downstream areas. Additionally, the non-carcinogenic potential risks of nitrate nitrogen were low and within controllable ranges, but the impact on children was significantly higher than that on adults. Therefore, it is recommended to strengthen water quality management downstream of urban areas within the region, rationally plan the structure of industrial and agricultural production, and reduce the concentration of nitrate nitrogen in water bodies to mitigate health risks for vulnerable young populations with weaker resistance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, N.; Jing, L.; Yu, P. Major ion chemistry and quality assessment of groundwater in and around a mountainous tourist town of China. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, J.; Zhou, C.; Nsabimana, A. Groundwater pollution source identification and apportionment using PMF and PCA-APCS-MLR receptor models in Tongchuan City, China. Ach. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 81, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Li, P.; Chen, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, P.; Guo, F. Major ion hydrogeochemistry and health risk of groundwater nitrate in selected rural areas of the Guanzhong Basin, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess 2023, 29, 701–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, P.; He, X.; He, S. Exploring the response of shallow groundwater to precipitation in the northern piedmont of the Qinling Mountains, China. Urban Clim. 2023, 47, 101379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.Q.; Yang, Z.F.; Wang, Y.P.; Ji, J.F.; Li, W.M.; Yuan, X.Y. Major ion chemistry in the Yangtze River. Earth Sci. Front. 2008, 15, 194–202. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Song, X.F.; Zhang, Y.H.; Ma, Y.; Tang, C.Y.; Yang, L.H.; Wang, Z.L. The interaction between surface water and groundwater and its effect on water quality in the Second Songhua River basin, northeast China. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 125, 1495–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.Y.; Wu, J.H.; Tian, R.; He, S.; He, X.D.; Xue, C.Y.; Zhang, K. Geochemistry, Hydraulic Connectivity and Quality Appraisal of Multilayered Groundwater in the Hongdunzi Coal Mine, Northwest China. Mine Water Environ. 2018, 37, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markich, S.J.; Brown, P.L. Relative importance of natural and anthropogenic influences on the fresh surface water chemistry of the Hawkesbury-Nepean River south-eastern Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 217, 201–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindshaw, R.S.; Tipper, E.T.; Reynolds, B.C.; Lemarchand, E.; Wiederhold, J.G.; Magnusson, J.; Bernasconi, S.M.; Kretzschmar, R.; Bourdon, B. Hydrologicalcontrol of stream water chemistry in a glacial catchment (DammaGlacier, Switzerland). Chem. Geol. 2011, 285, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.D.; Li, P.Y. Surface water pollution in the middle Chinese Loess Plateau with special focus on hexavalent chromium (Cr6+): Occurrence, sources and health risks. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.Y.; Tian, R.; Liu, R. Solute geochemistry and multivariate analysis of water quality in the GuohuaPhosphorite Mine, Guizhou Province, China. Expo. Health 2019, 11, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Li, P.Y.; Wang, D.; Ren, X.F.; Wei, M.J. Statistical and multivariate statistical techniques to trace the sources and affecting factors of groundwater pollution in a rapidly growing city on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess 2020, 26, 1603–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Water chemistry of the Amazon River. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1972, 36, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millot, R.; Gaillardet, J.; Dupré, B.; Allègre, C.J. Northern latitudechemical weathering rates: Clues from the Mackenzie River basin. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 1305–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, Y.; Tsoi, M.Y.; Zaitsev, A.; Edmond, J.M. The fluvial geochemistry ofthe rivers of the eastern Siberia: Tributaries of the Lena River draining the sedimentary platform of the Siberian Craton. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 1657–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaray, S.K. Application of multivariate statistical techniques in hydrogeochemical studies—A case study: Brahmani-Koel River (India). Environ. Monit. Assess 2010, 164, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.H.; Stallard, R.F.; Edmond, J.M. Major ion chemistry of some large Chinese rivers. Nature 1982, 298, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.S.; Wang, F.Y.; He, D.W. Geochemistry of water quality of the Yellow River basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2006, 13, 58–73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.P.; Wang, L.; Xu, C.X.; Yang, Z.F.; Ji, J.F.; Xia, X.Q.; An, Z.Y.; Yuan, J. Hydro-geochemistry and genesis of major ions in the Yangtze River, China. Geol. Bull. China 2010, 29, 446–456. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.W.; Tian, F.Q.; Hu, H.C.; Liu, Y.P.; Zhao, S.H. Characteristics and Significance of Stable Isotopes and Hydrochemistry in Surface Water and Groundwater in Nanxiaohegou Basin. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 682–690. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.X.; Li, W.P.; Cai, Y.M.; An, Y.H.; Shao, X.M.; Wu, X.; Yin, D.C. The hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2021, 28, 184–193. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.T.; Shi, Z.M.; Wang, G.C.; Jiang, J.; Yang, B.C. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the Dachaidan area, Qaidam Basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2021, 28, 194–205. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.Y.; Huang, G.X.; Jing, J.H.; Liu, J.T.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.X. Characteristics and driving mechanisms of evolution of groundwater chemistry in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain and suggestions for its exploitation and utilization. Geol. China 2022. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.J.; Zhang, Q.F.; Li, S.Y. Hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of trans-boundary rivers in China. Quat. Sci. 2023, 43, 425–438. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hagedorn, B.; Cartwright, I. Climatic and lithologic controls on thetemporal and spatial variability of CO2 consumption via chemicalweathering: An example from the Australian Victorian Alps. Chem. Geol. 2009, 260, 234–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.Q.; Jiang, Z.C.; Huang, Q.B.; Zhang, L.K.; Liu, P.Y.; Liang, Y.P. The influenceofsulfideacidon rock weathering and carbon cycle in catchment scale: Acase study in Sanchuan River basin of Huanghe River tributary. Quat. Sci. 2020, 40, 1070–1082. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhao, X.F. Overview on the studies of nitrate pollution in Groundwater. Prog. Geogr. 2006, 25, 34–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, E.A.; David, M.B.; Galloway, J.N.; Goodale, C.L.; Haeuber, R.; Harrison, J.A.; Howarth, R.W.; Jaynes, D.B.; Lowrance, R.R.; Nolan, B.T.; et al. Excess Nitrogen in the U.S. Environment: Trends, Risks, and Solutions. Issues Ecol. 2012, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.L.; Liu, H.Y.; Guo, H.M.; Sun, Z.X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, T.H. Occurrences and health risks of high nitrate groundwater in the typical piedmont areas of the North China Plain. Earth Sci. Front. 2023; early access. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukah, B.U.; Ameh, P.D.; Egbueri, J.C.; Unigwe, C.O. Impact of effluent-derived heavy metals on the groundwater quality in Ajao industrial area, Nigeria: An assessment using entropy water quality index (EWQI). Int. J. Energy Water Resour. 2020, 4, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund, Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A); US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1989.
- Wang, H.; Lu, K.; Shen, C.; Song, X.; Hu, B.; Liu, G. Human health risk assessment of groundwater nitrate at a two geomorphic units transition zone in northern China. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 110, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.F.; Zhai, Y.Z.; Lei, Y.; Li, J.; Teng, Y.G.; Lu, H.; Xia, X.L.; Yue, W.F.; Yang, J. Spatiotemporal evolution of groundwater nitrate nitrogen levels and potential human health risks in the Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, B.; Chidambaram, S.; Snow, D.; Malakar, A.; Singh, D.K.; Ramanathan, A.L. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of nitrate in foothill aquifers of Western Ghats, South India. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2022, 229, 113075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Y.; Cheng, X.L.; Gu, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.F. Hydro-chemical Characteristics in the Danjiangkou Reservoir (Water Source Area of the Middle Route of the South to North Water Transfer Project) China. Environ. Sci. 2008, 29, 2111–2116. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.F.; Tang, Y. Hydrogeochemistry of the water source area of the Middle Route of China’s South to North Water Transfer Project. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2011, 30, 26–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wu, T.R. Geochemistry of dissolved trace elements and heavy metals in the Dan River Drainage (China): Distribution, sources, and water quality assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2016, 23, 8091–8103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.C.; Li, P.; Lu, K.X.; Zhan, T.T.; Zhang, J.X.; Ren, Z.P.; Wang, X.K.; Yu, K.X.; Shi, P.; Cheng, Y.T. Seasonal changes in water quality and its main influencing factors in the Dan River basin. Catena 2019, 173, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.G.; Huang, C.C.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Pang, J.L.; Ma, Y.G. Hydrological reconstruction of extreme palaeoflood events 9000–8500a BP in the Danjiang River Valley, tributary of the Danjiangkou Reservoir, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.P.; Yang, W.J.; Sha, J.; Shang, Y.T.; Li, X. Spatial Characteristics of Nutrient Status in Danjiangkou Reservoir. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 43, 51–58. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.Z.; Deng, H.J.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, H.M.; Gao, Q.; Zhou, Y.H. Status Quo of Hydrochemical Characteristics in Danjiangkou Reservoir. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2020, 37, 49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.M.; Zhang, Q.M.; Zhao, T.Q.; Chao, J. Fluxes, characteristics and influence on the aquatic environment of inorganic nitrogen deposition in the Danjiangkou reservoir. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.R.; Ding, W.F.; Zhang, G.H. Study on the impact of land use change on runoff in Danjiang watershed based on Swat Model. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 29, 62–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.W.; Guo, A.L.; Dong, Y.P.; Yao, A.P. Rethinking of the Qinling Orogen. J. Geomech. 2019, 25, 746–768. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.Y.; Qian, H.; Wu, J.H. Ground water quality assessment based on improved water quality index in Pengyang County, Ningxia, Northwest China. E-J. Chem. 2010, 7, S209–S216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.J.; Bian, J.M.; Wan, H.L.; Wei, N.; Ma, Y.X. Health risk assessment of groundwater nitrogen pollution in Songnen Plain. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 3493–3500. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Y.Z.; Lei, Y.; Wu, J.; Teng, Y.G.; Wang, J.S.; Zhao, X.B.; Pan, X.D. Does the groundwater nitrate pollution in China pose a risk to human health? A critical review of published data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 3640–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.L.; Liu, C.Q. Water geochemistry controlled by carbonate dissolution: A study of the river waters draining karst-dominated terrain, Guizhou Province, China. Chem. Geol. 2004, 204, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, D.Z. Seawater as the source of minor elements in black shales, phosphorites, and other sedimentary rocks. Chem. Geol. 1994, 114, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilham, P. Mechanisms controlling the chemical composition of lakes and rivers: Data from Africa. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1990, 35, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, M.G.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Liu, T.; He, J. Hydrochemical characteristics and possible controls of the surface water in Ranwu Lake basin. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 4003–4010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.X.; Feng, M.Q. Hydrochemical characteristics and driving factors of surface water in the mining area of Changhe River Basin. Environ. Chem. 2022, 41, 632–642. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.H.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Wu, X.C.; Lü, Y.; Zhao, H. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation of the shallow groundwater in Fujin, Sanjiang plain. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2017, 47, 542–553. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupré, B.; Louvat, P.; Allègre, C.J. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.X.; Ding, Y.J.; Zeng, G.X.; Wu, J.K.; Qin, J. Majorion chemistry of surface water in the upper reach of Shule river basin and the possible controls. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 3315–3324. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhong, J.; Li, C.; Wang, W.F.; Xu, S.; Yan, Z.L.; Li, S.L. The chemical weathering characteristics of different litholoyic mixed small watersheds in Southwest China. Chin. J. Ecol. 2020, 39, 1288–1299. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.F.; Xu, F.; Liu, H.Z.; Deng, G.S. Application of hydrochemical and isotopic analysis to research a typical karst ground water system: Acase study at Xianrendong, Xichang city. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2019, 19, 76–83. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Gan, F.P.; Yan, B.K.; Wang, F.; Bai, J. Hydrochemical-isotopic characteristics of surface water in southwest Tibetan Plateau and controlling factors analysis. J. North China Univ. Water Resour. Electr. Power (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 43, 96–107. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.C.; Yang, W.H.; Wen, S.M.; Wang, H.; Zhao, W.J.; Han, G. Flotation of copper oxide minerals: A review. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 1351–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.C.; Wang, M.L.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, W.J.; Han, G. Enhanced adsorption of sulfide and xanthate on smithsonite surfaces by lead activation and implications for flotation intensification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 307, 122772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiatios, I. Nitrate source identification in groundwater of multiple land-use area by combining isotopes and multivariate statistical analysis: A case stydy of Asopos Basin (Central Greece). Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 541, 802–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, F.-J.; Li, S.-L.; Liu, C.-Q.; Zhao, Z.-Q.; Hu, J. Using dual isotopes to evaluate sources and transformation of nitrogen in the Liao River, northeast China. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 36, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.F.; Xia, Y.; Li, S.J.; Wang, W.Z.; Li, Z. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Source Analysis of Nitrate in Surface Water of Wuding River Basin. Environ. Sci. 2022; early access. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.Q.; Lu, C.Q.; Melillo, J.; Ren, W.; Huang, Y.; Xu, X.F.; Liu, M.L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, G.S.; Pan, S.F.; et al. Food benefit and climate warming potential of nitrogen fertilizer uses in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 044020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.L.; Yin, L.H.; He, C.Z.; Cun, D.X.; Ma, Y.Q.; Linghu, C.W. Hydrochemical composition characteristics and control factors of Xiaohuangni River basin in the upper pearl river. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 1885–1897. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.J.; Lai, C.Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Cheng, Z.H.; Yu, T. Natural water chemical change in the surface water of Chengdu and impact factors. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 5364–5374. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, J.Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Z.Q. Spatial and temporal variations in hydrochemical composition of river water in Yellow River basin, China. Chin. J. Ecol. 2017, 36, 1390–1401. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Guan, J.L.; Yao, Z.P.; Ding, Q.; Luo, Y.N.; Cheng, J.X. The variation characteristics of water quality in the Han River and Dan River of Shaanxi region. Environ. Monit. China 2015, 31, 73–77. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. Evaluation of water quality in the upper reaches of Danjiang River based on fuzzy comprehensive index method. Shaanxi Water Resour. 2022, 7, 98–100. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hord, N.G. Dietary nitrates, nitrites, and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2011, 13, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Reaches | Statistic | pH | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− | TDS | NO3-N | Total Alkalinity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper reaches | Min | 8.00 | 0.87 | 1.47 | 36.64 | 4.94 | 1.74 | 9.76 | 95.87 | 134.00 | 0.50 | 78.63 |
| Max | 8.77 | 2.32 | 3.89 | 61.07 | 28.39 | 6.95 | 58.55 | 287.62 | 272.00 | 2.64 | 235.89 | |
| Mean | 8.34 | 1.55 | 2.65 | 51.40 | 16.51 | 3.48 | 40.86 | 183.51 | 215.13 | 1.28 | 152.96 | |
| SD | 0.24 | 0.57 | 0.88 | 7.11 | 8.50 | 2.08 | 21.50 | 71.04 | 40.61 | 0.80 | 58.53 | |
| Middle reaches | Min | 8.07 | 0.95 | 2.06 | 36.64 | 7.41 | 3.48 | 4.88 | 119.84 | 154.00 | 0.95 | 98.29 |
| Max | 8.49 | 2.91 | 11.40 | 81.43 | 29.63 | 24.33 | 112.21 | 293.62 | 388.00 | 4.18 | 240.81 | |
| Mean | 8.28 | 1.64 | 5.19 | 60.21 | 17.54 | 8.51 | 48.79 | 207.52 | 257.95 | 2.51 | 171.75 | |
| SD | 0.13 | 0.48 | 2.84 | 10.84 | 7.31 | 4.63 | 24.12 | 56.43 | 53.16 | 0.99 | 44.49 | |
| Lower reaches | Min | 7.02 | 0.91 | 4.24 | 38.68 | 3.70 | 3.48 | 14.64 | 77.90 | 150.00 | 1.25 | 63.89 |
| Max | 8.57 | 2.51 | 10.56 | 73.28 | 24.69 | 15.64 | 121.97 | 245.68 | 350.00 | 4.88 | 211.32 | |
| Mean | 8.17 | 1.68 | 7.96 | 61.85 | 15.67 | 8.69 | 59.67 | 192.21 | 268.31 | 3.28 | 160.66 | |
| SD | 0.39 | 0.45 | 1.94 | 9.57 | 6.92 | 3.40 | 24.24 | 48.71 | 55.93 | 1.20 | 39.69 |
| Sample Number | EWQI | Water Quality | Sample Number | EWQI | Water Quality | Sample Number | EWQI | Water Quality | Sample Number | EWQI | Water Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W01 | 22.68 | I | W11 | 18.87 | I | W21 | 16.72 | I | W31 | 14.01 | I |
| W02 | 15.72 | I | W12 | 20.50 | I | W22 | 17.77 | I | W32 | 15.33 | I |
| W03 | 18.12 | I | W13 | 18.83 | I | W23 | 16.33 | I | W33 | 22.82 | I |
| W04 | 21.99 | I | W14 | 21.30 | I | W24 | 15.26 | I | W34 | 13.44 | I |
| W05 | 14.33 | I | W15 | 16.21 | I | W25 | 15.13 | I | W35 | 10.02 | I |
| W06 | 18.51 | I | W16 | 23.46 | I | W26 | 16.01 | I | W36 | 8.95 | I |
| W07 | 15.74 | I | W17 | 11.83 | I | W27 | 17.90 | I | W37 | 11.71 | I |
| W08 | 21.92 | I | W18 | 10.54 | I | W28 | 14.85 | I | W38 | 14.44 | I |
| W09 | 14.63 | I | W19 | 10.45 | I | W29 | 15.55 | I | W39 | 19.59 | I |
| W10 | 25.69 | I | W20 | 11.95 | I | W30 | 20.66 | I | W40 | 11.65 | I |
| Samples | Health Risk | Samples | Health Risk | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children | Adult Males | Adult Females | Children | Adult Males | Adult Females | ||
| W01 | 0.0217 | 0.0137 | 0.0122 | W21 | 0.1061 | 0.0668 | 0.0595 |
| W02 | 0.0226 | 0.0142 | 0.0127 | W22 | 0.1065 | 0.067 | 0.0597 |
| W03 | 0.0297 | 0.0187 | 0.0166 | W23 | 0.1112 | 0.07 | 0.0623 |
| W04 | 0.0401 | 0.0252 | 0.0225 | W24 | 0.1146 | 0.0721 | 0.0642 |
| W05 | 0.0411 | 0.0259 | 0.023 | W25 | 0.1197 | 0.0753 | 0.0671 |
| W06 | 0.0523 | 0.0329 | 0.0293 | W26 | 0.1248 | 0.0786 | 0.0699 |
| W07 | 0.0544 | 0.0342 | 0.0305 | W27 | 0.1376 | 0.0866 | 0.0771 |
| W08 | 0.0547 | 0.0344 | 0.0307 | W28 | 0.1376 | 0.0866 | 0.0771 |
| W09 | 0.0557 | 0.0351 | 0.0312 | W29 | 0.1402 | 0.0882 | 0.0785 |
| W10 | 0.063 | 0.0396 | 0.0353 | W30 | 0.1525 | 0.0959 | 0.0854 |
| W11 | 0.0632 | 0.0398 | 0.0354 | W31 | 0.1541 | 0.097 | 0.0863 |
| W12 | 0.0717 | 0.0451 | 0.0401 | W32 | 0.1541 | 0.097 | 0.0863 |
| W13 | 0.0755 | 0.0475 | 0.0423 | W33 | 0.1624 | 0.1022 | 0.091 |
| W14 | 0.0771 | 0.0485 | 0.0432 | W34 | 0.1743 | 0.1097 | 0.0977 |
| W15 | 0.0825 | 0.0519 | 0.0462 | W35 | 0.18 | 0.1132 | 0.1008 |
| W16 | 0.0946 | 0.0595 | 0.053 | W36 | 0.18 | 0.1132 | 0.1008 |
| W17 | 0.0967 | 0.0608 | 0.0542 | W37 | 0.1816 | 0.1143 | 0.1018 |
| W18 | 0.0984 | 0.0619 | 0.0551 | W38 | 0.2042 | 0.1285 | 0.1144 |
| W19 | 0.1042 | 0.0656 | 0.0584 | W39 | 0.2057 | 0.1294 | 0.1153 |
| W20 | 0.1046 | 0.0658 | 0.0586 | W40 | 0.2118 | 0.1333 | 0.1187 |
| pH | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− | NO3− | TDS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | |||||||||
| K+ | −0.130 | 1 | ||||||||
| Na+ | −0.135 | 0.432 ** | 1 | |||||||
| Ca2+ | −0.196 | 0.203 | 0.337 * | 1 | ||||||
| Mg2+ | −0.026 | −0.013 | −0.188 | 0.538 ** | 1 | |||||
| Cl− | −0.310 | 0.607 ** | 0.577 ** | 0.558 ** | 0.192 | 1 | ||||
| SO42− | −0.066 | 0.522 ** | 0.493 ** | 0.374 * | 0.143 | 0.422 ** | 1 | |||
| HCO3− | −0.073 | −0.188 | −0.140 | 0.685 ** | 0.851 ** | 0.194 | −0.182 | 1 | ||
| NO3− | −0.404 * | 0.439 ** | 0.693 ** | 0.592 ** | −0.009 | 0.598 ** | 0.488 ** | 0.074 | 1 | |
| TDS | −0.155 | 0.310 | 0.372 * | 0.907 ** | 0.733 ** | 0.598 ** | 0.564 ** | 0.681 ** | 0.544 ** | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, X.; Wang, Y. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Human Health Risk Assessment of Surface Water in the Danjiang River Source Basin of the Middle Route of China’s South-to-North Water Transfer Project. Water 2023, 15, 2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122203
Lin L, Zhang Y, Qian X, Wang Y. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Human Health Risk Assessment of Surface Water in the Danjiang River Source Basin of the Middle Route of China’s South-to-North Water Transfer Project. Water. 2023; 15(12):2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122203
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Longjian, Yafeng Zhang, Xinyu Qian, and Yingwei Wang. 2023. "Hydrochemical Characteristics and Human Health Risk Assessment of Surface Water in the Danjiang River Source Basin of the Middle Route of China’s South-to-North Water Transfer Project" Water 15, no. 12: 2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122203
APA StyleLin, L., Zhang, Y., Qian, X., & Wang, Y. (2023). Hydrochemical Characteristics and Human Health Risk Assessment of Surface Water in the Danjiang River Source Basin of the Middle Route of China’s South-to-North Water Transfer Project. Water, 15(12), 2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122203






