Unlocking the Secrets of River Pollution: Analyzing Organic Pollutants in Sediments—Experimental Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Chemical Analysis
2.3. Quality Assurance and Control
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Total Organic Carbon Method (TOC)
3. Result and Discussion
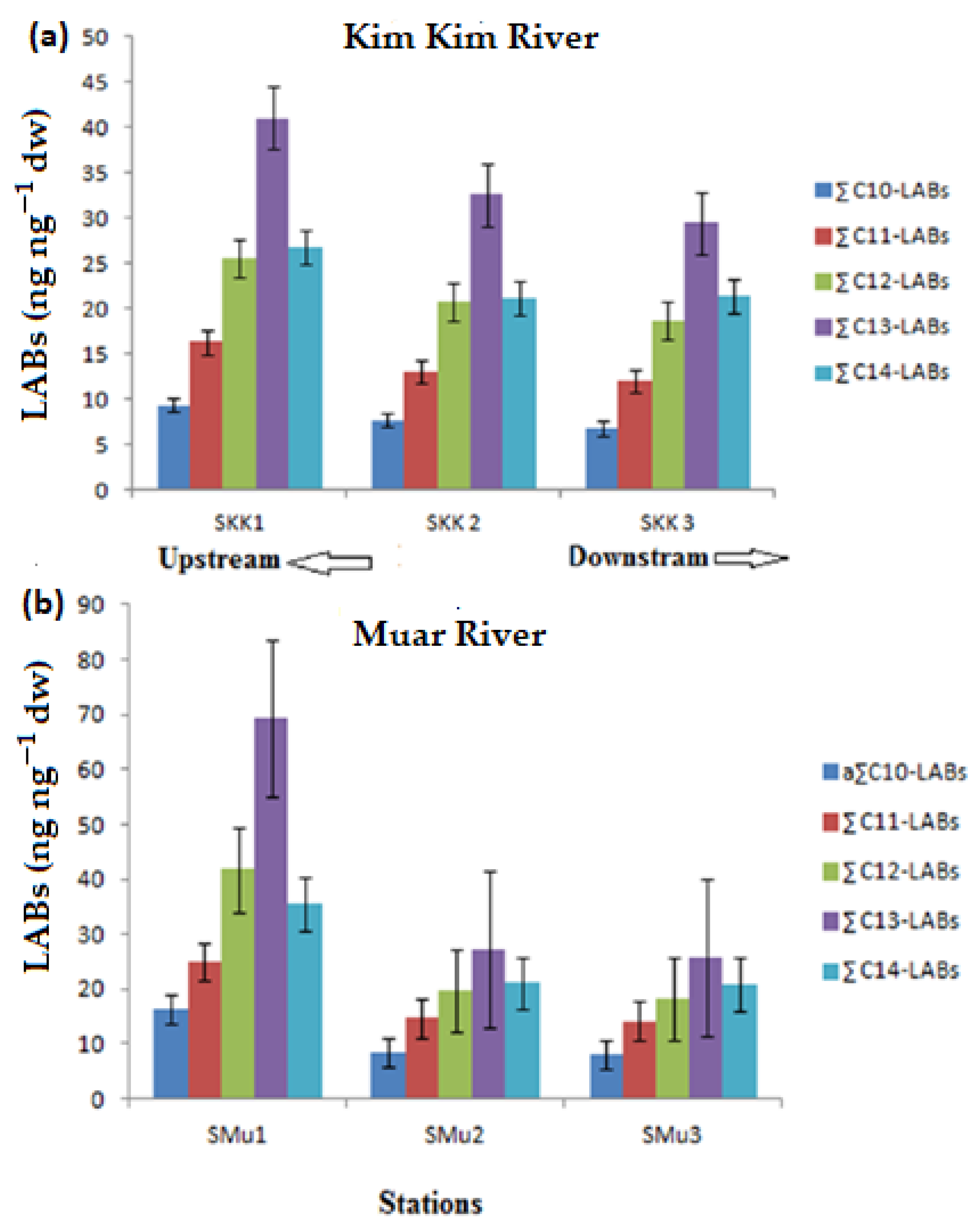
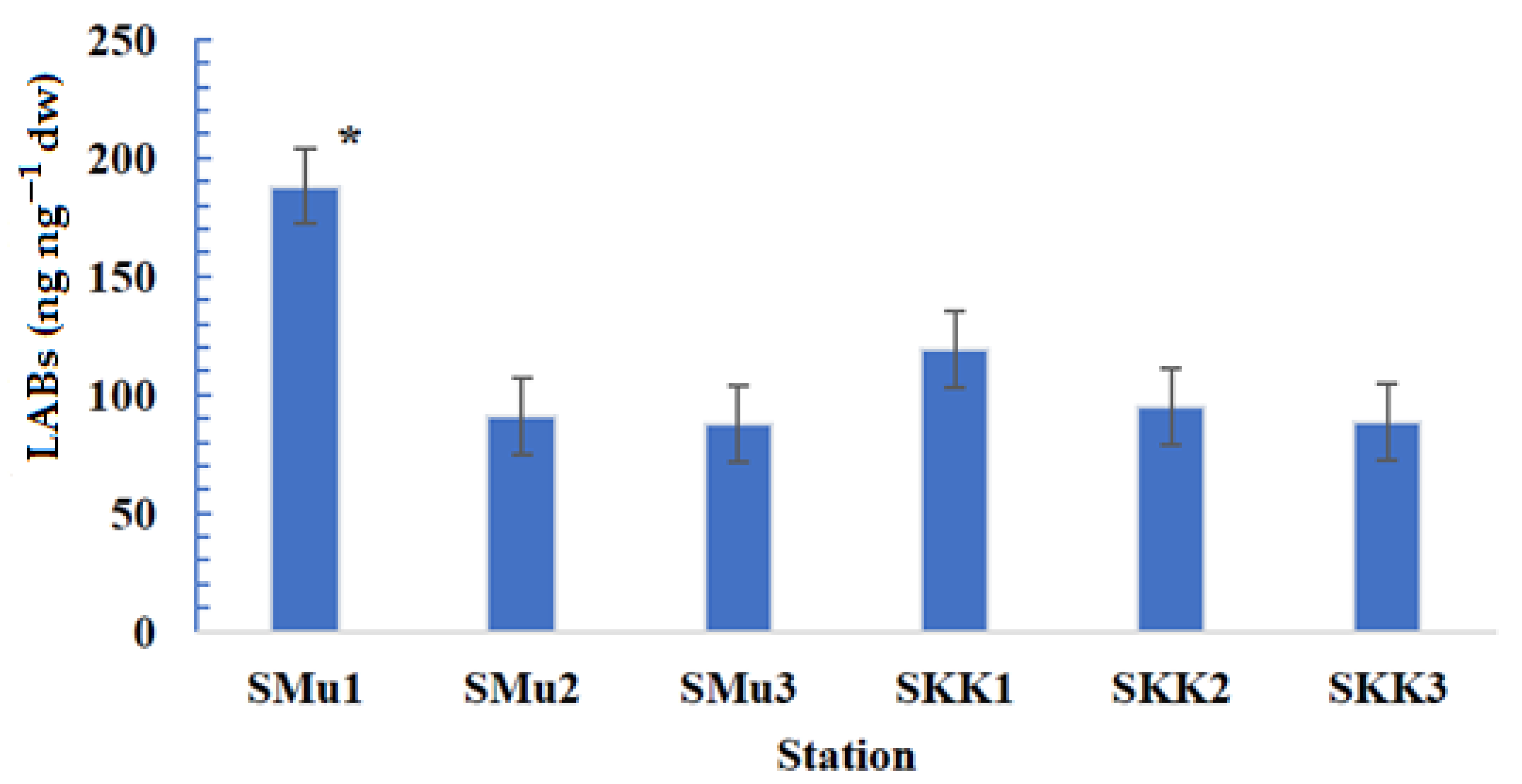
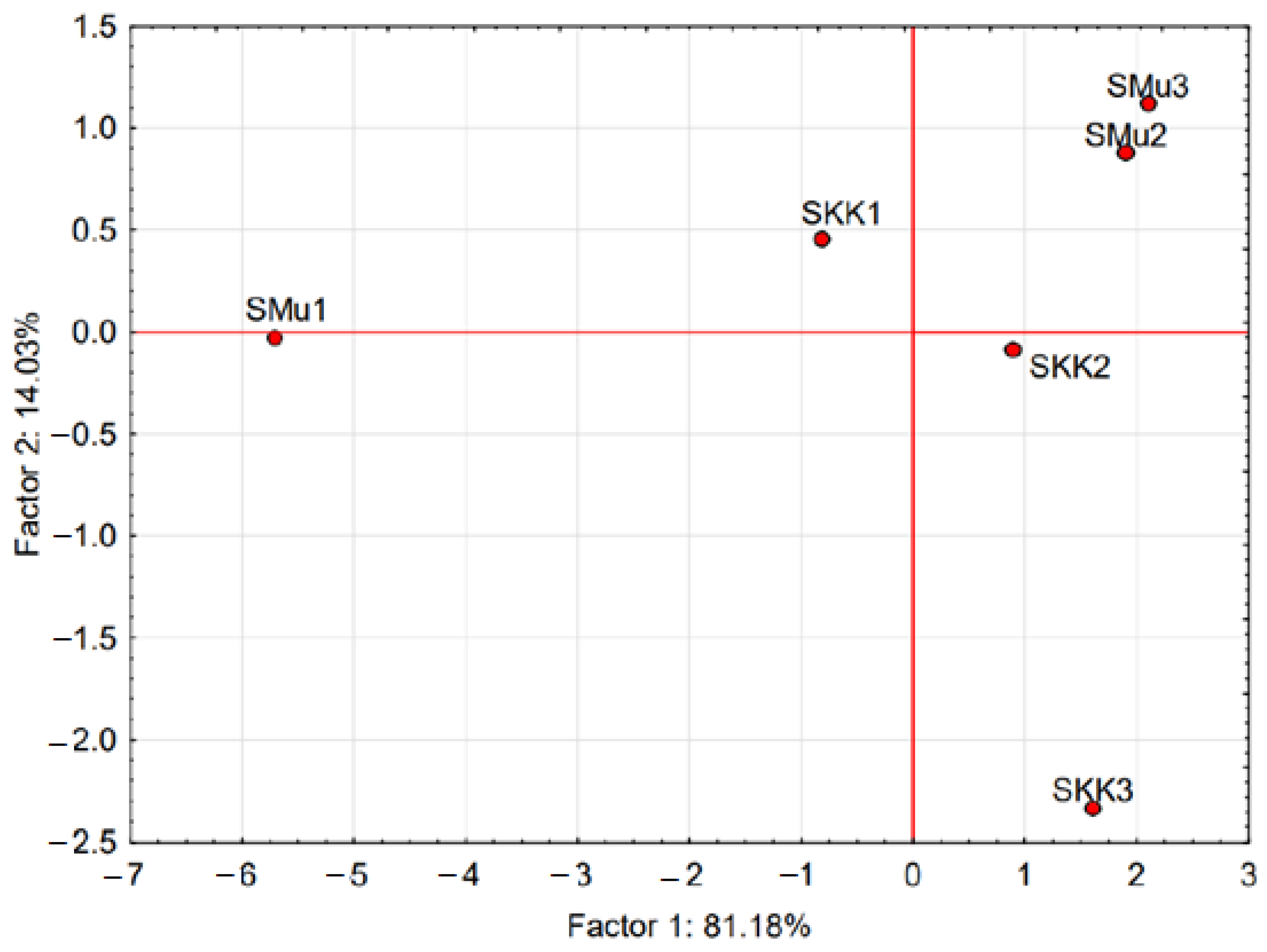
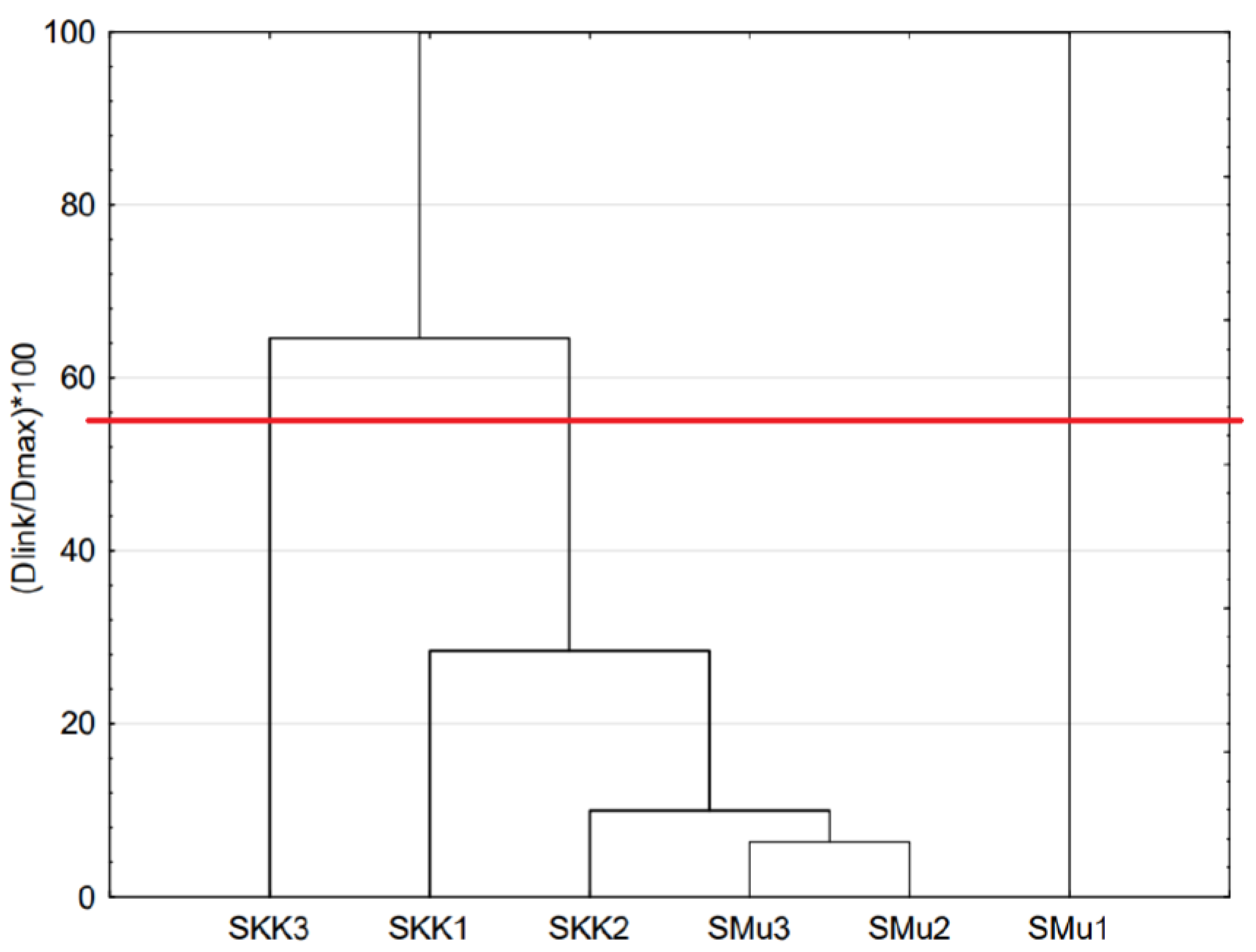
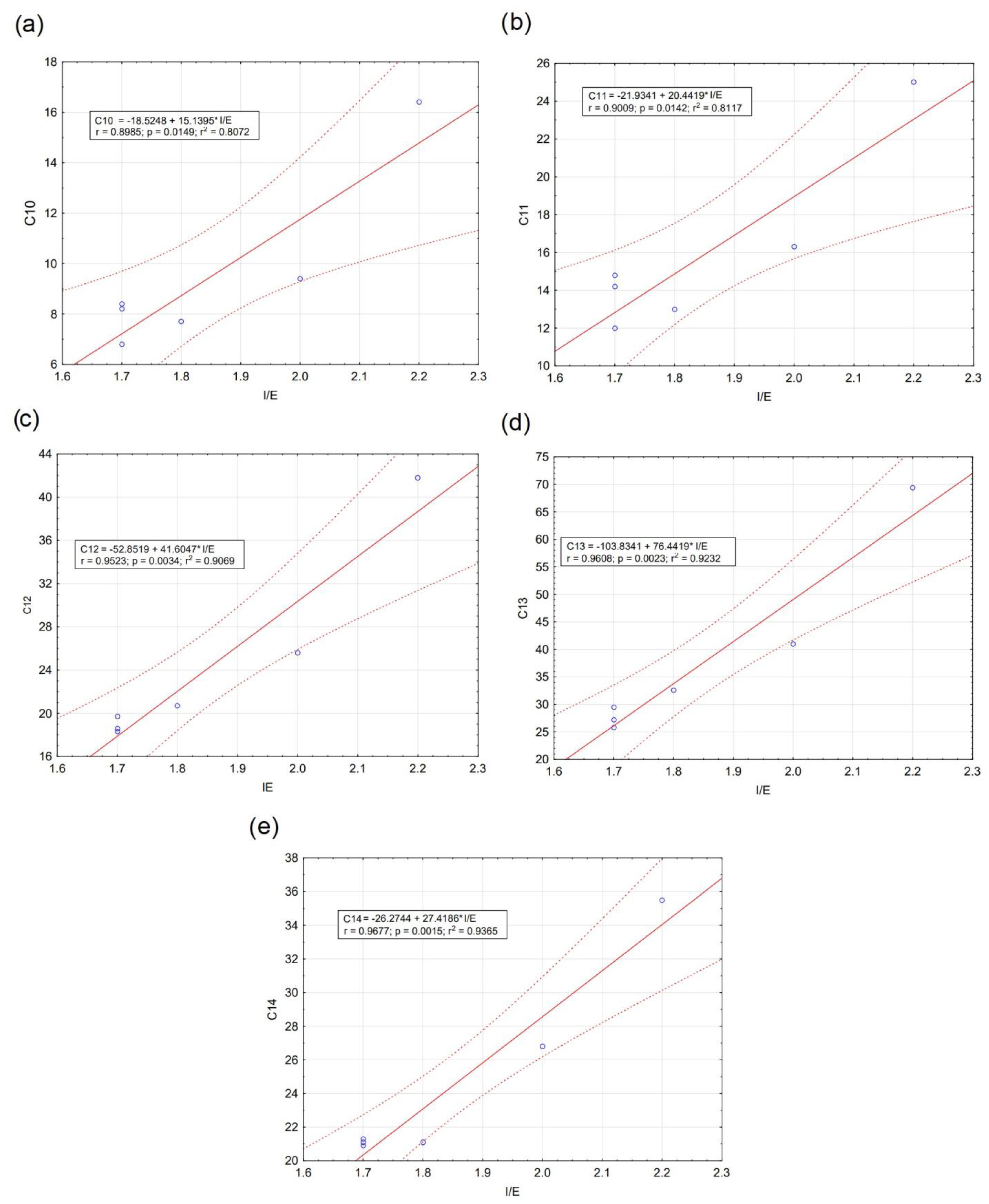
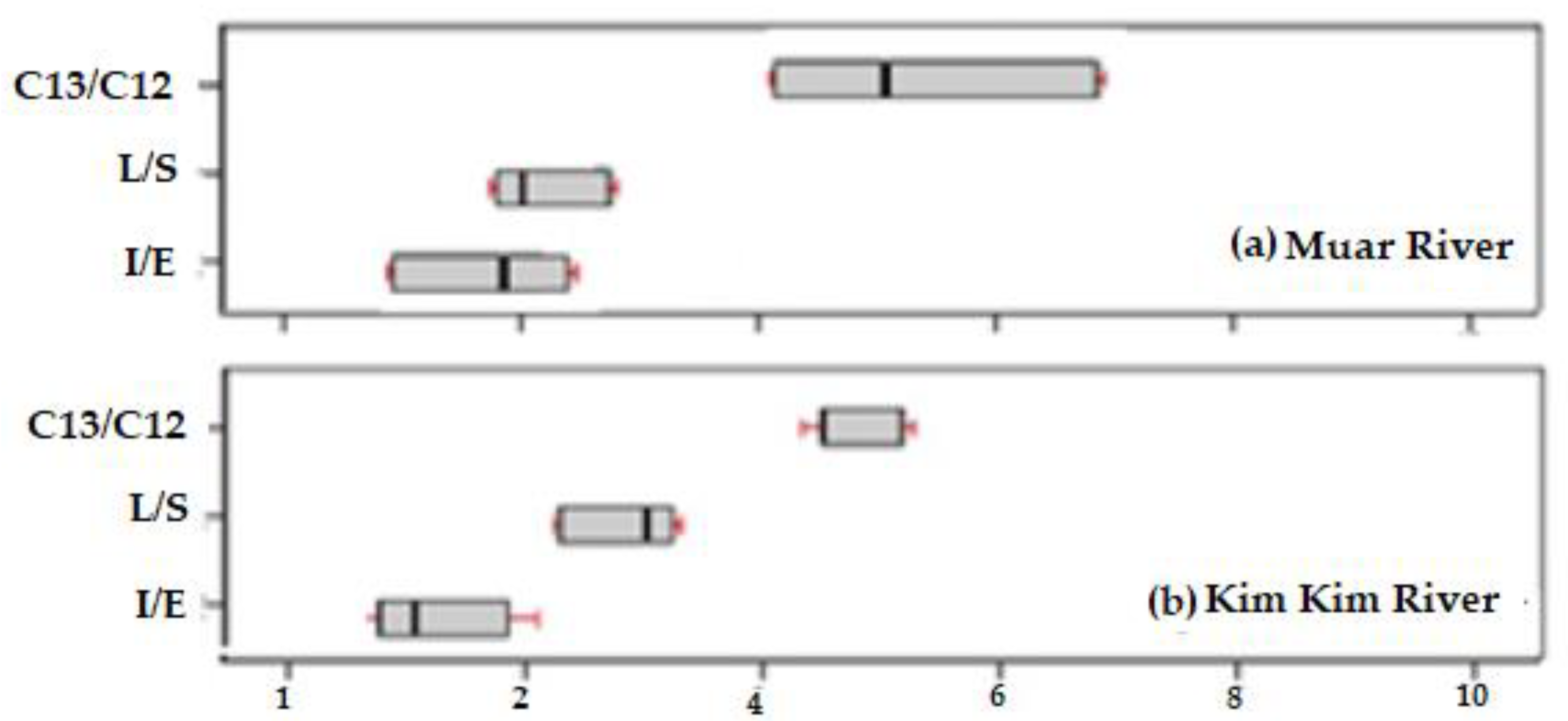
3.1. Composition, Distribution and Concentration LAB
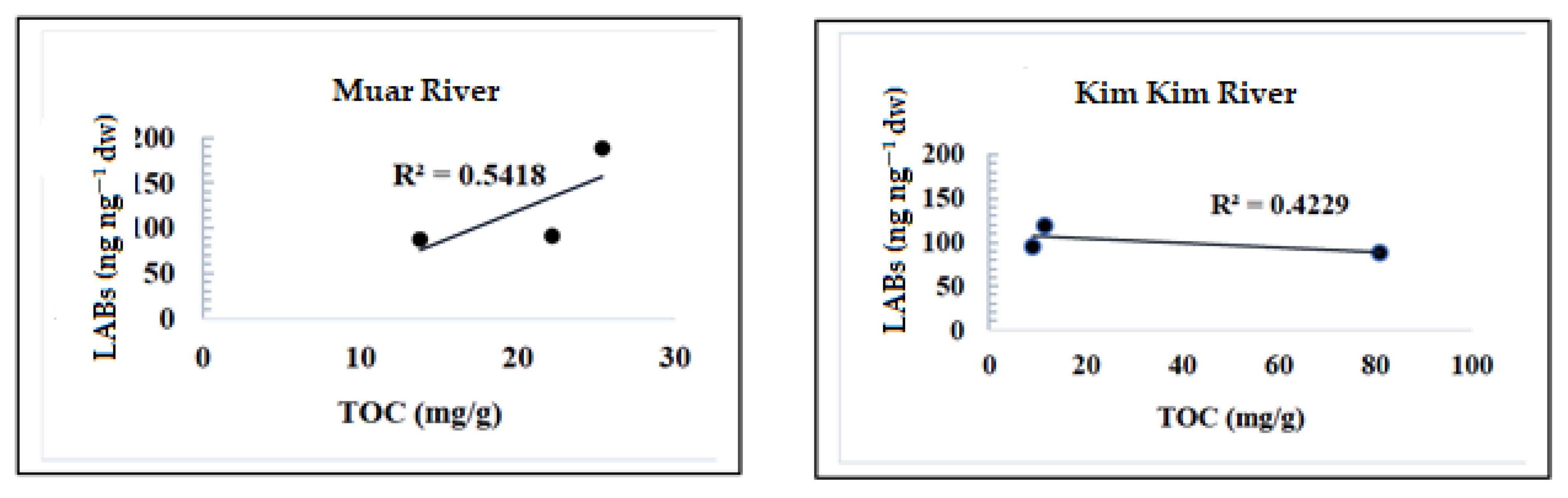
3.2. TOC Evaluation
3.3. Assessment of LAB Reduction and Effluents Treatments Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almasian, A.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Olya, M.E. Tectomer grafted nanofiber: Synthesis, characterization and dye removal ability from multicomponent system. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 32, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Bashiri, M.; Moeen, S.J. Synthesis of nickel–zinc ferrite magnetic nanoparticle and dye degradation using photocatalytic ozonation. Mater. Res. Bull. 2012, 47, 4403–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Ghezelbash, M.; Shabanian, M.; Aryanasab, F.; Sae, M.R. Efficient removal of cationic dyes from colored wastewaters by dithiocarbamate-functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets: From synthesis to detailed kinetics studies. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 81, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hazmi, H.E.; Hassan, G.K.; Maktabifard, M.; Grubba, D.; Majtacz, J.; Mąkinia, J. Integrating conventional nitrogen removal with anammox in wastewater treatment systems: Microbial metabolism, sustainability and challenges. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hazmi, H.E.; Grubba, D.; Majtacz, J.; Ziembińska-Buczyńska, A.; Zhai, J.; Mąkinia, J. Combined partial denitrification/anammox process for nitrogen removal in wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 108978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hazmi, H.E.; Lu, X.; Grubba, D.; Majtacz, J.; Badawi, M.; Mąkinia, J. Sustainable nitrogen removal in anammox-mediated systems: Microbial metabolic pathways, operational conditions and mathematical modelling. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 868, 161633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, F.; Sadighian, S.; Hosseini-Monfare, H.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Dye removal and kinetics of adsorption by magnetic chitosan nanoparticles. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 24378–24386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogacki, J.P.; Al-Hazmi, H. Automotive fleet repair facility wastewater treatment using air/ZVI and air/ZVI/H2O2 processes. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2017, 43, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Lu, X.; Al-Hazmi, H.; Mąkinia, J. An overview of the strategies for the deammonification process start-up and recovery after accidental operational failures. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 541–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.R.; Asghari, M.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Chitosan-wrapped multiwalled carbon nanotube as filler within PEBA thin film nanocomposite (TFN) membrane to improve dye remova. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 237, 116128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hazmi, H.; Grubba, D.; Majtacz, J.; Kowal, P.; Makinia, J. Evaluation of Partial Nitritation/Anammox (PN/A) Process Performance and Microorganisms Community Composition under Different C/N Ratio. Water 2019, 11, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Hazmi, H.E.; Lu, X.; Majtacz, J.; Kowal, P.; Xie, L.; Makinia, J. Optimization of the Aeration Strategies in a Deammonification Sequencing Batch Reactor for Efficient Nitrogen Removal and Mitigation of N 2 O Production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hazmi, H.; Lu, X.; Grubba, D.; Majtacz, J.; Kowal, P.; Mąkinia, J. Achieving Efficient and Stable Deammonification at Low Temperatures—Experimental and Modeling Studies. Energies 2021, 14, 3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hazmi, H.E.; Yin, Z.; Grubba, D.; Majtacz, J.B.; Mąkinia, J. Comparison of the Efficiency of Deammonification under Different DO Concentrations in a Laboratory-Scale Sequencing Batch Reactor. Water 2022, 14, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hazmi, H.E.; Shokrani, H.; Shokrani, A.; Jabbour, K.; Abida, O.; Mousavi Khadem, S.S.; Habibzadeh, S.; Sonawane, S.H.; Saeb, M.R.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; et al. Recent advances in aqueous virus removal technologies. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhadher, S.A.A.; Kadir, A.A.; Zakaria, M.P.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Keshavarzifard, M.; Masood, N.; Alenezi, K.M.; Magam, S.M. Linear alkylbenzenes in surface sediments of an estuarine and marine environment in peninsular Malaysia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153, 111013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhadher, S.A.A.; Kadir, A.A.; Zakaria, M.P.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Magam, S.M.; Masood, N. Monitoring of Sewage Pollution in the Surface Sediments of the Coastal Ecosystems using linear alkylbenzenes (LABs) as Molecular Markers. J. Soils Sediments. 2020, 20, 3230–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhadher, S.A.A.; Kadir, A.A.; Zakaria, M.P.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Asghar, B.H.M. Determination of Linear Alkylbenzenes (LABs) in Mangrove Ecosystems Using the Oyster Crassostrea Belcheri as a Biosensor. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magam, S.M.; Halimoon, N.; Zakaria, M.P.; Aris, A.Z.; Kannan, N.; Masood, N. Evaluation of distribution and sources of sewage molecular marker (LABs) in selected rivers and estuaries of Peninsular Malaysia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 23, 5693–5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhadher, S.A.A.; Suratman, S.; Zakaria, M.P. Lateral Distribution, Environmental Occurrence and Assessment of Organic Pollutants in Surface Sediments of the West and South Peninsular Malaysia. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhadher, S.A.A.; Suratman, S.; Zakaria, M.P. Lateral distribution, environmental occurrence, and assessment of organic pollutants in surface sediments of the East Malaysia. Environ. Monit Assess. 2023, 195, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masood, N.; Zakaria, M.P.; Halimoon, N.; Aris, A.Z.; Magam, S.M.; Kannan, N.; Mustafa, S.; Ali, M.M.; Keshavarzifard, M.; Vaezzadeh, V.; et al. Anthropogenic waste indicators (AWI) particularly PAHs and LABs in Malaysian sediments: Application of aquatic environment for identifying anthropogenic pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 102, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhadher, S.A.A.; Zakariab, M.; Suratman, S.; Alanazi, T.Y.A.; Al-Bagawi, A.H.; Magam, S.M.; Masood, N.; Kadir, A.A.; Al-Gheethi, A. Assessment of Sewage Molecular Markers in Port Dickson Coast and Kim Kim River with Sediment Linear Alkylbenzenes. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2021, 43, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, A.; Karimi, S. A Review in Linear Alkylbenzene (LAB) Production Processes in the Petrochemical Industry. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2020, 94, 1546–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhadher, S.A.A.; Suratman, S.; Zakaria, M.P. Occurrence and Assessment of Organic Pollutants Residues in the Aquatic Environment of the Coastal Sediments. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, B.; Yadav, D.; Singh, S.; Kumar, M.; Song, M. Insights into the Domestic Wastewater Treatment (DWWT) Regimes: A Review. Water 2022, 14, 3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhadher, S.A.A.; Zakaria, M.P.; Yusoff, F.M.; Kannan, N.; Suratman, S.; Keshavarzifard, M.; Magam, S.M.; Masood, N.; Vaezzadeh, V.; Sani, M.S.A. Baseline distribution and sources of linear alkylbenzenes (LABs) in surface sediments from Brunei Bay, Brunei. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okbah, M.A.; Ibrahim, A.M.A.; Gamal, M.N.A. Environmental monitoring of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates and physicochemical characteristics of seawater in El-Mex Bay (Alexandria, Egypt). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 185, 3103–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magam, S.M.; Zakaria, M.P.; Halimoon, N.; Masood, N.; Alsalahi, M.A. Aliphatic Distribution of Linear Alkylbenzenes (LABs) in Sediments of Sarawak and Sembulan Rivers, Malaysia. Environ. Asia 2012, 5, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbazi, A.; Zakaria, M.P.; Yap, C.K.; Tan, S.G.; Surif, S. Use of different tissues of Perna viridis as biomonitors of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the coastal waters of Peninsular Malaysia. Environ. Forensics 2010, 11, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, M.P.; Takada, H.; Tsutsumi, S.; Ohno, K.; Yamada, J.; Kouno, E.; Kumata, H. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in rivers and estuaries in Malaysia: A widespread input of petrogenic PAHs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 36, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, N.; Halimoon, N.; Aris, A.Z.; Zakaria, M.P.; Vaezzadeh, V.; Magam, S.M.; Bong, C.W. Seasonal variability of anthropogenic indices of PAHs in sediment from the Kuala Selangor River, west coast Peninsular Malaysia. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2551–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masood, N.; Alkhadher, S.; Magam, S.M.; Halimoon, N.; Alsukaibi, A.; Zakaria, M.P.; Vaezzadeh, V.; Keshavarzifard, M.; Maisara, S.; Khaled Bin Break, M. Monitoring of linear alkyl benzenes (LABs) in riverine and estuarine sediments in Malaysia. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 44, 3687–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, H.; Eganhouse, R.P. Molecular markers of anthropogenic waste: Their use in determining sources, transport pathways and fate of wastes in the environment. Encycl. Environ. Anal. Remediat. 1998, 5, 2883–2940. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.; Sommers, L. Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 3: Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 961–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Dauner, A.L.I.; Hernández, E.A.; MacCormack, W.P.; Martins, C.C. Molecular characterisation of anthropogenic sources of sedimentary organic matter from Potter Cove, King George Island, Antarctica. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eganhouse, R.P.; Pontolillo, J. Susceptibility of synthetic long-chain alkylbenzenes to degradation in reducing marine sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6361–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, Ö.; Long, C.M.; MacFarlane, J.; Gschwend, P.M. Fate of linear alkylbenzenes released to the coastal environment near Boston Harbor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2040–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherblom, P.M.; Gschwend, P.M.; Eganhouse, R.P. Aqueous solubilities, vapor pressures, and 1-octanol-water partition coefficients for C9-C14 linear alkylbenzenes. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1992, 37, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.J.; Chen, S.J.; Ni, H.G.; Yu, M.; Mai, B.X. Tracing sewage pollution in the Pearl River Delta and its adjacent coastal area of South China Sea using linear alkylbenzenes (LABs). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhtiari, A.R.; Javedankherad, I.; Mohammadi, J.; Taghizadeh, R. Distribution of linear alkylbenzenes as a domestic sewage molecular marker in surface sediments of International Anzali Wetland in the southwest of the Caspian Sea, Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 20920–20929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, K.O.; Zakaria, M.P.; Chiem, N.H.; Minh, L.Y.; Prudente, M.; Boonyatumanond, R.; Saha, M.; Sarkar, M.; Takada, H. Distribution of linear alkylbenzenes (LABs) in riverine and coastal environments in South and Southeast Asia. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2449–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacchi, F.L.; Flores-Nunes, F.; Mattos, J.J.; Lima, D.; Lüchmann, K.H.; Sasaki, S.T.; Bícego, M.C.; Satie Taniguchi, S.; Montone, R.C.; Almeida, E.A.; et al. Biochemical and molecular responses in oysters Crassostrea brasiliana collected from estuarine aquaculture areas in Southern Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull 2018, 135, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, A.C.; Dauner, A.L.L.; Xavier, F.C.B.; Garcia, M.R.D.; Wilhelm, M.M.; Santos, V.C.G.; Netto, S.A.; Martins, C.C. Tracking the sources of allochthonous organic matter along a subtropical fluvial-estuarine gradient using molecular proxies in view of land uses. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymundo, C.; Preston, M. The distribution of linear alkylbenzenes in coastal and estuarine sediments of the Western North Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1992, 24, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.G.; Lu, F.H.; Wang, J.Z.; Guan, Y.F.; Luo, X.L.; Zeng, E.Y. Linear alkylbenzenes in riverine runoff of the Pearl River Delta (China) and their application as anthropogenic molecular markers in coastal environments. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 154, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.C.; Ferreira, J.A.; Taniguchi, S.; Mahiques, M.M.; Bícego, M.C.; Montone, R.C. Spatial distribution of sedimentary linear alkylbenzenes and faecal steroids of Santos Bay and adjoining continental shelf, SW Atlantic, Brazil: Origin and fate of sewage contamination in the shallow coastal environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1359–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, J.Z.; Liang, B.; Shen, R.L.; Zeng, E.Y. Assessment of aquatic wastewater pollution in a highly industrialized zone with sediment linear alkylbenzenes. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinawati; Koike, T.; Koike, H.; Kurumisawa, R.; Ito, M.; Sakurai, S.; Togo, A.; Saha, M.; Arifinc, Z.; Takada, H. Distribution, source identification, and historical trends of organic micro pollutants in coastal sediment in Jakarta Bay, Indonesia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 217–218, 208–216. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, E.Y.; Khan, A.R.; Tran, K. Organic pollutants in the coastal environment Off San Diego, California. 3. Using linear alkylbenzenes to trace sewage-derived organic materials. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1997, 16, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, A.C.; Martins, C.C. Insights about sources, distribution, and degradation of sewage and biogenic molecular markers in surficial sediments and suspended particulate matter from a human-impacted subtropical estuary. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, N.; Yusof, R.; Sapar, M.; Yoneda, M.; Ali, M.M. Spatial analysis and source profiling of beta-agonists and sulfonamides in Langat River basin, Malaysia. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548–549, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Zhang, Y.X.; Chen, R.F. Distribution and partitioning of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in different size fractions in sediments from Boston Harbor, United States. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2001, 42, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzayus, K.M.; Dickhut, R.M.; Canuel, E.A. Fate of atmospherically deposited polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Chesapeake Bay. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2178–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accardi-Dey, A.; Gschwend, P.M. Assessing the combined roles of natural organic matter and black carbon as sorbents in sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinga, K.R. Degradation rates of low molecular weight PAH correlate with sediment TOC in marine sub tidal sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, H.; Ishiwatari, R. Linear alkylbenzenes in urban riverine environments in Tokyo: Distribution, source, and behavior. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1987, 21, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhadher, S.A.A.; Zakaria, M.P.; Yusoff, F.M.; Kannan, N.; Suratman, S.; Magam, S.M.; Masood, N.; Keshavarzifard, M.; Vaezzadeh, V.; Sani, M.S.A. Distribution and sources of linear alkylbenzenes (LABs) in surface sediments from Johor Bahru Coast and the Kim Kim River, Malaysia. Environ. Forensics 2016, 17, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwood, J.J. Molecular markers for identifying municipal, domestic and agricultural sources of organic matter in natural waters. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, A.C.; Stark, J.S.; Kolm, H.E.; Martins, C.C. An integrated evaluation of some faecal indicator bacteria (FIB) and chemical markers as potential tools for monitoring sewage contamination in subtropical estuaries. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Wang, J.Z.; Wong, C.S.; Qiu, J.W.; Zeng, E.Y. Application of multiplegeochemical markers to investigate organic pollution in a dynamic coastal zone. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Samah, B.; Yassin, S.M.; Shaffril, H.A.M.; Hassan, M.S.; Othman, M.S.; Abu Samah, A.; Ramli, S.A. Relationship to the river: The case of the Muar River community. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 7, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample Name | Geographical Coordination | Location Type | Weather Condition | Site Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMu1 | N 02°04′06.0″ E 102°33′18.1″ | River | Cloudy | Urban and industry area |
| SMu 2 | N 02°03′34.9″ E 102°34′27.0″ | River | Cloudy | Urban and industry area |
| SMu 3 | N 02°03′18.0″ E 102°32′23.9″ | River | Cloudy | Urban and industry area |
| SKK1 | N 01°27′28.2″ E 103°57′76.2″ | River | Rainy | Urban and industry area |
| SKK2 | N 01°26′77.6″ E 103°58′04.6″ | River | Rainy | Urban and industry area |
| SKK3 | N 01°25′09.6″ E 103°58′3.31″ | River | Rainy | Urban and industry area |
| Compound | b SMu1 | SMu2 | SMu3 | SKK1 | SKK2 | SKK3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a C10-LABs (ng·g−1dw) | 16.4 | 8.4 | 8.2 | 9.4 | 7.7 | 6.8 |
| C11-LABs (ng·g−1dw) | 25.0 | 14.8 | 14.2 | 16.3 | 13.0 | 12.0 |
| C12-LABs (ng·g−1dw) | 41.8 | 19.7 | 18.3 | 25.6 | 20.7 | 18.6 |
| C13-LABs (ng·g−1dw) | 69.4 | 27.2 | 25.8 | 41.0 | 32.6 | 29.5 |
| C14-LABs (ng·g−1dw) | 35.5 | 21.1 | 20.9 | 26.8 | 21.1 | 21.3 |
| LABs (ng.g−1dw) | 188.1 | 91.2 | 87.4 | 119 | 95.2 | 88.3 |
| c I/E | 2.2 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 1.7 |
| d L/S | 2.67 | 2.02 | 1.99 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 2.6 |
| e C13/C12 | 6.71 | 4.18 | 4.15 | 5.1 | 5.2 | 5.2 |
| f LAB Degradation (%) | 43 | 33 | 33 | 38 | 35 | 33 |
| g TOC(%) | 2.5 | 2.2 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 8.1 |
| TOC (mg/g) | 25.4 | 22.2 | 13.8 | 11.5 | 9.0 | 81 |
| C11 | C12 | C13 | C14 | Labs | I/E | L/S | C13/C12 | Labdegr | TOC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C10 | 1.000 | 0.714 | 0.543 | 0.551 | 0.714 | 0.698 | 0.086 | 0.116 | 0.698 | 0.029 |
| C11 | 0.714 | 0.543 | 0.551 | 0.714 | 0.698 | 0.086 | 0.116 | 0.698 | 0.029 | |
| C12 | 0.943 | 0.812 | 1.000 | 0.941 | 0.600 | 0.667 | 0.941 | 0.143 | ||
| C13 | 0.895 | 0.943 | 0.941 | 0.771 | 0.812 | 0.941 | 0.029 | |||
| C14 | R | 0.812 | 0.770 | 0.783 | 0.750 | 0.770 | 0.348 | |||
| Labs | >0.9 | very strong | 0.941 | 0.600 | 0.667 | 0.941 | 0.143 | |||
| I/E | 0.7–0.9 | strong | 0.577 | 0.647 | 1.000 | 0.213 | ||||
| L/S | <0.7 | medium | 0.986 | 0.577 | 0.429 | |||||
| C13/C122 | 0.647 | 0.290 | ||||||||
| Labdegr | 0.213 |
| Source | DF | Sum of Square | Mean Square | F Value | Sig * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Side | 1 | 92,278.39 | 9227.39 | 10.11 | <0.05 |
| Locations | 2 | 114,597.32 | 2291.46 | 50.20 | <0.05 |
| Error | 25 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| Corrected Total | 6 | 143,098.47 |
| Location | N | Maximum LABs (ng/g) a | I/E Ratio b | Degradation c (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Atlantic Estuary | 15 | 210 | 2.5 | 47 | [44] |
| Southern Brazil | 3 | 15.3 | 1.4 | 27 | [43] |
| Humber Estuary and Wash, UK | 18 | 84.8 | 2.1 | 41 | [45] |
| Anzali Wetland, Iran | 167 | 109,000 | 1.3 | 24 | [41] |
| Malacca, Malaysia | 1 | 1080 | 2.0 | 39 | [42] |
| Muar River, Malaysia | 1 | 32 | 2.8 | 51 | [42] |
| Penang Estuary, Malaysia | 1 | 3000 | 1.5 | 29 | [42] |
| Prai River, Malaysia | 1 | 25 | 3.4 | 58 | [42] |
| Kim Kim River, Malaysia | 1 | 122 | 1.8 | 36 | [42] |
| Kim Kim Estuary, Malaysia | 1 | 6 | 1.2 | 21 | [42] |
| Nibong Tebal, Malaysia | 1 | 168 | 2.1 | 41 | [42] |
| Indonesia | 20 | 42,600 | 2.1 | 41 | [42] |
| Sarawak River, Malaysia | 9 | 7390 | 1.0 | 15 | [29] |
| SembulanRiver, Malaysia | 6 | 5570 | 1.8 | 36 | [29] |
| Zhujiang River | 11 | 2330 | 1.5 | 29 | [40] |
| Dongjiang River | 10 | 566 | 1.9 | 38 | [40] |
| Xijiang River | 8 | 69.4 | 1 | 15 | [40] |
| Pearl River Estuary | 8 | 26 | 1.5 | 29 | [40] |
| South China Sea | 28 | 23 | 0.9 | 11 | [40] |
| The Pearl River Delta | 96 | 11,200 | 1.7 | 34 | [46] |
| Santos Bay, Brazil | 14 | 117 | 2.9 | 55 | [47] |
| Dongjiang River | 45 | 410 | 1.4 | 27 | [48] |
| Outfalls of paper mills | 3 | 3270 | 1.3 | 24 | [48] |
| Jakarta Bay | 7 | 86,800 | 0.9 | 12 | [49] |
| Tokyo Bay | 2 | 1110 | 2.8 | 51 | [49] |
| Detergents | 10 | 5,300,000 | 1.7 | 34 | [45] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alkhadher, S.A.A.; Suratman, S.; Al-Hazmi, H.E.; Zakaria, M.P.; Szeląg, B.; Majtacz, J.; Drewnowski, J. Unlocking the Secrets of River Pollution: Analyzing Organic Pollutants in Sediments—Experimental Study. Water 2023, 15, 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122216
Alkhadher SAA, Suratman S, Al-Hazmi HE, Zakaria MP, Szeląg B, Majtacz J, Drewnowski J. Unlocking the Secrets of River Pollution: Analyzing Organic Pollutants in Sediments—Experimental Study. Water. 2023; 15(12):2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122216
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlkhadher, Sadeq Abdullah Abdo, Suhaimi Suratman, Hussein E. Al-Hazmi, Mohamad Pauzi Zakaria, Bartosz Szeląg, Joanna Majtacz, and Jakub Drewnowski. 2023. "Unlocking the Secrets of River Pollution: Analyzing Organic Pollutants in Sediments—Experimental Study" Water 15, no. 12: 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122216
APA StyleAlkhadher, S. A. A., Suratman, S., Al-Hazmi, H. E., Zakaria, M. P., Szeląg, B., Majtacz, J., & Drewnowski, J. (2023). Unlocking the Secrets of River Pollution: Analyzing Organic Pollutants in Sediments—Experimental Study. Water, 15(12), 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122216










