Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in the Water, Sediment, and Organisms from The Sea Ranching Areas of Haizhou Bay in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
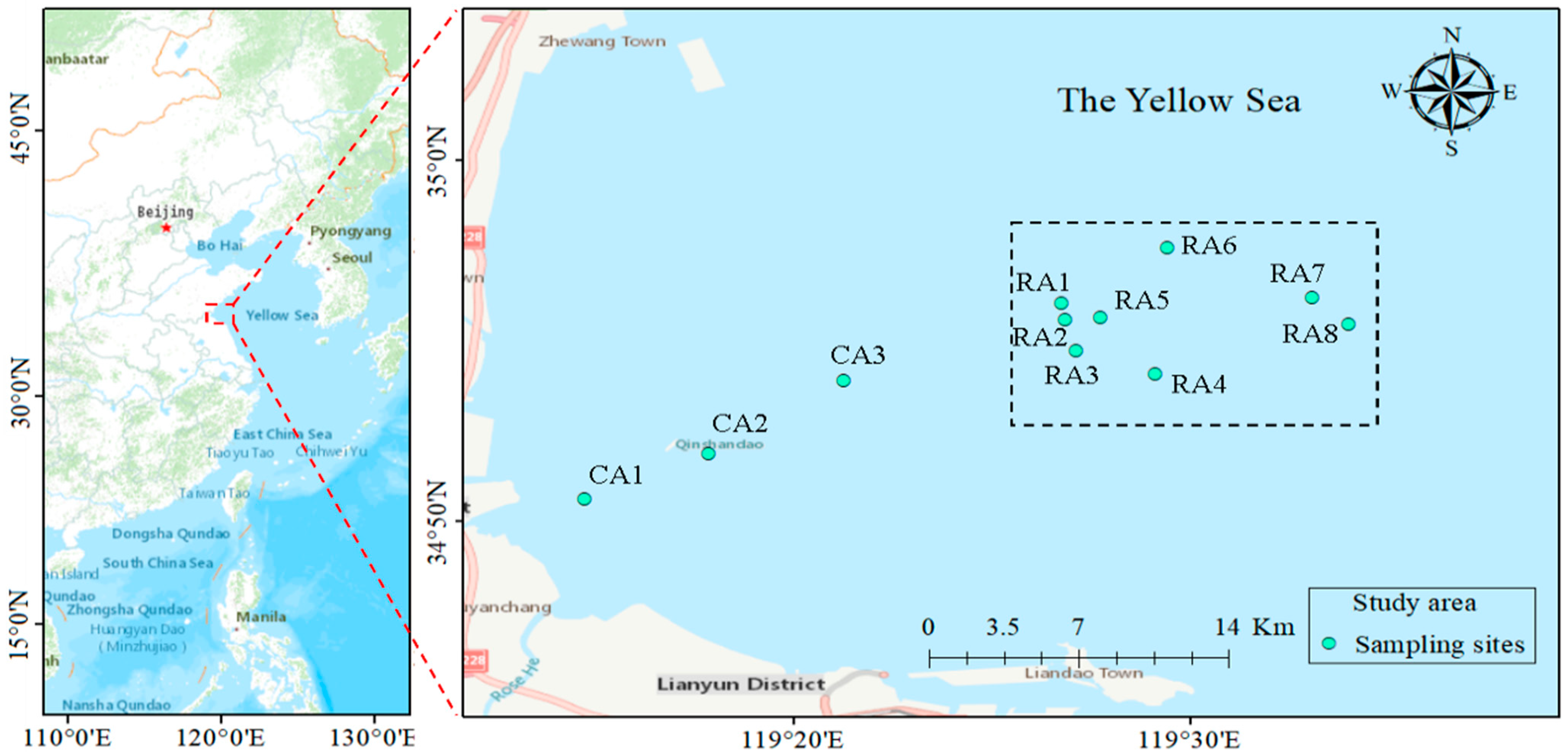
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Treatment and Analysis
2.4. Bioaccumulation Factor
2.5. Quality Control and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
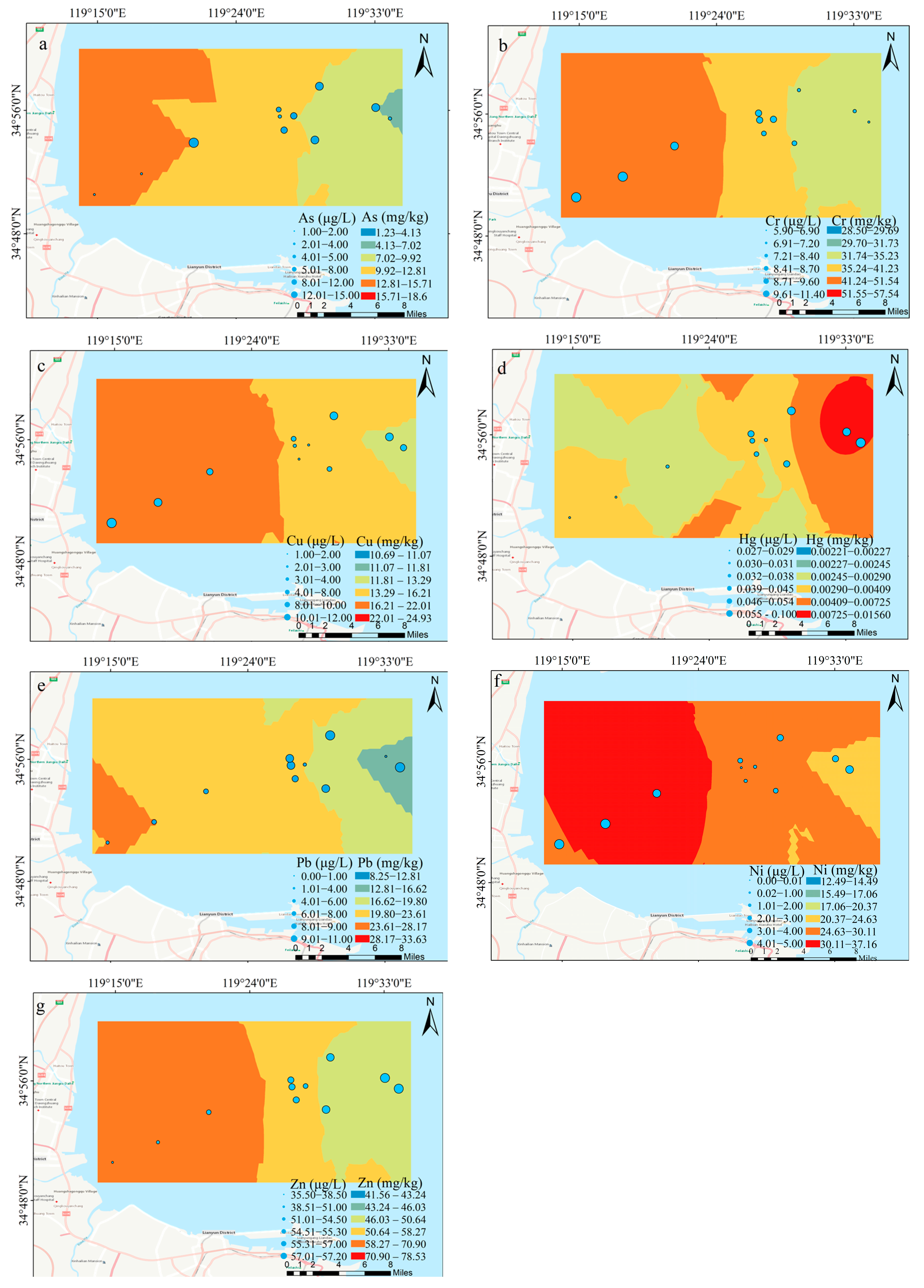
3.1. The Distribution of HMs in the Water and Sediments
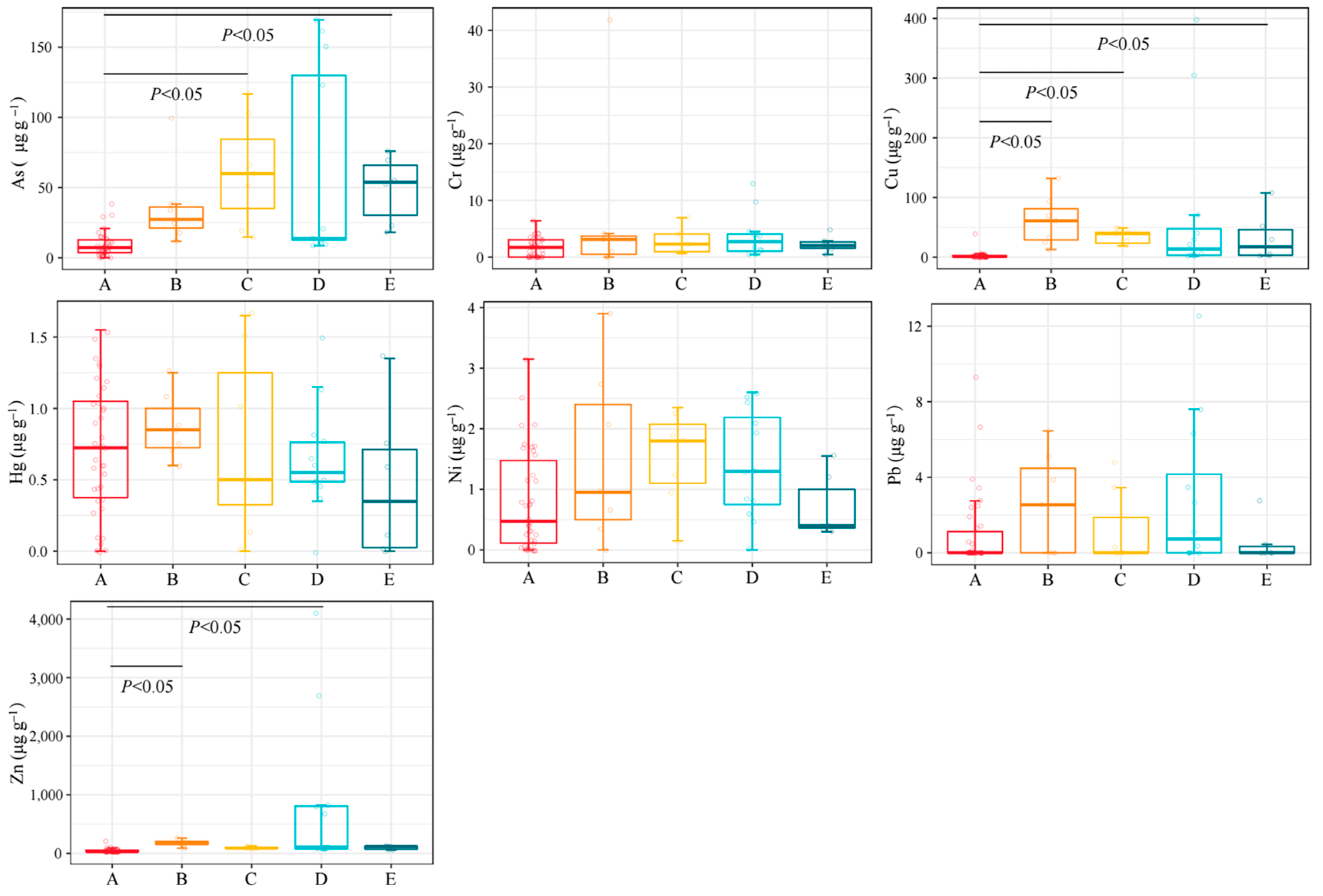
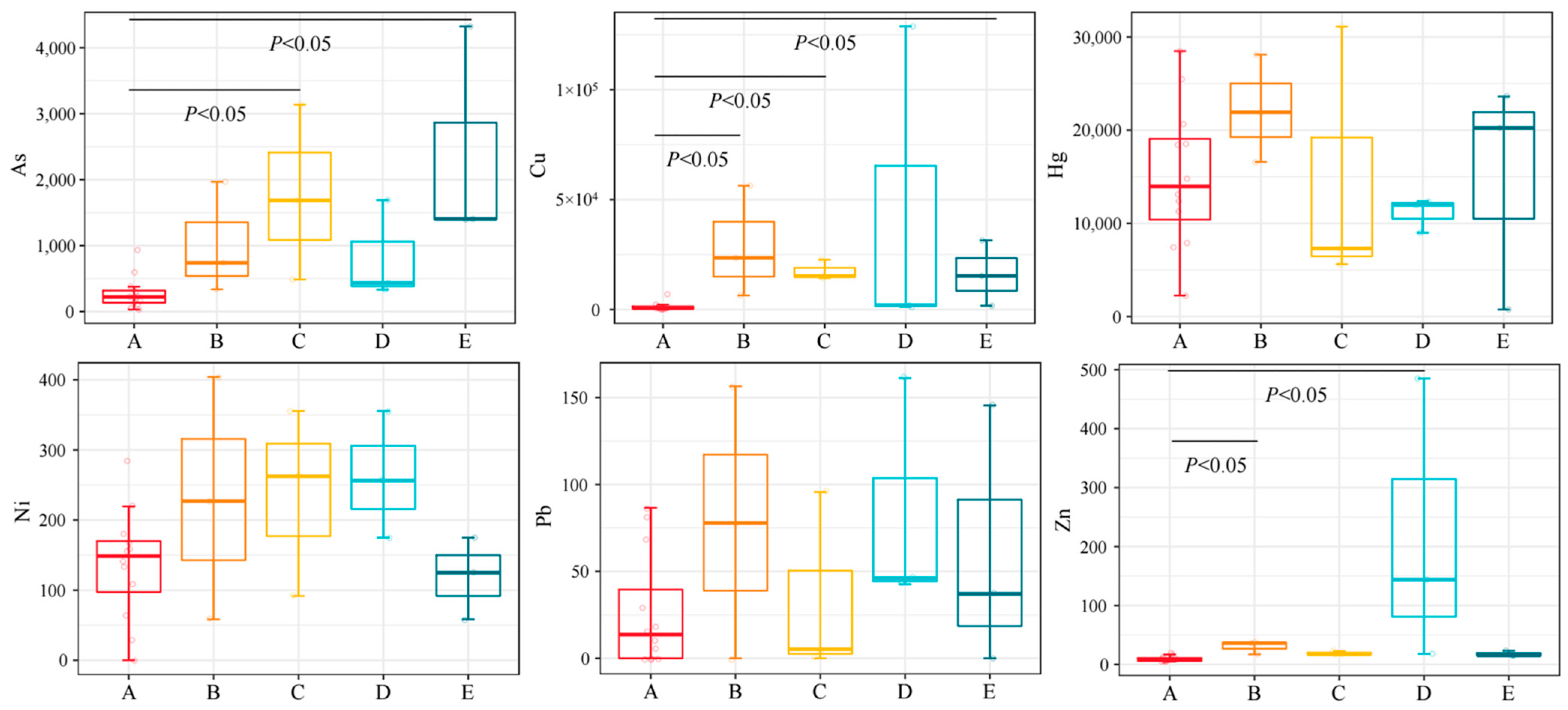
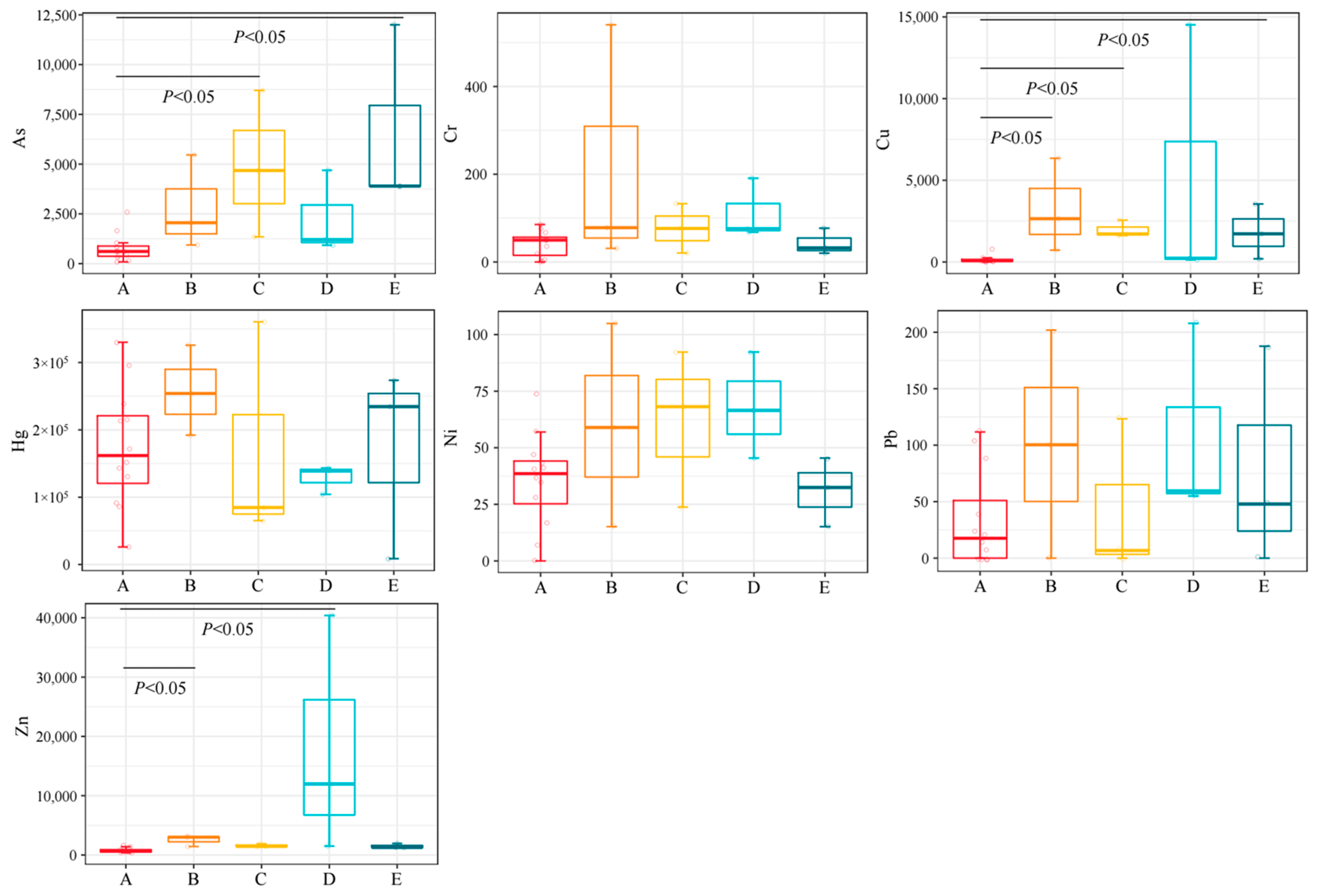
3.2. The Concentration of HMs in Different Groups
3.3. Bio-Water and Bio-Sediment Accumulation Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of HMs in the Water and Sediments
4.2. Characteristics of HMs in the Tissues of Organisms
4.3. Characteristics of HMs Accumulated by Organisms from Water and Sediments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sites | As | Pb | Ni | Cu | Zn | Hg | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RA1 | 8.1 | 4.1 | 1.1 | 2.3 | 54.5 | 0.0306 | 8.6 |
| RA2 | 4.3 | 9.2 | 0 | 3.3 | 54.9 | 0.0359 | 8.7 |
| RA3 | 8.5 | 8.2 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 54.8 | 0.0382 | 8.4 |
| RA4 | 7.1 | 9.3 | 2.1 | 4.1 | 55.3 | 0.0437 | 8.6 |
| RA5 | 12.2 | 10.0 | 2.2 | 4.3 | 56.9 | 0.0448 | 8.4 |
| RA6 | 10.3 | 11.4 | 3.0 | 9.2 | 57 | 0.0515 | 7.2 |
| RA7 | 12.0 | 1.0 | 3.2 | 10.2 | 57.2 | 0.054 | 7.2 |
| RA8 | 5.1 | 11.2 | 4.1 | 8.7 | 57.2 | 0.100 | 6.9 |
| CA3 | 15.0 | 6.1 | 4.3 | 7.6 | 54.0 | 0.030 | 9.6 |
| CA2 | 2.4 | 5.2 | 5.1 | 10.1 | 51.0 | 0.0286 | 10.9 |
| CA1 | 1.0 | 4.0 | 5.2 | 12.0 | 38.5 | 0.0268 | 11.4 |
Appendix B
| Sites | As | Cu | Pb | Zn | Cr | Ni | Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RA1 | 8.2 | 11.71 | 11.71 | 46.84 | 30.44 | 16.39 | 0.0031 |
| RA2 | 18.6 | 16.28 | 22.09 | 51.16 | 36.05 | 17.44 | 0.00419 |
| RA3 | 5.48 | 12.05 | 15.34 | 48.2 | 31.77 | 15.34 | 0.00221 |
| RA4 | 14.41 | 24.02 | 33.63 | 70.86 | 49.24 | 30.03 | 0.00282 |
| RA5 | 1.23 | 11.05 | 15.96 | 44.2 | 30.7 | 17.19 | 0.00227 |
| RA6 | 11.87 | 10.69 | 17.81 | 41.56 | 28.5 | 16.62 | 0.00233 |
| RA7 | 9.43 | 15.32 | 8.25 | 53.02 | 36.52 | 21.21 | 0.0156 |
| RA8 | 3.36 | 13.46 | 19.06 | 45.97 | 30.28 | 16.82 | 0.00353 |
| CA3 | 12.24 | 20.81 | 29.38 | 67.32 | 45.29 | 25.7 | 0.0024 |
| CA2 | 17.45 | 24.93 | 23.68 | 78.53 | 52.36 | 31.16 | 0.00305 |
| CA1 | 13.62 | 12.49 | 24.97 | 49.94 | 34.05 | 12.49 | 0.00314 |
Appendix C
| Groups | Species | As (μg/g) | Cr (μg/g) | Cu (μg/g) | Hg (μg/g) | Ni (μg/g) | Pb (μg/g) | Zn (μg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish | Konosirus punctatus | 3.93 | 3.17 | 0.70 | 0.58 | 0.17 | 0.47 | 66.13 |
| Trichiurus lepturus | 4.92 | 2.09 | 2.96 | 0.82 | 0.95 | 2.49 | 44.44 | |
| Lophius litulon | 32.65 | 2.78 | 0.97 | 0.50 | 0.65 | <LOQ | 41.55 | |
| Thamnaconus modestus | 13.17 | <LOQ | 0.38 | 1.13 | 0.93 | 1.95 | 30.58 | |
| Scomber japonicus | 1.95 | 0.05 | 0.80 | 0.83 | 0.85 | 2.33 | 30.98 | |
| Engraulis japonicus | 7.90 | 2.05 | 1.85 | 0.55 | 0.80 | 0.00 | 102.45 | |
| Jaydia lineata | 5.62 | 0.22 | 13.95 | 1.27 | 1.32 | 0.87 | 87.90 | |
| Larimichthys polyactis | 1.10 | 2.20 | 4.45 | 0.10 | 1.70 | 0.00 | 25.25 | |
| Conger myriaster | 7.55 | 3.55 | 2.69 | 0.33 | 1.08 | 0.55 | 44.65 | |
| Sebastes schlegelii | 8.00 | 0.77 | 1.70 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 0.15 | 24.80 | |
| Saurida elongata | 10.47 | 1.48 | 0.40 | 0.66 | 0.38 | 0.32 | 36.46 | |
| Lateolabrax japonicus | 20.85 | 2.10 | <LOQ | 0.35 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 53.10 | |
| Crustacean | Charybdis japonica | 25.90 | 1.29 | 47.01 | 0.74 | 1.36 | 2.24 | 196.33 |
| Oratosquilla oratoria | 68.88 | 22.48 | 112.65 | 0.98 | 2.43 | 4.50 | 187.90 | |
| Acetes chinensis | 11.80 | 3.25 | 12.85 | 1.25 | 0.35 | 0.00 | 89.65 | |
| Cephalopod | Octopus ocellatus | 59.00 | 0.85 | 28.67 | 1.38 | 2.13 | 2.75 | 85.33 |
| Loligo beka | 16.98 | 5.53 | 30.43 | 0.33 | 0.55 | 0.15 | 90.70 | |
| Sepiella maindroni | 109.78 | 3.18 | 45.43 | 0.25 | 1.58 | 0.00 | 118.78 | |
| Bivalvia | Pinna rudis | 15.18 | 2.83 | 2.35 | 0.40 | 1.05 | 1.33 | 750.00 |
| Scapharca subcrenata | 11.69 | 3.14 | 3.95 | 0.55 | 1.54 | 1.23 | 94.04 | |
| Ostrea denselamellosa | 59.15 | 7.93 | 257.63 | 0.53 | 2.13 | 4.63 | 2529.50 | |
| Gastropod | Neptunea cumingi | 151.33 | 0.83 | 30.57 | 1.05 | 0.75 | 4.18 | 77.33 |
| Rapana venosa | 49.13 | 1.33 | 3.45 | 0.90 | 1.05 | <LOQ | 79.67 | |
| Glossaulax didyma | 48.88 | 3.20 | 62.97 | 0.03 | 0.35 | 1.07 | 121.83 |
Appendix D
| Class I Biological Quality Standard in China | Zn (μg/g) | Cu (μg/g) | Cr (μg/g) | Ni (μg/g) | Hg (μg/g) | Pb (μg/g) | As (μg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bivalvia | 250 | 50.0 | 2.00 | — | 0.30 | 1.50 | 1.00 |
| Gastropoda | 250 | 50.0 | 2.00 | — | 0.30 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Cephalopod | 250 | 50.0 | 2.00 | — | 0.30 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Crustacean | 150 | 50.0 | 2.00 | — | 0.30 | 0.50 | 1.00 |
| Fish | 40.0 | 50.0 | 2.00 | — | 0.30 | 0.50 | 1.00 |
References
- Trevizani, T.H.; Petti, M.A.V.; Ribeiro, A.P.; Corbisier, T.N.; Figueira, R.C.L. Heavy metal concentrations in the benthic trophic web of Martel Inlet, Admiralty Bay (King George Island, Antarctica). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 130, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Javed, M.; Rehman, M.T.; Urooj, M.; Ahmad, M.I. Heavy metal pollution and risk assessment by the battery of toxicity tests. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubalingeswari, N.; Thulasimala, D.; Giridharan, L.; Gopal, V.; Jayaprakash, M. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in the water, sediment, and tissues of major fisheries from adyar estuary, southeast coast of India: An ecotoxicological impact of a metropolitan city. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokarram, M.; Saber, A.; Obeidi, R. Effects of heavy metal contamination released by petrochemical plants on marine life and water quality of coastal areas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 51369–51383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamood, M.; Javed, M.; Alhewairini, S.S.; Zahir, F.; Ahmad, M.I. Labeo rohita, a bioindicator for water quality and associated biomarkers of heavy metal toxicity. NPJ Clean Water 2021, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sivaperumal, P.; Manigandan, V.; Rajaram, R.; Hussain, M. Assessment of potential human health risk due to heavy metal contamination in edible finfish and shellfish collected around ennore coast, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 8151–8167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubeva, N.I.; Burtseva, L.V.; Ginzburg, V.A. Heavy metals in the atmospheric precipitation on the Barents Sea coast. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2010, 35, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.; Jamil, A.; Khan, T. Assessment of heavy metal contamination and human health risk with oxidative stress in fish (Cyprinus carpio) from shahpur dam, fateh jang, pakistan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Li, H.D.; Peng, X.J.; Zhang, W.P.; Lou, Q.S.; Gong, J.J.; Ye, J. Characteristics of heavy metals in seawater and sediments from Daya bay (South China): Environmental fates, source apportionment and ecological risks. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifti, N.S.; Ayas, D.; Bakan, M. The comparison of heavy metal level in surface water, sediment and biota sampled from the polluted and unpolluted sites in the northeastern mediterranean sea. Thalass. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 37, 319–330. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, H.M.; Cheung, K.C.; Chi, K.A.; Yung, K.; Li, W.C. An assessment of heavy metal contamination in the marine soil/sediment of Coles Bay area, svalbard, and greater bay area, China: A baseline survey from a rapidly developing bay. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 22170–22178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabetoglou, K.; Voutsa, D.; Samara, C. Toxicity and heavy metal contamination of surficial sediments from the bay of Thessaloniki (northwestern aegean sea) greece. Chemosphere 2002, 49, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Hua, P.; Gui, D.; Niu, J.; Krebs, P. A comparative analysis of artificial neural networks and wavelet hybrid approaches to long−term toxic heavy metal prediction. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnero, P.L.; Monferran, M.V.; Gonzalez, G.A.; Griboff, J.; Bistoni, M.D.L.A. Assessment of exposure to metals, as and se in the water and sediment of a freshwater reservoir and their bioaccumulation in fish species of different feeding and habitat preferences. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.N.; Rahaman, A.; Hasan, M.J.; Uddin, M.M.; Khatun, N.; Shamsuddin, S.M. Comparative seasonal assessment of pollution and health risks associated with heavy metals in the water, sediment and fish of buriganga and turag river in dhaka city, bangladesh. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Qian, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D. Assessment of long−term effects from cage culture practices on heavy metal accumulation in sediment and fish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 194, 110433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E. Assessment of potentially toxic heavy metals and health risk in the water, sediments, and different fish species of river Kabul, Pakistan. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2018, 8, 2101–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashkina, N.A.; Moiseenko, T.I.; Kudryavtseva, L.P. Fish response of metal bioaccumulation to reduced toxic load on long−term contaminated lake Imandra. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.K.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. The seasonal variation in heavy metal accumulation in the food web in the coastal waters of Jiangsu based on carbon and nitrogen isotope technology. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 11, 118649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, L. Assessment of the transfer of heavy metals in seawater, sediment, biota samples and determination the baseline tissue concentrations of metals in marine organisms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 30, 28764–28776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Oldham, D.; Minghetti, M. Role of metal speciation in the exposure medium on the toxicity, bioavailability and bio−reactivity of copper, silver, cadmium and zinc in the rainbow trout gut cell line (rtgutgc). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 236, 108816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayandiran, T.A.; Fawole, O.O.; Adewoye, S.O.; Ogundiran, M.A. Bioconcentration of metals in the body muscle and gut of Clarias gariepinus exposed to sublethal concentrations of soap and detergent effluent. J. Cell Anim. Biol. 2009, 3, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Waykar, B.; Petare, R. Studies on monitoring the heavy metal concentrations in the water, sediment and snail species in Latipada reservoir. J. Environ. Biol. 2016, 37, 585–589. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Jiao, J.P.; Li, Y.S.; Zhu, K.W. Changes of ecological environment of artificial reef in Haizhou Bay. J. Fish. China 2006, 30, 457–480. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.Z.; Wu, W.Q.; Lu, W.; Zhao, M. Exploration practice and prospect of ecological environment restoration in Haizhou Bay−Construction of sea ranching demonstration area in Jiangsu province. China Fish. 2012, 177, 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Xie, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. Ecosystem development of Haizhou bay ecological restoration area from 2003 to 2013. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2017, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xu, M. Source Characteristics and Contamination Evaluation of Heavy Metals in the Surface Sediments of Haizhou Bay. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 1035. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.P.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.F.; Luo, N.; Wei, Q.Q.; Zhang, R.; Huang, H. Heavy metals in the sediments from the Haizhou bay marine ranching based on geochemical characteristics. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z. Spatial distribution, source apportionment and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Haizhou bay national ocean park, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compilation Committee of China’s Gulf Chronicle. China’s Gulf Chronicle; China’s Gulf Chronicle Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, F.; Li, R.J. 3D Water Environment Simulation for North Jiangsu Offshore Sea Based on EFDC. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2009, 1, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. A review of the characteristics of the coastal waters in China. Mar. Limnetic Bull. 2020, 21, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.W.; Chen, W.; Gu, Y.J. Suggestions for Lianyungang to accelerate the construction of modern Marine industry system. Land Bridge Vis. 2022, 16, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, Z.; Li, Z.; Fan, Z.; Ding, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, J.; Yan, H.; Wei, S. Heavy metal pollution and assessment in the tidal flat sediments of Haizhou bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 74, 403–412. [Google Scholar]
- Authman, M.M.; Abbas, H.H. Accumulation and distribution of copper and zinc in bothwater and somevital tissues of two fish species (Tilapia zillii and Mugil cephalus) of Lake Qarun, Fayoum Province, Egypt. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. PJBS 2007, 10, 2106–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziyaadini, M.; Yousefiyanpour, Z.; Ghasemzadeh, J.; Zahedi, M.M. Biota—sediment accumulation factor and concentration of heavy metals (Hg, Cd, As, Ni, Pb and Cu) in the sediments and tissues of Chiton lamyi (Mollusca: Polyplacophora: Chitonidae) in Chabahar Bay, Iran. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2017, 16, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, S. Research progress of heavy metal pollution in offshore environment. J. Dongguan Univ. Technol. 2020, 27, 95–116. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Min, X.; Ding, Y.Z.; Xu, W.J. Haizhou Bay water pollution spatial distribution and sources. J. Ecol. 2014, 33, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Xue, J.; Zhu, Z. Comparison of heavy metal bioaccessibility between street dust and beach sediment: Particle size effect and environmental magnetism response. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.H.; Cheng, N.N.; Yu, S.M. The current situation and comprehensive evaluation of water quality in the Yangtze River estuary and adjacent waters in autumn 2019. Environ. Impact Assess. 2022, 85–89, 96. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.B.; Zhang, J.C.; Zhang, H.N. Contents of Heavy Metals in Pearl River Estuary and Ecological Risk Assessment. J. Dongguan Univ. Technol. 2021, 28, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhai, W. Spatial distribution of heavy metal contamination and uncertainty-based human health risk in the aquatic environment using multivariate statistical method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 22804–22822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, K.; Xu, M.; Xu, W. Sources Apportionment and Pollution Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Sediments of the Northern Haizhou Bay in China. J. Nanjing Norm. Univ. 2018, 41, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.Q.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.Y. Analysis of Marine environment changes before and after the construction of Marine pasture artificial reef area in Haizhou Bay. Bull. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 2021, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, C.; Dai, I.; Zhang, H.; Yan, L. Research on the multi−phase media enrichment characteristics of pb in typical offshore engineering marine district. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2019, 6, 669–673. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Wu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Mao, L.; Zhang, Y. Source apportionment of heavy metals in the sediments of the urban rivers flowing into Haizhou bay, eastern china: Using multivariate statistical analyses and pb−srisotope fingerprints. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 36354–36366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z. Potential bioremediation effects of seaweed Gracilaria lemaneiformis on heavy metals in coastal sediment from a typical mariculture zone. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chai, Z.; Wang, Q. Cultivation of seaweed Gracilaria in Chinese coastal waters and its contribution to environmental improvements. Algal Res. 2015, 9, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.W. Sedimentary Environmental Effects and Dynamic Mechanism of Kelp Culture in Shallow Waters; Graduate School of China Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Xu, M. Source characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Haizhou Bay. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Wang, Q.L.; Zeng, R.; Zhang, Y.J.L. Analysis of heavy metal pollution in surface sediments of Bohai Bay and its interannual variation. China Environ. Sci. 2022, 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.Q.; Zhao, X.; Lin, J. Pollution and sources of heavy metals in surface sediments based on total amount and morphology-taking Ma‘an Islands waters as an example. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.H.; Xiao, Y.Y.; Wang, T. Effects of heavy metals and oil pollution in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary on microbial community structure. Bull. Mar. Limnol. 2022, 44, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.Y. Sediment Migration Trend in Lianyungang Coastal Area. J. Oceanogr. 2013, 35, 172–178. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zou, X.; Feng, Z. Distribution and transport of heavy metals in estuarine−inner shelf regions of the East China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.D.; Song, J.M.; Yuan, H. The health status of the Bohai Sea in autumn 2020 and suggestions for the development and utilization of the sea area. Ocean. Dev. Manag. 2021, 38, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Wedyan, M.A.; Ababneh, F.A.; Al−Rousan, S. The correlations between mercury speciation and dissolved organic matter in the sediment of the red sea. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 8, 403–411. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Liao, Y.; Shou, L. Concentration and potential health risk of heavy metals in seafoods collected from Sanmen Bay and its adjacent areas, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baki, M.A.; Hossain, M.M.; Akter, J. Concentration of heavy metals in seafood (fishes, shrimp, lobster and crabs) and human health assessment in Saint Martin Island, Bangladesh. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.X. Speciation of Cu and Zn in Two Colored Oyster Species Determined by X−ray Absorption Spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6919–6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, W.X. Differential influences of Cu and Zn chronic exposure on Cd and Hg bioaccumulation in an estuarine oyster. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 148, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhelyazkov, G.I.; Yankovska−Stefanova, T.; Mineva, E. Risk assessment of some heavy metals in mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) and veined rapa whelks (Rapana venosa) for human health. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 128, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Rainbow, P.S. Significance of metallothioneins in metal accumulation kinetics in marine animals. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 152, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.T.; Zhen, J.; Leng, J.Y. Zinc as a countermeasure for cadmium toxicity. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lischka, A.; Lacoue−Labarthe, T.; Bustamante, P.; Piatkowski, U.; Hoving, H. Trace element analysis reveals bioaccumulation in the squid Gonatus fabricii from polar regions of the Atlantic ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, Y. Determination of heavy metal concentrations in squid organs of the East China Sea and evaluation as environmental indicators. Tokyo Ocean. Univ. 2016, 4, 25–43. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.P.L.; Yan, S.; Bin, B.X. Heavy metal concentrations and associated health risks in edible tissues of marine nekton from the outer Pearl River Estuary, South China Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 2108–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.H.; Fang, Z.; Chen, X.J. Research progress of heavy metal bioaccumulation in marine invertebrates. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2021, 16, 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.W.; Xu, D.P.; Wang, Y.; Xu, P. Trophic relationships based on small−scale fisheries in the nearshore zone of Jinjiang, Yangtze River: δ13C and δ15N stable isotope analysis. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2017, 26, 2091–2098. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Pan, B.; Li, D.; Liu, X. Assessment of heavy metal accumulation in freshwater fish of dongting lake, china: Effects of feeding habits, habitat preferences and body size. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 112, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, K.; Consonni, V.; Durjava, M.K. Assessing bioaccumulation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers for aquatic species by QSAR modeling. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahayu, D.R.; Anggoro, S.; Soeprobowati, T.R. Metal Concentrations and Bio−Concentration Factor (BCF) in Surface Water and Economical Fish Species from Wadaslintang Multipurpose Dam, Wonosobo, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 593, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cao, L.; Dou, S. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and health risk assessment in three benthic bivalves along the coast of Laizhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gu, Y.; Wang, Z. Biological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments and health risk assessment in bivalve mollusks from Kaozhouyang Bay, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, H.; Baker, P.; Webster, G. An assessment of potential heavy metal contaminants in bivalve shellfish from aquaculture zones along the coast of New South Wales, Australia. Food Prot. Trend 2018, 38, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.Z. Studies on the feeding habits and trophic levels of four cephalopods in the Taiwan Province Strait and its adjacent waters. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2004, 23, 331–340. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.H.; Liu, S.D.; Zhang, Y.L. Habitat distribution characteristics of octopus ocellatus in Haizhou Bay in spring and its relationship with environmental factors. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 34, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Barath, R.; Kumar, K. Trace metal distribution in crab organs and human health risk assessment on consumption of crabs collected from coastal water of south east coast of india. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 141, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H. Gender and size effects of metal bioaccumulation on the rock crab, Thalamita crenata, in Dapeng Bay, southwestern Taiwan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuan, O.M.; Ali, N.M.; Shazili, N.M. Selected heavy metals concentration in edible tissue of the mud crab, Genus scylla from Setiu Wetlands, Terengganu. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 2017, 12, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.G.; Lin, Q.; Huang, H.H.; Wang, L.G.; Ning, J.J.; Du, F.Y. Heavy metals in fish tissues/stomach concentrations in four marine wild commercially valuable fish species from the western continental shelf of South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcarthur, J.V.; Tuckfield, R.C.; Fletcher, D.E. Effect of heavy metal pollution on the incidence of antibiotic resistance in Aeromonas hydrophila isolates obtained from the surface of fish. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 79, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Groups | Species |
|---|---|
| Fish | Konosirus punctatus |
| Trichiurus lepturus | |
| Lophius litulon | |
| Thamnaconus modestus | |
| Scomber japonicus | |
| Engraulis japonicus | |
| Jaydia lineata | |
| Larimichthys polyactis | |
| Conger myriaster | |
| Sebastes schlegelii | |
| Saurida elongata | |
| Lateolabrax japonicus | |
| Crustacean | Charybdis japonica |
| Oratosquilla oratoria | |
| Acetes chinensis | |
| Cephalopod | Octopus ocellatus |
| Loligo beka | |
| Sepiella maindroni | |
| Bivalvia | Pinna rudis |
| Scapharca subcrenata | |
| Ostrea denselamellosa | |
| Gastropoda | Neptunea cumingi |
| Rapana venosa | |
| Glossaulax didyma |
| Elements | Water (μg/L) | Sediment (mg/kg) | Organism (μg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| As | 0.09 | 2 | 0.005 |
| Cr | 0.05 | 0.4 | 0.018 |
| Cu | 0.08 | 0.6 | 0.025 |
| Hg | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Pb | 0.09 | 2 | 0.005 |
| Ni | 0.06 | 1 | 0.002 |
| Zn | 0.67 | 1 | 0.008 |
| Cu | Pb | Zn | Cr | As | Hg | Ni | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haizhou Bay | Range | 0–12.0 | 0–11.0 | 38.5–57.3 | 4.30–11.4 | 0–15.0 | 0.0268–0.10 | 0–3.0 | This study |
| Average | 6.50 | 6.36 | 54.1 | 8.70 | 6.27 | 0.044 | 2.70 | ||
| Bohai Bay | 2.90 | 0.40 | 10.1 | 1.97 | 3.88 | 0.63 | n.d. | [39] | |
| Changjiang Estuary | 2.30 | 0.91 | 19.0 | 1.30 | 1.0 | n.d. | n.d. | [40] | |
| Zhujiang Estuary | 1.95 | 0.55 | 14.8 | 2.29 | 1.99 | 0.044 | 2.44 | [41] | |
| Class I standard of seawater in China | 5 | 1 | 20 | 50 | 20 | 0.05 | — | ||
| Cu | Pb | Zn | Cr | As | Hg | Ni | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haizhou Bay | Range | 10.7–25.2 | 8.25–33.6 | 41.6–78.5 | 28.5–57.5 | 3.36–18.6 | 0.0022–0.0156 | 12.5–37.2 | This study |
| Average | 16.5 | 20.6 | 57.4 | 38.6 | 11.1 | 0.004 | 21.5 | ||
| Bohai Bay | 22.9 | 21.2 | 63.5 | 50.4 | 6.6 | 0.026 | n.d. | [51] | |
| Changjiang Estuary | 19.2 | 25.4 | 68.1 | 63.7 | 11.6 | n.d. | 36.7 | [52] | |
| Zhujiang Estuary | 61.1 | 46.2 | 157.7 | 21.7 | 22.1 | 0.104 | n.d. | [53] | |
| Class I standard for sediments in China | 35 | 60 | 150 | 80 | 20 | 0.2 | — | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Fu, K.; Gao, S.; Liang, B.; Lu, J.; Fu, G. Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in the Water, Sediment, and Organisms from The Sea Ranching Areas of Haizhou Bay in China. Water 2023, 15, 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122218
Zhang S, Fu K, Gao S, Liang B, Lu J, Fu G. Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in the Water, Sediment, and Organisms from The Sea Ranching Areas of Haizhou Bay in China. Water. 2023; 15(12):2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122218
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shuo, Kang Fu, Shike Gao, Baogui Liang, Jikun Lu, and Guanghui Fu. 2023. "Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in the Water, Sediment, and Organisms from The Sea Ranching Areas of Haizhou Bay in China" Water 15, no. 12: 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122218
APA StyleZhang, S., Fu, K., Gao, S., Liang, B., Lu, J., & Fu, G. (2023). Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in the Water, Sediment, and Organisms from The Sea Ranching Areas of Haizhou Bay in China. Water, 15(12), 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122218






