Development of a Simple Bioponic Method Using Manure and Offering Comparable Lettuce Yield than Hydroponics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment 1: Comparison of Nutrient Solutions Made from Chicken or Goat Manure and Mineral Fertilizers
2.1.1. Plant Material and Growing Conditions
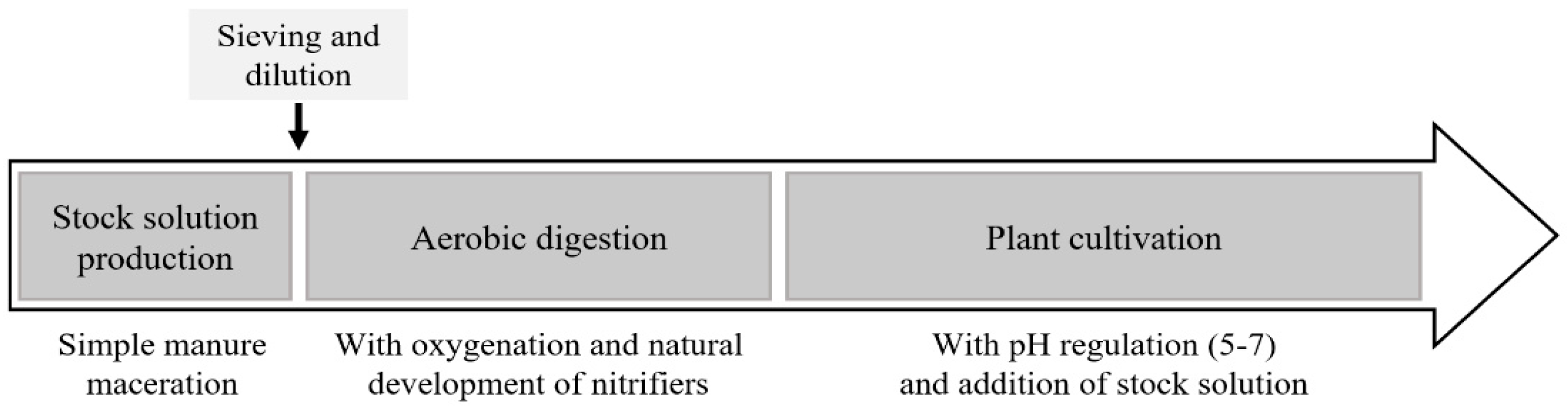
2.1.2. Production of Stock Solution from Chicken and Goat Manure
2.1.3. Aerobic Digestion within the Hydroponic Systems before Plant Cultivation—“Empty Circulation” Phase
2.1.4. Treatments and Experimental Setup
2.1.5. Measurements
2.1.6. Statistics and Treatment of Data
2.2. Experiment 2: Comparison of Different Stock Solution Concentrations for Aerobic Digestion to a Mineral Control Treatment
2.2.1. Plant Material and Growing Conditions
2.2.2. Stock Solution Production from Chicken Manure
2.2.3. Aerobic Digestion Phase within the Hydroponic Systems before Plant Cultivation
2.2.4. Treatments and Experimental Setup
2.2.5. Measurements
2.2.6. Statistical Analyses and Treatment of Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Production of Stock Solution via Simple Manure Maceration
3.2. Aerobic Digestion of the Organic Solutions with Respect to Physicochemical Parameters Dynamics
3.2.1. During the “Empty Circulation” Phase
3.2.2. During Plant Cultivation
3.3. Plant Growth and Shoot Mineral Content
4. General Discussion and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Resh, H.M. Hydroponic Food Production: A Definitive Guidebook for the Advanced Home Gardener and the Commercial Hydroponic Grower, 7th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, N.C.; Hasan, M.M.; Islam, M.R.; Banu, N.A. A Review on Present Status and Future Prospective of Hydroponics Technique. Plant Environ. Dev. 2016, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Gonnella, M.; Renna, M. The Evolution of Soilless Systems towards Ecological Sustainability in the Perspective of a Circular Economy. Is It Really the Opposite of Organic Agriculture? Agronomy 2021, 11, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez-Gonzalez, R.S.; Garcia-Garcia, A.L.; Ventura-Zapata, E.; Barceinas-Sanchez, J.D.O.; Sosa-Savedra, J.C. A Review on Hydroponics and the Technologies Associated for Medium-and Small-Scale Operations. Agriculture 2022, 12, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambo, P.; Nicoletto, C.; Giro, A.; Pii, Y.; Valentinuzzi, F.; Mimmo, T.; Lugli, P.; Orzes, G.; Mazzetto, F.; Astolfi, S.; et al. Hydroponic Solutions for Soilless Production Systems: Issues and Opportunities in a Smart Agriculture Perspective. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumisiriza, M.S.; Kabirizi, J.M.L.; Mugerwa, M.; Ndakidemi, P.A.; Mbega, E.R. Can Soilless Farming Feed Urban East Africa? An Assessment of the Benefits and Challenges of Hydroponics in Uganda and Tanzania. Environ. Chall. 2022, 6, 100413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogato, A.; Meggio, F.; Migliorati, M.D.A.; Marinello, F. Extreme Weather Events in Agriculture: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basosi, R.; Spinelli, D.; Fierro, A.; Jez, S. Mineral Nitrogen Fertilizers: Environmental Impact of Production and Use; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Cordell, D.; Drangert, J.O.; White, S. The Story of Phosphorus: Global Food Security and Food for Thought. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2009, 19, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, M.C.; Verdejo, M.M.; Sánchez, A.; Guzmán, M.; Valenzuela, J.L.; Montero, J.L. Vertical Gardening. Adaptation of Hydroponic Systems and Ornamental Species. Acta Hortic. 2012, 937, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianu, J.N.; Chianu, J.N.; Mairura, F. Mineral Fertilizers in the Farming Systems of Sub-Saharan Africa. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 545–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, M.; Aoyama, C.; Fujiwara, K.; Watanabe, A.; Ohmori, H.; Uehara, Y.; Takano, M. Microbial Mineralization of Organic Nitrogen into Nitrate to Allow the Use of Organic Fertilizer in Hydroponics. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2011, 57, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, A.; Fernández, J.A.; Pascual, J.A.; Ros, M.; Egea-Gilabert, C. Application of Directly Brewed Compost Extract Improves Yield and Quality in Baby Leaf Lettuce Grown Hydroponically. Agronomy 2020, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shinawy, M.Z.; Abd-Elmoniem, E.M.; Abou-Hadid, A.F. The Use of Organic Manure for Lettuce Plants Grown under Nft Conditions. Acta Hortic. 1999, 491, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Du, L.; Yang, Q. Biogas Slurry Added Amino Acids Decreased Nitrate Concentrations of Lettuce in Sand Culture. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2009, 59, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrand, K.-J.; Asp, H.; Hultberg, M. Utilizing Anaerobic Digestates as Nutrient Solutions in Hydroponic Production Systems. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelayo Lind, O.; Hultberg, M.; Bergstrand, K.J.; Larsson-Jönsson, H.; Caspersen, S.; Asp, H. Biogas Digestate in Vegetable Hydroponic Production: PH Dynamics and PH Management by Controlled Nitrification. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, E.; Cao, L.; Xiang, S.; Zhou, W.; Ruan, R.; Liu, Y. Feasibility of Using Pretreated Swine Wastewater for Production of Water Spinach (Ipomoea aquatic Forsk.) in a Hydroponic System. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 228, 105856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkiew, S.; Hu, Z.; Lee, J.W.; Chandran, K.; Nhan, H.T.; Marcelino, K.R.; Khanal, S.K. Nitrogen Recovery via Aquaponics–Bioponics: Engineering Considerations and Perspectives. ACS ES T Eng. 2021, 1, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikasz, P.; MacPherson, S.; Adamchuk, V.; Lefsrud, M. Aerated Chicken, Cow, and Turkey Manure Extracts Differentially Affect Lettuce and Kale Yield in Hydroponics. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2019, 8, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkin, K.; Nichols, M.A. Organic Hydroponics. Acta Hortic. 2004, 648, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowa, E. Organic Manure for Vegetable Production under Hydroponic Conditions in Arid Namibia. Int. Sci. Technol. J. Namibia 2015, 5, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wongkiew, S.; Koottatep, T.; Polprasert, C.; Prombutara, P.; Jinsart, W.; Khanal, S.K. Bioponic System for Nitrogen and Phosphorus Recovery from Chicken Manure: Evaluation of Manure Loading and Microbial Communities. Waste Manag. 2021, 125, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liedl, B.E.; Bombardiere, J.; Chatfield, J.M. Fertilizer Potential of Liquid and Solid Effluent from Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Poultry Waste. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancon, N.Q.; Pant, A.; Radovich, T.; Hue, N.V.; Potter, J.K.; Converse, C.E. Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Tomato and Lettuce as Affected by Vermicompost Water Extracts (Teas). HortScience 2012, 47, 1722–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leudtke, B. Use of Compost Tea as a Nutrient Amendment for Plant Growth in a Re-Circulating Hydroponic System; University of Wisconsin System: Madison, WI, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura-Aoyama, C.; Fujiwara, K.; Shinohara, M.; Takano, M. Study on the Hydroponic Culture of Lettuce with Microbially Degraded Solid Food Waste as a Nitrate Source. Japan Agric. Res. Q. 2014, 48, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnasamy, K.; Nair, J.; Bäuml, B. Hydroponic System for the Treatment of Anaerobic Liquid. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phibunwatthanawong, T.; Riddech, N. Liquid Organic Fertilizer Production for Growing Vegetables under Hydroponic Condition. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2019, 8, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekely, I.; Jijakli, M.H. Bioponics as a Promising Approach to Sustainable Agriculture: A Review of the Main Methods for Producing Organic Nutrient Solution for Hydroponics. Water 2022, 14, 3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaji, H.; Chandran, V.; Mathew, L. Organic Fertilizers as a Route to Controlled Release of Nutrients. In Controlled Release Fertilizers for Sustainable Agriculture; Lewu, F.B., Volova, T., Thomas, S., Rakhimol, K.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.W. Fertilizers in Aquaculture. In Feed and Feeding Practice in Aquaculture; Woodhead Publishing: Sawsto, UK, 2015; pp. 27–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghball, B.; Wienhold, B.J.; Gilley, J.E.; Eigenberg, R.A. Mineralization of Manure Nutrients. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2002, 57, 470–473. [Google Scholar]
- Goss, M.J.; Tubeileh, A.; Goorahoo, D. A Review of the Use of Organic Amendments and the Risk to Human Health. Adv. Agron. 2013, 120, 275–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenpakdee, S. Using Animal Manure to Grow Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) in a Homemade Hydroponics System. Asia-Pac. J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 19, 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Ingham, E.R. The Compost Tea Brewing Manual, 5th ed.; Soil Foodweb Institute: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shaban, H.; Fazeli-Nasab, B.; Alahyari, H.; Alizadeh, G.; Shahpesandi, S. An Overview of the Benefits of Compost Tea on Plant and Soil Structure. Adv. Biores. 2015, 6, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Garland, J.L.; Mackowiak, C.L. Utilization of the Water Soluble Fraction of Wheat Straw as a Plant Nutrient Source. NASA Tech. Memo. 1990, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Garland, J.L.; Mackowiak, C.L.; Sager, J.C. Hydroponic Crop Production Using Recycled Nutrients from Inedible Crop Residues. SAE Tech. Pap. 1993, 102, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackowiak, C.L.; Garland, J.L.; Strayer, R.F.; Finger, B.W.; Wheeler, R.M. Comparison of Aerobically-Treated and Untreated Crop Residue as a Source of Recycled Nutrients in a Recirculating Hydroponic System. Adv. Space Res. 1996, 18, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, B.W.; Strayer, R.F. Development of an Intermediate-Scale Aerobic Bioreactor to Regenerate Nutrients from Inedible Crop Residues. SAE Tech. Pap. 1994, 103, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedl, B.E.; Cummins, M.; Young, A.; Williams, M.L.; Chatfield, J.M. Hydroponic Lettuce Production Using Liquid Effluent from Poultry Waste Bioremediation as a Nutrient Source. Acta Hortic. 2004, 659, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronga, D.; Setti, L.; Salvarani, C.; De Leo, R.; Bedin, E.; Pulvirenti, A.; Milc, J.; Pecchioni, N.; Francia, E. Effects of Solid and Liquid Digestate for Hydroponic Baby Leaf Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) Cultivation. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 244, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mupambwa, H.A.; Namwoonde, A.S.; Liswaniso, G.M.; Hausiku, M.K.; Ravindran, B. Biogas Digestates Are Not an Effective Nutrient Solution for Hydroponic Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) Production under a Deep Water Culture System. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Müller, T. Effects of Anaerobic Digestion on Digestate Nutrient Availability and Crop Growth: A Review. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkoa, R. Agricultural Benefits and Environmental Risks of Soil Fertilization with Anaerobic Digestates: A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 473–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, R.R.; Brady, N.C. The Nature and Properties of Soils, 15th ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, R.; Ariz, I.; Cruz, C.; Moran, J.F. Review: Mechanisms of Ammonium Toxicity and the Quest for Tolerance. Plant Sci. 2016, 248, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britto, D.T.; Kronzucker, H.J. NH4+ Toxicity in Higher Plants: A Critical Review. J. Plant Physiol. 2002, 159, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, F. Effect of Ammonium and Nitrate Nutrition on Some Physiological Processes in Higher Plants—Growth, Photosynthesis, Photorespiration, and Water Relations. Plant Biol. 2007, 9, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Lv, J.; Dawuda, M.M.; Xie, J.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, C.; Wang, C.; Gan, Y. Appropriate Ammonium-Nitrate Ratio Improves Nutrient Accumulation and Fruit Quality in Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Agronomy 2019, 9, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Yu, J.; Liao, W.; Zhang, G.; Xie, J.; Lv, J.; Xiao, X.; Yang, B.; Zhou, R.; Bu, R. Moderate Ammonium:Nitrate Alleviates Low Light Intensity Stress in Mini Chinese Cabbage Seedling by Regulating Root Architecture and Photosynthesis. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 186, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, S.; Fatemi, L.; Fallahi, E. Effect of Ammonium: Nitrate Ratio on Yield, Calcium Concentration, and Photosynthesis Rate in Strawberry. J. Plant Nutr. 2007, 29, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Du, Q.; Li, J. Interactive Effects of Nitrate-Ammonium Ratios and Temperatures on Growth, Photosynthesis, and Nitrogen Metabolism of Tomato Seedlings. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 214, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinčič, A.; Mahne, I.; Megušar, F.; Paul, E.A.; Tiedje, J.M. Effects of PH and Oxygen and Ammonium Concentrations on the Community Structure of Nitrifying Bacteria from Wastewater. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochmah, W.N.; Mangkoedihardjo, S. Toxicity Effects of Organic Substances on Nitrification Efficiency. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 506, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.H.; Kim, J.O.; Kang, S.; Park, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.M. Achieving Enhanced Nitrification in Communities of Nitrifying Bacteria in Full-Scale Wastewater Treatment Plants via Optimal Temperature and PH. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 132, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanakis, A.; Akratos, C.S.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Treatment Processes in VFCWs. In Vertical Flow Constructed Wetland; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 57–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottet, A.; Tempio, G. Global Poultry Production: Current State and Future Outlook and Challenges. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2017, 73, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinmoladun, O.F.; Muchenje, V.; Fon, F.N.; Mpendulo, C.T. Small Ruminants: Farmers’ Hope in a World Threatened by Water Scarcity. Animals 2019, 9, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skapetas, B.; Bampidis, V. Goat Production in the World: Present Situation and Trends. Livest. Res. Rural Dev. 2016, 28, 200. [Google Scholar]
- Kondaveeti, S.; Choi, D.-H.; Noori, M.T.; Min, B. Ammonia Removal by Simultaneous Nitrification and Denitrification in a Single Dual-Chamber Microbial Electrolysis Cell. Energies 2022, 15, 9171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 17025; General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories. International Organization for Standardization: Vernier, Switzerland, 2017.
- NF EN 12014-7; Foodstuffs—Determination of Nitrate and/or Nitrite Content—Continuous Flow Method for the Determination of Nitrate Content of Vegetables and Vegetable Products after Cadmium Reduction. AFNOR Editions: La Plaine Saint-Denis, France, 1998.
- NF EN 15510; Animal Feeding Stuffs—Determination of Calcium, Sodium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Potassium, Iron, Zinc, Copper, Manganese, Cobalt, Molybdenum, Arsenic, Lead and Cadmium by ICP-AES. AFNOR Editions: La Plaine Saint-Denis, France, 2007.
- NF 1899-1; Qualité de l’eau—Détermination de la Demande Biochimique en Oxygène Après n Jours (DBOn)—Partie 1: Méthode par Dilution et Ensemencement Avec Apport d’allylthio-urée. AFNOR Editions: La Plaine Saint-Denis, France, 1998.
- NF EN ISO 6878; Water Quality—Determination of Phosphorus—Ammonium Molybdate Spectrometric Method. AFNOR Editions: La Plaine Saint-Denis, France, 2005.
- NF EN ISO 11885; Water Quality—Determination of Selected Elements by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES). International Organization for Standardization: Vernier, Switzerland, 2009.
- Bozorg-Haddad, O.; Delpasand, M.; Loáiciga, H.A. Water Quality, Hygiene, and Health. In Economical, Political, and Social Issues in Water Resources; Bozorg-Haddad, O., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 217–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NF EN ISO 16634-1; Food Products—Determination of the Total Nitrogen Content by Combustion According to the Dumas Principle and Calculation of the Crude Protein Content—Part 1: Oilseeds and Animal Feeding Stuffs. International Organization for Standardization: Vernier, Switzerland, 2008.
- Delaide, B.; Monsees, H.; Gross, A.; Goddek, S. Aerobic and Anaerobic Treatments for Aquaponic Sludge Reduction and Mineralisation. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems; Goddek, S., Joyce, A., Kotzen, B., Burnell, G.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburquerque, J.A.; de la Fuente, C.; Bernal, M.P. Chemical Properties of Anaerobic Digestates Affecting C and N Dynamics in Amended Soils. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 160, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigobelo, E.; Serra, A. Organic Nitrogen in Agricultural Systems. In Nitrogen Fixation; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerozi, B.d.S.; Fitzsimmons, K. The Effect of PH on Phosphorus Availability and Speciation in an Aquaponics Nutrient Solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddek, S.; Delaide, B.P.L.; Joyce, A.; Wuertz, S.; Jijakli, M.H.; Gross, A.; Eding, E.H.; Bläser, I.; Reuter, M.; Keizer, L.C.P.; et al. Nutrient Mineralization and Organic Matter Reduction Performance of RAS-Based Sludge in Sequential UASB-EGSB Reactors. Aquac. Eng. 2018, 83, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, J.; Couturier, M. Dissolution of Minerals during Hydrolysis of Fish Waste Solids. Aquaculture 2010, 298, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Patrick, W.H.; Broadbent, F.E. Nitrogen Transformations and Loss in Flooded Soils and Sediments. Crit. Rev. Environ. Control 1984, 13, 273–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehar, S.; Naz, I. Role of the Biofilms in Wastewater Treatment. In Microbial Biofilms—Importance and Applications; Dhanasekaran, D., Thajuddin, N., Eds.; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2016; pp. 121–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpongwana, N.; Rathilal, S. Exploiting Biofilm Characteristics to Enhance Biological Nutrient Removal in Wastewater Treatment Plants. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-C.; Shang, C. Air Stripping. In Advanced Physicochemical Treatment Processes; Wang, L.K., Hung, Y.-T., Shammas, N.K., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 4, pp. 47–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.B. Complete Guide for Growing Plants Hydroponically, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea-Cox, J.D.; Berry, W.L.; Stutte, G.W.; Wheeler, R.M. Nutrient Dynamics and PH/Charge-Balance Relationships in Hydroponic Solutions. Acta Hortic. 1999, 481, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, K.; Aoyama, C.; Takano, M.; Shinohara, M. Suppression of Ralstonia Solanacearum Bacterial Wilt Disease by an Organic Hydroponic System. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2012, 78, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, K.; Kitazawa, H.; Suzuki, K.; Widiastuti, A.; Odani, H.; Zhou, S.; Chinta, Y.D.; Eguchi, Y.; Shinohara, M.; Sato, T. Effects of Organic Fertilizer on Bok Choy Growth and Quality in Hydroponic Cultures. Agronomy 2021, 11, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancon, N.Q.; Owens, J.D.; Converse, C. The Effects of Vermicompost Tea on the Growth and Yield of Lettuce and Tomato in a Non-Circulating Hydroponics System. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 2447–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, M.; Razack Sare, A.; Massart, S.; Schmautz, Z.; Junge, R.; Smits, T.H.M.; Haïssam Jijakli, M. Exploring Bacterial Communities in Aquaponic Systems. Water 2019, 11, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stouvenakers, G.; Dapprich, P.; Massart, S.; Jijakli, M.H. Plant Pathogens and Control Strategies in Aquaponics. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 353–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartz, T.K.; Johnstone, P.R.; Williams, E.; Smith, R.F. Establishing Lettuce Leaf Nutrient Optimum Ranges through DRIS Analysis. HortScience 2007, 42, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Mukherjee, A.B. Trace Elements from Soil to Human; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savvas, D.; Passam, H.C.; Olympios, C.; Nasi, E.; Moustaka, E.; Mantzos, N.; Barouchas, P. Effects of Ammonium Nitrogen on Lettuce Grown on Pumice in a Closed Hydroponic System. HortScience 2006, 41, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmelak Gorenjak, A.; Cencič, A. Nitrate in Vegetables and Their Impact on Human Health. A Review. Acta Aliment. 2013, 42, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.; Nelson, J.S. Challenges of using organic fertilizers in hydroponic production systems. Acta Hortic. 2016, 1112, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

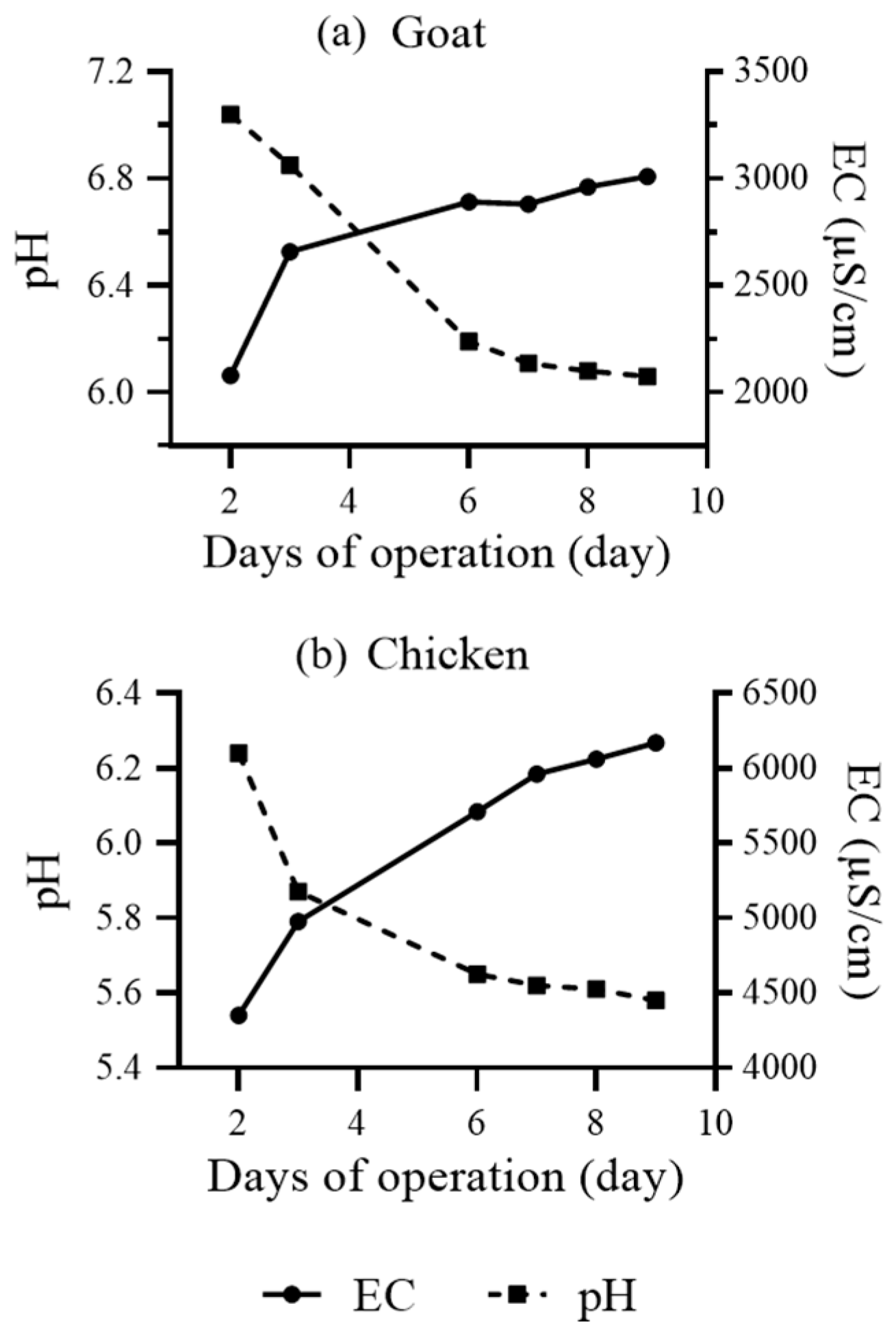
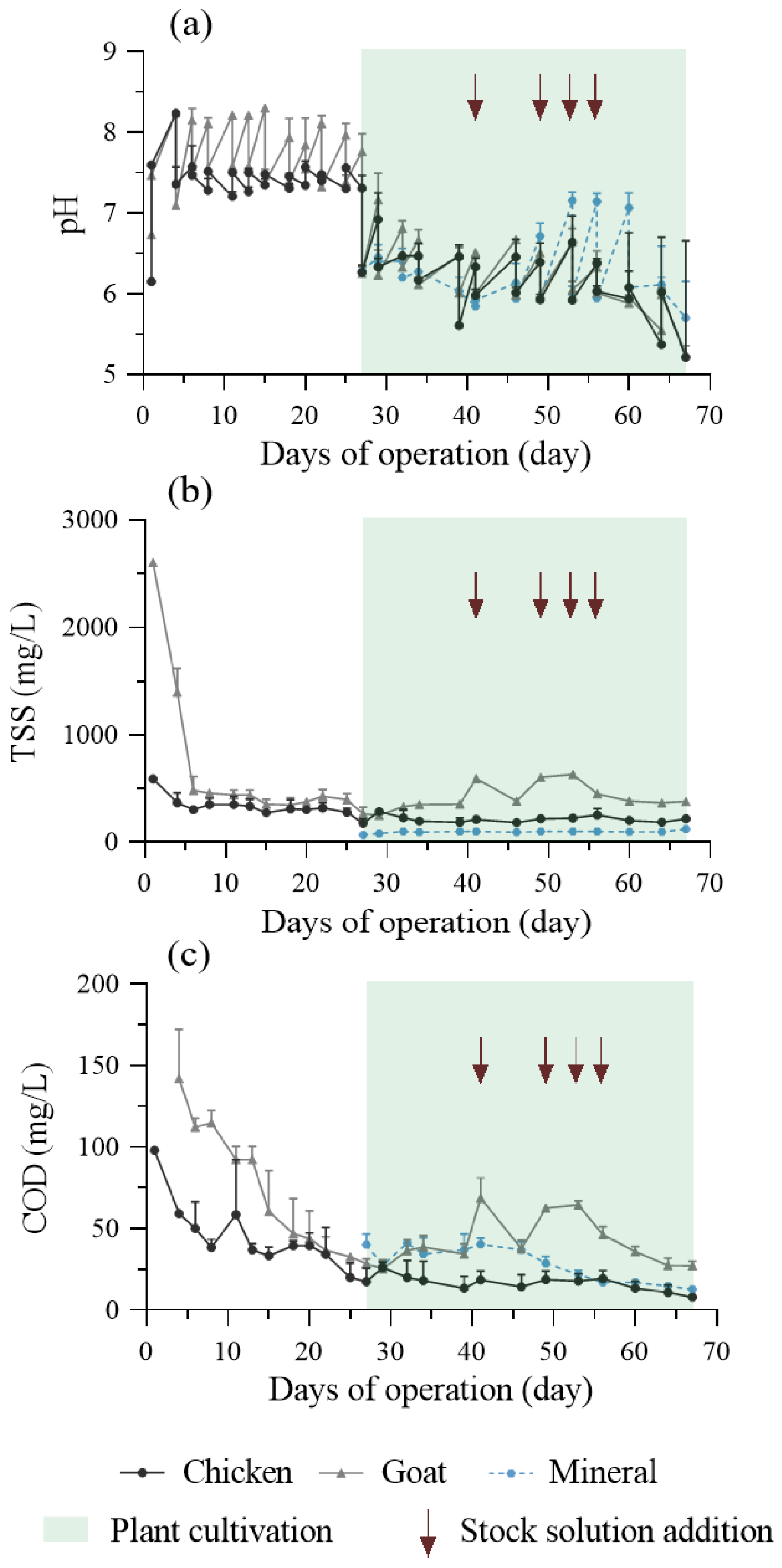


| Parameter | Chicken Manure-Based | Goat Manure-Based | Mineral Control Treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stock Solution | Solution before Aerobic Digestion | Solution after Aerobic Digestion | Stock Solution | Solution before Aerobic Digestion | Solution after Aerobic Digestion | ||
| pH | 5.6 | 6.2 | 7.3 ± 0.2 | 6.1 | 6.7 | 7.8 ± 0.2 | 6.3 |
| EC | 6170.0 | 937.3 | 613.7 ± 175.6 | 3010 | 1079.7 | 1019.3 ± 56.1 | 1301.0 |
| COD | n.a. 1 | 98.1 | 20.1 ± 8.9 | n.a. | n.a. | 32.6 ± 0.5 | 40.1 |
| TSS | n.a. | 590.3 | 277.4 ± 38.8 | n.a. | 2602.8 | 395.2 ± 56.3 | 69.0 |
| TAN | 415.0 | 63.2 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 65.0 | 31.3 | 1.6 ± 0.2 | 9.3 |
| N–NO3− | 0.0 | 0.0 | 44.2 ± 16.5 | 61.0 | 26.5 | 25.3 ± 9.8 | 111.9 |
| N–NO2− | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 ± 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.0 |
| TMN | 415.0 | 63.2 | 45.1 ± 16.1 | 126.0 | 57.8 | 27.0 ± 9.9 | 121.2 |
| P-PO43− | 170.0 | 24.5 | 18.9 ± 7.8 | 25.0 | 12.0 | 16.3 ± 3.8 | 44.0 |
| K | 550.0 | 79.4 | 75.8 ± 40.6 | 350.0 | 168.4 | 83.3 ± 5.8 | 186.7 |
| Parameter | Stock Solution | N60 | N80 | N100 | N120 | Mineral Control Treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solution before Aerobic Digestion | Solution after Aerobic Digestion | Solution before Aerobic Digestion | Solution after Aerobic Digestion | Solution before Aerobic Digestion | Solution after Aerobic Digestion | Solution before Aerobic Digestion | Solution after Aerobic Digestion | |||
| pH | 5.8 | 6.3 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.5 | 6.1 ± 0.0 | 6.1 | 6.1 ± 0.1 | 6.2 | 6.1 ± 0.0 | 6.2 |
| EC | 15,150.0 | 715.0 | 475.7 ± 48.6 | 953.3 | 528.0 ± 31.2 | 1190.0 | 671.7 ± 25.7 | 1424.3 | 755.0 ± 41.7 | 1302.3 |
| BOD5 | n.d. 1 | 610.0 | <2.0 | 773.0 | <2.0 | 983.0 | <2.0 | 1000.0 | <2.0 | 5.0 |
| COD | n.d. | 1280.0 | 71.7 ± 10.6 | 1822.0 | 86.0 ± 6.2 | 2312.0 | 117.3 ± 23.5 | 2896.0 | 133.7 ± 21.6 | 48.1 |
| TSS | n.d. | 962.4 | 245.8 ± 19.7 | 1348.4 | 245.5 ± 11.6 | 1608.3 | 292.0 ± 18.9 | 1920.0 | 319.0 ± 51.1 | 178.9 |
| DO | n.d. | n.d. | 8.0 ± 0.1 | n.d. | 8.0 ± 0.0 | n.d. | 7.7 ± 0.2 | n.d. | 7.7 ± 0.2 | 7.5 |
| TAN | 1590.0 | 53.1 | 0.1 ± 0 | 70.7 | 0.1 ± 0 | 92.6 | 0.1 ± 0 | 115.8 | 0.1 ± 0 | 9.9 |
| N–NO3− | 100.0 | 4.0 | 36.4 ± 13.5 | 5.0 | 32.3 ± 5.9 | 5.5 | 28.3 ± 9.2 | 7.0 | 25.1 ± 6.2 | 118.0 |
| N–NO2− | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0 | 0.1 | 0.0 ± 0 | 0.1 | 8.6 ± 14.8 | 0.1 | 17.2 ± 16.1 | 0.0 |
| TMN | 1690.0 | 57.2 | 36.5 ± 13.5 | 75.7 | 32.4 ± 5.9 | 98.2 | 37.0 ± 6.1 | 122.9 | 42.4 ± 10.5 | 127.9 |
| P | n.d. | 27.2 | 20.3 ± 1.0 | 37.2 | 23.3 ± 3.4 | 43.4 | 31.1 ± 1.7 | 48.0 | 33.9 ± 1.3 | 46.6 |
| K | n.d. | 65.8 | 58.2 ± 1.2 | 86.3 | 71.1 ± 5.6 | 99.4 | 93.8 ± 3.0 | 132.5 | 111.4 ± 4.2 | 202.8 |
| Ca | n.d. | 22.8 | 38.1 ± 8.2 | 30.2 | 38.9 ± 1.3 | 33.7 | 44.7 ± 1.8 | 41.3 | 47.3 ± 3.5 | 86.1 |
| Mg | n.d. | 12.6 | 11.6 ± 0.3 | 17.1 | 13.9 ± 1.1 | 20.7 | 18.3 ± 0.9 | 25.6 | 21.0 ± 0.9 | 34.2 |
| Experiment | Treatment | Fresh Weight (g/Lettuce) | Dry Weight (g/Lettuce) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment 1 | Mineral | 137.3 ± 25.0 a | 5.4 ± 1 a |
| Chicken | 91.6 ± 27.5 b | 4.0 ± 0.8 b | |
| Goat | 69.6 ± 23.2 b | 3.5 ± 0.7 b | |
| Experiment 2 | Mineral | 135.5 ± 18.0 a | 5.5 ± 0.8 a |
| N60 | 123.2 ± 23.7 a | 5.3 ± 0.8 a | |
| N80 | 121.4 ± 14.8 a | 5.1 ± 0.4 a | |
| N100 | 127.1 ± 15.3 a | 5.2 ± 0.6 a | |
| N120 | 131.3 ± 15.3 a | 4.6 ± 0.4 a |
| Nutrient | Experiment 1 | Experiment 2 | Normal Ranges in Healthy Plants 1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral | Chicken | Goat | Mineral | N60 | N80 | N100 | N120 | ||
| P | 7.4 ± 0.4 a | 6.4 ± 0.5 a | 7.1 ± 0.8 a | 8.4 ± 0.8 a | 6.5 ± 0.9 b | 7.4 ± 0.2 ab | 7.8 ± 0.5 ab | 7.7 ± 0.5 ab | 3.5–13.0 |
| N | n.d. 2 | n.d. | n.d. | 34.7 ± 5.7 a | 30.0 ± 1.9 a | 29.9 ± 3.4 a | 26.6 ± 0.4 a | 29.4 ± 1.0 a | 30.0–60.0 |
| Ca | 12.9 ± 0.5 a | 20.6 ± 7.7 a | 13.0 ± 1.3 a | 11.9 ± 1.0 b | 19.6 ± 3.8 a | 12.9 ± 1.8 ab | 13.2 ± 1.3 ab | 13.7 ± 4.0 ab | 6.0–21.0 |
| Mg | 4.4 ± 0.4 a | 4.7 ± 0.7 a | 3.1 ± 0.3 b | 3.4 ± 0.8 b | 5.4 ± 0.2 a | 3.8 ± 0.2 b | 3.9 ± 0.6 b | 3.9 ± 1.1 b | 2.5–9.0 |
| K | 65.2 ± 5.2 a | 37.8 ± 6.0 b | 55.7 ± 7.1 a | 84.2 ± 6.8 a | 44.3 ± 9.2 c | 47.7 ± 5.6 bc | 55.8 ± 3.1 bc | 70.7 ±16.1 ab | 29.0–108.0 |
| NO3− | 1.1 ± 0.2 a | 0.8 ± 0.3 ab | 0.5 ± 0.1 b | 1.2 ± 0.4 a | 0.7 ± 0.1 b | 0.6 ± 0.1 b | 0.5 ± 0.1 b | 0.6 ± 0.0 b | n.a. 3 |
| Fe | 144 ± 11 a | 126 ± 11 ab | 92 ± 26 b | 96 ± 16 a | 64 ± 12 a | 73 ± 16 a | 74 ± 7 a | 114 ± 35 a | 100–600 |
| Mn | 27 ± 6 b | 135 ± 28 b | 418 ± 114 a | 19 ± 4 b | 122 ± 4 ab | 121 ± 88 ab | 236 ± 60 ab | 324 ± 195 a | 20–500 |
| Cu | 3 ± 1 b | 6 ± 0 a | 5 ± 1 a | 2 ± 0 c | 8 ± 1 b | 10 ± 1 ab | 11 ± 1 ab | 12 ± 2 a | 5–17 |
| Zn | 40 ± 11 b | 152 ± 27 a | 102 ± 19 a | 98 ± 82 a | 209 ± 35 a | 182 ± 59 a | 219 ± 38 a | 254 ± 66 a | 25–300 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szekely, I.; Zeaiter, Z.; Jijakli, M.H. Development of a Simple Bioponic Method Using Manure and Offering Comparable Lettuce Yield than Hydroponics. Water 2023, 15, 2335. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132335
Szekely I, Zeaiter Z, Jijakli MH. Development of a Simple Bioponic Method Using Manure and Offering Comparable Lettuce Yield than Hydroponics. Water. 2023; 15(13):2335. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132335
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzekely, Iris, Ziad Zeaiter, and M. Haissam Jijakli. 2023. "Development of a Simple Bioponic Method Using Manure and Offering Comparable Lettuce Yield than Hydroponics" Water 15, no. 13: 2335. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132335
APA StyleSzekely, I., Zeaiter, Z., & Jijakli, M. H. (2023). Development of a Simple Bioponic Method Using Manure and Offering Comparable Lettuce Yield than Hydroponics. Water, 15(13), 2335. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132335







