Evaluation of Groundwater Quality and Suitability for Irrigation Purposes and Human Consumption in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Geological Setting
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Groundwater Quality Characterization
2.3.1. Sodium-Adsorption Ratio
2.3.2. Residual Sodium Carbonate (RSC)
2.3.3. Sodium Percentage (Na%)
2.3.4. Permeability Index (PI)
2.3.5. Magnesium Hazard (MH)
2.3.6. Kelly’s Ratio (KR)
2.3.7. Corrosivity Ratio (CR)
3. Results and Discussion
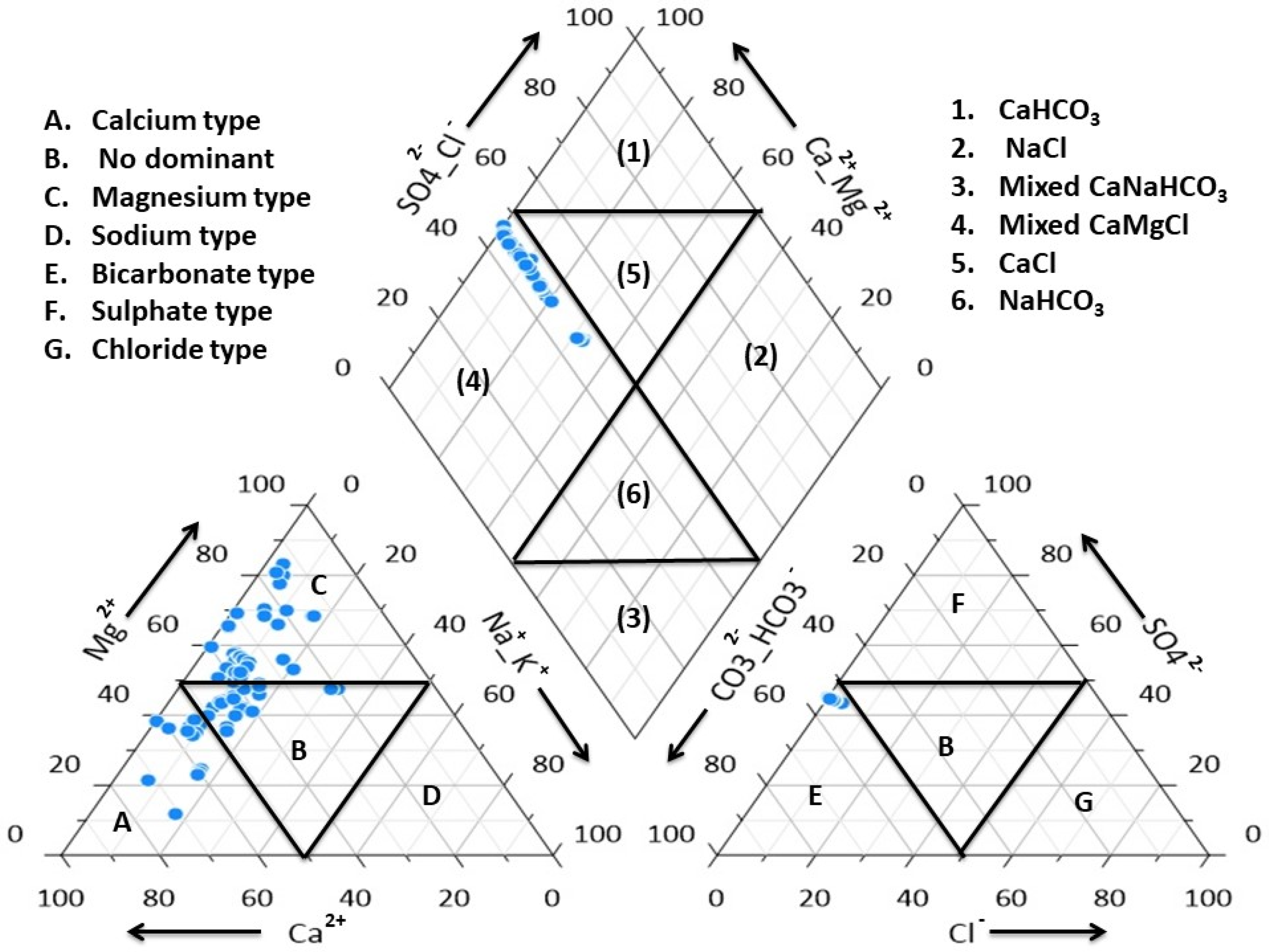
3.1. Hydrochemical Characterization
3.2. Characterization of Groundwater Chemistry
3.3. Assessment of Groundwater Quality
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saud, A.G.; Abdullah, S.A. Water Resources and Reuse in Al-Madinah. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Water Conservation in Arid Regions (ICWCAR’09), Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 12–14 October 2009; Organized by Water Research Center, King Abdulaziz University: Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 2009; pp. 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- Dirican, S. Assessment of water quality using physicochemical parameters of Camligoze Dam Lake in Sivas, Turkey. Ecologia 2015, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouslah, S.; Djemili, L.; Houichi, L. Water quality index assessment of Koudiat Medouar reservoir, northeast Algeria using weighted arithmetic index method. J. Water Land Dev. 2017, 35, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Husain, T.; Lumb, A. Water quality evaluation and trend analysis in selected watersheds of the Atlantic region of Canada. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2003, 88, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Shahnaz, M.; Jehan, N.; Rehman, S.; Shah, M.T.; Din, I. Drinking water quality and human health risk in Charsadda district, Pakistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 60, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chengcheng, X.; Guodong, L.; Hongye, X.; Fangting, J.; Yuchuan, M. Influence of saline intrusion on the wetland ecosystem revealed by isotopic and hydrochemical indicators in the Yellow River Delta, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108422. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, P.; Xue, L.; Dong, Z.; Li, D. Solute geochemistry and groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes: A case study in Xinle City, North China. Geochemistry 2020, 80, 125609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.Y.; Qian, H.; Wu, J.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.B. Major Ion Chemistry of Shallow Groundwater in the Dongsheng Coalfifield, Ordos Basin, China. Mine Water Environ. 2013, 32, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.K.; Vaid, U. Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes using hydrochemical studies in Nalbari district of Assam, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, S.F.; Hassani, A.H.; Torabian, A.; Karbassi, A.R.; Hosseinzadeh, L.F. Water quality index development using fuzzy logic: A case study of the Karoon river of Iran. Afr. J. Biotech. 2011, 10, 10125–10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.L.; Gui, H.R.; Fang, P.; Li, G.P. Hydrogeochemistry and Quality Assessment of Groundwater Based on Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchy Process: A Case Study from Sulin Coal-Mining District in Northern Anhui, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 3203–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ibrahim, A. Excessive use of groundwater resources in Saudi Arabia: Impacts and policy options. R. Swedish Acad. Sci. 1991, 20, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Fallatah, O.A.; Ahmed, M.; Cardace, D.; Boving, T.; Akanda, A.S. Assessment of modern recharge to arid region aquifers using an integrated geophysical, geochemical, and remote sensing approach. J. Hydrol. 2018, 569, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouadri, S.; Pande, C.B.; Panneerselvam, B.; Moharir, K.N.; Elbeltagi, A. Prediction of irrigation groundwater quality parameters using ANN, LSTM, and MLR models. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 21067–21091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebi, P.; Mahmudy-Gharaie, M.H.; Ghassemzadeh, F.; Karouyeh, A.K. Assessment of groundwater suitability for irrigation in a gold mine surrounding area, NE Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S. An assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation and drinking purposes around brick kilns in three districts of Balochistan province, Pakistan, through water quality index and multivariate statistical approaches. J. Geo-Chem. Explor. 2019, 197, 14–26. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, A.; Shetty, B.K.; Guddattu, V.; Chourasia, M.K.; Pundir, P. High prevalence of dental fluorosis among adolescents is a growing concern: A school based cross-sectional study from Southern India. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2017, 22, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keesari, T.; Ramakumar, K.L.; Chidambaram, S.; Pethperumal, S.; Thil-agavathi, R. Understanding the hydrochemical behavior of groundwater and its suitability for drinking and agricultural purposes in Pondicherry. South India-a step towards sustainable development. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 2, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Gupta, I.C. Management of Saline Soils and Waters; Oxford & IBH Pub. Co.: New Delhi, India, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Kopittke, P.M.; So, H.B.; Menzies, N.W. Effect of ionic strength and clay mineralogy on Na-Ca exchange and the SAR-ESP relationship. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 57, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falowo, O.O.; Akindureni, Y.; Ojo, O. Irrigation and drinking water quality index determination for groundwater quality evaluation in Akoko Northwest and Northeast Areas of Ondo State, Southwestern Nigeria. Am. J. Water Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdulhussein, F.M. Hydrochemical assessment of groundwater of Dibdibba Aquifer in Al-Zubair Area, Basra, south of Iraq and its suitability for irrigation purposes. Iraqi J. Sci. 2018, 59, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, C.M.; Huang, Y.; Ma, D.J.; Fan, X. Hydro-geochemistry evolution in Ordovician limestone water induced by mountainous coal mining: A case study from North China. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, B.K. Description and classification of media for hydrogeochemical investigations. In Symposium on Ground-Water Studies in Arid and Semiarid Regions; Roorkee, India, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Selvakumar, S.; Ramkumar, K.; Chandrasekar, N.; Magesh, N.S.; Kaliraj, S. Groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and irrigational use in the Southern Tiruchirappalli district, Tamil Nadu, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer, G.N.; McCarthy, D.L. Chemistry of Sanitary Engineers, 2nd ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1967; p. 518. [Google Scholar]
- Shiyang, Y.; Yong, X.; Pengli, H.; Qichen, H.; Xiaomin, G.; Baohui, M.; Linxian, H. Investigation of groundwater contamination and health implications in a typical semiarid basin of North China. Water 2020, 12, 1137. [Google Scholar]
- Kadri, A.; Baouia, K.; Kateb, S.; Al-Ansari, N.; Kouadri, S.; Najm, H.M.; Khedher, K.M. Assessment of Groundwater Suitability for Agricultural Purposes: A Case Study of South Oued Righ Region, Algeria. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.T.M.; Rahman, T.; Saadat, A.H.M.; Islam, M.S.; Abdullah, A.M.A.S. Groundwater characterization and selection of suitable water type for irrigation in the western region of Bangladesh. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 233–243. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Puri, A. A review of permissible limits of drinking water. Indian. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2012, 16, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Baloch, M.Y.J.; Zhang, W.; Chai, J.; Li, S.; Alqurashi, M.; Rehman, G.; Tariq, A.; Talpur, S.A.; Iqbal, J.; Munir, M.; et al. Shallow Groundwater Quality Assessment and Its Suitability Analysis for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes. Water 2021, 13, 3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.M. A Graphic Representation in the Geochemical Interpretation of Groundwater Analysis; American Geophysical Union Transactions: Washington, DC, USA, 1944; Volume 25, pp. 14–923. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, A.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhong, F.; Zheng, C.; Gao, N. Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Farmland Soils at the Northern Foot of the Qinling Mountains, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 17, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salifu, M.; Aidoo, F.; Hayford, M.S.; Adomako, D.; Asare, E. Evaluating the suitability of groundwater for irrigation-al purposes in some selected districts of the Upper West region of Ghana. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba-Rao, N.; Marghade, D.; Dinakar, A. Geochemical characteristics and controlling factors of chemical compo-sition of groundwater in a part of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitsazan, M.; Aghazadeh, N.; Mirzaee, Y.; Golestan, Y.; Mosavi, S. Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of urban groundwater in Urmia City, NW Iran. Water Sci. Technol.-Water Sup. 2017, 17, ws2017039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiefuna, G.I.; Sheriff, A. Assessment of shallow ground water quality of Pindiga Gombe Area, Yola Area, NE, Nigeria for irrigation and domestic purposes. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 3, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Singaraja, C.; Chidambaram, S.; Anandhan, P.; Prasanna, M.V.; Thivya, C.; Thilagavathi, R.; Sarathidasan, J. Hydrochemistry of groundwater in a coastal region and its repercussion on quality, a case study-Thoothukudi district, Tamil Nadu, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, S.; Hamza, S.; Bashir, E. Assessment of geochemistry of soils for agriculture at Winder, Balochistan, Paki-stan. In Water Quality, Soil and Managing Irrigation of Crops; InTech-Open Access Publisher: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Qian, H.; Wu, J. Conjunctive use of groundwater and surface water to reduce soil salinization in the Yinchuan Plain, North West China. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2018, 34, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Hu, Q.; Qi, W.; Tang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wan, P.; Chao, J.; Yang, X.J. Nitrate reduction in water by aluminum alloys particles. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 96, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajmohan, N.; Masoud, M.H.; Niyazi, B.A. Impact of evaporation on groundwater salinity in the arid coastal aquifer, Western Saudi Arabia. Catena 2021, 196, 104864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Variables | Temperature °C | pH -- | TDS mg/L | EC µS/cm | TH mg/L | ORP mV | ALK mg/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 |
| Mean | 15 | -- | 2483.4 | 4264.0 | 1018.1 | 368.06 | 213.3 |
| Median | 34.3 | 7.43 | 2179.5 | 3615.5 | 920.5 | 365.5 | 200 |
| Variance | 28.3 | 0.14 | 2,640,206.8 | 9,373,688 | 573,743.3 | 4826.3 | 5160.2 |
| Std. deviation | 0.21 | 0.38 | 1624.9 | 3061.6 | 757.5 | 69.5 | 71.83 |
| Minimum | 25 | 6.5 | 411 | 626 | 185 | 183 | 85 |
| Maximum | 41 | 8.1 | 11,167 | 21,733 | 6146 | 542 | 475 |
| Range | 2.1 | 1.7 | 10,756 | 21,107 | 5961 | 359 | 390 |
| Skewness | 0.22 | −1.78 | 8.03 | 9.86 | 0.15 | 1.66 | 4.19 |
| Kurtosis | 0.45 | 0.27 | 17 | 23.18 | 48.83 | 0.76 | 4.47 |
| Shapiro–Wilk | 0.11 | 0.036 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.078 | 0.200 |
| Kolmogorov–Smirnov | 0.1 | 0.200 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.200 | 0.00 |
| Desirable limit [26] | 12 | 6.5 | 500 | 500 | 200 | 300 | 20 |
| Permissible limit [26] | 25 | 8.5 | 1500 | 1500 | 500 | 500 | 200 |
| Cations | Anions | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Na+ mg/L | K+ mg/L | Ca2+ mg/L | Mg2+ mg/L | Cl− mg/L | SO42− mg/L | HCO3− mg/L | CO32− mg/L | NO32− mg/L | F− mg/L |
| N | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 |
| Mean | 413.1 | 3.7 | 269.2 | 82.5 | 793.9 | 597.9 | 341.3 | 279.7 | 38.3 | 1.05 |
| Median | 297 | 3 | 213.8 | 58 | 526 | 489 | 308 | 252.5 | 39.7 | 1 |
| Variance | 134,302 | 7.42 | 75,799.4 | 6525.7 | 733,109.8 | 258,167.4 | 14,638.4 | 9826.7 | 843.2 | 0.96 |
| Std. deviation | 366.5 | 2.7 | 275.3 | 80.8 | 856.2 | 508.1 | 121 | 99.1 | 29.04 | 0.98 |
| Minimum | 36 | 0.34 | 59.3 | 4 | 47.2 | 40.7 | 110 | 90 | 0.3 | 0 |
| Maximum | 1527 | 10.6 | 2452.3 | 338 | 6331 | 2106 | 600 | 492 | 120 | 4 |
| Range | 1491 | 10.3 | 2393 | 334 | 6283.8 | 2065.3 | 490 | 402 | 119.7 | 4 |
| Skewness | 6.02 | 3.07 | 24.1 | 7.94 | 14.44 | 6.29 | 1.646 | 1.65 | 2.45 | 2.7 |
| Kurtosis | 3.96 | −0.184 | 95.84 | 7.71 | 40.57 | 5.38 | −1.011 | −1.09 | 0.065 | 0.05 |
| Shapiro–Wilk | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.014 | 0.056 | 0.00 |
| Kolmogorov–Smirnov | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.078 |
| Desirable limit [26] | 200 | 10 | 75 | 50 | 250 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 25 | 1 |
| Permissible limit [26] | 600 | 12 | 200 | 100 | 500 | 250 | 600 | 600 | 45 | 1.5 |
| Parameter | Min | Max | Mean | SD | Median | Suitability for Irrigation [33] | Tabuk Groundwater Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAR | 1 | 19 | 6 | 4 | 5 |
|
|
| RSC | −118 | 5 | −10 | 16 | −6 |
|
|
| PI | 23 | 83 | 52 | 13 | 53 |
|
|
| CR | 0 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
|
|
| MH | 0 | 62 | 24 | 14 | 20 |
|
|
| Na% | 10 | 79 | 43 | 14 | 41 |
|
|
| KR | 0.3 | 1 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.7 |
|
|
| HI | 0.006 | 2 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.7 |
|
|
| ALK | pH | TDS | EC | TH | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− | CO32− | NO32− | F | ORP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALK | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| pH | −0.137 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| TDS | 0.006 | 0.249 * | 1 | |||||||||||||
| EC | −0.041 | 0.244 * | 0.986 ** | 1 | ||||||||||||
| TH | −0.134 | 0.103 | 0.855 ** | 0.833 ** | 1 | |||||||||||
| Na+ | 0.072 | 0.297 ** | 0.866 ** | 0.868 ** | 0.542 ** | 1 | ||||||||||
| K+ | −0.195 | 0.083 | 0.417 ** | 0.400 ** | 0.371 ** | 0.335 ** | 1 | |||||||||
| Ca2+ | −0.141 | 0.038 | 0.771 ** | 0.798 ** | 0.896 ** | 0.506 ** | 0.180 | 1 | ||||||||
| Mg2+ | −0.017 | 0.150 | 0.345 ** | 0.239 * | 0.419 ** | 0.190 | 0.463 ** | −0.026 | 1 | |||||||
| Cl− | −0.068 | 0.203 | 0.913 ** | 0.956 ** | 0.779 ** | 0.816 ** | 0.280 * | 0.861 ** | −0.009 | 1 | ||||||
| SO42− | −0.031 | 0.194 | 0.528 ** | 0.411 ** | 0.525 ** | 0.407 ** | 0.466 ** | 0.142 | 0.895 ** | 0.155 | 1 | |||||
| HCO3− | 0.361 ** | 0.000 | −0.076 | −0.094 | −0.121 | −0.018 | −0.030 | −0.117 | −0.030 | −0.112 | 0.003 | 1 | ||||
| CO32− | 0.361 ** | −0.001 | −0.077 | −0.094 | −0.121 | −0.018 | −0.029 | −0.118 | −0.030 | −0.113 | 0.004 | 1.000 ** | 1 | |||
| NO32− | 0.068 | −0.039 | 0.031 | 0.086 | −0.113 | 0.214 | −0.057 | −0.035 | −0.178 | 0.105 | −0.188 | 0.122 | 0.122 | 1 | ||
| F− | 0.061 | 0.229 * | 0.238 * | 0.229 * | 0.023 | 0.280 * | 0.011 | 0.116 | −0.194 | 0.226 * | −0.006 | 0.068 | 0.068 | 0.077 | 1 | |
| ORP | 0.087 | −0.220 * | −0.300 ** | −0.325 ** | −0.294 ** | −0.187 | −0.109 | −0.312 ** | −0.018 | −0.328 ** | −0.048 | 0.197 | 0.197 | 0.220 | −0.104 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fallatah, O.; Khattab, M.R. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality and Suitability for Irrigation Purposes and Human Consumption in Saudi Arabia. Water 2023, 15, 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132352
Fallatah O, Khattab MR. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality and Suitability for Irrigation Purposes and Human Consumption in Saudi Arabia. Water. 2023; 15(13):2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132352
Chicago/Turabian StyleFallatah, Othman, and Mahmoud R. Khattab. 2023. "Evaluation of Groundwater Quality and Suitability for Irrigation Purposes and Human Consumption in Saudi Arabia" Water 15, no. 13: 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132352
APA StyleFallatah, O., & Khattab, M. R. (2023). Evaluation of Groundwater Quality and Suitability for Irrigation Purposes and Human Consumption in Saudi Arabia. Water, 15(13), 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132352







