Abstract
Winter (December to March) precipitation is the major source of rainfed agriculture, storage, and perennial water flow in the western river system of Pakistan. Hence, this study uses precipitation data and variables of land–ocean and atmosphere from the Pakistan Meteorological Department and European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) and fifth-generation reanalysis data (ERA5), respectively, to investigate the changes in winter precipitation and its sensitivity to different land–ocean and atmosphere variables, which are rarely investigated in Pakistan. Non-parametric techniques, such as the modified Mann–Kendal, Sen slope, kernel density-based probability function (PDF), empirical orthogonal function (EOF), and correlation analysis, were used to assess the changes and modes of variability in winter precipitation. The overall seasonal precipitation showed a significant decreasing trend with a (−0.1 mm d−1 yr−1) in the seasonal mean and monthly precipitation, except in February which showed a significant increase (>0.11 mm d−1 yr−1). The highest decrease in daily precipitation (<−0.1 mm d−1 yr−1) was in the north, with a moderate decrease in the southeast. The extreme precipitation indices exhibited an erratic decreasing tendency, but the maximum daily precipitation index increased; post-2000 precipitation extremes displayed an increase, and the seasonal and monthly precipitation exhibited the highest deviations during the drought period (1995–2000). The leading precipitation mode (EOF1) is sensitive to the local land surface processes and significantly correlated (>0.60) with the central Pacific and Indian Ocean’s basin-wide sea surface temperature, corroborating the influence of ENSO-induced meridional/zonal deviation of Hadley–Walker circulations. The Hadley and Walker cells affect the south-westerlies’ jet stream strength, impacting the water vapor transport and precipitation over Pakistan. These changes in the precipitation magnitude will affect rain-fed agriculture, especially the Rabi cropping pattern and perennial river flow.
1. Introduction
Pakistan is among the top ten countries directly impacted by global warming and changing climate [1,2]. The climate change risks in Pakistan include frequent extreme temperature and precipitation events [3,4,5,6]. The threat of water availability to ensure food and water security becomes more viable when coupled with excess/deficit precipitation [7,8,9,10]. Monsoon and winter precipitation are the primary drivers of the hydrometeorological cycle in the country, with a ≥95% contribution to the annual precipitation budget [2,11]. The winter precipitation from the western disturbances (WD hereafter) over Pakistan is active from December to March [12,13]. WDs are low-pressure systems arising from the Mediterranean Sea, causing winter precipitation in Pakistan [14,15]. Winter precipitation is the second dominant precipitation system accounting for ≥35% of the annual precipitation after summer monsoon precipitation (≥60%) [12,16,17].
Many studies have focused on monsoonal precipitation, its extremes, and the related dynamic mechanisms [2,11,18], but limited literature is available for winter precipitation. The peak winter precipitation is in Pakistan’s northern, northwestern, and southwestern regions, and it decreases in the eastern, southeastern, coastal, and arid regions [19]. Safdar et al. [20] found a decrease in winter precipitation with a marked decrease in the number of rainy days concluding a temporal shift to the pre-monsoon season from winter. Hunt et al. [21] found that the current emission rates (RCP 8.5) will lead to a decrease in westerlies precipitation by the end of the 21st century. The findings revealed that this would be attributed to numerous factors, including the expansion and weakening of the subtropical jet during winter and a decrease in meridional wind shear. Ridley et al. [22] found an increase in the westerlies over the Karakoram by end of the 21st century, concluding growth of the regional glaciers or a slower retreat rate. Midhuna et al. [23] compared the westerlies’ intensities and frequencies from observations and models over the northern parts of South Asia. The results show a moderate deviation between the model and observations whereas a decrease in westerlies was found in the near future, an increase in the far future of the 21st century was also evident. Mishra et al. [24], from control and sensitivity simulations, found that the subtropical jet stream is sensitive to the Arabian Sea surface temperature. An increase in the Arabian sea surface temperature directly impacts the precipitation over South Asia [25]. From observations and reanalysis data, Ahmed et al. [12] found strong westerlies and deep vertically integrated moisture flux convergence in dry cases. Mid-level ascent with upper-level wind divergence aggravated moisture in the convective centers of Pakistan in wet cases. Hamal et al. [26] coupled the interannual variability of westerlies with atmospheric circulation patterns over Nepal and concluded that the temperature over northern parts of India, Nepal, and adjacent Tibetan Plateau regions has decreased in surplus years and increased in deficit years of precipitation. Yadav et al. [27] studied the variability and characteristics of winter precipitations over the northwest part of India and found that the seasonal and decadal precipitation patterns were linked with synoptic systems of westerlies. Some studies have linked these changes and variations in winter precipitation with the oceanic forcing across South Asia, including the Indian Ocean, Arabian Sea, ENSO, Arctic Oscillations, and regional circulation patterns [28,29,30]. These studies show the importance of the westerlies for the water resources, agriculture, food security, and cropping patterns of the region. These studies reported diverse results, with gaps, and lack of definitive consensus due to different choices of methods and dependency on models with coarse resolution unable to simulate the regional precipitation. Less attention and results are available from observations over Pakistan to supplement and provide more evidence of the diverse trends and variability of the westerlies over the region and how it will challenge food security and crop production.
There are two key cropping seasons in Pakistan, i.e., Kharif and Rabi, which start with the Kharif season from April to June and harvests from October to December [31]. The Rabi season crops are mainly dependent on winter precipitation (rainfed areas) for their crop water requirements [32]. In this regard, the westerlies serve directly as the water source for irrigation in the rainfed regions. Additionally, they accumulate snow in northern mountainous areas of the country that melts in early summer and provides runoff for Kharif crops, irrigation, and water for reservoir storage [31,33]. The precipitation magnitude and spatial patterns in winter vary widely in time and space [34]. The mean annual precipitation in Rabi is 119 mm/year, and in Kharif it is 191 mm/year. Ishaque et al. [35] reported from numerical simulations that climate change would result in the early maturity of wheat crops with enhanced water use efficiency and would decrease production by up to 30% in the rainfed regions of Pakistan. Ali et al. [36] found from social and climate data of the northern parts of Pakistan that change in winter precipitation and temperature will reduce the net revenue by USD 20 per hectare and USD 14 to USD 28 per hectare, with far more severe consequences for the arid and rainfed regions. Syed et al. [37] concluded from the review of climate change impacts on the food security of Pakistan that the changing climate will result in a 6% decrease in wheat and up to an 18% decrease in rice production. The changing climate impacts listed include direct and indirect factors, such as water availability, pesticide access, and labor. Alvar-Beltrán et al. [38], from a numerical simulation of the wheat and sugarcane crop under a selected climate change scenario in southern Pakistan, reported a stable trend in wheat production whereas sugarcane production will moderately decline in Sindh and increase in Punjab province up to 2080. In the post-2080 era, a decline in sugarcane crop production is projected in both provinces. In summary, these studies indicate a direct relationship between rainfed agriculture and Rabi crop production, which is further investigated in multiple studies [32,39,40].
The current study attempts to address the existing regional and local gaps regarding the changes in winter precipitation with relatively long-term observations of in situ rain gauge stations and state-of-the-art reanalysis datasets. Furthermore, the trend and variability of the dominant precipitation mode are assessed concerning the role of oceanic forcing and atmospheric circulations. The rest of the paper describes the study area, its seasonal and sub-seasonal climatology, and its variability in Section 2. Data and methods are in Section 3, followed by results in Section 4, and discussion and conclusions are shown in Section 5.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Climate Mean State and Topography of Pakistan
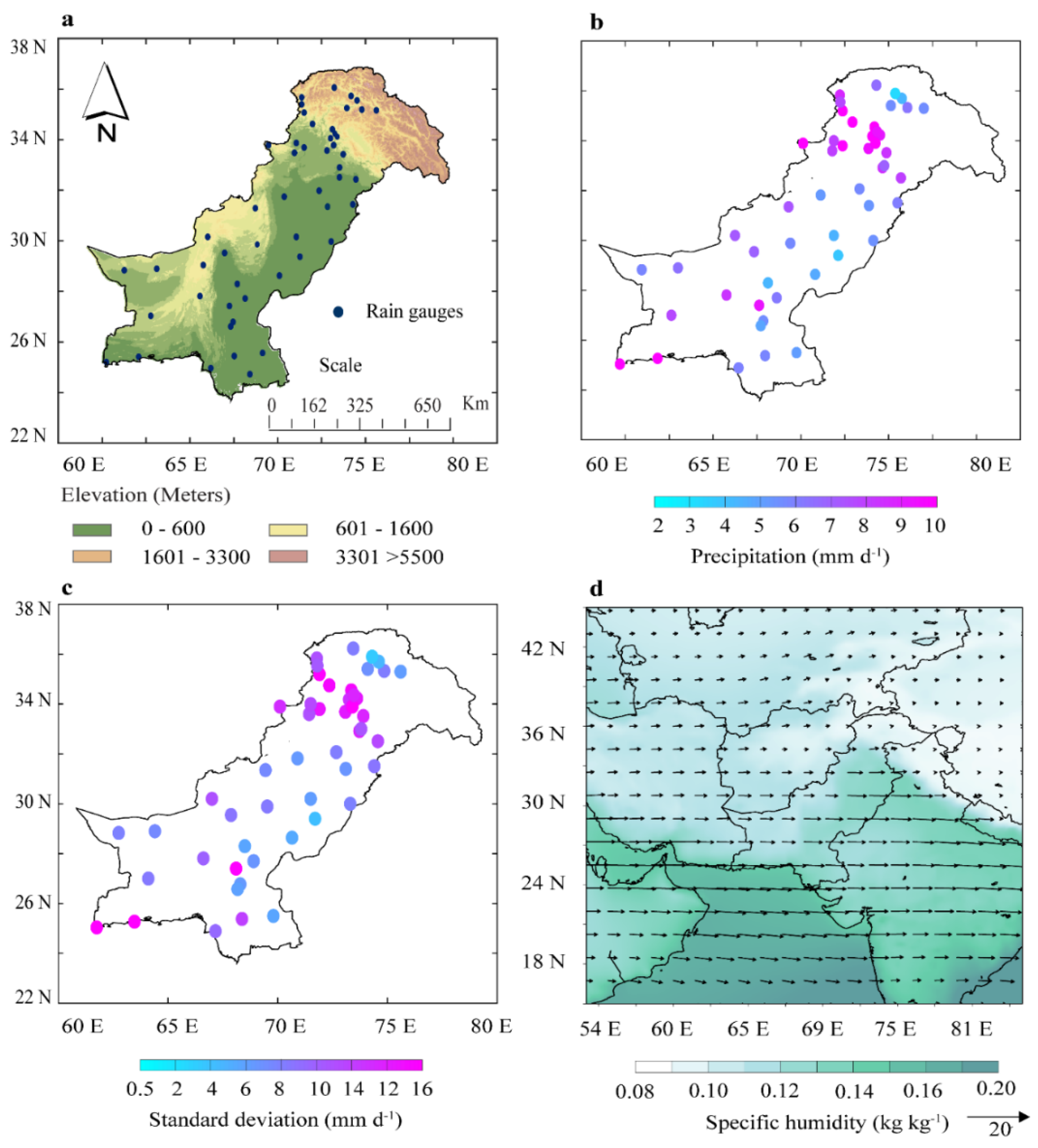
The topography of Pakistan (Figure 1a) varies from south to north with complex terrain, climate, land cover, and aridity. The temperature reaches <0 °C during winter in the northwestern regions, and in summer, the central regions experience >40 °C [41,42]. The water cycle of Pakistan is comprised of monsoon (June, July, August, and September; JJAS) and winter precipitation (December, January, February, and March; DJFM). Winter precipitation is the second major source of precipitation in Pakistan, with maximum daily mean precipitation (>10 mm d−1) (Figure 1b), exhibiting the highest standard deviation in the northwest (Figure 1c). The subtropical and extratropical westerly circulations are the regional drivers of winter precipitation, as shown in Figure 1d.
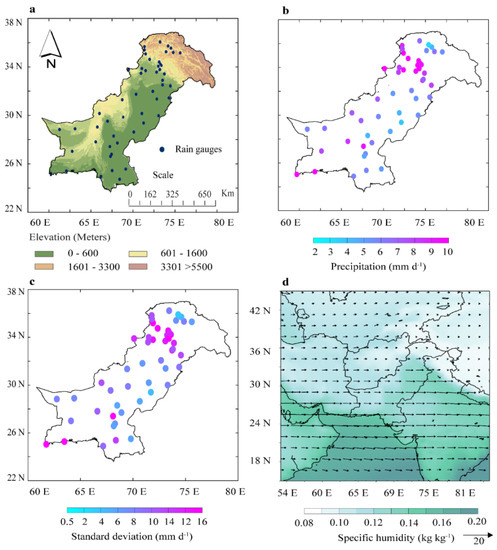
Figure 1.
(a) Topographic map and in situ precipitation rain-gauge density of Pakistan, (b) climatological mean, (c) standard deviation of the mean winter (DJFM) precipitation, and (d) wind components (vectors) and specific humidity (shaded) at 500 hPa during 1981–2018.
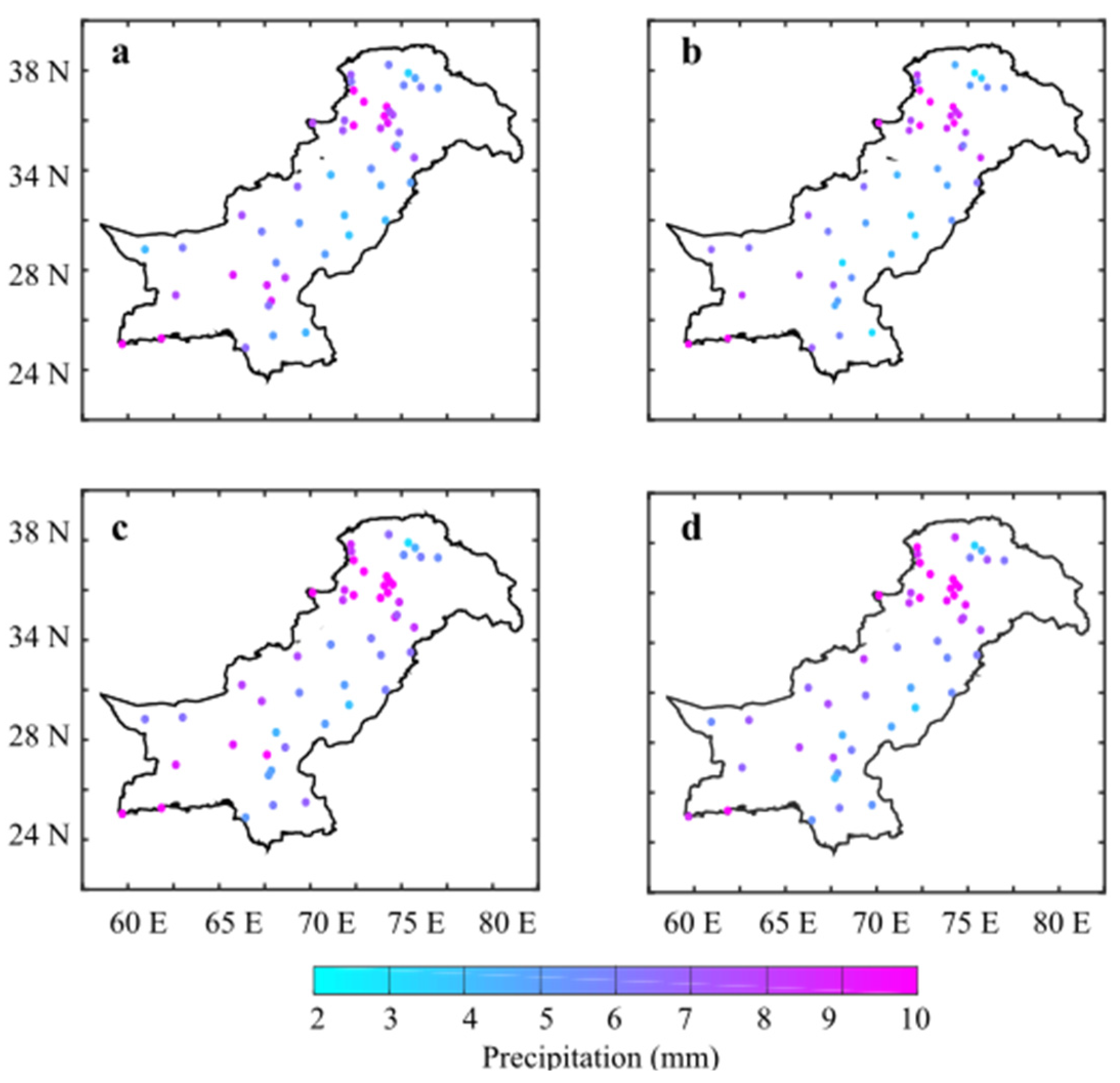
On a sub-seasonal and seasonal scale, large-scale atmospheric and oceanic forcing significantly affects the precipitation magnitude. February (Figure 2c) receives the highest daily precipitation (10 mm d−1), followed by January (Figure 2b), March (Figure 2d), and December (Figure 2a).
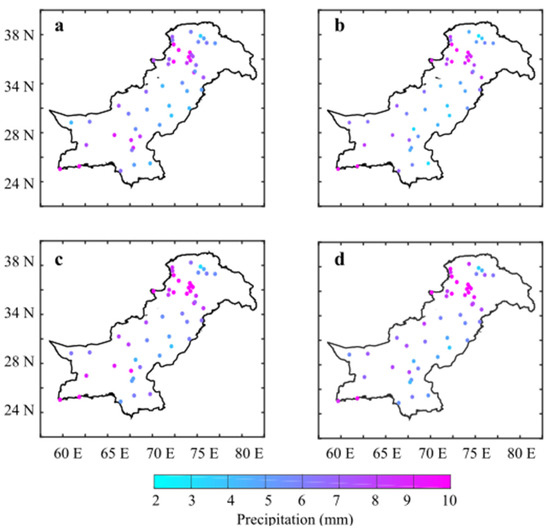
Figure 2.
The climatological mean of winter precipitations for (a) December, (b) January, (c) February, and (d) March over Pakistan during 1981–2018.
2.2. Data
The precipitation data used in this study was obtained from the Pakistan Meteorological Department for 1981–2018 from 50 in situ rain gauges. The data include daily observations for December, January, February, and March (DJFM), known as winter precipitation [43,44]; the network of in situ gauge stations has a relatively higher density in the north, where the terrain is complex and more diverse than that in the south arid plains, yet the precipitation means, extremes, and interannual variability can be best represented [6,45]. The homogeneity and consistency of precipitation data were checked using descriptive statistical methods, including the standard normal homogeneity test (SNHT) [46,47]. A few stations had some missing observations, which only accounted for <2% of the study duration and should not affect the overall conclusion.
The global land–ocean and atmospheric reanalysis data from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) and fifth-generation ERA5 reanalysis were further used [48]. The ERA5 variables used in this study include the 2 m temperature, top layer soil moisture (7cm), sea surface temperature (SST), relative vorticity, vertical velocity, and zonal and meridional wind components. The ERA5 reanalysis includes (as of the time of this analysis) hourly, three hourly, and monthly observations on a 31 and 62 km global resolution at 137 pressure levels reaching up to 1 hPa [48,49]. The strengths of the ERA5 relative to its predecessor ERA-Interim include improved spatial resolution, which benefits its application of extreme weather representation. For the current study, the monthly scale observations of the atmosphere were used during the study period at a spatial grid size resolution of 25 km. The data can be obtained from https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/home (accessed on 5 September 2022).
2.3. Methods
The winter precipitation trends were explored at an interannual scale using the daily mean precipitation for December, January, February, and March (DJFM) and individual months. Furthermore, trends in daily mean precipitation and its extremes were assessed using extreme precipitation indices defined by the Expert Team on Climate Change Detection and Indices (ETCCDI) of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) [50]. The extreme precipitation indices consider the frequency and intensity of daily precipitation characteristics over diverse climate classes using mean and percentile-based thresholds—the list of the extreme precipitation indices used in this study is provided in Table 1 with the respective definitions and units. The magnitude and intensity of the winter precipitation is relatively lower than summer precipitation and thus a range of moderate indices will sufficiently capture the precipitation dynamic variation.

Table 1.
List of extreme precipitation indices used in the study.
The non-parametric tools, such as the modified Mann–Kendal (mMK) [51] and Sen’s slope estimator (SSE) [52], were used to illustrate the changes in spatial and temporal variability of mean and extreme precipitation characteristics. Before trend estimation, the mMK test can remove the interannual autocorrelation signals from the data [53]. The mMK test identifies significant monotonic trends, and the SSE quantifies the magnitude of the monotonic trend. These approaches can identify where the precipitation mean and intensity are decreasing or increasing in time and space.
The coefficient of variation (CV) (relative standard deviation) and boxplot were used to capture daily precipitation variations on a decadal scale for seasonal and sub-seasonal monthly precipitation. A non-parametric kernel density-based probability function (PDF) was used to show the interannual changes in the precipitation density over a decadal scale concerning the mean precipitation of the study period. A 10-year moving mean signal was removed from the raw data before PDF analysis to account for the interdecadal variability signal. Changes in mean and extreme daily precipitation amplitudes beyond their normal distribution were quantified using mean, standard deviation, skewness, and kurtosis [10,54,55].
The Empirical Orthogonal Function (EOF) analysis was further employed to unveil the potential mechanism that drives the dominant coherent precipitation modes of winter precipitation on an interannual scale [10,56]. The presumed homogenously dimensioned precipitation data were decomposed into uncorrelated orthogonal eigenvectors. Principally, the leading mode of spatiotemporal variability explains most of the variance. For their empirical relationship, the dominant precipitation mode was correlated with 2 m temperature, soil moisture, atmospheric circulations, and SST. A composite analysis approach was used for a potential mechanism where the winter precipitation dominant circulation patterns for mean and extreme precipitation events were explored. For atmospheric circulations, we primarily focused on the influence of the Pacific and Indian Ocean Sea surface temperature and their interaction with the overlying atmosphere reflected in the circulation’s anomalies. Dimiri et al. [57] found a positive correlation between the ENSO warm phase and the winter precipitation over northwestern India due to higher moisture flux transport by the southwesterlies from Caspian and Arabian seas. Kar and Rana [58] found that the Atlantic and Arctic (NAO/AO) active phases are the leading drivers for the second mode of variability. These indices indicate the interactions of the SST with the circulation patterns and eventually affect the region’s water resources, precipitation, and the agriculture of Pakistan. Furthermore, the Walker and Hadley cell circulations were explored for their impact on the winter precipitation during the composite analysis. The Hadley cell is a large-scale atmospheric circulation pattern that dominates the tropical regions with its ascending motion in the tropical region [59,60,61]. The Walker cell is primarily associated with the tropical Pacific region, spanning a specific latitude of approximately 10 N and 10 S, and changes its pattern as a response to the Pacific Sea surface temperature patterns [62,63].
3. Results
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Daily Variability
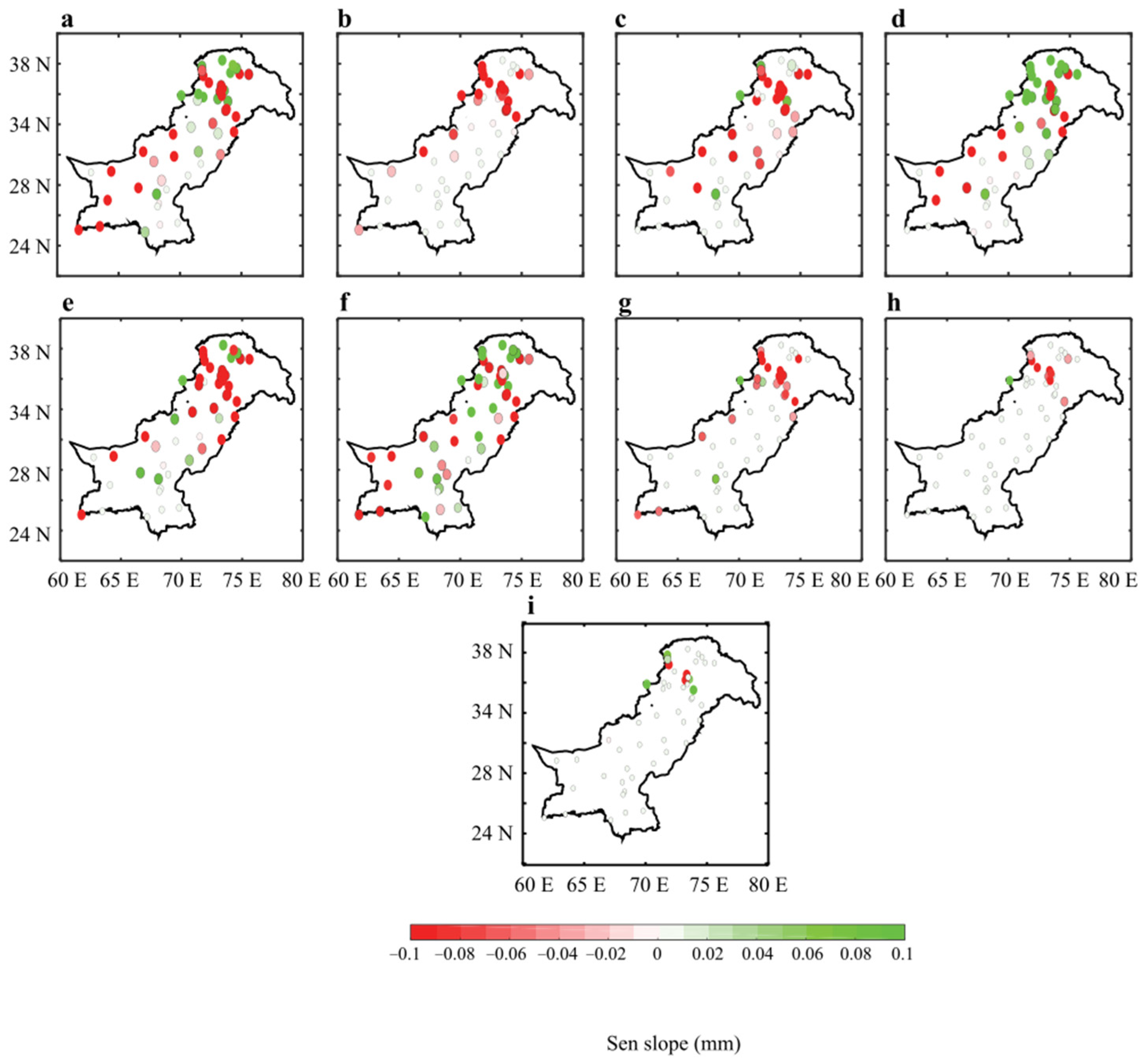
Figure 3 shows the spatial distribution of the SSE trend in the seasonal (DJFM) precipitation on a daily scale (Figure 3a) and the monthly trend for December, January, February, and March (Figure 3b–e), as well as the extreme precipitation indices of Rx1 day, R10mm, R20mm, and R95p TOT (Figure 3f–i). The significance of the trend was tested with a non-parametric mMK technique, and the stations that did not pass the significance test (at 95% confidence bound) were circled. The results show that seasonal (DJFM) precipitation has a mixed trend with a significant decrease in the southwest and westerlies-dominated regions (SSE: −0.1 mm d−1 yr−1). The significant increasing trend (SSE: >0.1 mm d−1 yr−1) is evident in the northern region of Pakistan. In December (Figure 3b), the daily precipitation showed a significant decrease in the majority of the stations (SSE: <−0.1 mm d−1 yr−1), with a slight non-significant increase in the stations located in the southeast. In January (Figure 3c), a significant decreasing pattern (SSE: <−0.1 mm d−1 yr−1) was evident in the northwestern and southwestern parts, with a moderate decrease in the rest of the country. In February (Figure 3d), the daily precipitation exhibited a significant increasing trend in the north (SSE: >0.1 mm d−1 yr−1) and a decreasing trend in the southwest of the country. A few stations in the complex northern terrain showed a decrease in daily precipitation (SSE: −0.08 mm d−1 yr−1), whereas an increase in daily precipitation was seen in the central-eastern parts (SSE: 0.06 mm d−1 yr−1). In March (Figure 3e), the main winter precipitation belt showed a significant decreasing trend (SSE: <0.1 mm d−1 yr−1), with a rather mixed trend in the southeastern parts of the country.
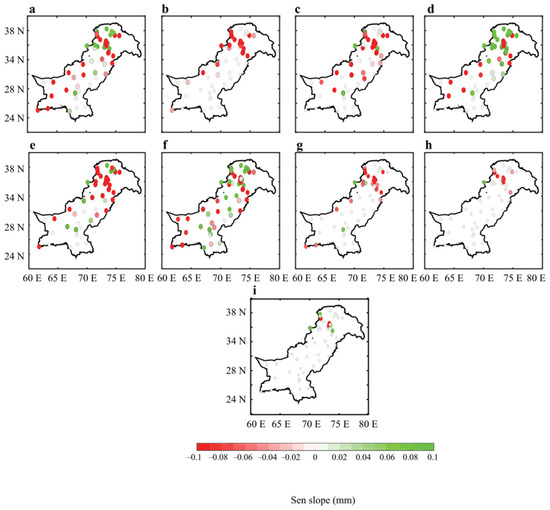
Figure 3.
The SS E trend of the daily precipitation over Pakistan during 1981–2018: (a) Seasonal, (b) December, (c) January, (d) February, (e) March, and in the extreme precipitation indices for (f) Rx1 day, (g) R10 mm, (h) R20 mm, and (i) R95p TOT. The stations with no significant trend are circled.
The maximum one-day precipitation (Rx1 day) (Figure 3f) showed an increase/decrease in northwest/northeast (SSE: 0.1/−0.1 d yr−1) and a uniform decrease in the southwest. The frequency of heavy precipitation days (Rx10 mm days) (Figure 3g) significantly decreased in the central region with a moderate non-significant decrease in the rest of the country. The number of very heavy precipitation days (Rx20 mm days) (Figure 3h) also showed a significant decrease in the northern parts (SSE: −0.1 d yr−1) and a rather low to negligible trend in the rest of the country. The very wet days (Rx95 p TOT) were unchanged (Figure 3i), except for a few stations in the mountainous terrainx.
Figure 3 shows that the winter precipitation magnitude significantly decreased in the northern and southwestern parts of the country during 1981–2018. The decrease in precipitation on a sub-seasonal scale was more significant in December, January, and March. In February, it showed a significant increasing trend in the north and a decreasing trend in the southwest. The maximum daily precipitation increased in the central and southeastern arid plains and decreased in the western and northern mountainous regions. The heavy and very heavy precipitation days decreased in the central westerlies-dominated regions, whereas the wet days’ precipitation did not change significantly.
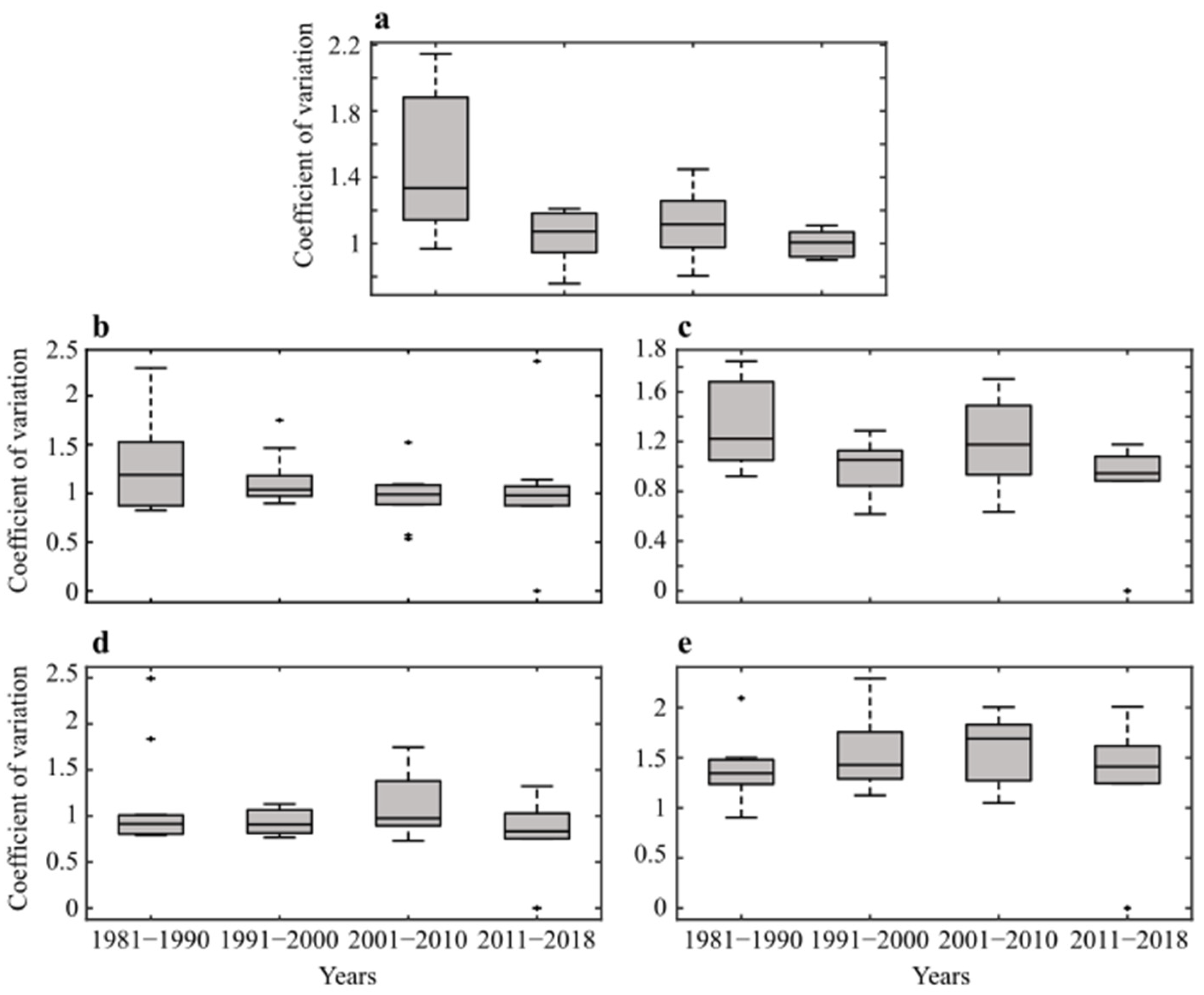
Figure 4 shows the box-and-whiskers plots of daily precipitation intra-decadal coefficients of seasonal and sub-seasonal precipitation variation. The seasonal precipitation (Figure 4a) intra-decadal variability was highest during 1981–1990, evidently showing positive skewed data with fewer extremes, and the majority of the precipitation was due to moderate or lower magnitude events, with the lowest during 1991–2000 and 2010–2018. In December (Figure 4b), the precipitation during the first decade showed more events in the >75% of the distribution where the interquartile range (IQR) and median had shown a uniform pattern in the first decade. In the rest of the decade, the precipitation events were more concentrated and homogenous with lower variability and a predictable pattern of the same magnitude. In January (Figure 4c), the 1981–1990 decade had the highest intra-decadal variability with positive skewness indicating more extreme events in the upper quartiles, followed by the post-drought decade, and the lowest variability with homogeneous pattern during 2010–2018. In February (Figure 4d), intra-decadal variability differed from the rest of the months, and moderate positive skewness existed in the upper quartiles from 2001–2010, indicating higher precipitation events. The rest of the decadal variability coefficients were uniform, with changes in the magnitude, with a moderate spread towards upper quartile.
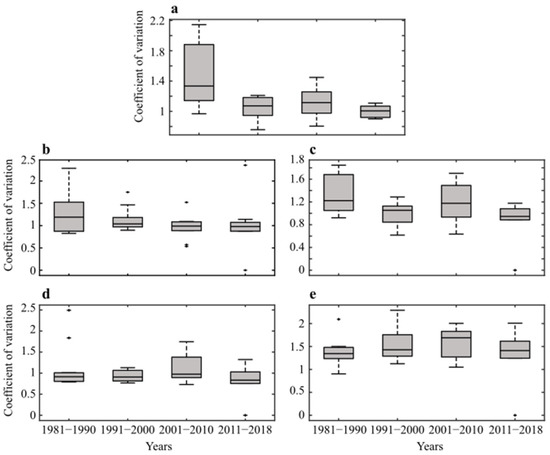
Figure 4.
Box-and-whisker plots of decadal daily precipitation variability coefficient for the seasonal and sub-seasonal monthly precipitation over Pakistan during 1981–2018: (a) Seasonal, (b) December, (c) January, (d) February, and (e) March. The box plot spans from the first quartile Q1 to the third quartile Q3, and the IQR = Q3-Q1. The horizontal line inside each box is the median whereas the line extending from the boxplot in both directions are whiskers.
In March (Figure 4e), intra-decadal variability was moderate with negative skewness during 1981–1990 and upper quartile positive skewness in the maximum variability during 1991–2000. Northern Pakistan, due to the terrain the precipitation received at the stations (Table S1), showed different variation dynamics than the rest of the stations in the south. The results (Figure S1a) show that the seasonal precipitation variability was moderate in the first and second decade with fewer high-magnitude events. The results from the third decade show a negative skewness with moderate events driving the events, and the whiskers indicate higher spread towards the upper >75% quartile. December (Figure S1b) followed a similar pattern with higher variability during the third and fourth decade, with both decades showing negative skewness and a decrease in variability. In January (Figure 1c), the variability was uniform with a higher interquartile range evident during the second decade, showing normal distribution. In February (Figure S1d) and March (Figure S1e), the precipitation variability coefficients showed lower variability in the first decade and higher variability in the last decade. In conclusion, the intra-decadal coefficient of precipitation variability generally decreased from 1981–2018. The overall variability of the seasonal precipitation was dynamic during January and March, and in the second decade (1991–2000), precipitation exhibited the lowest variability, followed by 2010–2018. In December, a consistent decrease in precipitation variability over the four decades was observed; however, a moderate precipitation variability was observed in February.
3.2. Interannual Variability
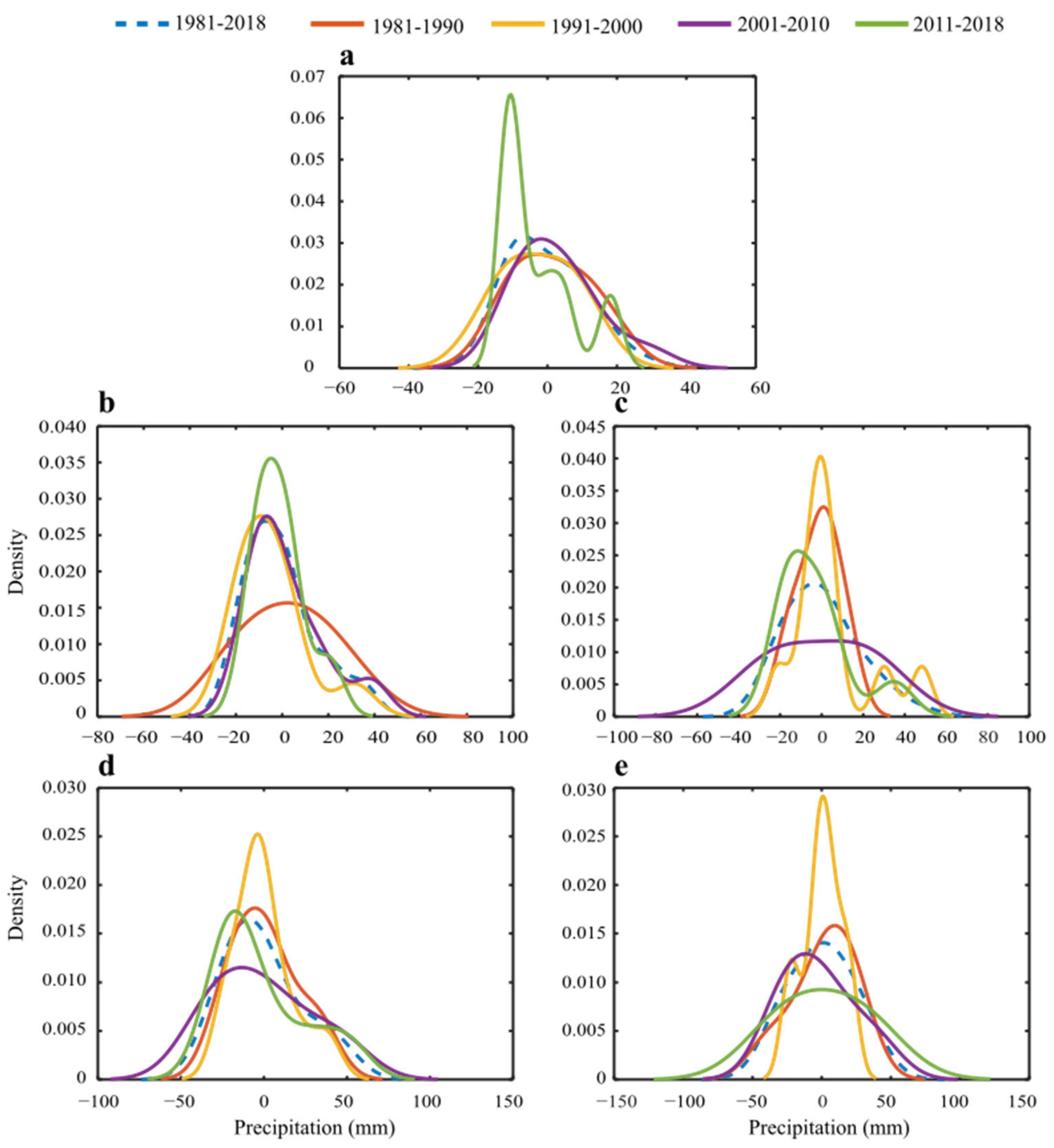
Figure 5 shows the PDF of the interannual winter regional average of the study area precipitation at seasonal and sub-seasonal scales from 1981 to 2018. For a decadal comparison, the study period is divided into four periods, each with ten years except for the last decade. The interannual PDF of winter (DJFM) precipitation (Figure 5a) has shown a moderate negative shift (skewed towards the left side) in most of the periods, with maximum density (higher kurtosis) during the last (2011–2018) and second last (2001–2010) decade. The December (Figure 5b), mean precipitation decadal variability showed a moderate decrease with a dynamic variability. The first period (1981–1990) exhibited a positive shift (skewed towards the right) with fewer extreme events, and the last period (2011–2018) showed higher density (peak kurtosis) probabilities. The January (Figure 5c) PDF shows a moderate increase, with the right-tailed relatively heavier than the left. The PDF of the first and second periods has a bimodal distribution with a moderate increase and a decrease in the last two decades. The February (Figure 5d), mean precipitation moderately increased with an obvious increasing probability during the last two periods and more dynamic variability than the left side. The March (Figure 5e) PDF shows a moderate increase with a skewed right-tailed distribution compared to the left side. The first and second periods showed an increase in moderate precipitation, while the heavy precipitation events showed an increase in the latter two periods, especially from 2011–2018.
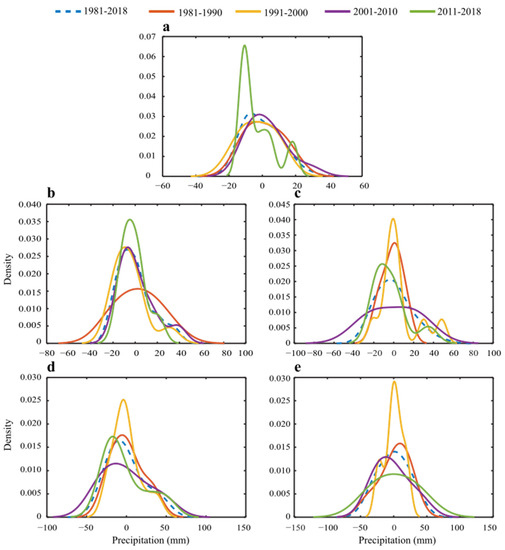
Figure 5.
PDF of the winter precipitation at (a) seasonal mean and sub-seasonal scales over Pakistan: (b) December, (c) January, (d) February, and (e) March during 1981–2018 and first decade; 1981–1990, second decade; 1991–2000, third decade; 2001–2010, and fourth decade; 2011–2018.
Figure 5 shows that the study region exhibited the highest precipitation density and distribution during the fourth and second decades in terms of both seasonal and sub-seasonal variations, indicating that the region has received frequent and intense precipitation episodes. December and January’s precipitation show a moderate decrease but a moderate increase in the frequency of heavy events. February and March show a consistent increase in the moderate and heavy precipitation frequency. The overall PDF shows a dynamic variability in the density of the heavy and moderate precipitation events when compared to the left-side skewed tails. The findings are critical for Pakistan’s sustainable water resource management, agricultural development, and disaster risk reduction.
3.3. Variability of Winter Precipitation and Its Drivers
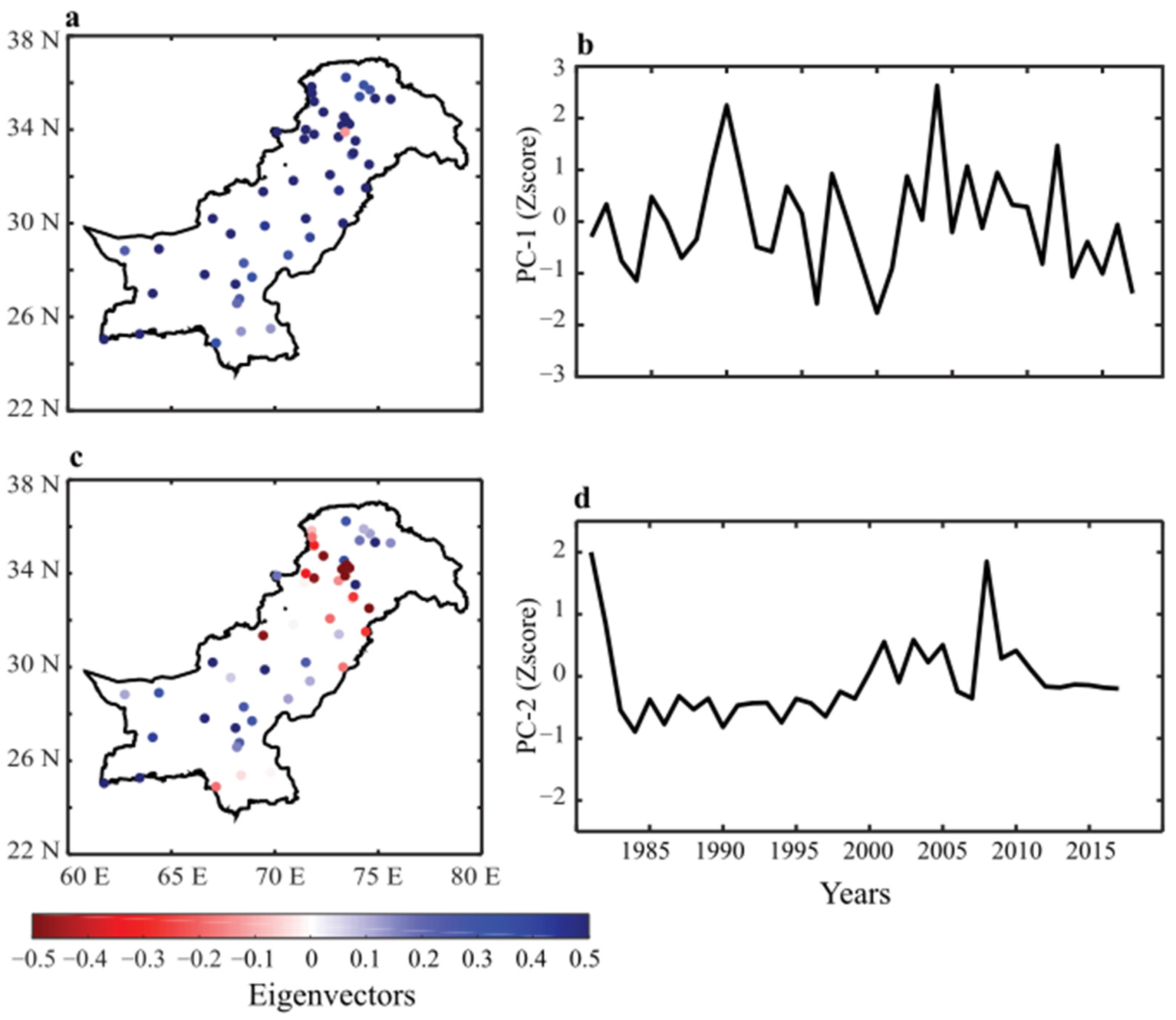
Figure 6 shows the eigenvalues and the principal components (PCs) of the two leading EOF modes showing 47.85% and 15% of the total variance in time and space. The variance explained, and spatiotemporal variability of the leading mode (Figure 6a,b) is much higher and more dynamic than the second mode (Figure 6c,d), so we only consider the leading mode for the rest of the analysis. The strength of eigenvalues (Figure 6a) closely followed the standard deviation and climatological mean precipitation variability, with higher values in northwestern regions. The dominant precipitation pattern across the country was uniform (except for one station), inferring that, unlike the monsoon precipitation, the dominant winter precipitation mode had uniformly impacted the regional precipitation. The PC1 (Figure 6b) further shows the temporal precipitation deviations and their impacts on the spatial precipitation variability. The strength of the standardized PC1 deviations from the mean show several extreme years, especially the drought of 1991–2000 and the wet episodes of 1990 and 2005.
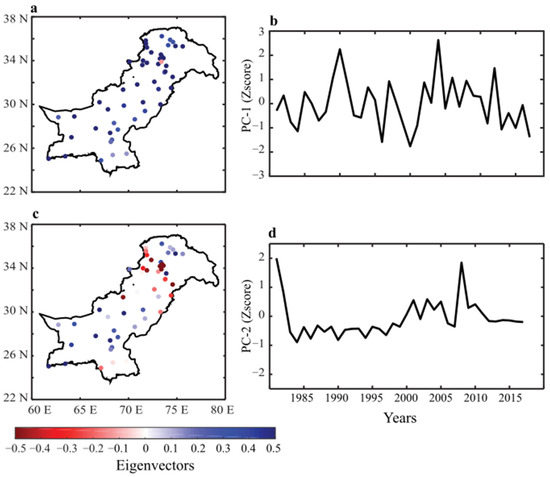
Figure 6.
The 1st EOF mode shows the (a) eigenvalues and (b) standardized principal component. The variance explained by the 1st EOF mode is 47.85%. The 2nd EOF mode shows the (c) eigenvalues and (d) standardized principal component. The variance explained by the 2nd EOF mode is 15%.
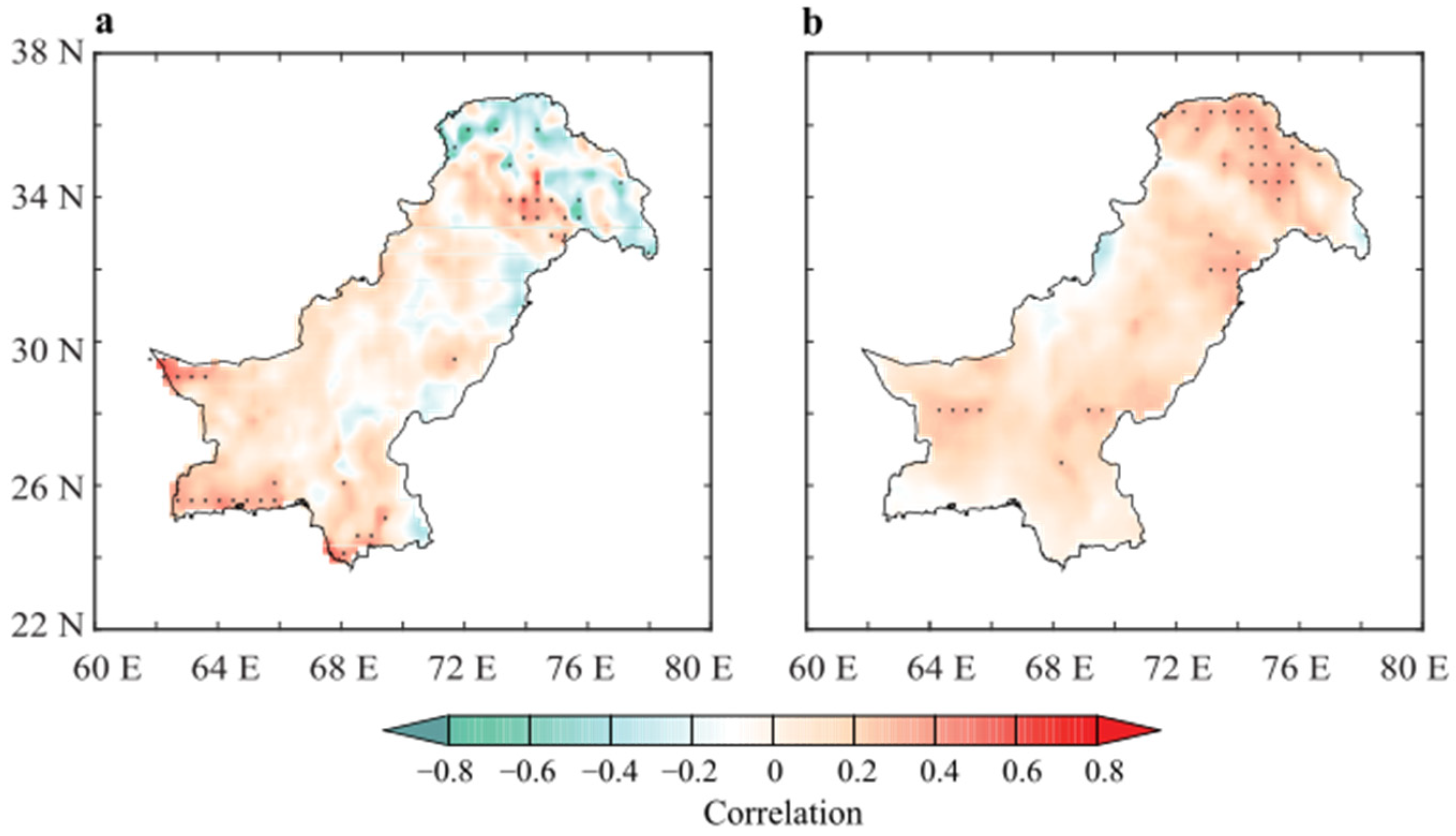
Using the PC1 as a benchmark for dynamic precipitation variability, we have explored the drivers of winter precipitation variability over Pakistan by looking into local land and near-surface variables, including soil moisture and t2m, atmospheric circulation pattern, and SST as potential drivers [64,65,66]. The local effects strongly affect the precipitation due to their influence on precipitation moisture recycling, land–atmosphere coupling, and convection replenishing in the lower atmospheric water column. In Figure 7, the PC1 is correlated with soil moisture (Figure 7a) and t2m (Figure 7b) on an interannual scale from 1981 to 2018. An obvious positive correlation exists between soil moisture and the PC1 across the country, except in the northern parts. The strength of the correlation is higher (>0.45) in the central and southern arid regions when compared to the northern parts (<−0.40). The t2m correlation shows a consistent and rather strong correlation with the PC1 than soil moisture. The correlation coefficients are stronger in the south and northern parts (>0.50), whereas no negative relationship was observed. From Figure 7, it can be inferred that strong land–atmosphere coupled processes affect the convective activities and precipitation due to local effects. Positive soil moisture and temperature correlation imply strong control of soil moisture on energy partitioning and transfer of water vapors to the atmosphere through latent heat fluxes, which upon condensation, affect the precipitation [10,67,68].
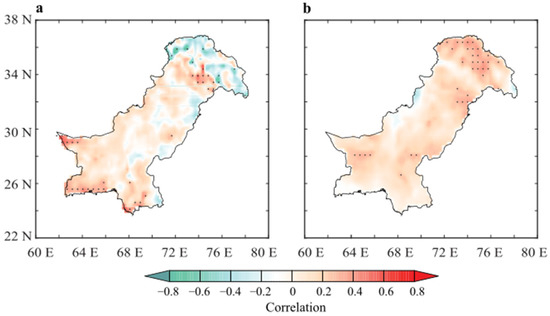
Figure 7.
Pixel-wise correlation of the PC1 and seasonal (a) soil moisture and (b) 2-m temperature at interannual scale during 1981–2018.
In Figure 8, we have shown the correlation between PC1 and 500 hPa relative vorticity and vertical velocity to relate the precipitation variability with ascending motion and convective activities driven by local effects, large-scale circulations, and oceanic forcing. The result shows a moderate to weaker negative correlation in the eastern and a positive correlation between relative vorticity (Figure 8a) and the PC1 over the northern and southern parts. A significant negative correlation can be seen in the tropical Indian Ocean, Bay of Bengal, and warm pool region. The vertical velocity (Figure 8b) also showed a significant negative (<−0.65) correlation over the study region and a positive correlation (>0.70) in the Bay of Bengal, warm pool regions of the western Pacific, and some continental regions. The significant positive/negative correlation between the PC1 and the relative vorticity and vertical velocity implies a direct relationship between cyclonic motion and a convective ascent of the wind over the study region, including the Arabian Sea and descending anticyclonic flow over the adjacent continental and Oceanic regions.
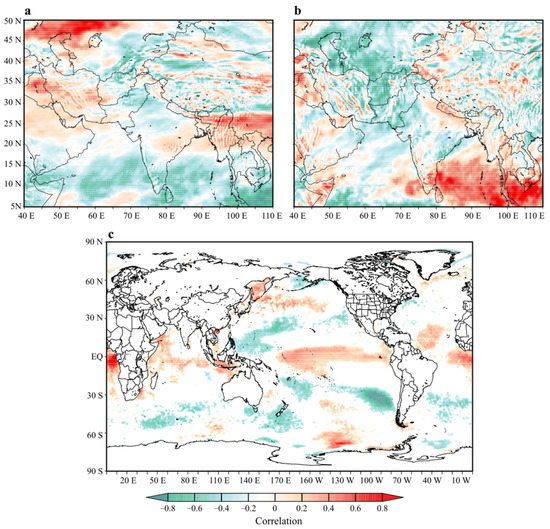
Figure 8.
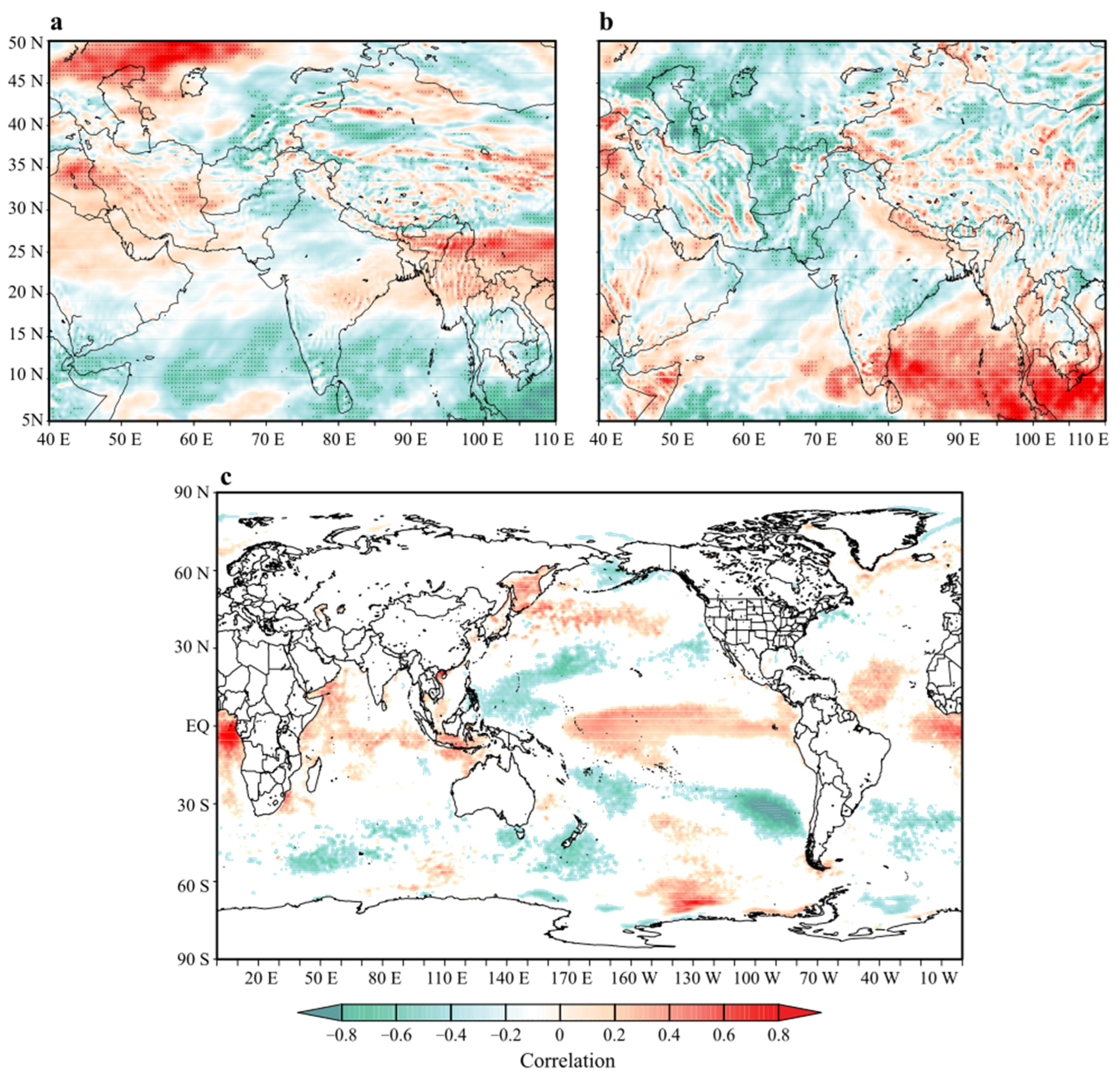
Pixel-wise correlation of the winter precipitation PC1 at interannual scale with (a) vorticity, (b) vertical velocity, and (c) SST during 1981–2018. The shaded regions are significant at a 95% significance level.
Furthermore, the SST coupling with the atmosphere may impact the geographical location of the anticyclone and corresponding circulations as an interaction affecting the precipitation [28,29]. To explore the role of SST forcing with emphasis on the Indian and Pacific Oceans, we have further correlated the PC1 with the average SST during December, January, and February (DJF), as highlighted by Syed et al. [28] and Yadav et al. [29]. The correlation between the PC1 and the DJF SST is shown in Figure 8c, where the shaded regions refer to significant correlations with SST (95% confidence). The results show a significant correlation between the PC1 and the SST in the tropical and western Arabian Sea and the horn of the African region of the Indian Ocean. A rather large geographical region in the central Pacific Ocean is significantly (>0.40) correlated with the PC1. Furthermore, it is important to note that in Figure 8, some regions, such as the southern Atlantic off the coast of western Africa, have positive correlation values, which simply are statistical noise or outliers that do not reflect a meaningful relationship.
The strength of the Pacific Ocean correlation corresponds to El Niño’s Southern Oscillation’s geographical location (ENSO-Nino-3.4), inferring that the above-normal SST in the central Pacific has a direct relationship with the winter precipitation over Pakistan. The Indian Ocean SST may represent the effect of the Indian Ocean basin-wide effect [69,70], as a consequence of the Pacific Ocean SST impacting the western Indian Ocean SST, resulting in a positive correlation. Some regions in the southern Pacific and eastern Pacific exhibited a negative correlation, and some regions in the north Pacific showed a significantly positive correlation with the PC1, these effects need a much more robust analysis for an analytical impact assessment and hence will not be discussed here. This relationship might be inferred to be impacting the Walker and Hadley cell in the tropical lower-latitude circulation domain, which is also suggested by previous studies [28,29,66].
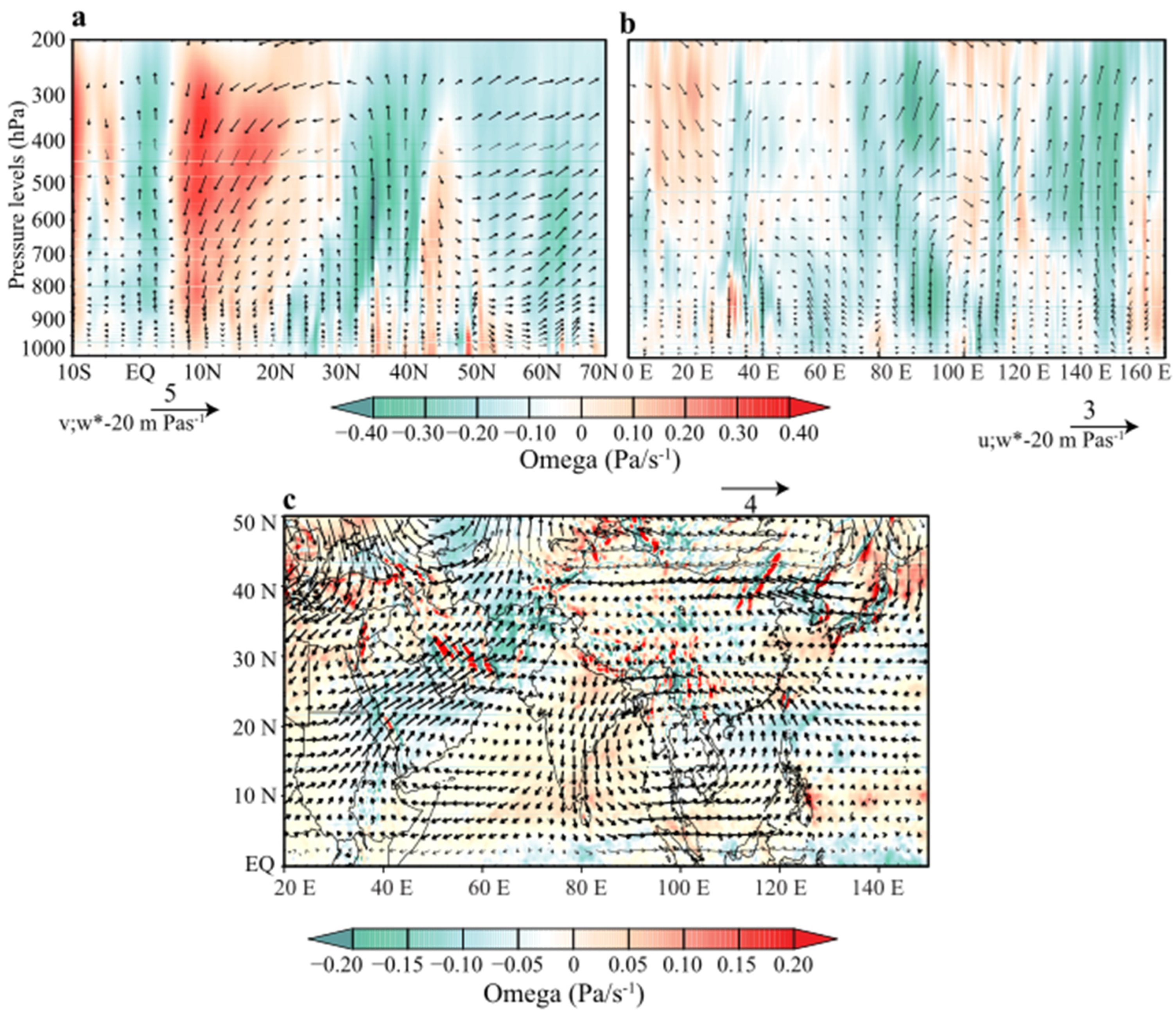
The relationship between the Walker and Hadley cells and precipitation is explored here with a composite analysis where the positive and negative years are derived from the PC1 (Figure 6b). The years with positive z-score deviations (1988, 1989, 2001, 2003, and 2011) and negative z-score deviations (1984, 1996, 2000, 2014, and 2018) are wet and dry composites, respectively. The respective extreme deviations of the PC1 standardized values during these years will easily identify potential anomalous patterns. To show the composite mean difference of the Hadley and Walker cells’ intensity during the wet and dry years, we calculated the composite mean difference of the wet and dry years from PC1 by simply subtracting the composite mean of the negative composite from the positive composite. Figure 9a shows that the Hadley cell composite difference results in a strong ascent over Pakistan (20° N–40° N), implying that the central Pacific SST is more favorable for the above-normal precipitation in Pakistan. The Walker cell (Figure 9b) intensity shows an intensified ascent across the 60° E to 95° E, covering the whole of Pakistan, which could be inferred as the potential driver of the dominant mode of precipitation variability.
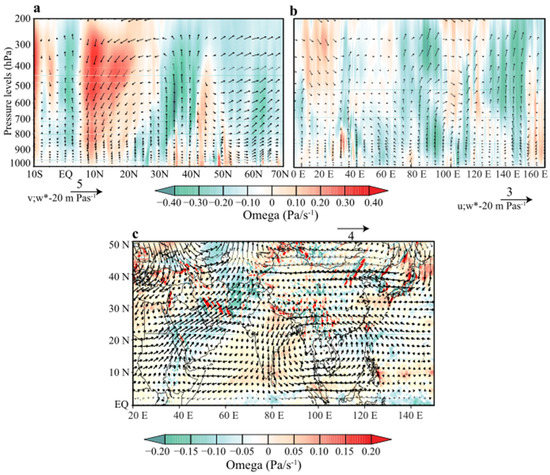
Figure 9.
Zonal and meridional wind (vectors) and vertical velocity (shaded) representing (a) Hadley cell composite difference averaged between 60° E and 80° E. The (b) Walker cell composite difference for the wet and dry composites averaged between 0–5° N. The (c) 500 hPa zonal and meridional wind (vectors) and vertical velocity (shaded) c composite difference between the wet and dry years during 1981–2018.
The Hadley and Walker circulations’ geographical movement during the wet and dry composites could impact the precipitation modes and their variability over Pakistan. The relevant dynamic peaks and troughs in the temporal precipitation variability can be associated with ENSO events, especially in the central Pacific Ocean [28,66]. The 500 hPa wind components (vectors) and vertical velocity (shaded) composite difference (Figure 9c) are further calculated to show the mid-tropospheric circulation pattern driven by the Hadley and Walker cells. The 500 hPa south westerlies jet streams, due to the intensified Hadley and Walker cell, are much stronger, and they ascend toward the study region and transport above normal water vapor content for precipitation. The vertical velocity shows an intensified ascent over Pakistan, indicating that the Oceanic forcing from the central Pacific Ocean and the western Indian Ocean mostly drives the leading mode of the precipitation variability.
4. Discussion
This study examines the changes in the daily winter precipitation on a seasonal (DJFM) and sub-seasonal monthly scale during 1981–2018 using observations from 50 in situ rain gauges and reanalysis of the land atmosphere and ocean. The analysis tools included non-parametric and parametric techniques such as Sen slope, modified Mann Kendall and kernel-based probability density function, EOF and composite analysis, including the atmospheric circulations and oceanic forcing.
The results show a decreasing trend (SSE: −0.1 mm d−1 yr−1) in the seasonal precipitation over central and southern Pakistan whereas a significant increase in the northern parts is evident (SSE: >0.1 mm d−1 yr−1). The daily maximum precipitation has increased and heavy precipitating days have also decreased, indicting an increase in wet days and decrease in the overall intensity and magnitude. Except in February, the monthly precipitation also shows a significant decrease in the arid regions of the country. The out-of-phase trend in northern Pakistan could be due to the terrain with limited spatial gauge density, restraining detailed insights into the trend variability [2,34]. Other forcings could include local land effects such as soil moisture and temperature, large-scale circulation, and Ocean forcing [65,71]. The decrease in the daily precipitation is much more significant than those reported for the summer monsoon season in the region, implying that the region has faced droughts during winter with severe precipitation-induced flash flood losses during summer [5,45,72,73]. The decrease in regional precipitation may also impact perennial river flows in the summer. On the other hand, the arid region’s agriculture and water resources may benefit from the moderate increase in precipitation during February [8,36,64].
The decreasing precipitation during the winter season in Pakistan has significant implications for crop water requirements, river flow, and sectoral uses, such as for industrial and domestic applications [37]. The water resources, cropping pattern, and socio-economic aspects are challenged by the changing hydrometeorological cycle [74,75,76,77,78]. The changing seasonality and mean precipitation maxima shift toward the west has been reported in many studies [2,14,79,80]. Further studies have reported an increase in precipitation magnitude in southeastern Pakistan and a decrease in the central Indus basin [3,19,81]. The northern and northeastern plateau of the region has experienced an increase in the overall extreme precipitation and in monsoon precipitation specifically [45,76]. The North Atlantic Oscillations (NAO) and ENSO mutual forcing are further indicators of the winter precipitation variability over Pakistan intensifying the western disturbances, as they encounter a low-pressure trough. The warm phase of the ENSO and positive NAO could extend the mean precipitation magnitude through enhanced moisture supply from the Arabian sea and Mediterranean region [28]. The ENSO warm phase enhances the precipitation through an intensified Walker cell and an anomalous ascent over the region [66]. These findings are further supported by another study by Library et al. [57] over India showing a significant influence of the ENSO warm phase on the mean precipitation variability.
The decreasing precipitation and changes in sub-seasonal mean would affect the water resources of the region with long-term consequences for crop production, cropping patterns, and community level adaptation would be in a state of uncertainty [38,82]. The uncertainties in trend and variability in mean magnitude are due to the latitudinal and longitudinal diversity of the study region, where the response of different land cover, climate classes, precipitation, and temperature towards global warming varies. The regional climate change threats include an intense frequency of hailstorms, windstorms, heatwaves, droughts, floodings, and diseases. The regional crop productivity is challenged in rainfed and irrigated agriculture, where a uniform increase in temperature and uncertain precipitation are challenging factors [32,36,38]. The regional dependency on the perennial river water supply from the Indus basin upstream glaciers would be challenged by increasing the sectoral water demand. The water supply exhibits significant deviations from the intra-seasonal scale, with less adequate and unreliable supplies in the Kharif than the Rabi season. The rainfed agriculture anticipated losses would peak due to uncertain precipitation mean at the critical crop growth cycle [8,83]. The increased socio-economic growth, agriculture activities, population, urban sprawl, and external climate change factors will result in an imbalance of regional water supply and demand [32,84,85]. Further studies should explore the projected changes in winter precipitation under different emissions scenarios for a long-term assessment and policy-making implications.
5. Conclusions
Based on the analyses of this study, it can be concluded that the winter seasonal mean and sub-seasonal daily precipitation significantly decreased in Pakistan during 1981–2018. Spatially, the highest decrease in daily precipitation (<−0.1 mm d−1 yr−1) was in the north, with a moderate decrease in the southeast. The maximum daily precipitation in February significantly increased in the northern westerlies-dominant region. Temporally, the seasonal and sub-seasonal precipitation exhibited the highest deviations during the drought period (1995–2000) and a moderate increase in the extremes after the drought phase. The dominant mode of precipitation variability is sensitive to local convection driven by land–atmosphere coupled processes that involve soil moisture and temperature. The Oceanic forcing from the ENSO-Nino3.4 and the Indian Ocean basin-wide SST are leading drivers of the precipitation variability, which therefore impact the Hadley, Walker cell’s zonal movement, and subtropical westerlies’ moisture-rich wind. These trends/changes have likely caused a decline in agricultural production, challenging food, and water security. Similarly, the increasing socioeconomic growth, agricultural activities, population, urban sprawl, and external climate change factors will result in an imbalance of regional water supply and demand [39,84,86,87,88,89]. A detailed assessment of the sectoral impact of the decreasing precipitation trend is suggested for future studies. Furthermore, using the observation data as a baseline, projected changes in the winter precipitation need to be explored using the coupled model intercomparison project version 6 (CMIP6) data.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w15132420/s1, Figure S1. Box and Whisker plot of the Coefficient of variability for seasonal mean and monthly precipitation over northern Pakistan during 1981–2018: (a) Seasonal, (b) December, (c) January, (d) February, and (e) March. The box plot spans from the first quartile Q1 to the third quartile Q3, which is the interquartile range (IQR = Q3-Q1). The horizontal line inside each box is the median whereas the line extending from the boxplot in both directions are whiskers. Figure S2. Kernal-based Probability density function plot of the winter precipitation at (a) seasonal mean and sub-seasonal scales (b) December, (c) January, (d) February, and (e) March over northern Pakistan during 1981–2018 and first decade; 1981–1990, second decade; 1991–2000, third decade; 2001–2010, and fourth decade; 2011–2018. Table S1. The station description located in the northern Pakistan.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed significantly to the preparation of this manuscript. Conceptualization, A.A. (Adnan Abbas), S.U. and W.U.; methodology, A.A. (Adnan Abbas), S.U., W.U. and G.A.; software, A.K., G.A. and A.S.B.; validation, S.U., M.A.J. and A.A. (Amjad Ali); formal analysis, A.A. (Adnan Abbas), S.U. and W.U.; investigation, A.K., M.W., M.A.J. and A.A. (Amjad Ali); resources, W.U. and C.Z.; data curation, G.A., A.S.B. and A.A. (Adnan Abbas); writing—original draft preparation, A.A. (Adnan Abbas), S.U. and W.U.; writing—review and editing, M.W. and M.A.J.; visualization, W.U. and A.S.B.; supervision, C.Z.; project administration, A.A. (Adnan Abbas), W.U. and C.Z.; funding acquisition, W.U. and C.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation, grant number 42130405; the Innovative and Entrepreneurial Talent Program of Jiangsu Province, grant number R2020SC04; and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, grant number XDA2006030201.
Data Availability Statement
The observed precipitation data can be obtained from the Pakistan Meteorological Department upon a formal request, while the ERA5 data can be obtained from https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/home (accessed on 5 September 2022).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Rabdan Academy for their support in Article Processing Charges. We also extend our special gratitude to the Pakistan Meteorological Department (PMD) and the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) ERA5 for granting access to this essential dataset through their specific data use and citation policies.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Eckstein, D.; Kreft, S. Global Climate Risk Index 2021. Who Suffers Most from Extreme Weather Events? Germanwatch: Bonn, Germany, 2020; ISBN 978-3-94370-414-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, S.; You, Q.; Ullah, W.; Ali, A. Observed Changes in Precipitation in China-Pakistan Economic Corridor during 1980–2016. Atmos. Res. 2018, 210, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.; Nasim, W.; Mubeen, M.; Kazmi, D.H.; Lin, Z.; Wahid, A.; Sultana, S.R.; Gibbs, J.; Fahad, S. Comparison of Future and Base Precipitation Anomalies by SimCLIM Statistical Projection through Ensemble Approach in Pakistan. Atmos. Res. 2017, 194, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J.; Toma, V.E.; Kim, H.M. Were the 2010 Pakistan Floods Predictable? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, K.L.; Hill, A.J.; Toma, V.E.; Zuluaga, M.D.; Webster, P.J.; Houze, R.A. Multiscale Analysis of Three Consecutive Years of Anomalous Flooding in Pakistan. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 1259–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; You, Q.; Ullah, W.; Ali, A.; Xie, W.; Xie, X. Observed Changes in Temperature Extremes over China–Pakistan Economic Corridor during 1980–2016. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 1457–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Waqas, T.; Samiullah; Ullah, S. Precipitation Variability and Its Trend Detection for Monitoring of Drought Hazard in Northern Mountainous Region of Pakistan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, M.; Ahmad, M.u.D.; Mainuddin, M.; Khaliq, T.; Cheema, M.J.M. Agricultural Production, Water Use and Food Availability in Pakistan: Historical Trends, and Projections to 2050. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, R.; Jia, S. Assessment of Impacts of Climate Change on the Water Resources of the Transboundary Jhelum River Basin of Pakistan and India. Water 2016, 8, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; You, Q.; Sachindra, D.A.; Nowosad, M.; Ullah, W.; Bhatti, A.S.; Jin, Z.; Ali, A. Spatiotemporal Changes in Global Aridity in Terms of Multiple Aridity Indices: An Assessment Based on the CRU Data. Atmos. Res. 2022, 268, 105998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, W.; Wang, G.; Lou, D.; Ullah, S.; Bhatti, A.S.; Ullah, S.; Karim, A.; Hagan, D.F.T.; Ali, G. Large-Scale Atmospheric Circulation Patterns Associated with Extreme Monsoon Precipitation in Pakistan during 1981–2018. Atmos. Res. 2021, 253, 105489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Adnan, S.; Latif, M. Impact of Jet Stream and Associated Mechanisms on Winter Precipitation in Pakistan. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2020, 132, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Chung, E.S.; Ismail, T.; Wang, X.J. Spatial Distribution of Secular Trends in Annual and Seasonal Precipitation over Pakistan. Clim. Res. 2017, 74, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmat, U.; Athar, H.; Nabeel, A.; Latif, M. An AOGCM Based Assessment of Interseasonal Variability in Pakistan. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 50, 349–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Ullah, S.; Ullah, W.; Waseem, M.; Dou, X.; Zhao, C.; Karim, A.; Zhu, J.; Hagan, D.F.T.; Bhatti, A.S.; et al. Evaluation and Projection of Precipitation in Pakistan Using the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 Model Simulations. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 6665–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimri, A.P.; Niyogi, D.; Barros, A.P.; Ridley, J.; Mohanty, U.C.; Yasunari, T.; Sikka, D.R. Western Disturbances: A Review. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.M.R.; Turner, A.G.; Shaffrey, L.C. The Evolution, Seasonality and Impacts of Western Disturbances. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Waseem, M.; Ullah, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, J. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Meteorological and Hydrological Droughts and Their Propagations. Water 2021, 13, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, F.; Ahmad, A.; Safeeq, M.; Ali, S.; Saleem, F.; Hammad, H.M.; Farhad, W. Changes in Precipitation Extremes over Arid to Semiarid and Subhumid Punjab, Pakistan. Appl. Clim. 2014, 116, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, F.; Khokhar, M.F.; Mahmood, F.; Khan, M.Z.A.; Arshad, M. Observed and Predicted Precipitation Variability across Pakistan with Special Focus on Winter and Pre-Monsoon Precipitation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 4510–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.M.R.; Turner, A.G.; Shaffrey, L.C. Falling Trend of Western Disturbances in Future Climate Simulations. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 5037–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, J.; Wiltshire, A.; Mathison, C. More Frequent Occurrence of Westerly Disturbances in Karakoram up to 2100. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 468–469, S31–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midhuna, T.M.; Kumar, P.; Dimri, A.P. A New Western Disturbance Index for the Indian Winter Monsoon. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 129, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Dubey, A.K.; Das, S. Identifying the Changes in Winter Monsoon Characteristics over the Indian Subcontinent Due to Arabian Sea Warming. Atmos. Res. 2022, 273, 106162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Bhatti, A.S.; Ullah, S.; Ullah, W.; Waseem, M.; Zhao, C.; Dou, X.; Ali, G. Projection of Precipitation Extremes over South Asia from CMIP6 GCMs. J. Arid. Land 2023, 15, 274–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamal, K.; Sharma, S.; Baniya, B.; Khadka, N.; Zhou, X. Inter-Annual Variability of Winter Precipitation Over Nepal Coupled with Ocean-Atmospheric Patterns During 1987–2015. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.K.; Rupa Kumar, K.; Rajeevan, M. Characteristic Features of Winter Precipitation and Its Variability over Northwest India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 121, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, F.S.; Giorgi, F.; Pal, J.S.; Keay, K. Regional Climate Model Simulation of Winter Climate over Central–Southwest Asia, with Emphasis on NAO and ENSO Effects. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.K.; Rupa Kumar, K.; Rajeevan, M. Increasing Influence of ENSO and Decreasing Influence of AO/NAO in the Recent Decades over Northwest India Winter Precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, 12112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.M.R.; Curio, J.; Turner, A.G.; Schiemann, R. Subtropical Westerly Jet Influence on Occurrence of Western Disturbances and Tibetan Plateau Vortices. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 8629–8636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Wang, X.; Nawaz, N.; Khan, N. Spatiotemporal Changes in Aridity of Pakistan during 1901–2016. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 3081–3096. Available online: hess.copernicus.org (accessed on 20 February 2023). [CrossRef]
- Azmat, M.; Ilyas, F.; Sarwar, A.; Huggel, C.; Vaghefi, S.A.; Hui, T.; Qamar, M.U.; Bilal, M.; Ahmed, Z. Impacts of Climate Change on Wheat Phenology and Yield in Indus Basin, Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Dastgeer, G. Analysing the Impacts of Climate Variability on the Yield of Kharif Rice over Punjab, Pakistan. Nat. Resour. Forum 2021, 45, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Cao, J.; Hussain, I.; Begum, S.; Akhtar, M.; Wu, X.; Guan, Y.; Zhou, J. Observed Trends and Variability of Temperature and Precipitation and Their Global Teleconnections in the Upper Indus Basin, Hindukush-Karakoram-Himalaya. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaque, W.; Osman, R.; Hafiza, B.S.; Malghani, S.; Zhao, B.; Xu, M.; Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T. Quantifying the Impacts of Climate Change on Wheat Phenology, Yield, and Evapotranspiration under Irrigated and Rainfed Conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 275, 108017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U.; Wang, J.; Ullah, A.; Ishtiaque, A.; Javed, T.; Nurgazina, Z. The Impact of Climate Change on the Economic Perspectives of Crop Farming in Pakistan: Using the Ricardian Model. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 308, 127219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.; Raza, T.; Bhatti, T.T.; Eash, N.S. Climate Impacts on the Agricultural Sector of Pakistan: Risks and Solutions. Environ. Chall. 2022, 6, 100433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvar-Beltrán, J.; Heureux, A.; Soldan, R.; Manzanas, R.; Khan, B.; Dalla Marta, A. Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on Wheat and Sugarcane with the AquaCrop Model along the Indus River Basin, Pakistan. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 253, 106909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, K.U.; Hussain, A.; Ejaz, N.; Shang, S.; Balkhair, K.S.; Jan Khan, K.U.; Khan, M.A.; Rehman, N.U.; Rahman, K.U.; Hussain, A.; et al. Analysis of Production and Economic Losses of Cash Crops under Variable Drought: A Case Study from Punjab Province of Pakistan. IJDRR 2023, 85, 103507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, M.; Rashid Ahmed, S.; Ahmed, M. Enhancing Water Use Efficiency and Grain Yield of Wheat by Optimizing Irrigation Supply in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions of Pakistan. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; You, Q.; Ali, A.; Ullah, W.; Jan, M.A.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, W.; Xie, X. Observed Changes in Maximum and Minimum Temperatures over China- Pakistan Economic Corridor during 1980–2016. Atmos. Res. 2019, 216, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; You, Q.; Ullah, W.; Hagan, D.F.T.; Ali, A.; Ali, G.; Zhang, Y.; Jan, M.A.; Bhatti, A.S.; Xie, W. Daytime and Nighttime Heat Wave Characteristics Based on Multiple Indices over the China–Pakistan Economic Corridor. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 6329–6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.F.; Athar, H. Variability, Trends, and Teleconnections of Observed Precipitation over Pakistan. Appl. Clim. 2018, 134, 613–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.I.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.J.; Khattak, M.U.K.; Yong, B.; Vergara, H.J. Evaluation of Three High-Resolution Satellite Precipitation Estimates: Potential for Monsoon Monitoring over Pakistan. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, A.S.; Wang, G.; Ullah, W.; Ullah, S.; Hagan, D.F.T.; Nooni, I.K.; Lou, D.; Ullah, I. Trend in Extreme Precipitation Indices Based on Long Term In Situ Precipitation Records over Pakistan. Water 2020, 12, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toreti, A.; Kuglitsch, F.G.; Xoplaki, E.; Della-Marta, P.M.; Aguilar, E.; Prohom, M.; Luterbacher, J. A Note on the Use of the Standard Normal Homogeneity Test to Detect Inhomogeneities in Climatic Time Series. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 630–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.H.; Deni, S.M. Homogeneity Test on Daily Rainfall Series for Malaysia. MATEMATIKA Malays. J. Ind. Appl. Math. 2013, 29, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ullah, S.; Meng, X.; Chen, G. Performance Evaluation of ERA5 Extreme Precipitation in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Alexander, L.; Hegerl, G.C.; Jones, P.; Tank, A.K.; Peterson, T.C.; Trewin, B.; Zwiers, F.W. Indices for Monitoring Changes in Extremes Based on Daily Temperature and Precipitation Data. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H.; Ramachandra Rao, A. A Modified Mann-Kendall Trend Test for Autocorrelated Data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, G.; Bao, Y.; Ullah, W.; Ullah, S.; Guan, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Lei, Y.; Li, G.; Ma, J. Spatiotemporal Trends of Aerosols over Urban Regions in Pakistan and Their Possible Links to Meteorological Parameters. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A.; Lintner, B.R.; Findell, K.L.; Malyshev, S.; Loikith, P.C.; Gentine, P. Impact of Soil Moisture–Atmosphere Interactions on Surface Temperature Distribution. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 7976–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, K.A.; Alemohammad, S.H.; Akbar, R.; Konings, A.G.; Yueh, S.; Entekhabi, D. The Global Distribution and Dynamics of Surface Soil Moisture. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Storch, H.; Zwiers, F.W. Statistical Analysis in Climate Research. In Statistical Analysis in Climate Research; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimri, A.P. Relationship between ENSO Phases with Northwest India Winter Precipitation. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 1917–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.C.; Rana, S. Interannual Variability of Winter Precipitation over Northwest India and Adjoining Region: Impact of Global Forcings. Appl. Clim. 2014, 116, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, S.; Schneider, T. Monsoons as Eddy-Mediated Regime Transitions of the Tropical Overturning Circulation. Nature Geoscience 2008, 1, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.; Bischoff, T.; Haug, G.H. Migrations and Dynamics of the Intertropical Convergence Zone. Nature 2014, 513, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachnik, J.P.; Schumacher, C. A Comparison of the Hadley Circulation in Modern Reanalyses. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 22102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, V.; Shukla, J. Intraseasonal and Interannual Variability of Rainfall over India. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 4366–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, R.; Lau, K.-M. Interannual Variability of the Asian Summer Monsoon: Contrasts between the Indian and the Western North Pacific–East Asian Monsoons. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 4073–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Yadav, B.P.; Gahlot, S.; Singh, M. Winter Frequency of Western Disturbances and Precipitation Indices over Himachal Pradesh, India: 1977–2007. Atmósfera 2015, 28, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Babovic, V. Analysis of Variability and Trends of Precipitation Extremes in Singapore during 1980–2013. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.K.; Ramu, D.A.; Dimri, A.P. On the Relationship between ENSO Patterns and Winter Precipitation over North and Central India. Glob. Planet Chang. 2013, 107, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Chen, H.; Li, G.; Ma, H.; Li, X.; Long, S.; Xu, B.; Li, X.; Zeng, X.; Yan, H.; et al. Land–Atmosphere Interaction over the Indo-China Peninsula during Spring and Its Effect on the Following Summer Climate over the Yangtze River Basin. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 6181–6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, D.F.T.; Wang, G.; Liang, X.S.; Dolman, H.A.J. A Time-Varying Causality Formalism Based on the Liang–Kleeman Information Flow for Analyzing Directed Interactions in Nonstationary Climate Systems. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 7521–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Kar, S.C. Mechanism of ENSO Influence on the South Asian Monsoon Rainfall in Global Model Simulations. Appl. Clim. 2018, 131, 1449–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.E.; Ha, K.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Wang, B.; Kim, B.H.; Chung, C.E. Future Change of the Indian Ocean Basin-Wide and Dipole Modes in the CMIP5. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, B.; Talukdar, S.; Shahfahad; Mahato, S.; Mondal, J.; Sharma, P.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Rahman, A. Analyzing Trend and Forecasting of Rainfall Changes in India Using Non-Parametrical and Machine Learning Approaches. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, H.; Buchanan, H. Trends in Extreme Precipitation Events in the Indus River Basin and Flooding in Pakistan. Atmos.-Ocean 2014, 52, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, H.; Andresky, L. Flooding in the Indus River Basin—A Spatiotemporal Analysis of Precipitation Records. Glob. Planet Chang. 2013, 107, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta-ur-Rahman; Dawood, M. Spatio-Statistical Analysis of Temperature Fluctuation Using Mann–Kendall and Sen’s Slope Approach. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta-ur-Rahman; Khan, A.N. Analysis of Flood Causes and Associated Socio-Economic Damages in the Hindukush Region. Nat. Hazards 2011, 59, 1239–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Befort, D.J.; Leckebusch, G.C.; Cubasch, U. Intraseasonal Variability of the Indian Summer Monsoon: Wet and Dry Events in COSMO-CLM. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 47, 2635–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, S.M.Z.; Ammar, A. Quantification of Impact of Changes in Land Use-Land Cover on Hydrology in the Upper Indus Basin, Pakistan. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2018, 21, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Adnan, S. Classification and Assessment of Aridity Over Pakistan Provinces (1960–2009). Int. J. Environ. 2014, 3, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.M.; Manzoor, N.; Ashraf, J.; Adnan, M.; Collins, D.; Hameed, S.; Manton, M.J.; Ahmed, A.U.; Baidya, S.K.; Borgaonkar, H.P.; et al. Trends in Extreme Daily Rainfall and Temperature Indices over South Asia. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethi, B.; Ramya, R.; Patwardhan, S.K.; Mujumdar, M.; Kripalani, R.H. Variability of Indian Summer Monsoon Droughts in CMIP5 Climate Models. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 1937–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.H.B.; Shafqat, M.N.; Eqani, S.A.M.A.S.; Shah, S.T.A. Trends of Climate Change in the Upper Indus Basin Region, Pakistan: Implications for Cryosphere. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazlbash, S.K.; Zubair, M.; Manzoor, S.A.; ul Haq, A.; Baloch, M.S. Socioeconomic Determinants of Climate Change Adaptations in the Flood-Prone Rural Community of Indus Basin, Pakistan. Environ. Dev. 2021, 37, 100603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Liedl, R.; Awan, U.K. Spatio-Temporal Estimation of Consumptive Water Use for Assessment of Irrigation System Performance and Management of Water Resources in Irrigated Indus Basin, Pakistan. J. Hydrol. 2015, 525, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehboob, M.S.; Kim, Y. Effect of Climate and Socioeconomic Changes on Future Surface Water Availability from Mountainous Water Sources in Pakistan’s Upper Indus Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chau, S.; Bhattarai, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Connor, T.; Li, Y. Impacts of Irrigated Agriculture on Food–Energy–Water–CO2 Nexus across Metacoupled Systems. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ullah, S.; Pepin, N.; Ma, Q. Changes in Snow Depth under Elevation-Dependent Warming over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2021, 22, e1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, X.; Kumar, R.; Barth, M.; Diao, C.; Gao, M.; Lin, L.; Jones, B.; Meehl, G.A. Substantial Increase in the Joint Occurrence and Human Exposure of Heatwave and High-PM Hazards Over South Asia in the Mid-21st Century. AGU Adv. 2020, 1, e2019AV000103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; You, Q.; Ren, G.; Ullah, S.; Normatov, I.; Chen, D. Inequality of Global Thermal Comfort Conditions Changes in a Warmer World. Earths Future 2023, 11, e2022EF003109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, M.; Khurshid, T.; Abbas, A.; Ahmad, I.; Javed, Z. Impact of Meteorological Drought on Agriculture Production at Different Scales in Punjab, Pakistan. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2022, 13, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).