Highly Efficient Removal of Mercury Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Thiol-Functionalized Graphene Oxide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Adsorbent Preparation
2.2. Batch Experiment
2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
2.4. Adsorption Isotherm Experiments
2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
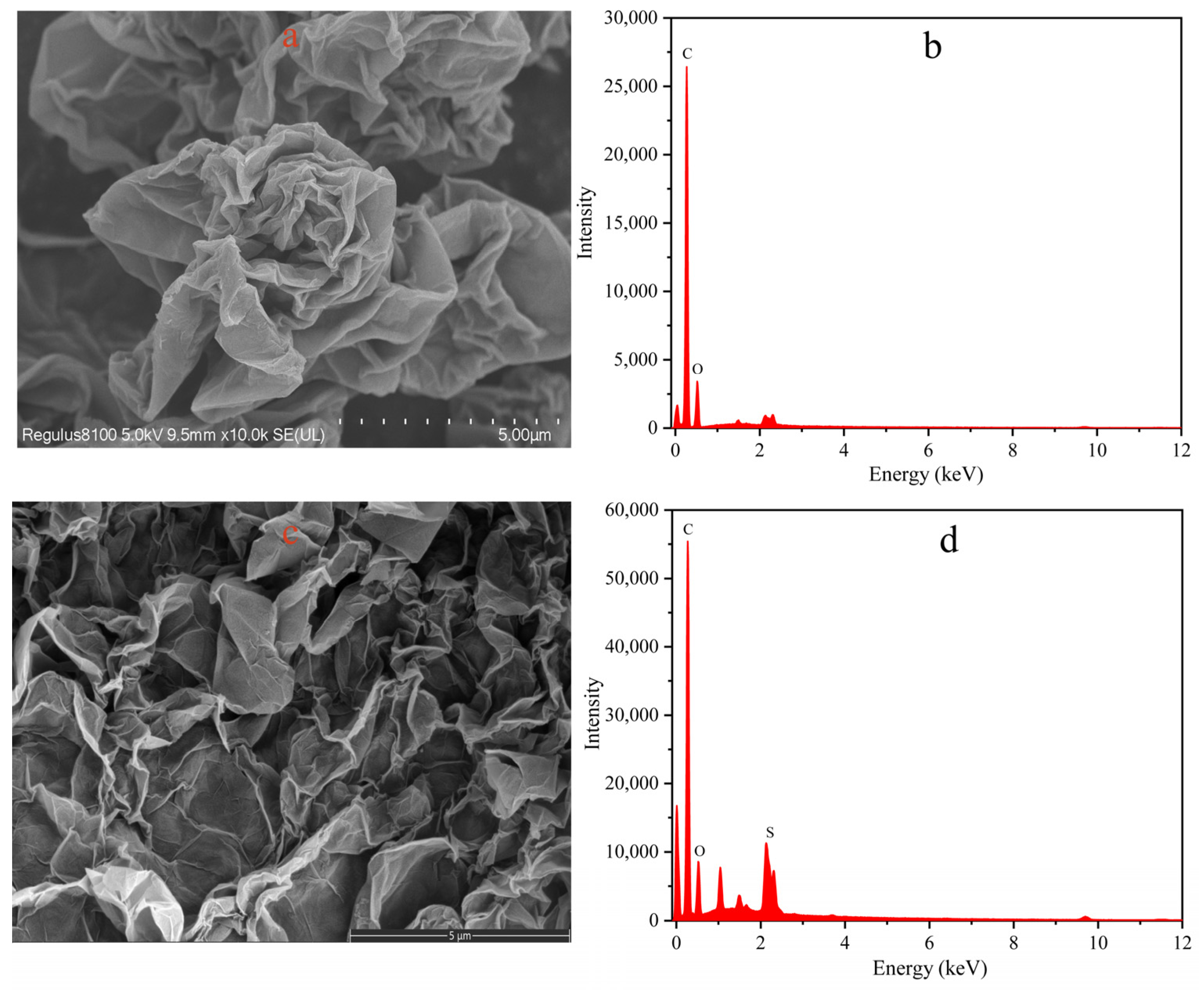
3.1. Characterization of the Prepared Materials
3.2. Adsorption Performance
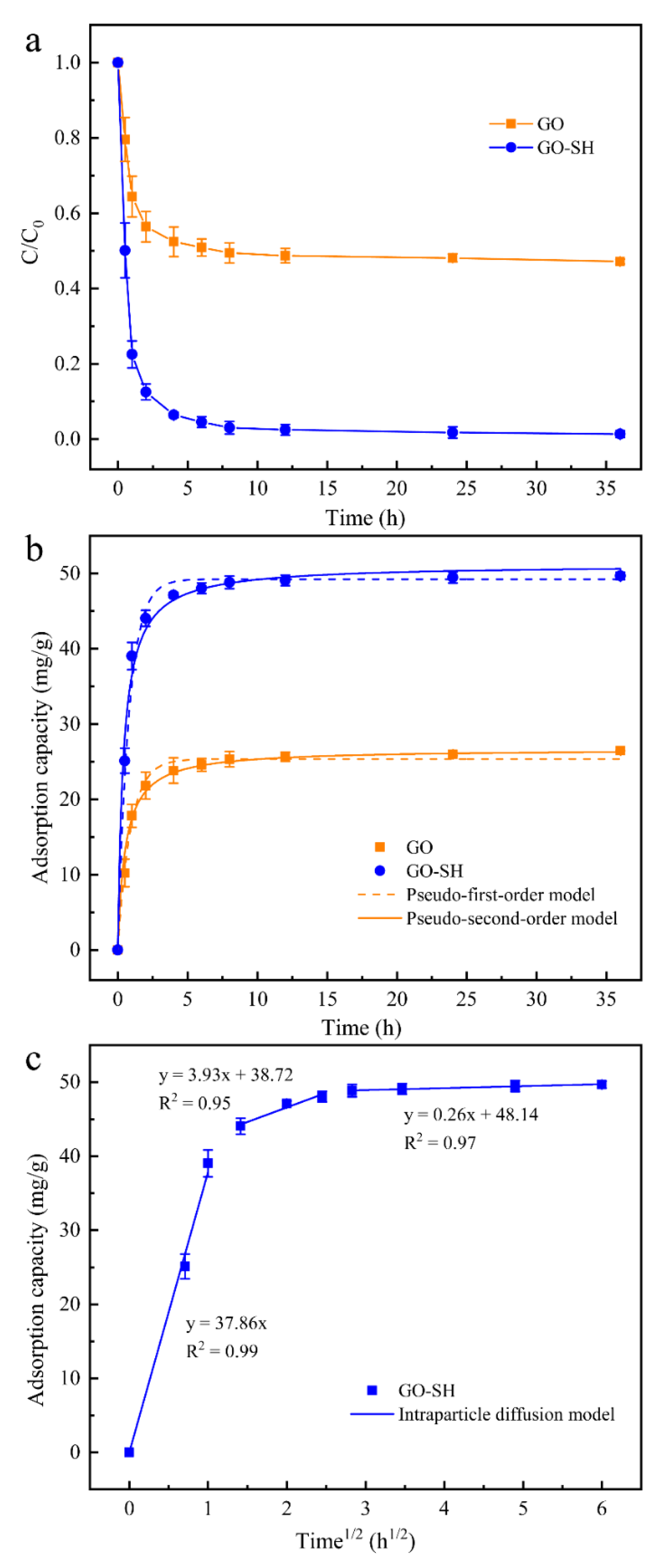
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
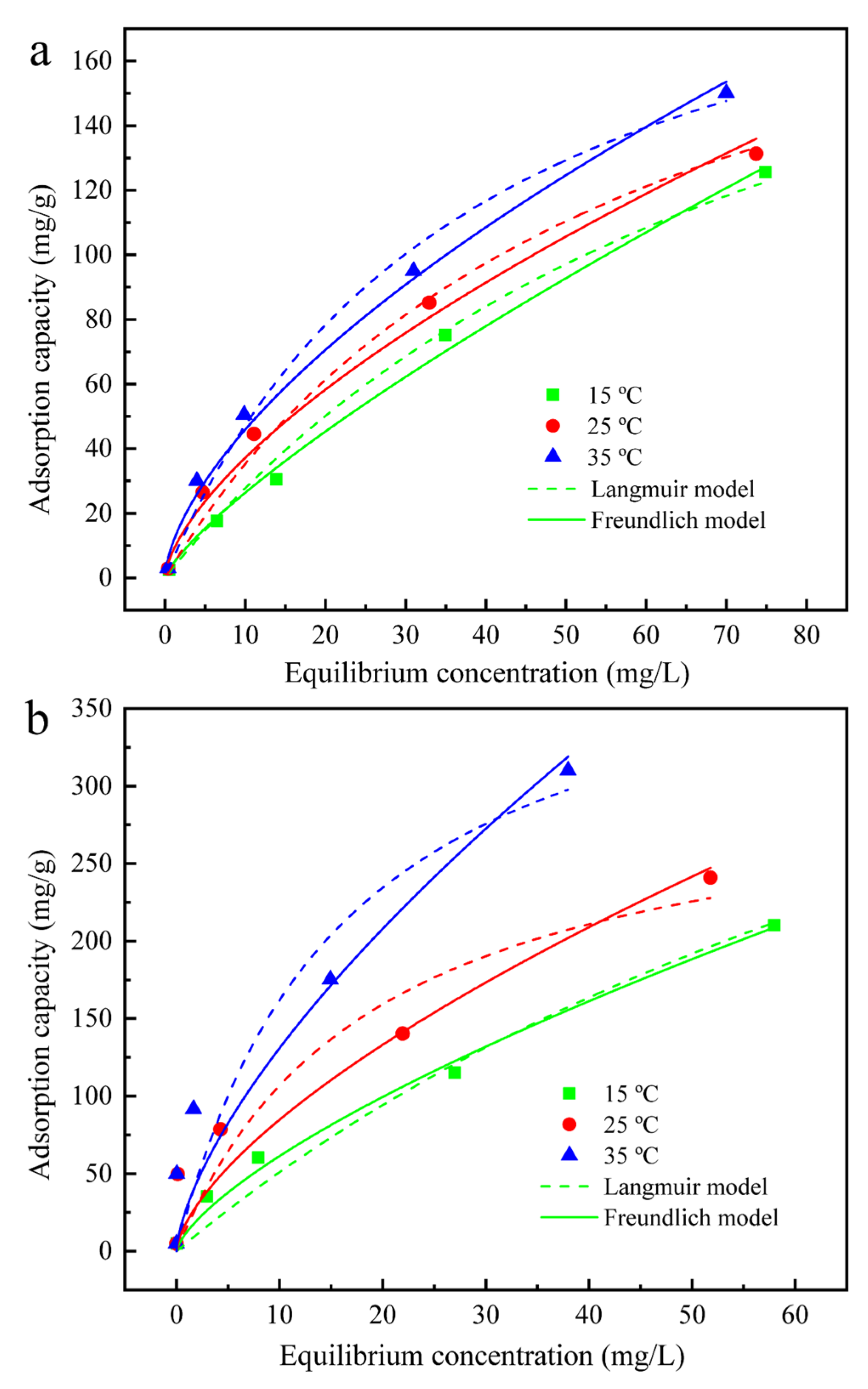
3.4. Adsorption Isotherms
3.5. Regeneration and Recyclability
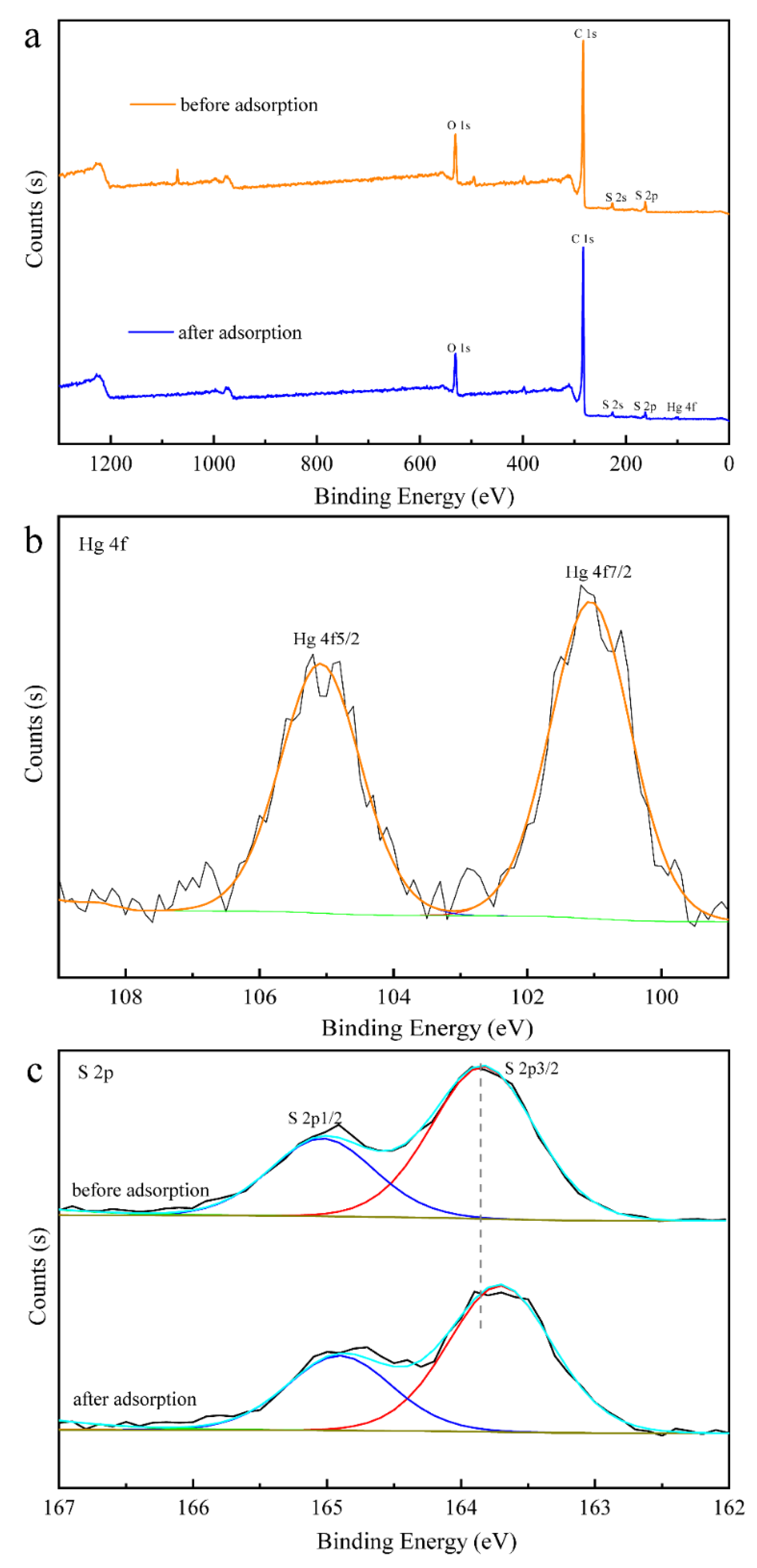
3.6. Proposed Mechanism for Adsorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Y.-X.; Kou, Y.-L.; Jin, P.-S.; Shao, W.-J.; Li, X. Adsorption of Hg(II) in aqueous solution by magnetic graphene oxide grafted polymaleicamide dendrimer nanohybrids. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdam, K.; Panahi, H.A.; Alaei, E.; Hasani, A.H.; Moniri, E. Preparation of functionalized graphene oxide and its application as a nanoadsorbent for Hg2+ removal from aqueous solution. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimohammady, M.; Ghaemi, M. Adsorptive removal of Hg2+ from aqueous solutions using amino phenyl-pyrazole-functionalized graphene oxide. Carbon Lett. 2020, 30, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Pashaei, S. Fabrication of novel magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposites for selective adsorption of mercury from aqueous solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 26807–26821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, C.; Meng, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y. A novel Sulfur-functionalized alkynyl carbon material for highly efficient removal of Hg(II) from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 290, 120891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; He, Y.; Baumann, Z.; Yu, C.; Ge, S.; Sun, X.; Cheng, M.; Shen, H.; Mason, R.P.; Chen, L.; et al. Traditional Tibetan Medicine Induced High Methylmercury Exposure Level and Environmental Mercury Burden in Tibet, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8838–8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Li, W.-K.; Zhou, Z.-P.; Li, Y.-Y.; Xiong, T.-W.; Du, Y.-Z.; Wei, L.-X.; Liu, J. The Tibetan medicine Zuotai differs from HgCl2 and MeHg in producing liver injury in mice. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 78, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Du, P.; Yu, C.; He, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Lin, H.; Luo, Y.; Xie, H.; Guo, J.; et al. Increases of Total Mercury and Methylmercury Releases from Municipal Sewage into Environment in China and Implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Singh, J.; Verma, A.; Karri, M. Precipitation of a chromium-rich α-phase in Alloy 693 and its effect on tensile properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 686, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Hu, L.; Zhong, H.; He, Z.; Sun, W.; Xiong, D. Efficient removal of Hg2+ from aqueous solution by a novel composite of nano humboldtine decorated almandine (NHDA): Ion exchange, reducing-oxidation and adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagaraj, P.; Nagendran, A.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Neelakandan, S.; Karthikkumar, T.; Muthumeenal, A. Influence of N-phthaloyl chitosan on poly (ether imide) ultrafiltration membranes and its application in biomolecules and toxic heavy metal ion separation and their antifouling properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 329, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariana, M.; Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Mistar, E.M.; Yahya, E.B.; Alfatah, T.; Danish, M.; Amayreh, M. Recent advances in activated carbon modification techniques for enhanced heavy metal adsorption. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 43, 102221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasimi, S.; Baghdadi, M.; Dorosti, M. Surface functionalization of recycled polyacrylonitrile fibers with ethylenediamine for highly effective adsorption of Hg(II) from contaminated waters. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, L.; Srivastav, A.L.; Kaushal, J.; Nguyen, X.C. Recent advances in nanomaterial developments for efficient removal of Hg(II) from water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 62851–62869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Liu, F.; Cai, C.; Wu, H.; Yang, L. Removal of Hg2+ from desulfurization wastewater by tannin-immobilized graphene oxide. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 17964–17976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, C.K.; Pumera, M. Monothiolation and Reduction of Graphene Oxide via One-Pot Synthesis: Hybrid Catalyst for Oxygen Reduction. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4193–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Gao, L.; Fu, X.; Siyal, S.H.; Sui, G.; Yang, X. Green synthesis of amino-functionalized carbon nanotube-graphene hybrid aerogels for high performance heavy metal ions removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 467–468, 1122–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.R.; Marsden, A.J.; Walker, M.; Wilson, N.R.; Rourke, J.P. Sulfur-Functionalized Graphene Oxide by Epoxide Ring-Opening. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7613–7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Jiang, J.; Sun, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Influence of the pore structure and surface chemical properties of activated carbon on the adsorption of mercury from aqueous solutions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 78, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Qi, D.; Wu, H.; Zhou, C.; Yang, H. Enhanced immobilization of mercury (II) from desulphurization wastewater by EDTA functionalized graphene oxide nanoparticles. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 1366–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tene, T.; Arias, F.A.; Guevara, M.; Nuñez, A.; Villamagua, L.; Tapia, C.; Pisarra, M.; Torres, F.J.; Caputi, L.S.; Gomez, C.V. Removal of mercury(II) from aqueous solution by partially reduced graphene oxide. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Shao, L.; Zhang, G. Adsorption of Phosphate from Aqueous Solution Using an Iron–Zirconium Binary Oxide Sorbent. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 4221–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcy, M.; Weiss, D.; Bluck, M.; Vilar, R. Adsorption kinetics, capacity and mechanism of arsenate and phosphate on a bifunctional TiO2–Fe2O3 bi-composite. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2011, 364, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H. Factors influencing adsorption and desorption of trimethoprim on marine sediments: Mechanisms and kinetics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21929–21937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragheb, E.; Shamsipur, M.; Jalali, F.; Mousavi, F. Modified magnetic-metal organic framework as a green and efficient adsorbent for removal of heavy metals. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yang, W.; Sun, Y. Cross-linked sulfydryl-functionalized graphene oxide as ultra-high capacity adsorbent for high selectivity and ppb level removal of mercury from water under wide pH range. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.; Wu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhu, N. Comparative study of Hg(II) adsorption by thiol- and hydroxyl-containing bifunctional montmorillonite and vermiculite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 356, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Absorbent | Initial Concentration (mg/L) | Equilibrium Time (min) | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified activated carbons | 24 | 500 | 2.226 | [19] |
| Partially reduced graphene oxide | 150 | 20 | 110.21 | [21] |
| Tannin-immobilized graphene oxide | 1 | 15 | 23.81 | [15] |
| EDTA functionalized graphene oxide nanoparticles | 1.2 | 160 | 18.6392 | [20] |
| GO-SH | 10 | 360 | 49.68 | This study |
| Absorbent | Temperature (°C) | Freundlich Model | Langmuir Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kF (L/g) | 1/n | R2 | Qm (mg/g) | KL (L/g) | R2 | ||
| GO | 15 | 4.35 | 0.78 | 0.99 | 259.01 | 0.01 | 0.99 |
| 25 | 8.33 | 0.65 | 0.99 | 236.61 | 0.02 | 0.98 | |
| 35 | 10.98 | 0.62 | 0.99 | 228.82 | 0.03 | 0.98 | |
| GO-SH | 15 | 12.36 | 0.70 | 0.99 | 618.27 | 0.01 | 0.96 |
| 25 | 18.99 | 0.65 | 0.91 | 312.41 | 0.05 | 0.89 | |
| 35 | 28.23 | 0.67 | 0.91 | 424.75 | 0.06 | 0.89 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Zhu, G. Highly Efficient Removal of Mercury Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Thiol-Functionalized Graphene Oxide. Water 2023, 15, 2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142529
Sun Q, Wang L, Li Y, Li L, Li S, Zhu G. Highly Efficient Removal of Mercury Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Thiol-Functionalized Graphene Oxide. Water. 2023; 15(14):2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142529
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Qi, Lixia Wang, Ying Li, Li Li, Shuping Li, and Guangcan Zhu. 2023. "Highly Efficient Removal of Mercury Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Thiol-Functionalized Graphene Oxide" Water 15, no. 14: 2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142529
APA StyleSun, Q., Wang, L., Li, Y., Li, L., Li, S., & Zhu, G. (2023). Highly Efficient Removal of Mercury Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Thiol-Functionalized Graphene Oxide. Water, 15(14), 2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142529






