Shape Factor for Analysis of a Slug Test
Abstract
:1. Introduction
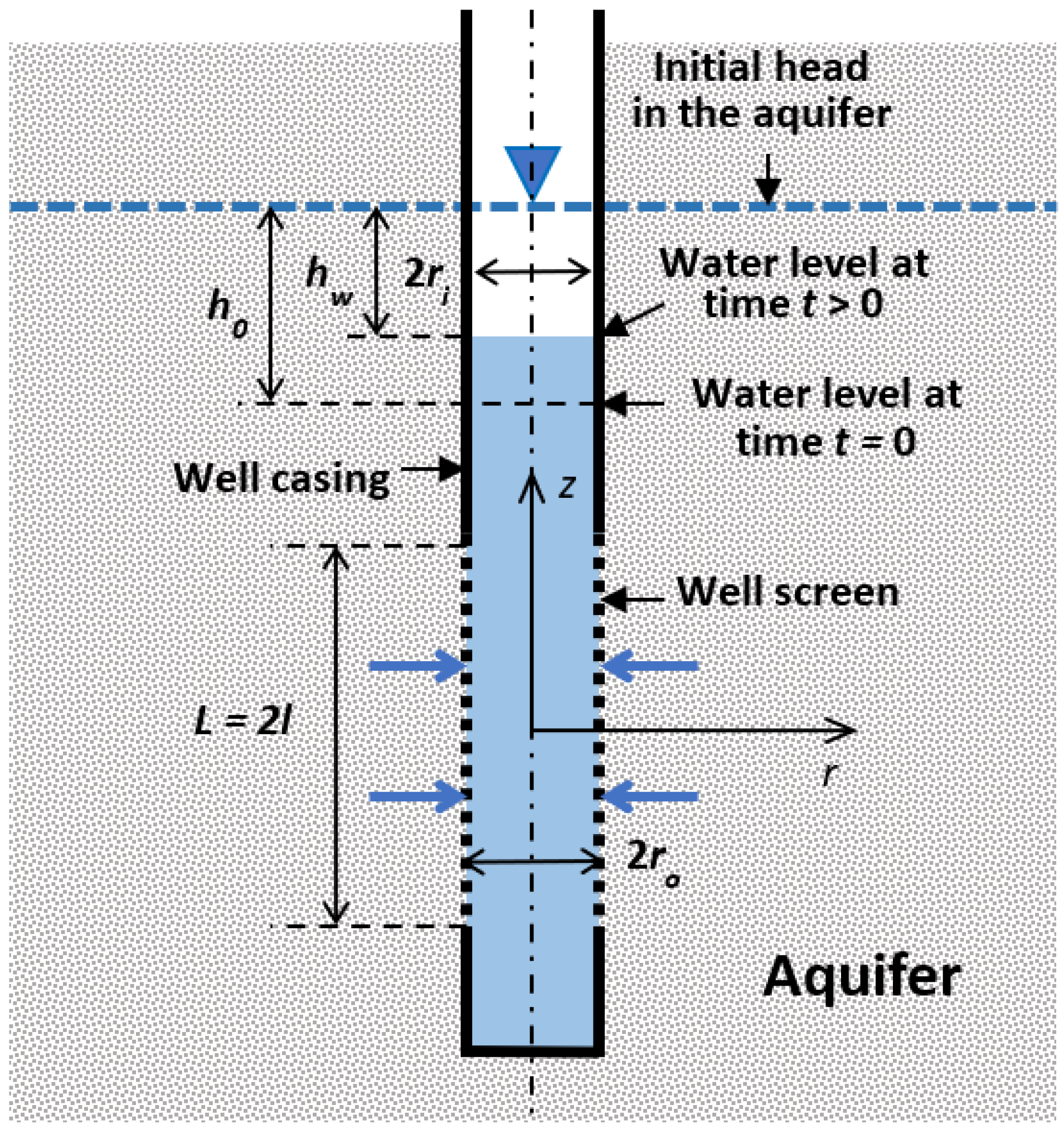
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
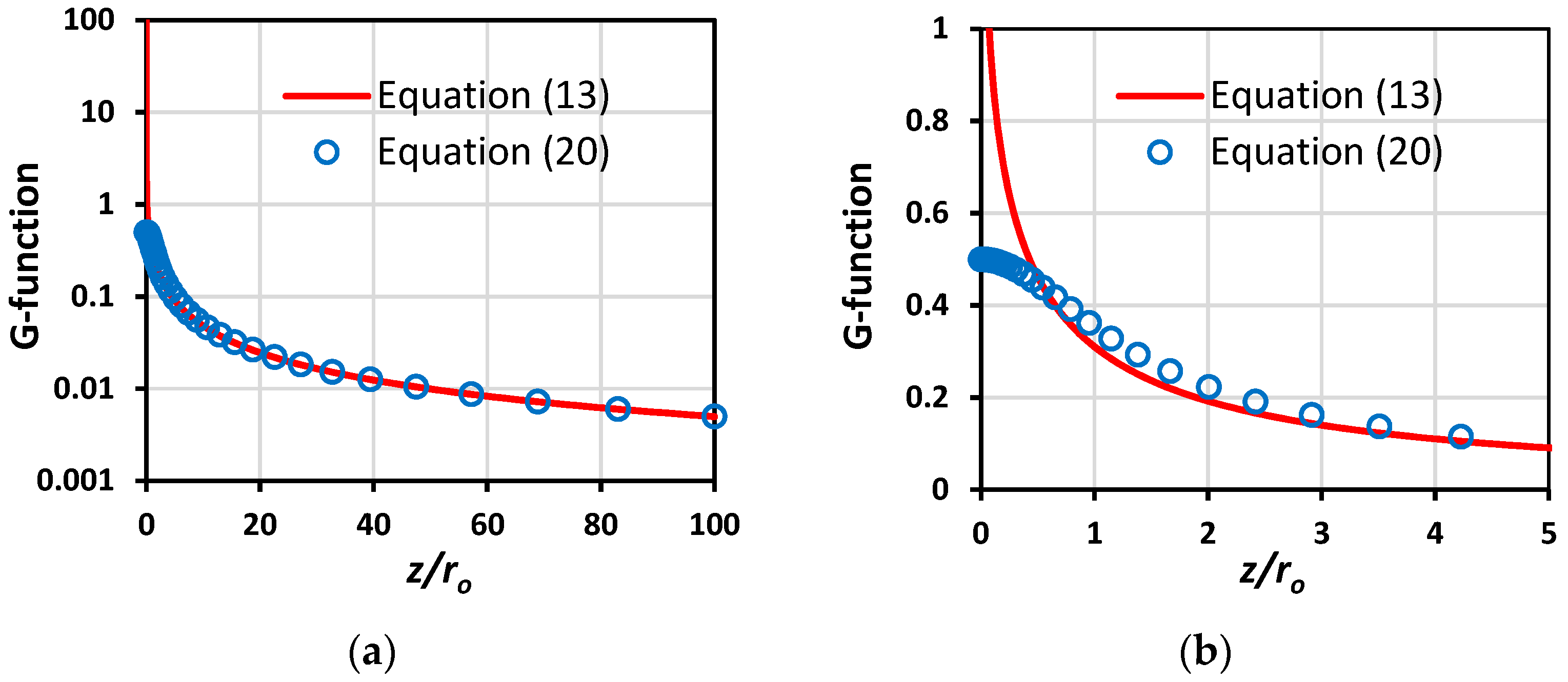
3.1. Numerical Solution
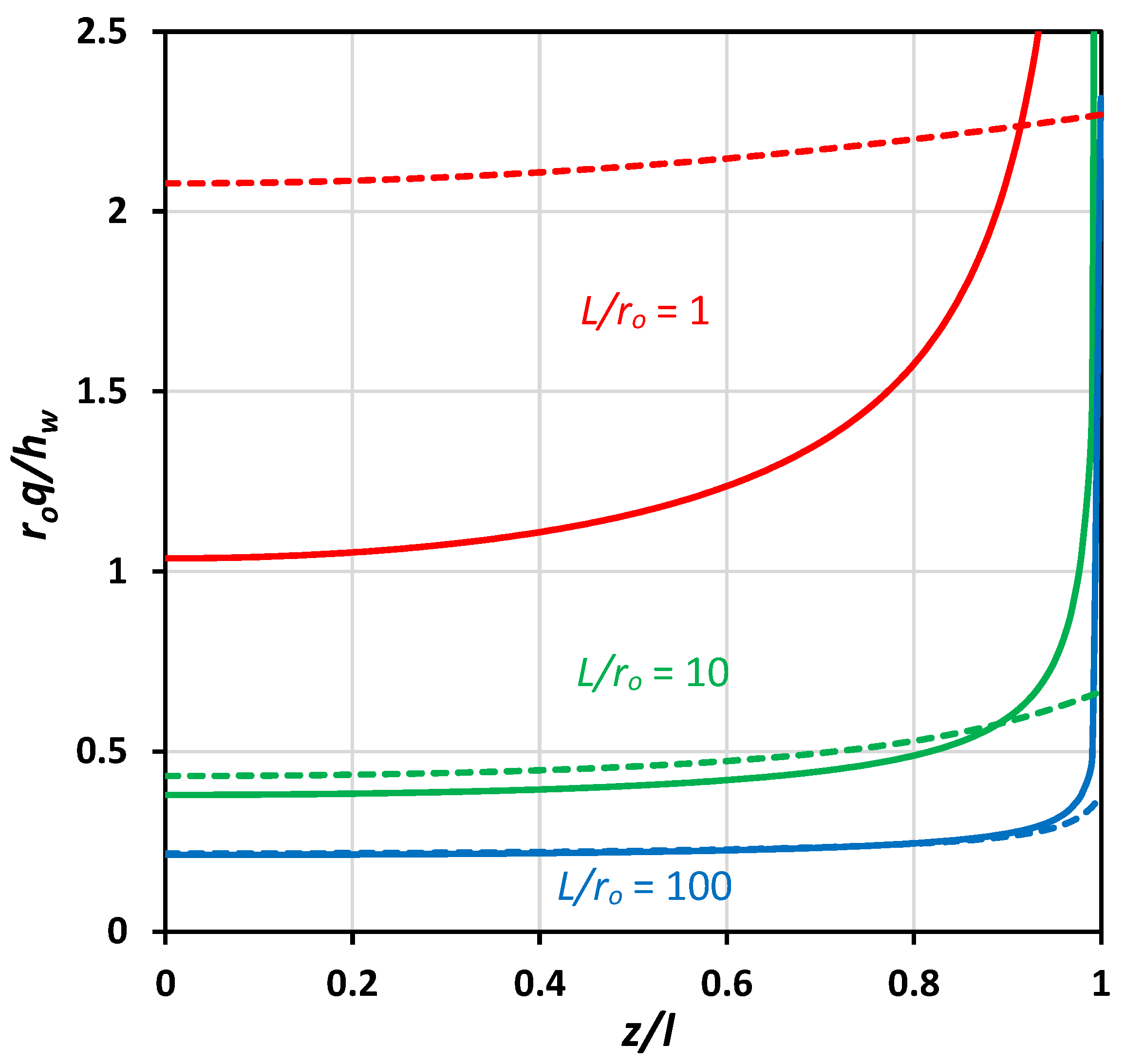
3.2. Approximate Analytical Solution
3.3. Shape Factor Values
3.4. Test Case
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hvorslev, M.J. Time Lag and Soil Permeability in Ground-Water Observations; Waterways Experimental Station, Corps of Engineers, Bulletin 36; U.S. Army: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 1951; 50p. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwer, H.; Rice, R.C. A slug test for determining hydraulic conductivity of unconfined aquifers with completely or partially penetrating wells. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batu, V. Aquifer Hydraulics: A Comprehensive Guide to Hydrogeological Data Analysis; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1998; 727p. [Google Scholar]
- Brand, E.W.; Premchitt, J. Shape factors of cylindrical piezometers. Géotechnique 1980, 30, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widdowson, M.A.; Molz, F.J.; Melville, J.C. An analysis technique for multilevel and partially penetrating slug test data. Groundwater 1990, 28, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, Z.; Narasimhan, T.N. Improved interpretation of Hvorslev tests. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1994, 120, 477–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnam, S.; Soga, K.; Whittle, R.W. Revisiting Hvorslev’s intake factors with the finite element method. Géotechnique 2001, 51, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, D.; Hammond, P.S. A perturbation method for mixed boundary-value problems in pressure transient testing. Transp. Porous Med. 1990, 5, 609–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehbinder, G. The double packer permeameter with long packers: An approximate analytical solution. Appl. Sci. Res. 1996, 56, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehbinder, G. Relation between non-steady supply pressure and flux for a double packer conductivity meter: An approximate analytical solution. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2005, 74, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, S.A.; Butler, A.P. An improvement on Hvorslev’s shape factors. Géotechnique 2006, 56, 705–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, S.A.; Butler, A.P. Shape factors for constant-head double-packer permeameters. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W06430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zlotnik, V.A.; Goss, D.; Duffield, G.M. General steady-state shape factor for a partially penetrating well. Groundwater 2010, 48, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klammler, H.; Hatfield, K.; Nemer, B.; Mathias, S.A. A trigonometric interpolation approach to mixed-type boundary problems associated with permeameter shape factors. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W03510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silvestri, V.; Abou-Samra, G.; Bravo-Jonard, C. Shape factors of cylindrical piezometers in uniform soil. Groundwater 2012, 50, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Smedt, F.; Zijl, W. Two- and Three-Dimensional Flow of Groundwater; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; 65p. [Google Scholar]
- Chapuis, R.P. Shape factors for permeability tests in boreholes and piezometers. Groundwater 1989, 27, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyder, Z.; Butler, J.J., Jr.; McElwee, C.D.; Liu, W. Slug tests in partially penetrating wells. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 2945–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyder, Z.; Butler, J.J., Jr. Slug tests in unconfined formations: An assessment of the Bouwer and Rice technique. Ground Water 1995, 33, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.L.; Narasimhan, T.N.; Demir, Z. An evaluation of the Bouwer Rice method of slug test analysis. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.J., Jr. The Design, Performance, and Analysis of Slug Tests; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997; 280p. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Chapuis, R.P.; Marefat, V. Numerical values of shape factors for field permeability tests in unconfined aquifers. Acta Geotech. 2020, 15, 1243–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiani, G.; Kabala, Z.J. Hydraulics of a partially penetrating well: Solution to a mixed-type boundary value problem via dual integral equations. J. Hydrol. 1998, 211, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chen, C.S. A flowing partially penetrating well in a finite-thickness aquifer: A mixed-type initial boundary value problem. J. Hydrol. 2003, 271, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-Y.; Yeh, H.-D. A simple approach using Bouwer and Rice’s method for slug test data analysis. Ground Water 2004, 42, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruud, N.C.; Kabala, Z.J. Response of a partially penetrating well in a heterogeneous aquifer: Integrated well-face flux versus uniform well-face flux boundary conditions. J. Hydrol. 1997, 194, 76–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiani, G.; Kabala, Z.J.; Medina, M.A., Jr. Flowing partially penetrating well: Solution to a mixed-type boundary value problem. Adv. Water Resour. 1999, 23, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perina, T.; Lee, T.-C. General well function for pumping from a confined, leaky, or unconfined aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2006, 317, 239–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Yeh, H.D. New solutions to the constant-head test performed at a partially penetrating well. J. Hydrol. 2009, 369, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | Solution Technique | Flow Distribution at the Well Screen | Aquifer Boundary Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hvorslev [1] | Analytical | Uniform | No |
| Bouwer and Rice [2] | Empirical | Non-uniform | Yes |
| Zlotnik et al. [13]. | Analytical | Uniform | Yes |
| This study 1 | Numerical | Non-uniform | No |
| This study 2 | Analytical | Non-uniform | No |
| Method | Shape Factor | Hydraulic Conductivity K (m/day) |
|---|---|---|
| Numerical, Equations (17) and (18) | 2.25 | 3.67 |
| Analytical, Equation (24) | 2.28 | 3.71 |
| Hvorslev [1], Equation (3) | 2.50 | 4.08 |
| Bouwer and Rice [2] | 2.00 | 3.26 |
| Zlotnik et al. [13] | 2.33 | 3.79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Smedt, F. Shape Factor for Analysis of a Slug Test. Water 2023, 15, 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142551
De Smedt F. Shape Factor for Analysis of a Slug Test. Water. 2023; 15(14):2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142551
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Smedt, Florimond. 2023. "Shape Factor for Analysis of a Slug Test" Water 15, no. 14: 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142551
APA StyleDe Smedt, F. (2023). Shape Factor for Analysis of a Slug Test. Water, 15(14), 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142551







