Developmental Toxicities in Zebrafish Embryos Exposed to Tri-o-cresyl Phosphate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
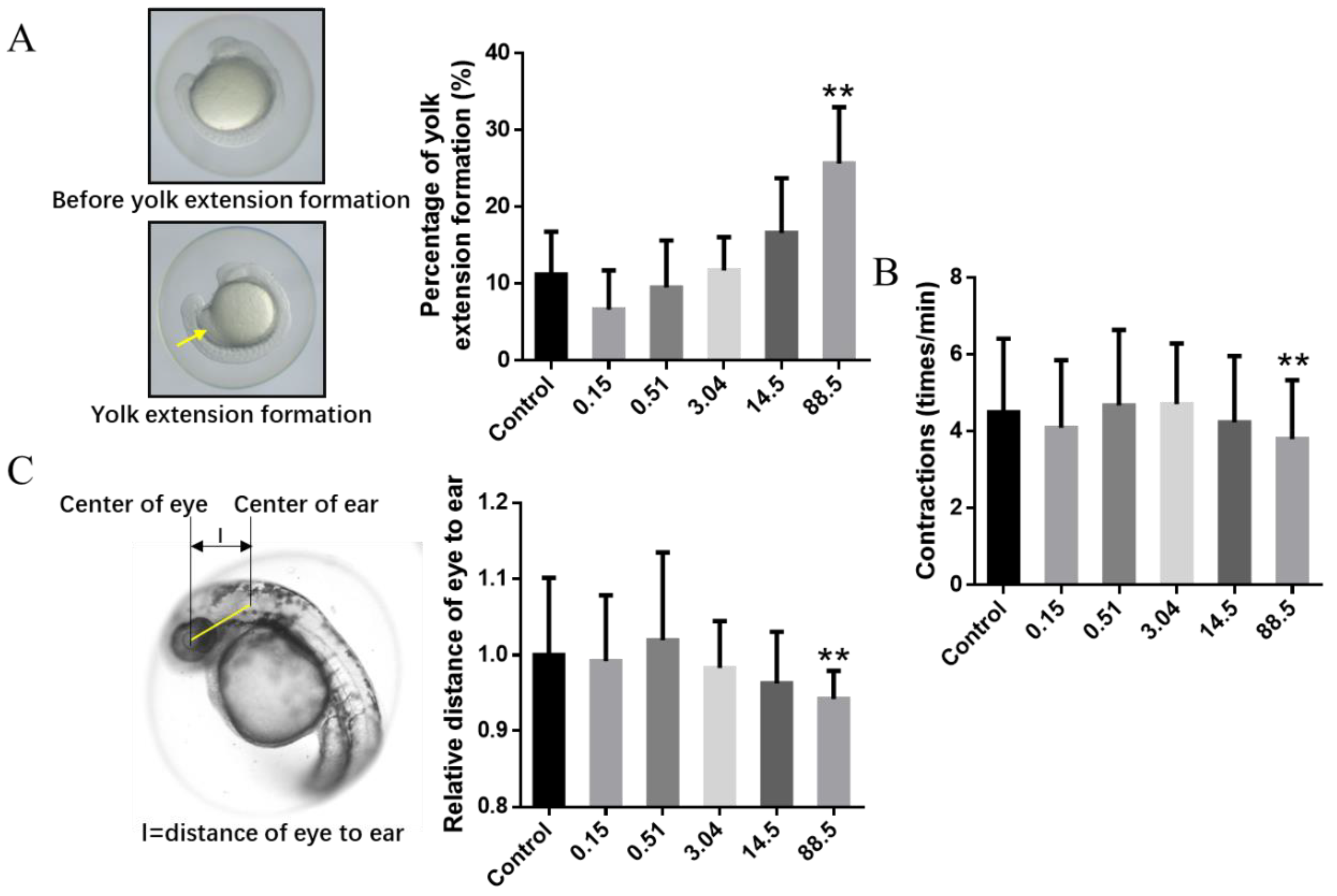
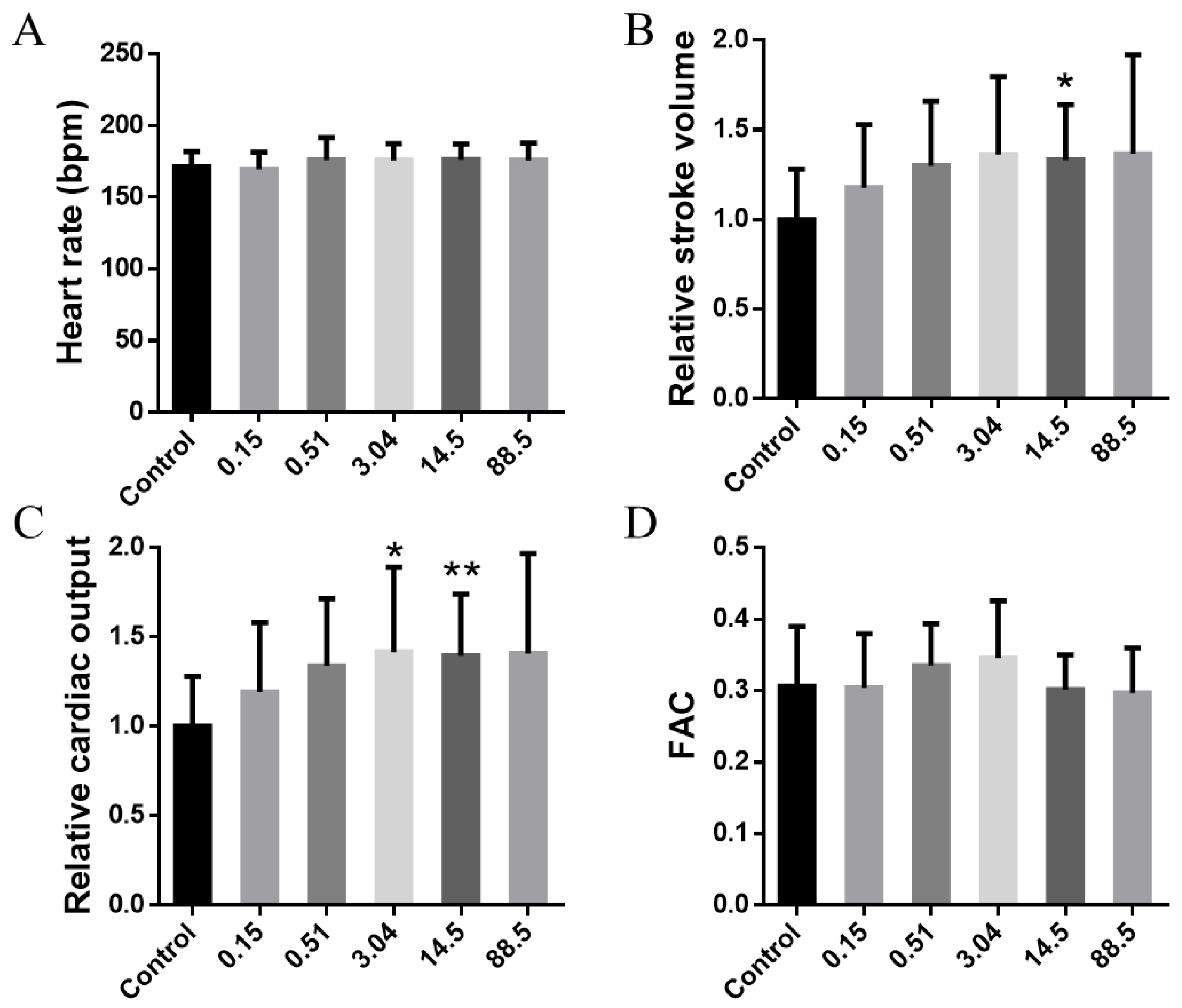
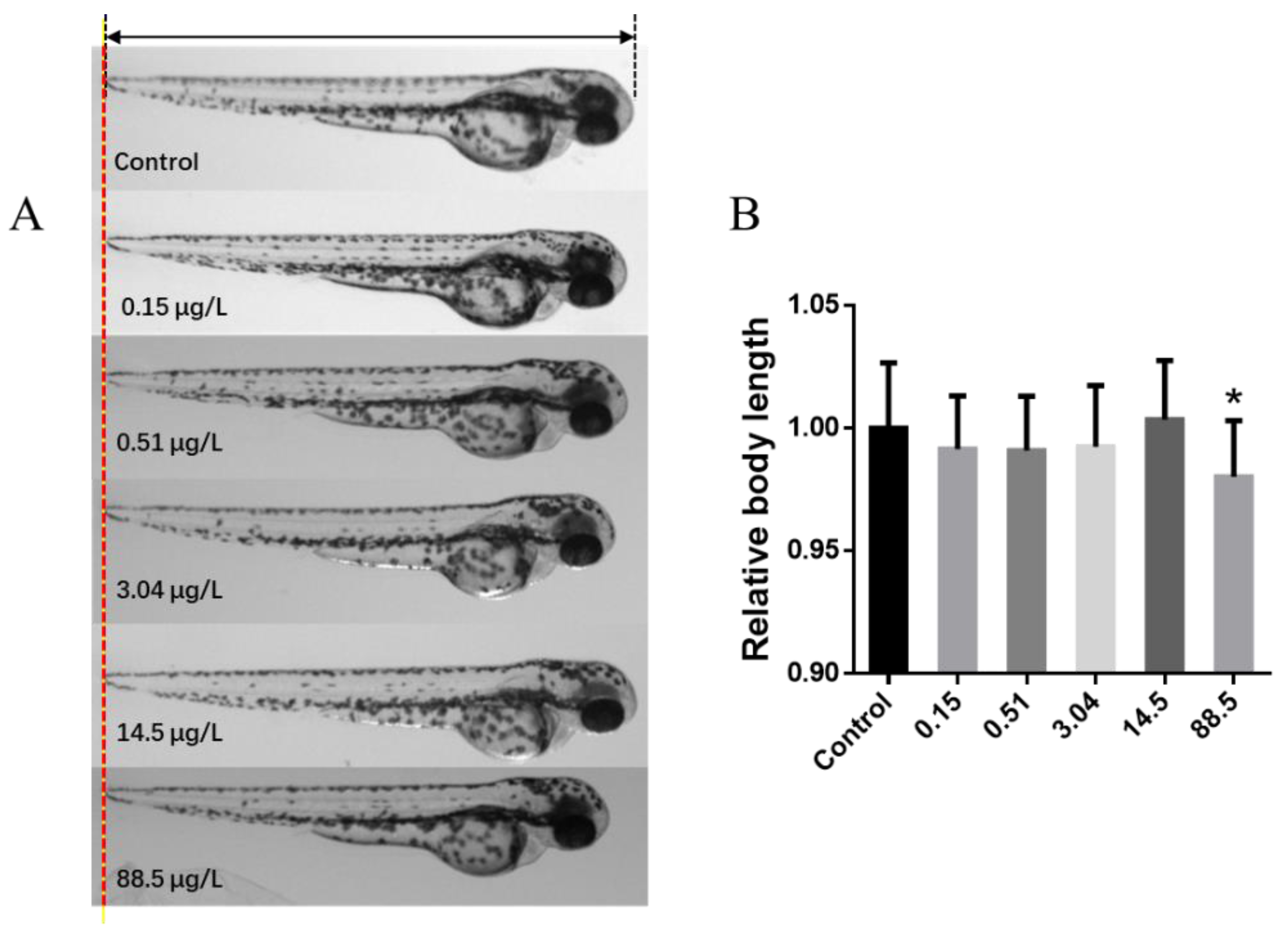
3. Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Ma, H.; Huang, J.; Li, H.; Mao, X.; Huang, T.; Gao, H.; Ma, J. Gridded emission inventory of organophosphorus flame retardants in China and inventory validation. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, G.; Li, L.; Breivik, K. Global Historical Stocks and Emissions of PBDEs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6330–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Qi, Z.; Chen, Z.F.; Cai, Z. Contamination profiles and potential health risks of organophosphate flame retardants in PM2.5 from Guangzhou and Taiyuan, China. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, R.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z. Review of OPFRs in animals and humans: Absorption, bioaccumulation, metabolism, and internal exposure research. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, H.; Xu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Jin, M.; Tang, J. A review of organophosphorus flame retardants (OPFRs): Occurrence, bioaccumulation, toxicity, and organism exposure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 22126–22136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ye, L.; Fang, M.; Su, G. Industrial Production of Organophosphate Flame Retardants (OPFRs): Big Knowledge Gaps Need to Be Filled? Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 108, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, P.H.; Barth, M.L. Evaluation of the hazards of industrial exposure to tricresyl phosphate: A review and interpretation of the literature. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 1999, 2, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, H.-C.; Hsieh, Y.-K.; Huang, B.-W.; Cheruiyot, N.K.; Chang-Chien, G.-P. An Overview: Organophosphate Flame Retardants in the Atmosphere. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 220148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.J.; Takimoto, K.; Okada, M. Fate of tricresyl phosphate isomers in Kurose River (Japan). Water Sci. Technol. 1994, 30, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.W.; Liu, J.F.; Yin, Y.G. Development of an ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for high throughput determination of organophosphorus flame retardants in environmental water. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 6705–6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jeong, W.; Kannan, K.; Moon, H.B. Occurrence and exposure assessment of organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs) through the consumption of drinking water in Korea. Water Res. 2016, 103, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; La Guardia, M.J.; Liu, H.; Hale, R.C.; Mainor, T.M.; Harvey, E.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J.; Peng, P. Brominated and organophosphate flame retardants along a sediment transect encompassing the Guiyu, China e-waste recycling zone. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.-T.; Zheng, J.; Qiao, L.; Chen, S.-J.; Yang, J.-Z.; Yuan, J.-G.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Mai, B.-X. Occurrence of organophosphorus flame retardants in indoor dust in multiple microenvironments of southern China and implications for human exposure. Chemosphere 2015, 133, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.D.; Seiber, J.N. Analysis of organophosphate hydraulic fluids in U.S. Air force base soils. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1999, 36, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Isobe, T.; Muto, M.; Tue, N.M.; Katsura, K.; Malarvannan, G.; Sudaryanto, A.; Chang, K.H.; Prudente, M.; Viet, P.H.; et al. Organophosphorus flame retardants (PFRs) in human breast milk from several Asian countries. Chemosphere 2014, 116, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; He, J.; Li, Y.; An, L.; Hu, J. Tricresyl phosphate inhibits fertilization in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes): Emphasizing metabolic toxicity. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 297, 118809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ji, K.; Choi, K. Endocrine disruption potentials of organophosphate flame retardants and related mechanisms in H295R and MVLN cell lines and in zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 114–115, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Tricresyl Phosphate. In Environmental Health Criteria 110; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1990; Available online: https://inchem.org/documents/ehc/ehc/ehc110.htm (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Chen, J.X.; Xu, L.L.; Mei, J.H.; Yu, X.B.; Kuang, H.B.; Liu, H.Y.; Wu, Y.J.; Wang, J.L. Involvement of neuropathy target esterase in tri-ortho-cresyl phosphate-induced testicular spermatogenesis failure and growth inhibition of spermatogonial stem cells in mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 211, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.L.; Wang, J.L.; Wei, J.; Xu, L.L.; Yu, M.; Liu, X.M.; Ruan, W.L.; Chen, J.X. Tri-ortho-cresyl phosphate induces autophagy of rat spermatogonial stem cells. Reproduction 2015, 149, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bockers, M.; Paul, N.W.; Efferth, T. Organophosphate ester tri-o-cresyl phosphate interacts with estrogen receptor alpha in MCF-7 breast cancer cells promoting cancer growth. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 395, 114977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarema, K.A.; Hunter, D.L.; Shaffer, R.M.; Behl, M.; Padilla, S. Acute and developmental behavioral effects of flame retardants and related chemicals in zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2015, 52, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behl, M.; Hsieh, J.H.; Shafer, T.J.; Mundy, W.R.; Rice, J.R.; Boyd, W.A.; Freedman, J.H.; Hunter, E.S., 3rd; Jarema, K.A.; Padilla, S.; et al. Use of alternative assays to identify and prioritize organophosphorus flame retardants for potential developmental and neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2015, 52, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Meng, H.; Zhou, J.; Yin, Y.; Zhen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, K. Simultaneous Occurrence of Psychotropic Pharmaceuticals in Surface Water of the Megacity Shanghai and Implication for Their Ecotoxicological Risks. ACS ES T Water 2021, 1, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yuan, G.; Werdich, A.A.; Zhao, Y. Ibuprofen and diclofenac impair the cardiovascular development of zebrafish (Danio rerio) at low concentrations. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, A.; Elrod-Erickson, M.; Otter, R.R. Consistency of morphological endpoints used to assess developmental timing in zebrafish (Danio rerio) across a temperature gradient. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 34, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, T.J.; Szaszkiewicz, J.; Krook, J.; Burggren, W. Analysis of the potential behavioral impact of methanol when used as a solvent: Dataset from zebrafish (Danio rerio) behavioral research. Data Brief 2021, 36, 107018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Ji, K.; Choi, K. Effects of tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate (TDCPP) and triphenyl phosphate (TPP) on sex-dependent alterations of thyroid hormones in adult zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, S.; Chen, R.; Hu, J. Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of the Organophosphorus Flame Retardant Triphenyl Phosphate Impaired Testicular Development and Reproductive Behaviors in Japanese Medaka (Oryzias latipes). Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftery, T.D.; Volz, D.C. Abamectin induces rapid and reversible hypoactivity within early zebrafish embryos. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2015, 49, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Yuan, S.; Sun, Q.; Liu, C. Toxicity of tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate in Daphnia magna after lifetime exposure: Changes in growth, reproduction, survival and gene transcription. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 200, 110769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiojima, I.; Komuro, I. Cardiac developmental biology: From flies to humans. Jpn. J. Physiol. 2005, 55, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.T.; Pomerantsev, E.V.; Mably, J.D.; MacRae, C.A. High-resolution cardiovascular function confirms functional orthology of myocardial contractility pathways in zebrafish. Physiol. Genomics. 2010, 42, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, Z.; Wang, G.; Gao, S.; Wang, Z. Aryl organophosphate flame retardants induced cardiotoxicity during zebrafish embryogenesis: By disturbing expression of the transcriptional regulators. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 161, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Liang, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, Y. Using a high-throughput zebrafish embryo screening approach to support environmental hazard ranking for cardiovascular agents. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Liao, X.; Yan, S.C.; Gao, Y.; Yang, C.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Tsang, S.Y.; Chen, Z.F.; et al. Uptake, Accumulation, and Biomarkers of PM2.5-Associated Organophosphate Flame Retardants in C57BL/6 Mice after Chronic Exposure at Real Environmental Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9519–9528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Jia, Y.; Dai, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Yu, L. Tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate disrupts axonal growth, cholinergic system and motor behavior in early life zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 192, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhyu, D.; Lee, H.; Tanguay, R.L.; Kim, K.T. Tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl)phosphate (TDCIPP) disrupts zebrafish tail fin development. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, M.; Shi, F.; Yang, L.; Guo, Y.; Feng, C.; Liu, J.; Zhou, B. Developmental neurotoxicity of triphenyl phosphate in zebrafish larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 203, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Su, G.; Zou, M.; Yu, L.; Letcher, R.J.; Yu, H.; Giesy, J.P.; Zhou, B.; Liu, C. Effects of Tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) Phosphate on Growth, Reproduction, and Gene Transcription of Daphnia magna at Environmentally Relevant Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12975–12983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, S.; Hunter, D.L.; Padnos, B.; Frady, S.; MacPhail, R.C. Assessing locomotor activity in larval zebrafish: Influence of extrinsic and intrinsic variables. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2011, 33, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Hwang, K.S.; Kan, H.; Yang, J.Y.; Son, Y.; Shin, D.S.; Lee, B.H.; Chae, C.H.; Bae, M.A. Neurotoxicological profiling of paraquat in zebrafish model. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 2294–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Fukushima, N.; Hasumi, A. Standardized method for the assessment of behavioral responses of zebrafish larvae. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Qian, Q.; Gao, M.; Wang, H. Tris (1-chloro-2-propyl) phosphate exposure to zebrafish causes neurodevelopmental toxicity and abnormal locomotor behavior. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazer, L.; Hawkey, A.B.; Wells, C.N.; Drastal, M.; Odamah, K.A.; Behl, M.; Levin, E.D. Developmental Exposure to Low Concentrations of Organophosphate Flame Retardants Causes Life-Long Behavioral Alterations in Zebrafish. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 165, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Qing, X.; Wang, J.; He, T.; Fan, R.; Huang, Y. Bioaccumulation and potential risk of organophosphate flame retardants in coral reef fish from the Nansha Islands, South China Sea. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, T.G.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J. Bioaccumulation and Trophic Transfer of Emerging Organophosphate Flame Retardants in the Marine Food Webs of Laizhou Bay, North China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13417–13426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Nominal Conc. | Control | 0.32 | 1.6 | 8 | 40 | 200 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | <LOQ | 0.146 | 0.47 | 2.51 | 15.1 | 89.4 |
| Day 3 | <LOQ | 0.154 | 0.55 | 3.58 | 13.8 | 87.6 |
| Mean Conc. | <LOQ | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.51 ± 0.06 | 3.04 ± 0.78 | 14.5 ± 0.9 | 88.5 ± 1.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Wang, C.; Gui, W.; Wang, P.; Chen, J.; Zuo, S.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, J.; Zhang, K. Developmental Toxicities in Zebrafish Embryos Exposed to Tri-o-cresyl Phosphate. Water 2023, 15, 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162942
Li M, Wang C, Gui W, Wang P, Chen J, Zuo S, Zhao Y, Dai J, Zhang K. Developmental Toxicities in Zebrafish Embryos Exposed to Tri-o-cresyl Phosphate. Water. 2023; 15(16):2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162942
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Meng, Congcong Wang, Wanying Gui, Peng Wang, Jierong Chen, Shaoqi Zuo, Yanbin Zhao, Jiayin Dai, and Kun Zhang. 2023. "Developmental Toxicities in Zebrafish Embryos Exposed to Tri-o-cresyl Phosphate" Water 15, no. 16: 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162942





