Abstract
This study investigated the beach nourishment effect and topographical changes when using nourishment sand with relatively large particle diameters to perform beach nourishment on a beach subject to erosion. A physical model test was conducted in a 2D wave flume with an installed wind tunnel. The experiment examined the sediment transport mechanism under conditions with wind and waves. Although applying nourishment sand with large particle diameters attenuated sediment transport, the increase in particle diameter was not always proportional to the reduction in topographical changes. Increasing the particle diameter of the nourishment sand increased the friction force between particles, resulting in large-scale erosion and accretion around the coastline, and this trend increased with winds. Also, with wind, the wave run-up height increased, the undertow became stronger, and large-scale scouring occurred at the boundary between the nourishment sand and the existing beach. Increasing the particle diameter of the nourishment sand played a role in reducing the run-up phenomenon (d50: 1.0 mm with 24–50%, d50: 5.0 mm with 59–83%), and the range of particles moved by winds also decreased (d50: 1.0 mm with 10–38%, d50: 5.0 mm with 5–37%).
1. Introduction
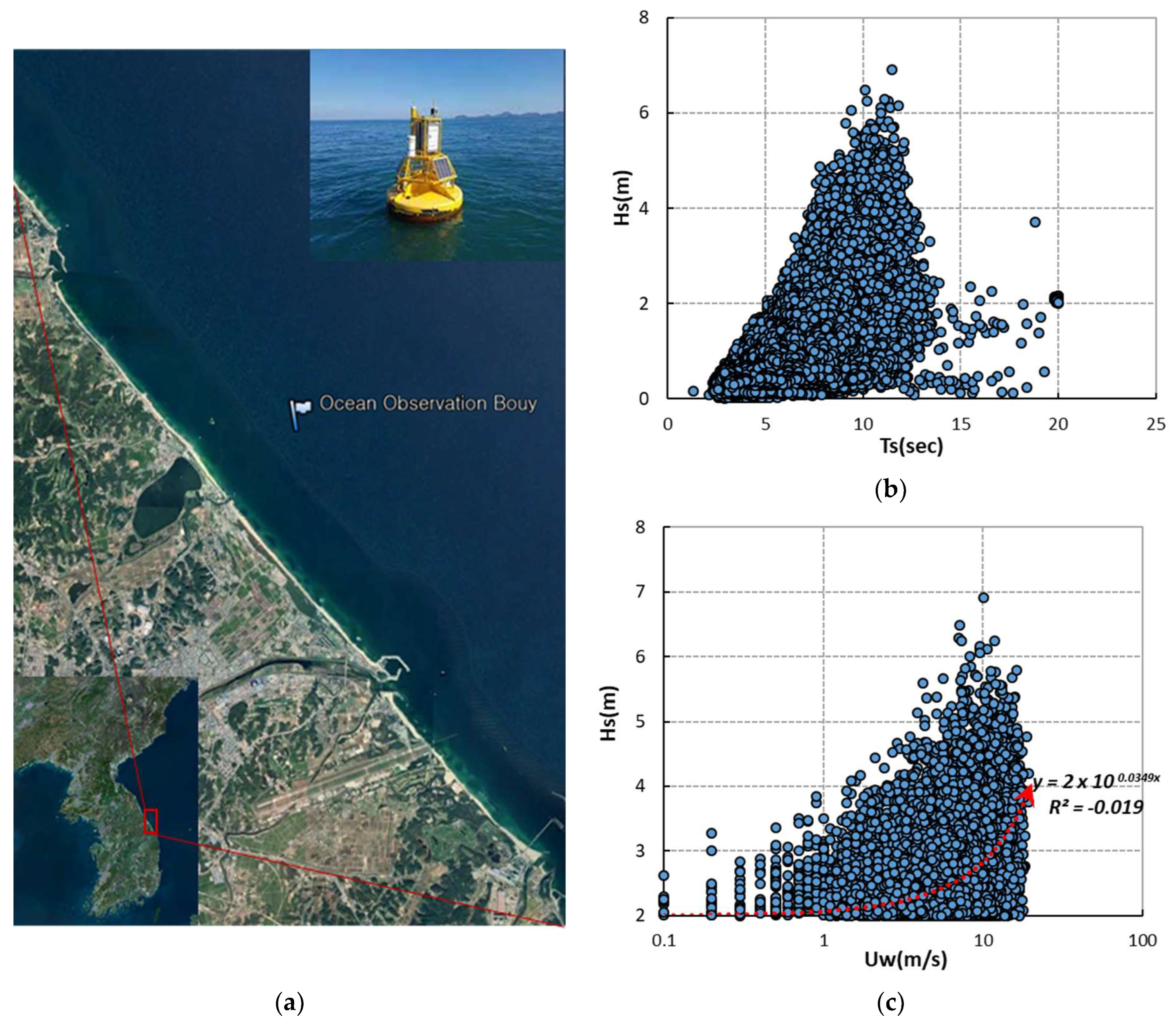
On ordinary days, the range of waves formed on the coast is small, so the beach width only changes slightly. However, when an abnormal wave hits the coast, such as a storm surge, the high wave run-up exceeds the morphological threshold and causes large-scale topographic change [1,2,3]. In particular, when high waves along with typhoons hit the coast, the sea level rises, and sand movement is promoted in the backshore [4]. As a countermeasure, many construction methods are applied, and the coastal environment is maintained and changed by the characteristics of each method. As a beach erosion countermeasure to control sand loss, hard-type structures such as submerged breakwaters are effective in controlling waves [5,6,7]. However, secondary damages caused by the formation of diffracted waves and an increase in current velocity occur around the structure, so careful consideration is needed to form a stable coast. In contrast, soft-type methods such as beach nourishment and vegetation use eco-friendly materials, so there is no secondary damage after application, but there is a problem in that the wave attenuation effect is reduced compared to hard-type methods. However, in the case of beach nourishment, when nourishing sand with a larger grain size than the existing sand is applied to the coast where erosion occurs, sediment transport is reduced [8,9,10,11]. When the grain size of the nourishing sand increases, the weight of the particles also increases. As a result, the sediment’s fall velocity increases, leading to a reduced transport range, which is advantageous for maintaining a stable beach shape. Furthermore, beach nourishment also offers advantages in terms of maintenance and repair, allowing for proactive countermeasures with regard to issues such as sea-level rise caused by climate change. Until now, most of the research on beach nourishment has mainly focused on the application of waves as external forces [12,13,14]. It is true that the size of a wave can cause topographical changes. However, it is important to consider that high waves are usually accompanied by strong winds. Figure 1 shows data from wave buoys on the east coast of South Korea for five years (2018 to 2022). Figure 1 shows that when a strong wind speed of 10 m/s or more occurs, the wave height can vary from 2 to 7 m, while in circumstances where the wave height is 5 m or higher, the wind speed is in the range of 8 m/s or more. Sediment transport is mainly observed during high-wave events, which are often accompanied by strong winds. Thus, when considering beach profile changes, it is necessary to simultaneously consider the influence of both wave height and wind, given their association [15,16,17]. As the wind magnitude increases, the range of the surf zone and the wave run-up height change [18,19], so it is possible to reproduce the situation of the actual coast accurately.

Figure 1.
(a) Location of ocean observation bouy; (b) Distribution of wave period () for wave height (); (c) Distribution of wind speed () for wave height ().
To study the aforementioned situations precisely, various parameters need to be considered at the same time. In the case of increasing particle size, such as gravel, it is necessary to determine the appropriate grain size. In addition, it is vital to examine the range of the nourishment zone, the compatibility with the existing sand, and the long-term changes in the nourished beach. However, research findings regarding grain size changes are limited, and most of the available data are based on field observations [20,21,22]. Thus, it is essential to investigate the topographical changes in a situation where various wave height conditions and winds coexist. Furthermore, it is important to closely examine the beach profile changes and characteristics resulting from variations in the grain size of nourishing sand. However, there are limitations to the numerical approach when many parameters exist simultaneously. Building a high-resolution numerical model is time-consuming and costly. Moreover, due to uncertain input parameters of the model and inadequate process descriptions, there can be significant uncertainty that can lead to deterministic simulations. Thus, to quantify uncertainty, it is necessary to conduct a greater number of simulations [23]. However, a physical model test is easier to interpret and derive results from compared to field monitoring or numerical simulation.
When a physical model test is applied, it is possible to simultaneously apply various parameters, such as grain size of sand and wave deformation due to wind speed, which allows interpretation with a higher degree of accuracy [24,25]. Thus, this study examines the suitability of beach nourishment as a method for maintaining a stable beach profile using hydraulic model experiments, among various interpretation techniques. It also aims to investigate the impact of coexisting wave and wind fields on beach profile changes by using wave height and wind speed distribution extracted from buoy data.
2. Methods
2.1. Setup for Test Profile
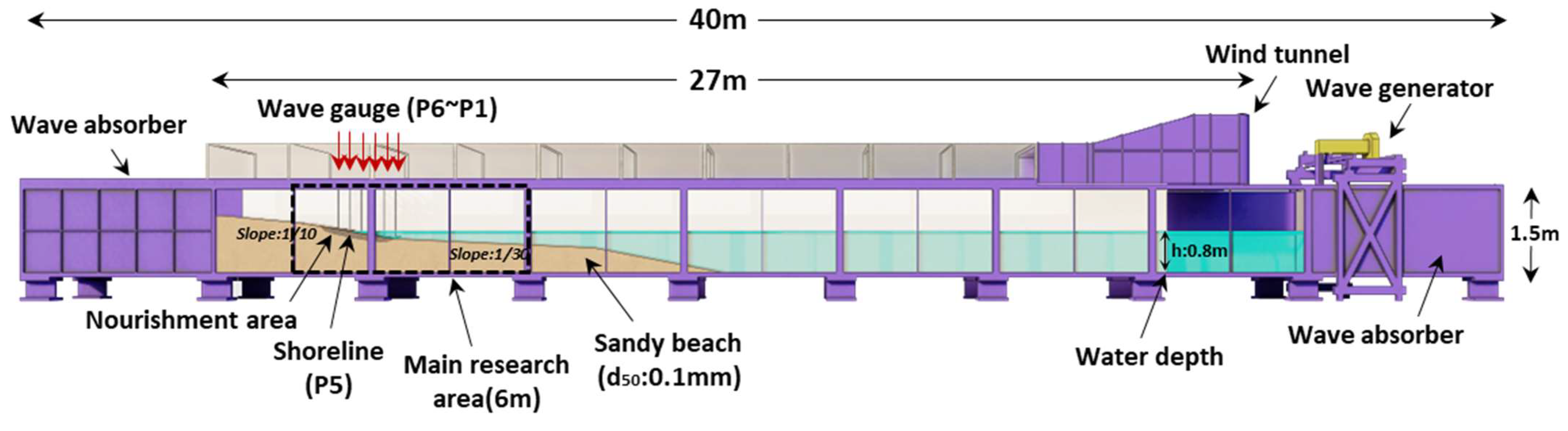
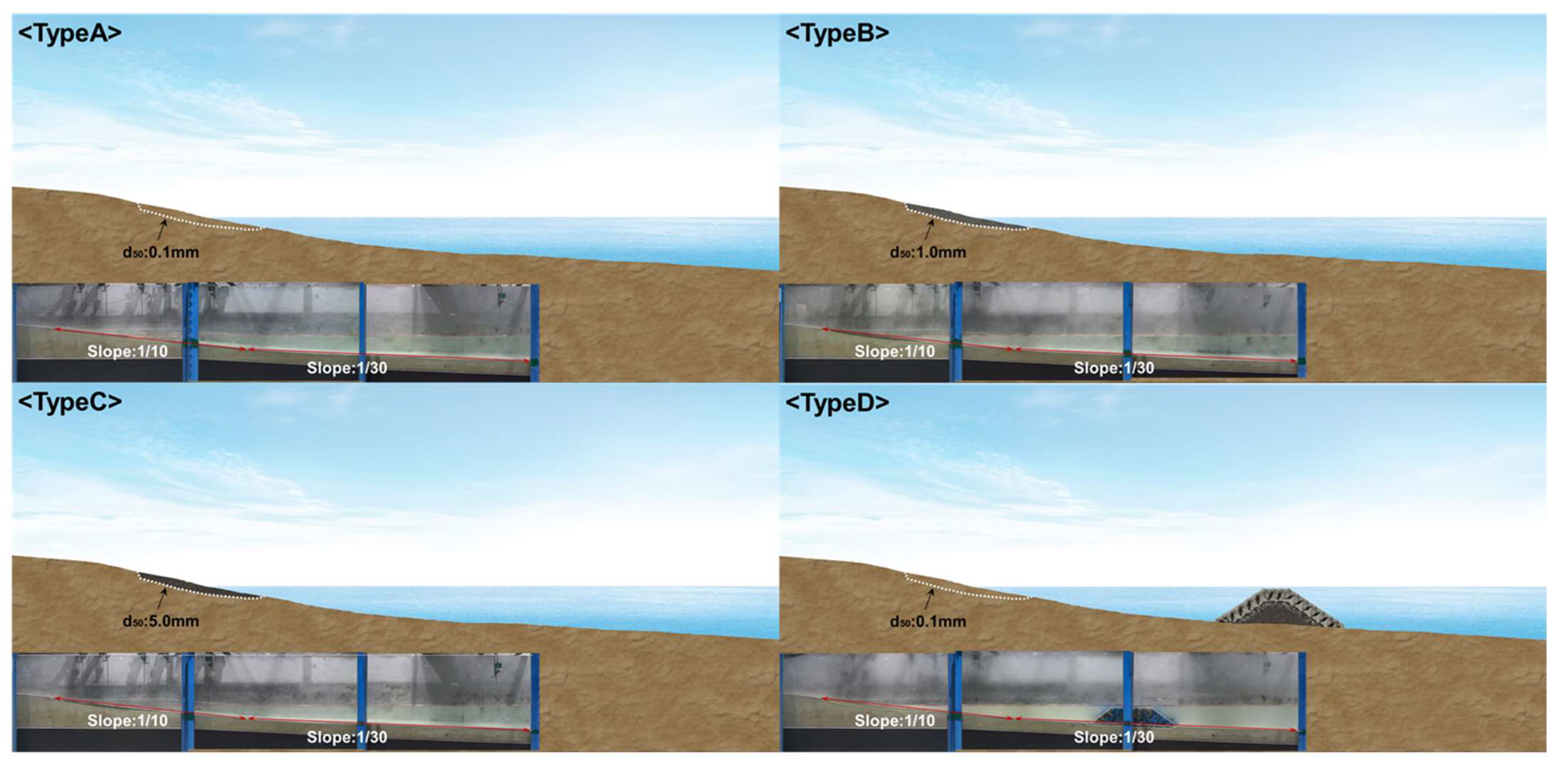
This study is an extension of the study conducted by [24], and the overall experimental concept is the same as that of [24]. The beach profile change was analyzed in a two-dimensional (2D) wave flume. The specifications of the wave flume and topography condition are shown in Figure 2. The wind tunnel is installed at the upper part of the flume. Among the profiles used in the experiment, Type A represents the reference profile in this study. It is a natural beach composed of a d50: 0.1 mm grain size (Figure 3).

Figure 2.
2d wave flume and layout of beach profile.

Figure 3.
Test profiles for cross-sectional topography; Type A (d50: 0.1 mm), Type B (d50: 1.0 mm), Type C (d50: 5.0 mm), Type D (d50: 0.1 mm + submerged breakwater).
Type A is designed to induce erosion around the shoreline where the boundary line between water and land is when only waves act as the external force. This was set up by configuring the wave steepness and sea bottom slope to promote erosion. The profile shape has a sea bottom slope of 1:10 (X: 0–300 cm) from the backshore to the foreshore and 1:30 (X: 300–800 cm) from the foreshore to the offshore. These conditions are set up so that topographical changes are generated by the waves but reach a quasi-equilibrium state about 4.5 h after the wave invasion. In the erosion section that occurred in the Type A profile, nourishing sand with increased grain size was applied. In this study, 1.0 mm (Type B) and 5.0 mm (Type C) nourishing sand were applied, and the change in erosion and accretion compared to that of Type A was examined through experiments. At this time, only the particles selected through sieve analysis test were applied to the experiment. In addition, the suitability of the nourishing sand was examined by comparing the beach profile change under the nourishing sand with the increased grain size (Type B, C) with that of Type D, where a submerged breakwater, a representative hard type structure, was applied to the Type A condition to prevent erosion. In this case, the total length of the reproduced profile was 800 cm, and the length of the nourishment zone was 120 cm. The submerged breakwater of Type D is located 260 cm from the shoreline, with a crest level of −2 cm from the water surface and a crest width of 45 cm (Figure 3).
2.2. External Force Condition
The main parameters applied to this experiment are the profile shape (Type A–D) and wind speed. The single condition of the wave height ( with 10 cm), the wave period ( with 1.414 s), and the still water level ( with 80 cm) was adapted to the test. The wave steepness (: 0.05) is somewhat steep to form an erosive wave (Table 1). As evident from the buoy data shown in Figure 1, on the surface of 20 m depth where the buoy was located, significant wave heights reached a maximum of 7 m, and wave periods occurred up to 20 s. Sediment transport is proportional to the size of high waves, but if the magnitude of the waves is too large, excessive topographical changes can occur in a short period of time. In this regard, the appropriate range of wave specifications was determined by changing the sea bottom slope and wave steepness in the process of determining the beach profile. Based on the examination results, the waves were determined to have a of 5 m and of 10 s, according to the buoy data. According to the wave height and wind relationship in the buoy data, a wave height of 5 m corresponds to wind speeds () ranging from approximately 8 m/s to 20 m/s. The wave and wind values that were derived from buoy observation data were applied to the physical model experiment. The overall parameters were scaled according to the Froude similarity law of 1/50. Regarding wind speed, the value of 20 m/s corresponds to approximately 3 m/s in the model scale. However, considering the conditions during a typhoon event, the set wind speed of 8 m/s in this study falls within the range of research feasibility. Thus, wind speeds were set at 0, 3, 6, and 8 m/s to examine the impact of wind intensity on beach profile changes. Other parameters are the same as those studied by [24].

Table 1.
Test conditions for Type A–D.
In this paper, theoretical formulas [26,27] examined whether erosion is caused by wave action before the experiment. The profile applied to the theoretical formulas was Type A, and it was used to identify the grain sizes and range of the nourishing sand caused by erosion. There are many empirical formulas available for calculating sediment erosion, but one of them is the formula proposed by Sunamura and Horikawa [26]. The formula is as follows:
Here, is a dimensionless coefficient that determines erosion or deposition. is the deep water wave height, is the deep water wavelength, is the sea bottom slope and is the median grain size of the sand. Parameter may vary depending on local and experimental modeling conditions. In the case of local conditions, ≤ 9 signifies a depositional coast, 9 ≤ ≤ 18 signifies a coast where erosion and deposition occur, and ≥ 18 signifies an erosional coast. In model experimental conditions, ≤ 4 signifies a depositional coast, 4 ≤ ≤ 8 signifies a coast where erosion and deposition occur, and ≥ 8 signifies an erosional coast. Using the values in Table 1, Type A’s C value is 17.69, which is classified as an erosional coast. However, [26] is difficult to apply in the conditions of partial beach nourishment or where submerged breakwaters are installed. Although grain sizes of 1 mm and 5 mm are applied to the nourishment zone if the grain size of the beach sand is assumed to be the same as the grain size of the nourishing sand, the grain size values are 3.78 and 1.28, respectively, and they are classified as composing a depositional beach. Accordingly, it is expected that Types B and C can mitigate topographical changes compared to Type A. Another empirical formula [27] was applied to increase the reliability of theoretical approach. The parameter [27] can be expressed by the following equation.
Here, refers to the Dean number, is the deep sea wave height, is fall velocity, and is the time period. Here, the was applied for the Rubey equation [28], which is expressed as follows
Here, : fall velocity, S: specific gravity of particle, : gravitational acceleration, d: particle radius, : dynamic viscosity. By applying the Rubey equation, the fall velocities of 0.1 mm, 1 mm, and 5 mm grain sizes are 0.84, 9.8, and 73.4 cm/s, respectively. Here, are 8.44, 0.72, and 0.097, respectively. According to [27], erosion occurs when the value is > 1 and deposition occurs when it is < 1. In the above Equations (1) and (2), the erosive shore is formed in the grain size condition of 0.1 mm, and sedimentation occurs in the grain size condition of 1.0 mm and 5.0 mm, so the predictions of the theoretical equations are the same. In fact, the preliminary experiment on Type A was analyzed, and the result showed that Type A was an erosive coast, so it is expected that the same results as the theoretical formula will be generated in our experiment. However, the range of the nourishment zone and the effect of wind on topographical change need to be examined in detail, and the goal of this study was to understand the phenomenon through conducting experiments.
2.3. Method of Measurement and Analysis
The measurement of topographical changes was carried out every 0.5 h based on the Type A profile. The measurements of morphological change were taken up to 4.5 h, at which time a quasi-equilibrium state was reached. In the experimental results, the results of each wind speed action after 4.5 h were summarized compared to that of the initial condition. In this study, quasi-equilibrium is defined as a situation in which the beach deformation caused by waves changes the beach only horizontally. For Type A, which is an erosive coast, erosion occurs around the shoreline. In this case, the condition was defined as the change in the area where erosion occurs has significantly decreased, and the position of the berm formed in the foreshore due to erosion changes only horizontally. As mentioned earlier, in the case of Type A, the sediment transport significantly happened over 4.5 h, so this study was conducted for up to 4.5 h.
To measure the topographical change, two methods were used. In the first method, measurements were taken at 1 cm intervals using a beach slope gauge (WH-501RS). The measurement section was 8 m long, and the results were analyzed for the 6 m section where the main sediment transport occurred. The second method was to draw the topography on the side glass surface of the water tank using a 3 mm-thick pen and then extract the image through image analysis and digitize each coordinate. The measurement was performed in the center of the wave flume, and the digitization results were obtained from the side wall, so the measurement results may have some variation. The two conditions overlapped, and the data obtained from the point gauge was compared using the results from the digitization process. At some points, interpolation was performed. Before performing each experiment, it was checked whether the conditions of the initial topography were the same.
In the setup for wave signal, progressive waves were reviewed by installing a wave height gauge at the shoreline position (P5) with no topographical profile applied. Wave measurements during the experimental process after the installation of the topographical features were conducted at points P1 to P6, as shown in Figure 2. In the Type A section, the erosion area is widely formed, so the wave run-up height and the wave fluctuation on the shoreline are expected to increase. At the same time, the energy density of the waves generated during the experiment was analyzed using the spectrum method for the wave height at the shoreline (P5) and the point located on the backshore (P6). In addition, the wave run-up height was calculated to analyze the characteristics according to wind speed changes.
The wind speed was set in the same way as the wave signal setting process before the installation of topographical features. The target wind speed was set using a wind speed gauge (6332D, Kanomax) at point P5, where only the water level was reproduced. Here, the wind speed gauge was 30 cm away from the surface of the water. The wind speeds were acquired as the average value over 1 s, and the experiment was conducted after confirming the constant wind speed condition for 5–10 min.
3. Results
3.1. Sediment Transport Variation According to Cross-Sectional Profile Changes
3.1.1. Topography Change
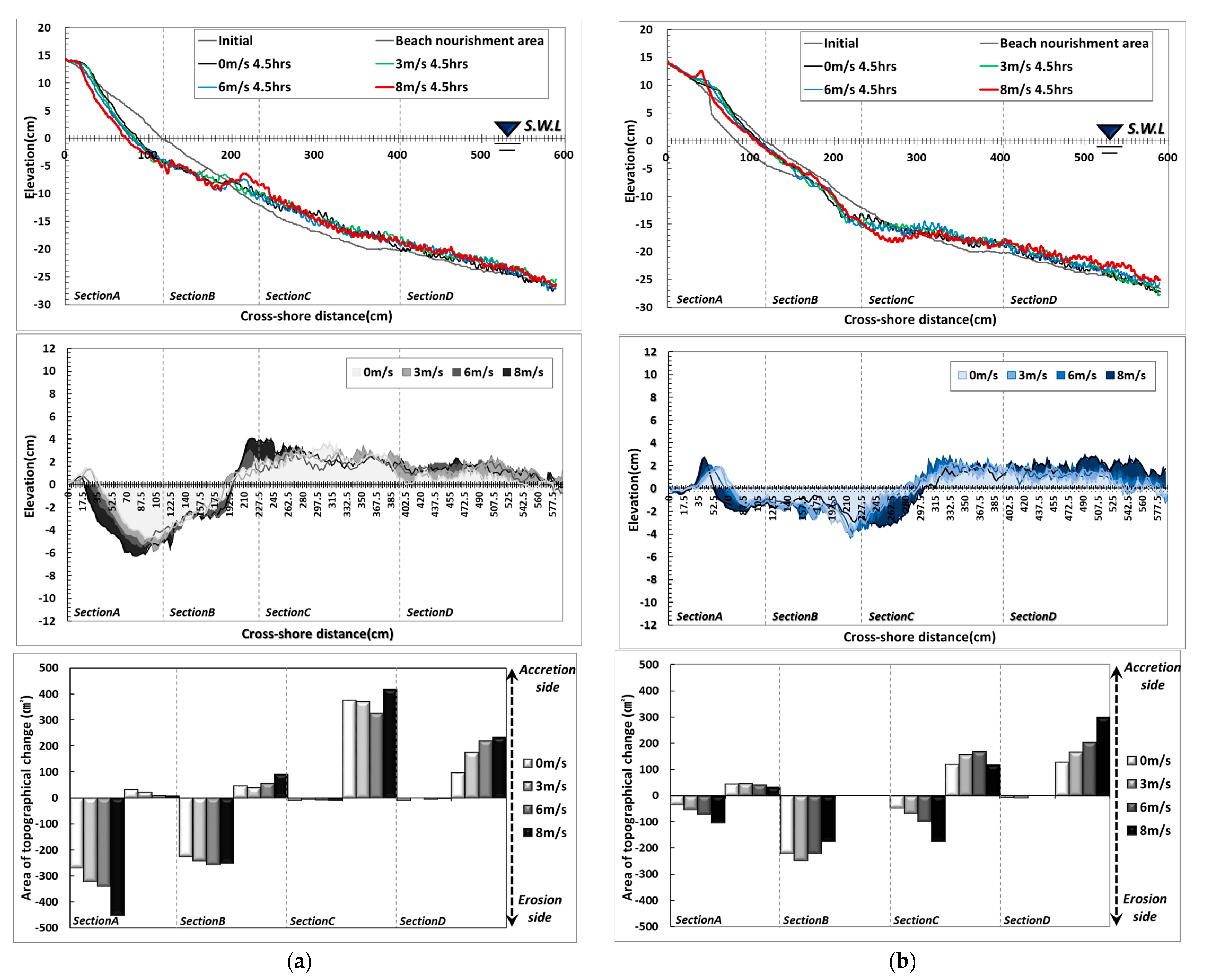
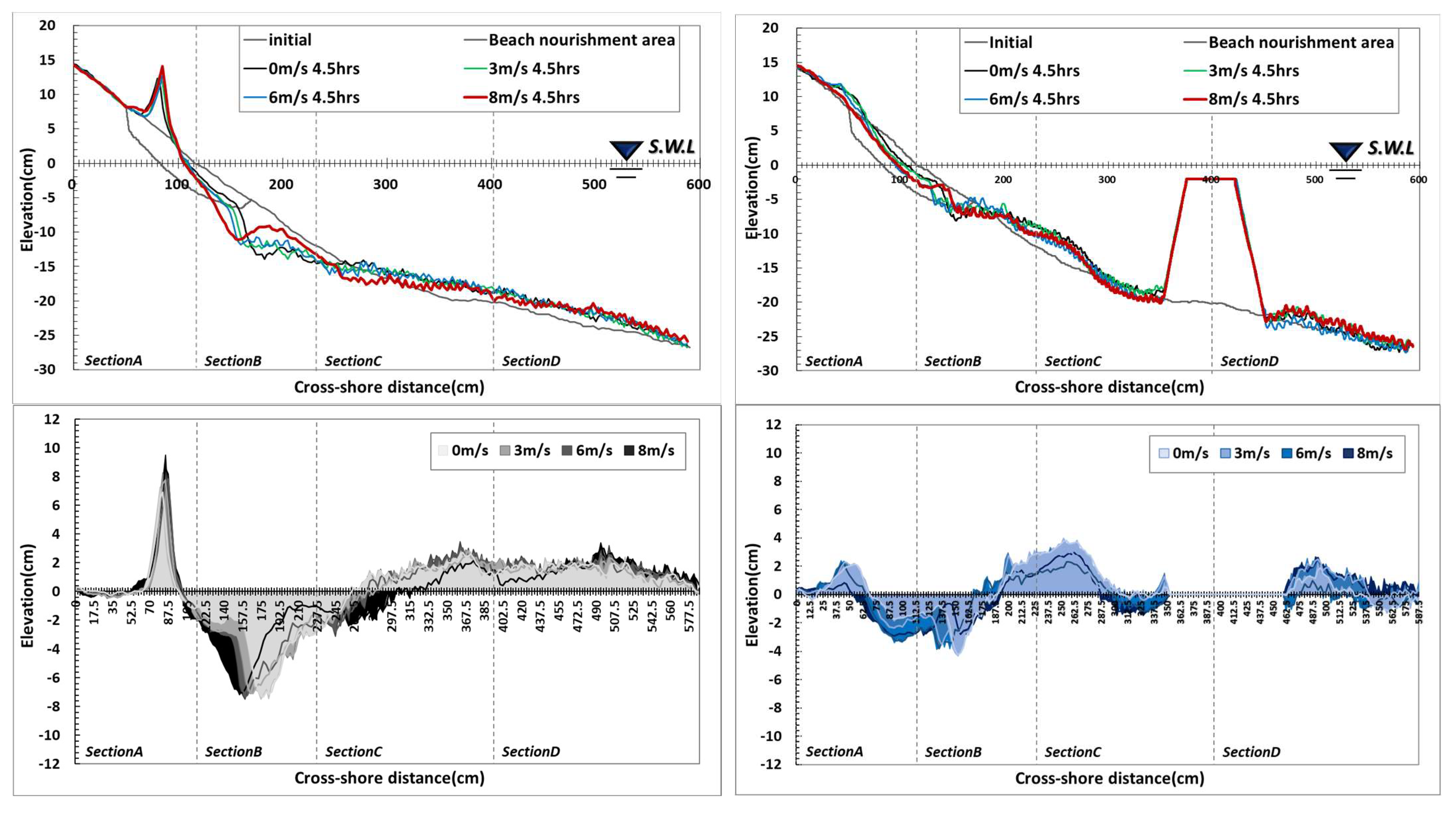
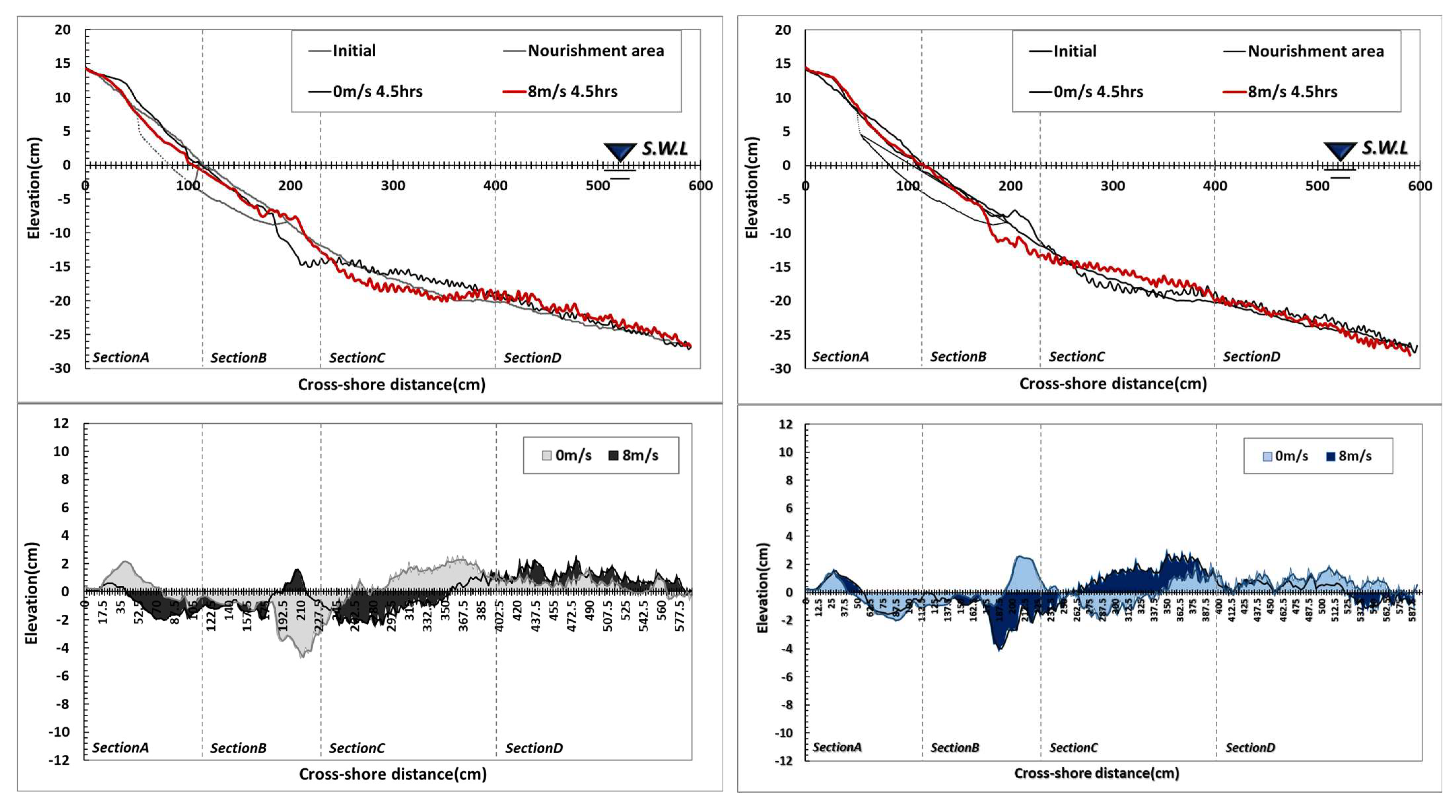
Examining the topographical changes in Type A, the shoreline was found to have retreated due to wave action under windless conditions, and large-scale sand loss occurred on the foreshore and backshore. Some sand was deposited in the backshore by wave run-up, while most of the sand that made up the shoreline moved to the seaside and formed a sand bar. With 3 m/s wind, the beach profile was similar to that without wind conditions. However, the range of sand loss increased in the direction of the backshore from the water surface, and the lost sand was deposited at the 200 cm point. With 6 m/s wind, the amount of sand loss increased in the direction of the backshore from the shoreline, and the sand dune formed in the backshore decreased. With 8 m/s wind, the erosion area increased, and the lost sand moved to the seaside, increasing the size of the sand bar. The test results showed that wind action did not have a significant effect on sand movement when the wind was 3 m/s, but the erosion area tended to increase in proportion to the wind speed. Also, the extent of erosion caused by wind action was prominent in areas from the coastline to the backshore and above the water surface, and the amount of erosion in the foreshore affected the formation of the sand bar at point X: 200 cm.
As shown in Figure 4, four sections were used to quantitatively compare topographical changes. The sections were divided based on the results of a cross-section composed of 0.1 mm sand under 6 m/s wind condition: Section A (backshore~shoreline), Section B (shoreline~sand bar), and Sections C and D were divided into the sand bar~offshore. The experiment domain was broader, but the analysis results were organized for X: 0–600 cm and Y: −25–15 cm, where changes in topography are distinct. As for the sectional erosion and accretion situation, erosion was predominant in Section 1, and erosion and accretion occurred in Section 2, but erosion trends were somewhat stronger. In Section 3, accretion was dominant in the section where lost sand was deposited, and in Section 4, accretion occurred due to the influence of sand movement by the undertow.

Figure 4.
Results of topography change with wind speed variation: (a) Type A; (b) Type B.
In Type B, the sediment transport rate around the shoreline decreased significantly compared to Type A due to the increased particle diameter. The moved sand was deposited in the backshore direction, and the bottom level was lowered in section X: 200–250 cm due to the influence of scour. The decrease in topographical changes around the shoreline was due to the impact of the larger particle diameter, and the increased weight and settlement velocity caused the sand particles to be suspended instantaneously when waves impacted the nourishment particles, but the time suspended in water was significantly reduced compared to Type A. Also, the nourishment area with a larger particle diameter accelerated the seawater velocity when the waves that rose to the shore returned to the seaside, and scour occurred at the boundary between the existing ground and the nourishment area due to a strong undertow. At 3 m/s wind speed, the beach profile did not show a significant difference compared to when there was no wind, and when the wind speed was 6 m/s, the erosion area in the backshore increased slightly due to strong run-up. With an 8 m/s wind, the erosion area in the backshore increased relative to the shoreline, and some particles formed a dune in the backshore. Also, the strong run-up developed by the wind accelerated when propagating toward the seaside, increasing the range of scour. Small topographical changes occurred in the area located between X: 200 cm in the nourishment area, even though the existing fine particles were distributed. Some of the nourishment particles were moved to that area while repeating wave run-up and run-down, which affected the erosion and accretion trends. In terms of comparing erosion and accretion by area, Section A, located on the backshore based on the shoreline, showed similar erosion and accretion areas. In Section B, erosion was strong due to the influence of scour, and in Section C, some erosion areas were formed due to the influence of scour, but accretion was dominant overall due to the deposition of sand transported from the shoreline. In Section 4, accretion was strong due to the transport of scoured sand.
In Type C, wave action moved the particles distributed near the shoreline to the backshore, and the accretion rate gradually increased over time to form a steep dune. The topography behind the dune remained unchanged due to the influence of the deposited riprap dune, and large-scale scouring occurred in front of the shoreline. Also, the sand transported by scour was deposited over a wide range toward the seaside. With a 3 m/s wind, the riprap dune’s slope became steeper, and its location also advanced slightly toward the shoreline. Also, the extent of scour in front of the shoreline was the same as when there was no wind, but the depth was slightly decreased while the width was increased. The distribution of deposited sand on the seaside was similar to that without wind. With a 6 m/s wind, the riprap dune became steeper compared to a 3 m/s wind, and its peak became sharper. In addition, the extent of scour in the front increased in the X direction, and the shape of the sand deposited toward the seaside was similar with or without wind. With an 8 m/s wind, the riprap dune’s slope became steeper, and its location moved toward the shoreline. The scour area also moved toward the shoreline, forming a wide erosion zone from it to the coastline. The extent of erosion at the foreshore ranged from the shoreline to X: 300 cm, based on the initial topography, considering the run-down phenomenon developed by the dune and the topographical changes related to wave breaking. This phenomenon indicates that the wind’s action must have been strong enough to increase the position of the surf zone and the magnitude of wave breaking, and an 8 m/s wind speed was analyzed to have slightly different effects from 3 m/s and 6 m/s winds under the conditions applied to the tests. In other words, based on the tests, the topography is more affected by waves at wind speeds between 0 m/s and 6 m/s, but when the wind speed reaches 8 m/s or more, the effect of the wind is greater than that of the waves. Comparing the extent of erosion and accretion shows that accretion was dominant in Section A due to forming a large-scale riprap dune. In Section B, erosion was dominant due to particles moving behind the shoreline and scouring at the beach nourishment boundary. In Section C, erosion and accretion were mixed, but accretion was more dominant, and accretion was dominant in Section D (Figure 5).
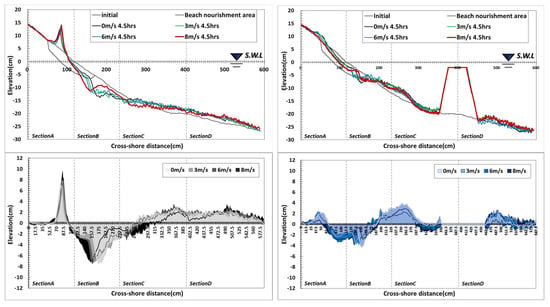

Figure 5.
Results of topography change with wind speed variation: (a) Type C; (b) Type D.
In Type D, a submerged breakwater was installed, and beach nourishment was not applied. Under wave-only conditions, the submerged breakwater reduced the incident waves, and the erosion area near the shoreline was significantly reduced compared to Type A. However, the run-up and run-down caused by incident waves moved the sand on the shoreline, with some of it deposited behind the coast, while the rest was deposited to the seaside. With a 3 m/s wind, the shoreline retreated slightly, and the erosion area increased. Wind action moved the scour generated in the foreshore toward the coastline, and the depth of the scour decreased while the width increased. With 6 m/s winds, the topographical changes around the shoreline slightly increased compared to 3 m/s winds. However, both of the conditions generally showed similar topographical changes in terms of the size of the sand dune formed in the backshore and the area where scour occurred in the foreshore. With 8 m/s winds, the sand dune formed in the backshore was reduced, and the scour area on the foreshore moved to the seaside. The remaining areas showed similar patterns to other conditions. Since wind increases the force of waves toward the shore, the larger the wave crest, the more the wave is affected by the wind and increases damage on the coast. However, the submerged breakwater reduces wave energy, so waves with relatively less energy reach the shore. Therefore, even if the wind is strong, the waves reaching the coast are not large in size, so there are limits to creating high run-ups and large-scale topographical changes. As for the trend of erosion and accretion by area, both were similar in Section A, but the erosion trend was proportional as the wind increased. In Section B, the amount of erosion was similar, but the amount of accretion decreased as the wind increased. In Section C, the amount of accretion decreased relative to the wind strength. Overall, there were accretion trends. In Section D, accretion increased proportionally to wind strength, indicating an accretion trend (Figure 5).
3.1.2. Spectrum Analysis
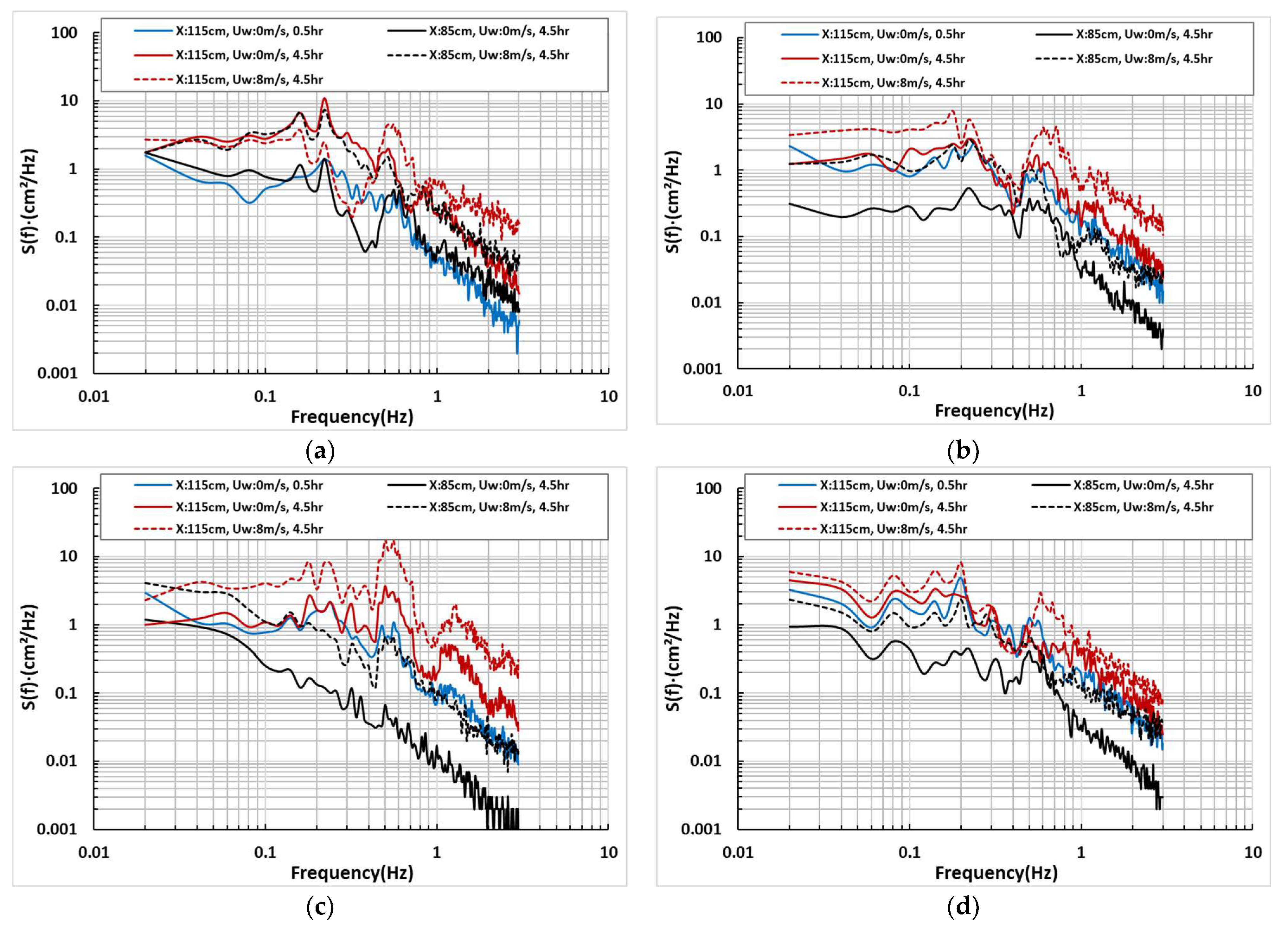
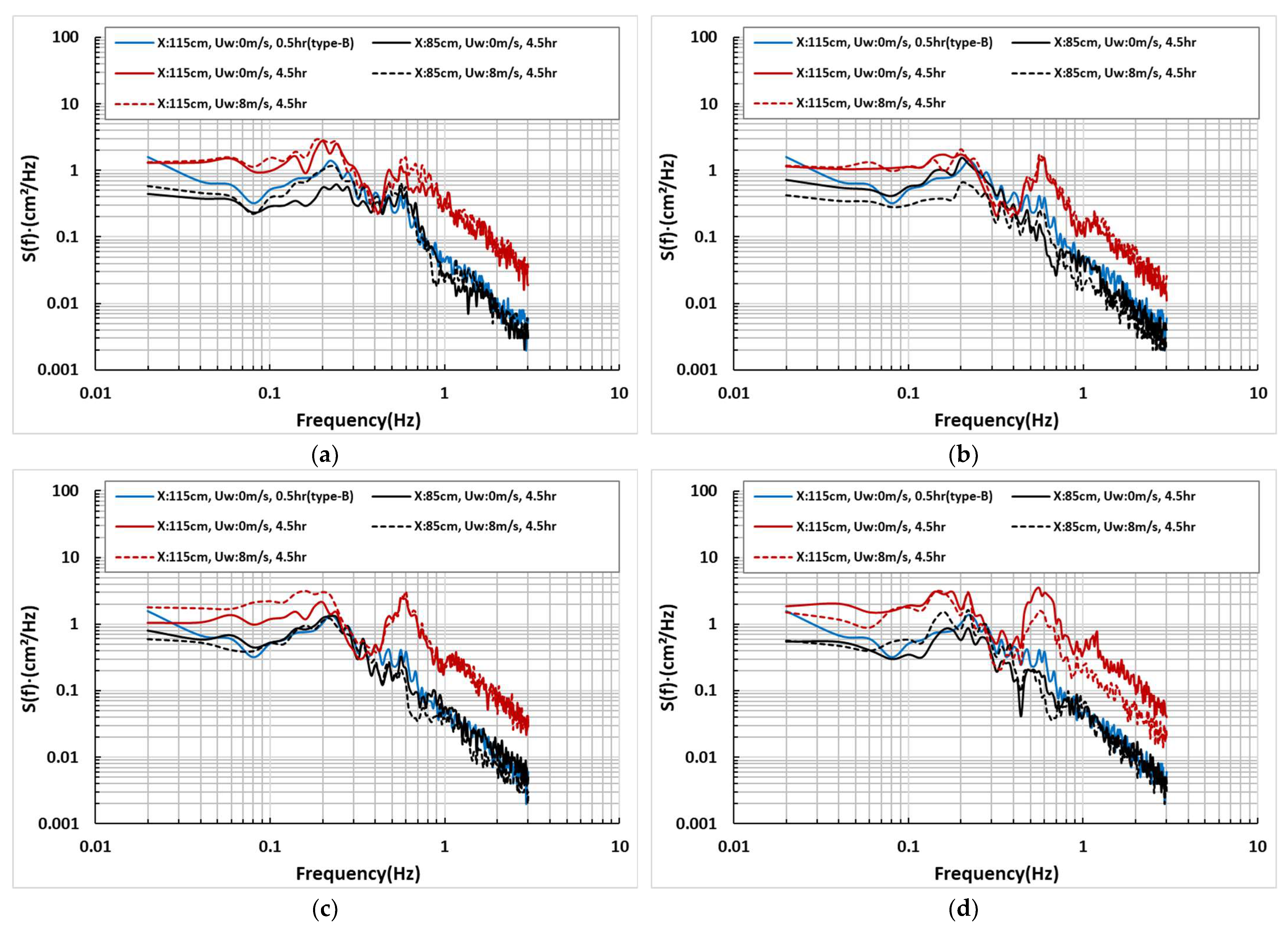
The magnitude and duration of waves determine the size of topographical changes in the foreshore, and differences occurred even under the same incident waves in the four beach profiles reviewed above. Since topographical changes in the foreshore mean that the wave distribution formed at the beginning of the test has changed, changes in wave energy were examined at each time interval. Wave analysis was performed on the shoreline (X: 115 cm) and behind the shoreline (X: 85 cm) among the various measurement points. Based on data generated between 0 and 0.5 h, without considering winds, the results between 4.0 and 4.5 h were compared when the cross-sectional topography reached quasi-equilibrium. The frequency spectrum method was used to analyze the data, and wind speed changes (0 m/s, 8 m/s) for each cross-section were also examined. The irregular wave applied to the test is composed of a synthesis of several regular waves. When it has a single direction, as in this study, the frequency spectrum is used to analyze the wave’s energy density. Although there are other standardized methods through various probability distributions and statistical analyses, this study used the modified Brestschneider–Mitsuyasu spectrum for wave signal settings and spectrum analysis (Figure 6).

Figure 6.
Results of spectrum analysis on the shoreline and backshore area with beach profile changes: (a) Type A; (b) Type B; (c) Type C; (d) Type D.
According to the spectrum analysis, beach profile Type A with 0.1 mm reached quasi-equilibrium based on the state at the beginning of the test with only waves (blue line) and the energy density (red line) at the shoreline (X: 115 cm) showed an increased distribution in most frequency ranges, although there were some differences related to changes in the wave breaking points. This phenomenon is likely due to the increased water depth at the shoreline due to erosion and the increased size of the waves reaching the shoreline since the beginning of the test. The long wave period zone 4.5 h after wave generation showed similar trends with or without wind. However, in the range of Hz:0.1~1, slightly higher energy density values were generated under windless conditions, likely due to wave breaking. The wave energy on the rear side of the shoreline was proportional to the topographical changes. Based on the waves measured at the coastline (blue line in Figure 6), the results 4.5 h after wave generation (X: 85 cm, block line) were similar because a topography like the initial shoreline was formed at X: 85 cm over time. Under winds, the energy density also increased because the scale of the waves increased due to the widened extent of the erosion.
In Type B, the wave energy values at the beginning of the test and the results after 4.5 h were similar. This was because less sand loss occurred due to the higher nourishment sand particle diameter, as shown in the topographical change results. During wind action, the amount of sand loss increased, creating a higher energy density. At X: 85 cm, the magnitude of the waves decreased due to the absence of wind, resulting in a low energy density. When accompanied by wind, the increase in topographical changes and high wave run-up increased the energy density, resulting in a distribution similar to that of the shoreline at the beginning of the test.
In Type C, rapid topographical changes occurred on the foreshore and backshore based on the shoreline, and the wave energy also changed over time. The amount of energy change increased when incorporating wind. The wave distribution behind the shoreline was similar to the initial measurements in the long wave period domain when there was no wind. However, a sharp decline in energy occurred as the period decreased. Under long wave period conditions, the density values increased and were similar to the wave energy at the initial shoreline.
In Type D, the range of topographical changes was small, resulting in smaller wave changes at the shoreline. The analysis found that the energy density values increased slightly compared to the initial measurements, but the overall distribution was similar. However, the values increased when incorporating wind, but the difference decreased compared to other conditions. The distribution of waves at X: 85 cm showed a low energy density with only waves, similar to the wave height distribution at the shoreline with winds. The test results showed that wave energy is closely related to changes in water depth, and when incorporating wind, the wave height distribution increased not only shoreline but backshore.
3.2. Sediment Transport according to Changes in Nourishment Area
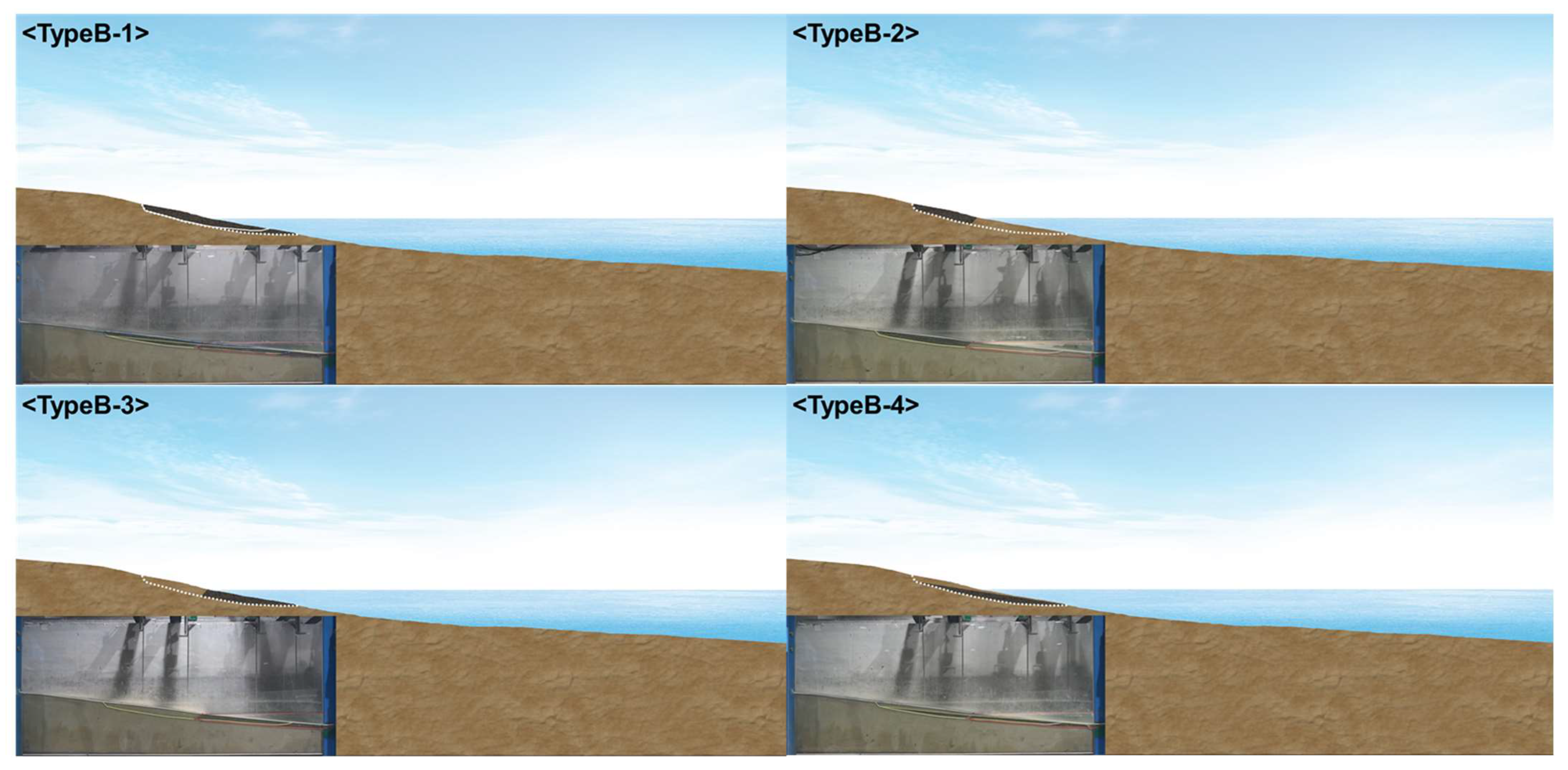
The previous section examined beach profile changes after applying beach nourishment with larger particle diameters to an erosive beach and compared the results with installing a submerged breakwater. The beach profile change was the smallest when the nourishment sand particle diameter was 1.0 mm, and the topographical changes were similar to those when installing a submerged breakwater. In this section, test profiles were constructed, as shown in Figure 7, to examine the beach profile evolution when the nourishment area changed with a sand diameter of 1.0 mm, which was most effective among the test conditions for beach profile conservation. The basic shape is Type B, and when applying nourishment sand with higher particle diameters, severe scouring occurs at the boundary between the nourished area and the existing sand (X: 200–300 cm). Thus, shapes like Type B-1 were configured to examine the difference in scour and sand movement when increasing the range of beach nourishment. In addition, Type B-2, 3, and 4 were configured to investigate the effects on topographical changes depending on whether all of the erosive area was nourished or only parts of it. The test conditions are summarized in Table 2. Most conditions are the same as in Table 1. The results without wind are compared with those that had 8 m/s winds.

Figure 7.
Test profiles for cross-sectional topography. Type B-1: the nourishment area (dark shade) is enlarged more than Type B; Type B-2: nourishment is applied to only the left side of the shoreline; Type B-3: nourishment is applied to only the right side of the shoreline; Type B-4: nourishment is applied to only bottom side of the shoreline.

Table 2.
Test conditions for Type B1–4.
3.2.1. Topography Change
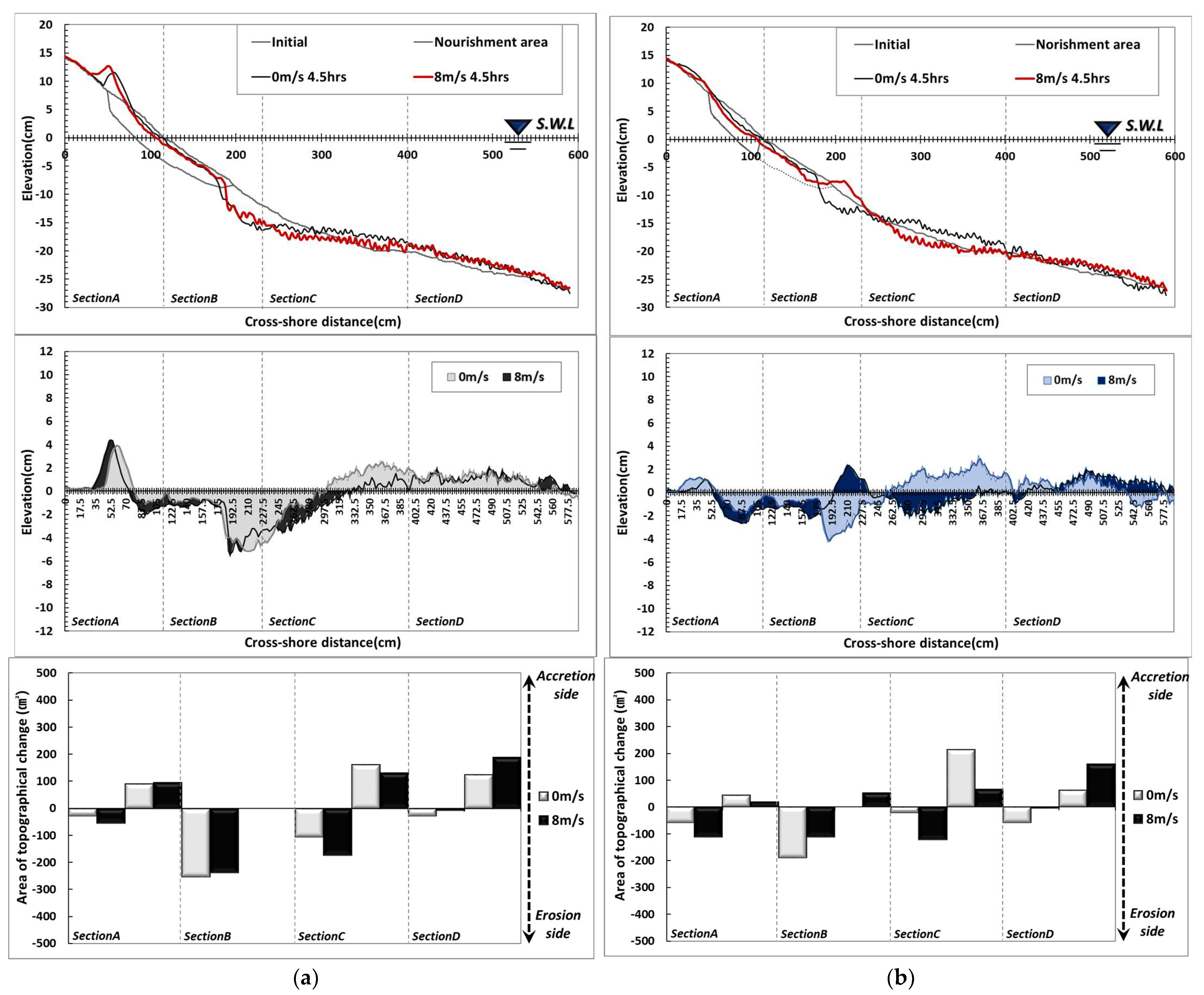
Examining the topographical changes in Type B-1, it was found that the transport of nourishment sand around the shoreline occurred only in some areas on the surface, and the transported particles moved landward and formed a dune (Figure 8).

Figure 8.
Results of topography change with wind speed variation: (a) Type B-1; (b) Type B-2.
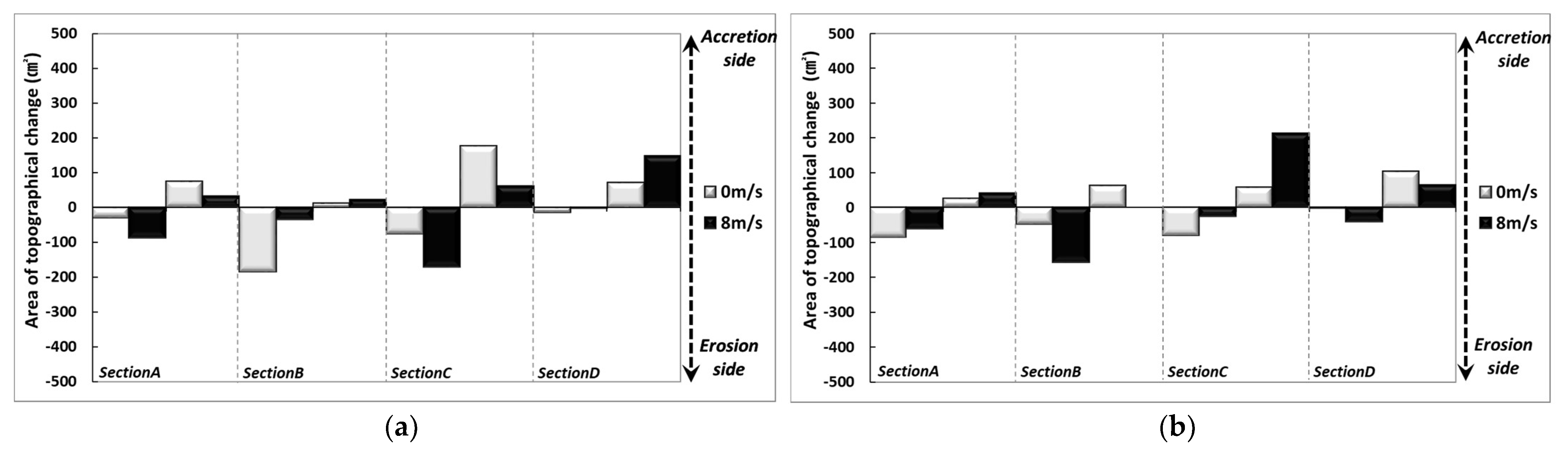
Sand loss due to scouring occurred over a range of about 1 m at the foreshore (200 cm). At this point, the undertow accelerated due to the increased nourishment range when waves that rose to the dune returned offshore, with the effect of forming a surf zone, resulting in rapid scouring from the nourishment area’s boundary. The scoured sand was transported offshore and created a sand bar. With 8 m/s winds, erosion increased around the shoreline, and the dune formed behind the shoreline moved toward the backshore direction. Also, scouring and sand loss at the foreshore increased, and the transported sand was deposited offshore. In terms of comparison by section, both erosion and accretion increased according to wind action in Section A, and the extent of erosion caused by scour was slightly decreased in Section B. In Section C, wind action increased erosion and decreased accretion. In Section D, wind action slightly reduced erosion and increased accretion.
In Type B-2, transport of nourishment sand occurred in the wet and dry zone where wave run-up and run-down took place, as in Type B-1 when there was no wind, and some of the sand moved to the backshore direction to form a dune (Figure 8). At X: 200 cm, scour occurred due to the current toward the offshore direction, and the scoured sand was transported and deposited near X: 300 cm. With 8 m/s winds, the extent of erosion increased along the coast, and the formation of dunes decreased on the backshore. Topographical changes due to wind action occurred because beach nourishment was concentrated in the backshore relative to the shoreline and also because some of the nourishment sand was moved and distributed on the foreshore due to sand movement from the foreshore. Although nourishment was not applied between 100 and 200 cm, no significant topographical change occurred, and changes in the width of the surf zone caused by the wind and the strength of the undertow moved the nourishment sand near point X: 200 cm. Analyzing by section, erosion increased in Sections A and C with wind action, and the amount of accretion increased in Sections B and D.
In Type B-3, small-scale topographical changes occurred around the shoreline with waves only (Figure 9). In particular, the front of it, where nourishment sand was applied, maintained features similar to the initial topography, and an accretion trend could be observed behind the shoreline. Scouring occurred in the boundary layer of beach nourishment (X: 200 cm), and the scoured sand moved to the seaside to form a sand bar. Under wind incidence, sand loss occurred from the shoreline towards the backshore, while a generally constant cross-section was formed on the foreshore. Sand transport occurred in section X: 220–380 cm, but section X: 200–220 cm was less affected by topographical changes due to the movement of nourishment sand. However, topographical changes occurred in sections where nourishment sand was not moved. In terms of topographical changes by section, erosion increased in Sections A and C due to wind action, and the amount of accretion increased in Sections B and D.
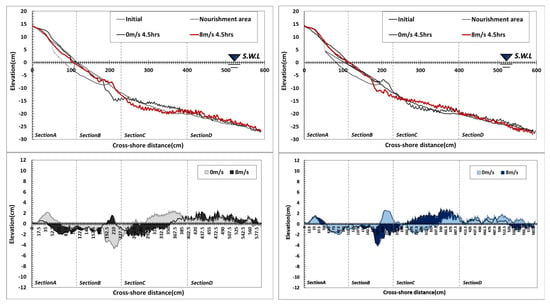

Figure 9.
Results of topography change with wind speed variation: (a) Type B-3; (b) Type B-4.
In Type B-4, the entire nourishment area was divided into upper and lower sections and beach nourishment was only applied to the lower part (Figure 9). According to the wave-only test results, sand moved behind the shoreline and formed a dune in the backshore. In the foreshore, scour occurred due to the influence of wave breaking and current and undertow, and the scoured sand was transported to the seaside and deposited. When wind was incorporated, the extent of sand transport in the foreshore increased slightly, while the size of the dune on the backshore decreased. Wave action moved the nourishment sand to the seaside and formed a sand bar and sand loss occurred in front of the sand bar due to the influence of the undertow. In terms of topographical changes by section, erosion was slightly increased in Sections A and C due to the wind’s action, while accretion was dominant in Sections B and D. The analysis showed that topographical changes occurred with and without winds at 200 cm under the conditions of Type B-2–4. These results were due to changes in the surf zone formed at the beginning of the test, changes in wave run-up, and changes in the range of sediment transport due to nourishment sand transport.
3.2.2. Spectrum Analysis
As a comparison of the wave signals, as shown in Figure 10, the results generated at the shoreline (X: 115 cm) and behind the shoreline (X: 85 cm) were compared based on the initial test conditions when there was no wind in Type B, and the trend of wave energy according to changes in nourishment area was examined for each cross-section.

Figure 10.
Results of spectrum analysis on the shoreline and backshore area with beach profile variations: (a) Type B-1; (b) Type B-2; (c) Type B-3; (d) Type B-4.
Waves in Type B-1, where the nourishment area extended to the seaside based on Type B conditions, created increased energy density values at the shoreline. As shown in Figure 10 (L), the shoreline regressed when the entire nourishment area was filled with 1.0 mm sand, and the wave height increased as the range of the waves approached the land due to the effect of the increased water depth. However, there was no significant difference with wind variation, which was likely because the influence of wind on sediment transport was relatively small under increased particle diameter conditions. Behind the shoreline, most of the trends were similar to the initial test values in the short wave period domain, and the difference increased moving to the long wave period domain. However, with winds, the results were similar in the range of 0.1 Hz and above, but there were density differences in the long wave period domain.
In Type B-2, the energy density tended to decrease relatively. Waves measured at the shoreline showed a smaller energy distribution at 0.2–0.4 Hz compared to the initial conditions. The differences in the increase or decrease were also smaller in the rest of the domains compared to Type B-1. The difference with or without wind was also insignificant. Waves behind the shoreline generally showed small density values, and the long wave period component had a greater effect on wave energy when there was no wind.
In Type B-3, the difference in energy density increased compared to Type B-1. When wind along the shoreline was considered, the short wave period domain showed a distribution similar to waves-only conditions. However, the energy density tended to increase in the long-wave period domain. Behind the shoreline, most trends were similar to the initial test values, and there was no significant difference with or without wind.
Type B-4 showed an increase in energy density at the shoreline compared to Type B-1. In particular, the wave energy density above 0.3 Hz was higher when there was no wind, and the distribution was also rather large in the long wave period domain. Behind the shoreline, the wave signal increased slightly under winds in the mid-domain, but there was no significant difference in the remaining sections. The analysis showed that energy density changed according to the beach nourishment conditions, and in some cases, the influence of wind components was smaller than that under wave-only conditions. However, overall, the increase in water depth at the observation points was proportional to the increase in energy density.
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Topographical Evolution According to Cross-Sectional Changes
The critical value of sedimentation momentum is generally interpreted using the critical shield number (), a function of the particle Reynolds number [29]:
where is the bottom shear velocity, is the fluid density, is the particle’s specific gravity, is the gravitational acceleration, is the particle’s median diameter, and is the particle’s kinematic viscosity. In terms of the transport condition of suspended solids, particles instantly move in the vertical direction by the fluid’s interference, and depending on the magnitude of the shear stress, they will move in the flow direction or settle under the influence of gravity [30].
As shown in the tests, the smaller the particle diameter, the longer the suspension state continues, and the suspended sediment mainly forms the topographical changes. However, under 1.0 mm conditions, the suspension phenomenon is the same, but due to the faster settlement velocity, the floating force decreases, and the drag force is relatively increased. This phenomenon can be interpreted using the following equation [31]:
where : surface friction force, : maximum shear stress, : porosity of sedimentation, : average drag force of a single moving sediment, : wave number, : velocity component on the sea bottom, : fluid density, : particle density, : concentration of sediment suspended on the sea bottom, and : surface friction velocity. is expressed as:
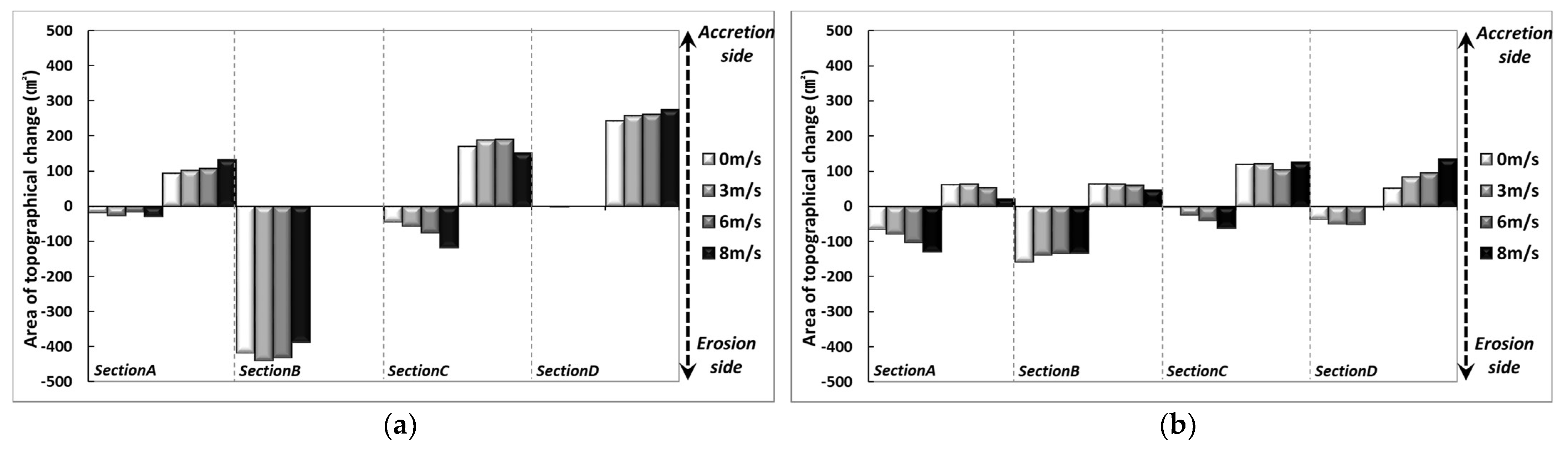
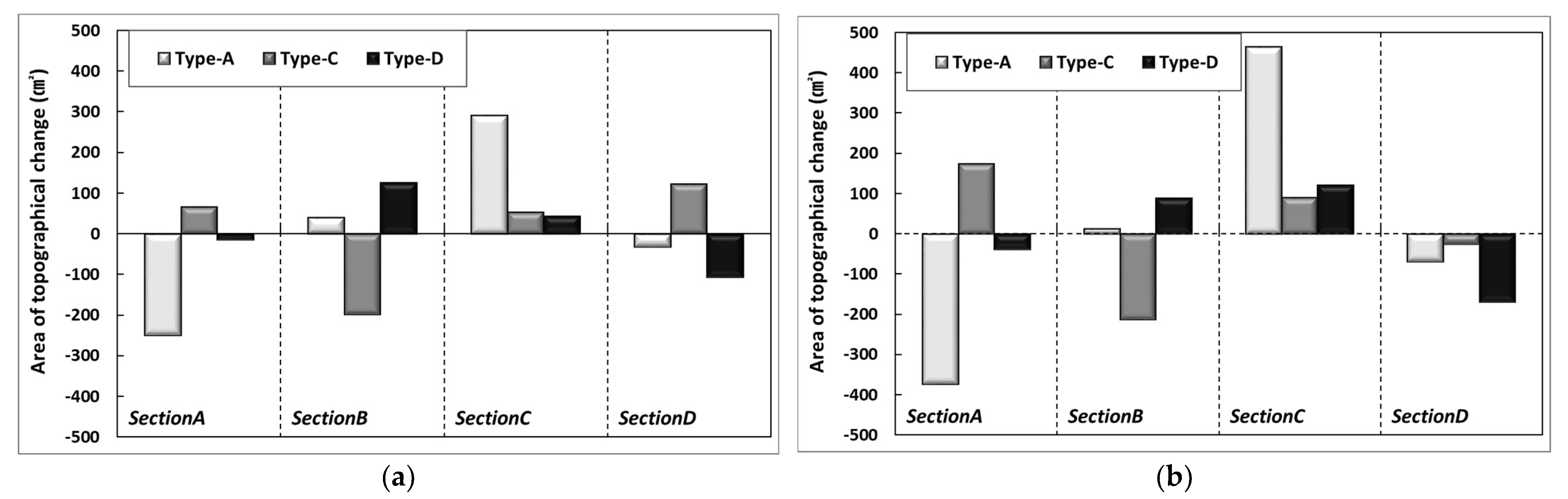
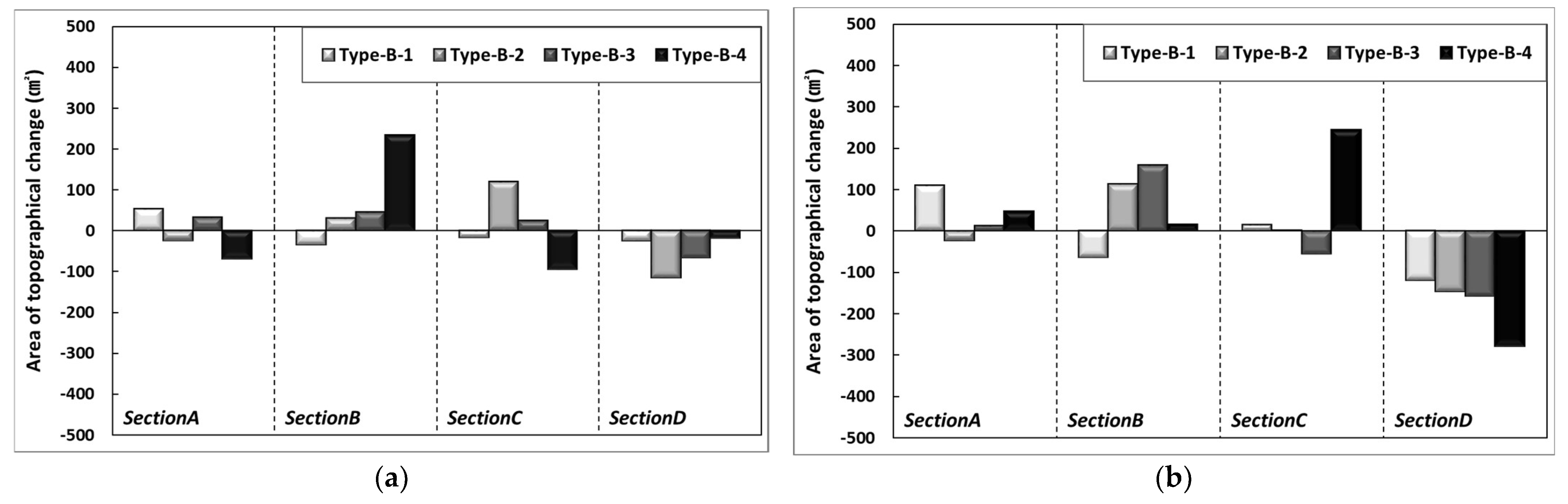
where is the drag force coefficient, and is the mean transfer rate of the particles. The test results showed that 1.0 mm particles have a smaller movement range than 0.1 mm particles. Although a clearer trend can be found by examining the sediment transport characteristics according to changes in particle diameter, this study focused on investigating the overall sediment transport mechanism for particle diameter and external force change. Thus, it is necessary to configure detailed experimental sections in the future to identify the critical points for erosion and accretion. As shown in the results in Figure 11, in the area located between the shoreline and the backshore, the differences in beach profile changes due to applying 1.0 mm nourishment sand show that the extent of erosion increased as the particle diameter decreased. On the other hand, accretion increased as the particle diameter increased. Although increasing the particle diameter resulted in different characteristics, the results of 1.0 mm conditions were similar to that of installing a submerged breakwater, showing that applying 1.0 mm nourishment sand has an effect equivalent to installing hard structures. Section 2, located near the shoreline, shows an opposite trend due to the influence of strong scour caused by wave run-down and forming a surf zone for incident waves. Section 3 was the main section in which the sand moved from Section 1 and Section 2 was deposited, and this phenomenon increased by the wind’s effect. Figure 12 shows the difference from Type B when changing the range of beach nourishment for the same particle diameter (d50: 1.0 mm). Accretion was observed around the shoreline when the nourishment area was extended to the seaside (Type B-1) and when beach nourishment was applied in the seaside direction relative to the coastline (Type B-3). Sand loss occurred when beach nourishment was performed toward the land based on the shoreline (Type B-2) and when beach nourishment was applied to the lower section (Type B-4). Some sand loss occurred under the extended beach nourishment conditions in the area directly in front of the shoreline, while other conditions showed an accretion trend. The influence of wind reduced as the particle diameter of the nourishment sand increased. Although some differences occurred depending on the conditions, the 1.0 mm diameter particle applied to the test was not significantly affected by the wind compared to the 0.1 mm diameter particle.

Figure 11.
Comparison results of beach evolution of Type A, C, and D against Type B: (a) Wind 0 m/s; (b) Wind 8 m/s.

Figure 12.
Comparison results of beach evolution of Type B-1–4 against Type B: (a) Wind 0 m/s; (b) Wind 8 m/s.
4.2. Analysis of Wave Run-Up Characteristic
The high wave run-up is directly related to sediment transport. The high wave run-up is the formation of a water surface curve above the still water level (the sea level in the absence of waves). The run-up height increases proportionally as the wave energy increases. The high wave run-up leads to a rise in water level due to wave setup [32], and the increased water level plays a role in increasing the size of the incident waves. In addition, the wave run-up phenomenon can define the boundary of the region of wave action, which directly affects onshore sand transport, deposition, and erosion and is of obvious importance in planning coastal setback distances or assessing coastal flooding probabilities [33]. In particular, during the invasion of high waves with strong winds, the high wave run-up can cause large-scale topographical changes, so it is necessary to review it carefully [34]. The waves used in this study are high-wave strong wind data extracted from buoy data, so the analysis of high-wave run-up is considered to be useful as a review of the phenomenon of topographical changes and mitigation measures.
The tests show that the extent of topographical changes is proportional to the increase in wind speed. Many studies have conducted tests on winds, but [17] shows similar trends to this study for wind and waves. Demirbilek examined the wave run-up height under wind, waves, and wind + waves for submerged breakwater installation conditions through 2D cross-sectional experiments and installed a wave height meter in front of the shoreline to present the wave height change at each point through spectrum analysis. The results also suggested that the wave run-up height and wave set up behind the shoreline increase when waves and wind coexist. However, [17] used the Jonswap spectrum to create wave signals and applied Froude similarity (1 V = 10 H) with distorted horizontal and vertical scales. The submarine topography and structures were also installed in a fixed condition, so there are limits to making a quantitative comparison with this study. Therefore, this section examines the tendency according to time history with the ratio of the incident wave height to the wave run-up height when the wind speed and cross-section change. This was conducted using the method for wave run-up height according to the external force change among the analysis results in [17]. The wave run-up height was estimated based on measurements using the empirical formula presented by [31] below:
where , : wave setup height, : significant wave height on the offshore side, an : surf similarity parameter calculated as follows:
where is the significant wave length on the offshore side and refers to the sea bottom slope. A foreshore slope of 1/10 is applied in the equation above. The wave length was calculated using the wave height measured at the shoreline and the wave period measured at the front of the wave generating panel according to the time history. This study used the empirical formula proposed by [35] for wave run-up height and Hunt’s formula [31] for . is arranged as follows:
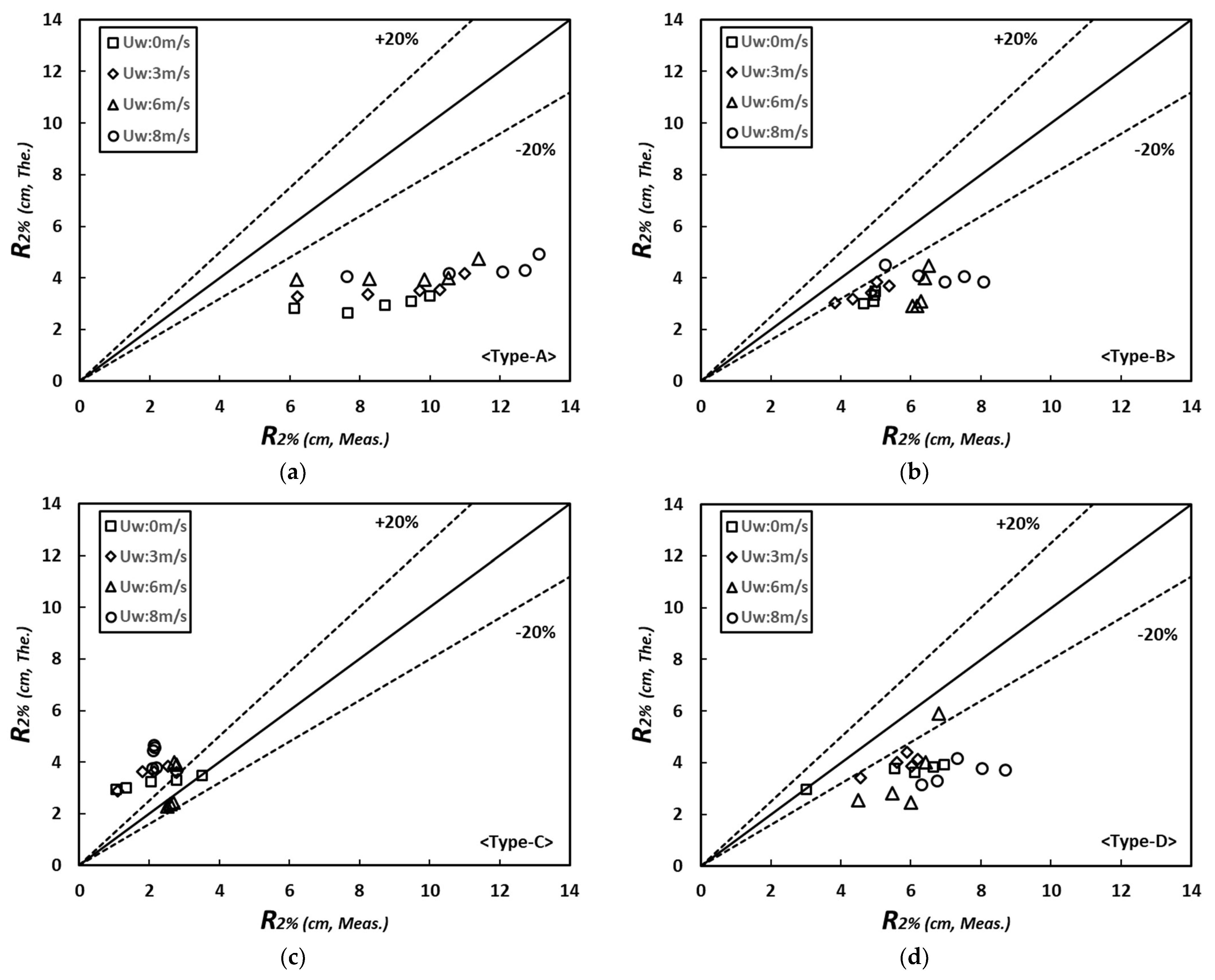
where is the wave setup height, is the run-up height for incident waves, and is the run-up value associated with gravity wave. Examining for different wind speeds, it was found that the wave run-up height tended to increase with time. In the case of Uw: 0 m/s, the run-up phenomenon at the beginning of wave generation was similar in all cross-sections. However, the run-up height also changed according to topographical changes (Figure 13). When waves were generated for 4.5 h, the highest wave run-up height occurred in Type A, where topographical changes occurred actively around the shoreline, and the erosion range was also the largest. On the other hand, the lowest wave run-up height occurred in Type B, which had the smallest change in water depth. In conditions accompanied by wind, the run-up phenomenon increased, and with 8 m/s winds, the run-up in Type A was about twice as high as that of Type B. The results of comparing the run-up height () estimated above and the run-up height () examined through the experiment are as follows. In Type A, the wave run-up phenomenon in the experiment had a greater effect than the theoretical results. This tendency occurred with or without wind, and as the wind speed increased, changes in wave run-up increased. The difference in run-up height is because the effect of wind is not considered in the theoretical equation. The difference occurs even without wind effect because the wave action caused erosion over a wide range. Therefore, it is analyzed that the height of wave run-up was gradually developed. Therefore, since the run-up phenomenon is closely related to erosion, the calculation of run-up height in erosive beaches, like the test conditions, should be reviewed through experiments. In Type B, the topographical changes were reduced compared to Type A, so the difference between the theoretical and test results was relatively lower but was still more than 20%. Although the beach nourishment particle of a larger diameter in Type B is suspended momentarily by waves, the fast settlement velocity induces a reduction in topographical changes near the shoreline and controls the development of wave run-up. In Type C, the theoretical results were larger than the experimental results. This is because the erosion around the shoreline due to topographical changes in the experiment is small, and waves are dissipated by large-scale riprap dunes deposited by wave action. Type D shows limitations in the development of wave run-up because the waves reduced by the submerged breakwater cause topographical changes to a limited extent. However, the difference between the theoretical and experimental wave run-up increased because continuous wave attacks caused the shoreline to regress and developed wave run-up, which in turn increased the drag force towards the shore when combined with wind.

Figure 13.
Variation of values with dependence on the time, wind speeds, and beach profiles change: (a) Type A; (b) Type B; (c) Type C; (d) Type D.
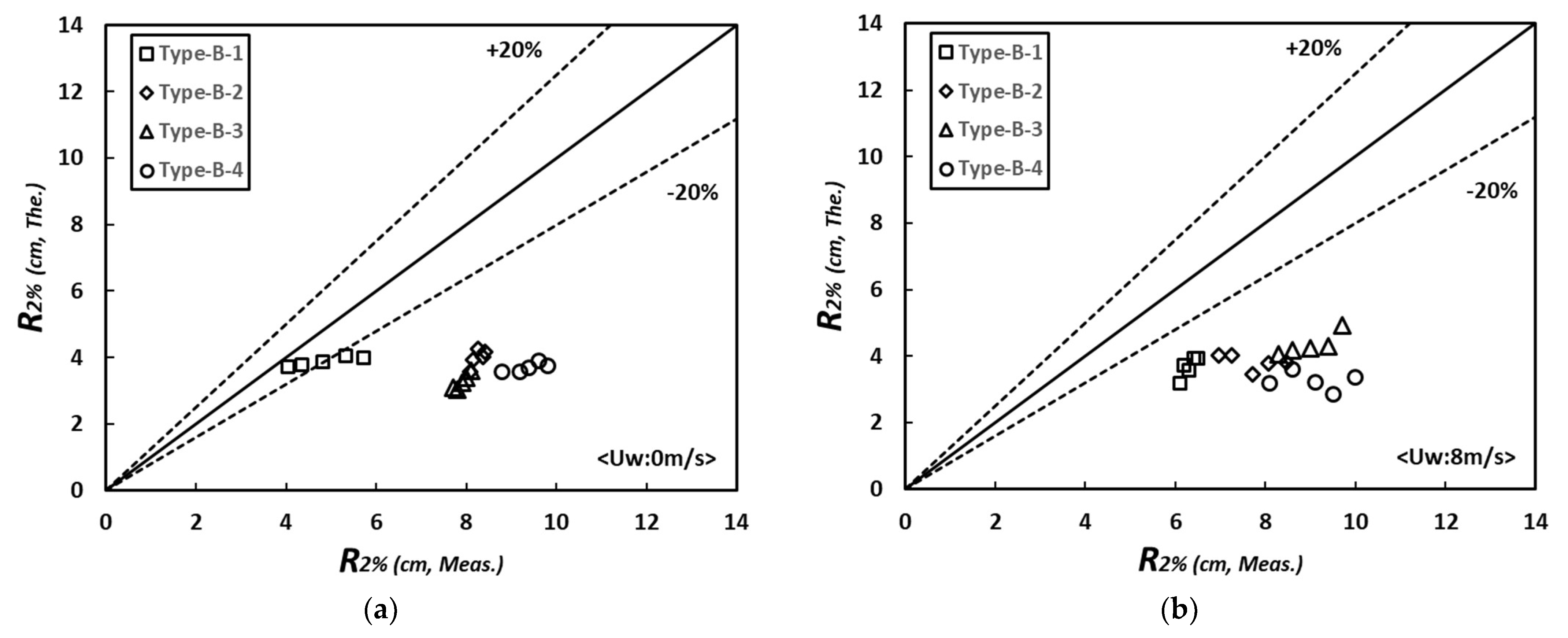
The results of applying the theoretical formula to Type B-1–4, which are the conditions of changing the nourishment area on Type B (which has the lowest degree of topographical changes), show similar trends, although there were some differences depending on the nourishment area. Compared with the experimental results, Type B-1 showed a similar trend to the theoretical formula when there was no wind in the initial part of the test. However, as the wave generation time increased, the range of topographical change increased, and the wave run-up height increased proportionally. When the range of beach nourishment was changed based on the shoreline (Type B-2–4), the extent of topographical changes increased due to the reduced beach nourishment, and the corresponding wave run-up height was about twice as high as that of Type B-1. However, compared to the initial change, the change in wave run-up height was small because the difference in topographical changes after the end of wave generation was also small (Figure 14). With 8 m/s winds, the extent of topographical changes increased, and the amount of change in wave run-up also increased. Type B-1, in which the entire beach was nourished, showed a 1.5 times difference compared to the theoretical formula, Type B-2 showed around 2.0 times, and Type B-3 and 4 showed up to 2.5 times, indicating that performing beach nourishment toward land based on the shoreline is better for reducing wave run-up and topographical changes.

Figure 14.
Variation of values with dependence on the time, wind speeds, and beach profiles change: (a) ; (b) .
5. Conclusions
In this paper, a hydraulic model experiment was conducted to examine the topographical changes in response to grain size changes of nourishing material under the influence of wind and waves. The external forces were scaled down based on buoy data using the Froude similarity law. The grain type used for the natural beach was 0.1 mm quartz sand, which is the smallest among the various types of particles that can be used in the experiment. The application of quartz sand allows for traction and suspension to take effect. In addition, if the sand grains are smaller than 0.1 mm, they turn into clay, ashes, or fine powder, making it difficult to examine the topographical changes on coasts composed of sand. The grain size of the nourishing sand was increased to larger sizes than that which is typically found in the sand on a natural beach to attenuate sediment transport. In conditions where the movement of the waves was significant, 1.0 mm and 5.0 mm grains were applied after considering Equations (1) and (2) in advance. When the particles applied to the experiment are scaled up, the grain size of the natural beach becomes larger than the grains typically found on an actual beach. Therefore, the results of this study need to be examined from a qualitative perspective.
The frequency of occurrence rate of test waves propagating to the coast is increasing, and the scale of erosion is also increasing in proportion. Most research on sediment transport mainly applies waves as an external force, but on the actual coast, strong winds are accompanied by high wave incidence, so it is necessary to review topographical changes under conditions where waves and wind coexist. In this study, when erosive waves that cause sediment transport occur, topographical changes according to changes in wind speed were analyzed. The study was conducted in a two-dimensional wave flume equipped with a wind tunnel. As a result of the experiment, it was confirmed that the increase in wind speed expands the erosion area of the natural coast (Type A). The results also showed that topographical changes varied according to the diameter of the nourishment sand particles. Increasing the particle diameter of the nourishment sand played a role in reducing the run-up phenomenon (d50: 1.0 mm with 24–50%, d50: 5.0 mm with 59–83%), and the range of particles moved by winds was also decreased (d50: 1.0 mm with 10–38%, d50: 5.0 mm with 5–37%). Among them, Type B, with a d50: 1.0 mm particle diameter, was the most effective in reducing beach profile change. This was because increasing the settlement velocity had the effect of reducing the distance traveled by suspended sand. Similar tendencies were found in each profile when changing the nourishment area based on Type B. However, Type B-2, which performed beach nourishment in the rear-side direction based on the shoreline, was favorable in reducing sediment transport (Figure 8 and Figure 12). Beach movement was affected by the strong run-up phenomenon during the high wave attack, and the extent of erosion increased when there were waves and wind in combination (Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 8 and Figure 9). However, the effect of wind on sediment transport declined as the particle diameter increased, and the topography formed on the foreshore also showed a difference from when there was no wind. This was due to changes in the wave velocity, surf zone, wave run-up, and undertow characteristics under wind action, resulting in changes in erosion and accretion trends in the foreshore (Figure 8 and Figure 9). Although this study investigated cross-sectional topography according to changes in particle diameter and wind speed, a detailed sensitivity analysis of each parameter (nourishment particle diameter, wind speed, and wave size) is necessary to identify erosion and accretion characteristics more accurately.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—original draft preparation: K.-T.S.; writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition: K.-H.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data available in a publicly accessible repository.
Acknowledgments
This research was conducted at the Waterfront and Coastal Research Center, Catholic Kwandong University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Masselink, G.; McCall, R.; Poate, T.; van Geer, P. Modelling storm response on gravel beaches using XBeach-G. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Marit. Eng. 2014, 167, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.I.; Dickson, M.E.; Kench, P.S.; Bergillos, R.J. Modelling gravel barrier response to storms and sudden relative sea-level change using XBeach-G. Mar. Geol. 2019, 410, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, K.; Poate, T.; Masselink, G.; King, E.; Saulter, A.; Ely, N. Forecasting coastal overtopping at engineered and naturally defended coastlines. Coast. Eng. 2021, 164, 103827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, J.A.; Christie, E.K.; Brooks, S.M.; Spencer, T. Impact of Management Regime and Regime Change on Gravel Barrier Response to a Major Storm Surge. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranzini, E.; Anfuso, G.; Cinelli, I.; Piccardi, M.; Vitale, G. Shore Protection Structures Increase and Evolution on the Northern Tuscany Coast (Italy): Influence of Tourism Industry. Water 2018, 10, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masria, A.; Iskander, M.; Negm, A. Coastal protection measures, case study (Mediterranean zone, Egypt). J. Coast. Conserv. 2015, 19, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, N.; Nunn, P. Trends of Beach Erosion and Shoreline Protection in Rural Fiji. J. Coast. Res. 1998, 14, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Liew, M.; Xiao, M.; Jones, B.M.; Farquharson, L.M.; Romanovsky, V.E. Prevention and control measures for coastal erosion in northern high-latitude communities: A systematic review based on Alaskan case studies. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 093002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreadi, O.; Chatzipavlis, A.; Hasiotis, T.; Monioudi, I.; Manoutsoglou, E.; Velegrakis, A. Assessment of and Adaptation to Beach Erosion in Islands: An Integrated Approach. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, D.; Pais-Barbosa, J.; Baptista, P.; Silva, P.A.; Bernardes, C.; Pinto, C. Beach Response to a Shoreface Nourishment (Aveiro, Portugal). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, C.A.; Taborda, R.; Andrade, C.; Baptista, P.; Silva, P.A.; Mendes, D.; Pais-Barbosa, J. Morphological Development and Behaviour of a Shoreface Nourishment in the Portuguese Western Coast. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, K.-T.; Kim, K.-H.; Kim, H.-D.; Kwak, K.-S. Analysis on Sediment Transport System in the East Coast of Korea. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 95, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frandsen, J.B.; Xharde, R.; Berube, F.; Tremblay, O.G. Large Scale Experimental Storm Impact on Nourished Beach using Cobble-Gravel-Sand Mix. In Proceedings of the ASME 2015 34th International Conference on Ocean, Offshre and Arctic Engineering, Newfoundland, Canada, 31 May 2015; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- McCall, R.T.; Masselink, G.; Poate, T.G.; Roelvink, J.A.; Almeida, L.P.; Davidson, M.; Russe, P.E. Modelling Strom Hydrody-namics on Gravel Beaches with XBeach-G. Coast. Eng. 2014, 91, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frades, J.L.; Negro, V.; Barba, J.G.; Martín-Antón, M.; López-Gutiérrez, J.S.; Esteban, M.D.; Blasco, L.J.M. Preliminary Design for Wave Run-Up in Offshore Wind Farms: Comparison between Theoretical Models and Physical Model Tests. Energies 2019, 12, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrhaug, D.; Sunde, T. Wave runup and wave rundown estimation based on long-term variation of wind statistics. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Marit. Eng. 2018, 171, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbilek, Z.; Nwogu, O.G.; Ward, D.L. Laboratory Study of Wind Effect on Runup over Fringing Reefs, Data Report, Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Techical Report ERDC/CHL-TR-07-4 2007; U.S. Army Engineering Research and Development Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Medvedev, A.V.; Ratovsky, K.G.; Tolstikov, M.V.; Vasilyev, R.V.; Artamonov, M.F. Method for Determining Neutral Wind Velocity Vectors Using Measurements of Internal Gravity Wave Group and Phase Velocities. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemer, L. On Evolution of Young Wind Waves in Time and Space. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, D.J.; Orford, J.D.; Carter, R.W.G. Development of cusp-related, gravel size and shape facies at Malin Head, Ireland. Sedimentology 1993, 40, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscombe, D.; Masselink, G. Concepts in gravel beach dynamics. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2006, 79, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.M.; Wang, P.; Puleo, J.A. Storm-driven cyclic beach morphodynamics of a mixed sand and gravel beach along the Mid-Atlantic Coast, USA. Mar. Geol. 2013, 346, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ions, K.; Karunarathna, H.; Reeve, D.E.; Pender, D. Gravel Barrier Beach Morphodynamic Response to Extreme Conditions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, K.-T.; Kim, K.-H.; Park, J.-H. The Effectiveness of Adaptive Beach Protection Methods under Wind Application. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, K.-T.; Kim, K.-H. A Study of Hydraulic Characteristics in Front of the Seawall under the Coexistence of Wave and Wind. J. Korean Soc. Coast. Ocean Eng. 2020, 32, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunamura, T.; Horikawa, K. Two-dimensional Beach Transformation due to Waves. In Proceedings of the 14th Conference on Coastal Engineering, Copenhagen, Denmark, 24–28 June 1974; pp. 920–938. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, R.G. Heuristic Models of Sand Transport in the Surf Zone. In Proceedings of the Conference on Engineering Dynamics in the Surf Zone; Institution of Engineers: Sydney, Australia, 1973; pp. 208–214. [Google Scholar]
- Rubey, W.W. Settling velocity of gravel, sand, and silt particles. Am. J. Sci. 1933, 148, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.J.; Bridge, J.S.; Best, J.L. Fluid and sediment dynamics of upper stage plane beds. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1998, 103, 1239–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, M.P.; Venditti, J.G. The grain size gap and abrupt gravel-sand transitions in rivers due to suspension fallout. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 3777–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, I.A. Design of seawalls and breakwaters. J. Waterw. Harb. Div. 1959, 85, 123–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longuet-Higgins, M.; Stewart, R. Radiation stresses in water waves; a physical discussion, with applications. Deep. Sea Res. Oceanogr. Abstr. 1964, 11, 529–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, C.J.; Taylor, P.H.; Orszaghova, J.; Borthwick, A.G.; Whittaker, C.; Raby, A.C. Irregular wave runup statistics on plane beaches: Application of a Boussinesq-type model incorporating a generating–absorbing sponge layer and second-order wave generation. Coast. Eng. 2016, 114, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.N.; Brodie, K.L.; Cohn, N.T.; Giddings, S.N.; Merrifield, M. Observations of beach change and runup, and the performance of empirical runup parameterizations during large storm events. Coast. Eng. 2023, 184, 104357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockdon, H.F.; Holman, R.A.; Howd, P.A.; Sallenger, A.H., Jr. Empirical parameterization of setup, swash, and runup. Coast. Eng. 2006, 53, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).