Influence of the Plateau Pika Mound Numbers on Soil Water Erosion Properties in Alpine Meadows of the Yellow River Source Zone, Western China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
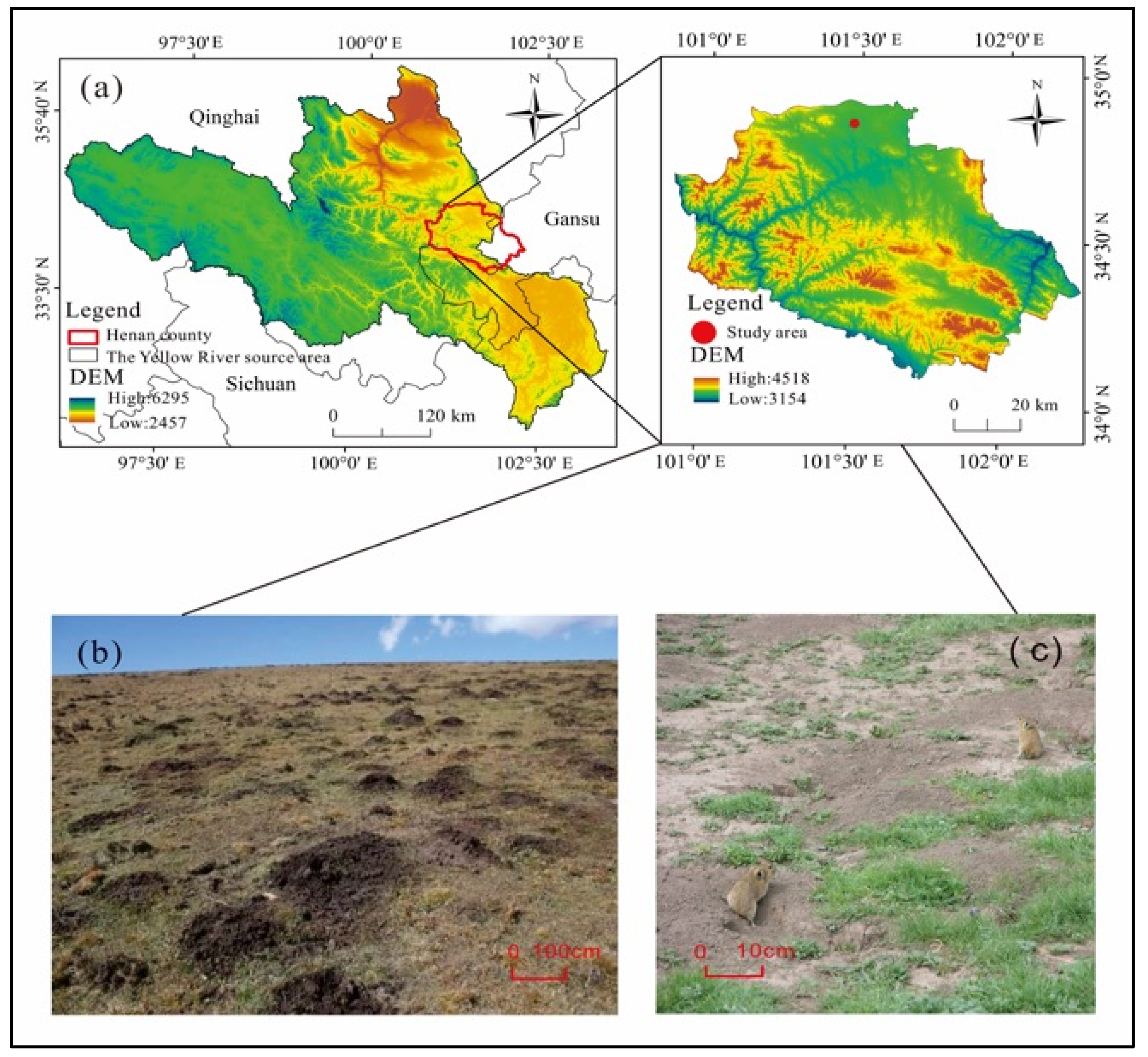
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Indicator Testing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Erosion Regulation under Different Pika Mound Numbers
3.1.1. Comparison of Total Soil Loss under Different Pika Mound Numbers
3.1.2. Soil Loss Characteristics under Different Pika Mound Numbers
3.1.3. Soil Erosion Regimes under Different Pika Mound Numbers
3.1.4. Relationship between the Pika Mound Numbers and Soil Erosion in a Degraded Meadow Area
3.2. Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Alpine Meadows under Different Pika Mound Numbers
3.2.1. Average Flow Rate
3.2.2. Flow Regime
3.2.3. Flow Resistance
3.3. Relationship between Landscape Pattern with Soil Water Erosion Properties under Different Pika Mound Numbers
3.3.1. Analysis of Landscape Pattern Indicators of Pika Mound Patches
3.3.2. Relationship between Landscape Pattern and Soil Erosion under Different Pika Mound Patches
3.3.3. Relationship between Landscape Pattern and Hydrodynamic Characteristics under Different Pika Mound Patches
3.3.4. Relationship between Soil Erosion and Hydrodynamic Characteristics under the Different Pika Mound Patches
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Other Similar Studies
4.2. Response Mechanisms of Plateau Pika Activities to Soil Erosion and Meadow Degradation
4.3. Properties of Alpine Pika Mound Patches and Their Effects on Ecological Processes in Alpine Meadows
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Q.; Jin, H.-J.; Bense, V.F.; Luo, D.-L.; Marchenko, S.S.; Harris, S.A.; Lan, Y.-C. Impacts of degrading permafrost on streamflow in the source area of Yellow River on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2019, 10, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, T.; Yong, B.; Krysanova, V.; Shi, P.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X. Impacts of climate change on flow regime and sequential threats to riverine ecosystem in the source region of the Yellow River. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.; Du, Y.; Li, Q.; Guo, X.; Fan, B.; Cao, G. Impacts of alpine shrub-meadow degradation on its ecosystem services and spatial patterns in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liu, M.; Xue, X.; Zhai, D. Warming effects on plant biomass allocation and correlations with the soil environment in an alpine meadow, China. J. Arid. Land 2016, 8, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ganjurjav, H.; Dong, S.; Gao, Q. Excessive plant compensatory growth: A potential endogenous driver of meadow degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2020, 6, 1816500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Li, G.; Yin, Y. The impacts of grassland vegetation degradation on soil hydrological and ecological effects in the source region of the Yellow River—A case study in Junmuchang region of Maqin country. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.P.; Guo, Z.G. Plateau pika disturbances alter plant productivity and soil nutrients in alpine meadows of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Rangel. J. 2017, 39, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.N.; Li, X.L.; Li, C.Y.; Duan, C.W. Response of Soil Microbial Diversity to Long-term Enclosure in Degraded Patches of Alpine Meadow in the Source Zone of the Yellow River. Huanjing Kexue 2023, 44, 2293–2303. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Yang, H.; Bao, G.S.; Pang, X.P.; Guo, Z.G. Effect of the presence of plateau pikas on the ecosystem services of alpine meadows. Biogeosciences 2022, 19, 4521–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Guo, Z. Effect of Plateau Pika Disturbance on Plant Aboveground Biomass of Alpine Meadows at Two Different Scales. Plants 2022, 11, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-X.; Li, X.-L.; Gao, J.; Shi, Y.; Ma, G.-L.; Rang, K.Z.C. Influences of pika and simulated grazing disturbances on bare patches of alpine meadow in the Yellow River Source Zone. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Chen, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, J.; Hu, X. Influences of Plateau Zokor Burrowing on Soil Erosion and Nutrient Loss in Alpine Meadows in the Yellow River Source Zone of West China. Water 2019, 11, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Qin, Q.; You, H.; Han, X.; Zhou, G. Patch Pattern and Ecological Risk Assessment of Alpine Grassland in the Source Region of the Yellow River. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, H.; Salahou, M.K. Watershed-level spatial pattern of degraded alpine meadow and its key influencing factors in the Yellow River Source Zone of West China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.-J.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, Z.-Q.; Li, X.G.; Liu, W.; Zakari, S. Lateral flow between bald and vegetation patches induces the degradation of alpine meadow in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 751, 142338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Wu, F.; Xie, X. The spatial characteristics and relationships between landscape pattern and ecosystem service value along an urban-rural gradient in Xi’an city, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Yan, D.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Luan, Z. GEE-Based Spatial-Temporal Dynamics in a Ramsar Wetland, Honghe National Nature Reserve, Northeast China from 1985 to 2021. Land 2022, 11, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N.; Lignola, G.; Brigante, M.; Bosso, L.; Chirico, G. Residual life and degradation assessment of wood elements used in soil bioengineering structures for slope protection. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 90, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lyu, S.; Chen, H.; Ao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Meng, X. Changes in climate and snow cover and their synergistic influence on spring runoff in the source region of the Yellow River. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Meng, B.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Jiang, H.; Yu, Y.; Yi, S. Using UAVs to assess the relationship between alpine meadow bare patches and disturbance by pikas in the source region of Yellow River on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 26, e01517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gu, K.; Li, W. Quantitative assessment of biocrust distribution patterns using landscape indices benefits the study of their soil conservation functions. Geoderma 2023, 429, 116257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LiLi, J.; Qi, H.H.; Duan, Y.Y.; Guo, Z.G. Effects of Plateau Pika Disturbance on the Spatial Heterogeneity of Vegetation in Alpine Meadows. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 771058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, G.; Wells, T. Predicting soil organic carbon movement and concentration using a soil erosion and Landscape Evolution Model. Geoderma 2021, 382, 114759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fan, W.; Li, Y.; Yi, Y. The influence of changes in land use and landscape patterns on soil erosion in a watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Guo, H.; Liu, B.; Wu, S.; Weckler, P.R.; Yang, J. Characterizing erosion processes on a convex slope based on 3D reconstruction method. Geoderma 2021, 402, 115364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Xu, S.S.; Ji, X.Y.; Wang, S.Q.; Ding, S.Y. Relationships between Riparian Vegetation Pattern and the Hydraulic Characteristics of Upslope flow. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.C.; Liu, T.T.; Chu, L.; Li, Z.X.; Wang, T.W.; Cai, H.F. Effects of temporal and spatial variations in source-sink landscape patterns on soil erosion and sediment yield from typical watershed in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 7476–7492. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Huang, J.; Liu, W.; Ding, Y.; Ge, L. Research on the Coastal Landscape Pattern Index in the District of Nansha. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, D.C.; Ascough, J.C., II; Nieber, J.L.; Misra, D.; Douglas-Mankin, K.R. Advances in Soil Erosion Research: Processes, Measurement, and Modeling. Trans. ASABE 2013, 56, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, Y.H.; Fu, B.J. Implication and limitation of landscape metrics in delineating relationship between landscape pattern and soil erosion. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 4923–4935. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Pan, C. Overland runoff erosion dynamics on steep slopes with forages under field simulated rainfall and inflow. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 1794–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Peng, R.; Huang, L.; Cao, W.; Huhe, T. Spatio-Temporal Analysis and Driving Factors of Soil Water Erosion in the Three-River Headwaters Region, China. Water 2022, 14, 4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xu, G.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, Y. Response Relationship between Microtopographic Variation and Slope Erosion under Sand-Cover. Water 2019, 11, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, G.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; Fan, Z.; Wen, T. Spatiotemporal Variations and Causes of Wind/Rainfall Erosion Climatic Erosivity in Qinghai Province, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaboz, P.; Dengiz, O.; Demir, S.; Şenol, H. Digital mapping of soil erodibility factors based on decision tree using geostatistical approaches in terrestrial ecosystem. CATENA 2021, 207, 105634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SuSu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Lei, N.; Li, P.; Wang, J. Interactive Effects of Rainfall Intensity and Initial Thaw Depth on Slope Erosion. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Liang, Z.Q.; Xie, Z.Y.; Zhuo, M.N.; Liao, Y.S.; Guo, T.L.; Li, D.Q. Mechanisms of grass in slope erosion control in red soil region of southern China. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 30, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.; Li, M. Effects of grass coverage and distribution patterns on erosion and overland flow hydraulic characteristics. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Tian, P.; Mu, X.; Tian, X. Linkages between soil erosion and long-term changes of landscape pattern in a small watershed on the Chinese Loess Plateau. CATENA 2023, 220, 106659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, X.; Strauss, P.; Zhang, Z. Effects of shrub-grass cover on the hillslope overland flow and soil erosion under simulated rainfall. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Fan, D.; Yu, X.; Li, H. Hydraulic characteristics of varying slope gradients, rainfall intensities and litter cover on vegetated slopes. Hydrol. Res. 2018, 49, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Bao, Z.; He, R. Impacts of climate change on hydrology in the Yellow River source region, China. J. Water Clim. Change 2020, 11, 916–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Yu, Z.; Yuan, F.; Acharya, K. The Multi-Scale Temporal Variability of Extreme Precipitation in the Source Region of the Yellow River. Water 2019, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paruchuri, S.; Smith, A.T.; Fan, Z.; Dobson, F.S. Microhabitat use by plateau pikas: Living on the edge. J. Mammal. 2019, 100, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Li, G.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhai, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Hu, X. Soil Water Erosion and Its Hydrodynamic Characteristics in Degraded Bald Patches of Alpine Meadows in the Yellow River Source Area, Western China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Zheng, F.; Lu, J.; Li, G. Investigating the Role of Raindrop Impact on Hydrodynamic Mechanism of Soil Erosion Under Simulated Rainfall Conditions. Soil Sci. 2012, 177, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, D.B.; Hamidreza, K.; Mohammadreza, Y. Investigation on ecosystem degradation induced by LU/LC changes using landscape pattern indices analysis. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 443. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, O.S.; Ra, J.H.; Ku, J.N.; Kim, J.H. Temporal-Spatial Analysis of Landscape Diversity using FRAGSTATS. J. Korea Soc. Environ. Restor. Technol. 2015, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Ma, L.; Zhang, S.; Yu, Y.; Shen, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Study on Landscape Patches Influencing Hillslope Erosion Processes and Flow Hydrodynamics in the Loess Plateau of Western Shanxi Province, China. Water 2020, 12, 3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, J. Study on the influence of ecological vegetation revetment on river flow and sediment environment. Water Supply 2020, 20, 3141–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzen, M.; Iserloh, T.; Casper, C.M.; Ries, B.J. Quantification of particle detachment by rain splash and wind-driven rain splash. CATENA 2015, 127, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.D.; Xin, Z.B.; Jiang, Q.L.; Yu, X.X.; Fan, D.X. Slope erosion and its hydrodynamic characteristic of Cinnamon soil under continuous rainfall. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 34, 14–20+30. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Zi, H.; Ade, L.; Lerdau, M.; Wang, C. Effects of zokors (Myospalax baileyi) on plant, on abiotic and biotic soil characteristic of an alpine meadow. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 103, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Yi, S.H.; Ding, Y.J.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Hou, X.M.; Yu, H.Y.; Meng, B.P.; Zhang, H.F.; et al. Effects of plateau pikas’ foraging and burrowing activities on vegetation biomass and soil organic carbon of alpine grasslands. Plant Soil 2020, 458, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.R.; Li, X.L.; Li, J.F.; Zhu, H.L.; Chen, W.T.; Zhao, J.Y.; Hu, X.S.; Cui, Y.P.; Li, C.L. Soil wind erosion law in Ochotona Curzoniae mound of alpine meadow in the Yellow River. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 33, 110–114+168. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.R.; He, J.D.; Zheng, Q.Y. Plateau pikas (Ochotona curzoniae) at low densities have no destructive effect on winter pasture in alpine meadows. Rangel. J. 2020, 42, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, G.; Li, X.-L.; Fryirs, K.; Gao, J.; Shi, Y.; Perry, G.L.W.; Cullum, C. Degradation and recovery of alpine meadow catenas in the source zone of the Yellow River, Western China. J. Mt. Sci. 2022, 19, 2487–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Zhu, H. Comprehensive analysis of relationship between vegetation attributes and soil erosion on hillslopes in the Loess Plateau of China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, P. Changes in key driving forces of soil erosion in the Middle Yellow River Basin: Vegetation and climate. Nat. Hazards 2013, 70, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, X.; Jin, L.; Su, X.; Li, C.; Kou, J. Effects of biological soil crusts on soil labile organic carbon of patchy alpine meadows in the Source Zone of the Yellow River, West China. CATENA 2023, 220, 106715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lu, Q.S.; Gao, Z.Q. Changes in Herdsmen’s Pastoral Behaviour Triggered by Rangeland Degradation in the Source Region of the Yellow River, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Outlook Agric. 2015, 44, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Zhu, H.; Hu, X.; Zhou, H.; Sun, H. Effects of degradation severity on the physical, chemical and mechanical properties of topsoil in alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, west China. CATENA 2019, 187, 104370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Bhatt, A.; Tang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Gallacher, D.; Zhou, S. Disturbance of plateau zokor-made mound stimulates plant community regeneration in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. J. Arid. Land 2021, 13, 1054–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Pika Mounds Type | Moisture Content | Density | Porosity | Cohesion | Firmness | Below a Certain Soil Grain Size (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (g m−3) | (%) | (kPa) | (kPa) | d < 2 mm | d < 0.5 mm | d < 0.075 mm | |
| Fresh pika mounds | 9.35 ± 1.75 | 0.87 ± 0.11 | 17.34 ± 0.16 | 11.56 ± 1.02 | 10.01 ± 1.95 | 88.79 | 59.72 | 8.88 |
| Revegetated pika mounds | 15.16 ± 2.08 | 1.51 ± 0.15 | 11.38 ± 0.14 | 26.61 ± 3.24 | 59.64 ± 2.38 | 75.26 | 48.97 | 8.15 |
| Healthy meadows | 38.25 ± 2.16 | 1.68 ± 0.08 | 4.75 ± 0.07 | 35.86 ± 3.53 | 153.50 ± 5.18 | 68.55 | 45.39 | 7.70 |
| Landscape Index | Equations | Description and Meaning of Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| NP | The total number of all pika mound patches (N) to reflect the landscape’s spatial pattern and the whole landscape’s qualitative heterogeneity. | |
| TE | The sum of the edge lengths (E) of all pika mound patches can describe the degree of agglomeration and extension trends of a given patch type. | |
| PD | The overall heterogeneity and fragmentation of the landscape and the degree of fragmentation of a given patch type are examined. | |
| AREA | The area of all pika mound patches is the basis for calculating other landscape indicators with implications for species abundance, energy nutrients, and productivity levels. | |
| V | The volume of all pika mound patches can describe the overall spatial characteristics of the landscape and accurately reflect the degree of landscape disturbance by external or human factors. | |
| Ni | The level of dispersion or aggregation of the individual spatial distribution of a specific type of patch in the landscape. |
| Slope (°) | The Number of Pika Mounds (pcs) | Runoff Depth (h, mm) | Flow Velocity (v, cm s−1) | Reynolds Number (Re) | Froude Number (Fr) | Darcy–Weisbach Resistance (f) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10° | Revegetated pika mound | 3.57 ± 0.74 Aa | 2.29 ± 0.27 Cf | 57.85 ± 18.45 Cd | 0.143 ± 0.009 Be | 159.07 ± 31.77 Aa |
| 1 pika mound | 3.25 ± 0.73 Ab | 2.61 ± 0.26 Ce | 66.08 ± 20.63 Ccd | 0.168 ± 0.016 Cd | 99.10 ± 13.41 Ab | |
| 2 pika mounds | 3.06 ± 0.75 Ac | 3.20 ± 0.32 Cd | 75.01 ± 25.91 Cbc | 0.236 ± 0.024 Bc | 71.56 ± 13.54 Ac | |
| 3 pika mounds | 2.83 ± 0.76 Ad | 3.56 ± 0.33 Cc | 80.79 ± 31.53 Cb | 0.281 ± 0.037 Bb | 51.89 ± 9.71 Ad | |
| 4 pika mounds | 2.75 ± 0.74 Ade | 3.95 ± 0.34 Cb | 76.36 ± 35.42 Cbc | 0.289 ± 0.049 Cb | 38.86 ± 8.56 Ae | |
| 5 pika mounds | 2.85 ± 0.77 Ad | 4.26 ± 0.29 Ca | 93.15 ± 39.01 Ca | 0.322 ± 0.073 Ca | 34.89 ± 6.56 Ae | |
| 20° | Revegetated pika mound | 3.33 ± 0.72 Ba | 2.65 ± 0.32 Bf | 86.55 ± 25.82 Bd | 0.157 ± 0.010 Af | 125.80 ± 17.73 Ba |
| 1 pika mound | 3.00 ± 0.72 Bb | 3.03 ± 0.35 Be | 89.75 ± 27.57 Bd | 0.180 ± 0.018 Be | 86.71 ± 16.54 Bb | |
| 2 pika mounds | 2.82 ± 0.76 Bc | 3.56 ± 0.33 Bd | 99.19 ± 33.12 Bc | 0.271 ± 0.021 Ac | 57.98 ± 9.70 Bc | |
| 3 pika mounds | 2.66 ± 0.79 Bd | 4.05 ± 0.42 Bc | 114.18 ± 38.56 Bb | 0.253 ± 0.040 Cd | 42.56 ± 9.68 Bd | |
| 4 pika mounds | 2.45 ± 0.70 Be | 4.63 ± 0.37 Bb | 105.39 ± 37.84 Bc | 0.310 ± 0.045 Bb | 29.81 ± 6.33 Be | |
| 5 pika mounds | 2.61 ± 0.71 Bd | 5.19 ± 0.42 Ba | 131.92 ± 42.18 Ba | 0.361 ± 0.065 Ba | 34.51 ± 5.41 Ade | |
| 30° | Revegetated pika mound | 2.79 ± 0.61 Ca | 2.98 ± 0.40 Af | 105.12 ± 28.83 Ad | 0.161 ± 0.017 Af | 71.47 ± 8.71 Ca |
| 1 pika mound | 2.56 ± 0.63 Cb | 3.56 ± 0.38 Ae | 116.64 ± 34.92 Acd | 0.203 ± 0.016 Ae | 50.29 ± 7.68 Cb | |
| 2 pika mounds | 2.37 ± 0.66 Cc | 4.36 ± 0.39 Ad | 134.71 ± 37.62 Abc | 0.270 ± 0.026 Ad | 30.55 ± 5.33 Cc | |
| 3 pika mounds | 2.29 ± 0.73 Ccd | 4.57 ± 0.35 Ac | 125.36 ± 41.09 Ac | 0.293 ± 0.034 Ac | 23.66 ± 5.11 Ccd | |
| 4 pika mounds | 2.38 ± 0.79 Bc | 5.22 ± 0.38 Ab | 141.86 ± 45.26 Ab | 0.329 ± 0.047 Ab | 17.87 ± 4.76 Cd | |
| 5 pika mounds | 2.18 ± 0.82 Cd | 5.82 ± 0.44 Aa | 153.63 ± 51.49 Aa | 0.385 ± 0.055 Aa | 16.99 ± 4.76 Bd |
| Hydrodynamic Parameters | The Number of Pika Mounds (pcs) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10° Slope | 20° Slope | 30° Slope | |
| v | y = 0.4066x + 2.2952(R2 = 0.9917) | y = 0.514x + 2.5667 (R2 = 0.9963) | y = 0.554x + 3.0333 (R2 = 0.9875) |
| Re | y = 60.234e0.0826x (R2 = 0.8717) | y = 85.092e0.078x (R2 = 0.8532) | y = 108.2e0.0689x (R2 = 0.8825) |
| Fr | y = 0.0433x + 0.1663 (R2 = 0.9782) | y = 0.0398x + 0.1559 (R2 = 0.9305) | y = 0.0374x + 0.1474 (R2 = 0.9418) |
| f | y = 140.93e–0.306x (R2 = 0.9738) | y = 112.19e–0.285x (R2 = 0.9653) | y = 64.547e–0.301x (R2 = 0.9733) |
| Slope (°) | The Number of Pika Mounds (pcs) | NP | TE | AREA | V | PD | Ni | r | h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10° | Revegetated pika mound | 1 e | 1.130 f | 0.0712 f | 0.0033 f | 14.042 a | 14.894 a | 0.180 c | 0.063 b |
| 1 pika mound | 1 e | 1.413 e | 0.1130 e | 0.0066 e | 8.846 c | 9.383 b | 0.225 ab | 0.080 a | |
| 2 pika mounds | 2 d | 2.700 d | 0.2106 d | 0.0118 d | 9.495 b | 7.121 c | 0.215 b | 0.078 a | |
| 3 pika mounds | 3 c | 4.145 c | 0.3357 c | 0.0193 c | 8.936 c | 5.472 d | 0.220 b | 0.081 a | |
| 4 pika mounds | 4 b | 5.903 b | 0.4841 b | 0.0296 b | 8.263 d | 4.382 e | 0.235 a | 0.082 a | |
| 5 pika mounds | 5 a | 7.065 a | 0.5864 a | 0.0345 a | 8.527 cd | 4.045 e | 0.225 ab | 0.083 a | |
| 20° | Revegetated pika mound | 1 e | 1.036 f | 0.0632 f | 0.0027 f | 15.821 a | 16.780 a | 0.165 c | 0.061 b |
| 1 pika mound | 1 e | 1.382 e | 0.1147 e | 0.0066 e | 8.721 c | 9.249 b | 0.220 b | 0.083 a | |
| 2 pika mounds | 2 d | 2.889 d | 0.2311 d | 0.0138 d | 8.654 cd | 6.491 c | 0.230 a | 0.080 a | |
| 3 pika mounds | 3 c | 4.239 c | 0.3476 c | 0.0204 c | 8.631 c | 5.285 d | 0.225 ab | 0.082 a | |
| 4 pika mounds | 4 b | 5.903 b | 0.4664 b | 0.0284 b | 8.577 d | 4.549 e | 0.235 a | 0.079 a | |
| 5 pika mounds | 5 a | 7.222 a | 0.5561 a | 0.0332 a | 8.991 b | 4.265 e | 0.230 a | 0.077 a | |
| 30° | Revegetated pika mound | 1 e | 1.005 f | 0.0553 f | 0.0022 f | 18.095 a | 19.193 a | 0.160 c | 0.055 b |
| 1 pika mound | 1 e | 1.444 e | 0.1156 e | 0.0069 e | 8.654 c | 9.179 b | 0.230 ab | 0.080 a | |
| 2 pika mounds | 2 d | 2.700 d | 0.2133 d | 0.0120 d | 9.375 b | 7.031 c | 0.215 b | 0.079 a | |
| 3 pika mounds | 3 c | 4.427 c | 0.3675 c | 0.0225 c | 8.164 d | 4.999 d | 0.235 a | 0.083 a | |
| 4 pika mounds | 4 b | 6.029 b | 0.4582 b | 0.0284 b | 8.730 c | 4.630 de | 0.240 a | 0.076 a | |
| 5 pika mounds | 5 a | 6.908 a | 0.5388 a | 0.0309 a | 9.279 b | 4.402 e | 0.220 b | 0.078 a |
| Slope (°) | Correlation | NP | AREA | TE | V | PD | Ni | r | h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10° | Grey correlation | 0.947 | 0.932 | 0.938 | 0.908 | 0.626 | 0.547 | 0.681 | 0.685 |
| Pearson correlation | 0.992 ** | 0.997 ** | 0.995 ** | 0.995 ** | −0.693 | −0.896 * | 0.691 | 0.741 | |
| Sig. (two-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.127 | 0.016 | 0.128 | 0.092 | |
| 20° | Grey correlation | 0.948 | 0.958 | 0.948 | 0.949 | 0.661 | 0.584 | 0.710 | 0.702 |
| Pearson correlation | 0.990 ** | 0.998 ** | 0.995 ** | 0.997 ** | −0.595 | −0.843 * | 0.706 | 0.416 | |
| Sig. (two-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.213 | 0.035 | 0.117 | 0.413 | |
| 30° | Grey correlation | 0.919 | 0.908 | 0.921 | 0.883 | 0.667 | 0.594 | 0.742 | 0.731 |
| Pearson correlation | 0.984 ** | 0.994 ** | 0.990 ** | 0.987 ** | −0.624 | −0.840 * | 0.629 | 0.555 | |
| Sig. (two-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.186 | 0.036 | 0.181 | 0.253 |
| Slope (°) | NP | AREA | TE | V | PD | Ni | r | h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10° | v | 0.977 ** | 0.991 ** | 0.986 ** | 0.987 ** | −0.634 | −0.853 * | 0.638 | 0.566 |
| H | −0.841 * | −0.908 * | −0.884 * | −0.928 ** | 0.817 * | 0.952 ** | −0.842 * | −0.758 | |
| Re | 0.902 * | 0.916 * | 0.893 * | 0.895 * | −0.658 | −0.841 * | 0.591 | 0.650 | |
| Fr | 0.943 ** | 0.972 ** | 0.955 ** | 0.970 ** | −0.663 | −0.873 * | 0.656 | 0.622 | |
| f | −0.851 * | −0.910 * | −0.885 * | −0.920 ** | 0.854 * | 0.979 ** | −0.846 * | −0.802 | |
| 20° | v | 0.991 ** | 0.998 ** | 0.996 ** | 0.998 ** | −0.592 | −0.842 * | 0.706 | 0.408 |
| H | −0.848 * | −0.899 * | −0.873 * | −0.910 * | 0.805 | 0.954 ** | −0.885 * | −0.672 | |
| Re | 0.907 * | 0.903 * | 0.899 * | 0.892 * | −0.509 | −0.759 | 0.583 | 0.368 | |
| Fr | 0.954 ** | 0.959 ** | 0.961 ** | 0.960 ** | −0.564 | −0.819 * | 0.699 | 0.356 | |
| f | −0.854 * | −0.904 * | −0.878 * | −0.914 * | 0.829 * | 0.979 ** | −0.904 * | −0.695 | |
| 30° | v | 0.970 ** | 0.977 ** | 0.973 ** | 0.968 ** | −0.643 | −0.855 * | 0.631 | 0.576 |
| H | −0.833 * | −0.877 * | −0.844 * | −0.869 * | 0.796 | 0.934 ** | −0.730 | −0.792 | |
| Re | 0.907 * | 0.902 * | 0.903 * | 0.884 * | −0.626 | −0.823 * | 0.582 | 0.557 | |
| Fr | 0.958 ** | 0.957 ** | 0.958 ** | 0.944 ** | −0.617 | −0.831 * | 0.599 | 0.543 | |
| f | −0.862 * | −0.915 * | −0.892 * | −0.923 ** | 0.810 | 0.960 ** | −0.799 | −0.76 |
| Slope (°) | Correlation | H | v | Re | Fr | f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10° | Grey correlation | 0.672 | 0.798 | 0.760 | 0.817 | 0.571 |
| Pearson correlation | −0.887 * | 0.991 ** | 0.919 ** | 0.957 ** | −0.905 * | |
| Sig. (two-tailed) | 0.018 | 0 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.013 | |
| 20° | Grey correlation | 0.690 | 0.836 | 0.793 | 0.834 | 0.587 |
| Pearson correlation | −0.907 * | 0.998 ** | 0.919 ** | 0.953 ** | −0.914 * | |
| Sig. (two-tailed) | 0.013 | 0 | 0.012 | 0.004 | 0.011 | |
| 30° | Grey correlation | 0.674 | 0.786 | 0.729 | 0.817 | 0.569 |
| Pearson correlation | −0.910 * | 0.993 ** | 0.938 ** | 0.994 ** | −0.933 ** | |
| Sig. (two-tailed) | 0.012 | 0 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.007 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, S.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Hu, X. Influence of the Plateau Pika Mound Numbers on Soil Water Erosion Properties in Alpine Meadows of the Yellow River Source Zone, Western China. Water 2023, 15, 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173111
Tong S, Li G, Li J, Li X, Jiang C, Zhao J, Zhu H, Liu Y, Chen W, Hu X. Influence of the Plateau Pika Mound Numbers on Soil Water Erosion Properties in Alpine Meadows of the Yellow River Source Zone, Western China. Water. 2023; 15(17):3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173111
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Shengchun, Guorong Li, Jinfang Li, Xilai Li, Chengdong Jiang, Jianyun Zhao, Haili Zhu, Yabin Liu, Wenting Chen, and Xiasong Hu. 2023. "Influence of the Plateau Pika Mound Numbers on Soil Water Erosion Properties in Alpine Meadows of the Yellow River Source Zone, Western China" Water 15, no. 17: 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173111
APA StyleTong, S., Li, G., Li, J., Li, X., Jiang, C., Zhao, J., Zhu, H., Liu, Y., Chen, W., & Hu, X. (2023). Influence of the Plateau Pika Mound Numbers on Soil Water Erosion Properties in Alpine Meadows of the Yellow River Source Zone, Western China. Water, 15(17), 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173111







