Can Selenium Be Removed in a Pilot Plant for Biological Iron and Manganese Removal?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Modelling
2.2. Chemicals and Stock Solutions
2.3. Pilot Plant Description
2.4. Pilot-Scale Experiments
2.5. Lab-Scale Batch Experiments
2.6. Analyses
3. Results
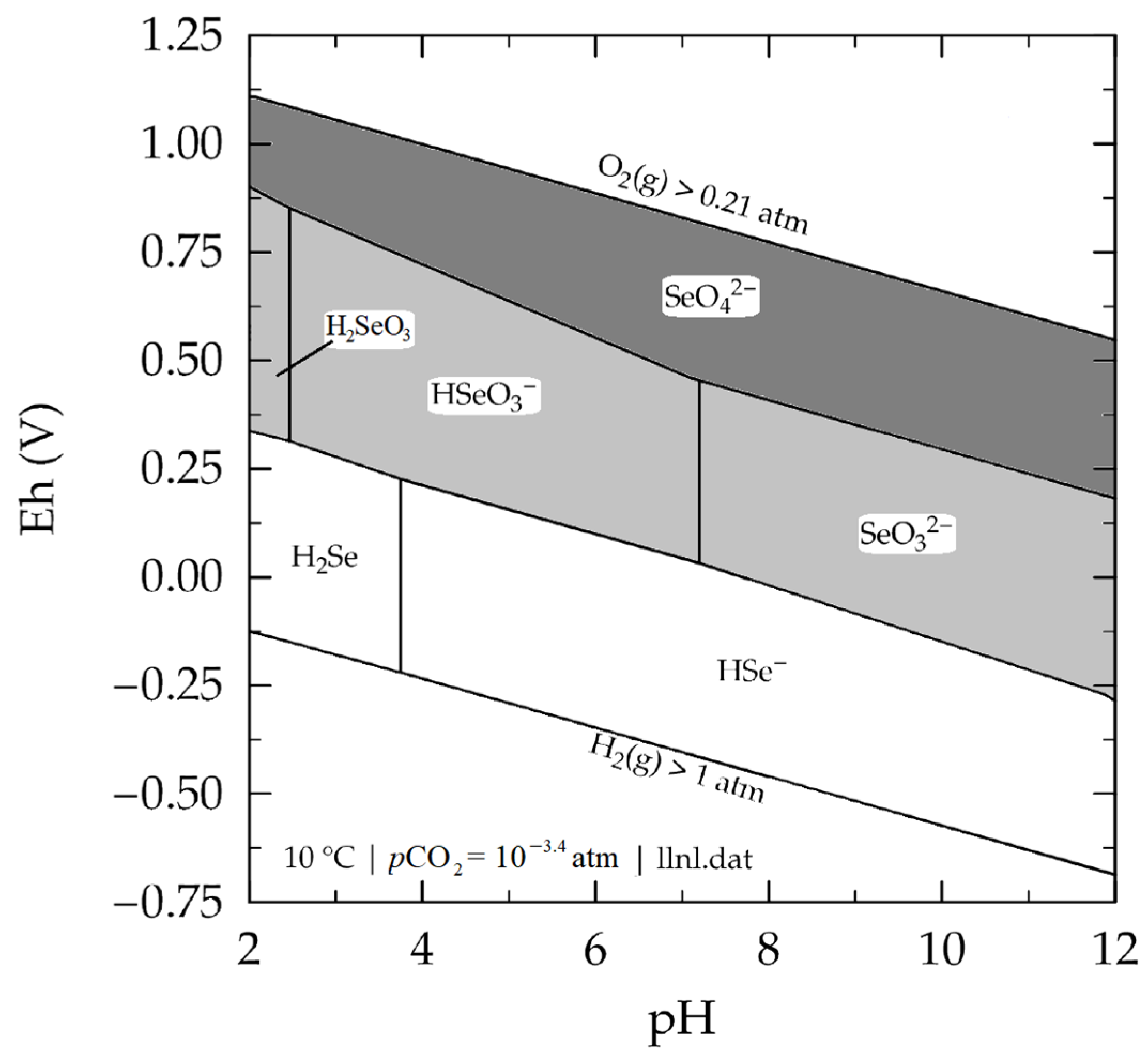
3.1. Modelling
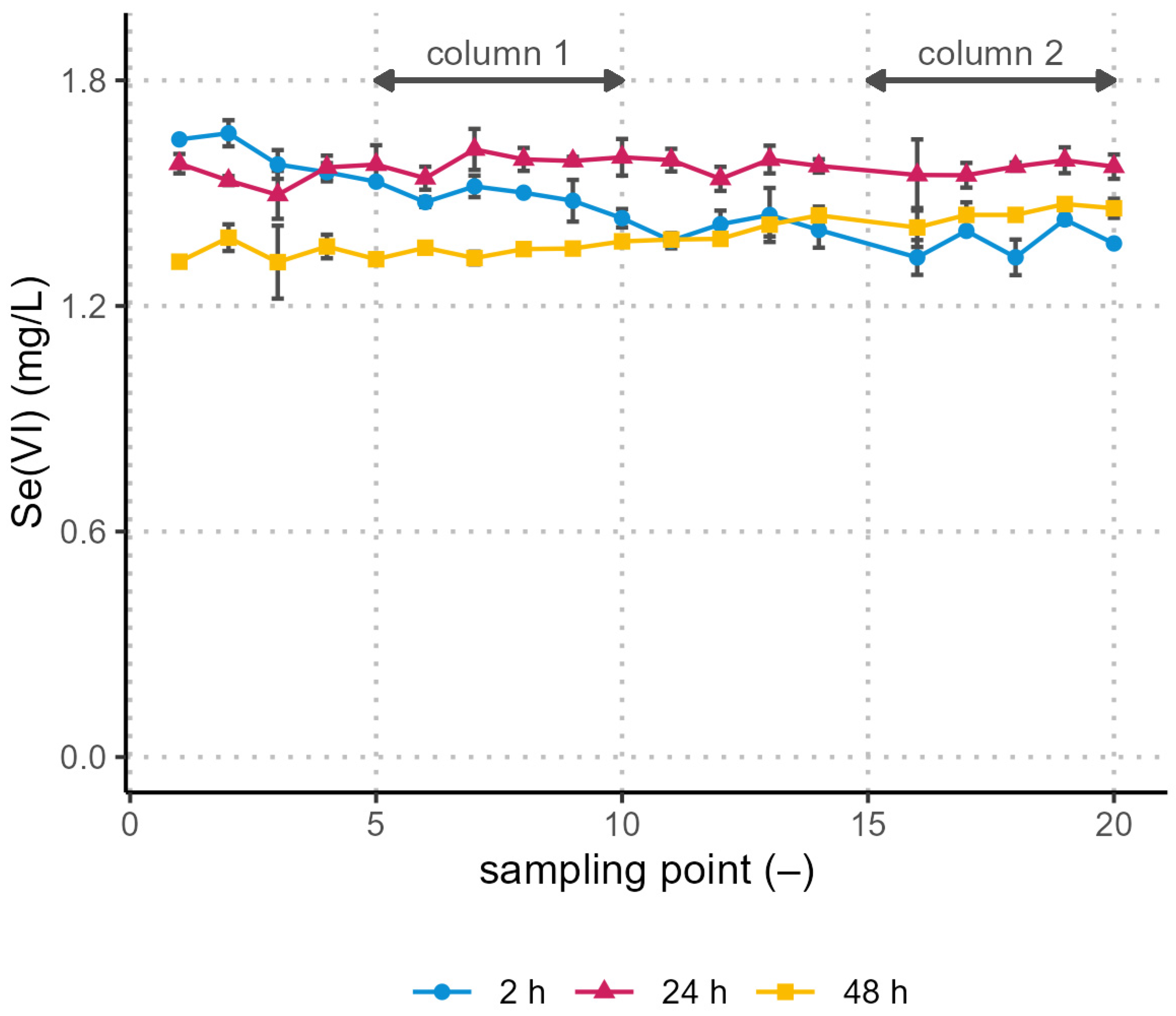
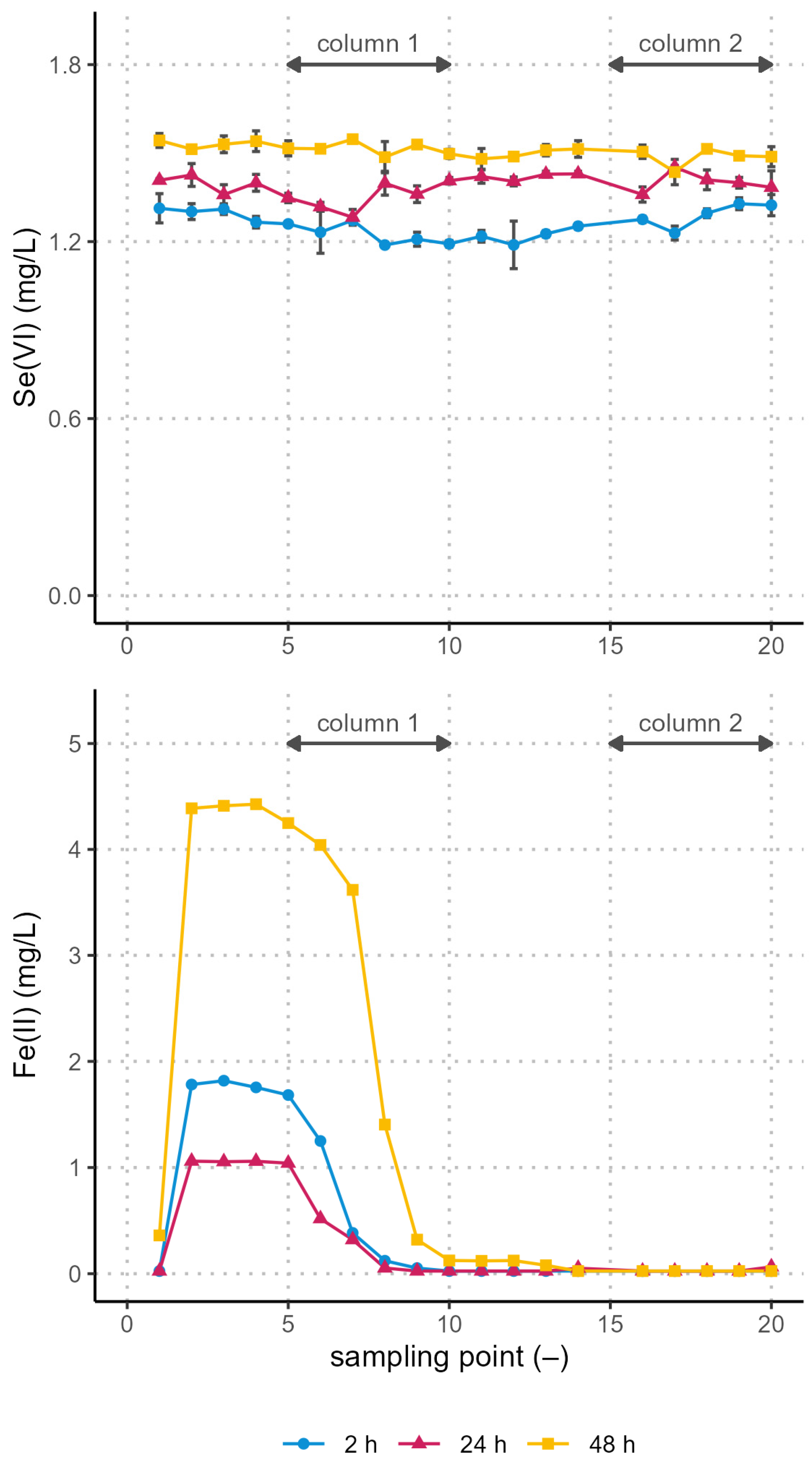
3.2. Removal in the Pilot Plant
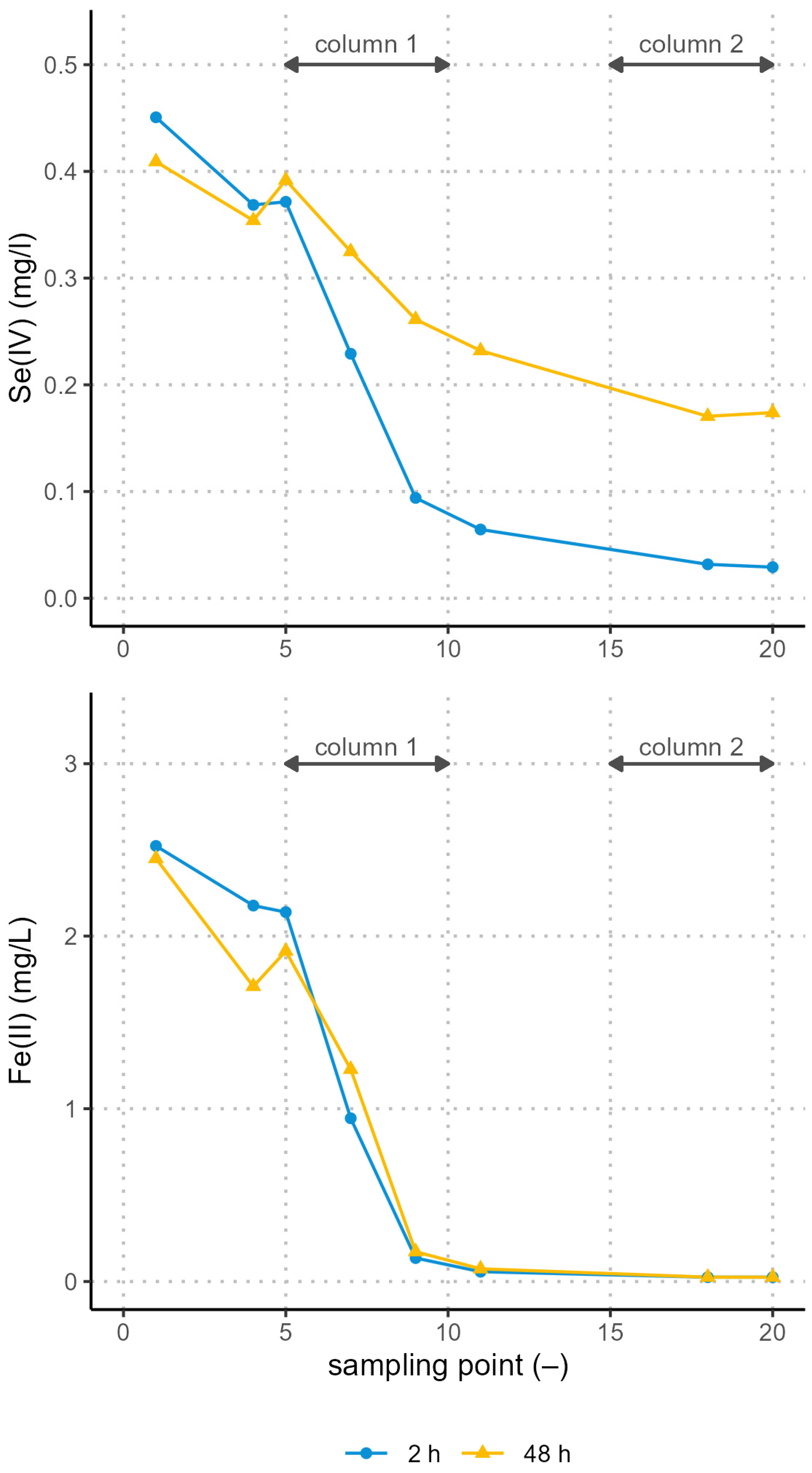
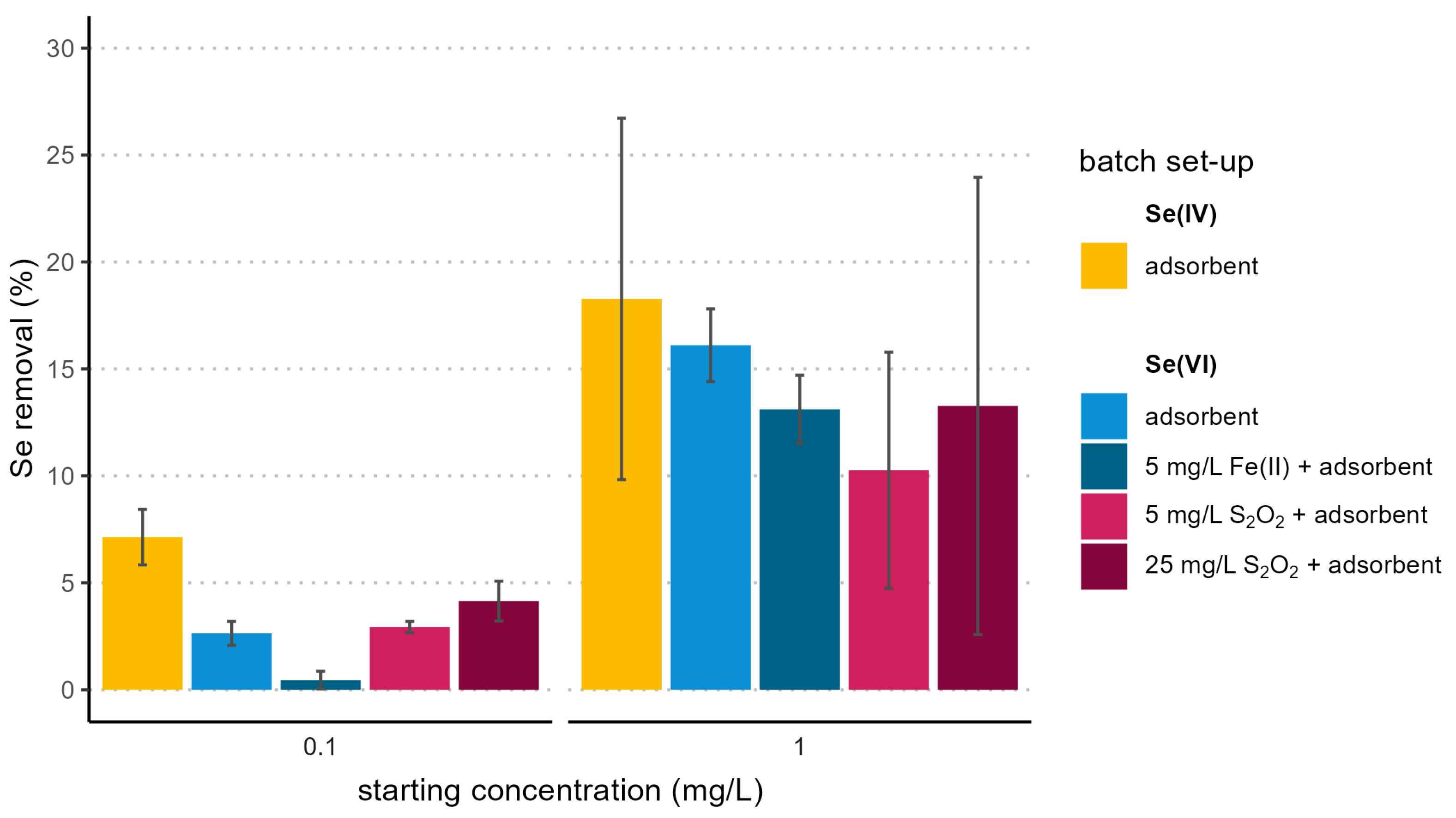
3.3. Reduction and Adsorption Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bajaj, M.; Eiche, E.; Neumann, T.; Winter, J.; Gallert, C. Hazardous Concentrations of Selenium in Soil and Groundwater in North-West India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fordyce, F.M. Selenium Deficiency and Toxicity in the Environment. In Essentials of Medical Geology: Revised Edition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 375–416. [Google Scholar]
- Gebreeyessus, G.D.; Zewge, F. A Review on Environmental Selenium Issues. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.T. Review: Selenium Contamination, Fate, and Reactive Transport in Groundwater in Relation to Human Health. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 1191–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, S.J.; Goodknight, C.S.; Tigar, A.D.; Bush, R.P.; Gil, A. Naturally Occurring Contamination in the Mancos Shale. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating First Addendum, 4th ed.; +1st add.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-92-4-154995-0. [Google Scholar]
- Publications Office of the European Union. Directive (EU) 2020/2184 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2020 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption (Recast); Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020; Volume 32020L2184, p. 62. [Google Scholar]
- Bundesamt für Justiz. Verordnung über die Qualität von Wasser für den Menschlichen Gebrauch; Bundesamt für Justiz: Bonn, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Elrashidi, M.A.; Adriano, D.C.; Workman, S.M.; Lindsay, W.L. Chemical Equilibria of Selenium in Soils: A Theoretical Developemnt. Soil Sci. 1987, 144, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.; Ungureanu, G.; Boaventura, R.; Botelho, C. Selenium Contaminated Waters: An Overview of Analytical Methods, Treatment Options and Recent Advances in Sorption Methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521–522, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ippolito, J.A.; Scheckel, K.G.; Barbarick, K.A. Selenium Adsorption to Aluminum-Based Water Treatment Residuals. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 338, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantino, L.V.; Quirino, J.N.; Monteiro, A.M.; Abrão, T.; Parreira, P.S.; Urbano, A.; Santos, M.J. Sorption-Desorption of Selenite and Selenate on Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxide in Competition with Nitrate, Sulfate and Phosphate. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzidou, K.; Nikoletopoulos, A.-A.; Tsiftsakis, N.; Pinakidou, F.; Mitrakas, M. Adsorption of Se(IV) and Se(VI) Species by Iron Oxy-Hydroxides: Effect of Positive Surface Charge Density. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.C.; Rigali, M.J.; Brady, P. Selenite Sorption by Carbonate Substituted Apatite. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, K.; Takahashi, Y. Effective Removal of Selenite and Selenate Ions from Aqueous Solution by Barite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9194–9201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, T.; Hashimoto, H.; Nakayama, M. Removal of Selenium(VI) from Aqueous Solution with Polyamine-type Weakly Basic Ion Exchange Resin. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 3155–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, B.D.; Blowes, D.W.; Lindsay, M.B.J.; Ptacek, C.J. Mechanistic Investigations of Se(VI) Treatment in Anoxic Groundwater Using Granular Iron and Organic Carbon: An EXAFS Study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 241–242, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, I.-H.; Bang, S.; Kim, K.-W.; Kim, M.G.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, W.-K. Selenate Removal by Zero-Valent Iron in Oxic Condition: The Role of Fe(II) and Selenate Removal Mechanism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, A.P. Removal of Selenate from Water by Chemical Reduction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1988, 27, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniatis, T.; Adams, D.J. Biological Treatment of Surface and Groundwater for Selenium and Nitrate. ASMR 2003, 2003, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvil, D.; Liang, H.C.; Baker, B.; Sundar, V. Industrial Scale Non-Biological Selenate Removal—Examples of Plants & Criteria behind Process Selection. In Proceedings of the Mine Water Solutions 2022, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 14–16 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mahringer, D.; Zerelli, S.S.; Dippon, U.; Ruhl, A.S. Pilot Scale Hexavalent Chromium Removal with Reduction, Coagulation, Filtration and Biological Iron Oxidation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 253, 117478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey PHREEQC 2019. Version 3.7.3 Build-Number 15968. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/software/phreeqc-version-3 (accessed on 19 January 2022).
- Kinniburgh, D.G.; Cooper, D.M. PhreePlot—Creating Graphical Output with PHREEQC 2011. Original Date June 2011, Last Updated 15 February 2023. 606p. Available online: http://www.phreeplot.org/ (accessed on 19 January 2022).
- Kumar, A.R.; Riyazuddin, P. Speciation of Selenium in Groundwater: Seasonal Variations and Redox Transformations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.J. Review of Selenium Toxicity in the Aquatic Food Chain. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 326, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Martínez, A.; Charlet, L. Selenium Environmental Cycling and Bioavailability: A Structural Chemist Point of View. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2009, 8, 81–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuisi, M.A.; Abdel-Fattah, A. Groundwater Vulnerability to Selenium in Semi-Arid Environments: Amman Zarqa Basin, Jordan. Env. Geochem. Health 2010, 32, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senatsverwaltung für Mobilität, Verkehr, Klimaschutz und Umwelt Wasserportal: Gewässerkundliche Messdaten. (database). Last updated 6 December 2022. Available online: https://www.govdata.de/dl-de/by-2-0 (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Senatsverwaltung für Mobilität, Verkehr, Klimaschutz und Umwelt. In Grundwasser in Berlin: Vorkommen, Nutzung, Schutz, Gefährdung; Umwelt und Verbraucherschutz Berlin: Berlin, Germany, 2007.
- Gonzalez, C.M.; Hernandez, J.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Botez, C.E.; Parsons, J.G.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Sorption Kinetic Study of Selenite and Selenate onto a High and Low Pressure Aged Iron Oxide Nanomaterial. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211–212, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheha, R.R.; El-Shazly, E.A. Kinetics and Equilibrium Modeling of Se(IV) Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Metal Oxides. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzidou, K.; Nikoletopoulos, A.; Bakouros, L.; Zouboulis, A.; Mitrakas, M. Selenite Removal from Water. In Proceedings of the 4th EWaS International Conference: Valuing the Water, Carbon, Ecological Footprints of Human Activities, Leftkada, Greece, 24 June–27 September 2020; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2020; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Chen, X.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, J. Effects of Selenium Fertilizer Application on Yield and Selenium Accumulation Characteristics of Different Japonica Rice Varieties. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Jin, Z.; Tumrani, S.H.; Ji, X. Selenium in Wastewater Can Be Adsorbed by Modified Natural Zeolite and Reused in Vegetable Growth. Sci. Prog. 2021, 104, 003685042110198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staicu, L.C.; Van Hullebusch, E.D.; Lens, P.N.L. Production, Recovery and Reuse of Biogenic Elemental Selenium. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2015, 13, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellowes, J.W.; Pattrick, R.A.D.; Green, D.I.; Dent, A.; Lloyd, J.R.; Pearce, C.I. Use of Biogenic and Abiotic Elemental Selenium Nanospheres to Sequester Elemental Mercury Released from Mercury Contaminated Museum Specimens. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Yang, L.; Shao, P.; Shi, H.; Chang, Z.; Fang, D.; Wei, Y.; Feng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yu, K.; et al. Proton Self-Enhanced Hydroxyl-Enriched Cerium Oxide for Effective Arsenic Extraction from Strongly Acidic Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 10412–10422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myneni, S.C.B.; Tokunaga, T.K.; Brown, G.E. Abiotic Selenium Redox Transformations in the Presence of Fe(II,III) Oxides. Science 1997, 278, 1106–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffroy, N.; Demopoulos, G.P. Reductive Precipitation of Elemental Selenium from Selenious Acidic Solutions Using Sodium Dithionite. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 10240–10246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Kaushik, V.; Jung, B.; Batchelor, B.; Abdel-Wahab, A. Kinetic Study of Selenium Removal Using Advanced Reduction Process with Dithionite. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiers, D.T.; Wichlacz, P.L.; Thompson, D.L.; Bruhn, D.F. Selenate Reduction by Bacteria from a Selenium-Rich Environment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 2591–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sposito, G.; Yang, A.; Neal, R.H.; Mackzum, A. Selenate Reduction in an Alluvial Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, B.; He, C.; Zhang, H. Hydrodynamics- and Hydrochemistry-Affected Microbial Selenate Reduction in Aquifer: Performance and Mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 145331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.N.H.; Beydoun, D.; Amal, R. Photocatalytic Reduction of Selenite and Selenate Using TiO2 Photocatalyst. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2005, 171, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, A.S.; Ramteke, P.; Singh, S.K.; Labhasetwar, N.K. Sustainable Selenium Remediation from Water Using Aluminium–Iron Mixed Oxide: Batch and Column Adsorption Studies. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 48, 102824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, S.S.; Memon, S.A.; Rafi-ul-Zaman; Ram, N.; Saeed, S.; Mubarak, N.M.; Karri, R.R. Rapid Adsorption of Selenium Removal Using Iron Manganese-Based Micro Adsorbent. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Steuer, A.; Dippon-Deißler, U.; Mahringer, D.; Ruhl, A.S. Can Selenium Be Removed in a Pilot Plant for Biological Iron and Manganese Removal? Water 2023, 15, 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173147
Steuer A, Dippon-Deißler U, Mahringer D, Ruhl AS. Can Selenium Be Removed in a Pilot Plant for Biological Iron and Manganese Removal? Water. 2023; 15(17):3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173147
Chicago/Turabian StyleSteuer, Andrea, Urs Dippon-Deißler, Daniel Mahringer, and Aki S. Ruhl. 2023. "Can Selenium Be Removed in a Pilot Plant for Biological Iron and Manganese Removal?" Water 15, no. 17: 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173147
APA StyleSteuer, A., Dippon-Deißler, U., Mahringer, D., & Ruhl, A. S. (2023). Can Selenium Be Removed in a Pilot Plant for Biological Iron and Manganese Removal? Water, 15(17), 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173147





